WetSegNet: An Edge-Guided Multi-Scale Feature Interaction Network for Wetland Classification
Abstract
Highlights
- The proposed WetSegNet model significantly improves wetland classification accuracy, achieving an overall accuracy of 90.81% and a Kappa coefficient of 0.88 on GF-2 imagery from Dongting Lake wetlands.
- It attains classification accuracies of over 90% for key habitat types such as water, sedge, and reeds, outperforming the U-Net baseline by 3.3% in overall accuracy and 0.05 in Kappa.
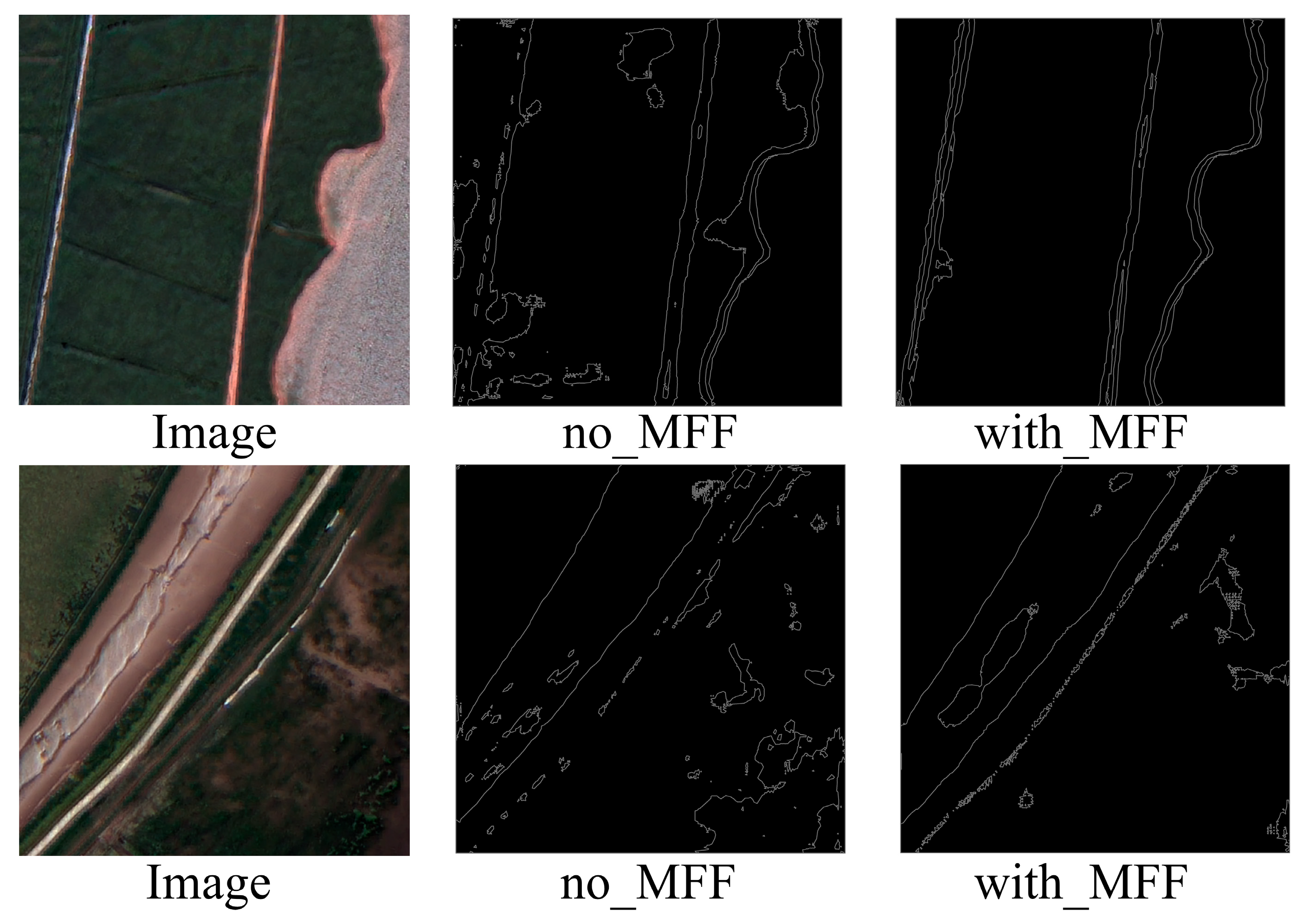
- The integration of CNN and Swin Transformer within an edge-guided multi-scale network effectively combines local texture and global semantic information, enhancing the model’s ability to handle complex wetland landscapes.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials
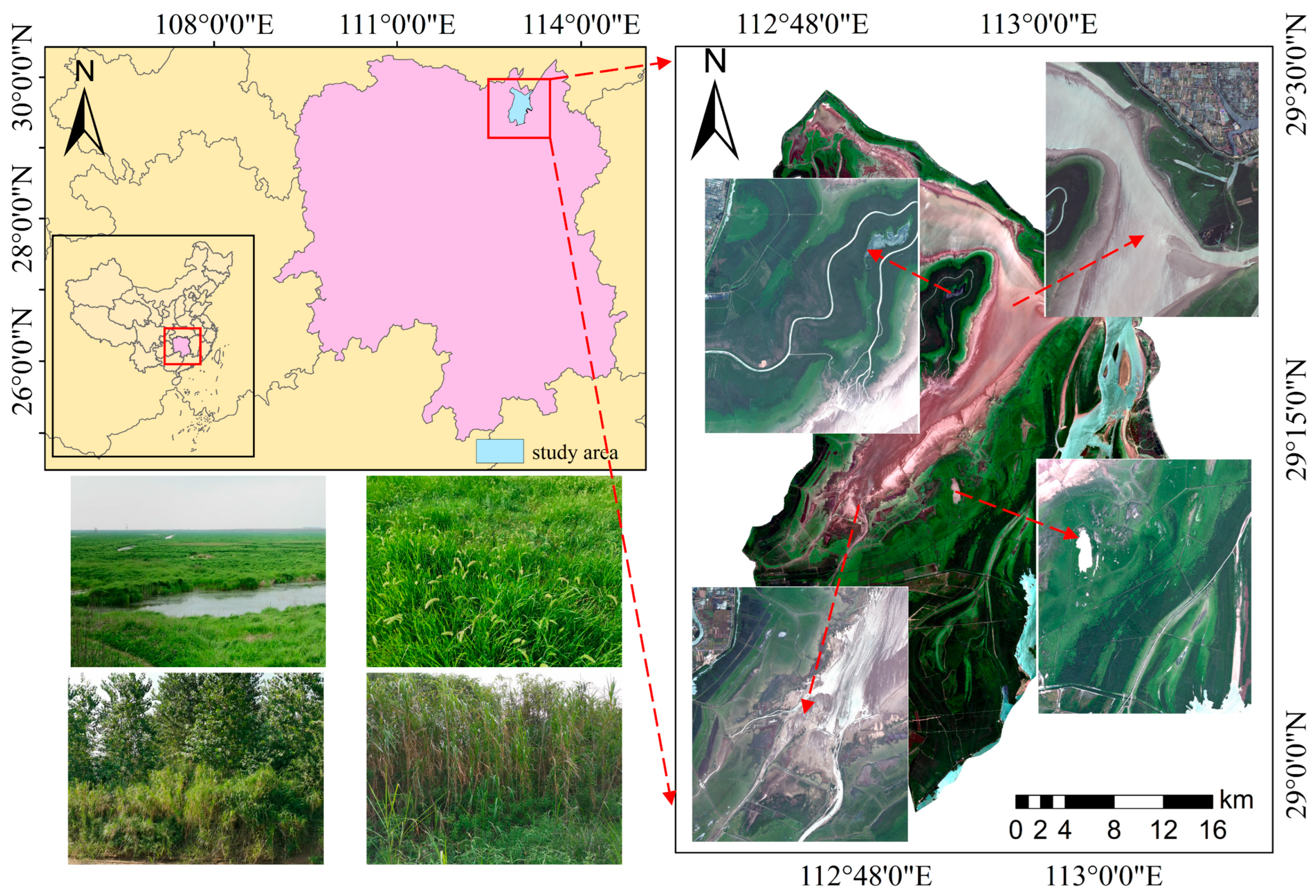
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
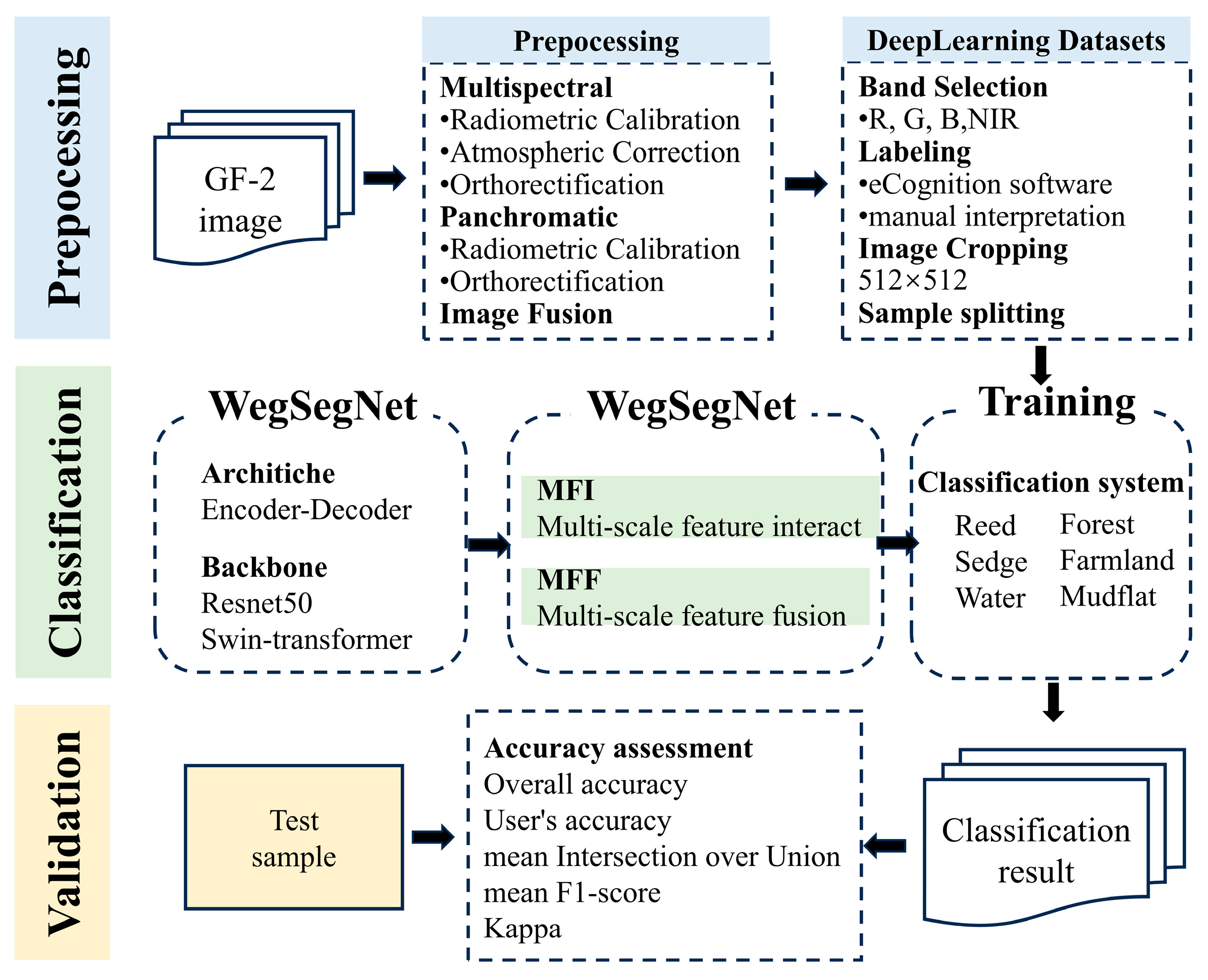
3. Methodology
3.1. Framework and Design of WetSegNet
3.2. Components of WetSegNet
3.2.1. ResNet
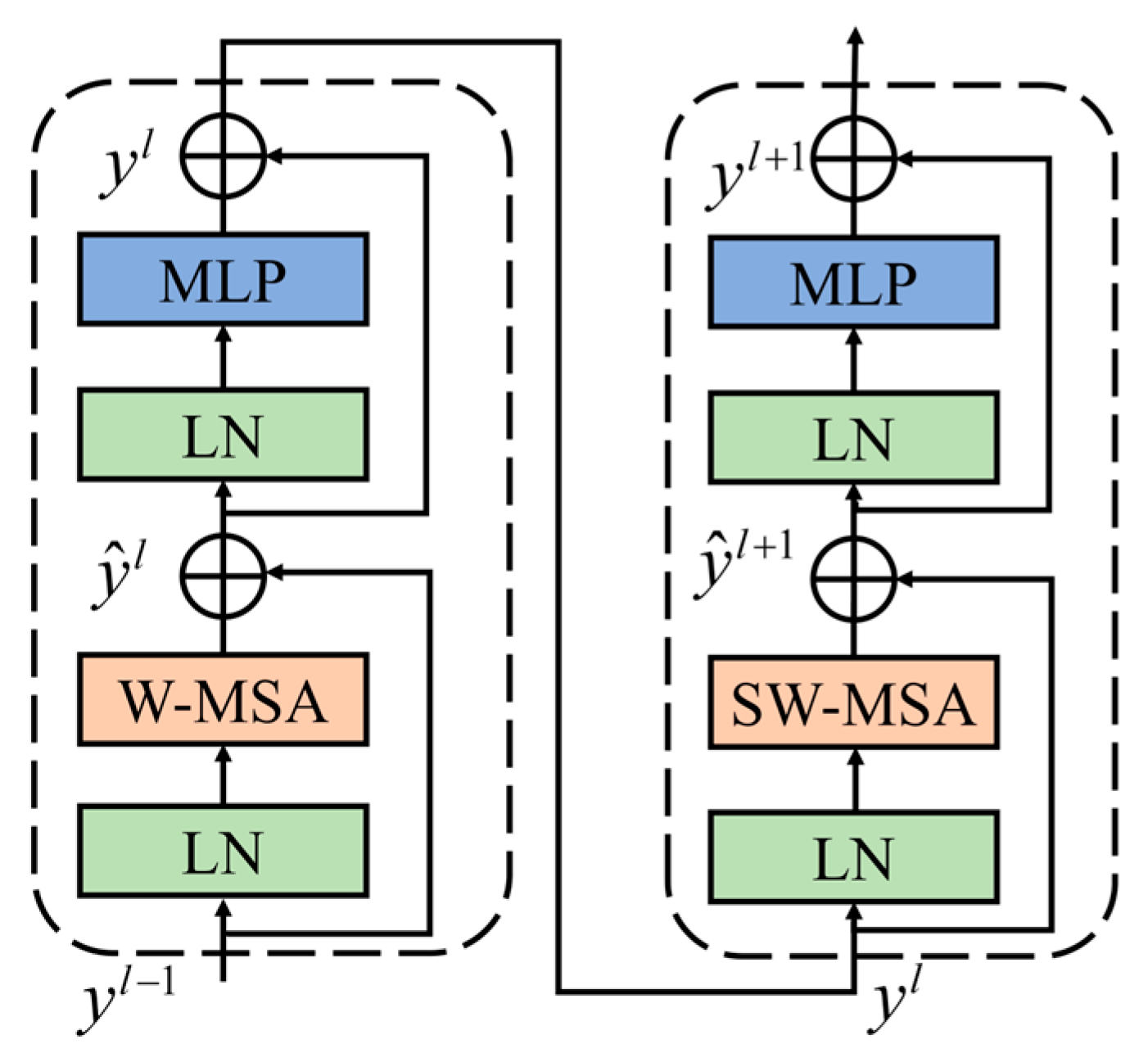
3.2.2. Swin Transformer
3.2.3. Multi-Scale Feature Interaction Module
3.2.4. Multi-Feature Fusion Module
3.3. Experimental Settings
3.4. Evaluation Metrics
4. Results
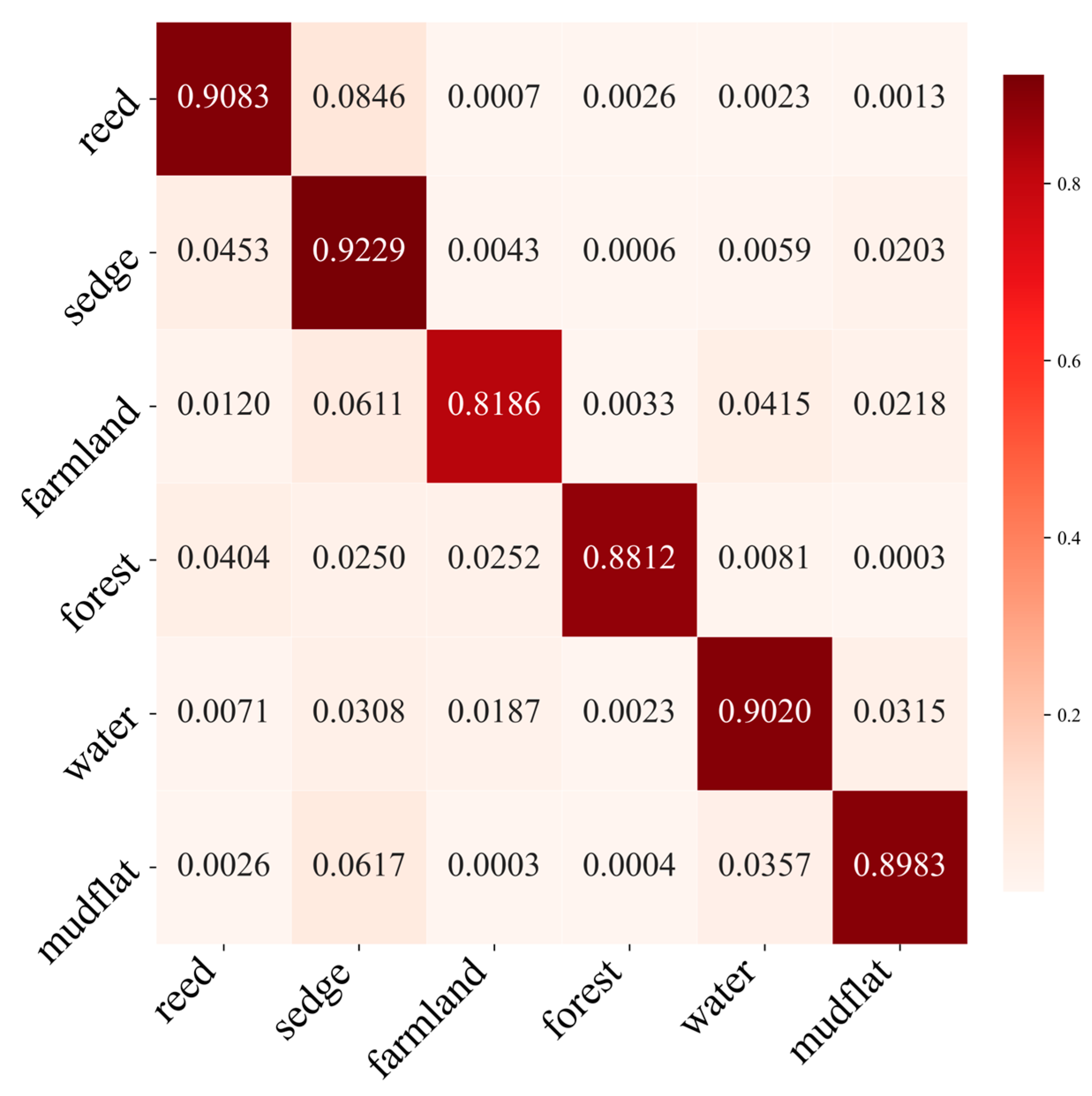
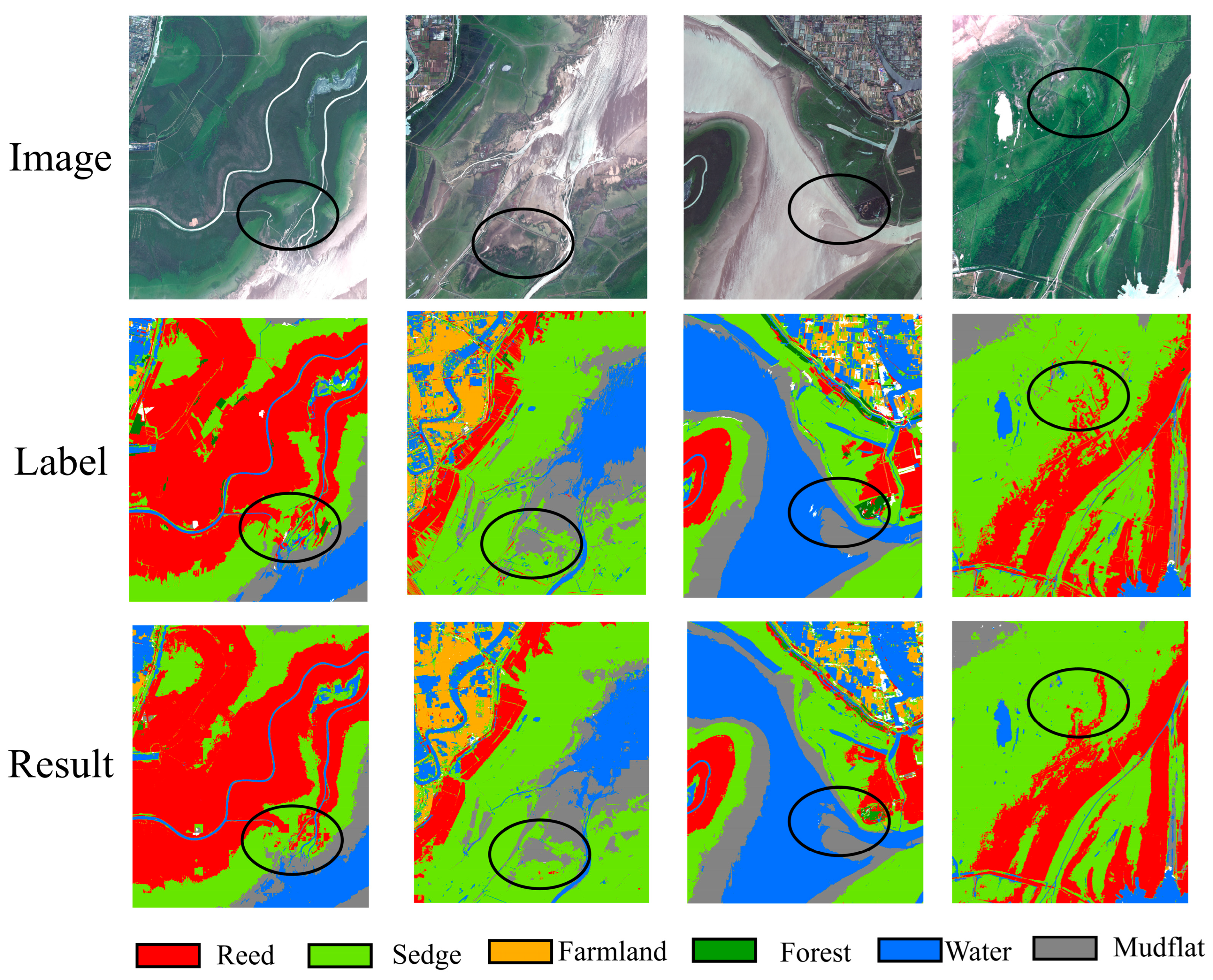
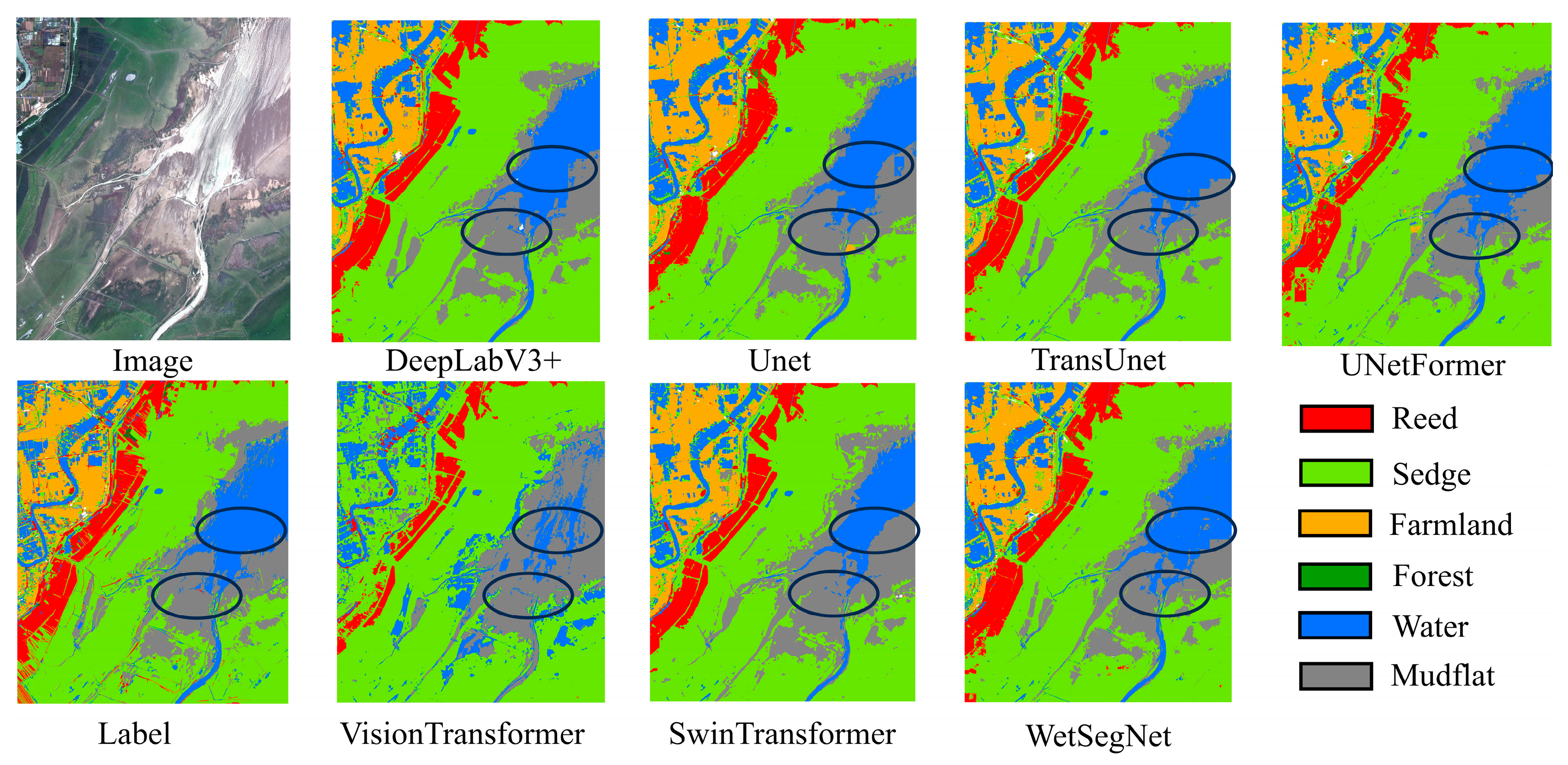
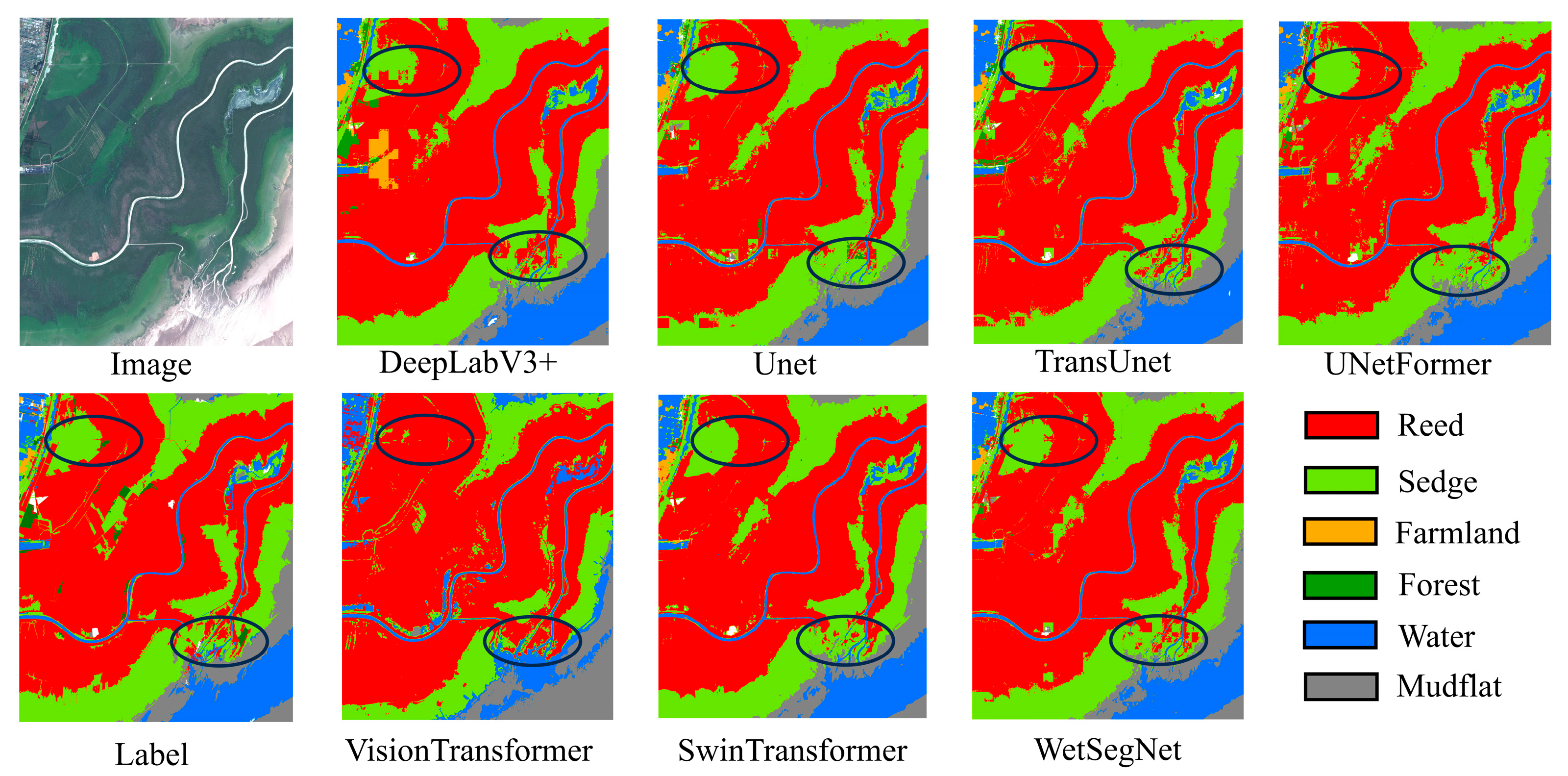
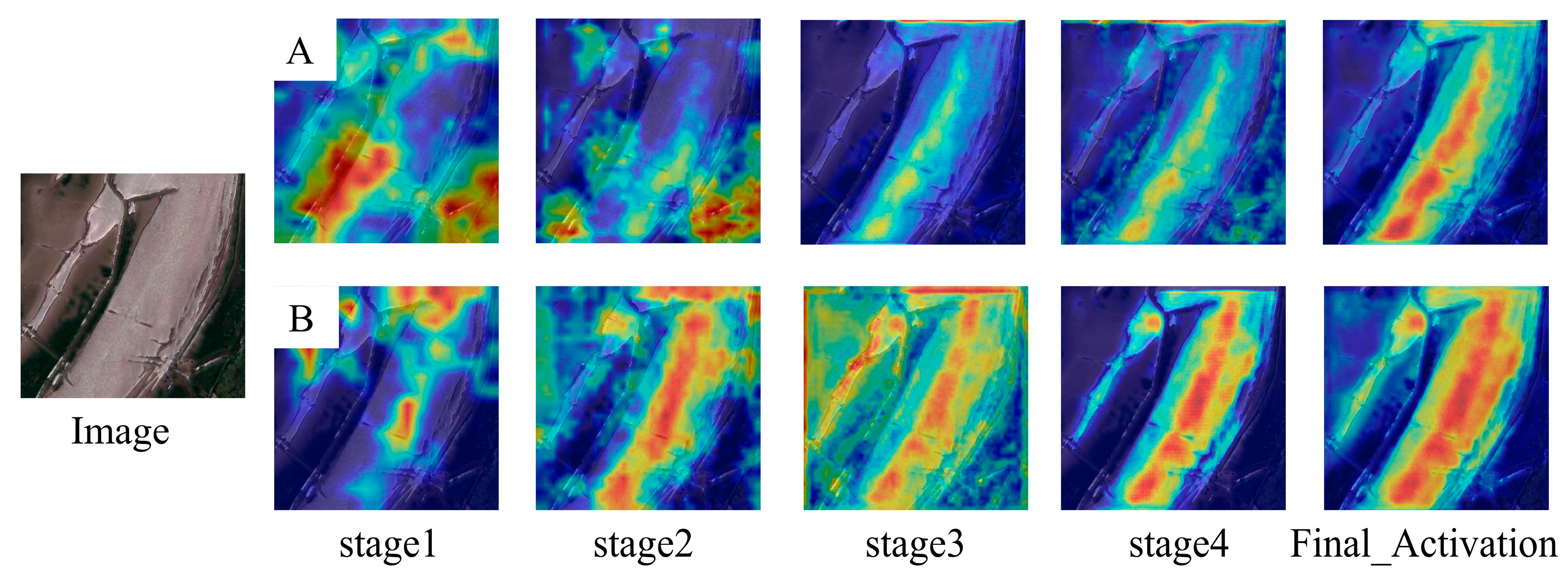
4.1. Results and Analysis
4.2. Comparison of Wetland Classification Results with Different Models
4.3. Ablation Study
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CNN | Convolutional neural network |
| MFI | multiscale feature interaction |
| MFF | multi-feature fusion |
| LN | Layer Normalization |
| MLP | Multi-Layer Perceptron |
| K, Key | keys |
| V, Value | values |
| OA | overall accuracy |
| Kappa | kappa coefficient |
| mIoU | mean intersection over union ratio |
| TP | true positives |
| FP | false positives |
| TN | true negatives |
| FN | false negatives |
| no_MFF | not using MFF |
| WetSegNet | wetland classification model |
References
- Gardner, R.C.; Finlayson, C.M. Global wetland outlook: State of the world’s wetlands and their services to people. In Proceedings of the Ramsar Convention Secretariat, Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 22 October 2018; Ramsar Convention Secretariat: Gland, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 2020–2025. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, X.; Niu, Z.; Liu, L.; Jing, Y. Integration of ecological knowledge with Google Earth Engine for diverse wetland sampling in global mapping. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 134, 104249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemas, V. Using remote sensing to select and monitor wetland restoration sites: An overview. J. Coast. Res. 2013, 29, 958–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Chen, S.; Zhou, M.; Sui, H.; Hu, L.; Li, H.; Hua, L.; Zhou, Q. DepthSeg: Depth prompting in remote sensing semantic segmentation. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2506.14382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Chen, D.; Li, Z.; Li, S.; Cheng, S.; Niu, X.; Cai, Y.; Shi, Z.; Wu, C.; Yang, G. Monitoring wetland plant diversity from space: Progress and perspective. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 130, 103943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Z.; Li, J.-Z.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, Z.-L.; Li, X.-J.; Wang, J.-H. High Spatial Resolution Remote Sensing Monitoring of Artificial Wetlands: A Case Study of the Yuqiao Reservoir Estuary Wetland. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2024–2024 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Athens, Greece, 7–12 July 2024; pp. 5104–5107. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Mao, D.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Xiang, H.; Feng, K.; Luo, L.; Jia, M.; Song, K.; Wang, Z. Wetland mapping in East Asia by two-stage object-based Random Forest and hierarchical decision tree algorithms on Sentinel-1/2 images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 297, 113793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, J.M.; Knight, J.F.; Gallant, A.L. Influence of multi-source and multi-temporal remotely sensed and ancillary data on the accuracy of random forest classification of wetlands in Northern Minnesota. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 3212–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, M. Random forest classifier for remote sensing classification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mountrakis, G.; Im, J.; Ogole, C. Support vector machines in remote sensing: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, A.; Mahdianpari, M.; Brisco, B.; Granger, J.; Mohammadimanesh, F.; Salehi, B. Deep Forest classifier for wetland mapping using the combination of Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 data. GISci. Remote Sens. 2021, 58, 1072–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Liu, H.; Yang, M.; Chen, L.; Wan, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Qian, Y. STransFuse: Fusing swin transformer and convolutional neural network for remote sensing image semantic segmentation. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 10990–11003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yuan, L.; Sui, X.; Chen, Q. Hyperspectral image super-resolution via dual-domain network based on hybrid convolution. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5512518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Liu, M.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Sheng, H. Dual-branch Feature Interaction Network for Coastal Wetland Classification Using Sentinel-1 and 2. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 14368–14379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Wu, P.; Li, X.; Hao, Z.; Ma, X.; Fan, R.; Liu, C.; Ling, F. Super-resolution water body mapping with a feature collaborative CNN model by fusing Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 images. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 134, 104176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Proceedings, Part III 18. pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, Z.; Huang, H.; Sun, W.; Lei, T.; Benediktsson, J.A.; Li, J. Novel enhanced UNet for change detection using multimodal remote sensing image. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 2505405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ates, G.C.; Mohan, P.; Celik, E. Dual cross-attention for medical image segmentation. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 126, 107139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Cao, P.; Wang, J.; Zaiane, O.R. Uctransnet: Rethinking the skip connections in u-net from a channel-wise perspective with transformer. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Virtual, 22 February–1 March 2022; pp. 2441–2449. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, W.; Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Sun, W.; Zhang, L. Global–local 3-D convolutional transformer network for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Tang, C.; Wang, X.; Zheng, B. A ViT-based multiscale feature fusion approach for remote sensing image segmentation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liao, Z.; Zhou, B.; Yu, G.; Luo, W. SwinURNet: Hybrid transformer-cnn architecture for real-time unstructured road segmentation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 5035816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, C. Transformer and CNN hybrid deep neural network for semantic segmentation of very-high-resolution remote sensing imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 4408820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibtehaz, N.; Rahman, M.S. MultiResUNet: Rethinking the U-Net architecture for multimodal biomedical image segmentation. Neural Netw. 2020, 121, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Siddiquee, M.M.R.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. Unet++: Redesigning skip connections to exploit multiscale features in image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 39, 1856–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.03762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.14030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleissaee, A.A.; Kumar, A.; Anwer, R.M.; Khan, S.; Cholakkal, H.; Xia, G.-S.; Khan, F.S. Transformers in Remote Sensing: A Survey. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Li, J.; An, Z.; Fan, H.; Fan, L. CTMFNet: CNN and transformer multiscale fusion network of remote sensing urban scene imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 61, 5900314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Xu, M.; Shen, B.; Hou, K.; Liu, S.; Sheng, H.; Liu, Y.; Wan, J. ViT-UNet: A Vision Transformer Based UNet Model for Coastal Wetland Classification Based on High Spatial Resolution Imagery. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 19575–19587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, D.; Yao, R.; Xue, Y. Swin transformer embedding UNet for remote sensing image semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 4408715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Fu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wen, W. Semantic Segmentation of Remote Sensing Image via Self-Attention-Based Multi-Scale Feature Fusion. J. Comput.-Aided Des. Comput. Graph. 2023, 35, 1259–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takikawa, T.; Acuna, D.; Jampani, V.; Fidler, S. Gated-scnn: Gated shape cnns for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 5229–5238. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.; Cheng, X.; Wu, X.; Shen, D. Cat: Cross attention in vision transformer. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), Taipei, Taiwan, 18–22 July 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Lin, H.; Long, X. Wetland classification method using fully convolutional neural network and Stacking algorithm. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 257–264. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Gao, H.; Feng, S.; Wei, B.; Hou, Z.; Xiao, F.; Jing, L.; Liao, X. The impact of land use and landscape pattern on ecosystem services in the Dongting lake region, China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.-D.; Xie, F.; Zhang, L. Preprocessing and fusion analysis of GF-2 satellite Remote-sensed spatial data. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Information Systems and Computer Aided Education (ICISCAE), Changchun, China, 6–8 July 2018; pp. 24–29. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, Nevada, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Jaderberg, M.; Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A.; Kavukcuoglu, K. Spatial Transformer Networks. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1506.02025. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.-C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 801–818. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Lu, Y.; Yu, Q.; Luo, X.; Adeli, E.; Wang, Y.; Lu, L.; Yuille, A.L.; Zhou, Y. Transunet: Transformers make strong encoders for medical image segmentation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.04306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, R.; Zhang, C.; Fang, S.; Duan, C.; Meng, X.; Atkinson, P.M. UNetFormer: A UNet-like transformer for efficient semantic segmentation of remote sensing urban scene imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 190, 196–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radman, A.; Mohammadimanesh, F.; Mahdianpari, M. Wet-ConViT: A Hybrid Convolutional–Transformer Model for Efficient Wetland Classification Using Satellite Data. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2673. [Google Scholar]
- Marjani, M.; Mahdianpari, M.; Mohammadimanesh, F.; Gill, E.W. CVTNet: A fusion of convolutional neural networks and vision transformer for wetland mapping using sentinel-1 and sentinel-2 satellite data. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, C.; Cui, Y.; Hodgson, M. Mapping salt marsh along coastal South Carolina using U-Net. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 179, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, J.; Yue, Y.; Lan, Y.; Ling, M.; Li, X.; You, H.; Han, X.; Zhou, G. Tradeoffs among multi-source remote sensing images, spatial resolution, and accuracy for the classification of wetland plant species and surface objects based on the MRS_DeepLabV3+ model. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 81, 102594. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, T.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, M.; Yang, G. Enhancing multiscale representations with transformer for remote sensing image semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5605116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cai, Y.; Li, Q.; Kou, M.; Zhang, T. A review of remote sensing image segmentation by deep learning methods. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2024, 17, 2328827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Xiao, X.; Yao, M.; Cui, H.; Fu, Y. Light4Mars: A lightweight transformer model for semantic segmentation on unstructured environment like Mars. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2024, 214, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yun, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, H.; Nie, Y. LightFormer: A lightweight and efficient decoder for remote sensing image segmentation. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2504.10834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.; Lin, H.; An, X.; Chen, S.; Qi, S.; Zhang, M. Evaluation and analysis of ecosystem service value based on land use/cover change in Dongting Lake wetland. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 136, 108619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Chi, L.; Han, S.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Jiao, C.; Zhou, X. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Wetland in Dongting Lake Based on Multi-Source Satellite Observation Data during Last Two Decades. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Tang, X.; Wang, H.; Fan, W.; Wang, G. Monitoring monthly surface water dynamics of Dongting Lake using Sentinel-1 data at 10 m. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, D.; Jin, X.; Li, L.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Pellissier, L.; Johnson, A.C.; Wu, F.; Zhang, X. Long-term wetland biomonitoring highlights the differential impact of land use on macroinvertebrate diversity in Dongting Lake in China. Commun. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huth, J.; Gessner, U.; Klein, I.; Yesou, H.; Lai, X.; Oppelt, N.; Kuenzer, C. Analyzing water dynamics based on Sentinel-1 time series—A study for Dongting lake wetlands in China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Tang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Shi, Q.; Li, L.; Chen, H. Geospatial perspective for monitoring SDG 6.6.1 based on spatial and temporal analysis of lake water storage variations in Dongting Lake, China. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2025, 57, 102175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, C.; Feng, J. The protected areas system policy enhances habitat quality conservation effectiveness in Dongting Lake Eco-Economic Zone. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 504, 145425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Setting | Detail |
|---|---|
| Framework | PyTorch |
| GPU | NVIDIA RTX3060 |
| Learning rate | 0.0001 |
| Optimizer | SGD |
| Batch size | 8 |
| Epoch | 300 |
| Metric | UA (%) | mIoU (%) | Kappa | OA (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Reed | Sedge | Farmland | Forest | Water | Mudflat | ||||
| CNN | DeepLabV3+ | 79.84 | 82.82 | 77.84 | 62.84 | 59.87 | 30.38 | 63.50 | 0.78 | 83.61 |
| UNet | 88.97 | 89.42 | 81.61 | 80.07 | 89.48 | 80.21 | 77.01 | 0.83 | 87.51 | |
| Transformer | Vision Transformer | 53.71 | 76.24 | 27.42 | 45.28 | 59.87 | 30.38 | 34.03 | 0.38 | 56.32 |
| Swin Transformer | 71.98 | 86.54 | 72.39 | 64.56 | 75.68 | 86.45 | 64.32 | 0.72 | 79.11 | |
| CNN+ Transformer | TransUNet | 84.94 | 91.26 | 81.70 | 82.04 | 90.93 | 80.87 | 76.92 | 0.85 | 88.38 |
| UNetFormer | 88.84 | 87.48 | 88.87 | 90.27 | 87.91 | 83.19 | 77.69 | 0.84 | 87.65 | |
| WetSegNet | 90.83 | 92.29 | 81.86 | 88.12 | 90.20 | 89.83 | 82.91 | 0.88 | 90.81 | |
| Module | UA (%) | mIoU (%) | Kappa | OA (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MFF | MFI | Reed | Sedge | Farmland | Forest | Water | Mudflat | |||
| √ | - | 88.25 | 89.82 | 81.84 | 83.84 | 87.37 | 83.59 | 80.21 | 0.85 | 88.46 |
| - | √ | 89.52 | 89.95 | 81.33 | 84.30 | 88.72 | 85.88 | 79.22 | 0.86 | 89.43 |
| √ | √ | 90.83 | 92.29 | 81.86 | 88.12 | 90.20 | 89.83 | 82.91 | 0.88 | 90.81 |
| Method | Backbone | Inference Time (ms) | Parameters (M) |
|---|---|---|---|
| UNet | ResNet-50 | 45.99 | 27.48 |
| DeepLabV3+ | ResNet-50 | 95.99 | 39.64 |
| Vision Transformer | ViT | 66.93 | 7.00 |
| Swin Transformer | Swin-T | 19.99 | 10.02 |
| TransUNet | ResNet-50 | 144.72 | 93.23 |
| WetSegNet | ResNet-50 | 41.98 | 297.75 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, L.; Xia, S.; Liu, X.; Xie, Z.; Chen, H.; Long, F.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, M. WetSegNet: An Edge-Guided Multi-Scale Feature Interaction Network for Wetland Classification. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3330. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17193330
Chen L, Xia S, Liu X, Xie Z, Chen H, Long F, Wu Y, Zhang M. WetSegNet: An Edge-Guided Multi-Scale Feature Interaction Network for Wetland Classification. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(19):3330. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17193330
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Li, Shaogang Xia, Xun Liu, Zhan Xie, Haohong Chen, Feiyu Long, Yehong Wu, and Meng Zhang. 2025. "WetSegNet: An Edge-Guided Multi-Scale Feature Interaction Network for Wetland Classification" Remote Sensing 17, no. 19: 3330. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17193330
APA StyleChen, L., Xia, S., Liu, X., Xie, Z., Chen, H., Long, F., Wu, Y., & Zhang, M. (2025). WetSegNet: An Edge-Guided Multi-Scale Feature Interaction Network for Wetland Classification. Remote Sensing, 17(19), 3330. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17193330






