Detection of Larch Caterpillar Infestation in Typical Forest Areas of Changbai Mountain, China, Based on Integrated Satellite Hyperspectral and Multispectral Data
Abstract
Highlights
- Integrating Zhuhai-1 hyperspectral and Sentinel-2 multispectral data enabled collaborative monitoring of larch caterpillar infestations.
- The 682–689 nm band and FOD features were highly sensitive to infestations, effectively capturing vegetation stress.
- Demonstrates the potential of multi-source remote sensing for forest pest monitoring.
- Provides sensitive indicators for detecting vegetation stress, supporting forest health protection and management.
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Extracting spectral indices, texture features, and FOD features from the combined image and selecting the optimal feature subset using GA.
- (2)
- Comparing the accuracy of different machine learning models and data sources in detecting larch caterpillar infestations and identifying the most effective model.
- (3)
- Revealing sensitive features and bands related to larch caterpillar infestation and assessing the role of FOD features, providing a reference for future pest detection research.
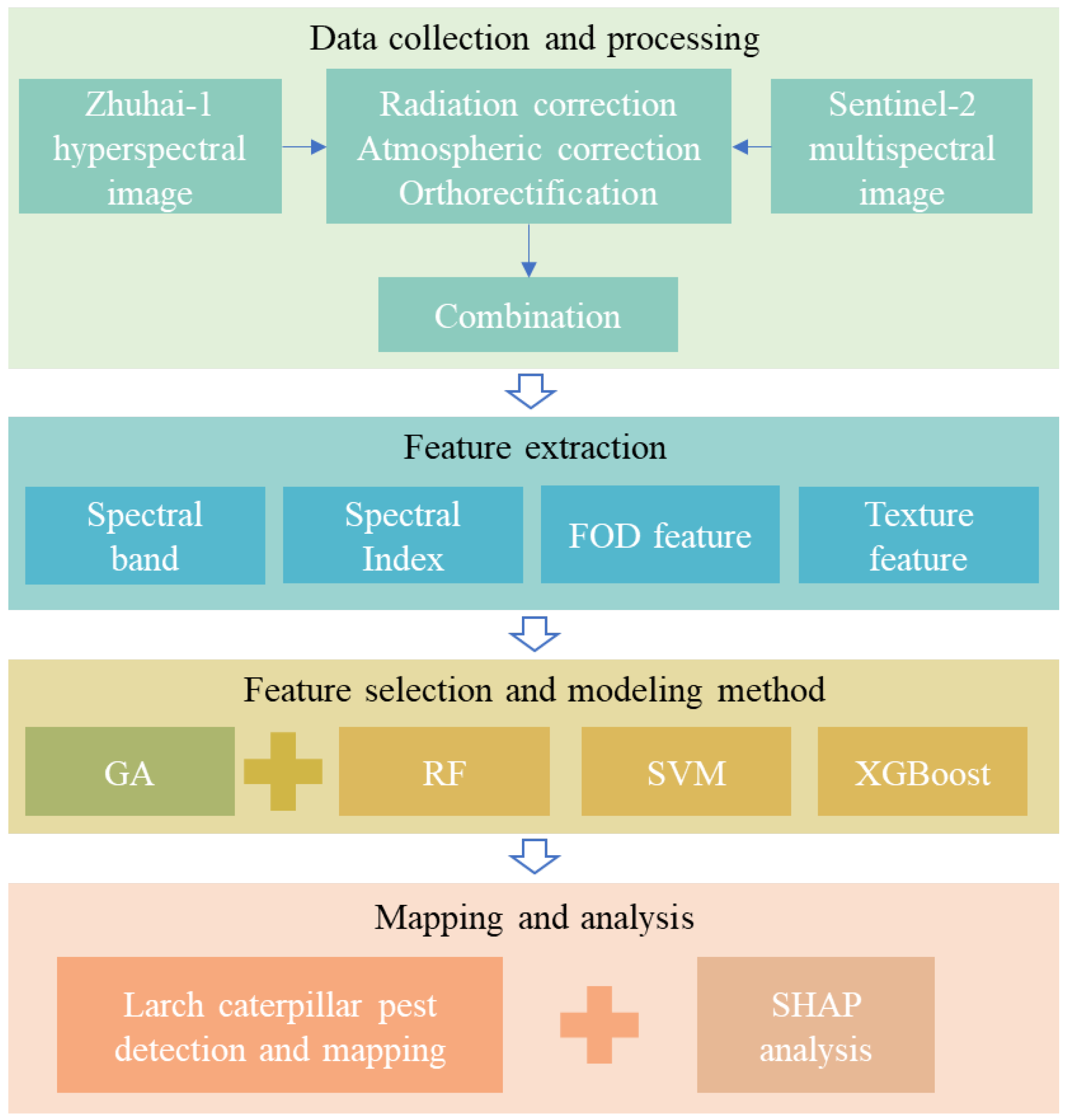
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Remote Sensing Data Sources and Processing
2.3. Method
2.3.1. Feature Extraction
2.3.2. Feature Selection
2.3.3. Model Construction and Evaluation
2.3.4. SHAP Analysis
3. Results
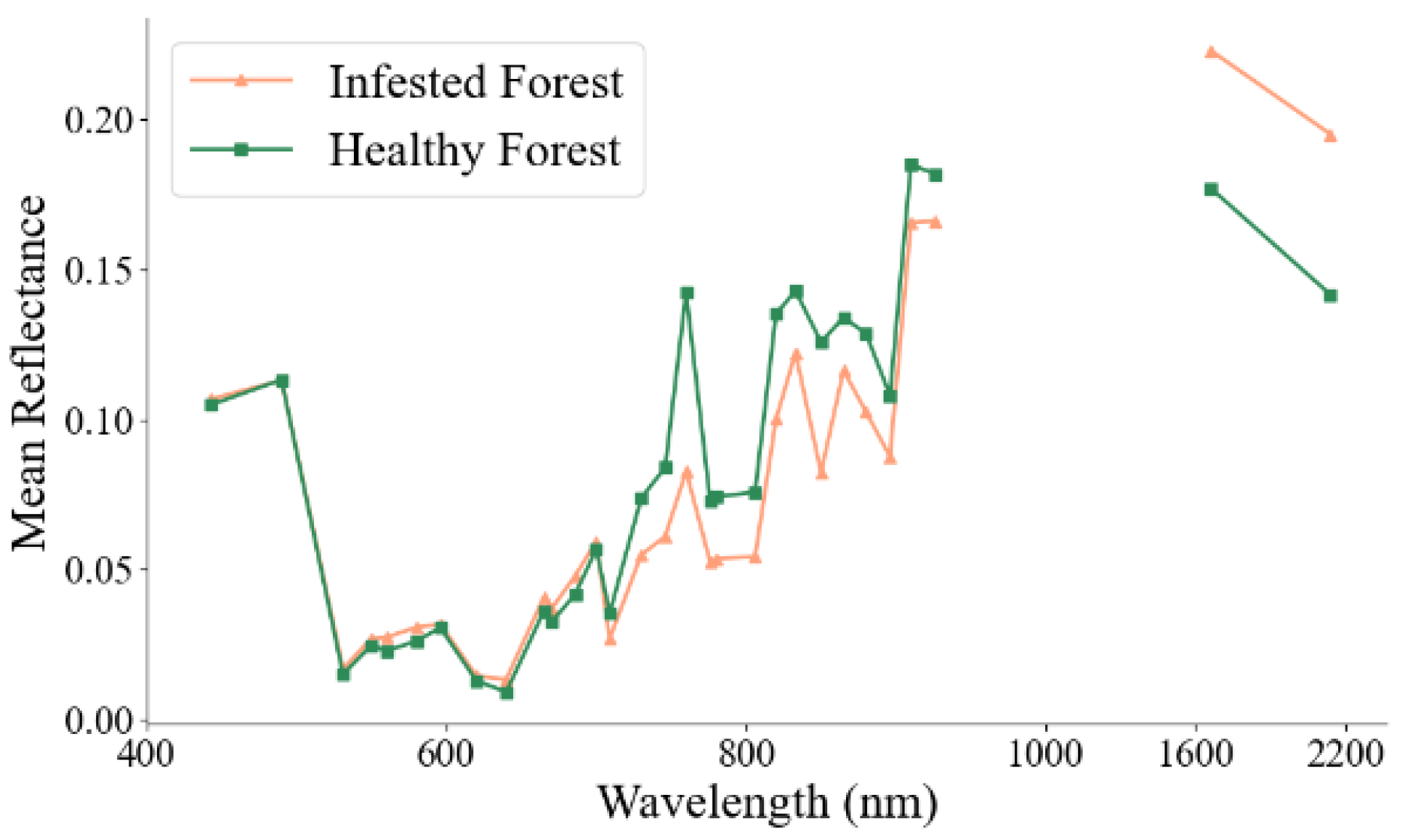
3.1. Spectral Features of the Combined Image
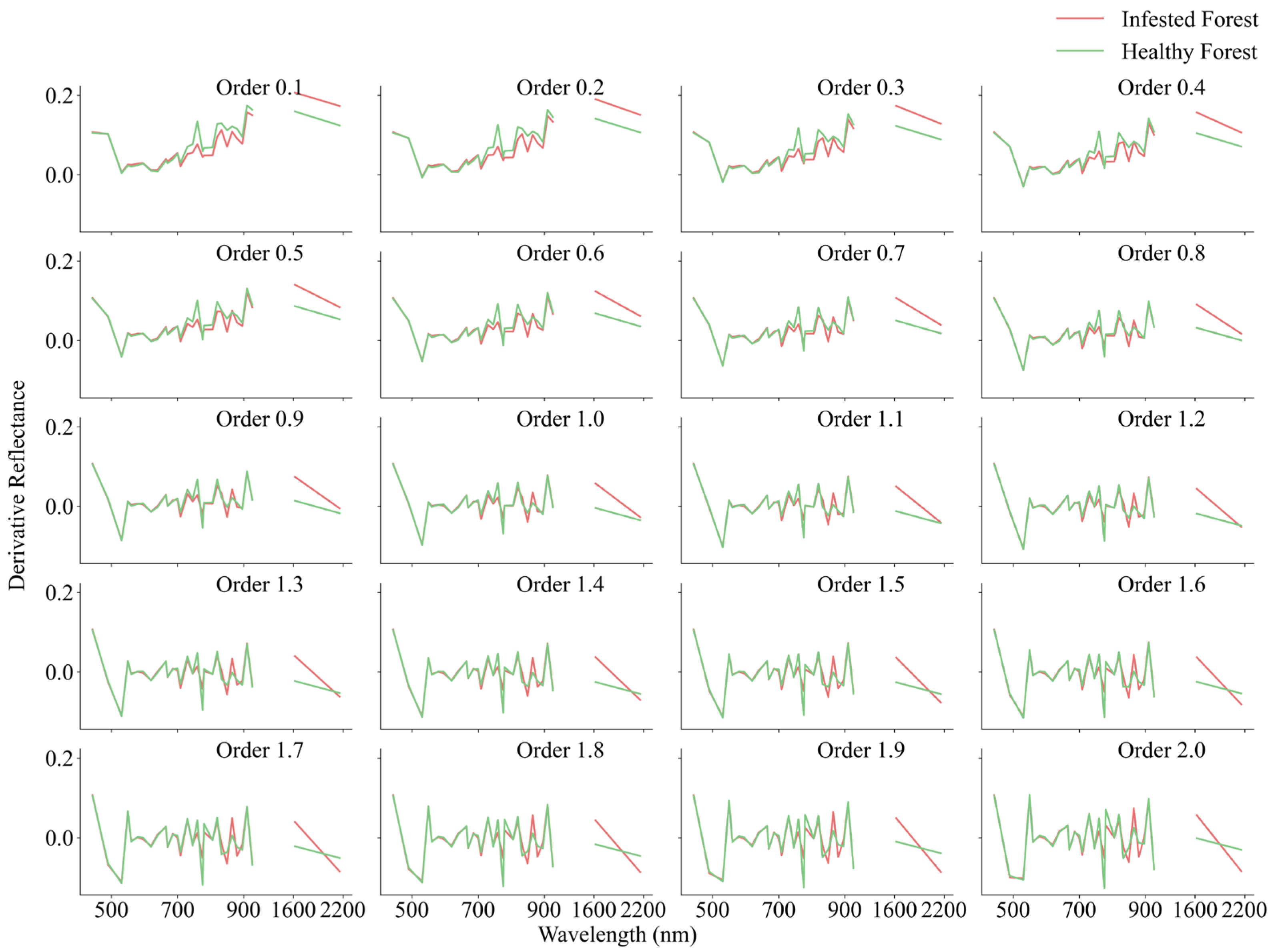
3.2. Feature Extraction and Selection Results
3.3. Comparison of Accuracy and Applicability Across Different Models
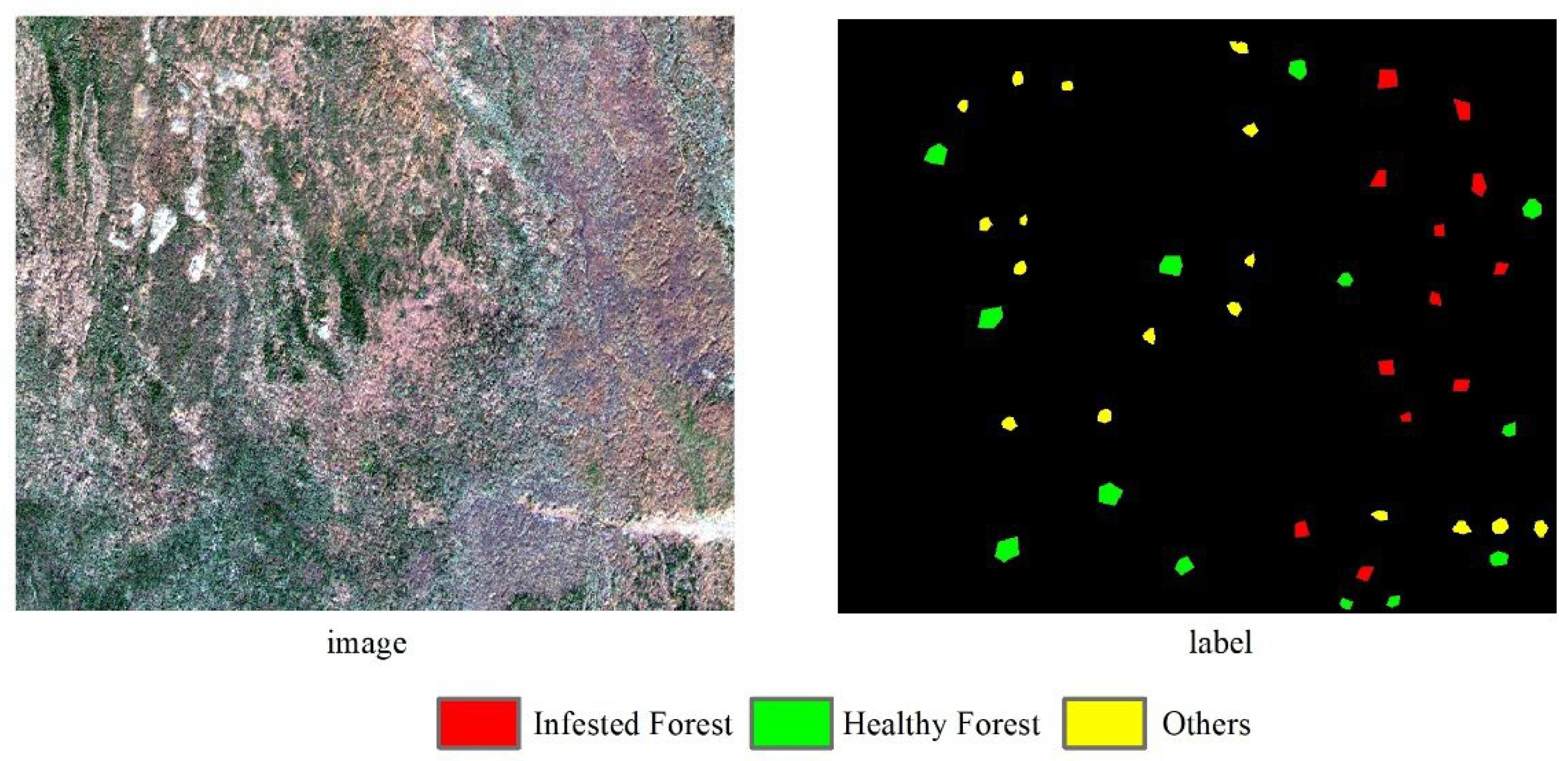
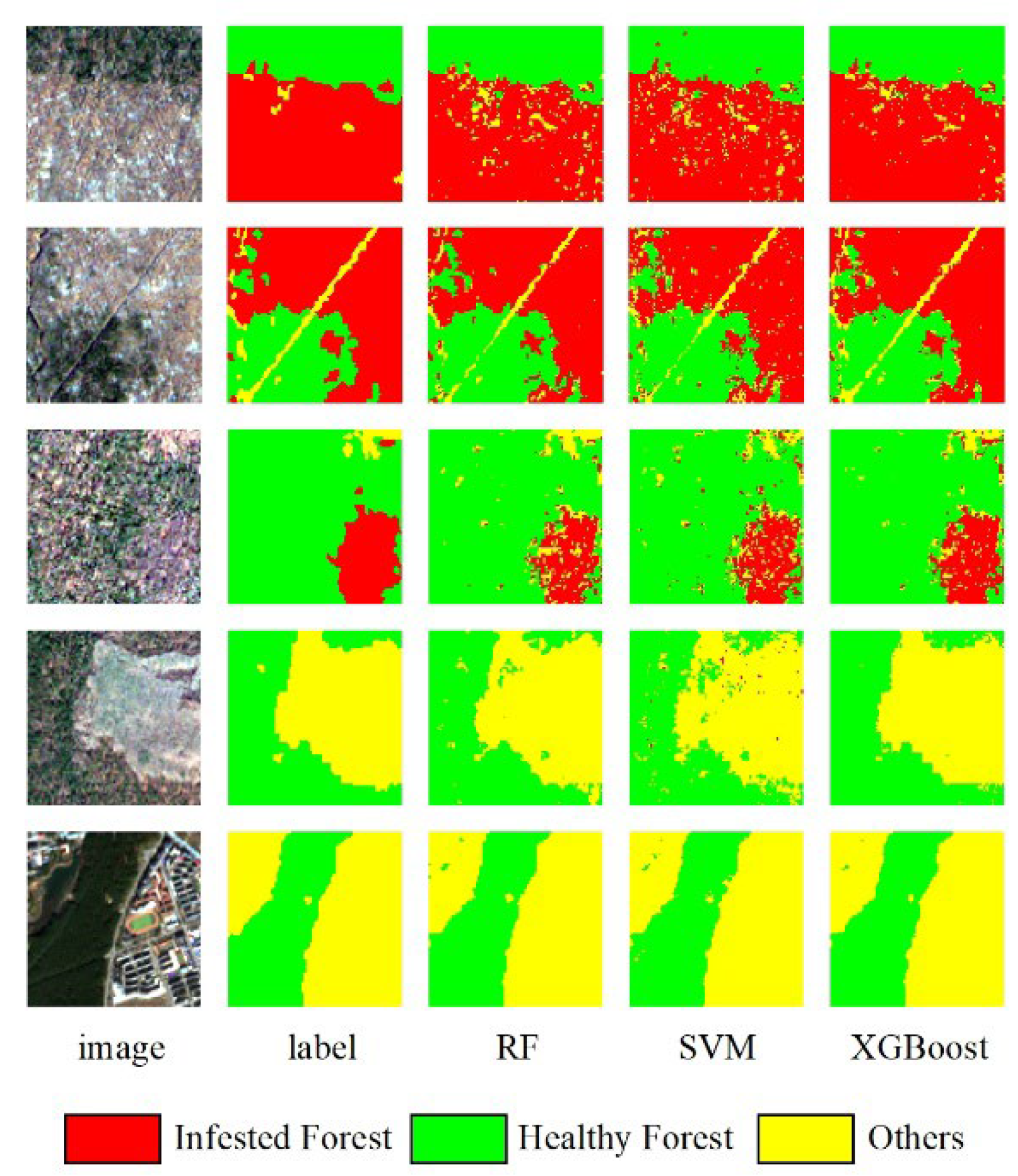
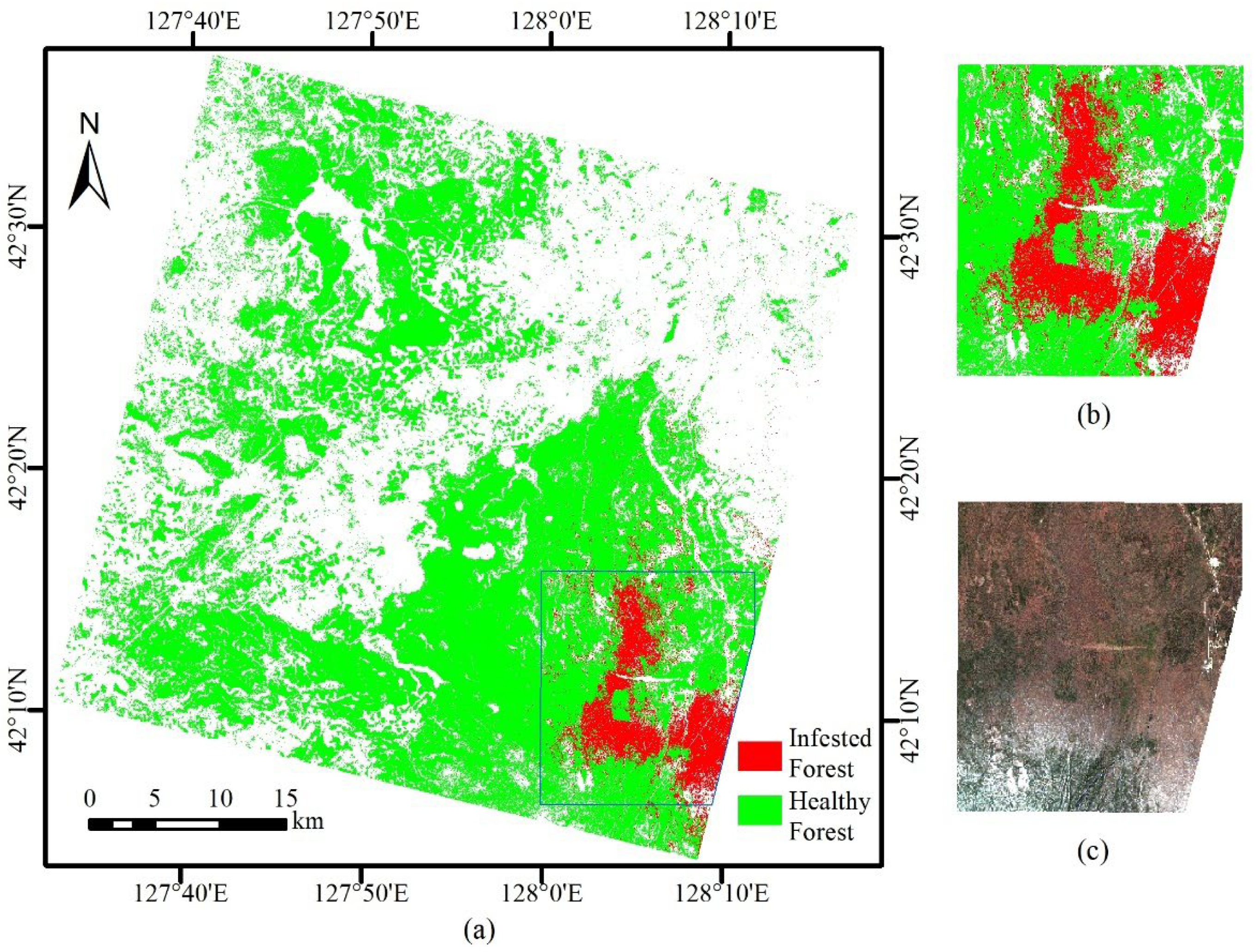
3.4. Mapping of Infested Forest Detection Results
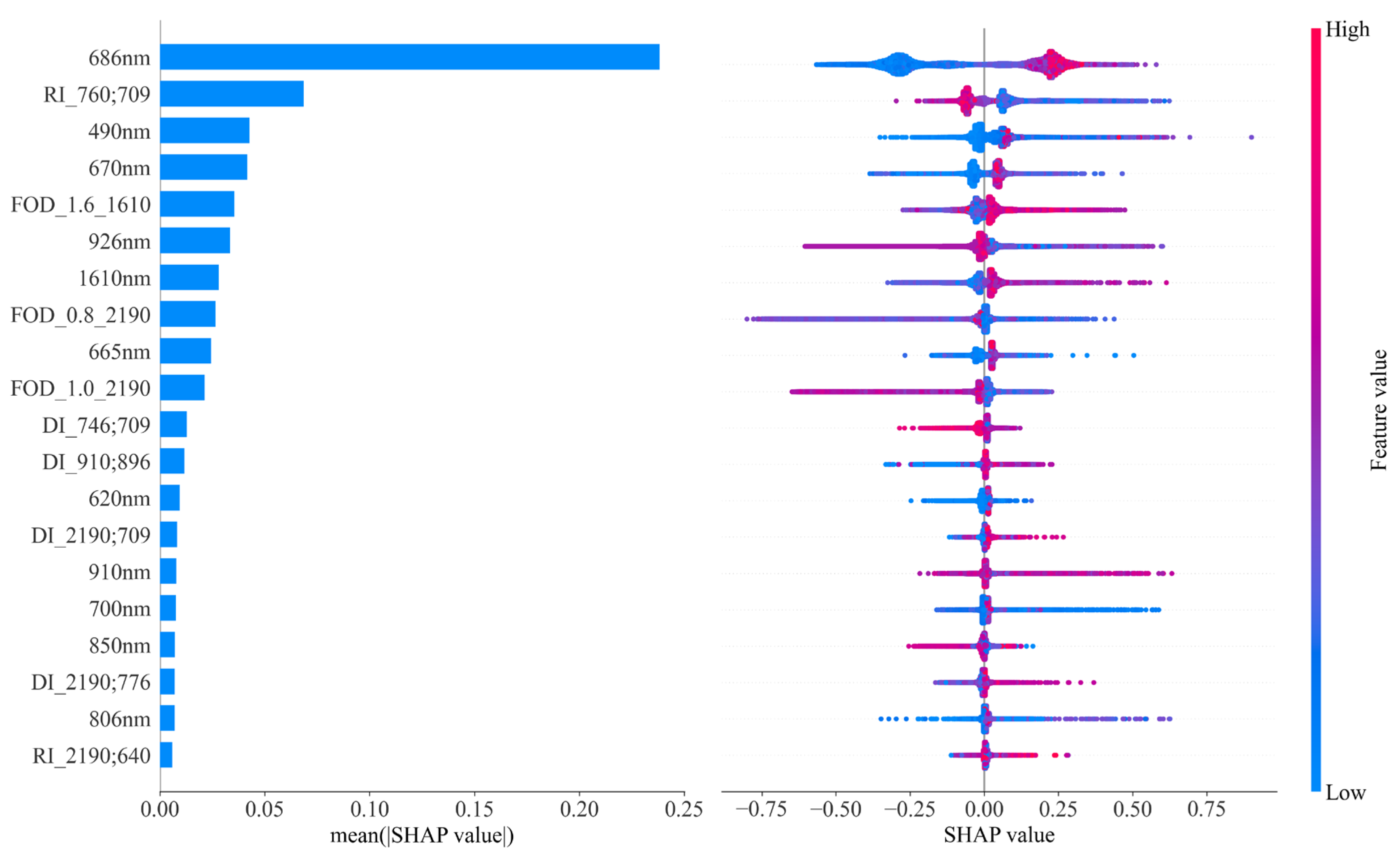
3.5. Interpretability Analysis of Feature Importance Based on the SHAP Method
4. Discussion
4.1. Effectiveness of Combining Hyperspectral and Multispectral Bands and Feature Selection
4.2. Effectiveness of the XGBoost Model and Sensitivity of FOD Features to Pest Infestation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Freer-Smith, P.H.; Webber, J.F. Tree Pests and Diseases: The Threat to Biodiversity and the Delivery of Ecosystem Services. Biodivers. Conserv. 2017, 26, 3167–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mngadi, M.; Germishuizen, I.; Mutanga, O.; Naicker, R.; Maes, W.H.; Odebiri, O.; Schroder, M. A Systematic Review of the Application of Remote Sensing Technologies in Mapping Forest Insect Pests and Diseases at a Tree-Level. Remote Sens. Appl. 2024, 36, 101341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, G.Z.; Fa, X.W.; Zhen, Z.; Jie, C.C.; Wen, Z.X. Utilization of Remote Sensing for Detecting Forest Damage Caused by Insect Infestations or Diseases. J. Nat. Disasters 2003, 12, 73–81. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulridha, J.; Ehsani, R.; Abd-Elrahman, A.; Ampatzidis, Y. A Remote Sensing Technique for Detecting Laurel Wilt Disease in Avocado in Presence of Other Biotic and Abiotic Stresses. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 156, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Lao, J.; Liu, Y.; Chang, C.-C.; Zhang, Z.; Li, H.; Zhou, H. Pine Pest Detection Using Remote Sensing Satellite Images Combined with a Multi-Scale Attention-UNet Model. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 72, 101906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimzadeh-Bajgiran, P.; Weiskittel, A.; Kneeshaw, D.; MacLean, D. Detection of Annual Spruce Budworm Defoliation and Severity Classification Using Landsat Imagery. Forests 2018, 9, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.-H.; Huang, X.-Y.; Lin, L.; Wang, Q.-F.; Liu, J.; Chen, C.-C.; Yu, K.-Y.; Zhou, H.-K.; Zhang, H.-F. Dendrolimus Punctatus Walker Damage Detection Based on Fisher Discriminant Analysis and Random Forest. Spectrosc. Spect Anal. 2018, 38, 2888–2896. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, H.; Skidmore, A.K.; Darvishzadeh, R.; Heurich, M. Sentinel-2 Accurately Maps Green-attack Stage of European Spruce Bark Beetle (Ips typographus, L.) Compared with Landsat-8. Remote Sens. Ecol. Conserv. 2019, 5, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, N.; Hassan, M.A.; Zhao, L. Assessing the Defoliation of Pine Forests in a Long Time-Series and Spatiotemporal Prediction of the Defoliation Using Landsat Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He-Ya, S.; Huang, X.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, J.; Bao, G.; Tong, S.; Bao, Y.; Ganbat, D.; Tsagaantsooj, N.; Altanchimeg, D. Identification of Larch Caterpillar Infestation Severity Based on Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Multispectral and LiDAR Features. Forests 2024, 15, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Zhang, X.; Yang, G.; Zhu, C.; Huo, L.; Feng, H. Assessment of Defoliation during the Dendrolimus tabulaeformis Tsai et Liu Disaster Outbreak Using UAV-Based Hyperspectral Images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 217, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Ren, L.; Luo, Y. Early Detection of Pine Wilt Disease in Pinus tabuliformis in North China Using a Field Portable Spectrometer and UAV-Based Hyperspectral Imagery. For. Ecosyst. 2021, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, G.; Li, X.; Wu, J. Geometric Processing and Accuracy Verification of Zhuhai-1 Hyperspectral Satellites. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassnacht, F.E.; Latifi, H.; Ghosh, A.; Joshi, P.K.; Koch, B. Assessing the Potential of Hyperspectral Imagery to Map Bark Beetle-Induced Tree Mortality. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 533–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, M.; Liu, Z.; Bao, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, F.; Ji, X. Improving Spatial Prediction of Soil Organic Matter in Typical Black Soil Area of Northeast China Using Structural Equation Modeling Integration Framework. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 236, 110404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haralick, R.M.; Shanmugam, K.; Dinstein, I.H. Textural Features for Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1973, 3, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrecilla, E.; Piera, J.; Vilaseca, M. Derivative Analysis of Hyperspectral Oceanographic Data. In Advances in Geoscience and Remote Sensing; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, A.; Zhao, J.; Xiong, H.; Gan, S.; Fu, C. Application of Fractional Differential Calculation in Pretreatment of Saline Soil Hyperspectral Reflectance Data. J. Sens. 2018, 2018, 8017614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Zhao, F.; Liu, Y. Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Images Feature Extraction Based on Spectral Fractional Differentiation. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, H.; Yang, Y.; Xie, J.; Chen, D. Application of Fractional-Order Differential and Ensemble Learning to Predict Soil Organic Matter from Hyperspectra. J. Soils Sediments 2024, 24, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yang, W.; Zhang, M.; Feng, M.; Xiao, L.; Ding, G. Estimation of Water Content in Corn Leaves Using Hyperspectral Data Based on Fractional Order Savitzky-Golay Derivation Coupled with Wavelength Selection. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 182, 105989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Wang, Q.; Jin, J. Estimation of Leaf Photosynthetic Capacity Parameters Using Spectral Indices Developed from Fractional-Order Derivatives. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 212, 108068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Lu, J.; Huang, X. Damage Diagnosis of Pinus yunnanensis Canopies Attacked by Tomicus Using UAV Hyperspectral Images. Forests 2022, 14, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lausch, A.; Heurich, M.; Gordalla, D.; Dobner, H.-J.; Gwillym-Margianto, S.; Salbach, C. Forecasting Potential Bark Beetle Outbreaks Based on Spruce Forest Vitality Using Hyperspectral Remote-Sensing Techniques at Different Scales. For. Ecol. Manag. 2013, 308, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gewali, U.B.; Monteiro, S.T.; Saber, E. Machine Learning Based Hyperspectral Image Analysis: A Survey. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.08701. [Google Scholar]
- Marvasti-Zadeh, S.M.; Goodsman, D.; Ray, N.; Erbilgin, N. Early Detection of Bark Beetle Attack Using Remote Sensing and Machine Learning: A Review. ACM Comput. Surv. 2024, 56, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S.-I. A Unified Approach to Interpreting Model Predictions. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 4768–4777. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, K. On the Local Fractional Derivative. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2010, 362, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaagac, B. New Exact Solutions for Some Fractional Order Differential Equations via Improved Sub-Equation Method. Discret. Contin. Dyn. Syst.-S 2019, 12, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadra, S.; Sagan, V.; Maimaitijiang, M.; Maimaitiyiming, M.; Newcomb, M.; Shakoor, N.; Mockler, T.C. Quantifying Leaf Chlorophyll Concentration of Sorghum from Hyperspectral Data Using Derivative Calculus and Machine Learning. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitley, D. A Genetic Algorithm Tutorial. Stat. Comput. 1994, 4, 65–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, Z.Y.; Abdullah, A.A.; Rashid, T.A. Optimizing Feature Selection with Genetic Algorithms: A Review of Methods and Applications. Appl. Sci. 2025, 36, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogutu, J.O.; Piepho, H.-P.; Schulz-Streeck, T. A Comparison of Random Forests, Boosting and Support Vector Machines for Genomic Selection. BMC Proc. 2011, 5, S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breiman, L. Random Forest. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-Vector Networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ester, M.; Kriegel, H.P.; Xu, X. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. In Proceedings of the 22Nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.; Shao, Z.; Huang, X.; He, L.; Lv, X.; Zhuang, Q. Integrating Zhuhai-1 Hyperspectral Imagery with Sentinel-2 Multispectral Imagery to Improve High-Resolution Impervious Surface Area Mapping. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 2410–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; Shang, K.; Feng, R.; Wang, Y.; Ding, S.; Xiao, Q. Estimation of Soil Organic Matter Content by Combining Zhuhai-1 Hyperspectral and Sentinel-2A Multispectral Images. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 226, 109377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wang, M.; Du, J.; Zhao, J.; Wang, F. Monitoring of Larch Caterpillar (Dendrolimus superans) Infestation Dynamics Using Time-Series Sentinel Images in Changbai Mountains National Nature Reserve, Northeast China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2025, 35, 737–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Jin, Y.; Ye, H.; Huang, W.; Dong, Y.; Fan, L.; Ma, H.; Jiang, J. Remote Sensing Monitoring of Areca Yellow Leaf Disease Based on UAV Multi-Spectral Images. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 54–61. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.; Ma, R.; Melack, J.M.; Duan, H.; Liu, M.; Kutser, T.; Xue, K.; Shen, M.; Qi, T.; Yuan, H. Landsat Observations of Chlorophyll-a Variations in Lake Taihu from 1984 to 2019. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 106, 102642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goebel, M.; Iwaszczuk, D. Spectral Analysis of Images of Plants Under Stress Using a Close-Range Camera. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2023, 48, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Jing, X.; Song, X.; Zhang, T.; Duan, W.; Su, J. Hyperspectral Estimation of Wheat Stripe Rust Using Fractional Order Differential Equations and Gaussian Process Methods. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 206, 107671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zununjan, Z.; Turghan, M.A.; Sattar, M.; Kasim, N.; Emin, B.; Abliz, A. Combining the Fractional Order Derivative and Machine Learning for Leaf Water Content Estimation of Spring Wheat Using Hyper-Spectral Indices. Plant Methods 2024, 20, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Data Source | Band Name | Central Wavelength (nm) | Data Source | Band Name | Central Wavelength (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sentinel-2 | B1 | 443 | Zhuhai-1 | B19 | 746 |
| Sentinel-2 | B2 | 490 | Zhuhai-1 | B20 | 760 |
| Zhuhai-1 | B06 | 531 | Zhuhai-1 | B21 | 776 |
| Zhuhai-1 | B07 | 550 | Zhuhai-1 | B22 | 780 |
| Zhuhai-1 | B08 | 560 | Zhuhai-1 | B23 | 806 |
| Zhuhai-1 | B09 | 580 | Zhuhai-1 | B24 | 820 |
| Zhuhai-1 | B10 | 596 | Zhuhai-1 | B25 | 833 |
| Zhuhai-1 | B11 | 620 | Zhuhai-1 | B26 | 850 |
| Zhuhai-1 | B12 | 640 | Zhuhai-1 | B27 | 865 |
| Zhuhai-1 | B13 | 665 | Zhuhai-1 | B28 | 880 |
| Zhuhai-1 | B14 | 670 | Zhuhai-1 | B29 | 896 |
| Zhuhai-1 | B15 | 686 | Zhuhai-1 | B30 | 910 |
| Zhuhai-1 | B16 | 700 | Zhuhai-1 | B31 | 926 |
| Zhuhai-1 | B17 | 709 | Sentinel-2 | B11 | 1610 |
| Zhuhai-1 | B18 | 730 | Sentinel-2 | B12 | 2190 |
| OA | Recall | F1 | Kappa | Precision | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RF | 91.20% | 92.57% | 90.48% | 87.33% | 88.48% |
| SVM | 90.86% | 89.74% | 88.17% | 84.92% | 86.65% |
| XGBoost | 93.47% | 93.21% | 92.78% | 89.81% | 92.35% |
| OA | Recall | F1 | Kappa | Precision | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RF | 91.22% | 92.22% | 90.13% | 86.12% | 88.13% |
| SVM | 89.29% | 89.68% | 87.85% | 83.02% | 86.09% |
| XGBoost | 93.03% | 93.61% | 92.12% | 88.92% | 90.68% |
| OA | Recall | F1 | Kappa | Precision | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sentinel-2 | 82.90% | 82.08% | 79.97% | 73.20% | 77.97% |
| Zhuhai-1 | 87.67% | 86.11% | 84.94% | 86.32% | 83.80% |
| Combined | 88.78% | 87.40% | 86.21% | 87.36% | 85.05% |
| Band + Index | 92.44% | 90.61% | 90.47% | 88.28% | 90.33% |
| Band + FOD | 91.86% | 90.42% | 91.13% | 88.73% | 91.85% |
| Band + Texture | 89.50% | 87.41% | 88.34% | 87.62% | 89.29% |
| GA Feature | 93.47% | 93.21% | 92.78% | 89.81% | 92.35% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, M.; Cai, D.; Wang, F.; Zhao, J.; Ding, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Cai, J.; Liu, L.; Xu, X. Detection of Larch Caterpillar Infestation in Typical Forest Areas of Changbai Mountain, China, Based on Integrated Satellite Hyperspectral and Multispectral Data. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3274. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17193274
Wang M, Cai D, Wang F, Zhao J, Ding Q, Zhou Y, Cai J, Liu L, Xu X. Detection of Larch Caterpillar Infestation in Typical Forest Areas of Changbai Mountain, China, Based on Integrated Satellite Hyperspectral and Multispectral Data. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(19):3274. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17193274
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Mingchang, Dong Cai, Fengyan Wang, Jingzheng Zhao, Qing Ding, Yanbing Zhou, Jialin Cai, Luming Liu, and Xiaolong Xu. 2025. "Detection of Larch Caterpillar Infestation in Typical Forest Areas of Changbai Mountain, China, Based on Integrated Satellite Hyperspectral and Multispectral Data" Remote Sensing 17, no. 19: 3274. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17193274
APA StyleWang, M., Cai, D., Wang, F., Zhao, J., Ding, Q., Zhou, Y., Cai, J., Liu, L., & Xu, X. (2025). Detection of Larch Caterpillar Infestation in Typical Forest Areas of Changbai Mountain, China, Based on Integrated Satellite Hyperspectral and Multispectral Data. Remote Sensing, 17(19), 3274. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17193274






