Geometry and Topology Preservable Line Structure Construction for Indoor Point Cloud Based on the Encoding and Extracting Framework
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
2.1. Point Cloud Feature Representation
2.2. Geometric Structure Computation
3. Methods
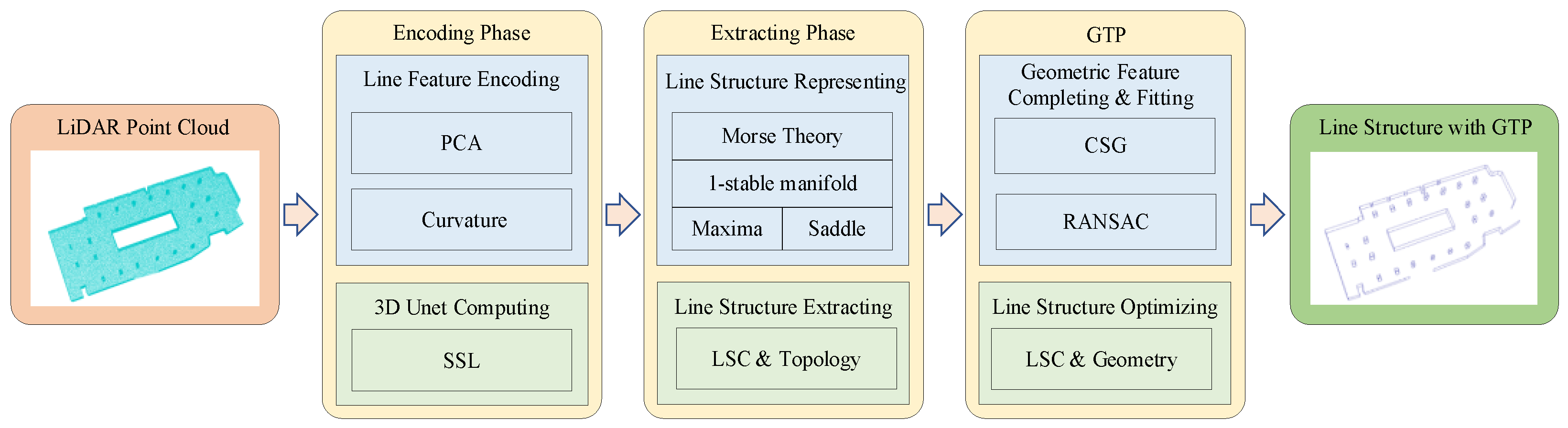
3.1. The Encoding and Extracting Framework
3.2. Encoding Phase
3.2.1. Line Feature Encoding
3.2.2. SSL Computing
3.3. Extracting Phase
3.3.1. Line Structure Representing
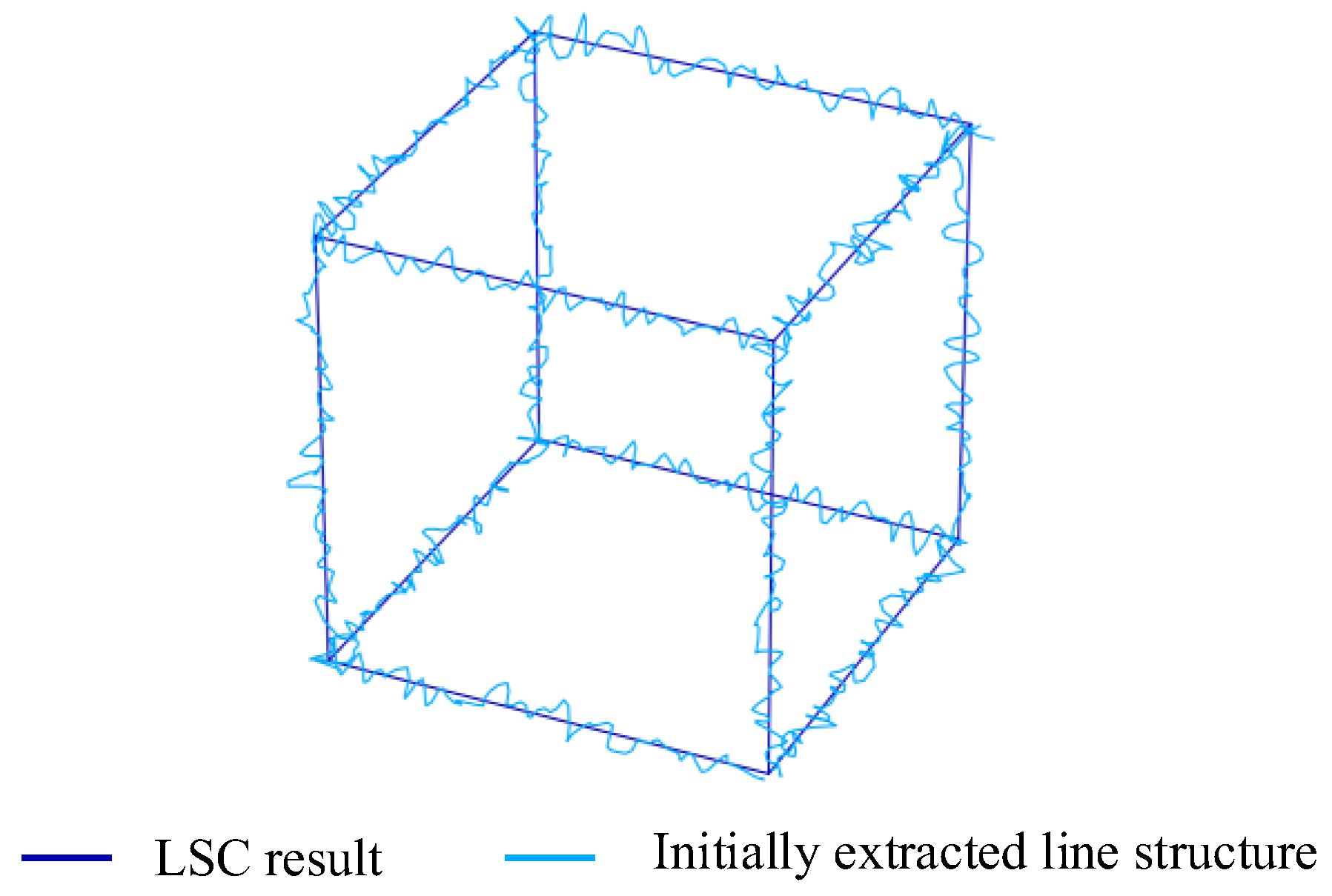
3.3.2. LSC with Topological Connectivity Preserving
3.4. Geometry and Topology Preservation
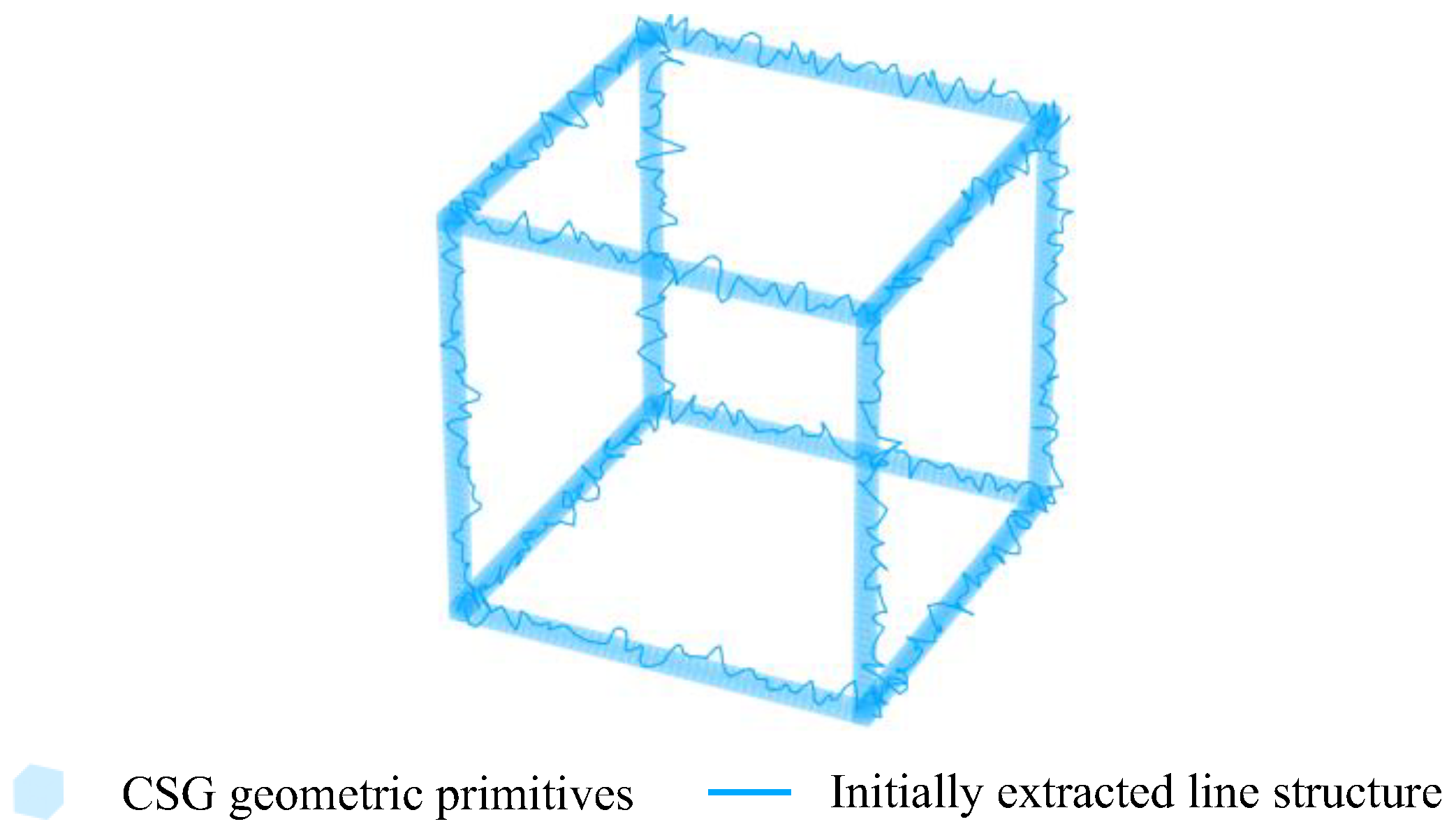
3.4.1. Geometric Structure Decomposing
3.4.2. Line Structure Optimizing
3.4.3. Geometric Feature Completing and GTP Validating
3.5. The GTP-LSC Algorithm
| Algorithm 1 GTP-LSC based on EEF. |
| Input: Point Cloud P, searching distance r |
| Output: Line Structure LS |
| //Encoding Phase |
| FOREACH p in P // for each point in P |
| Ωp = Neighborhood(p, r) // search neighborhood |
| {f1, f2} = ComputePCA(Ωp) // compute PCA, based on Equations (1)–(4) |
| {f3} = ComputeCurvature(Ωp) // compute curvature, based on Equation (5) |
| END |
| S = 3DU-Net(p, {f1, f2, f3}) // compute SSL using the U-Net, based on Equations (6)–(11) |
| //Extracting Phase |
| Cp = MorseAnalysis(S, f3) // compute critical points based on the Morse theory, based on Equations (12)–(14) |
| L = BuildLineStructure(Cp) // constructing initial line structure, based on Equations (15) and (16) |
| //GTP Phase |
| Lcsg = BuildCSGModel (L) // build CSG model, based on Equations (17)–(22) |
| LS = OptimizeLineStructure(Lcsg) // optimize line structure, based on Equations (23)–(29) |
| RETURN LS |
4. Materials and Results
4.1. The Experimental Dataset
4.2. Line Feature Encoding and SSL Computing
4.3. Line Structure Extracting and Optimizing
4.4. LSC Results
4.5. LSC Results for Different Datasets
5. Discussion
5.1. Performance Analysis
5.2. Applicability and Limitation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, W.; Gu, J. Edge-semantic learning strategy for layout estimation in indoor environment. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2019, 50, 2730–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, H.; Hu, Q.; Liu, H.; Liu, L.; Bennamoun, M. Deep learning for 3D point clouds: A survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 43, 4338–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Wang, C.; Cheng, J.; Chen, B.; Jia, F.; Chen, Z.; Li, J. Line segment extraction for large scale unorganized point clouds. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 102, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, H.; Thoennessen, U. Extraction of lines from laser point clouds. In Symposium of ISPRS Commission III: Photogrammetric Computer Vision PCV06; International Archives of Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences: Ettlingen, Germany, 2006; Volume 36, Part 3; pp. 86–91. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, P.; Hua, X.; Tao, W.; Zhang, M. Robust extraction of 3D line segment features from unorganized building point clouds. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langlois, P.A.; Boulch, A.; Marlet, R. Surface reconstruction from 3D line segments. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Quebec City, QC, Canada, 16–19 September 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 553–563. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Lyu, M.R. A Hough transform based line recognition method utilizing both parameter space and image space. Pattern Recognit. 2005, 38, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.K.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, K.H. Multi-scale tensor voting for feature extraction from unstructured point clouds. Graph. Models 2012, 74, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.H.; Chen, J.Y.; Su, P.L.; Chen, C.H. Eigen-feature analysis of weighted covariance matrices for LiDAR point cloud classification. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 94, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, R.; Kang, Q.; Wang, S.; Tay, W.P.; Zhao, K.; Song, Y.; Geng, T.; Xu, Y.; Navarro, D.N.; Hartmannsgruber, A. PointDifformer: Robust point cloud registration with neural diffusion and transformer. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Jing, K.; Cheng, S.; Liu, C.; Ru, J.; Bo, J.; Wang, L. Linnet: Linear network for efficient point cloud representation learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 37, 43189–43209. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Yang, R.; Tan, J.; Liu, Y. Floor plan reconstruction from indoor 3D point clouds using iterative RANSAC line segmentation. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 89, 109238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, A.; Song, S.; Nießner, M.; Fisher, M.; Xiao, J.; Funkhouser, T. 3DMatch: Learning local geometric descriptors from RGB-D reconstructions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1802–1811. [Google Scholar]
- Nurunnabi, A.; Belton, D.; West, G. Robust segmentation for large volumes of laser scanning three-dimensional point cloud data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 4790–4805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauly, M.; Keiser, R.; Gross, M. Multi-scale feature extraction on point-sampled surfaces. Comput. Graph. Forum 2003, 22, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Shi, G.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, M. Multi-scale neighborhood feature extraction and aggregation for point cloud segmentation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2020, 31, 2175–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, R.B.; Blodow, N.; Beetz, M. Fast point feature histograms (FPFH) for 3D registration. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Kobe, Japan, 12–17 May 2009; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 3212–3217. [Google Scholar]
- Tombari, F.; Salti, S.; Di Stefano, L. Unique signatures of histograms for local surface description. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2010: 11th European Conference on Computer Vision, Heraklion, Crete, Greece, 5–11 September 2010; Proceedings, Part III. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 356–369. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, C.R.; Su, H.; Mo, K.; Guibas, L.J. PointNet: Deep learning on point sets for 3D classification and segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 652–660. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, C.R.; Yi, L.; Su, H.; Guibas, L.J. PointNet++: Deep hierarchical feature learning on point sets in a metric space. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 5105–5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bu, R.; Sun, M.; Wu, W.; Di, X.; Chen, B. PointCNN: Convolution on X-transformed points. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2018, 31, 828–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Tuzel, O. VoxelNet: End-to-end learning for point cloud based 3D object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 4490–4499. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Proceedings, Part III. Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Muller, M.; Thabet, A.; Ghanem, B. DeepGCNs: Can GCNs go as deep as CNNs? In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2November 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 9267–9276. [Google Scholar]
- Dewez, T.J.; Girardeau-Montaut, D.; Allanic, C.; Rohmer, J. FACETS: A CloudCompare plugin to extract geological planes from unstructured 3D point clouds. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2016, 41, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, X.; Chrysathou, Y.; Sharf, A.; Cohen-Or, D.; Mitra, N.J. GlobFit: Consistently fitting primitives by discovering global relations. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2011 Papers; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, K. Fast 3D line segment detection from unorganized point cloud. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1901.02532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, F.; Feng, F.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, L. Geometry and Topology Reconstruction of BIM Wall Objects from Photogrammetric Meshes and Laser Point Clouds. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Yang, R.; Chen, X.; Tan, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Tan, J.; Liu, H. A New Framework for Generating Indoor 3D Digital Models from Point Clouds. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayolle, P.A.; Pasko, A. An evolutionary approach to the extraction of object construction trees from 3D point clouds. Comput. Aided Des. 2016, 74, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Hou, S.; Wen, C.; Gong, Z.; Li, Q.; Sun, X.; Li, J. Semantic line framework-based indoor building modeling using backpacked laser scanning point cloud. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 143, 150–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnabel, R.; Wahl, R.; Klein, R. Efficient RANSAC for point-cloud shape detection. Comput. Graph. Forum 2007, 26, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousbie, T. The persistent cosmic web and its filamentary structure–I. Theory and implementation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 414, 350–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tierny, J.; Favelier, G.; Levine, J.A.; Gueunet, C.; Michaux, M. The topology toolkit. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2017, 24, 832–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Yang, B.; Song, S.; Peng, X.; Huang, R. Automatic clearance anomaly detection for transmission line corridors utilizing UAV-Borne LIDAR data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshelham, K.; Díaz Vilariño, L.; Peter, M.; Kang, Z.; Acharya, D. The Isprs Benchmark on Indoor Modelling. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2017, 42, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshelham, K.; Tran, H.; Díaz-Vilariño, L.; Peter, M.; Kang, Z.; Acharya, D. An Evaluation Framework for Benchmarking Indoor Modelling Methods. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, 42, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshelham, K.; Tran, H.; Acharya, D.; Díaz Vilariño, L.; Kang, Z.; Dalyot, S. The Isprs Benchmark on Indoor Modelling—Preliminary Results. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2020, 43, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Dong, Z. A shape-based segmentation method for mobile laser scanning point clouds. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 81, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



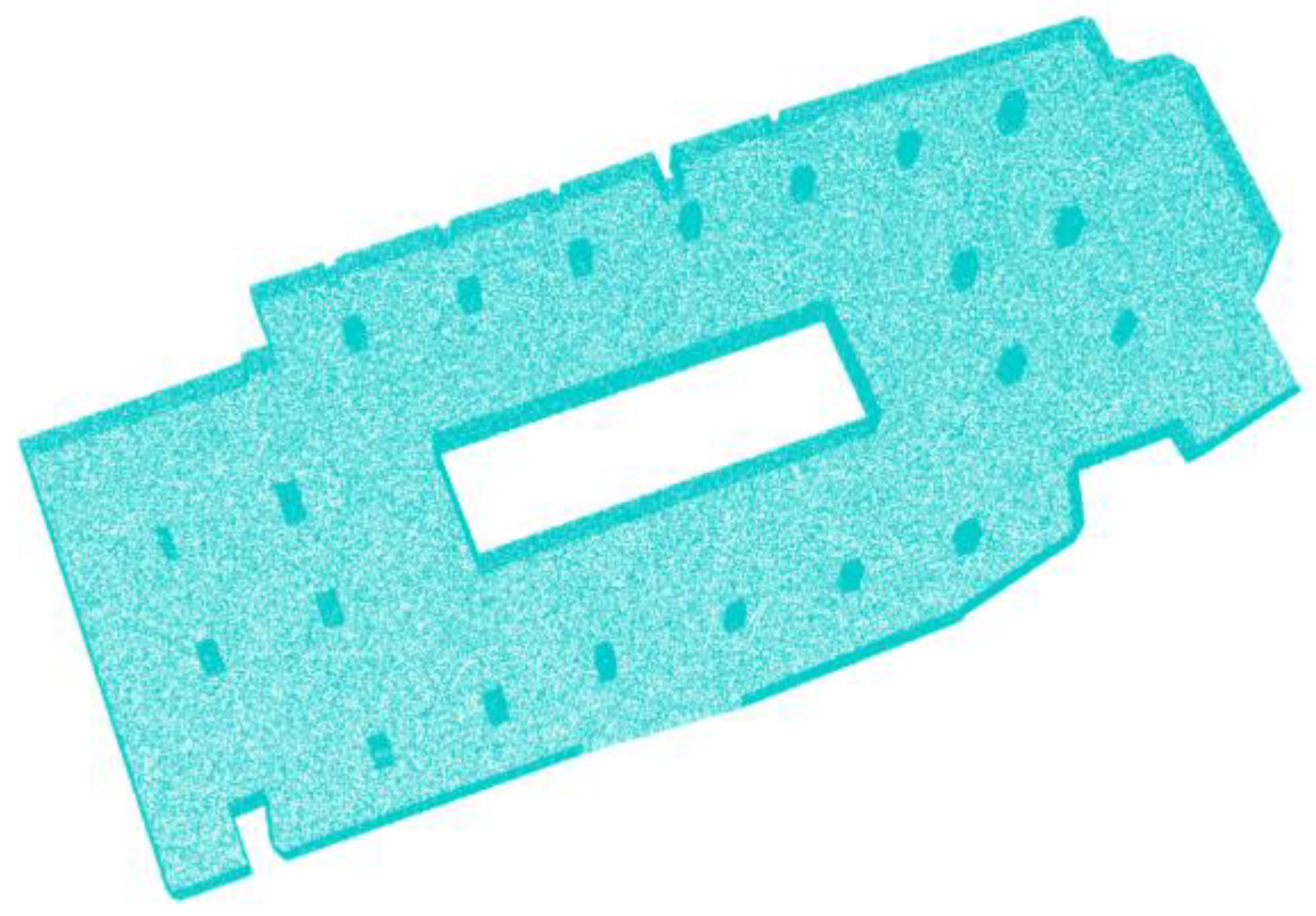
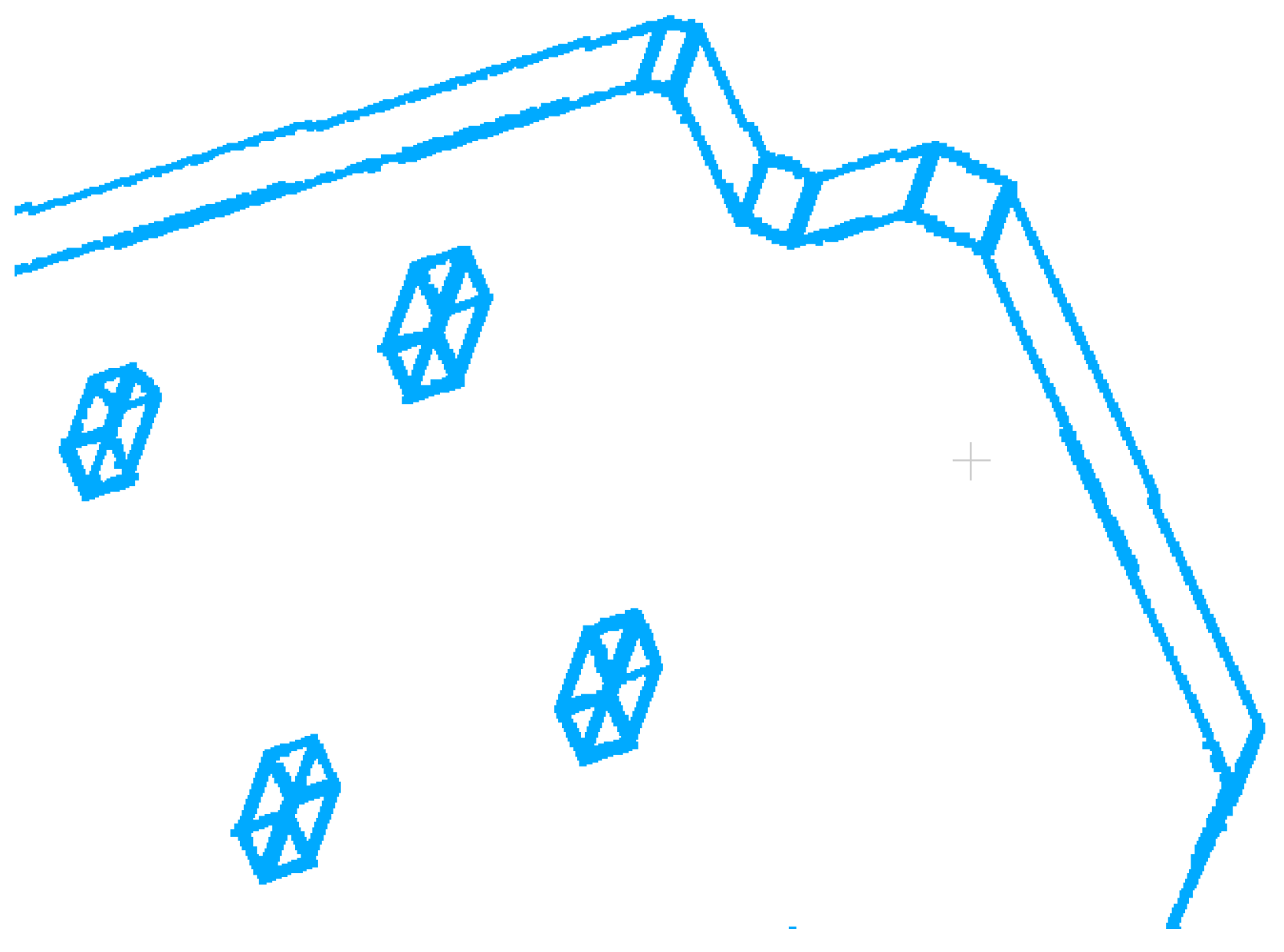



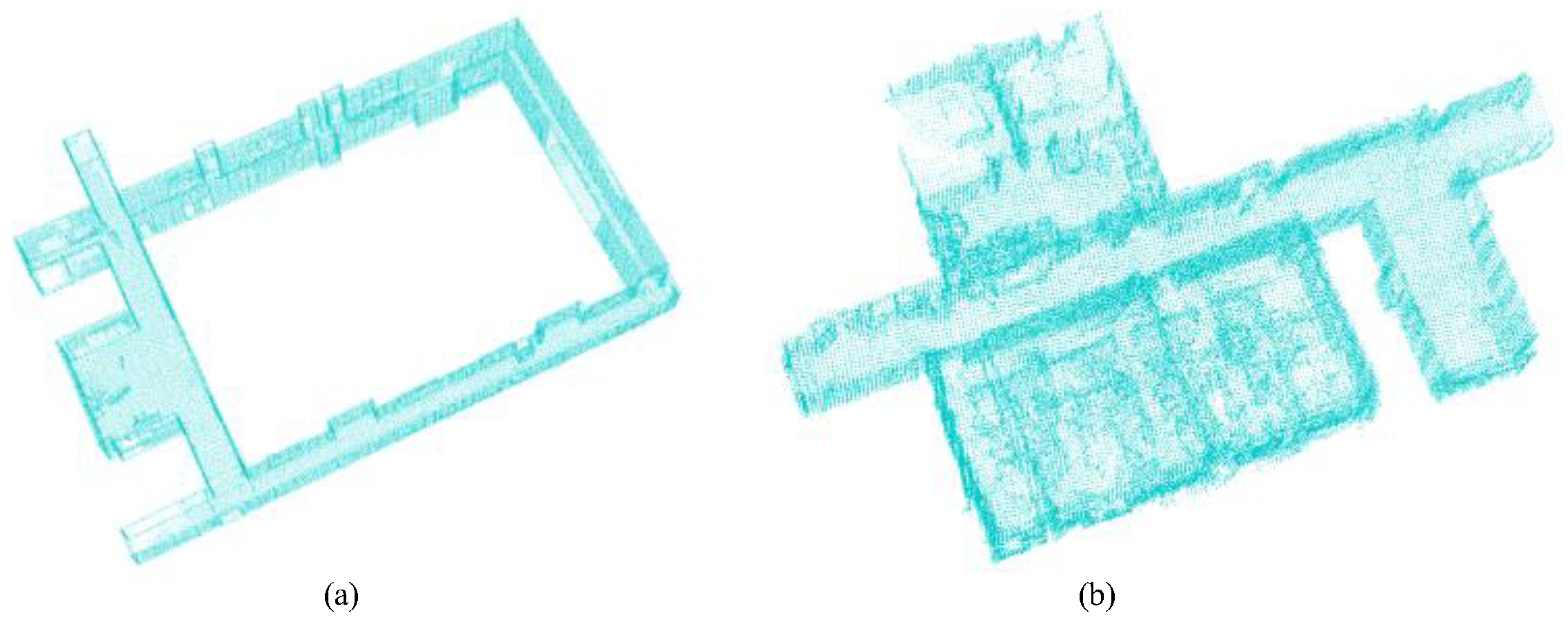
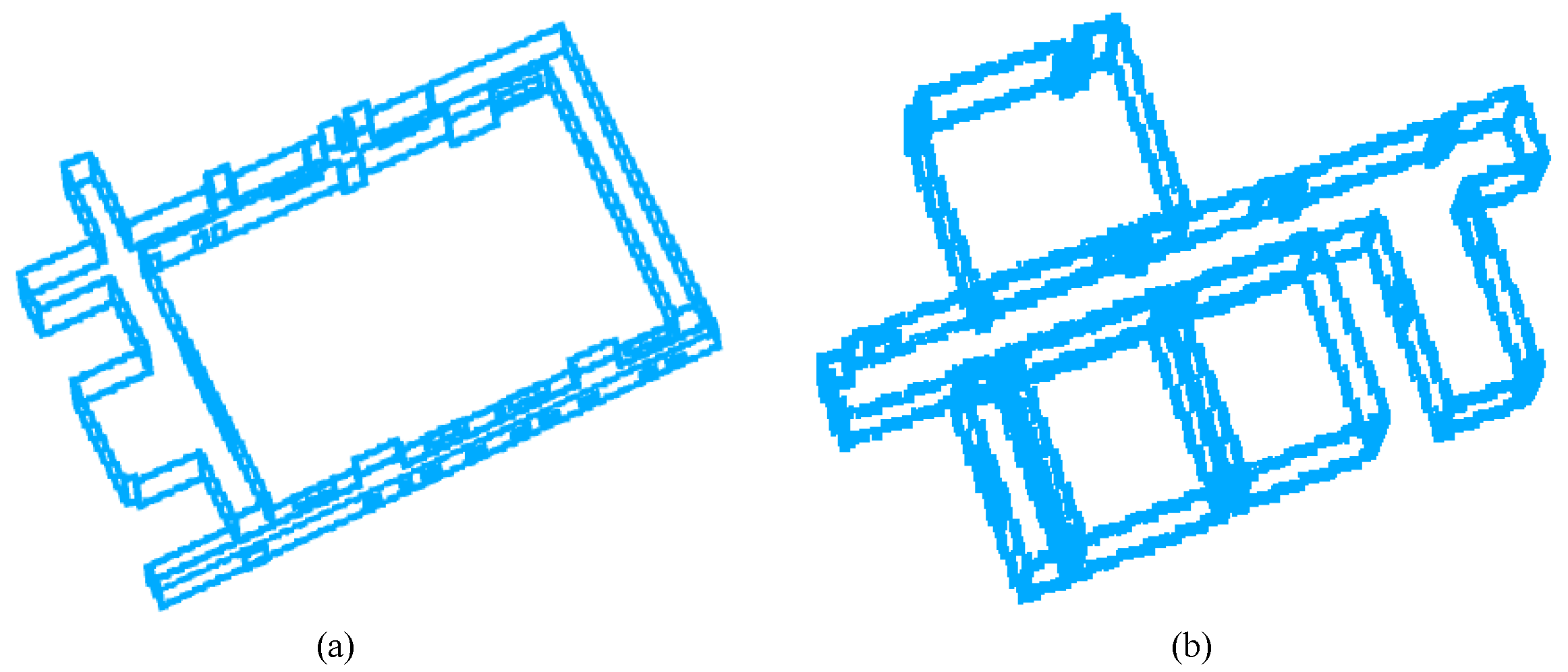



| Dataset | 3D Range (m3) | Point Num. | Scene Type | Scene Descriptions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | 100 × 50 × 5 | 7.9 million | parking garage | Simple; Complete coverage; Medium point density; Low noise |
| D2 | 50 × 5 × 3 | 2.1 million | Corridor | Simple; Complete coverage; Medium point density; Medium noise |
| D3 | 20 × 20 × 3 | 8.62 million | Multi-room Structure | Complex; Complete coverage; Dense point density; Medium noise |
| Dataset | Method | IBR | Precision | Recall | F-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | GTP-LSC | 92.5% | 88.5% | 89.5% | 0.89 |
| FE | 83.2% | 74.6% | 79.6% | 0.77 | |
| PSLF | 85.7% | 80.6% | 83.5% | 0.82 | |
| D2 | GTP-LSC | 94.2% | 92.5% | 91.5% | 0.92 |
| FE | 83.4% | 77.9% | 80.1% | 0.79 | |
| PSLF | 87.1% | 85.8% | 84.2% | 0.85 | |
| D3 | GTP-LSC | 90.8% | 90.0% | 88.0% | 0.89 |
| FE | 78.4% | 78.1% | 75.9% | 0.77 | |
| PSLF | 83.5% | 79.5% | 82.6% | 0.81 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lyu, H.; Xu, H.; Jiao, D.; Zhang, H. Geometry and Topology Preservable Line Structure Construction for Indoor Point Cloud Based on the Encoding and Extracting Framework. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3033. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17173033
Lyu H, Xu H, Jiao D, Zhang H. Geometry and Topology Preservable Line Structure Construction for Indoor Point Cloud Based on the Encoding and Extracting Framework. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(17):3033. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17173033
Chicago/Turabian StyleLyu, Haiyang, Hongxiao Xu, Donglai Jiao, and Hanru Zhang. 2025. "Geometry and Topology Preservable Line Structure Construction for Indoor Point Cloud Based on the Encoding and Extracting Framework" Remote Sensing 17, no. 17: 3033. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17173033
APA StyleLyu, H., Xu, H., Jiao, D., & Zhang, H. (2025). Geometry and Topology Preservable Line Structure Construction for Indoor Point Cloud Based on the Encoding and Extracting Framework. Remote Sensing, 17(17), 3033. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17173033









