Differential Urban-Rural Inequalities and Driving Mechanisms of PM2.5 Exposure in the Central Plains Urban Agglomeration, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Methods
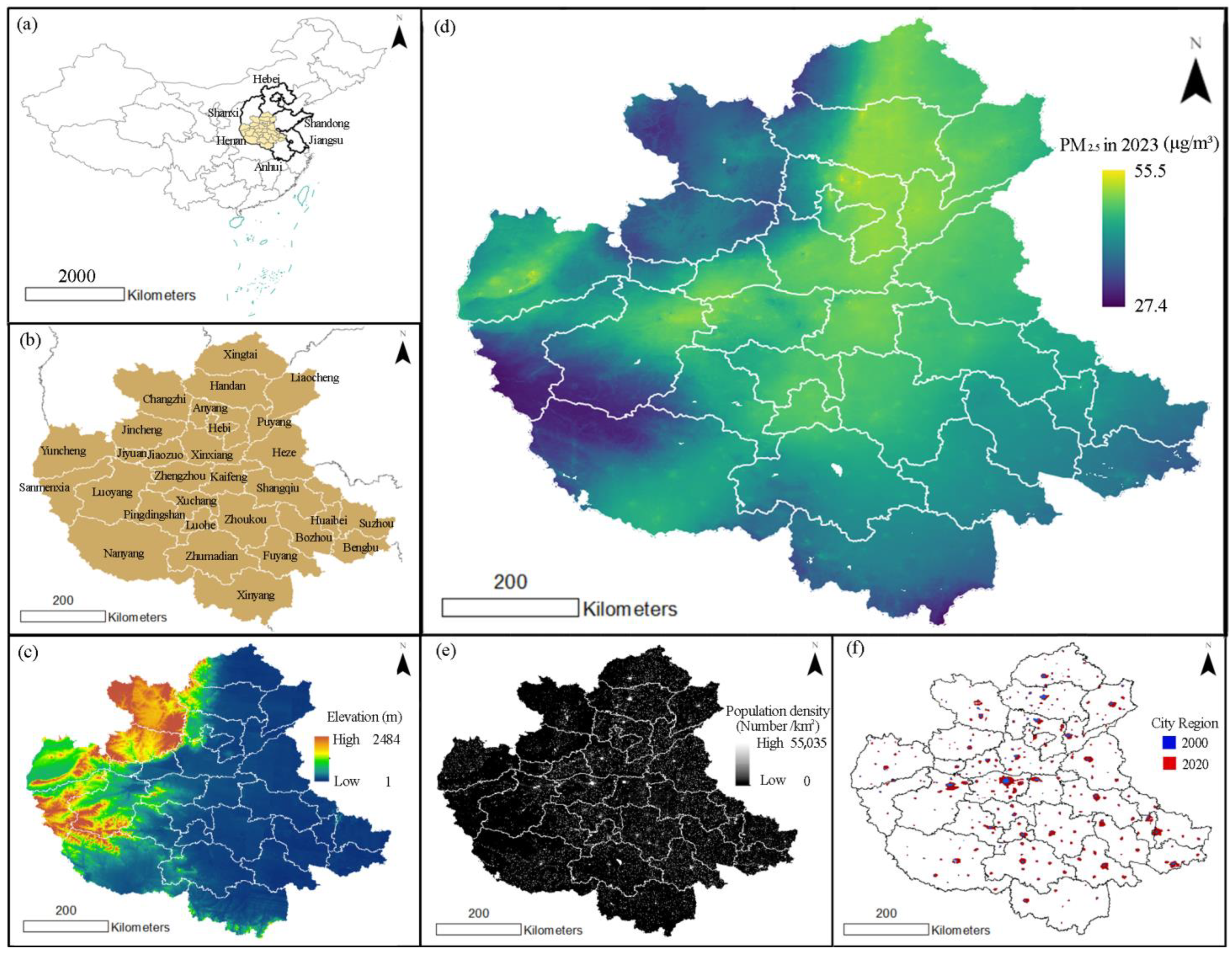
2.1. Research Area
2.2. Data Preparation
2.2.1. PM2.5 Data
2.2.2. Urban−Rural Boundary Data
2.2.3. Control Factor Data
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Spatial and Temporal Trends of PM2.5 in the Central Plains Urban Agglomeration
2.3.2. Predicted Changes in PM2.5 in the Central Plains Urban Agglomeration
2.3.3. Inequality of PM2.5 Exposure in the Central Plains Urban Agglomeration
2.3.4. Driving Factors of PM2.5 Inequality in the Central Plains Urban Agglomeration
2.3.5. Spatial Concentration Effects of PM2.5 in the Central Plains Urban Agglomeration
3. Results and Analysis
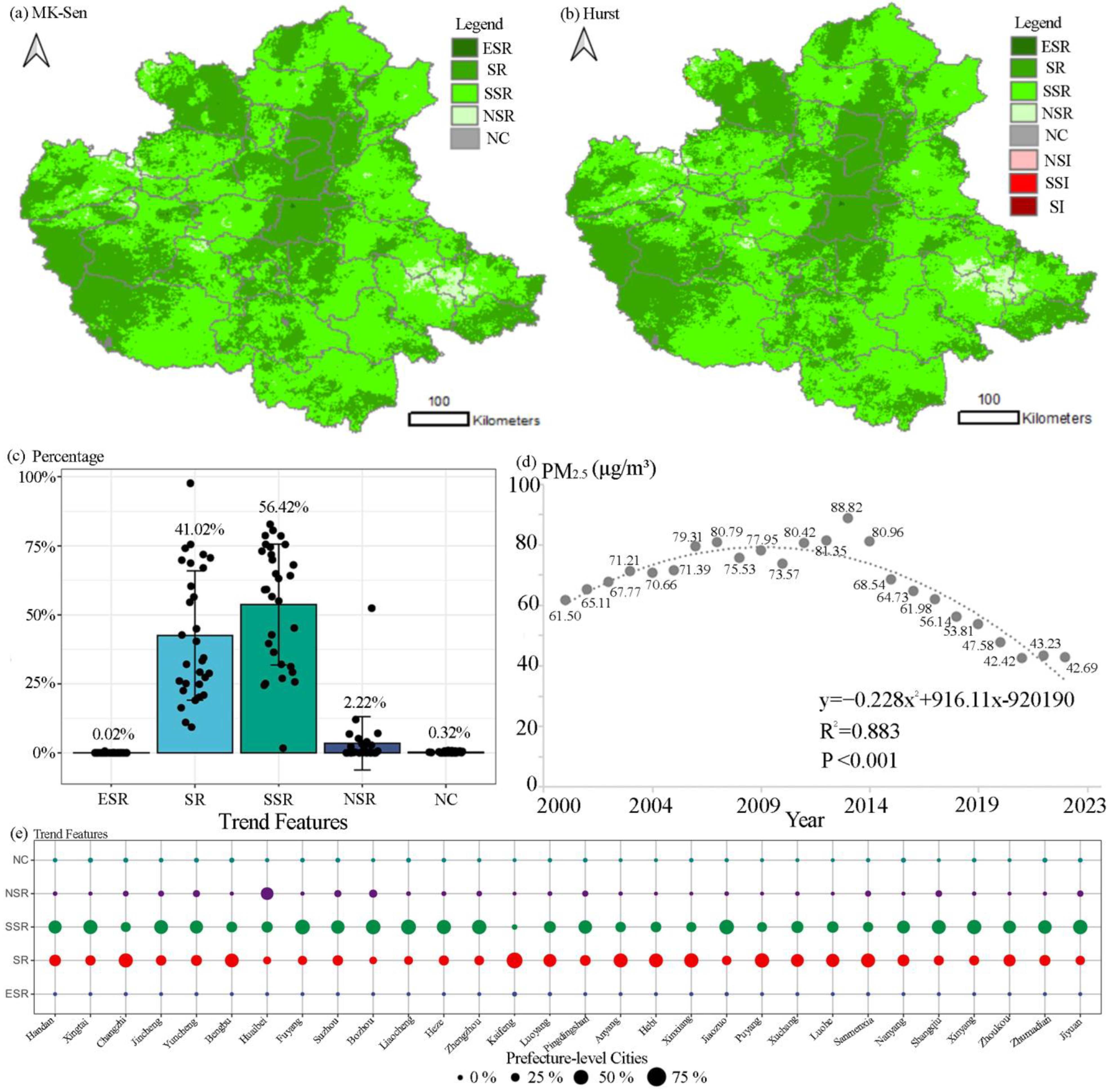
3.1. Spatio-Temporal Trends and Forecasts of PM2.5
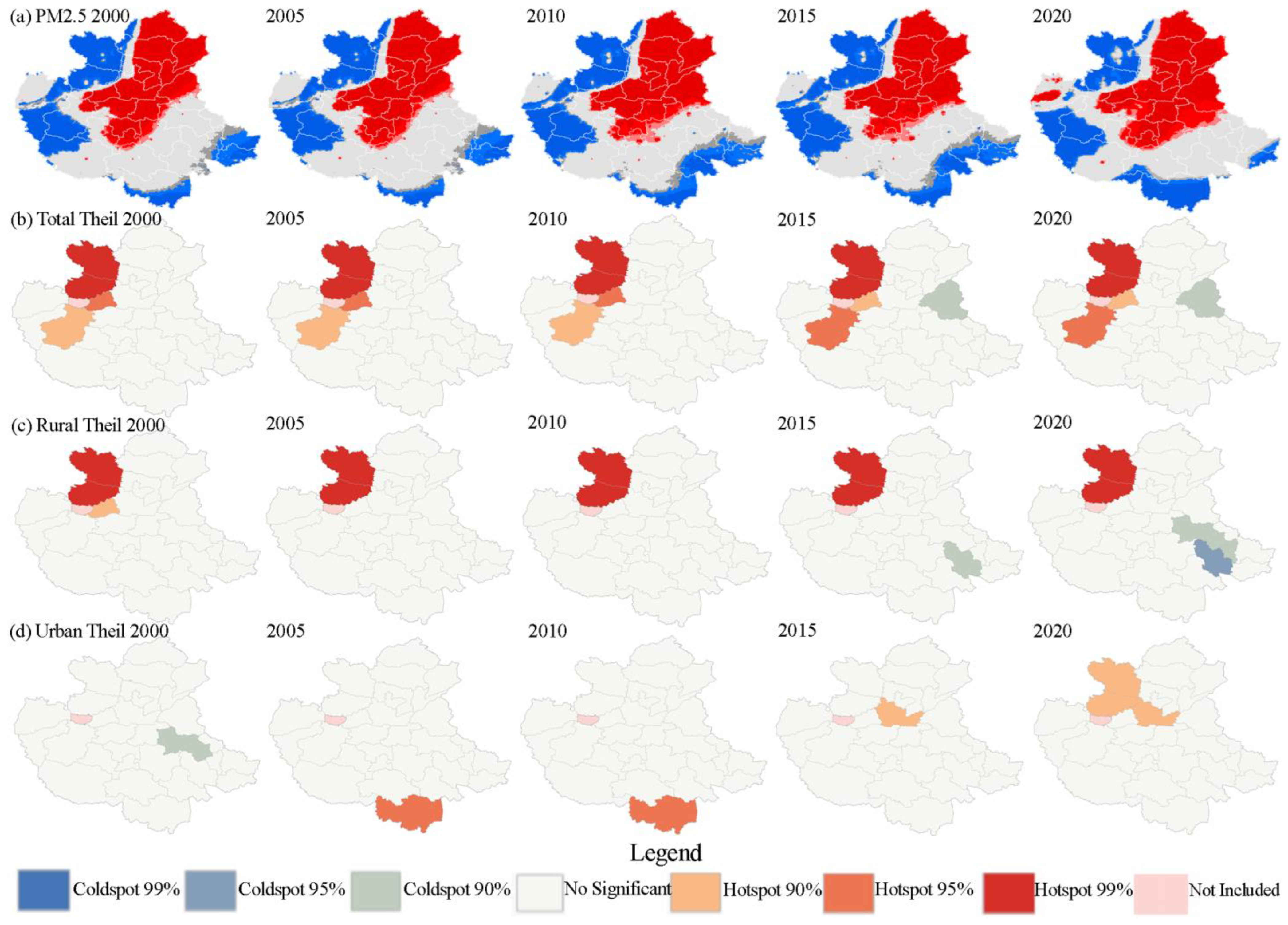
3.2. Regional Inequalities in the PM2.5 Concentration
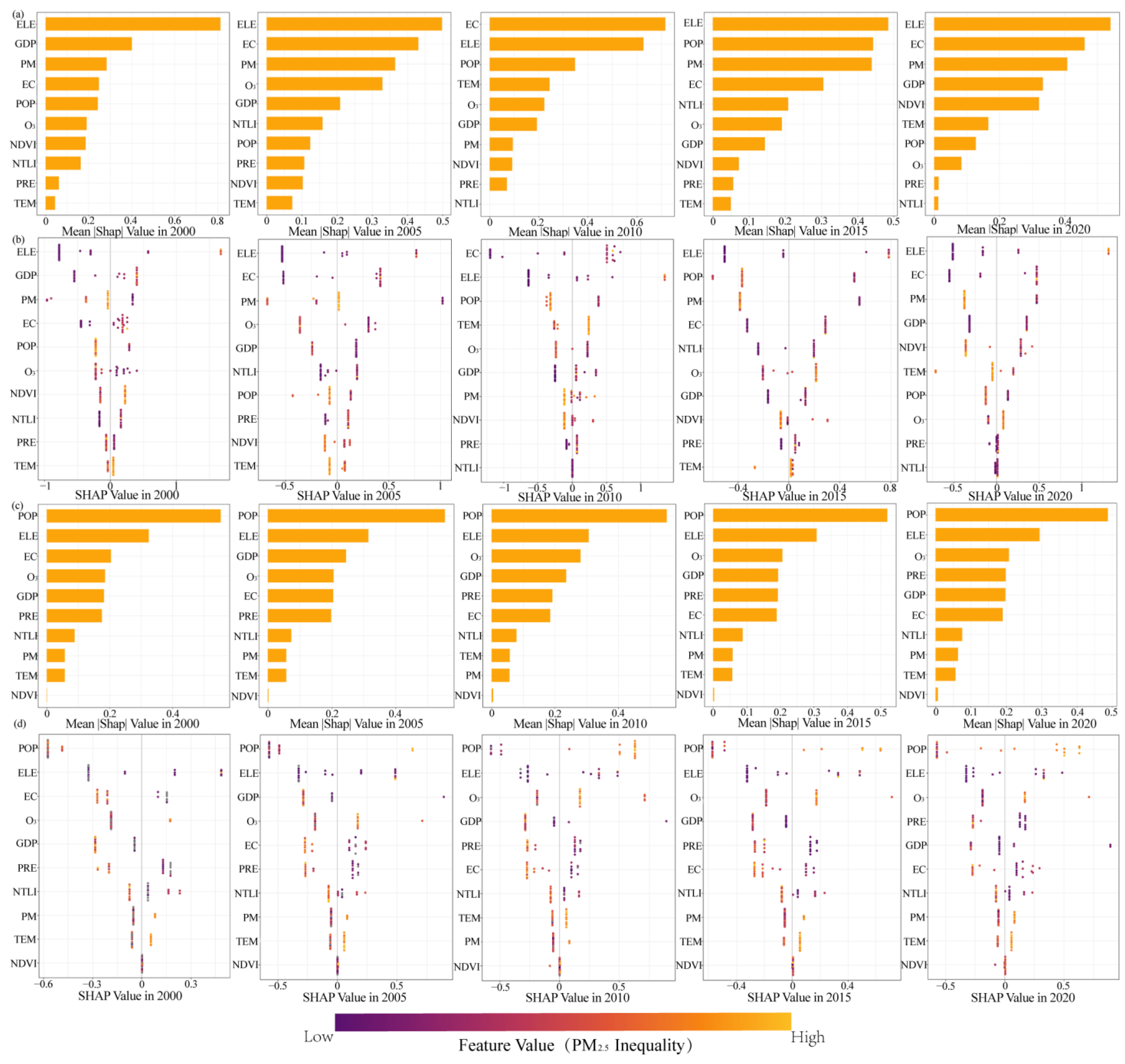
3.3. The Differences in the Driving Factors of Urban−Rural PM2.5 Exposure Inequality
3.4. Identifying Hotspots of PM2.5 Exposure Inequality
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatial and Temporal Change of PM2.5 Exposure in CPUA
4.2. Rural−Urban Differences in PM2.5 Exposure
4.3. Differences in the Drivers of Inequality in PM2.5 Exposure Between Urban and Rural Areas
4.4. Limitations of the Study and Future Outlook
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, F.; Xu, Q.; Li, K.; Yuen, K.F.; Shi, W. The Inhibition Effect of Bank Credits on PM2.5 Concentrations: Spatial Evidence from High-Polluting Firms in China. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 308, 119639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Ma, Y.; Xu, R.; Wu, Y.; Li, S.; Hu, Y.; Guo, Y. Landscape Fire PM2.5 and Hospital Admissions for Cause-Specific Cardiovascular Disease in Urban China. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 9604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Zheng, H.; Li, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhao, B.; Jin, L.; Lyu, R.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; et al. Achieving Health-Oriented Air Pollution Control Requires Integrating Unequal Toxicities of Industrial Particles. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Chen, D.-H.; Ding, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Q.-Y.; Wang, J.-Q.; Cheng, Q.; Jiang, H.; et al. Different Roles of Primary and Secondary Sources in Reducing PM2.5: Insights from Molecular Markers in Pearl River Delta, South China. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 294, 119487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, G.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xue, T.; Zhao, H.; Tong, D.; Zheng, B.; Li, M.; Liu, F.; Hong, C.; et al. Drivers of PM2.5 Air Pollution Deaths in China 2002–2017. Nat. Geosci. 2021, 14, 645–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heft-Neal, S.; Burney, J.; Bendavid, E.; Burke, M. Robust Relationship between Air Quality and Infant Mortality in Africa. Nature 2018, 559, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Ye, T.; Chen, Z.; Xu, R.; Song, J.; Li, S.; Guo, Y. Global Analysis Reveals Region-Specific Air Pollution Exposure Inequalities. One Earth 2024, 7, 2063–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Tong, D.; Shao, M.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, J.; He, H.; Liu, W.; et al. Drivers of Improved PM2.5 Air Quality in China from 2013 to 2017. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 24463–24469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; Chen, B.; Gu, B. Mitigating Air Pollution Benefits Multiple Sustainable Development Goals in China. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 349, 123992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goforth, T.; Nock, D. Air Pollution Disparities and Equality Assessments of US National Decarbonization Strategies. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Dai, Q.; Song, C.; Liu, B.; Guo, F.; Dai, T.; Li, L.; Liu, B.; Bi, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Revealing Drivers of Haze Pollution by Explainable Machine Learning. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2022, 9, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, L.; Ma, P.; He, Y.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, W. Urban and Suburban Decadal Variations in Air Pollution of Beijing and Its Meteorological Drivers. Environ. Int. 2023, 181, 108301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, L.; Wang, T.; Liu, J.; Chen, Z.; Wu, H.; Qu, Y.; Li, M.; Xie, M. Elucidating Drivers of Severe Wintertime Fine Particulate Matter Pollution Episodes in the Yangtze River Delta Region of Eastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Wang, H.; Jiao, L. Heterogeneity of Population Exposure to Particulate Matter Pollution and Its Socioeconomic Driving Mechanism in Shaanxi Province, China. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 363, 125274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, Y.; van Vliet, J. Spatiotemporal Patterns and Drivers of the Urban Air Pollution Island Effect for 2273 Cities in China. Environ. Int. 2024, 184, 108455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, W.; Li, Q. Spatio-Temporal Variations and Socio-Economic Drivers of Air Pollution: Evidence from 332 Chinese Prefecture-Level Cities. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2023, 14, 101782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushing, L.J.; Li, S.; Steiger, B.B.; Casey, J.A. Historical Red-Lining Is Associated with Fossil Fuel Power Plant Siting and Present-Day Inequalities in Air Pollutant Emissions. Nat. Energy 2023, 8, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Tang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, J. National Environmental Monitoring and Local Enforcement Strategies. Nat. Cities 2025, 2, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Chen, L.; Sun, N.; Jin, Y.; Wang, Y. Pollution, Hazards, and Health Inequalities: A Longitudinal Exploration of the Impact of PM2.5 on Depression among Rural Older Adults with Different Incomes in China. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2024, 11, 1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deguen, S.; Zmirou-Navier, D. Social Inequalities Resulting from Health Risks Related to Ambient Air Quality—A European Review. Eur. J. Public Health 2010, 20, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Du, M.; Chen, Z. Environmental Pollution and Socioeconomic Health Inequality: Evidence from China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 95, 104579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, R.; Ding, C.; Zhou, G.; Han, L. How Magnitude of PM2.5 Exposure Disparities Have Evolved across Chinese Urban-Rural Population during 2010–2019. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 382, 135333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunez, Y.; Benavides, J.; Shearston, J.A.; Krieger, E.M.; Daouda, M.; Henneman, L.R.F.; McDuffie, E.E.; Goldsmith, J.; Casey, J.A.; Kioumourtzoglou, M.-A. An Environmental Justice Analysis of Air Pollution Emissions in the United States from 1970 to 2010. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testi, I.; Wang, A.; Paul, S.; Mora, S.; Walker, E.; Nyhan, M.; Duarte, F.; Santi, P.; Ratti, C. Big Mobility Data Reveals Hyperlocal Air Pollution Exposure Disparities in the Bronx, New York. Nat. Cities 2024, 1, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, J.; Lu, K.; Wang, Q.; Li, T. Climate Change Will Amplify the Inequitable Exposure to Compound Heatwave and Ozone Pollution. One Earth 2022, 5, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, B.; Liao, H.; Zhou, B.-B.; Wei, J.; Wang, Y.; Zang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, R.; Wang, X. Changes in PM2.5-Related Health Burden in China’s Poverty and Non-Poverty Areas during 2000–2020: A Health Inequality Perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 861, 160517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.S.; Anjum, E.; Francis, C.; Deanes, L.; Acey, C. Climate Change, Environmental Disasters, and Health Inequities: The Underlying Role of Structural Inequalities. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2022, 9, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; Dang, A. Quantifying the Effects of Different Containment Policies on Urban NO2 Decline: Evidence from Remote Sensing and Ground-Station Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Song, H. A Novel Approach to Assess the Urban Land-Use Efficiency of 767 Resource-Based Cities in China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 151, 110298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, F.P.; Closs, J.G.; Waked, D.; Saldiva, P.H.N.; Veras, M.M. Positive Impacts of Air Pollution Reduction on SDG 3 Targets in Urban Environment. In Integrated Science for Sustainable Development Goal 3: Universal Good Health and Well-Being; Rezaei, N., Ed.; Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 269–292. ISBN 978-3-031-64292-0. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Liu, S.; Feng, T.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Yang, L.; Niu, Q.; Mao, X. Is the Assessment Approach of Sustainable Development Goal 11.3.1 Justified? Evidence from the Drivers of Future Urban Land Use Efficiency. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 444, 141147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhai, Y.; Feng, S.; Tan, Y.; Wei, W. Trade-Offs and Synergies among Air-Pollution-Related SDGs as Well as Interactions between Air-Pollution-Related SDGs and Other SDGs. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 331, 129890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, W.; Zhu, X.; Ma, W.; Han, Y.; Huang, H.; Huang, X. Impact Assessment of Urbanization on Vegetation Net Primary Productivity: A Case Study of the Core Development Area in Central Plains Urban Agglomeration, China. Environ. Res. 2023, 229, 115995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Lyapustin, A.; Sun, L.; Peng, Y.; Xue, W.; Su, T.; Cribb, M. Reconstructing 1-Km-Resolution High-Quality PM2.5 Data Records from 2000 to 2018 in China: Spatiotemporal Variations and Policy Implications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 252, 112136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Cribb, M.; Huang, W.; Xue, W.; Sun, L.; Guo, J.; Peng, Y.; Li, J.; Lyapustin, A.; et al. Improved 1 Km Resolution PM2.5 Estimates across China Using Enhanced Space–Time Extremely Randomized Trees. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 3273–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Cheng, C.; Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Shen, S.; Song, C. A Global Dataset of Annual Urban Extents (1992–2020) from Harmonized Nighttime Lights. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 517–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Dong, J.; Xiao, X.; Dai, J.; Wu, C.; Xia, J.; Zhao, G.; Zhao, M.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Divergent Shifts in Peak Photosynthesis Timing of Temperate and Alpine Grasslands in China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 233, 111395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielson, J.J.; Gesch, D.B. Global Multi-resolution Terrain Elevation Data 2010 (GMTED2010); USGS Open-File Report 2011-1073; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2011.
- Peng, S. 1-Km Monthly Precipitation Dataset for CHINA (1901–2024); National Tibetan Plateau/Third Pole Environment Data Center: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S. 1-km Monthly Mean Temperature Dataset for China (1901-2024); National Tibetan Plateau/Third Pole Environment Data Center: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Gao, M.; Cheng, S.; Hou, W.; Song, M.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y. Global 1 Km × 1 Km Gridded Revised Real Gross Domestic Product and Electricity Consumption during 1992–2019 Based on Calibrated Nighttime Light Data. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Li, K.; Dickerson, R.R.; Pinker, R.T.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Sun, L.; Xue, W.; Cribb, M. Full-Coverage Mapping and Spatiotemporal Variations of Ground-Level Ozone (O3) Pollution from 2013 to 2020 across China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 270, 112775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, B.; Yang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, S.; Qian, X.; Wang, C.; Wu, B.; Wu, J. An Extended Time Series (2000–2018) of Global NPP-VIIRS-like Nighttime Light Data from a Cross-Sensor Calibration. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 889–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaduri, B.; Bright, E.; Coleman, P.; Dobson, J. LandScan. Geoinformatics 2002, 5, 34–37. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Jiang, D.; Yang, X.; Luo, C. Spatialization Approach to 1 Km Grid GDP Supported by Remote Sensing. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2005, 7, 120–123. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Li, C.; Hu, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Wang, Y. Quantitative Estimation of the PM2.5 Removal Capacity and Influencing Factors of Urban Green Infrastructure. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 867, 161476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Zhang, M.; Chen, E.; Zhang, C.; Han, Y. Impact of Seasonal Global Land Surface Temperature (LST) Change on Gross Primary Production (GPP) in the Early 21st Century. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 110, 105572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods; Charles Griffin: London, UK, 1948. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric Tests Against Trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the Regression Coefficient Based on Kendall’s Tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, H.E. Long-Term Storage Capacity of Reservoirs. Trans. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 1951, 116, 770–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conceicao, P.; Ferreira, P. The Young Person’s Guide to the Theil Index: Suggesting Intuitive Interpretations and Exploring Analytical Applications; University of Texas at Austin: Austin, TX, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, T.; Zhang, X.; Liu, W.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, L. Increase in per Capita Cropland Imbalance across Countries from 1985 to 2022: A Threat to Achieving Sustainable Development Goals. Geogr. Sustain. 2025, 6, 100239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shi, M.; Liu, B.; Yi, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, H. Contribution of Ecological Restoration Projects to Long-Term Changes in PM2.5. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 159, 111630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13 August 2016; ACM: New York, NY, USA; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Van den Broeck, G.; Lykov, A.; Schleich, M.; Suciu, D. On the Tractability of SHAP Explanations. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2022, 74, 851–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ma, W.; Zheng, F.; Wang, Z.; Hua, C.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, B.; Jiang, J.; Yan, C.; et al. Identifying Driving Factors of Atmospheric N2O5 with Machine Learning. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 11568–11577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, T.; Wang, P.; Yu, W.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, D.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, H. Drivers of Alleviated PM2.5 and O3 Concentrations in China from 2013 to 2020. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 197, 107110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, B.; Xu, W.; Wang, F.; Gao, J.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Feng, Y.; Shi, G. Machine Learning Combined with the PMF Model Reveal the Synergistic Effects of Sources and Meteorological Factors on PM2.5 Pollution. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manepalli, U.; Bham, G.H.; Kandada, S. Evaluation of Hotspots Identification Using Kernel Density Estimation (K) and Getis-Ord (Gi*) on I-630. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Road Safety and Simulation; National Academy of Sciences Indianapolis Indiana, Indianapolis, IN, USA, 14–16 September 2011; Volume 21, pp. 14–16. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Yu, J.; Zhang, C.; Li, L.; Lei, Y.; Wu, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X. Spatio-Temporal Differentiation Characteristics and the Influencing Factors of PM2.5 Emissions from Coal Consumption in Central Plains Urban Agglomeration. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 945, 173778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Z. Relationship between Land Surface Temperature and Air Quality in Urban and Suburban Areas: Dynamic Changes and Interaction Effects. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2025, 118, 106043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Li, L.; Lei, Y.; Wu, S.; Yan, D.; Fu, X.; Luo, X.; Wu, L. Decoupling Analysis between Economic Growth and Resources Environment in Central Plains Urban Agglomeration. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 142284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yi, P.; Yu, H.; Lin, W.; Wu, X. Assessment on Sustainable Development of Three Major Urban Agglomerations in China Based on Sustainability-Differentiation-Combined Weighting Method. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 31, 2678–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaén, C.; Titos, G.; Castillo, S.; Casans, A.; Rejano, F.; Cazorla, A.; Herrero, J.; Alados-Arboledas, L.; Grimalt, J.O.; van Drooge, B.L. Diurnal Source Apportionment of Organic and Inorganic Atmospheric Particulate Matter at a High-Altitude Mountain Site under Summer Conditions (Sierra Nevada; Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Wang, F.; Du, W.; Wang, S.; Sun, Y.; Yang, W.; Wang, X.; Han, B.; Bai, Z. Elucidating Particle Number Concentrations and Unveiling Source Mechanisms at a Prominent National Background Site on the Northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 969, 178928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Liu, W.; Wang, C. Air Pollution Transmission Networks in China’s Urban Agglomerations: Drivers and Vulnerabilities. Cities 2025, 166, 106237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shuai, C.; Bian, J.; Chen, X.; Wu, Y.; Shen, L. Socioeconomic Factors of PM2.5 Concentrations in 152 Chinese Cities: Decomposition Analysis Using LMDI. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 218, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Yuan, Z.; Wu, Y.; Huang, J.; Yang, F.; Zhang, X.; Huang, D.; Jiang, R. Identification of Synergistic Control for Ozone and PM2.5 Pollution during a Large-Scale Emission Reduction in China. Atmos. Res. 2023, 295, 107025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, A.; Allam, Z.; Bibri, S.E.; Khavarian-Garmsir, A.R. Smart Cities and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): A Systematic Literature Review of Co-Benefits and Trade-Offs. Cities 2024, 146, 104659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Long, T.; Sun, S.; Gao, J. Mega-City Region Sustainability Assessment and Obstacles Identification with GIS–Entropy–TOPSIS Model: A Case in Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 294, 126147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Chen, B. Assessing the Energy-Saving Effect of Urbanization in China Based on Stochastic Impacts by Regression on Population, Affluence and Technology (STIRPAT) Model. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 163, S306–S314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Cao, Z.; Liu, Y. Assessing Rural Revitalization Potential through Rural Transformation Degree and Sustainability: A Quantitative Study of 460 Case Villages in Lingbao, China. Habitat Int. 2024, 153, 103194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xue, L.; Huang, X.; Wang, Z.; Lou, S.; Ding, A. Intensified Haze Formation and Meteorological Feedback by Complex Terrain in the North China Plain Region. Atmospheric Ocean. Sci. Lett. 2023, 16, 100273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Traub, G.; Kroll, C.; Teksoz, K.; Durand-Delacre, D.; Sachs, J.D. National Baselines for the Sustainable Development Goals Assessed in the SDG Index and Dashboards. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, S.; Zhou, S.; Zhou, J.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, T.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Lai, Z.; et al. Spatial-Temporal Patterns of Urban Expansion by Land Use/Land Cover Transfer in China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 155, 111009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Chau, S.N.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Dietz, T.; Wang, J.; Winkler, J.A.; Fan, F.; Huang, B.; et al. Assessing Progress towards Sustainable Development over Space and Time. Nature 2020, 577, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Dimension | Indicator | Spatial Resolution | Source | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pollution | PM2.5 (PM) | 1000 m | https://zenodo.org/records/13340222 | [34,35] |
| Urban | Urban Built Area | 1000 m | https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.16602224.v1 | [36] |
| Natural | Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) | 1000 m | https://www.earthdata.nasa.gov/ | [37] |
| Elevation (ELE) | 1000 m | https://search.earthdata.nasa.gov/ | [38] | |
| Climate | Precipitation (PRE) | 1000 m | https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/zh-hans/data | [39] |
| Temperature (TEM) | 1000 m | https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/zh-hans/data | [40] | |
| Discharge | Electricity consumption (EC) | 1000 m | https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.17004523.v1 | [41] |
| Ozone Concentration(O3) | 1000 m | http://geodata.nnu.edu.cn/data | [42] | |
| Social-Economic | Nighttime light (NTL) | 1000 m | http://geodata.nnu.edu.cn/ | [43] |
| Population density (POP) | 1000 m | https://www.eastview.com/resources/e-collections/landscan/ | [44] | |
| Gross Domestic Product (GDP) | 1000 m | https://www.resdc.cn/doi/doi.aspx?DOIid = 33 | [45] |
| β | Z | Trend Type | Trend Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| >0 | |Z| > 2.58 | 4 | Extremely significant increase (ESI) |
| 1.96 < |Z| ≤ 2.58 | 3 | Significant increase (SI) | |
| 1.65 < |Z| ≤ 1.96 | 2 | Slightly significant increase (SSI) | |
| |Z| ≤ 1.65 | 1 | No significant increase (NSI) | |
| 0 | Z = 0 | 0 | No change (NC) |
| <0 | |Z| ≤ 1.65 | −1 | No significant reduction (NSR) |
| 1.65 < |Z| ≤ 1.96 | −2 | Slightly significant reduction (SSR) | |
| 1.96 < |Z| ≤ 2.58 | −3 | Significant reduction (SR) | |
| |Z| > 2.58 | −4 | Extremely significant reduction (ESR) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, X.; Wang, C.; Ji, Y.; Dang, Q.; Fu, Z.; Mao, X.; Wang, E.; Jiang, Y.; Fan, W. Differential Urban-Rural Inequalities and Driving Mechanisms of PM2.5 Exposure in the Central Plains Urban Agglomeration, China. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2982. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17172982
Sun X, Wang C, Ji Y, Dang Q, Fu Z, Mao X, Wang E, Jiang Y, Fan W. Differential Urban-Rural Inequalities and Driving Mechanisms of PM2.5 Exposure in the Central Plains Urban Agglomeration, China. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(17):2982. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17172982
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Xiaofan, Chengyuan Wang, Yaqin Ji, Qiuling Dang, Zhicong Fu, Xuegang Mao, Enheng Wang, Yan Jiang, and Weizhao Fan. 2025. "Differential Urban-Rural Inequalities and Driving Mechanisms of PM2.5 Exposure in the Central Plains Urban Agglomeration, China" Remote Sensing 17, no. 17: 2982. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17172982
APA StyleSun, X., Wang, C., Ji, Y., Dang, Q., Fu, Z., Mao, X., Wang, E., Jiang, Y., & Fan, W. (2025). Differential Urban-Rural Inequalities and Driving Mechanisms of PM2.5 Exposure in the Central Plains Urban Agglomeration, China. Remote Sensing, 17(17), 2982. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17172982







