Incorporating Building Morphology Data to Improve Urban Land Use Mapping: A Case Study of Shenzhen
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
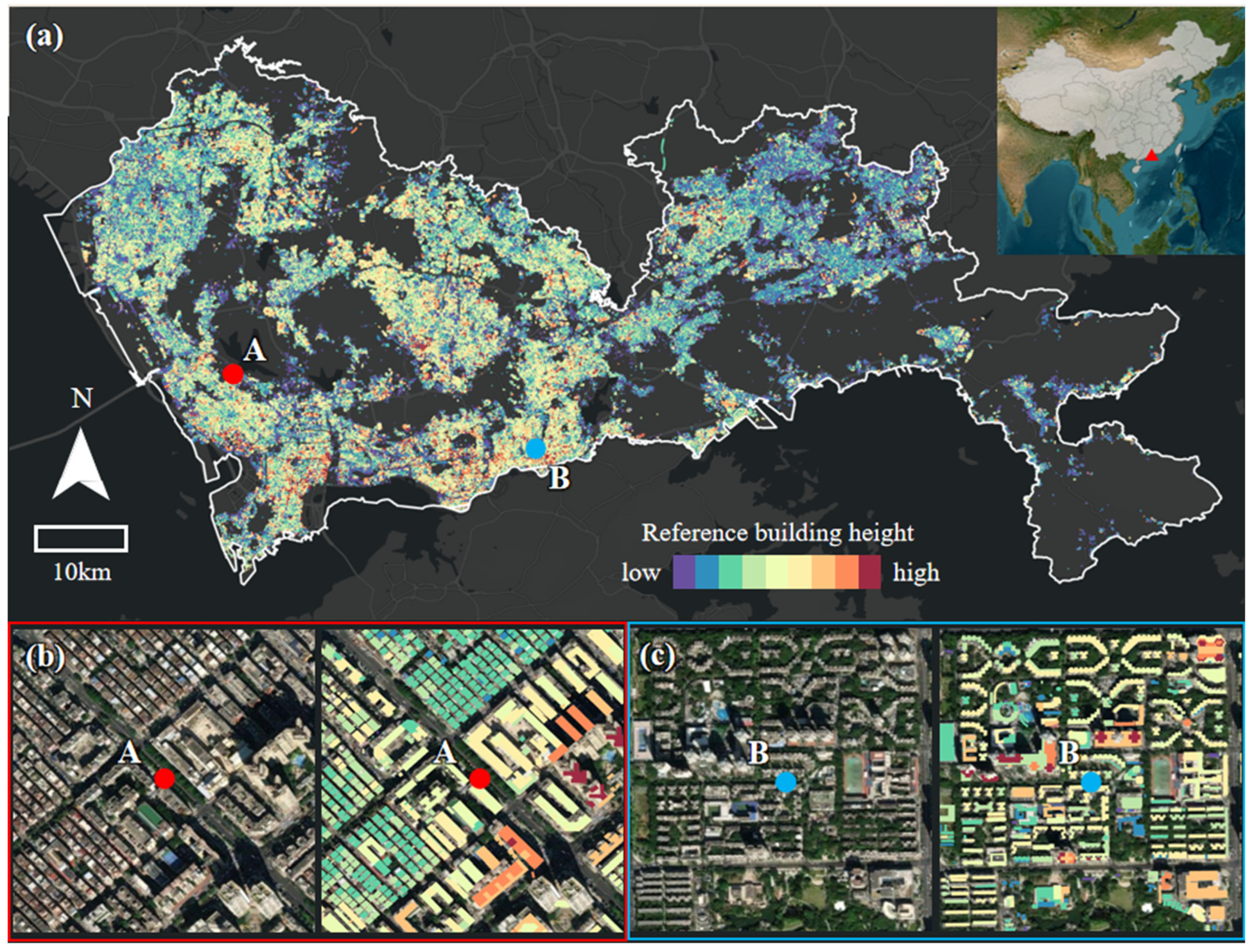
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Datasets
2.2.1. Urban Land Use Data
2.2.2. Remote Sensing Data
2.2.3. Socio-Economic Data
2.2.4. Building Morphology Data
2.3. Data Preprocessing
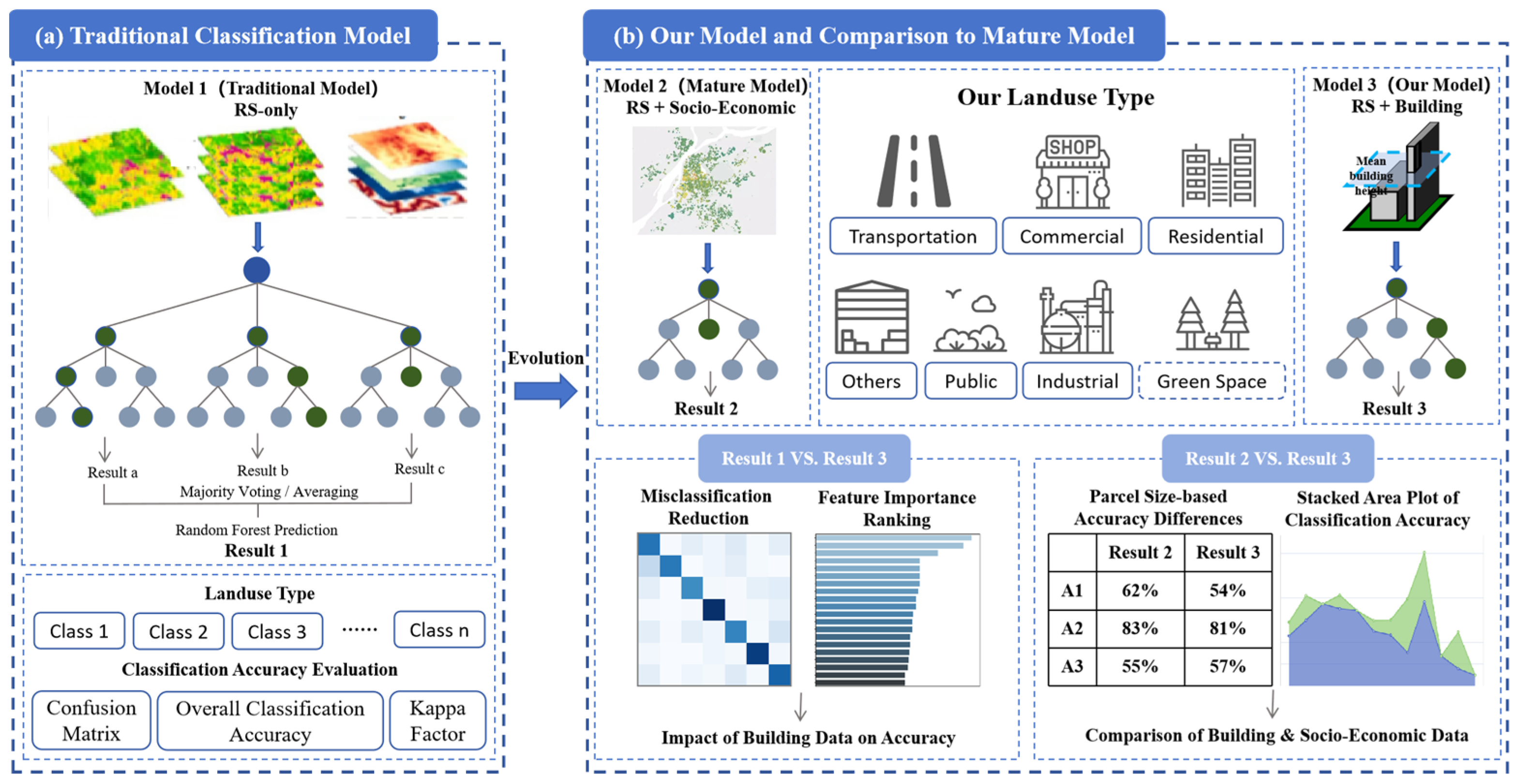
2.4. Methodology
2.4.1. Traditional Classification Model and Accuracy Evaluation
2.4.2. Building Data Classification and Socio-Economic Comparison
3. Results
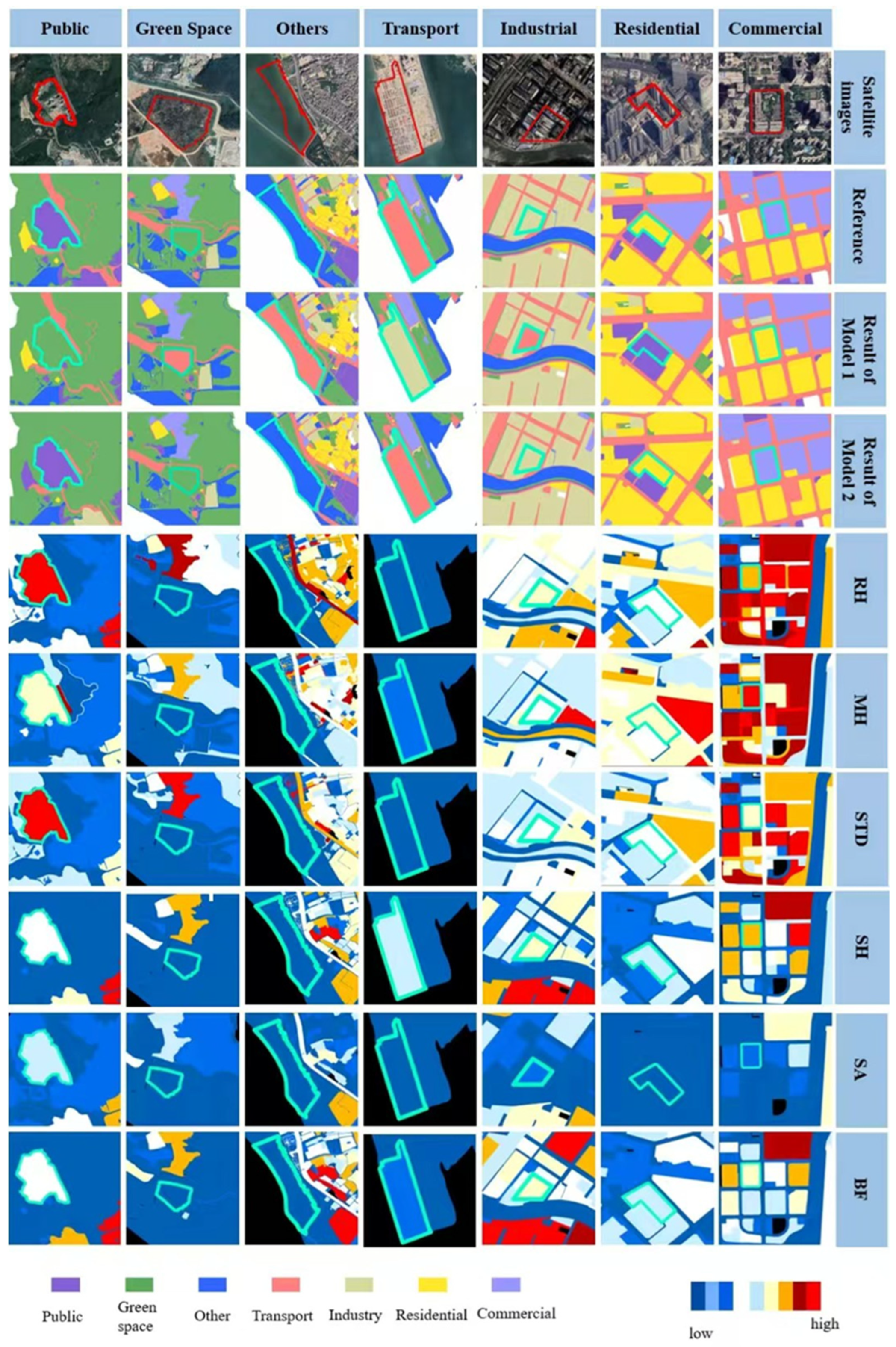
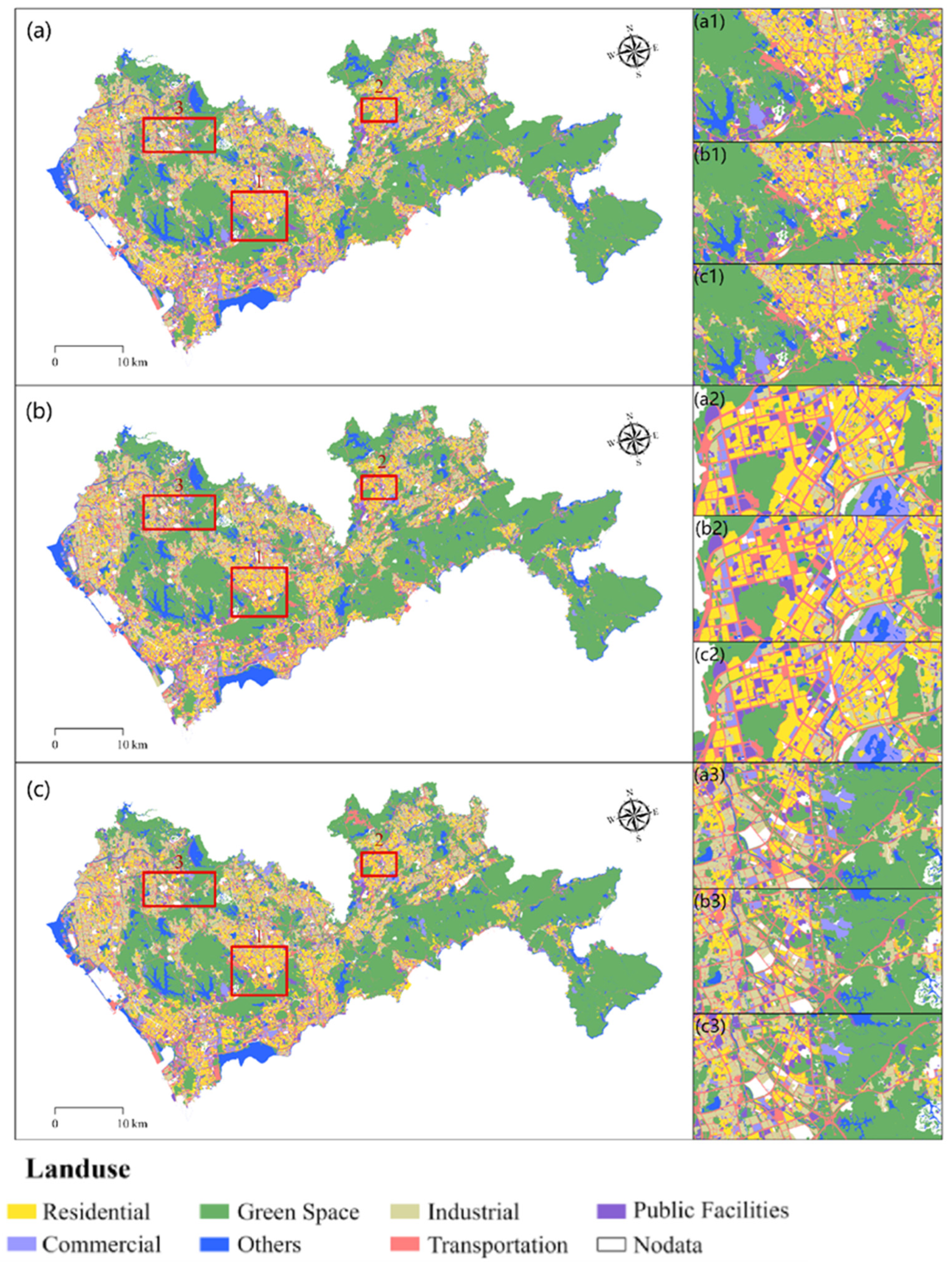
3.1. Enhancing Urban Land Use Classification with Building Morphology
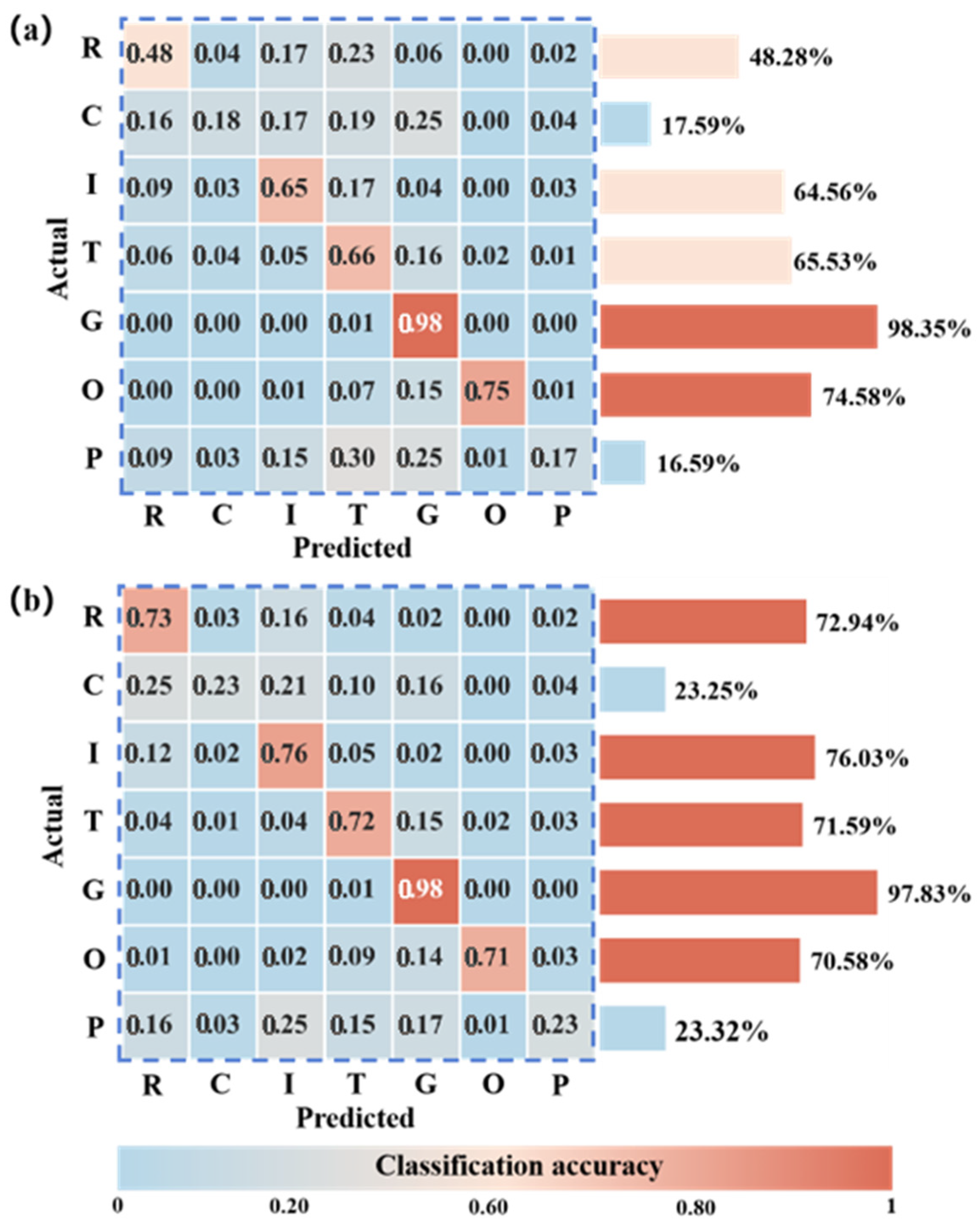
3.1.1. Classification Results and Evaluation of Accuracy
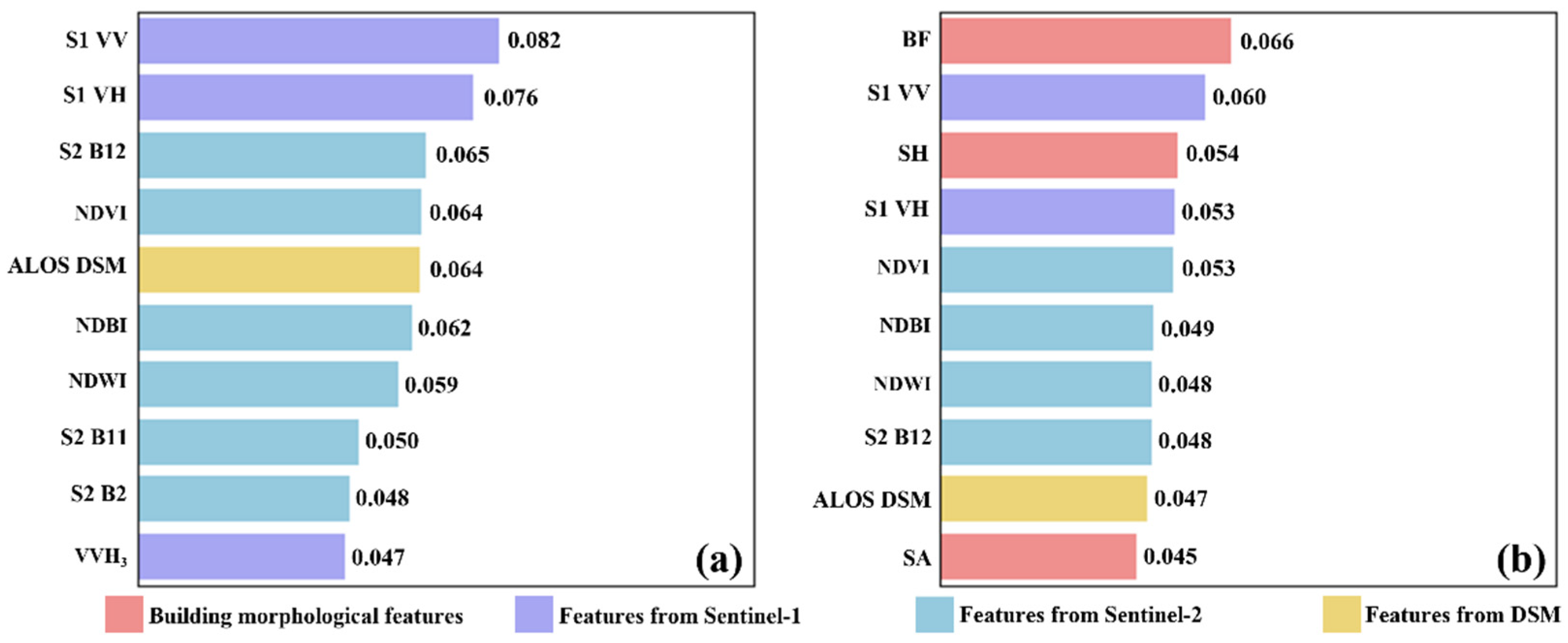
3.1.2. Feature Importance Evaluation and Analysis
3.2. Building vs. Socio-Economic Data
3.2.1. Area-Based Comparison
3.2.2. Category-Based Comparison
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chaturvedi, V.; de Vries, W.T. Machine learning algorithms for urban land use planning: A review. Urban Sci. 2021, 5, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Fuente, B.; Bertzky, B.; Delli, G.; Mandrici, A.; Conti, M.; Florczyk, A.J.; Freire, S.; Schiavina, M.; Bastin, L.; Dubois, G. Built-up areas within and around protected areas: Global patterns and 40-year trends. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 24, e01291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohlhase, J.E. The new urban world 2050: Perspectives, prospects and problems. Reg. Sci. Policy Pract. 2013, 5, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fang, F.; Li, Y. Key issues of land use in China and implications for policy making. Land Use Policy 2014, 40, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Hejazi, M.; Wise, M.; Vernon, C.; Iyer, G.; Chen, W. Global urban growth between 1870 and 2100 from integrated high resolution mapped data and urban dynamic modeling. Commun. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.S. Rapid Global Urbanization. In Building Digital Twin Metaverse Cities: Revolutionizing Cities with Emerging Technologies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- He, W.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Sang, X.; Xie, X. Research on the interactive relationship and the optimal adaptation degree between land use benefit and industrial structure evolution: A practical analysis of Jiangsu province. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 303, 127016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Xu, B.; Gong, P. Mapping essential urban land use categories (EULUC) using geospatial big data: Progress, challenges, and opportunities. Big Earth Data 2021, 5, 410–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, W.; Long, Y.; Chen, T. Rediscovering Chinese cities through the lens of land-use patterns. Land Use Policy 2018, 79, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Peng, Z.; Yu, Y.; Jiao, H. Deep convolutional autoencoder for urban land use classification using mobile device data. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2022, 36, 2138–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanov, W.L.; Ramsey, M.S.; Christensen, P.R. Monitoring urban land cover change: An expert system approach to land cover classification of semiarid to arid urban centers. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 77, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Chen, B.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Bai, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Fang, L.; Feng, S. Mapping essential urban land use categories in China (EULUC-China): Preliminary results for 2018. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, B.; Wu, S.; Su, M.; Chen, J.M.; Xu, B. Deep learning for urban land use category classification: A review and experimental assessment. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 311, 114290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Wang, L. Automated urban land-use classification with remote sensing. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 790–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okujeni, A.; Canters, F.; Cooper, S.D.; Degerickx, J.; Heiden, U.; Hostert, P.; Priem, F.; Roberts, D.A.; Somers, B.; van der Linden, S. Generalizing machine learning regression models using multi-site spectral libraries for mapping vegetation-impervious-soil fractions across multiple cities. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 216, 482–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q.; Hu, X.; Liu, H. Estimating impervious surfaces using linear spectral mixture analysis with multitemporal ASTER images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 4807–4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latty, R.; Nelson, R.; Markham, B.; Williams, D.; Toll, D. Performance comparisons between information extraction techniques using variable spatial resolution data. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1985, 51, 1459–1470. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, P.-F.; Lee, L.C.; Chen, N.-Y. Effect of spatial resolution on classification errors of pure and mixed pixels in remote sensing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 2657–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, R.; Alves, A.; Bento, C. POI mining for land use classification: A case study. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.A.; Iizuka, K. Integrating OpenStreetMap crowdsourced data and Landsat time-series imagery for rapid land use/land cover (LULC) mapping: Case study of the Laguna de Bay area of the Philippines. Appl. Geogr. 2016, 67, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grippa, T.; Georganos, S.; Zarougui, S.; Bognounou, P.; Diboulo, E.; Forget, Y.; Lennert, M.; Vanhuysse, S.; Mboga, N.; Wolff, E. Mapping urban land use at street block level using openstreetmap, remote sensing data, and spatial metrics. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Gong, P. Mapping urban land use by using landsat images and open social data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, A.; Fast, V.; Nelson, T.; Laberee, K. Crowdsourcing the pedestrian experience: Who’s represented in the data? Spat. Knowl. Inf. 2023, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhu, A.-X. The representativeness and spatial bias of volunteered geographic information: A review. Ann. Gis 2018, 24, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raifer, M.; Troilo, R.; Kowatsch, F.; Auer, M.; Loos, L.; Marx, S.; Przybill, K.; Fendrich, S.; Mocnik, F.-B.; Zipf, A. OSHDB: A framework for spatio-temporal analysis of OpenStreetMap history data. Open Geospat. Data Softw. Stand. 2019, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psyllidis, A.; Gao, S.; Hu, Y.; Kim, E.-K.; McKenzie, G.; Purves, R.; Yuan, M.; Andris, C. Points of Interest (POI): A commentary on the state of the art, challenges, and prospects for the future. Comput. Urban Sci. 2022, 2, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Im, J.; Rhee, J.; Hodgson, M. Building type classification using spatial and landscape attributes derived from LiDAR remote sensing data. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 130, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X. Characterizing the 3-D structure of each building in the conterminous United States. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 105, 105318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, W.; Meng, L.; Wu, Q.; Gong, P.; Seto, K.C. Satellite mapping of urban built-up heights reveals extreme infrastructure gaps and inequalities in the Global South. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2214813119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, K.Y.; Yang, Z.-L.; Niyogi, D. Improving the local climate zone classification with building height, imperviousness, and machine learning for urban models. Comput. Urban Sci. 2022, 2, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zheng, G.; Chi, X.; Yang, L.; Geng, Q.; Li, J.; Qiao, Y. Mapping fine-scale building heights in urban agglomeration with spaceborne lidar. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 285, 113392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Ou, J.; Wen, Y.; Liu, X.; He, J.; Zhang, J. Developing a data-fusing method for mapping fine-scale urban three-dimensional building structure. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 80, 103716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Yu, G.; Li, X.; Taubenböck, H.; Hu, G.; Zhou, Y.; Peng, C.; Liu, D.; Huang, J.; Liu, X. A flexible framework for built-up height mapping using ICESat-2 photons and multisource satellite observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2025, 318, 114572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Yu, G.; Li, X.; Li, L.; Liu, D.; Guo, J.; Li, Y. Reconstructing Long-Term Synthetic Aperture Radar Backscatter in Urban Domains Using Landsat Time Series Data: A Case Study of Jing–Jin–Ji Region. J. Remote Sens. 2024, 4, 0172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Gong, P.; Seto, K.C.; Clinton, N. Developing a method to estimate building height from Sentinel-1 data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 240, 111705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhaldiyal, A.; Gupta, K.; Gupta, P.K.; Thakur, P.; Kumar, P. Urban Morphology Extractor: A spatial tool for characterizing urban morphology. Urban Clim. 2018, 24, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labetski, A.; Vitalis, S.; Biljecki, F.; Arroyo Ohori, K.; Stoter, J. 3D building metrics for urban morphology. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2023, 37, 36–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Xu, X.; Huang, K.; Zhu, P.; Shi, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Q.; Arehart, J.H. Mapping of individual building heights reveals the large gap of urban-rural living spaces in the contiguous US. Innov. Geosci. 2024, 2, 100069-1–100069-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wu, A.N.; Biljecki, F. Classification of urban morphology with deep learning: Application on urban vitality. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2021, 90, 101706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Yigitcanlar, T.; Nepal, M.; Nguyen, K.; Dur, F. Machine learning and remote sensing integration for leveraging urban sustainability: A review and framework. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 96, 104653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Guo, R.; Chen, B.; Hong, W.; Wang, J.; Feng, Y.; Xu, B. Sampling strategy for detailed urban land use classification: A systematic analysis in Shenzhen. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Stein, A.; Bijker, W.; Zhan, Q. Urban land use extraction from Very High Resolution remote sensing imagery using a Bayesian network. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 122, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feltynowski, M. Urban green spaces in land-use policy–types of data, sources of data and staff–the case of Poland. Land Use Policy 2023, 127, 106570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, W.; Zhang, C.; Hanink, D.M.; Li, X.; Wang, W. Parcel-based urban land use classification in megacity using airborne LiDAR, high resolution orthoimagery, and Google Street View. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2017, 64, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, D.; Yin, H.; Tischbein, B.; Verleysdonk, S.; Adamou, R.; Kumar, N. Land use mapping using Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 time series in a heterogeneous landscape in Niger, Sahel. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 178, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deus, D. Integration of ALOS PALSAR and Landsat Data for Land Cover and Forest Mapping in Northern Tanzania. Land 2016, 5, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julzarika, A.; Djurdjani, D. DEM classifications: Opportunities and potential of its applications. J. Degrad. Min. Lands Manag. 2019, 6, 1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, H.; Song, Z.; Lu, J.; Meng, P.; Qin, S. Mapping Essential Urban Land Use Categories in Nanjing by Integrating Multi-Source Big Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, L.; He, S.; Lian, J.; Bie, Q.; Wang, X.; Dong, J.; Xie, Y. Detailed Mapping of Urban Land Use Based on Multi-Source Data: A Case Study of Lanzhou. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estima, J.; Painho, M. Investigating the potential of OpenStreetMap for land use/land cover production: A case study for continental Portugal. In OpenStreetMap in GIScience: Experiences, Research, and Applications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 273–293. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Xu, G.; Guo, Q. Street centralities and land use intensities based on points of interest (POI) in Shenzhen, China. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Deal, B.; Chen, Y.; Hewings, G. A reassessment of urban structure and land-use patterns: Distance to CBD or network-based?—Evidence from Chicago. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2018, 70, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Liao, W.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, X.; Xu, X.; Shi, Q.; Zhu, J.; et al. 3D-GloBFP: The first global three-dimensional building footprint dataset. Earth Syst. Sci. Data Discuss. 2024, 2024, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, X. Semantic classification of urban buildings combining VHR image and GIS data: An improved random forest approach. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 105, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Zhao, Y.; Gong, P. A multi-resolution global land cover dataset through multisource data aggregation. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 2317–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Heremans, S.; Somers, B. Urban land cover mapping with Sentinel-2: A spectro-spatio-temporal analysis. Urban Inf. 2022, 1, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osgouei, P.E.; Kaya, S.; Sertel, E.; Alganci, U. Separating built-up areas from bare land in mediterranean cities using Sentinel-2A imagery. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Najjar, H.A.; Kalantar, B.; Pradhan, B.; Saeidi, V.; Halin, A.A.; Ueda, N.; Mansor, S. Land cover classification from fused DSM and UAV images using convolutional neural networks. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, N.; Miao, S.; Kong, F.; Zhang, Y.; Li, N. Urban morphological parameters of the main cities in China and their application in the WRF model. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2021, 13, e2020MS002382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C. Building height restrictions, land development and economic costs. Land Use Policy 2013, 30, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Vargas-Muñoz, J.E.; Tuia, D. Understanding urban landuse from the above and ground perspectives: A deep learning, multimodal solution. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 228, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Zhou, X.; Cheng, W. Water effects on urban heat islands in summer using WRF-UCM with gridded urban canopy parameters—A case study of Wuhan. Build. Environ. 2022, 225, 109528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burian, S.J.; Velugubantla, S.P.; Brown, M.J. Morphological analyses using 3d building databases: Salt lake city, utah. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 4, 55–56. [Google Scholar]
- Fushiki, T. Estimation of prediction error by using K-fold cross-validation. Stat. Comput. 2011, 21, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, S.; Saber, M.; Rabiei-Dastjerdi, H.; Homayouni, S. Urban Land Use and Land Cover Change Analysis Using Random Forest Classification of Landsat Time Series. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.H.; Joshi, D.R.; Clay, D.E.; Henebry, G.M. Characterizing land cover/land use from multiple years of Landsat and MODIS time series: A novel approach using land surface phenology modeling and random forest classifier. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 238, 111017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rwanga, S.S.; Ndambuki, J.M. Accuracy assessment of land use/land cover classification using remote sensing and GIS. Int. J. Geosci. 2017, 8, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatit, P.; Adhinugraha, K.; Taniar, D. Navigating the maps: Euclidean vs. road network distances in spatial queries. Algorithms 2024, 17, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, W.; Zhang, C.; Li, X. Incorporating spectral similarity into Markov chain geostatistical cosimulation for reducing smoothing effect in land cover postclassification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 10, 1082–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, D.; Chen, J.; Wang, C.; Shen, M. The mixed pixel effect in land surface phenology: A simulation study. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 211, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Avtar, R.; Ahmad, S.; Inostroza, L.; Misra, P.; Kumar, P.; Takeuchi, W.; Surjan, A.; Saito, O. Does building development in Dhaka comply with land use zoning? An analysis using nighttime light and digital building heights. Sustain. Sci. 2021, 16, 1323–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Lin, Z.; Jiang, X.; Qiu, M.; Sun, J. How do the industrial land use intensity and dominant industries guide the urban land use? Evidences from 19 industrial land categories in ten cities of China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 53, 101978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, A. Monitoring land cover change in urban and peri-urban areas using dense time stacks of Landsat satellite data and a data mining approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 689–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukiou, G. SAR Features and Techniques for Urban Planning—A Review. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bellefon, M.-P.; Combes, P.-P.; Duranton, G.; Gobillon, L.; Gorin, C. Delineating urban areas using building density. J. Urban Econ. 2021, 125, 103226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Xie, Z.; Zhai, S. Urban Land Use Classification Model Fusing Multimodal Deep Features. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2024, 13, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kwan, M.P.; Yu, B.; Liu, Y.; Song, L.; Chen, N. Quantitative Identification of Mixed Urban Functions: A Probabilistic Approach Based on Physical and Social Sensing Data. Trans. GIS 2025, 29, e13272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Feng, Q.; Niu, B.; Chen, B.; Yan, F.; Gong, J.; Liu, J. Mapping urban villages based on point-of-interest data and a deep learning approach. Cities 2025, 156, 105549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Hetrick, S.; Moran, E. Land cover classification in a complex urban-rural landscape with QuickBird imagery. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2010, 76, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Plantinga, A.J. The influence of public open space on urban spatial structure. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2003, 46, 288–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovell, S.T.; Johnston, D.M. Designing landscapes for performance based on emerging principles in landscape ecology. Ecol. Soc. 2009, 14, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Zhang, X.; Lei, Y.; Huang, X.; Tu, W.; Liu, B.; Meng, Q.; Du, S. Mapping urban functional zones with remote sensing and geospatial big data: A systematic review. GISci. Remote Sens. 2024, 61, 2404900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, X. Effectiveness of Semi-Supervised Learning and Multi-Source Data in Detailed Urban Landuse Mapping with a Few Labeled Samples. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.S. A probabilistic explanation of Pearson′s correlation. Teach. Stat. 2019, 41, 115–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorutti, B.; Michel, B.; Saint-Pierre, P. Correlation and variable importance in random forests. Stat. Comput. 2017, 27, 659–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dovey, K.; van Oostrum, M.; Chatterjee, I.; Shafique, T. Towards a morphogenesis of informal settlements. Habitat Int. 2020, 104, 102240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamalipour, H.; Dovey, K. Mapping the visibility of informal settlements. Habitat Int. 2019, 85, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Liu, S.; Li, X.; Pei, L.; Geng, M.; Yu, G.; Shi, Z.; Hu, T. Urbanization induced Urban Canopy Parameters enhance the heatwave intensity: A case study of Beijing. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2025, 119, 106089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Agrawal, S. Urban modelling and forecasting of landuse using SLEUTH model. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 6499–6518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, N.; Cao, X.; Zhuo, L. Identifying the Central Business Districts of global megacities using nighttime light remote sensing data. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2024, 17, 2356118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Cao, W.; He, C.; Yu, B.; Li, X.; Elvidge, C.D.; Cheng, W.; Zhou, C. Applications of satellite remote sensing of nighttime light observations: Advances, challenges, and perspectives. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerland, P. Socio-economic data and GIS: Datasets, databases, indicators, and data integration issues. In Proceedings of the UNEP/CGIAR (Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research), Arendal, Norway, 17 June 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, T. Building change detection from multitemporal high-resolution remotely sensed images based on a morphological building index. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 7, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanal, N.; Uddin, K.; Matin, M.A.; Tenneson, K. Automatic detection of spatiotemporal urban expansion patterns by fusing OSM and landsat data in Kathmandu. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoimchev, M.; Levatić, J.; Kocev, D.; Džeroski, S. Semi-supervised multi-label classification of land use/land cover in remote sensing images with predictive clustering trees and ensembles. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Type | Name | Characteristic Indicators | Description | Time | Format | Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land use data | Land use data | / | Provided by the Shenzhen Municipal Bureau of Planning and Natural Resources | 2022 | Vector | / |
| Remote sensing data | Sentinel-1 | VV | Measures like polarized returns sensitive to bare surfaces | 2022 | Raster | 10 m |
| VH | Captures depolarized scattering from vegetation and complex structures | |||||
| VVHn | VVHn = VV × nVH (n = 3, 4, 5, 6) | |||||
| Sentinel-2 | NDVI | NDVI = | 2022 | Raster | 10 m/20 m | |
| NDBI | NDBI = | |||||
| NDWI | NDWI = | |||||
| B2-B8, B8A, B11, B12 | Sentinel-2 Level-1C data provided spectral bands from visible to SWIR | |||||
| ALOS DSM Global 30 | Global digital surface model (DSM) data for elevation | Represents Earth’s surface elevation including vegetation and infrastructure | 2022 | Raster | 30 m | |
| Socio-economic data | OSM road data | Various road network data | Used for road information extraction | 2022 | Vector | / |
| POI | Various types of POI data | Includes the point’s name, latitude, longitude, and its social function | 2022 | Vector | / | |
| Building morphology data | 3D-GloBFP | RH | 2020 | Vector | / | |
| MH | ||||||
| STD | ||||||
| SH | ||||||
| SA | ||||||
| BF |
| Area Category | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| <10% | 58.99% | 60.65% | 59.94% |
| >90% | 80.59% | 84.49% | 85.15% |
| <20% | 58.90% | 58.25% | 60.06% |
| >80% | 77.71% | 82.38% | 82.86% |
| <33% | 58.52% | 56.77% | 60.52% |
| 33–67% | 59.13% | 59.33% | 60.94% |
| >67% | 76.07% | 80.96% | 81.93% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Song, F.; Wang, Y.; Chen, T.; Li, X.; Tang, X.; Hu, T.; Zhou, S.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; et al. Incorporating Building Morphology Data to Improve Urban Land Use Mapping: A Case Study of Shenzhen. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2811. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162811
Zhang J, Song F, Wang Y, Chen T, Li X, Tang X, Hu T, Zhou S, Liu H, Wang J, et al. Incorporating Building Morphology Data to Improve Urban Land Use Mapping: A Case Study of Shenzhen. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(16):2811. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162811
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jiapeng, Fujun Song, Yimin Wang, Tuo Chen, Xuecao Li, Xiayu Tang, Tengyun Hu, Siyao Zhou, Han Liu, Jiaqi Wang, and et al. 2025. "Incorporating Building Morphology Data to Improve Urban Land Use Mapping: A Case Study of Shenzhen" Remote Sensing 17, no. 16: 2811. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162811
APA StyleZhang, J., Song, F., Wang, Y., Chen, T., Li, X., Tang, X., Hu, T., Zhou, S., Liu, H., Wang, J., & Su, M. (2025). Incorporating Building Morphology Data to Improve Urban Land Use Mapping: A Case Study of Shenzhen. Remote Sensing, 17(16), 2811. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162811






