Remote Sensing Perspective on Monitoring and Predicting Underground Energy Sources Storage Environmental Impacts: Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
- How do geological storage facilities influence the environment, and what impacts are considered to be the most critical in terms of sustainability and long-term stability?
- What surface monitoring techniques are used at UGS facilities, and how do the capabilities and limitations of these techniques affect the effectiveness in detecting environmental impacts?
- What are the critical gaps and future research directions for integrating multi-source remote sensing data and data-driven models to create a holistic monitoring framework for UGS sites?
2. Review Methodology
3. Review of Geological Storage
3.1. Types and Stored Materials
3.2. Environmental Impacts
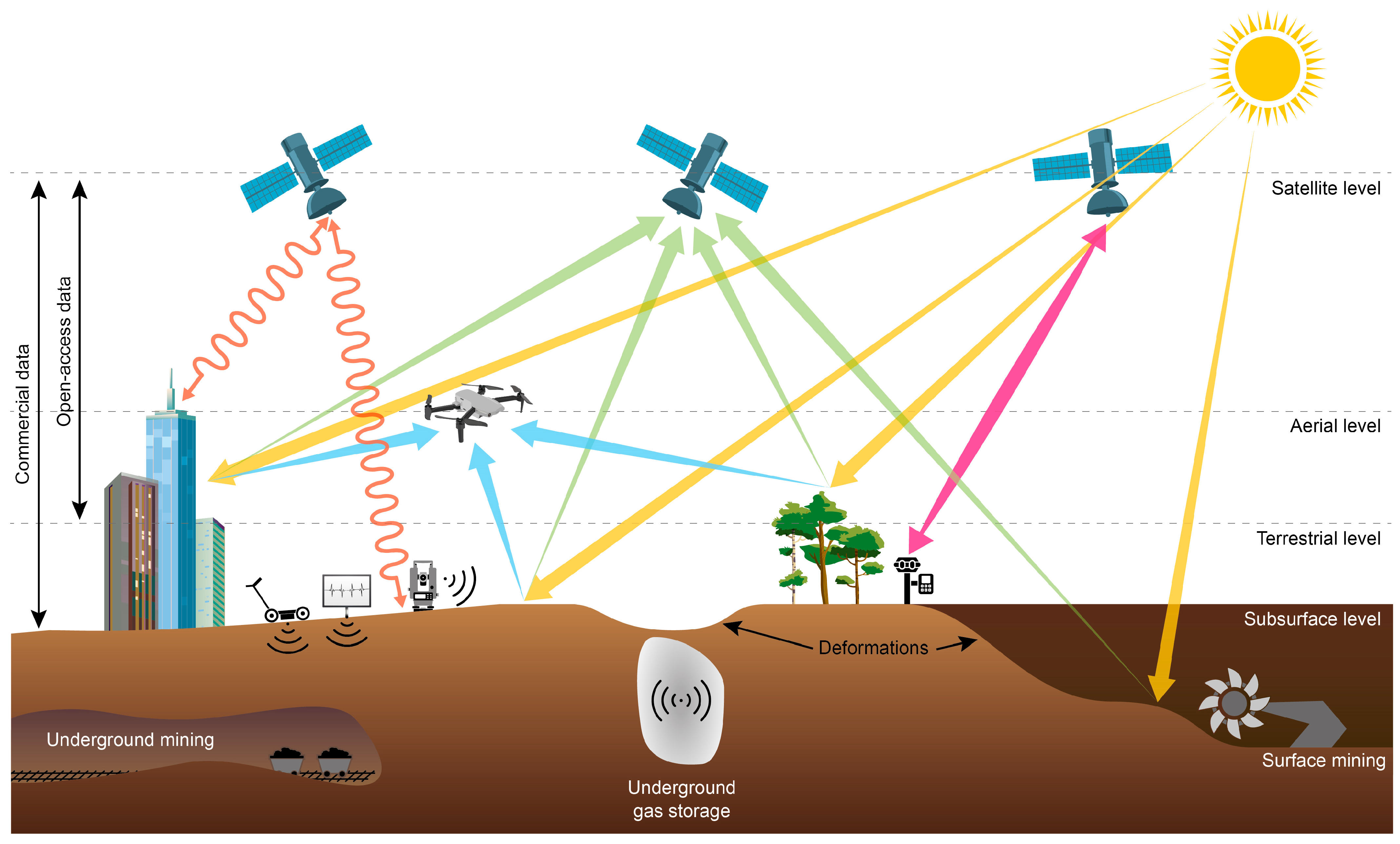
3.3. Monitoring Methods
3.3.1. Geodetic Monitoring Methods
3.3.2. Active Remote Sensing
3.3.3. Passive Remote Sensing
3.4. Modelling and Prediction Methods
3.4.1. Empirical Models and Influence Functions
3.4.2. Deterministic Models
3.4.3. Data-Driven Models
3.4.4. Hybrid Models
4. Critical Analysis and Discussion
4.1. Strengths and Weaknesses
4.2. Opportunities and Threats
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial intelligence |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| BPNN | Back propagation neural network |
| CAES | Compressed air energy storage |
| CCS | Carbon capture and storage |
| CDEM | Continuous-discontinuous element method |
| CEOS | Committee on Earth observation satellites |
| CH4 | Methane |
| CNN | Convolutional neural network |
| CO2 | Carbon dioxide |
| DEM | Digital elevation model |
| DEM | Discrete element method |
| DIAL | Differential absorption LiDAR |
| D-InSAR | Differential InSAR |
| DL | Deep learning |
| DOM | Digital orthophoto mosaic |
| DSM | Digital surface model |
| DTM | Digital terrain model |
| EGMS | Exploratory spatial data analysis |
| EGS | Environmental, social, and governance |
| EM | Electromagnetic |
| EO | Earth observation |
| ESDA | Exploratory spatial data analysis |
| FDCD | Fractional derivative creep damage |
| FEM | Finite element method |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared |
| GAN | Generate adversarial network |
| GNSS | Global navigation satellite system |
| GRNN | Generalized regression neural network |
| H2 | Hydrogen |
| H2S | Hydrogen sulphide |
| IDW | Inverse distance weighted |
| InSAR | Interferometric synthetic aperture radar |
| IRF | Intrinsic random function |
| LiDAR | Light detection and ranging |
| LoS | Line of sight |
| LSTM | Long short-term memory network |
| LWIR | Long wavelength infrared |
| ML | Machine learning |
| MS | Mass spectrometry |
| MT-InSAR | Multi-temporal InSAR |
| N2 | Nitrogen |
| NDVI | Normalized difference vegetation index |
| NG | Natural gas |
| NGSI | Natural gas stress index |
| NIR | Near-infrared |
| NN | Nearest neighbour |
| O2 | Oxygen |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| PS-InSAR | Persistent Scatterer InSAR |
| RNN | Recurrent neural network |
| RS | Remote sensing |
| RTK | Real-time kinematic |
| SAR | Synthetic aperture radar |
| SBAS | Small baseline subset |
| SDG | Sustainable development goal |
| SMMI | Soil moisture monitoring index |
| SWIR | Short wavelength infrared |
| SWOT | Strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats |
| TDL | Tunable diode laser |
| TIR | Thermal infrared |
| UAV | Unmanned aerial vehicle |
| UCG | Underground coal gasification |
| UGS | Underground gas storage |
| UHS | Underground hydrogen storage |
| UN | United Nations |
| WoS | Web of Science |
References
- Iwaszczuk, N.; Zapukhliak, I.; Iwaszczuk, A.; Dzoba, O.; Romashko, O. Underground Gas Storage Facilities in Ukraine: Current State and Future Prospects. Energies 2022, 15, 6604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosowski, P.; Kosowska, K.; Nawalaniec, W. Application of Bayesian Networks in Modeling of Underground Gas Storage Energy Security. Energies 2022, 15, 5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekebrok, H.; Langnickel, H.; Pluta, A.; Zobel, M.; Dyck, A. Underground Storage of Green Hydrogen—Boundary Conditions for Compressor Systems. Energies 2022, 15, 5972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goal 7|Department of Economic and Social Affairs. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal7#progress_and_info (accessed on 13 November 2023).
- Ang, T.-Z.; Salem, M.; Kamarol, M.; Das, H.S.; Nazari, M.A.; Prabaharan, N. A Comprehensive Study of Renewable Energy Sources: Classifications, Challenges and Suggestions. Energy Strat. Rev. 2022, 43, 100939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goal 12|Department of Economic and Social Affairs. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal12 (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- Goal 13|Department of Economic and Social Affairs. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal13 (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- Omer, A.M. Energy, Environment and Sustainable Development. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2008, 12, 2265–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Liu, D.; Huang, A.; Lin, J.; Xu, L. Critical Transformation Pathways and Socio-Environmental Benefits of Energy Substitution Using a LEAP Scenario Modeling. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 135, 110116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkemai, R.M.; Bin, G. A Modeling and Numerical Simulation Study of Enhanced CO2 Sequestration into Deep Saline Formation: A Strategy towards Climate Change Mitigation. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Change 2020, 25, 901–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wang, T.; Li, Y.; Yang, H.; Li, J.; Qu, D.; Xu, B.; Yang, Y.; Daemen, J.J.K. Feasibility Analysis of Using Abandoned Salt Caverns for Large-Scale Underground Energy Storage in China. Appl. Energy 2015, 137, 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaisant, A.; Maiu, A.; Maggio, E.; Pettinau, A. Pilot-Scale CO2 Sequestration Test Site in the Sulcis Basin (SW Sardinia): Preliminary Site Characterization and Research Program. Energy Procedia 2017, 114, 4508–4517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wang, T.; Li, J.; Ma, H.; Shi, X.; Daemen, J.J.K. Feasibility Analysis of Using Closely Spaced Caverns in Bedded Rock Salt for Underground Gas Storage: A Case Study. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wanyan, Q.; Ding, G.; Li, K.; Kou, Y.; Bai, S.; Ran, L.; Wu, J.; Deng, J. Geomechanical Feasibility Analysis of Salt Cavern Gas Storage Construction in Sanshui Basin, Guangdong Province. Eng 2022, 3, 709–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winecki, S.; Nowaczewski, S.; Johnson, K.L.; Lord, A.S.; Lord, D.L.; Moriarty, D.M.; Scharenberg, M.; Moody, M.A.; Argumedo, D.; Larsen, G.E.; et al. Quantitative Assessment Approach to Assess Benefits of Subsurface Safety Valves and Tubing and Packer Systems in Depleted Reservoir and Aquifer Gas Storage Wells. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 2022, 208, 109392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Thienen-Visser, K.; Hendriks, D.; Marsman, A.; Nepveu, M.; Groenenberg, R.; Wildenborg, T.; van Duijne, H.; den Hartogh, M.; Pinkse, T. Bow-Tie Risk Assessment Combining Causes and Effects Applied to Gas Oil Storage in an Abandoned Salt Cavern. Eng. Geol. 2014, 168, 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Economides, M.J. Purposefully Built Underground Natural Gas Storage. J. Nat. Gas Eng. 2012, 9, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanyan, Q.; Ding, G.; Zhao, Y.; Li, K.; Deng, J.; Zheng, Y. Key Technologies for Salt-Cavern Underground Gas Storage Construction and Evaluation and Their Application. Nat. Gas Ind. B 2018, 5, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrail, B.P.; Schaef, H.T.; Spane, F.A.; Horner, J.A.; Owen, A.T.; Cliff, J.B.; Qafoku, O.; Thompson, C.J.; Sullivan, E.C. Wallula Basalt Pilot Demonstration Project: Post-Injection Results and Conclusions. Energy Procedia 2017, 114, 5783–5790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tackie-Otoo, B.N.; Haq, M.B. A Comprehensive Review on Geo-Storage of H2 in Salt Caverns: Prospect and Research Advances. Fuel 2024, 356, 129609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, R.A.; Hubbard, D.W.; Evans, D.J.; Savage, S.L. Characterization of Historical Methane Occurrence Frequencies from U.S. Underground Natural Gas Storage Facilities with Implications for Risk Management, Operations, and Regulatory Policy. Risk Anal. 2020, 40, 588–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Shi, X.; Ma, H.; Zhao, K.; Dong, Z.; Hou, B.; Shangguan, S. Creep Monitoring and Parameters Inversion Methods for Rock Salt in Extremely Deep Formation. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 229, 212092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, M.; Karaliūtė, V.; Malik, S. Exploring the Potential of Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage in Baltic Sea Region Countries: A Review of CCUS Patents from 2000 to 2022. Processes 2023, 11, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiatowski, M.; Kapusta, K.; Stańczyk, K.; Szyja, M.; Masum, S.; Sadasivam, S.; Thomas, H.R. Large-Scale Ex Situ Tests for CO2 Storage in Coal Beds. Energies 2023, 16, 6326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Shi, X.; Li, Y.; Li, P.; Ban, S.; Zhao, K.; Ma, H.; Liu, H.; Yang, C. A Comprehensive Feasibility Evaluation of Salt Cavern Oil Energy Storage System in China. Appl. Energy 2023, 351, 121807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shafi, M.; Massarweh, O.; Abushaikha, A.S.; Bicer, Y. A Review on Underground Gas Storage Systems: Natural Gas, Hydrogen and Carbon Sequestration. Energy Rep. 2023, 9, 6251–6266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yan, Y.; Sheng, Z.; Yan, X. Uncertainty Failure Risk Quantitative Assessments for Underground Gas Storage Near-Wellbore Area. J. Energy Storage 2021, 36, 102393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Xu, H.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Zhao, K.; Li, C.; Shi, L.; Tang, L. Key Evaluation Techniques in the Process of Gas Reservoir Being Converted into Underground Gas Storage. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2017, 44, 840–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Liu, G.; Chen, R.; Sun, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X. Evaluation on the Dynamic Sealing Capacity of Underground Gas Storages Rebuilt from Gas Reservoirs: A Case Study of Xinjiang H Underground Gas Storage. Nat. Gas Ind. B 2021, 8, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taiwo, G.O.; Tomomewo, O.S.; Oni, B.A. A Comprehensive Review of Underground Hydrogen Storage: Insight into Geological Sites (Mechanisms), Economics, Barriers, and Future Outlook. J. Energy Storage 2024, 90, 111844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh Kumar, K.; Honorio, H.; Chandra, D.; Lesueur, M.; Hajibeygi, H. Comprehensive Review of Geomechanics of Underground Hydrogen Storage in Depleted Reservoirs and Salt Caverns. J. Energy Storage 2023, 73, 108912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligen, T.; Weiyao, Z.; Huayin, Z.; Yan, W.; Huaquan, J.; Ping, P.; Deshu, L.; Jieming, W.; Chun, L.; Ying, Y.; et al. Monitoring Well Pattern Deployment in China Gas Storage and Its Initial Success Rate. J. Energy Storage 2020, 32, 101950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Zheng, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Hou, H.; Zhu, Q.; Du, P. Spatial Estimates of Surface Deformation and Topsoil Moisture in Operating CO2-EOR Project: Pilot Environmental Monitoring Using SAR Technique. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 236, 117606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, S.; Sedaee, B. Cushion and Working Gases Mixing during Underground Gas Storage: Role of Fractures. J. Energy Storage 2022, 55, 105530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Fan, J.; Jiang, D.; Li, Z.; Chen, J. Research on Gas Leakage and Collapse in the Cavern Roof of Underground Natural Gas Storage in Thinly Bedded Salt Rocks. J. Energy Storage 2020, 31, 101669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, C.; Liu, J.; Zhao, C.; Ren, Y.; Liang, C. Creep-Damage Constitutive Model Based on Fractional Derivatives and Its Application in Salt Cavern Gas Storage. J. Energy Storage 2021, 44, 103403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, M.; Liu, H.; Cao, L. Study on Multi-Cavern Optimization Allocation for Injection and Production of Salt Cavern Gas Storage. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 227, 042025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Martín, L.; Rouabhi, A.; Billiotte, J.; Hadj-Hassen, F.; Tessier, B.; Hévin, G.; Balland, C.; Hertz, E. Experimental and Numerical Investigation into Rapid Cooling of Rock Salt Related to High Frequency Cycling of Storage Caverns. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2018, 102, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Ding, W.; Fan, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, W.; Jiang, D. Creep Properties and Constitutive Model of Salt Rocks under a Slow Cyclic Loading Path. J. Energy Storage 2023, 72, 108761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabab, S.; Théveneau, P.; Coquelet, C.; Corvisier, J.; Paricaud, P. Measurements and Predictive Models of High-Pressure H2 Solubility in Brine (H2O + NaCl) for Underground Hydrogen Storage Application. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 32206–32220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarkowski, R.; Lankof, L.; Luboń, K.; Michalski, J. Hydrogen Storage Capacity of Salt Caverns and Deep Aquifers versus Demand for Hydrogen Storage: A Case Study of Poland. Appl. Energy 2024, 355, 122268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Ding, S.; Wang, H.; Yang, C.; Shi, X.; Ma, H.; Daemen, J.J.K. Mathematic Modelling of the Debrining for a Salt Cavern Gas Storage. J. Nat. Gas Eng. 2018, 50, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fibbi, G.; Beni, T.; Fanti, R.; Del Soldato, M. Underground Gas Storage Monitoring Using Free and Open Source InSAR Data: A Case Study from Yela (Spain). Energies 2023, 16, 6392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Ma, H.; Hou, W.; Yu, C.; Liu, H.; Feng, C.; Yang, C. Feasibility Analysis of Salt Cavern Gas Storage in Extremely Deep Formation: A Case Study in China. J. Energy Storage 2022, 47, 103649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, M.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, X. A Review on Well Integrity Issues for CO2 Geological Storage and Enhanced Gas Recovery. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 59, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeannin, L.; Myagkiy, A.; Vuddamalay, A. Modelling the Operation of Gas Storage in Salt Caverns: Numerical Approaches and Applications. Sci. Tech. Energ. Transit. 2022, 77, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fais, S.; Ligas, P.; Cuccuru, F.; Maggio, E.; Plaisant, A.; Pettinau, A.; Casula, G.; Bianchi, M.G. Detailed Petrophysical and Geophysical Characterization of Core Samples from the Potential Caprock-Reservoir System in the Sulcis Coal Basin (Southwestern Sardinia—Italy). Energy Procedia 2015, 76, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, D.Y.C.; Caramanna, G.; Maroto-Valer, M.M. An Overview of Current Status of Carbon Dioxide Capture and Storage Technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 39, 426–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novakova, L.; Broz, M.; Zaruba, J.; Sosna, K.; Najser, J.; Rukavickova, L.; Franek, J.; Rudajev, V. Βedrock Instability of Underground Storage Systems in the Czech Republic, Central Europe. Appl. Geophys. 2016, 13, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, Z.; Ping, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L. Discrete Element Analysis of Hydro-Mechanical Behavior of a Pilot Underground Crude Oil Storage Facility in Granite in China. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2014, 40, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, S.; Qiao, L. Assessment of Hydro-Mechanical Behavior of a Granite Rock Mass for a Pilot Underground Crude Oil Storage Facility in China. Rock. Mech. Rock Eng. 2015, 48, 2459–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.K.; Sigl, O.; Krenn, F.; Höfer-Öllinger, G. Underground Crude Oil Storage Projects in India / Unterirdische Rohölkavernen in Indien. Geomech. Tunn. 2013, 6, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, A.; Ozawa, A.; Kusakabe, Y.; Furukawa, T.; Yamaguchi, K.; Yageta, M.; Otake, T. Geochemical Monitoring of Deionized Seawater Injected Underground during Construction of an LPG Rock Cavern in Namikata, Japan, for the Safety Water Curtain System. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, A.; Glatz, G.; Gholami, R.; Mahmoud, M.; Alafnan, S. Carbon Mineralization and Geological Storage of CO2 in Basalt: Mechanisms and Technical Challenges. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2022, 229, 104036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loisy, C.; Cohen, G.; Laveuf, C.; Le Roux, O.; Delaplace, P.; Magnier, C.; Rouchon, V.; Cerepi, A.; Garcia, B. The CO2-Vadose Project: Dynamics of the Natural CO2 in a Carbonate Vadose Zone. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2013, 14, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, B.; Rhino, K.; Loisy, C.; Le Roux, O.; Cerepi, A.; Rouchon, V.; Noirez, S.; Le Gallo, C.; Delaplace, P.; Willequet, O.; et al. CO2-Vadose and DEMO-CO2 Projects: Two Complementary Projects about Geochemical and Geophysical Monitoring During CO2 Leakage. Energy Procedia 2017, 114, 3695–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptacek, J. Structural Analysis within the Rozna and Olsi Uranium Deposits (Strazek Moldanubicum) for the Estimation of Deformation and Stress Conditions of Underground Gas Storage. Acta Geodyn. Geomater. 2013, 10, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Luis, S.; Rita, S.; Ana, G.; Euripedes, V.; Zhang, N. Risk Assessment of CO2 Injection Processes and Storage in Carboniferous Formations: A Review. J. Rock Mech Geotech. 2011, 3, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newmark, R.L.; Friedmann, S.J.; Carroll, S.A. Water Challenges for Geologic Carbon Capture and Sequestration. Environ. Manag. 2010, 45, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnis, J.; Singh, S.; Huq, I. Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies for Global Change via the Implementation of Underground Coal Gasification. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Change 2016, 21, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Yin, J.; Hu, Y.; Wang, J.; Yin, H.; Qi, H. Monitoring and Control in Underground Coal Gasification: Current Research Status and Future Perspective. Sustainability 2019, 11, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Park, S.-G.; Yi, M.-J.; Son, J.-S.; Cho, S.-J. Borehole Radar Investigations for Locating Ice Ring Formed by Cryogenic Condition in an Underground Cavern. J. Appl. Geophys. 2007, 62, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.-S.; Jung, Y.-B.; Song, W.-K.; Lee, D.-H.; Chung, S.-K. Pilot Study on the Underground Lined Rock Cavern for LNG Storage. Eng. Geol. 2010, 116, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glamheden, R.; Curtis, P. Excavation of a Cavern for High-Pressure Storage of Natural Gas. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2006, 21, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Wang, T.; Shan, B.; An, G.; Yang, J.; Daemen, J.J.K. Fatigue Damage of Wellbore Cement Sheath in Gas Storage Salt Cavern Under Alternating Internal Pressure. Rock. Mech. Rock Eng. 2022, 55, 715–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lempp, C.; Shams, K.M.; Jahr, N. Approaches to Stress Monitoring in Deep Boreholes for Future CCS Projects. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 67, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yang, C.; Liu, J.; Hou, Z.; Xie, Y.; Shi, X. An Overview of Underground Energy Storage in Porous Media and Development in China. Gas Sci. Eng. 2023, 117, 205079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Hu, L.; Wu, X.; Yang, Y.; Gai, P.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y. The Underground Performance Analysis of Compressed Air Energy Storage in Aquifers through Field Testing. Appl. Energy 2024, 366, 123329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Cai, Z.; Li, C.; He, Q.; Ma, Y.; Guo, C. Numerical Investigation of Cycle Performance in Compressed Air Energy Storage in Aquifers. Appl. Energy 2020, 269, 115044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Yaseri, A.; Esteban, L.; Giwelli, A.; Sarout, J.; Lebedev, M.; Sarmadivaleh, M. Initial and Residual Trapping of Hydrogen and Nitrogen in Fontainebleau Sandstone Using Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Core Flooding. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 22482–22494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raad, S.M.J.; Leonenko, Y.; Hassanzadeh, H. Hydrogen Storage in Saline Aquifers: Opportunities and Challenges. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 168, 112846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanpouryouzband, A.; Adie, K.; Cowen, T.; Thaysen, E.M.; Heinemann, N.; Butler, I.B.; Wilkinson, M.; Edlmann, K. Geological Hydrogen Storage: Geochemical Reactivity of Hydrogen with Sandstone Reservoirs. ACS Energy Lett. 2022, 7, 2203–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benetatos, C.; Catania, F.; Giglio, G.; Pirri, C.F.; Raeli, A.; Scaltrito, L.; Serazio, C.; Verga, F. Workflow for the Validation of Geomechanical Simulations through Seabed Monitoring for Offshore Underground Activities. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadwick, R.A. 10—Offshore CO2 Storage: Sleipner Natural Gas Field beneath the North Sea. In Geological Storage of Carbon Dioxide (CO2); Gluyas, J., Mathias, S., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Thornton, UK, 2013; pp. 227–253. ISBN 978-0-85709-427-8. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, N.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, S.; Liu, N.; Su, X. Geochemical Impact of Aquifer Storage for Impure CO2 Containing O2 and N2: Tongliao Field Experiment. Appl. Energy 2015, 145, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, P.G.; Mura, J.; Castéran, F.; Guignard, M.; Ranchou-Peyruse, M.; Sénéchal, P.; Larregieu, M.; Isaure, M.-P.; Svahn, I.; Moonen, P.; et al. Biological, Geological and Chemical Effects of Oxygen Injection in Underground Gas Storage Aquifers in the Setting of Biomethane Deployment. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Luo, X.; Evans, D.; Busby, J.; Garvey, S.; Parkes, D.; Wang, J. Exergy Storage of Compressed Air in Cavern and Cavern Volume Estimation of the Large-Scale Compressed Air Energy Storage System. Appl. Energy 2017, 208, 745–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-M.; Rutqvist, J.; Kim, H.; Park, D.; Ryu, D.-W.; Park, E.-S. Failure Monitoring and Leakage Detection for Underground Storage of Compressed Air Energy in Lined Rock Caverns. Rock. Mech. Rock Eng. 2016, 49, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Ma, H.; Liang, X.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Cai, R.; Ye, L.; Yang, C. Damage Evaluation of Rock Salt under Multilevel Cyclic Loading with Constant Stress Intervals Using AE Monitoring and CT Scanning. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 2022, 208, 109517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heemann, R.; Ketzer, J.M.M.; Hiromoto, G.; Scislewski, A. Assessment of the Geological Disposal of Carbon Dioxide and Radioactive Waste in Brazil, and Some Comparative Aspects of Their Disposal in Argentina. In Geological Disposal of Carbon Dioxide and Radioactive Waste: A Comparative Assessment; Toth, F.L., Ed.; Advances in Global Change Research; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 589–611. ISBN 978-90-481-8712-6. [Google Scholar]
- Rapantova, N.; Pospisil, P.; Koziorek, J.; Vojcinak, P.; Grycz, D.; Rozehnal, Z. Optimisation of Experimental Operation of Borehole Thermal Energy Storage. Appl. Energy 2016, 181, 464–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Yang, H.; Wang, B.; Zhuang, J. Seismological Investigations of Induced Earthquakes Near the Hutubi Underground Gas Storage Facility. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2019, 124, 8753–8770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meguerdijian, S.; Jha, B. Quantification of Fault Leakage Dynamics Based on Leakage Magnitude and Dip Angle. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2021, 45, 2303–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhn, D.; De Nil, D.; al Hagrey, S.A.; Rabbel, W. A Combination of Waveform Inversion and Reverse-Time Modelling for Microseismic Event Characterization in Complex Salt Structures. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quattrocchi, F.; Galli, G.; Gasparini, A.; Magno, L.; Pizzino, L.; Sciarra; Voltattorni, N. Very Slightly Anomalous Leakage of CO2, CH4 and Radon along the Main Activated Faults of the Strong L’Aquila Earthquake (Magnitude 6.3, Italy). Implications for Risk Assessment Monitoring Tools & Public Acceptance of CO2 and CH4 Underground Storage. Energy Procedia 2011, 4, 4067–4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducellier, A.; Seyedi, D.; Foerster, E. A Coupled Hydromechanical Fault Model for the Study of the Integrity and Safety of Geological Storage of CO2. Energy Procedia 2011, 4, 5138–5145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Xie, J. Lost Gas Mechanism and Quantitative Characterization during Injection and Production of Water-Flooded Sandstone Underground Gas Storage. Energies 2018, 11, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Gonzales, D.A.; Popoola, O.; Bright, V.B.; Paulson, S.E.; Wang, Y.; Jones, R.L.; Jerrett, M. Associations among Particulate Matter, Hazardous Air Pollutants and Methane Emissions from the Aliso Canyon Natural Gas Storage Facility during the 2015 Blowout. Environ. Int. 2019, 132, 104855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Yang, C.; Chen, J.; Daemen, J.J.K. Geomechanical Investigation of Roof Failure of China’s First Gas Storage Salt Cavern. Eng. Geol. 2018, 243, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafortune, S.; Gombert, P.; Pokryszka, Z.; Lacroix, E.; de Donato, P.; Jozja, N. Monitoring Scheme for the Detection of Hydrogen Leakage from a Deep Underground Storage. Part 1: On-Site Validation of an Experimental Protocol via the Combined Injection of Helium and Tracers into an Aquifer. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gombert, P.; Lafortune, S.; Pokryszka, Z.; Lacroix, E.; de Donato, P.; Jozja, N. Monitoring Scheme for the Detection of Hydrogen Leakage from a Deep Underground Storage. Part 2: Physico-Chemical Impacts of Hydrogen Injection into a Shallow Chalky Aquifer. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djizanne, H.; Murillo Rueda, C.; Brouard, B.; Bérest, P.; Hévin, G. Blowout Prediction on a Salt Cavern Selected for a Hydrogen Storage Pilot. Energies 2022, 15, 7755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Oldenburg, C.M.; Freifeld, B.M.; Jordan, P.D. Modeling the Aliso Canyon Underground Gas Storage Well Blowout and Kill Operations Using the Coupled Well-Reservoir Simulator T2Well. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 2018, 161, 158–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freifeld, B.M.; Oldenburg, C.M.; Jordan, P.; Pan, L.; Perfect, S.; Morris, J.; White, J.; Bauer, S.; Blankenship, D.; Roberts, B. Well Integrity for Natural Gas Storage in Depleted Reservoirs and Aquifers; Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL): Berkeley, CA, USA, 2016.
- Thorpe, A.K.; Duren, R.M.; Conley, S.; Prasad, K.R.; Bue, B.D.; Yadav, V.; Foster, K.T.; Rafiq, T.; Hopkins, F.M.; Smith, M.L.; et al. Methane Emissions from Underground Gas Storage in California. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 045005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, L.M.; Blair, B.; Hughes, J.; Allshouse, W.B.; Blake, N.J.; Helmig, D.; Milmoe, P.; Halliday, H.; Blake, D.R.; Adgate, J.L. Ambient Nonmethane Hydrocarbon Levels Along Colorado’s Northern Front Range: Acute and Chronic Health Risks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 4514–4525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michanowicz, D.R.; Williams, S.R.; Buonocore, J.J.; Rowland, S.T.; Konschnik, K.E.; Goho, S.A.; Bernstein, A.S. Population Allocation at the Housing Unit Level: Estimates around Underground Natural Gas Storage Wells in PA, OH, NY, WV, MI, and CA. Environ. Health 2019, 18, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Huang, S. A Fully Coupled Thermo-Hydro-Mechanical Model for Rock Mass under Freezing/Thawing Condition. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2013, 95, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, R.J.; Mahgerefteh, H. Investigating the Impact of Flow Rate Ramp-up on Carbon Dioxide Start-up Injection. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2019, 88, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verga, F. What’s Conventional and What’s Special in a Reservoir Study for Underground Gas Storage. Energies 2018, 11, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, M.-J.; Kim, J.-H.; Park, S.-G.; Son, J.-S. Investigation of Ground Condition Changes Due to Cryogenicconditions in an Underground LNG Storage Plant. Explor. Geophys. 2005, 36, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, P.P.; Werner, K.-D.; Petrov, S.; Bartholmai, M.; Lazik, D. Setup of a Large-Scale Test Field for Distributed Soil Gas Sensors and Testing of a Monitoring Method Based on Tomography. tm-Tech. Mess. 2016, 83, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, S.A.; Keating, E.; Mansoor, K.; Dai, Z.; Sun, Y.; Trainor-Guitton, W.; Brown, C.; Bacon, D. Key Factors for Determining Groundwater Impacts Due to Leakage from Geologic Carbon Sequestration Reservoirs. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2014, 29, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerard, D.; Wilson, E.J. Environmental Bonds and the Challenge of Long-Term Carbon Sequestration. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orujov, A.; Coddington, K.; Aryana, S.A. A Review of CCUS in the Context of Foams, Regulatory Frameworks and Monitoring. Energies 2023, 16, 3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; Chen, T.; Ma, Z.; Tian, H.; Meguerdijian, S.; Chen, B.; Pawar, R.; Huang, L.; Xu, T.; Cather, M.; et al. A Review of Risk and Uncertainty Assessment for Geologic Carbon Storage. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 189, 113945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, J.H.; Shaw, J.A.; Lawrence, R.L.; Lewicki, J.L.; Dobeck, L.M.; Repasky, K.S.; Spangler, L.H. Multi-Spectral Imaging of Vegetation for Detecting CO2 Leaking from Underground. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 60, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ma, X.; Wu, Y.; Gao, Q.; Li, Y. A Plant Tolerance Index to Select Soil Leaking CO2 Bio-Indicators for Carbon Capture and Storage. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 170, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, H.; Xing, W.; Hou, Z.; Were, P. Study of the Relationship between Surface Subsidence and Internal Pressure in Salt Caverns. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 6899–6910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misa, R.; Sroka, A.; Dudek, M.; Tajduś, K.; Meyer, S. Determination of Convergence of Underground Gas Storage Caverns Using Non-Invasive Methodology Based on Land Surface Subsidence Measurement. J. Rock Mech Geotech. 2023, 15, 1944–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Liu, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z. Ground Subsidence Prediction Model and Parameter Analysis for Underground Gas Storage in Horizontal Salt Caverns. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, e9504289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonneville, A.; Heggy, E.; Strickland, C.; Normand, J.; Dermond, J.; Fang, Y.; Sullivan, C. Geophysical Monitoring of Ground Surface Deformation Associated with a Confined Aquifer Storage and Recovery Operation. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 4667–4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, H.; Ajalloeian, R. Mechanical Behavior of Salt Rock under Uniaxial Compression and Creep Tests. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2018, 110, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Gutierrez, M. A Time-Dependent Creep Model for Rock Based on Damage Mechanics. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Shi, X.; Li, Y.; Li, P.; Ban, S.; Xue, T.; Zhu, S.; Liu, H.; Yang, C. Field Experimental and Theoretical Research on Creep Shrinkage Mechanism of Ultra-Deep Energy Storage Salt Cavern. Rock. Mech. Rock Eng. 2024, 57, 287–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, K.; Daemen, J.J.K.; Liu, W. Time-Dependent Subsidence Prediction Model and Influence Factor Analysis for Underground Gas Storages in Bedded Salt Formations. Eng. Geol. 2015, 187, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ma, H.; Yang, C.; Zhao, K.; Hu, Z.; Daemen, J.J.K. Acoustic Emission Characteristics of Rock Salt under Multi-Stage Cyclic Loading. Int. J. Fatigue 2023, 176, 107911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struhár, J.; Rapant, P.; Kačmařík, M.; Hlaváčová, I.; Lazecký, M. Monitoring Non-Linear Ground Motion above Underground Gas Storage Using GNSS and PSInSAR Based on Sentinel-1 Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codegone, G.; Rocca, V.; Verga, F.; Coti, C. Subsidence Modeling Validation Through Back Analysis for an Italian Gas Storage Field. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2016, 34, 1749–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benetatos, C.; Codegone, G.; Ferraro, C.; Mantegazzi, A.; Rocca, V.; Tango, G.; Trillo, F. Multidisciplinary Analysis of Ground Movements: An Underground Gas Storage Case Study. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapant, P.; Struhár, J.; Lazecký, M. Radar Interferometry as a Comprehensive Tool for Monitoring the Fault Activity in the Vicinity of Underground Gas Storage Facilities. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hu, J.; Sun, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhu, J. Deriving 3-D Time-Series Ground Deformations Induced by Underground Fluid Flows with InSAR: Case Study of Sebei Gas Fields, China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellini, R.; Vasile, N.S.; Bassani, I.; Vizzarro, A.; Coti, C.; Barbieri, D.; Scapolo, M.; Pirri, C.F.; Verga, F.; Menin, B. Investigating the Activity of Indigenous Microbial Communities from Italian Depleted Gas Reservoirs and Their Possible Impact on Underground Hydrogen Storage. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1392410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dopffel, N.; An-Stepec, B.A.; Bombach, P.; Wagner, M.; Passaris, E. Microbial Life in Salt Caverns and Their Influence on H2 Storage—Current Knowledge and Open Questions. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 58, 1478–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dopffel, N.; Jansen, S.; Gerritse, J. Microbial Side Effects of Underground Hydrogen Storage—Knowledge Gaps, Risks and Opportunities for Successful Implementation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 8594–8606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazina, T.N.; Abukova, L.A.; Tourova, T.P.; Babich, T.L.; Bidzhieva, S.K.; Filippova, D.S.; Safarova, E.A. Diversity and Possible Activity of Microorganisms in Underground Gas Storage Aquifers. Microbiology 2021, 90, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkiewicz, A.; Steliga, T.; Kluk, D.; Gminski, Z. Biomonitoring Studies and Preventing the Formation of Biogenic H2S in the Wierzchowice Underground Gas Storage Facility. Energies 2021, 14, 5463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, L.; Popp, D.; Nowack, G.; Bombach, P.; Vogt, C.; Richnow, H.H. Structural Analysis of Microbiomes from Salt Caverns Used for Underground Gas Storage. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 20684–20694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadariya, V.; Kaur, J.; Sapale, P.; Rasane, P.; Singh, J. Hydrogen Storage in Porous Media: Understanding and Mitigating Microbial Risks for a Sustainable Future. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 67, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajooie, S.; Gaus, G.; Dohrmann, A.B.; Krüger, M.; Littke, R. Methanogenic Conversion of Hydrogen to Methane in Reservoir Rocks: An Experimental Study of Microbial Activity in Water-Filled Pore Space. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 50, 272–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mura, J.; Ranchou-Peyruse, M.; Guignard, M.; Haddad, P.G.; Ducousso, M.; Casteran, F.; Sénéchal, P.; Larregieu, M.; Isaure, M.-P.; Moonen, P.; et al. Comparative Study of Three H2 Geological Storages in Deep Aquifers Simulated in High-Pressure Reactors. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 63, 330–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiyagarajan, S.R.; Emadi, H.; Hussain, A.; Patange, P.; Watson, M. A Comprehensive Review of the Mechanisms and Efficiency of Underground Hydrogen Storage. J. Energy Storage 2022, 51, 104490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, S.; Carey, J.W.; Dzombak, D.; Huerta, N.J.; Li, L.; Richard, T.; Um, W.; Walsh, S.D.C.; Zhang, L. Review: Role of Chemistry, Mechanics, and Transport on Well Integrity in CO2 Storage Environments. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2016, 49, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.-P.; Song, G.-L.; Zhu, Y.-X.; Deng, Y.-J.; Zheng, D.-J. An Intelligent Mg Anode for Protection of the Concrete-Covered Steel Tubing in Carbon Capture and Storage. Compos. Part B 2022, 243, 110165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priolo, E.; Zinno, I.; Guidarelli, M.; Romanelli, M.; Lanari, R.; Sandron, D.; Garbin, M.; Peruzza, L.; Romano, M.A.; Zuliani, D.; et al. The Birth of an Underground Gas Storage in a Depleted Gas Reservoir—Results From Integrated Seismic and Ground Deformation Monitoring. Earth Space Sci. 2024, 11, e2023EA003275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustawa z Dnia 27 Kwietnia 2001 r. Prawo Ochrony Środowiska (Dz.U. z 2025 r. poz. 647). Available online: https://isap.sejm.gov.pl/isap.nsf/DocDetails.xsp?id=wdu20010620627 (accessed on 23 July 2025).
- API Publishes Two Updated Standards for Underground Natural Gas Storage. Available online: https://www.api.org/news-policy-and-issues/news/2022/11/29/api-publishes-two-updated-standards-for-underground-natural-gas-storage (accessed on 25 July 2025).
- Blachowski, J.; Ellefmo, S.L. Mining Ground Deformation Estimation Based on Pre-Processed InSAR Open Data—A Norwegian Case Study. Minerals 2023, 13, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajduś, K.; Sroka, A.; Misa, R.; Tajduś, A.; Meyer, S. Surface Deformations Caused by the Convergence of Large Underground Gas Storage Facilities. Energies 2021, 14, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Yu, X.; Zhu, M.; Guo, Z.; Chen, H. Deformation Monitoring and Spatiotemporal Evolution of Mining Area with Unmanned Aerial Vehicle and D-InSAR Technology. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2022, 2022, e8075611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; He, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yang, W.; Chen, Y.; Sun, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Cao, S. A ConvLSTM Neural Network Model for Spatiotemporal Prediction of Mining Area Surface Deformation Based on SBAS-InSAR Monitoring Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5201722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, W.; Yang, R.; Cao, D.; Chen, L.; Li, D.; Meng, L. CO2 Injection Deformation Monitoring Based on UAV and InSAR Technology: A Case Study of Shizhuang Town, Shanxi Province, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lian, X.; Ge, L.; Liu, X.; Du, Z.; Yang, W.; Wu, Y.; Hu, H.; Cai, Y. Surface Subsidence Monitoring Induced by Underground Coal Mining by Combining DInSAR and UAV Photogrammetry. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, K.; Zhang, J.; Hong, L.; Chi, H. Monitoring and Analysis of Ground Surface Settlement in Mining Clusters by SBAS-InSAR Technology. Sensors 2022, 22, 3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palamà, R.; Crosetto, M.; Rapinski, J.; Barra, A.; Cuevas-González, M.; Monserrat, O.; Crippa, B.; Kotulak, N.; Mróz, M.; Mleczko, M. A Multi-Temporal Small Baseline Interferometry Procedure Applied to Mining-Induced Deformation Monitoring. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, G.; Li, Z.; Xu, W.; Zhu, J.; He, L.; Xiong, Z.; Qiao, X. Retrieving the Displacements of the Hutubi (China) Underground Gas Storage during 2003–2020 from Multi-Track InSAR. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 268, 112768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fibbi, G.; Del Soldato, M.; Fanti, R. Review of the Monitoring Applications Involved in the Underground Storage of Natural Gas and CO2. Energies 2023, 16, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Acosta, M.; Sirorattanakul, K.; Bourne, S.; Avouac, J.-P. Geodetic Monitoring of Elastic and Inelastic Deformation in Compacting Reservoirs Due To Subsurface Operations. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2025, 130, e2024JB030794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Z.X.; Xue, Y.G.; Su, M.X.; Qiu, D.H.; Zhang, K.; Li, Z.Q.; Liu, Y.M. Deformation Characteristics Observed during Multi-Step Excavation of Underground Oil Storage Caverns Based on Field Monitoring and Numerical Simulation. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, R.V. 1.16—Microwave Sensors. In Comprehensive Remote Sensing; Liang, S., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2018; pp. 435–474. ISBN 978-0-12-803221-3. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Choi, Y. Applications of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles in Mining from Exploration to Reclamation: A Review. Minerals 2020, 10, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarnogorska, M.; Samsonov, S.V.; White, D.J. Airborne and Spaceborne Remote Sensing Characterization for Aquistore Carbon Capture and Storage Site. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 42, 274–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateson, L.; Vellico, M.; Beaubien, S.E.; Pearce, J.M.; Annunziatellis, A.; Ciotoli, G.; Coren, F.; Lombardi, S.; Marsh, S. The Application of Remote-Sensing Techniques to Monitor CO2-Storage Sites for Surface Leakage: Method Development and Testing at Latera (Italy) Where Naturally Produced CO2 Is Leaking to the Atmosphere. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2008, 2, 388–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, W.; Yang, R.; Liu, Y.; Jafari, M. CO2 Capture and Storage Monitoring Based on Remote Sensing Techniques: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 281, 124409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uys, D. InSAR: An Introduction. Preview 2016, 2016, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, W.; Yang, R.; Gao, H.; Cao, D. Analysis of Available Conditions for InSAR Surface Deformation Monitoring in CCS Projects. Energies 2022, 15, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubitz, C.; Kempka, T.; Motagh, M. Integrated Assessment of Ground Surface Displacements at the Ketzin Pilot Site for CO2 Storage by Satellite-Based Measurements and Hydromechanical Simulations. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 186–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent Scatterers in SAR Interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A New Algorithm for Surface Deformation Monitoring Based on Small Baseline Differential SAR Interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.; Chen, J.; Wen, T.; Chen, E.J.; Xu, J.; Gao, J.; Shen, L.W. Investigating Geohazard Risk in Mountainous Areas for Underground Gas Storage Using InSAR and Development of a Protocol for Hazard Prevention. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0318860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codegone, G.; Benetatos, C.; Uttini, A.; Rucci, A.; Fiaschi, S.; Mantegazzi, A.; Coti, C. Defining the Influence Area of Uplift and Subsidence from Underground Gas Storage in Anticline Structural Traps: Insights from InSAR Cross-Correlation. Gondwana Res. 2025, 143, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fibbi, G.; Montalti, R.; Soldato, M.D.; Cespa, S.; Ferretti, A.; Fanti, R. Unlocking the InSAR Potential for Managing Underground Gas Storage in Salt Caverns. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2025, 141, 104656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janna, C.; Castelletto, N.; Ferronato, M.; Gambolati, G.; Teatini, P. A Geomechanical Transversely Isotropic Model of the Po River Basin Using PSInSAR Derived Horizontal Displacement. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2012, 51, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutqvist, J.; Vasco, D.W.; Myer, L. Coupled Reservoir-Geomechanical Analysis of CO2 Injection and Ground Deformations at In Salah, Algeria. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2010, 4, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasco, D.W.; Ferretti, A.; Novali, F. Reservoir Monitoring and Characterization Using Satellite Geodetic Data: Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar Observations from the Krechba Field, Algeria. Geophysics 2008, 73, WA113–WA122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rucci, A.; Vasco, D.W.; Novali, F. Monitoring the Geologic Storage of Carbon Dioxide Using Multicomponent SAR Interferometry. Geophys. J. Int. 2013, 193, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onuma, T.; Ohkawa, S. Detection of Surface Deformation Related with CO2 Injection by DInSAR at In Salah, Algeria. Energy Procedia 2009, 1, 2177–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fibbi, G.; Landini, N.; Intrieri, E.; Ventisette, C.D.; Soldato, M.D. Open-Source InSAR Data to Detect Ground Displacement Induced by Underground Gas Storage Reservoirs. Earth Syst. Env. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Even, M.; Westerhaus, M.; Simon, V. Complex Surface Displacements above the Storage Cavern Field at Epe, NW-Germany, Observed by Multi-Temporal SAR-Interferometry. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fibbi, G.; Novellino, A.; Bateson, L.; Fanti, R.; Del Soldato, M. Multidisciplinary Assessment of Seasonal Ground Displacements at the Hatfield Moors Gas Storage Site in a Peat Bog Landscape. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 22521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comola, F.; Janna, C.; Lovison, A.; Minini, M.; Tamburini, A.; Teatini, P. Efficient Global Optimization of Reservoir Geomechanical Parameters Based on Synthetic Aperture Radar-Derived Ground Displacements. Geophysics 2016, 81, M23–M33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Oldenburg, C.M.; Zhou, Q.; Pan, L.; Freifeld, B.M.; Jeanne, P.; Rodríguez Tribaldos, V.; Vasco, D.W. Advanced Monitoring and Simulation for Underground Gas Storage Risk Management. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 2022, 208, 109763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, M.C.; Ulaby, F.T.; Hallikainen, M.T.; El-rayes, M.A. Microwave Dielectric Behavior of Wet Soil-Part II: Dielectric Mixing Models. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1985, GE-23, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, J. Chapter 11—Spacecraft. In Spatial Cognitive Engine Technology; Zhang, J., Li, J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 129–162. ISBN 978-0-323-95107-4. [Google Scholar]
- Hogan, J.A.; Shaw, J.A.; Lawrence, R.L.; Lewicki, J.L.; Dobeck, L.M.; Spangler, L.H. Detection of Leaking CO2 Gas With Vegetation Reflectances Measured By a Low-Cost Multispectral Imager. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2012, 5, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiruchittampalam, S.; Raval, S.A.; Glenn, N.F.; Le-Hussain, F. Indirect Remote Sensing Techniques for Long Term Monitoring of CO2 Leakage in Geological Carbon Sequestration: A Review. J. Nat. Gas Eng. 2022, 100, 104488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.E.; Shaw, J.A.; Lawrence, R.L.; Nugent, P.W.; Hogan, J.A.; Dobeck, L.M.; Spangler, L.H. Comparison of Long-Wave Infrared Imaging and Visible/Near-Infrared Imaging of Vegetation for Detecting Leaking CO2 Gas. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 1651–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellante, G.J.; Powell, S.L.; Lawrence, R.L.; Repasky, K.S.; Dougher, T.A.O. Aerial Detection of a Simulated CO2 Leak from a Geologic Sequestration Site Using Hyperspectral Imagery. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2013, 13, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Steven, M.D.; He, R.; Chen, Y.; Du, P. Identification of Plants Responding to CO2 Leakage Stress Using Band Depth and the Full Width at Half Maxima of Canopy Spectra. Energy 2016, 100, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindan, R.; Korre, A.; Durucan, S.; Imrie, C.E. Comparative Assessment of the Performance of Airborne and Spaceborne Spectral Data for Monitoring Surface CO2 Leakages. Energy Procedia 2011, 4, 3421–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, C.J.; Repasky, K.S.; Lawrence, R.L.; Jay, S.C.; Carlsten, J.L. Monitoring Effects of a Controlled Subsurface Carbon Dioxide Release on Vegetation Using a Hyperspectral Imager. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2009, 3, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellante, G.J.; Powell, S.L.; Lawrence, R.L.; Repasky, K.S.; Dougher, T. Hyperspectral Detection of a Subsurface CO2 Leak in the Presence of Water Stressed Vegetation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, C.; Repasky, K.S.; Lawrence, R.; Powell, S. Multi-Temporal Mesoscale Hyperspectral Data of Mixed Agricultural and Grassland Regions for Anomaly Detection. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 131, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, M.; Lawrence, R.; Repasky, K.; Sterling, T.; McCann, C.; Powell, S. Agreement Analysis and Spatial Sensitivity of Multispectral and Hyperspectral Sensors in Detecting Vegetation Stress at Management Scales. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2017, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindan, R.; Korre, A.; Durucan, S.; Imrie, C.E. A Geostatistical and Probabilistic Spectral Image Processing Methodology for Monitoring Potential CO2 Leakages on the Surface. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2011, 5, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, W.; Jiang, J.; Pan, Y.; Yuan, D. Spectral Responses and Identification of Surface Vegetation Stressed by Natural Gas Leakage. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 132–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Jiang, J.; Li, K.; Wang, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, R.; Jiang, D.; Yue, G. A Baseline Slope Index to Detect Natural Gas Microleakage-Stressed Vegetation Considering Shadow Removal in Hyperspectral Imagery. Energy 2025, 331, 137037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinbao, J.; Steven, M.D.; Qingkong, C.; Ruyan, H.; Haiqiang, G.; Yunhao, C. Detecting Bean Stress Response to CO2 Leakage with the Utilization of Leaf and Canopy Spectral Derivative Ratio. Greenh. Gases 2014, 4, 468–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Hou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, F.; Liu, X.; Yang, Y. Influence of CO2 Leakage from Oil-Producing Wells on Crop Growth Based on Improved CASA Model. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 290–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacroix, E.; de Donato, P.; Lafortune, S.; Caumon, M.-C.; Barres, O.; Liu, X.; Derrien, M.; Piedevache, M. In Situ Continuous Monitoring of Dissolved Gases (N2, O2, CO2, H2) Prior to H2 Injection in an Aquifer (Catenoy, France) by on-Site Raman and Infrared Spectroscopies: Instrumental Assessment and Geochemical Baseline Establishment. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 3806–3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Abdulhameed, D.; Tao, G.; Xu, T.; Wang, J.; Xu, D.; Soga, K.; Wu, Y. Large-Scale Experimental Validation of Real-Time Monitoring in Underground Gas Storage Wells Using Distributed Fiber Optic Sensing. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 19523–19532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirman, P.; Franců, J.; Jurenka, L.; Čejková, B.; Jačková, I.; Krejčí, O. Methane Anomaly in Soil Gas above an Abandoned Oil & Gas Exploration Borehole in NE Czechia. Gas Sci. Eng. 2023, 115, 205014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Liu, M.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, L. Long-Term Landsat Monitoring of Mining Subsidence Based on Spatiotemporal Variations in Soil Moisture: A Case Study of Shanxi Province, China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 102, 102447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaryka, A.; Benndorf, J. Ground Subsidence above Salt Caverns for Energy Storage: A Comparison of Prediction Methods with Emphasis on Convergence and Asymmetry. Mining 2023, 3, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misa, R.; Sroka, A.; Mrocheń, D. Evaluating Surface Stability for Sustainable Development Following Cessation of Mining Exploitation. Sustainability 2025, 17, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratzsch, H. Mining Subsidence Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1983; ISBN 978-3-642-81925-4. [Google Scholar]
- Knothe, S. A Profile Equation for Definitely Shaped Subsidence Trough. Arch. Górnictwa I Hut. 1953, 1, 22–38. [Google Scholar]
- Sroka, A.; Schober, F. The Calculation of the Maximum Ground Movements over Salt Caverns Considering the Cavity Geometry (Die Berechnung Der Maximalen Bodenbewegungen Über Kavernenartigen Hohlräumen Unter Berücksichtigung Der Hohlraumgeometrie). Kali Und Steinsalz 1982, 8, 273–277. [Google Scholar]
- Litwiniszyn, J. The Differential Equation of Displacements of Rock Masses. Równanie Rózniczkowe Przemieszczeń Górotworu). Arch. Górnictwa I Hut. 1953, 1, 9–21. [Google Scholar]
- Sroka, A.; Hejmanowski, R. Prediction of Surface Subsidence Due to Oil- or Gasfield Development. In Proceedings of the 3rd IAG/12th FIG Symposium, Baden, Germany, 22–24 May 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kwinta, A.; Hejmanowski, R.; Sroka, A. A Time Function Analysis Used for the Prediction of Rock Mass Subsidence. In Mining Science and Technology: Proceedings of the ‘96 International Symposium on Mining Science and Technology, Xuzhou, China, 16–18 October 1996; Guo, Y., Golosinski, T.S., Eds.; Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands; Brookfield, VT, USA, 1996; pp. 419–424. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Yan, X.; Yang, X.; Yang, H. Dynamic Subsidence Prediction of Ground Surface above Salt Cavern Gas Storage Considering the Creep of Rock Salt. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2010, 53, 3197–3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Yinping, L.; Chunhe, Y.; Deyi, J.; Daemen, J.J.K.; Jie, C.; Junfeng, K. A New Method of Surface Subsidence Prediction for Natural Gas Storage Cavern in Bedded Rock Salts. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazanowski, M.; Szostak-Chrzanowski, A. Salt Rock Deformations Caused by Mining Activity; Wydział Geoinżynierii, Górnictwa i Geologii Politechniki Wrocławskiej: Wrocław, Poland, 2016; ISBN 978-83-942205-6-3. [Google Scholar]
- Mandal, A.; Chakravarthy, C.P.; Nanda, A.; Rath, R.; Usmani, A. Analysis and Design Approach for Large Storage Caverns. Int. J. Geomech. 2013, 13, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhong, S.; Qiao, L.; Li, W.; Guo, J. Hydrogeological Model for Underground Oil Storage in Rock Caverns. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2023, 132, 104880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J. Surface Subsidence Induced by Salt Cavern Gas Storage and Its Impact on Railway Safety: Numerical Simulation and Fuzzy Evaluation. Results Eng. 2025, 26, 105331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Tang, C.A.; Wang, L.X.; Tang, D.H.; Zhuang, D.Y.; Zhang, Q.B.; Zhao, J. Stability Analysis of Underground Oil Storage Caverns by an Integrated Numerical and Microseismic Monitoring Approach. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2016, 54, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Ye, L.; Ma, H.; Shi, X.; Liu, H.; Yang, C. Subsidence above Gas Storage in Salt Caverns Predicted with Viscoelastic Theory. J. Nat. Gas Eng. 2022, 103, 104620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Chen, F.; Ma, H.; Shi, X.; Li, H.; Yang, C. Subsidence above Rock Salt Caverns Predicted with Elastic Plate Theory. Environ. Earth Sci. 2022, 81, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, B.; Yu, X.; Xu, N.; Ye, J. Long-Term Stability and Deformation Behaviour of Anhydrite Mine-Out for Crude Oil Storage. Rock. Mech. Rock Eng. 2020, 53, 1719–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arancibia, R.G.; Llop, P.; Lovatto, M. Nonparametric Prediction for Univariate Spatial Data: Methods and Applications. Pap. Reg. Sci. 2023, 102, 635–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’erba, S. Exploratory Spatial Data Analysis. In International Encyclopedia of Human Geography; Kitchin, R., Thrift, N., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2009; pp. 683–690. ISBN 978-0-08-044910-4. [Google Scholar]
- Blachowski, J.; Dynowski, A.; Buczyńska, A.; Ellefmo, S.L.; Walerysiak, N. Integrated Spatiotemporal Analysis of Vegetation Condition in a Complex Post-Mining Area: Lignite Mine Case Study. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merry, K.; Bettinger, P.; Crosby, M.; Boston, K. 8—Geographic Data Processing—Raster Data. In Geographic Information System Skills for Foresters and Natural Resource Managers; Merry, K., Bettinger, P., Crosby, M., Boston, K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 231–267. ISBN 978-0-323-90519-0. [Google Scholar]
- Buczyńska, A.; Blachowski, J.; Bugajska-Jędraszek, N. Analysis of Post-Mining Vegetation Development Using Remote Sensing and Spatial Regression Approach: A Case Study of Former Babina Mine (Western Poland). Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goovaerts, P.; Jacquez, G.M.; Marcus, A. Geostatistical and Local Cluster Analysis of High Resolution Hyperspectral Imagery for Detection of Anomalies. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 95, 351–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sica, F.; Calvanese, F.; Scarpa, G.; Rizzoli, P. A CNN-Based Coherence-Driven Approach for InSAR Phase Unwrapping. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.J.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative Adversarial Networks. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1406.2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koldasbayeva, D.; Tregubova, P.; Gasanov, M.; Zaytsev, A.; Petrovskaia, A.; Burnaev, E. Challenges in Data-Driven Geospatial Modeling for Environmental Research and Practice. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 10700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Hu, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Qiao, T.; Li, Z.; Cheng, S. Identifying Spatiotemporal Pattern and Trend Prediction of Land Subsidence in Zhengzhou Combining MT-InSAR, XGBoost and Hydrogeological Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, R.; Wu, C.; Goh, A.T.C.; Wang, L. Assessment of Basal Heave Stability for Braced Excavations in Anisotropic Clay Using Extreme Gradient Boosting and Random Forest Regression. Undergr. Space 2022, 7, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imani, M.; Beikmohammadi, A.; Arabnia, H.R. Comprehensive Analysis of Random Forest and XGBoost Performance with SMOTE, ADASYN, and GNUS Under Varying Imbalance Levels. Technologies 2025, 13, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia Navarro, A.M.; Rocca, V.; Capozzoli, A.; Chiosa, R.; Verga, F. Investigation of Ground Movements Induced by Underground Gas Storages via Unsupervised ML Methodology Applied to InSAR Data. Gas Sci. Eng. 2024, 125, 205293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Zhang, L.; Lu, H.; Chen, D.; Wang, J.; Zhu, W.; Lee, W.J. Transient Pressure Prediction in Large-Scale Underground Natural Gas Storage: A Deep Learning Approach and Case Study. Energy 2024, 311, 133411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hu, Z.; Yan, X.; Yao, J.; Sun, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, J. Gradient-Boosted Spatiotemporal Neural Network for Simulating Underground Hydrogen Storage in Aquifers. J. Comput. Phys. 2025, 521, 113557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, D.; Fu, K.; Xue, Y.; Li, Z.; Ning, Z.; Zhou, B.; Tao, Y. Seepage Field Prediction of Underground Water-Sealed Oil Storage Cavern Based on Long Short-Term Memory Model. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, T.; Wang, S.; Chang, Y.; Jia, P. An Automatic P-Wave Onset Time Picking Method for Mining-Induced Microseismic Data Based on Long Short-Term Memory Deep Neural Network. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2022, 13, 908–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wamriew, D.; Dorhjie, D.B.; Bogoedov, D.; Pevzner, R.; Maltsev, E.; Charara, M.; Pissarenko, D.; Koroteev, D. Microseismic Monitoring and Analysis Using Cutting-Edge Technology: A Key Enabler for Reservoir Characterization. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieślik, K.; Milczarek, W. Application of Machine Learning in Forecasting the Impact of Mining Deformation: A Case Study of Underground Copper Mines in Poland. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Guo, H.; Gong, X.; Lu, N.; Zhang, K. A Theory and Data-Driven Method for Rapid Bottom Hole Pressure Calculation in UGS. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 8878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCay, A.T.; Valyrakis, M.; Younger, P.L. A Meta-Analysis of Coal Mining Induced Subsidence Data and Implications for Their Use in the Carbon Industry. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2018, 192, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammut-Bonnici, T.; Galea, D. SWOT Analysis. In Wiley Encyclopedia of Management; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 1–8. ISBN 978-1-118-78531-7. [Google Scholar]
- Blachowski, J.; Benndorf, J.; Babaryka, A.; Gießler, G.; Głąbicki, D.; Grzempowski, P.; Kaczmarek, A.; Kubisch, F.; Owczarz, K.; Ashfaque, N. Ground Movement Control in Energy Transition Areas—Status of the Bilateral German-Polish Project CLEAR. Markscheidewesen 2024, 131, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spreckels, V.; Engel, T. Set-up and Application of Multisensor-Referencestations (MSST) for Levelling, GNSS and InSAR in the Former Mining Regions Saarland and Ruhrgebiet within Germany. In Proceedings of the 5th Joint International Symposium on Deformation Monitoring, Valencia, Spain, 20–22 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; López-Dekker, P.; Dheenathayalan, P.; Liao, M.; Hanssen, R.F. On the Value of Corner Reflectors and Surface Models in InSAR Precise Point Positioning. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 158, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasco, D.W.; Samsonov, S.V.; Wang, K.; Burgmann, R.; Jeanne, P.; Foxall, W.; Zhang, Y. Monitoring Natural Gas Storage Using Synthetic Aperture Radar: Are the Residuals Informative? Geophys. J. Int. 2022, 228, 1438–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wnuk, K.; Zhou, W.; Gutierrez, M. Mapping Urban Excavation Induced Deformation in 3D via Multiplatform InSAR Time-Series. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xu, W.; Li, Z. Review of the SBAS InSAR Time-Series Algorithms, Applications, and Challenges. J. Geod. Geodyn. 2022, 13, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlögel, R.; Owczarz, K.; Orban, A.; Havenith, H.-B. Investigating Earth Surface Deformation with SAR Interferometry and Geomodeling in the Transborder Meuse–Rhine Region. Front. Remote Sens. 2024, 5, 1366944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, M.; Minati, F.; Trillo, F.; Ferretti, A.; Novali, F.; Passera, E.; Dehls, J.; Larsen, Y.; Marinkovic, P.; Eineder, M.; et al. European Ground Motion Service (EGMS). In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS, Brussels, Belgium, 11–16 July 2021; pp. 3293–3296. [Google Scholar]
- Cedigaz Underground Gas Storage: Pillar of Global Energy Security. Available online: https://www.cedigaz.org/underground-gas-storage-pillar-of-global-energy-security/ (accessed on 26 February 2025).
- Raza, A.; Arif, M.; Glatz, G.; Mahmoud, M.; Al Kobaisi, M.; Alafnan, S.; Iglauer, S. A Holistic Overview of Underground Hydrogen Storage: Influencing Factors, Current Understanding, and Outlook. Fuel 2022, 330, 125636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikäheimo, J.; Lindroos, T.J.; Kiviluoma, J. Impact of Climate and Geological Storage Potential on Feasibility of Hydrogen Fuels. Appl. Energy 2023, 342, 121093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoodi, S.; Al-Shargabi, M.; Wood, D.A.; Longe, P.O.; Mehrad, M.; Rukavishnikov, V.S. Underground Hydrogen Storage: A Review of Technological Developments, Challenges, and Opportunities. Appl. Energy 2025, 381, 125172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, P.; Chen, Z.; Peng, X.; Zhu, S.; Liu, B.; Lei, X.; Di, C. Converting Underground Natural Gas Storage for Hydrogen: A Review of Advantages, Challenges and Economics. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2025, 213, 115438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oni, B.A.; Bade, S.O.; Sanni, S.E.; Orodu, O.D. Underground Hydrogen Storage in Salt Caverns: Recent Advances, Modeling Approaches, Barriers, and Future Outlook. J. Energy Storage 2025, 107, 114951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbadamosi, A.O.; Muhammed, N.S.; Patil, S.; Al Shehri, D.; Haq, B.; Epelle, E.I.; Mahmoud, M.; Kamal, M.S. Underground Hydrogen Storage: A Critical Assessment of Fluid-Fluid and Fluid-Rock Interactions. J. Energy Storage 2023, 72, 108473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Cook, P.; Robinson, S.; Anderson, C. Regulatory Challenges and Managing Public Perception in Planning a Geological Storage Pilot Project in Australia. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2007, 1, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderssohn, J.; Benndorf, J.; Busch, W.; Isaac, M.; Lohsträter, O.; Reitze, A.; Rudolph, T.; Spreckels, V.; Walter, D.; Wenzig, E.; et al. Radarinterferometrie (InSAR) Grundsätze zur Erfassung von Bodenbewegungen mithilfe der Radarinterferometrie. Markscheidewesen Sonderdruck 2025, 1, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searchable Table of Earth Observation Satellite Missions|CEOS Database. Available online: https://database.eohandbook.com/database/missiontable.aspx (accessed on 24 September 2024).
- Kropuenske, T.; Clauson, J.; Shaw, J.; Vrabel, J.; Ali, M.; Ranjitkar, B.; Rusten, T.; Anderson, C. Earth Observing Sensing Satellites Online Compendium: U.S. Geological Survey Digital Data. Available online: https://calval.cr.usgs.gov/apps/compendium (accessed on 23 July 2025).
- Ustin, S.L.; Middleton, E.M. Current and Near-Term Earth-Observing Environmental Satellites, Their Missions, Characteristics, Instruments, and Applications. Sensors 2024, 24, 3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-Scale Geospatial Analysis for Everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, T.-W.; Jo, S. Artificial Intelligence in Geoenergy: Bridging Petroleum Engineering and Future-Oriented Applications. J. Petrol. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2025, 15, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassalle, G.; Credoz, A.; Hédacq, R.; Fabre, S.; Dubucq, D.; Elger, A. Assessing Soil Contamination Due to Oil and Gas Production Using Vegetation Hyperspectral Reflectance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1756–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhou, K.; Zhou, S. Data Mining of the Best Spectral Indices for Geochemical Anomalies of Copper: A Study in the Northwestern Junggar Region, Xinjiang. J. Geochem. Explor. 2019, 204, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, R.; Rachdi, I.; Thiele, S.; Booysen, R.; Kirsch, M.; Lorenz, S.; Gloaguen, R.; Sebari, I. A Spectral and Spatial Comparison of Satellite-Based Hyperspectral Data for Geological Mapping. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Li, B.; Li, J.; Guo, B.; Feng, Q. Hyperspectral Remote Sensing for Soil Heavy Metal Inversion: Insights and Applications. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2025, 18, 2520474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massop, H.T.L.; Hessel, R.; van den Akker, J.J.H.; van Asselen, S.; Erkens, G.; Gerritsen, P.A.; Gerritsen, F.H.G.A. Monitoring Long-Term Peat Subsidence with Subsidence Platens in Zegveld, The Netherlands. Geoderma 2024, 450, 117039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishita, Y.; Hanssen, R.F. Temporal Decorrelation in L-, C-, and X-Band Satellite Radar Interferometry for Pasture on Drained Peat Soils. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
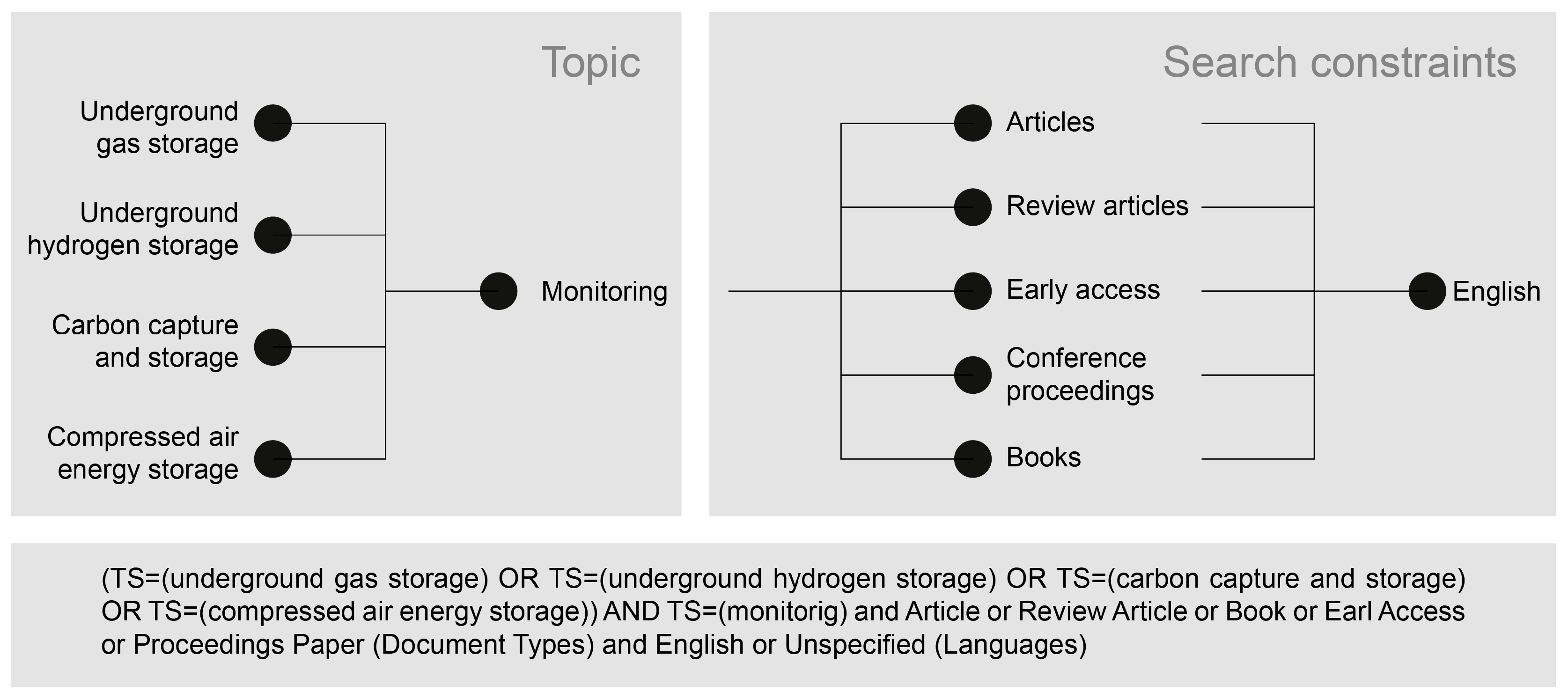
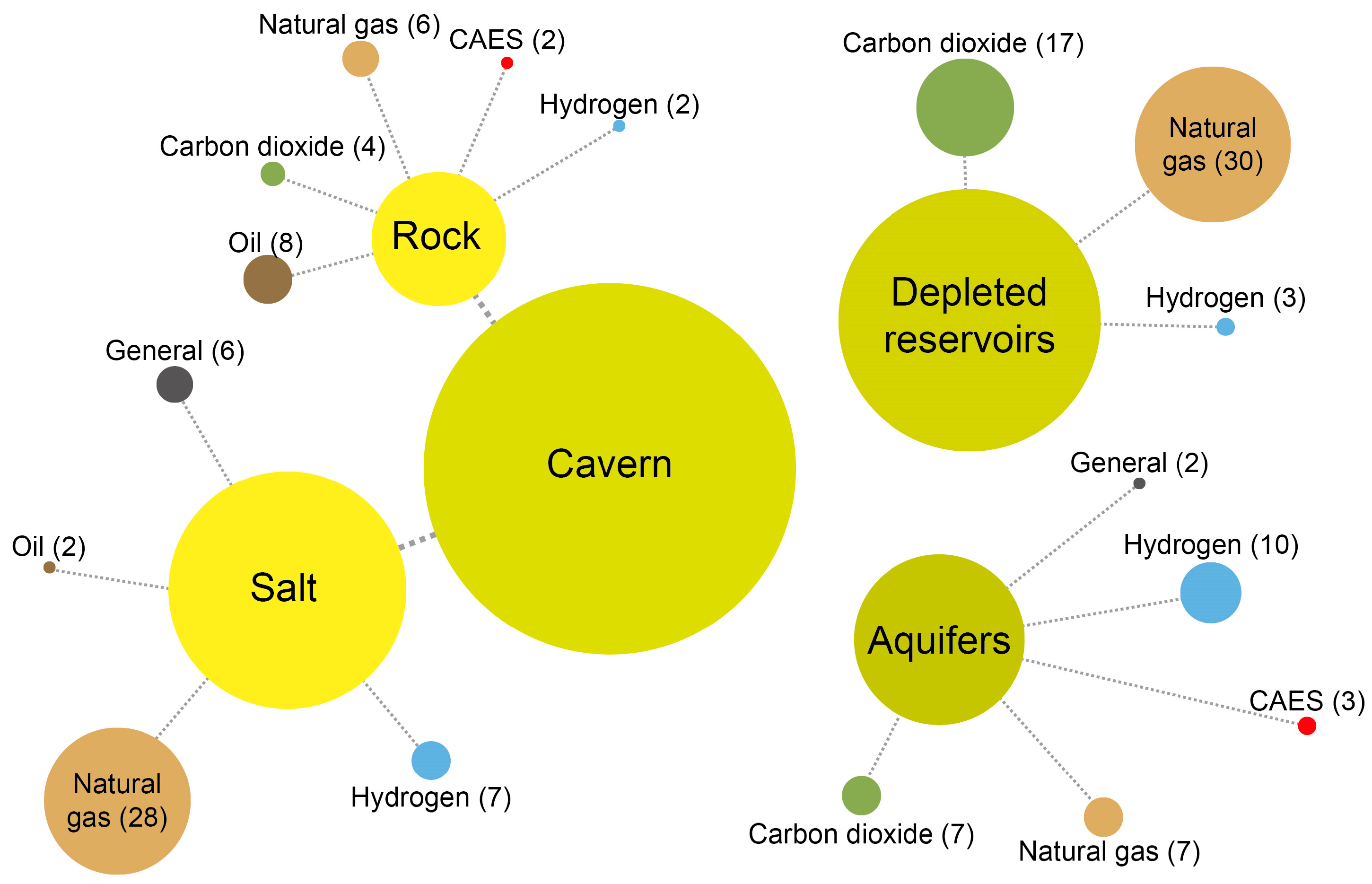
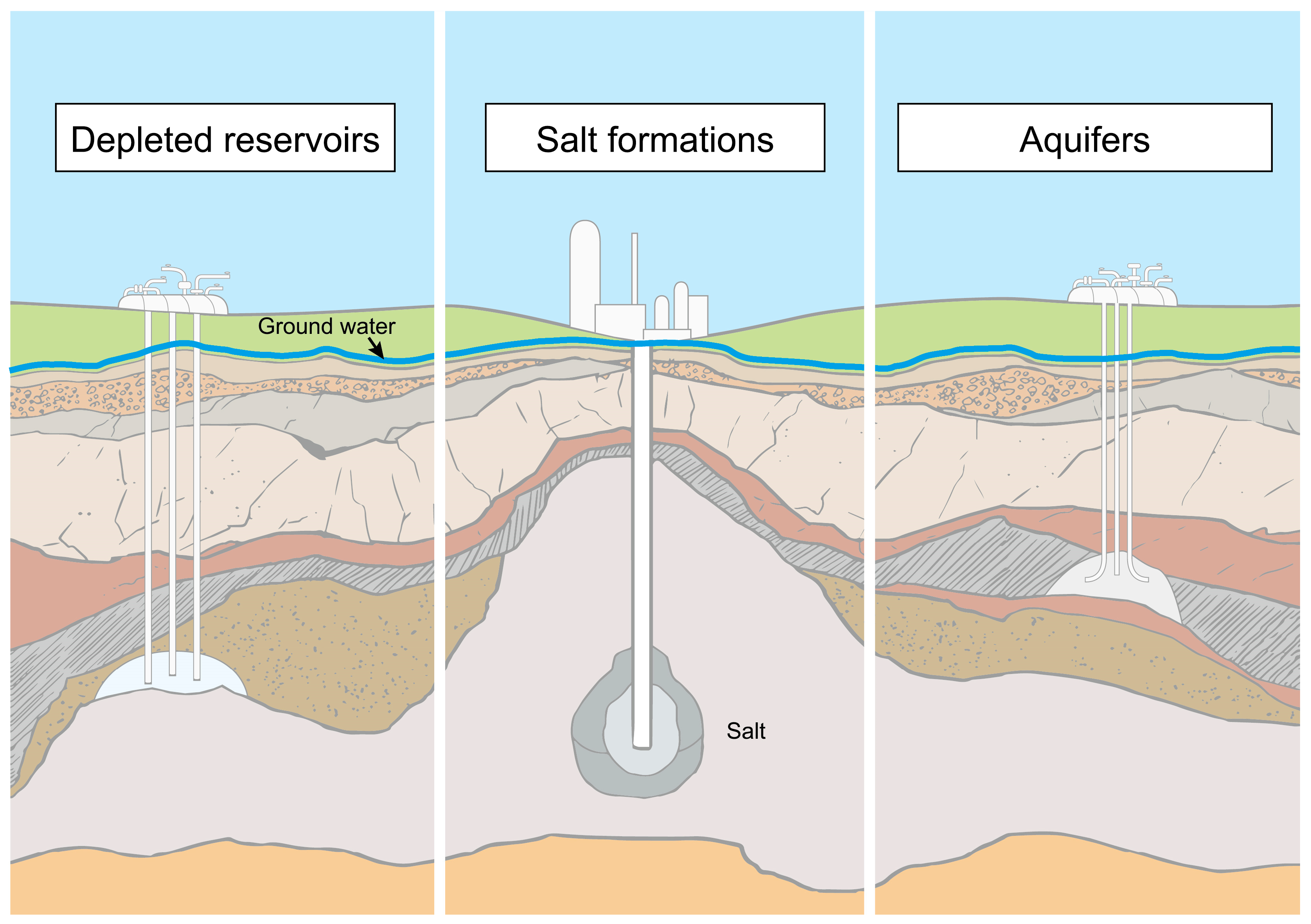





| Geological Type | Environmental Impacts | Stored Material * | Benefits and Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aquifer | Blowout | Hydrogen (H2), natural gas (NG) | + Working gas capacity greater than in cavern storage. + Natural ability to hold gas. − Risk of leakage through improperly sealed abandoned wells. − Reduced storage efficiency due to gas trapping. |
| Changes in the microbial community | Oxygen (O2) (in biomethane or carbon dioxide (CO2)), H2 | ||
| Mineral oxidation of surrounding rocks, chemical changes in rocks and gas, corrosion | |||
| Pollution of groundwater, soil and vegetation disturbance | CO2, NG | ||
| Seismic activity | |||
| Cavern | Blowout | H2, NG | + Ability to work at a high injection-withdrawal rate. + Salt provides long-term stability and safety. + Salt as a natural barrier prevents leakage. + Storage in reactive (e.g., basalt) allows mineral trapping of CO2 − Requires construction. − Lower volume than in the other types of storage. |
| Surface displacement—subsidence and cyclical movement | |||
| Mineral oxidation of surrounding rocks, chemical changes in rocks and gas, corrosion | |||
| Pollution of groundwater, soil and vegetation disturbance | CO2, NG | ||
| Seismic activity | |||
| Depleted reservoir | Blowout | H2, NG | + Greater volume compared to other types of storage. + Overlying impermeable rocks prevent leakage. − Risk of gas loss through pores. − Reduced storage efficiency due to gas trapping and escaping through pores. |
| Surface displacement—subsidence and cyclical movement | |||
| Mineral oxidation of surrounding rocks, chemical changes in rocks and gas, corrosion | |||
| Pollution of groundwater, soil and vegetation disturbance | CO2, NG | ||
| Seismic activity |
| Study Site | Geological Type | Stored Material | Methods | Satellite Mission | Geodetic Reference | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sulcis Coal Basin, Sardinia, Italy | Coal deposit | Carbon dioxide (CO2) | Persistent scatter interferometric synthetic aperture radar (PS-InSAR) | ERS-1/2 | Global Positioning System (GPS)—12 permanent stations | [47] |
| Tvrdonice, Czech Republic | Depleted reservoir | Natural gas (NG) | PS-InSAR | Sentinel-1 | GPS—39 permanent stations | [118] |
| Underground gas storage (UGS) sites in Czech Republic (7), UGS sites in Slovakia (3) | Depleted reservoir (9), aquifer (1) | NG | Stanford Method for Persistent Scatterers (StaMPS) | Sentinel-1 | - | [121] |
| Po Plain, Italy | Depleted gas reservoir | NG | PS-InSAR | Radarsat-1/2, Sentinel-1 | Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) station | [120] |
| PS-InSAR | Radarsat-1 | - | [163] | |||
| Small Baseline Subset InSAR (SBAS) | ERS-1/2, ENVISAT, Sentinel-1 | GNSS permanent station and seismic monitoring | [135] | |||
| SqueeSAR | Sentinel-1 | GNSS | [161] | |||
| Ketzin, Germany | Aquifer | CO2 | PS-InSAR, SBAS | TerraSAR-X | - | [157] |
| Krechba, Salah, Algieria | Depleted gas reservoir | CO2 | PS-InSAR | Envisat ASAR | - | [164,165,166] |
| Differential InSAR (D-InSAR) | Envisat ASAR | - | [167] | |||
| Pendleton, Oregon, USA | Aquifer | CO2 | SBAS | Radarsat-2 | GNSS and gravity measurements | [112] |
| Hutubi, China | Depleted gas reservoir | NG | SBAS, Point Target Analysis (IPTA-InSAR) | ALOS-1, Envisat ASAR, TerraSAR-X, TanDEM-X, Sentinel-1 | GNSS permanent stations | [146] |
| Shizhuang, Shanxi Province, China | Coal deposit | CO2 | SBAS | Sentinel-1 | GNSS Real Time Kinematic measurements, unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) 3D surface model | [142] |
| Groningen gas field, Norg UGS, the Netherlands | Depleted gas reservoir | NG | PS-InSAR | Radarsat-3, TerraSAR-X, Sentinel-1 | GNSS, optical levelling | [148] |
| XiangGuoSi, China | Depleted gas reservoir | NG | PS-InSAR, SBAS | Sentinel-1 | - | [160] |
| Lower Saxony, Germany | Depleted gas reservoir (1), aquifer (1), salt cavern (1) | NG | PS-InSAR from European Ground Motion Service (EGMS) | Sentinel-1 | - | [168] |
| Salt cavern (2) | NG | SqueeSAR | Sentinel-1 | [162] | ||
| Epe, Germany and the Netherlands | Salt cavern | NG | StaMPS | Sentinel-1 | - | [169] |
| Hatfield Moors, the Netherlands | Depleted gas reservoir | CO2 | PS-InSAR from EGMS | Sentinel-1 | - | [170] |
| Study Site | Stored Material | Platform | Instrument | Spectral Resolution | Method | Year Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zero Emissions Research and Technology (ZERT) field experiment, Bozeman, USA | Carbon dioxide (CO2) | Terrestrial | Multispectral imager MS3100 (Geospatial Systems Inc., West Henrietta, NY, USA) | Green (500–580 nm), red (630–710 nm), near-infrared (NIR) (735–865 nm) | Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) | 2010 [107] |
| Multispectral imager, PixeLink PL-B741U camera with CMOS sensor and Thorlabs FW102B filter (NAVITAR, Rochester, NY, USA) | Red (630–670 nm), NIR (780–820 nm) | NDVI, spectral reflectance in red and NIR, regression analysis | 2012 [175] | |||
| Hyperspectral imager (Resonon Inc., Bozeman, MT, USA) | 160 spectral bands with 3.21 nm channel width, visible—NIR (400–900 nm) | Spectral reflectance in red edge, random forest regression | 2009 [181] | |||
| Multispectral imager, PixeLink PL-B741U camera with CMOS sensor and Thorlabs FW102B Filter (NAVITAR, Rochester, NY, USA) | Red (630–670 nm), NIR (780–820 nm) | NDVI, linear regression analysis | 2014 [177] | |||
| FLIR photon 320 LWIR camera (Teledyne FLIR LLC, Wilsonville, OR, USA) | Long-wave infrared (LWIR) | Thermal brightness temperature, linear regression analysis | ||||
| ASD Field Spec Pro 350 (Malvern Panalytical, Almelo, the Netherlands; Malvern, UK) | 1512 spectral bands with sampling interval: 1.4 nm (350–1000 nm), 2 nm (1000–2500 nm) | Classification tree analysis | 2014 [182] | |||
| Aerial | Pika II hyperspectral imager (Resonon Inc., Bozeman, MT, USA) | 80 spectral bands with 6.3 nm channel width, visible—NIR (424–929 nm) | Red Edge Index (REI), unsupervised classification | 2013 [178] | ||
| Big Sky Carbon Sequestration Partnership (BSCSP), Montana, USA | CO2 | Aerial | Pika II hyperspectral imager (Resonon Inc., Bozeman, MT, USA) | 80 spectral bands with 6.3 nm channel width, visible—NIR (424–929 nm) | Unsupervised classification of spectral data, Median Absolute Deviation (MAD) | 2017 [183] |
| Aerial | Pika II hyperspectral imager (Resonon Inc., Bozeman, MT, USA) | 80 spectral bands with 6.3 nm channel width, visible—NIR (424–929 nm) | Stress indicator threshold values, classification of pixels based on stress indicators | 2017 [184] | ||
| Satellite | Landsat 8 Operational Land Imager (OLI) (Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corporation, Boulder, CO, USA) | 11 spectral bands (433–12,500 nm) | ||||
| RapidEye Earth-imaging System (REIS) (Jena-Optronik GmbH, Jena, Germany) | Blue (440–510 nm), green (510–590 nm), red (630–730 nm), red edge (690–730 nm), NIR (760–850 nm) | |||||
| CCS natural analogue site, Latera, Italy | CO2 | Aerial | Daedalus 1268 Airborne Thematic Mapper (ATM) (Daedalus Enterprises, Ann Arbor, MI, USA) | 11 spectral bands, visible, NIR, SWIR and TIR, spatial resolution 2.5 m | Ratio NIR/red, EVI, atmospheric resistant vegetation index (ARVI), red edge normalized difference, Vogelmann red edge index, red edge position index, Anthocyan reflectance index, NDVI, spectral signature analysis | 2008 [153] |
| CASI 2 (Itres Research Limited, Calgary, Alberta, Canada) | 15 spectral bands, visible and NIR, spatial resolution 2 m | |||||
| AISA Eagle 1K hyperspectral push broom scanning system (Specim, Oulu, Finland) | 63 spectral bands, visible—NIR (402.35–989.09 nm) | |||||
| Rollei 6008 db45 digital camera (Rollei, Braunschweig, Germany) | - | RGB orthoimage | ||||
| Aerial | AISA Eagle 1K hyperspectral push broom scanning system (Specim, Oulu, Finland) | 63 spectral bands, visible—NIR (402.35–989.09 nm) | Spectral reflectance in red and NIR, geostatistical and probabilistic analysis, ICA | 2011 [185] | ||
| Aerial | AISA Eagle 1K hyperspectral pushbroom scanning system (Specim, Oulu, Finland) | 63 spectral bands, visible—NIR (402.35–989.09 nm) | Spectral reflectance in red, NIR and SWIR, geostatistical and probabilistic analysis, fuzzy clustering | 2011 [180] | ||
| Satellite | Terra ASTER multispectral Instrument (Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI), Japan) | 14 spectral bands, visible, NIR, SWIR, thermal infrared (TIR) (520–11,650 nm) | ||||
| Field experiment, Daxing District, Beijing, China | Natural gas (NG) | Terrestrial | SVC HR-1024i spectrometer (Spectra Vista Corporation, Poughkeepsie, NY, USA) | 1024 spectral bands, channel width: 1.5 nm (350–1000 nm), 3.8 nm (1000–1890 nm), 2.5 nm (1890–2500 nm) | Spectral reflectance investigation using analysis of variance (ANOVA), Natural Gas Stress Index (NGSI) | 2020 [186] |
| Terrestrial (platform 5 m above ground) | SOC710-VP spectrometer (Surface Optics Corporation, San Diego, CA, USA) | 128 spectral channels, channel width: 4.69 nm (370–1045 nm) | Baseline Slope Index (BLSI) to identity stress, Otsu thresholding | 2025 [187] | ||
| Sutton Bonington Campus test field, Nottingham University, UK | CO2 | Terrestrial | ASD Fieldspec FR Spectroradiometer (Malvern Panalytical, Almelo, the Netherlands; Malvern, UK) | Channel width: 3 nm (350–1050 nm) with 1.4 nm sampling interval, 10–12 nm (1050–2500 nm) with 2 nm sampling interval | Statistical processing and analysis of spectral bands | 2016 [179] |
| First derivative of reflectance data | 2014 [188] | |||||
| 12 UGS sites, California, USA | Methane (CO4) | Aerial | AVIRIS-C (Jet Propulsion Laboratory, La Cañada Flintridge, CA, USA) | 224 spectral bands with 10 nm channel width (400–2500 nm) | Analysis of spectral reflectance in the range 2100–2500 nm | 2020 [95] |
| AVIRIS-NG (Jet Propulsion Laboratory, La Cañada Flintridge, CA, USA) | 425 spectral bands with 5 nm channel width (380–2510 nm) | |||||
| CO2- Enhanced Oil Recovery experimental area, Shandong Province, China | CO2 | Satellite | Pleiades High Resolution Imager (HiRI) (Thales Alenia Space (TAS-F), Cannes, France) | PAN (480–820 nm), blue (450–530 nm), green (510–590 nm), red (620–700 nm), NIR (775–915 nm) | Modified and adjusted NDWI | 2016 [189] |
| Geodesy | Remote Sensing | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measurement Method | Precise Levelling | GNSS, Total Station | UAV LiDAR & Photogrammetry | InSAR | Multispectral and Hyperspectral Imaging | |
| Observation | Vertical displacements | Horizontal and vertical displacements | Horizontal and vertical displacements | Horizontal and vertical displacements | Land surface changes | |
| Precision | Approx. ±1 mm | Approx. ±1.5 to 2 mm | Approx. ±20 mm vertically, ±40 mm horizontally | Approx. ±1 to 2 mm vertically and horizontally in the East–West direction | Depending on the sensor, ground pixel size varies from centimetres to tens of metres | |
| Verification | Not required | Not required | Not required | Comparison to geodetic measurements | In situ measurement, ground truth validation | |
| Measurement frequency | Low (usually on an annual basis) | Low (survey campaigns, on an annual basis) or high (permanent monitoring stations) | High (as requested) | High (every few days) | High (every few days) | |
| Data geometry | Point | Point | Point cloud/pixel | Pixel/point | Pixel/point | |
| Information | Absolute vertical displacements of benchmark points (height difference) | Absolute horizontal and vertical displacements (coordinate difference) | Digital surface/elevation/terrain model | Relative surface LoS displacements or translated to vertical and horizontal (W-E) components | Change in pixel value (reflectance in spectral bands) | |
| Cost | High | High | Medium | Low | Low | |
| Strengths | - Highest accuracy and precision - Reliable - Relatively easy processing that does not require large computing power - Information on absolute surface displacements | - Highest accuracy and precision - Reliable - Relatively easy processing that does not require large computing power - Information on absolute surface displacements | - Detailed information continuous in the space domain - Possibility to carry out measurements with high temporal frequency | - High accuracy in determining vertical displacements - High temporal coverage of data - Wide area coverage - Semi-continuous data coverage in the space domain - Independent of weather and illumination (day/night) | - Information on selected land surface characteristics - Versatile environmental applications | |
| Weaknesses | - Time-consuming - Limited to benchmark locations - Dependent on weather - Unstable reference points as source of errors | - Limited to survey points locations - Unstable reference points as source of errors | - Dependent on weather and illumination - Limited time of acquisition/single flight - Limited area coverage due to limited operational time - Processing of point clouds require large computing power and storage | - Processing requires large computing power and storage - Inability to derive horizontal displacements in the North–South direction - Reduced data coverage due to shadows in varied topography regions - Limited use in areas of vegetation, which is a course of low coherence and measurement quality | - Dependent on weather - Processing requires large computing power and storage | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaczmarek, A.; Blachowski, J. Remote Sensing Perspective on Monitoring and Predicting Underground Energy Sources Storage Environmental Impacts: Literature Review. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2628. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152628
Kaczmarek A, Blachowski J. Remote Sensing Perspective on Monitoring and Predicting Underground Energy Sources Storage Environmental Impacts: Literature Review. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(15):2628. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152628
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaczmarek, Aleksandra, and Jan Blachowski. 2025. "Remote Sensing Perspective on Monitoring and Predicting Underground Energy Sources Storage Environmental Impacts: Literature Review" Remote Sensing 17, no. 15: 2628. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152628
APA StyleKaczmarek, A., & Blachowski, J. (2025). Remote Sensing Perspective on Monitoring and Predicting Underground Energy Sources Storage Environmental Impacts: Literature Review. Remote Sensing, 17(15), 2628. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152628









