Distinct Regional and Seasonal Patterns of Atmospheric NH3 Observed from Satellite over East Asia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Satellite and Chemical Transport Model Data
2.1. IASI NH3
2.2. CAM-Chem
2.3. CAMS
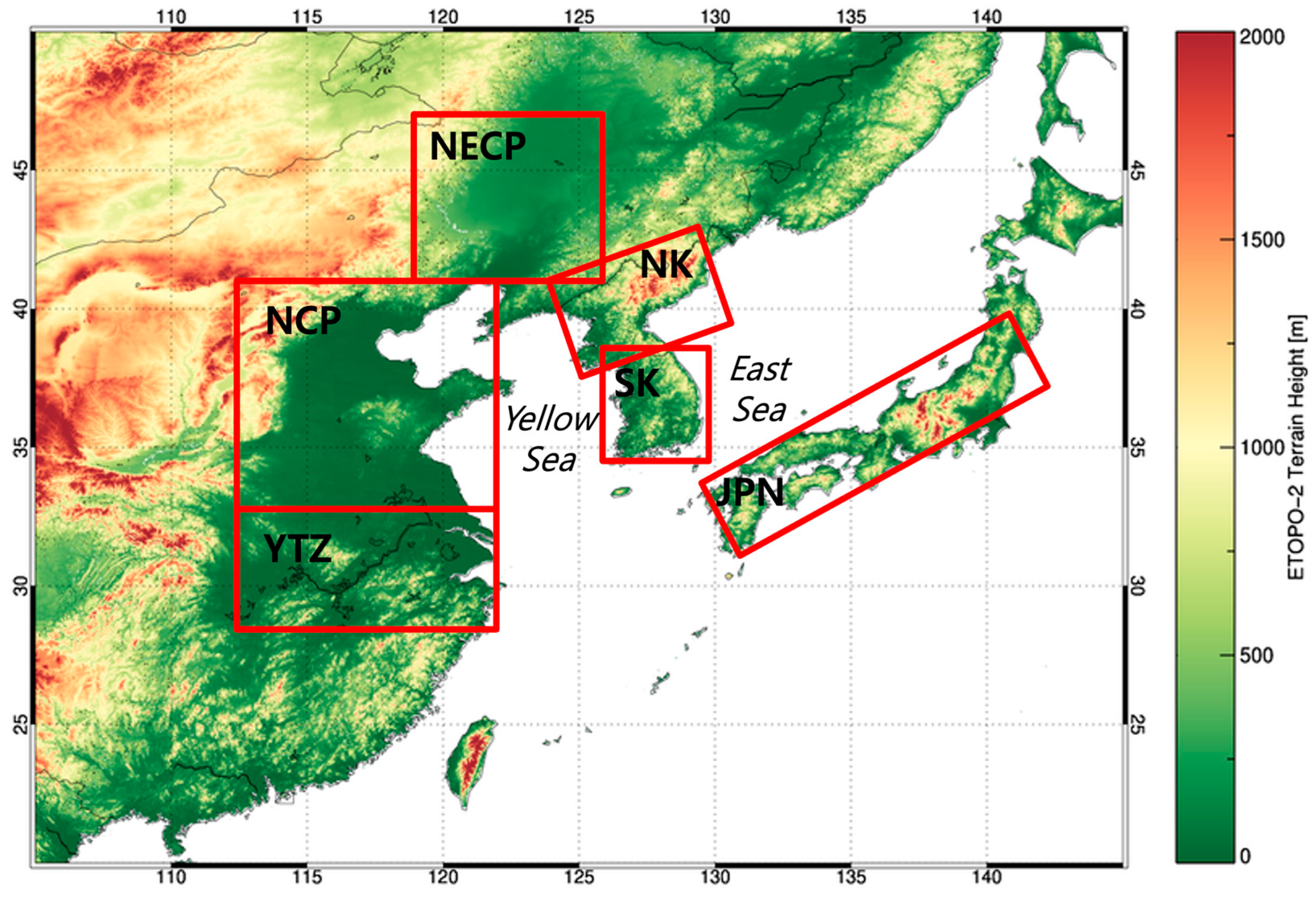
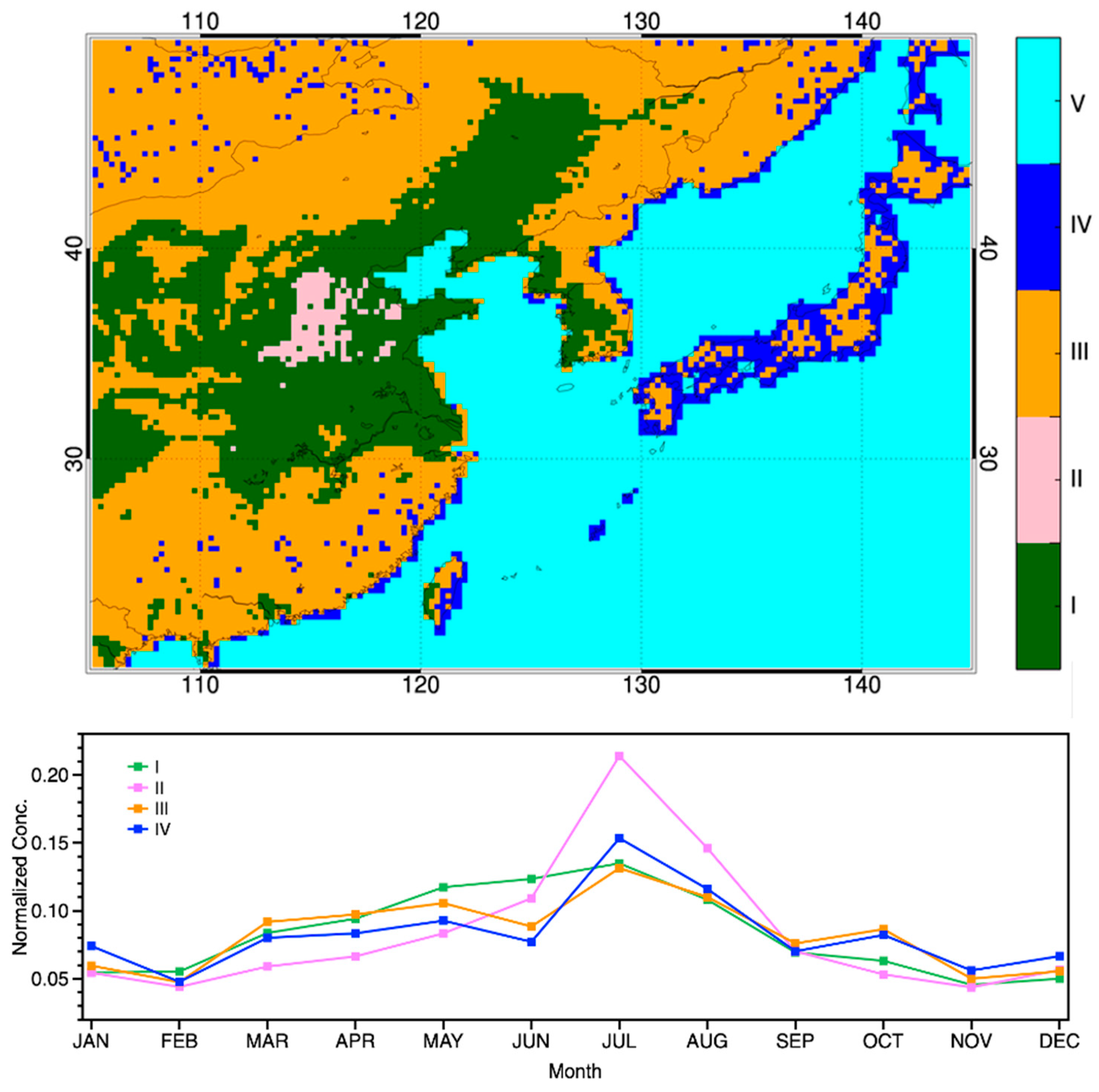
2.4. Region Selection
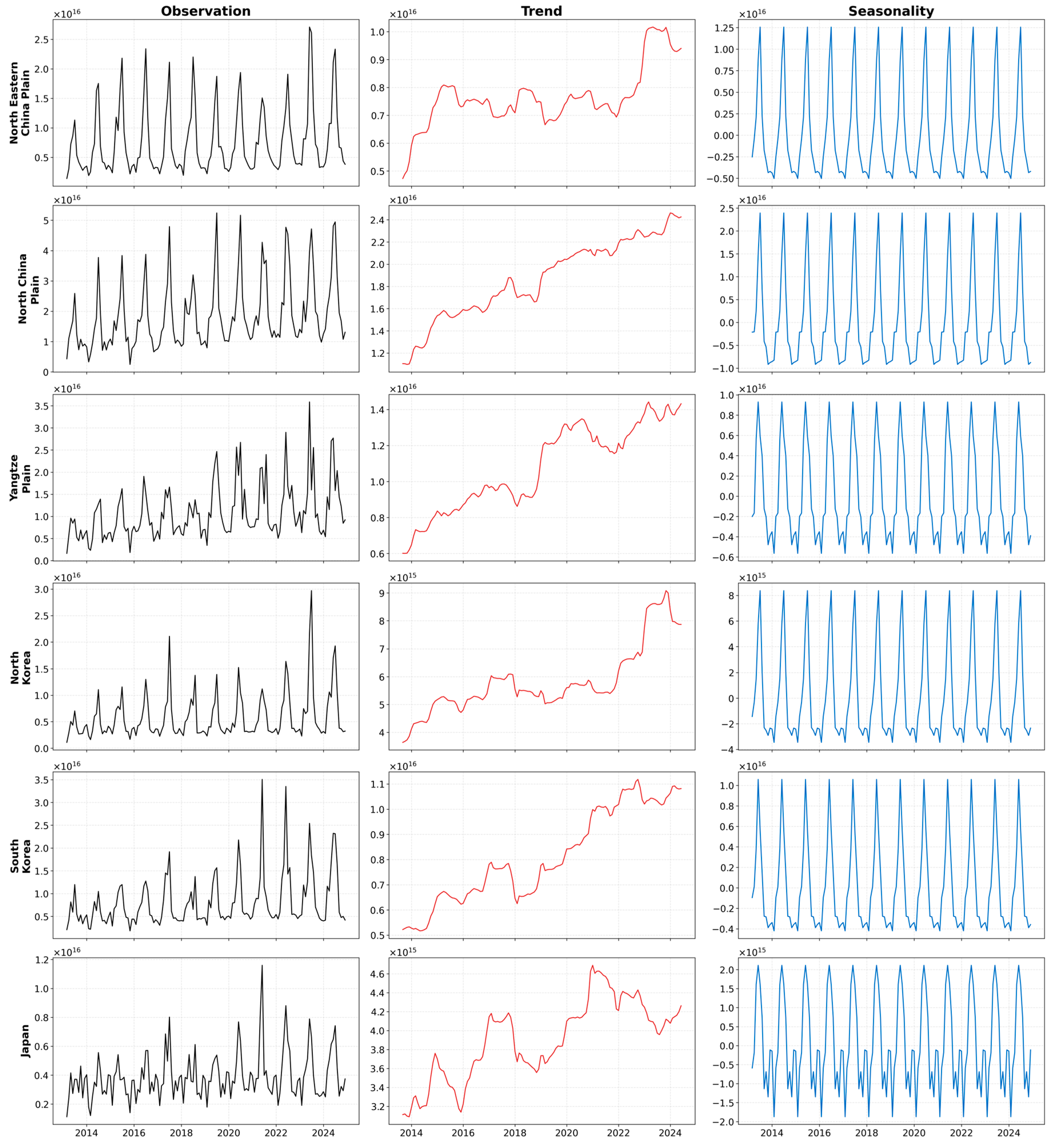
2.5. Time Series Decomposition Analysis
3. Results
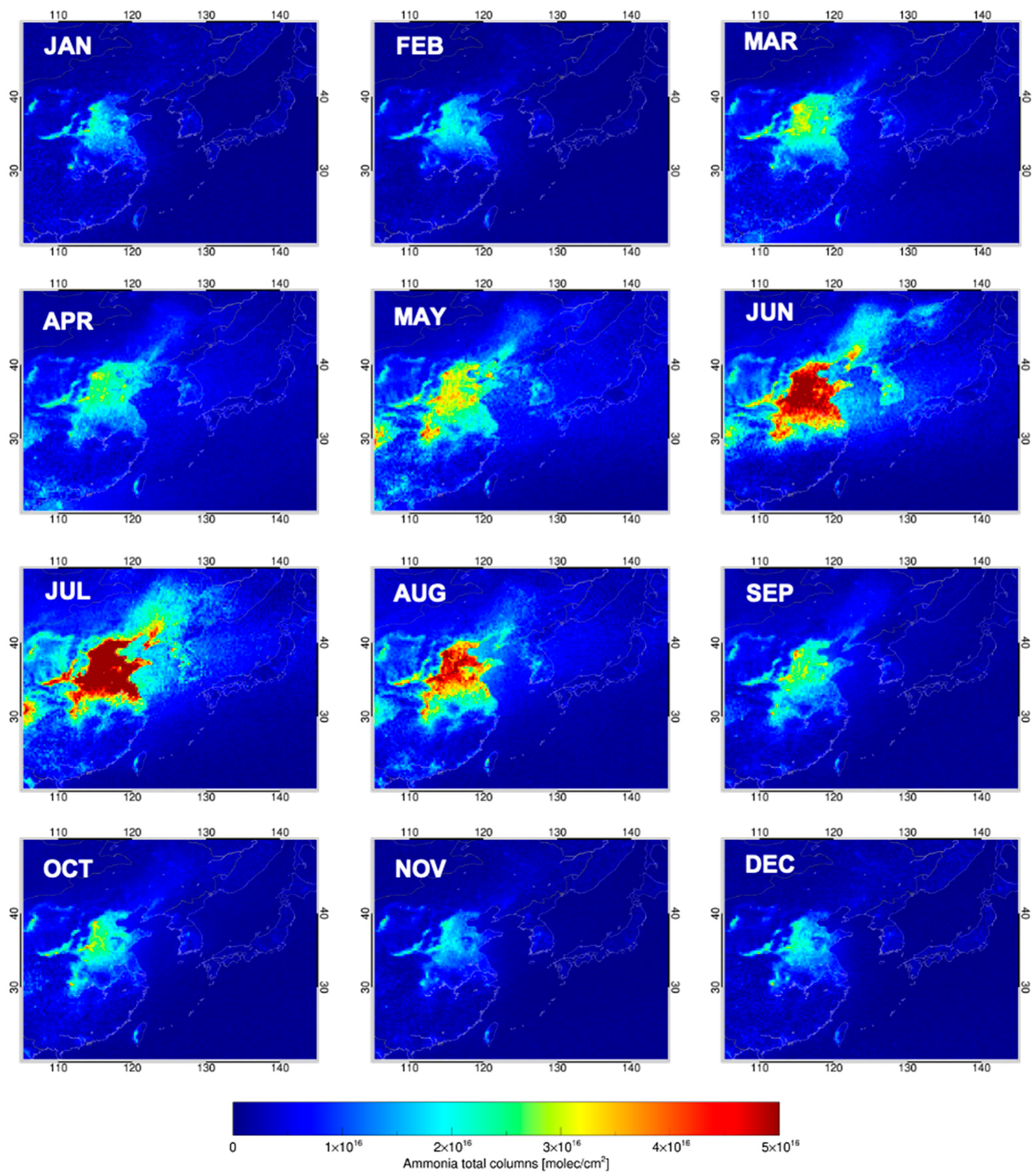
3.1. Spatiotemporal Distribution of NH3
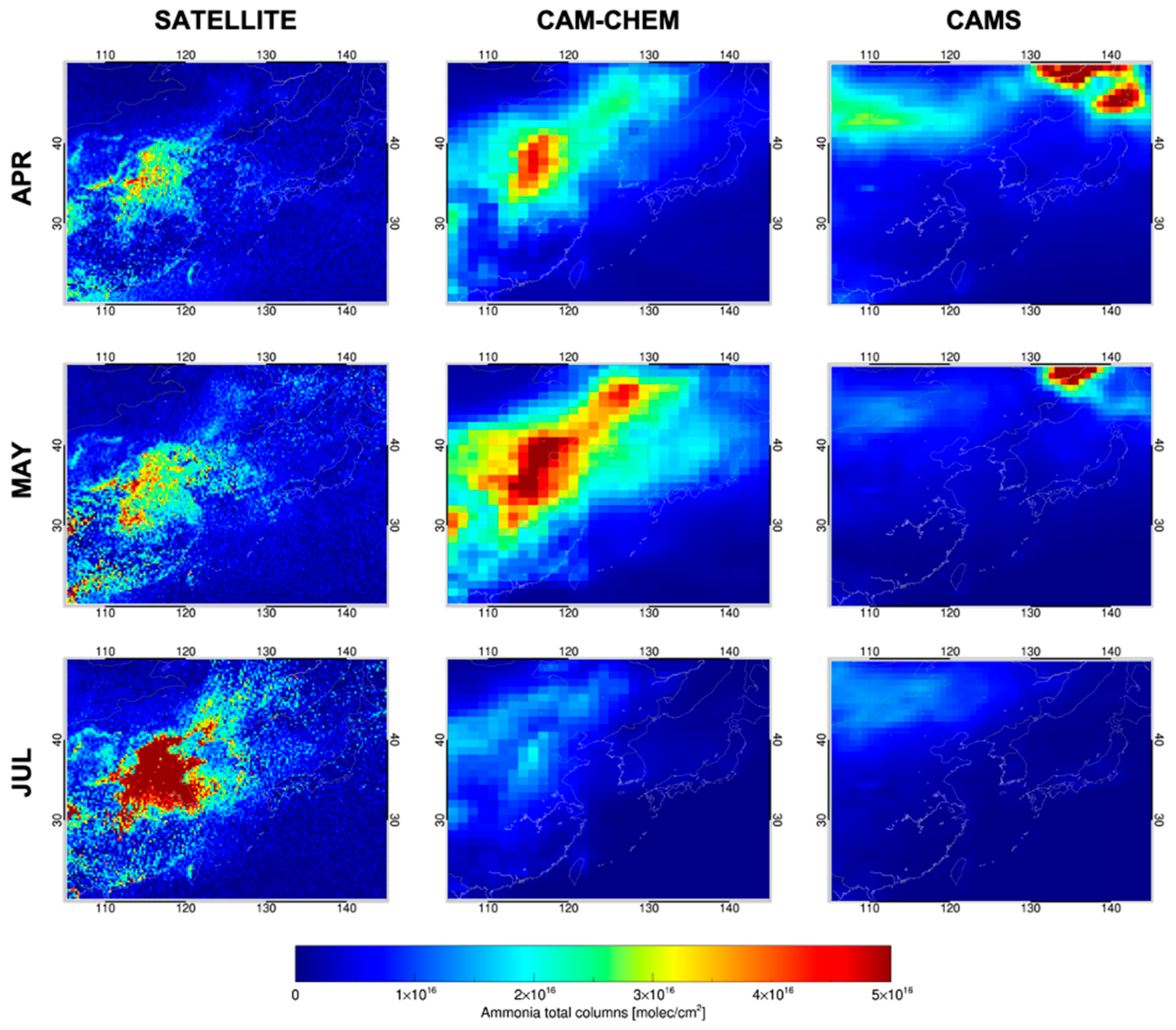
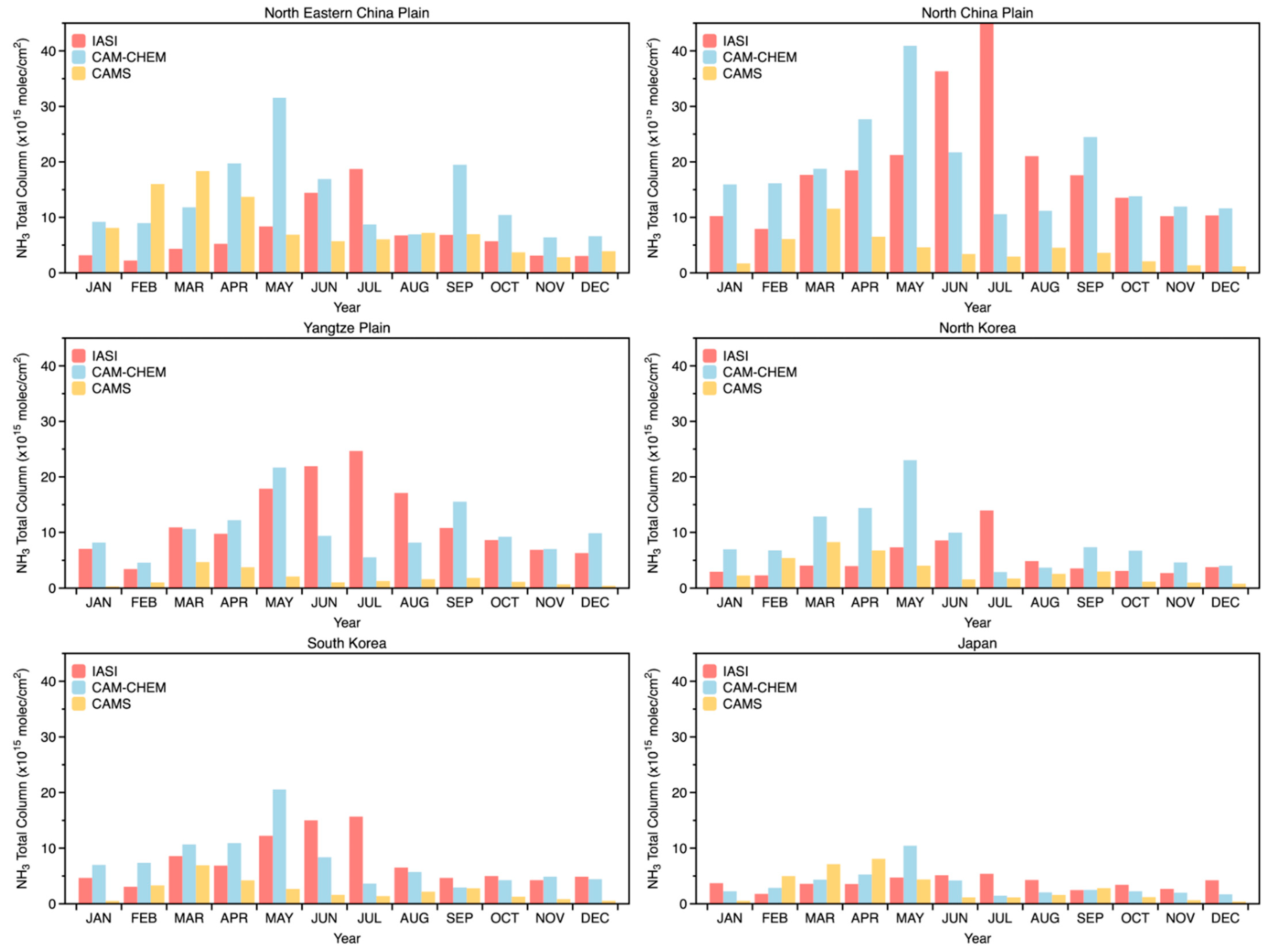
3.2. Comparison Between Satellite Observation and Global Chemical Transport Model
4. Discussion and Conclusions
4.1. Clear Evidence of Seasonal and Spatial Variability
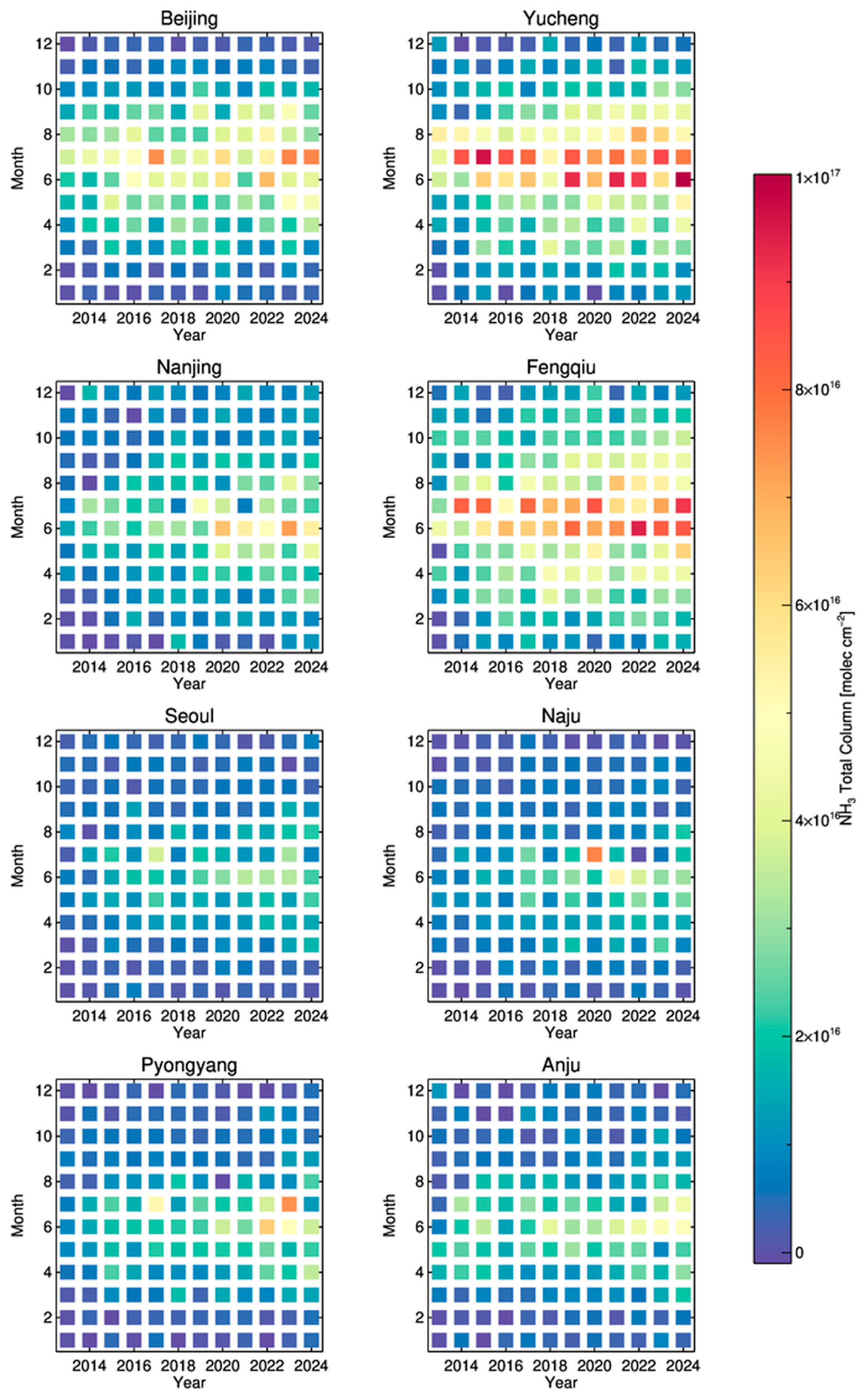
4.2. Transition of the Regional Temporal Trends
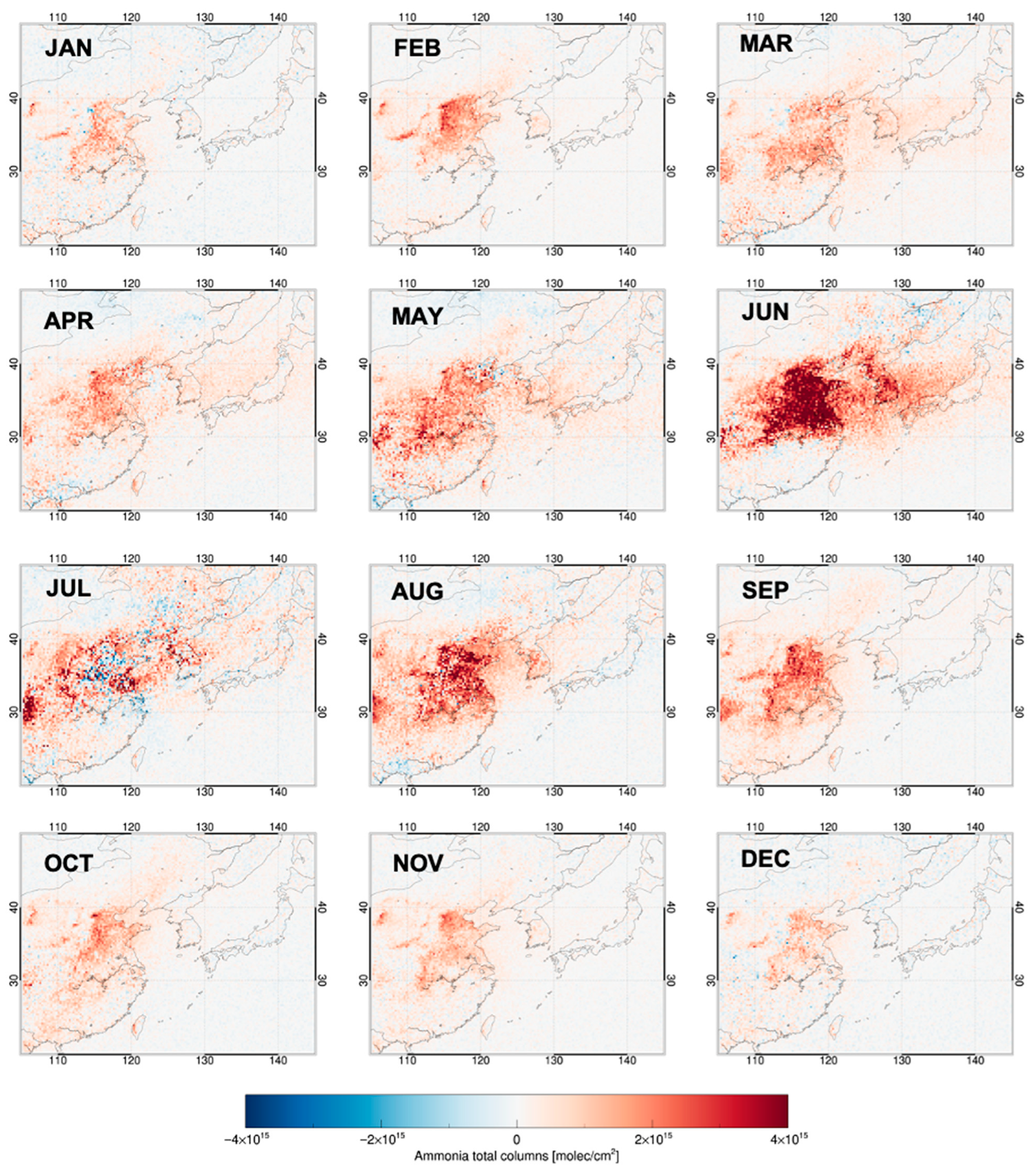
4.3. Spatiotemporal Discrepancies Between Satellite and Chemical Transport Models
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AOD | Aerosol Optical Depth |
| AIRS | Atmospheric Infrared Sounder |
| CAM | Community Atmosphere Model |
| CAMS | Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service |
| CAMSRA | CAMS ReAnalysis |
| CB05 | Carbon Bond 2005 chemistry scheme |
| CEDS | Community Emissions Data System |
| CESM | Community Earth System Model |
| CTMs | Chemical Transport Models |
| CV | Coefficient of Variation |
| ECMWF | European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts |
| EDGAR | Emission Database for Global Atmospheric Research |
| EUMETSAT | European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites |
| ETOPO | Earth Topography |
| FAO | Food and Agriculture Organization |
| FINN | Fire INventory for NCAR |
| GLOB-ANT | GLOBal ANThropogenic emissions |
| IASI | Infrared Atmospheric Sounding Interferometer |
| IFS | Integrated Forecast System |
| MAM4–VBS | Modal Aerosol Model with 4 modes—Volatility Basis Set |
| MEGAN | Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosols from Nature |
| MERRA2 | Modern-Era Retrospective analysis for Research and Applications, version 2 |
| MetOp | Meteorological Operational satellite |
| MOZART–T1 | Model for OZone And Related chemical Tracers–Tropospheric chemistry scheme |
| NCAR | National Center for Atmospheric Research |
| NH3 | Ammonia |
| NH4NO3 | Ammonium nitrate |
| (NH4)2SO4 | Ammonium sulfate |
| NOx | Nitrogen oxides |
| SO2 | Sulfur dioxide |
| QFED | Quick Fire Emissions Dataset |
| TM5 | Transport Model 5 |
| TOA | Top Of Atmosphere |
| ULB | Université Libre de Bruxelles |
References
- Behera, S.N.; Sharma, M.; Aneja, V.P.; Balasubramanian, R. Ammonia in the atmosphere: A review on emission sources, atmospheric chemistry and deposition on terrestrial bodies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 8092–8131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erisman, J.W.; Galloway, J.N.; Seitzinger, S.; Bleeker, A.; Dise, N.B.; Petrescu, A.M.R.; Leach, A.M.; de Vries, W. Consequences of human modification of the global nitrogen cycle. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 368, 20130116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, M.A.; Bleeker, A.; Howard, C.M.; Bekunda, M.; Grizzetti, B.; de Vries, W.; van Grinsven, H.J.M.; Abrol, Y.P.; Adhya, T.K.; Billen, G.; et al. Our Nutrient World: The Challenge to Produce More Food and Energy with Less Pollution; Centre for Ecology and Hydrology: Wallingford, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bouwman, A.F.; Lee, D.S.; Asman, W.A.H.; Dentener, F.J.; Van Der Hoek, K.W.; Olivier, J.G.J. A global high-resolution emission inventory for ammonia. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1997, 11, 561–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, M.A.; Reis, S.; Riddick, S.N.; Dragosits, U.; Nemitz, E.; Theobald, M.R.; Tang, Y.S.; Braban, C.F.; Vieno, M.; Dore, A.J.; et al. Towards a climate-dependent paradigm of ammonia emission and deposition. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 368, 20130166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, B.; Zhang, L.; Van Dingenen, R.; Vieno, M.; Van Grinsven, H.J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Ren, C.J.S. Abating ammonia is more cost-effective than nitrogen oxides for mitigating PM2.5 air pollution. Science 2021, 374, 758–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauglustaine, D.A.; Balkanski, Y.; Schulz, M.L. A global model simulation of present and future nitrate aerosols and their direct radiative forcing of climate. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 11031–11063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoenix, G.K.; Hicks, W.K.; Cinderby, S.; Kuylenstierna, J.C.I.; Stock, W.D.; Dentener, F.J. Atmospheric nitrogen deposition in world biodiversity hotspots: The need for a greater global perspective in assessing N deposition impacts. Glob. Change Biol. 2006, 12, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pye, H.O.T.; Liao, H.; Wu, S.; Mickley, L.J.; Jacob, D.J.; Henze, D.K.; Seinfeld, J.H. Effect of changes in climate and emissions on future sulfate-nitrate-ammonium aerosol levels in the United States. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, D01205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Wong, A.Y.H.; Xu, W.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Mi, H.; Lu, X.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Z.; et al. Estimating global surface ammonia concentrations inferred from satellite retrievals. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 12051–12066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, W.; Chen, Y.; Qian, Z.; Chen, J.; Tong, J.; Li, L.; Yue, Y.; Chen, K.; Chu, Z.; et al. NH3 Emissions and Lifetime Estimated by Satellite Observations with Differential Evolution Algorithm. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, J.X.; Wei, Z.; Strow, L.L.; Dickerson, R.R.; Nowak, J.B. The global tropospheric ammonia distribution as seen in the 13-year AIRS measurement record. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 5467–5479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Damme, M.; Clarisse, L.; Heald, C.L.; Hurtmans, D.; Ngadi, Y.; Clerbaux, C.; Dolman, A.J.; Erisman, J.W.; Coheur, P.F. Global distributions, time series and error characterization of atmospheric ammonia (NH3) from IASI satellite observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 2905–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Damme, M.; Wichink Kruit, R.J.; Schaap, M.; Clarisse, L.; Clerbaux, C.; Coheur, P.F. Evaluating 4 years of atmospheric ammonia (NH3) over Europe using IASI satellite observations and LOTOS-EUROS model results. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 9549–9566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Damme, M.; Clarisse, L.; Dammers, E.; Liu, X.; Nowak, J.B.; Clerbaux, C.; Flechard, C.R.; Galy-Lacaux, C.; Xu, W.; Neuman, J.A.; et al. Towards validation of ammonia (NH3) measurements from the IASI satellite. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 1575–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, J.X.; Dickerson, R.R.; Wei, Z.; Strow, L.L.; Wang, Y.; Liang, Q. Increased atmospheric ammonia over the world’s major agricultural areas detected from space. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 2875–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, A.A.; Yu, F.; Luo, G. Spatioseasonal variations of atmospheric ammonia concentrations over the United States: Comprehensive model-observation comparison. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 6571–6582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Damme, M.; Clarisse, L.; Whitburn, S.; Hadji-Lazaro, J.; Hurtmans, D.; Clerbaux, C.; Coheur, P.F. Industrial and agricultural ammonia point sources exposed. Nature 2018, 564, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiferl, L.D.; Heald, C.L.; Damme, M.V.; Clarisse, L.; Clerbaux, C.; Coheur, P.-F.; Nowak, J.B.; Andrew Neuman, J.; Herndon, S.C.; Roscioli, J.R.; et al. Interannual variability of ammonia concentrations over the United States: Sources and implications. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 12305–12328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tran, D.A.; Van Nguyen, D.; Sato, H.; Eto, Y.; Aikawa, M. Concentration characteristics and wavelet analysis of ambient NH3 in Kitakyushu, Japan over the period of 2018–2022. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2025, 236, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Deng, Z.; Robert, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Qi, C.; Wang, P.; De Mazière, M. The first global map of atmospheric ammonia (NH3) as observed by the HIRAS/FY-3D satellite. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2024, 41, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Shi, H.; Zhu, Y.; Li, R.; Wang, S.; Lu, N.; Yao, Y.; Bian, Z.; Huang, K. The evolution of global surface ammonia concentrations during 2001–2019: Magnitudes, patterns, and drivers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 5066–5079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silveira, B.B.; Fourrié, N.; Guidard, V.; Chambon, P.; Mahfouf, J.-F.; Brousseau, P.; Moll, P.; August, T.; Hultberg, T. Preliminary Assessment of MetOp-Based Temperature and Humidity Statistical Retrievals within the 3D-Var AROME-France Prediction System. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2022, 150, 733–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Fera, S.; Fabiano, F.; Raspollini, P.; Ridolfi, M.; Cortesi, U.; Barbara, F.; von Hardenberg, J. On the use of Infrared Atmospheric Sounding Interferometer (IASI) spectrally resolved radiances to test the EC-Earth climate model (v3.3.3) in clear-sky conditions. Geosci. Model Dev. 2023, 16, 1379–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarisse, L.; Franco, B.; Van Damme, M.; Di Gioacchino, T.; Hadji-Lazaro, J.; Whitburn, S.; Noppen, L.; Hurtmans, D.; Clerbaux, C.; Coheur, P. The IASI NH3 version 4 product: Averaging kernels and improved consistency. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2023, 16, 5009–5028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarisse, L.; Shephard, M.W.; Dentener, F.; Hurtmans, D.; Cady-Pereira, K.; Karagulian, F. Satellite monitoring of ammonia: A case study of the San Joaquin Valley. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D13302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Guo, X.; Pan, D.; Kelly, J.T.; Bash, J.O.; Sun, K. Monthly patterns of ammonia over the contiguous United States at 2-km resolution. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2020GL090579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Van Damme, M.; Coheur, P.F.; Clarisse, L. Estimating global ammonia (NH3) emissions based on IASI observations from 2008 to 2018. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 10375–10388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamarque, J.-F.; Emmons, L.K.; Hess, P.G.; Kinnison, D.E.; Tilmes, S.; Vitt, F.; Heald, C.L.; Holland, E.A.; Lauritzen, P.H.; Neu, J.; et al. CAM-chem: Description and evaluation of interactive atmospheric chemistry in the Community Earth System Model. Geosci. Model Dev. 2012, 5, 369–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchholz, R.R.; Emmons, L.K.; Tilmes, S.; The CESM2 Development Team. CESM2.1/CAM-chem Instantaneous Output for Boundary Conditions. UCAR/NCAR—Atmospheric Chemistry Observations and Modeling Laboratory 2019, Subset Used Lat: 10 to 80, Lon: 60 to 240, January 2013–December 2021. Available online: https://wiki.ucar.edu/spaces/camchem/pages/372834733/CESM2.1+CAM-chem+as+Boundary+Conditions (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- Emmons, L.K.; Schwantes, R.H.; Orlando, J.J.; Tyndall, G.; Kinnison, D.; Lamarque, J.-F.; Marsh, D.; Mills, M.J.; Tilmes, S.; Bardeen, C.; et al. The chemistry mechanism in the community earth system model version 2 (CESM2). J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2020, 12, e2019MS001882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ma, P.-L.; Wang, H.; Tilmes, S.; Singh, B.; Easter, R.C.; Ghan, S.J.; Rasch, P.J. Description and evaluation of a new four-mode version of the Modal Aerosol Module (MAM4) within version 5.3 of the Community Atmosphere Model. Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 505–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilmes, S.; Hodzic, A.; Emmons, L.K.; Mills, M.J.; Gettelman, A.; Kinnison, D.E.; Park, M.; Lamarque, J.-F.; Vitt, F.; Shrivastava, M.; et al. Climate forcing and trends of organic aerosols in the Community Earth System Model (CESM2). J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2019, 11, 4323–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crippa, M.; Guizzardi, D.; Muntean, M.; Schaaf, E.; Dentener, F.; van Aardenne, J.A.; Monni, S.; Doering, U.; Olivier, J.G.J.; Pagliari, V.; et al. Gridded emissions of air pollutants for the period 1970–2012 within EDGAR v4.3.2. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2018, 10, 1987–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoesly, R.M.; Smith, S.J.; Feng, L.; Klimont, Z.; Janssens-Maenhout, G.; Pitkanen, T.; Seibert, J.J.; Vu, L.; Andres, R.J.; Bolt, R.M.; et al. Historical (1750–2014) anthropogenic emissions of reactive gases and aerosols from the Community Emissions Data System (CEDS). Geosci. Model Dev. 2018, 11, 369–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenther, A.B.; Karl, T.; Harley, P.; Wiedinmyer, C.; Palmer, P.I.; Geron, C. Estimates of global terrestrial isoprene emissions using MEGAN (Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosols from Nature). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 3181–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenther, A.B.; Jiang, X.; Heald, C.L.; Sakulyanontvittaya, T.; Duhl, T.; Emmons, L.K.; Wang, X. The Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosols from Nature version 2.1(MEGAN2.1): An extended and updated framework for modeling biogenic emissions. Geosci. Model Dev. 2012, 5, 1471–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedinmyer, C.; Akagi, S.K.; Yokelson, R.J.; Emmons, L.K.; Al-Saadi, J.A.; Orlando, J.J.; Soja, A.J. The Fire INventory from NCAR (FINN): A high resolution global model to estimate the emissions from open burning. Geosci. Model Dev. 2011, 4, 625–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inness, A.; Ades, M.; Agustí-Panareda, A.; Barré, J.; Benedictow, A.; Blechschmidt, A.-M.; Dominguez, J.J.; Engelen, R.; Eskes, H.; Flemming, J.; et al. The CAMS reanalysis of atmospheric composition. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 3515–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarwood, G.; Rao, S.; Yocke, M.; Whitten, G. Updates to the Carbon Bond Chemical Mechanism: CB05. Final Report to the US EPA; EPA Report Number: RT-0400675; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2005.
- Huijnen, V.; Williams, J.; van Weele, M.; van Noije, T.; Krol, M.; Dentener, F.; Segers, A.; Houweling, S.; Peters, W.; de Laat, J.; et al. The global chemistry transport model TM5: Description and evaluation of the tropospheric chemistry version 3.0. Geosci. Model Dev. 2010, 3, 445–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granier, C.; Bessagnet, B.; Bond, T.; D’Angiola, A.; Denier van der Gon, H.; Frost, G.J.; Heil, A.; Kaiser, J.W.; Kinne, S.; Klimont, Z.; et al. Evolution of anthropogenic and biomass burning emissions of air pollutants at global and regional scales during the 1980–2010 period. Clim. Change 2011, 109, 163–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindelarova, K.; Granier, C.; Bouarar, I.; Guenther, A.; Tilmes, S.; Stavrakou, T.; Müller, J.-F.; Kuhn, U.; Stefani, P.; Knorr, W. Global data set of biogenic VOC emissions calculated by the MEGAN model over the last 30 year. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 9317–9341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, J.W.; Heil, A.; Andreae, M.O.; Benedetti, A.; Chubarova, N.; Jones, L.; Morcrette, J.-J.; Razinger, M.; Schultz, M.G.; Suttie, M.; et al. Biomass burning emissions estimated with a global fire assimilation system based on observed fire radiative power. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 527–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, M.; Nicolas, G.; Cinardi, G.; Boeckel, T.P.V.; Vanwambeke, S.O.; Wint, G.R.W.; Robinson, T.P. Global distribution data for cattle, buffaloes, horses, sheep, goats, pigs, chickens and ducks in 2010. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otte, J.; Pica-Ciamarra, U.; Morzaria, S. A comparative overview of the livestock-environment interactions in Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaveri, R.A.; Easter, R.C.; Singh, B.; Wang, H.; Lu, Z.; Tilmes, S.; Emmons, L.K.; Vitt, F.; Zhang, R.; Liu, X.; et al. Development and evaluation of chemistry-aerosol-climate model CAM5-Chem-MAM7-MOSAIC: Global atmospheric distribution and radiative effects of nitrate aerosol. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2021, 13, e2020MS002346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Henze, D.K.; Zhu, L.; Song, Y.; Paulot, F.; Liu, X.; Pan, Y.; Lin, Y.; et al. Agricultural ammonia emissions in China: Reconciling bottom-up and top-down estimates. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 339–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Damme, M.; Clarisse, L.; Franco, B.; Sutton, M.A.; Erisman, J.W.; Kruit, R.W.; Van Zanten, M.; Whitburn, S.; Hadji-Lazaro, J.; Hurtmans, D. Global, Regional and National Trends of Atmospheric Ammonia Derived from a Decadal (2008–2018) Satellite Record. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 055017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, S.-Y.; Hong, S.-W.; Na, R.; Oh, Y. Spatio-temporal change analysis of ammonia emission estimation for fertilizer application cropland using high-resolution farmland data. J. Korean Soc. Rural. Plan. 2021, 27, 33–41. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, R.T.; Pan, S.F.; Chen, J.; Chen, G.S.; Yang, J.; Dangal, S.R.S.; Shepard, J.P.; Tian, H.Q. Half-century ammonia emissions from agricultural systems in southern Asia: Magnitude, spatiotemporal patterns, and implications for human health. Geohealth 2018, 2, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Cheng, M.; Krol, M.; de Vries, W.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhang, F.; Xu, W. Trends in anthropogenic ammonia emissions in China since 1980: A review of approaches and estimations. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1133753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuttippurath, J.; Patel, V.K.; Kashyap, R.; Singh, A.; Clerbaux, C. Anomalous increase in global atmospheric ammonia during COVID-19 lockdown: Need policies to curb agricultural emissions. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 434, 140424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momeni, M.; Choi, Y.; Yeganeh, A.K.; Pouyaei, A.; Jung, J.; Park, J.; Shephard, M.W.; Dammers, E.; Cady-Pereira, K.E. Constraining East Asia ammonia emissions through satellite observations and iterative Finite Difference Mass Balance (iFDMB) and investigating its impact on inorganic fine particulate matter. Environ. Int. 2024, 184, 108473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawar, P.V.; Ghude, S.D.; Jena, C.; Móring, A.; Sutton, M.A.; Kulkarni, S.; Lal, D.M.; Surendran, D.; Van Damme, M.; Clarisse, L. Analysis of Atmospheric Ammonia over South and East Asia Based on the MOZART-4 Model and Its Comparison with Satellite and Surface Observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 6389–6409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, H.; Park, M.E.; Bae, J.-H. Distinct Regional and Seasonal Patterns of Atmospheric NH3 Observed from Satellite over East Asia. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2587. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152587
Choi H, Park ME, Bae J-H. Distinct Regional and Seasonal Patterns of Atmospheric NH3 Observed from Satellite over East Asia. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(15):2587. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152587
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Haklim, Mi Eun Park, and Jeong-Ho Bae. 2025. "Distinct Regional and Seasonal Patterns of Atmospheric NH3 Observed from Satellite over East Asia" Remote Sensing 17, no. 15: 2587. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152587
APA StyleChoi, H., Park, M. E., & Bae, J.-H. (2025). Distinct Regional and Seasonal Patterns of Atmospheric NH3 Observed from Satellite over East Asia. Remote Sensing, 17(15), 2587. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152587







