Elevation-Aware Domain Adaptation for Sematic Segmentation of Aerial Images
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose EADA, a novel cross-domain adaptation framework that co-jointly performs monoscopic elevation estimation and semantic segmentation for aerial imagery. By leveraging digital surface models (DSMs)—intermediate products of orthorectification pipelines—as auxiliary data, EADA exploits correlated feature representations between elevation and semantics to significantly enhance primary task performance while generating high-precision DSMs for downstream applications.
- The model incorporates a shared backbone network for efficient feature transfer, augmented by a task–feature correlation module. This module distills cross-task dependencies through spatial attention mechanisms, dynamically reinforcing mutually beneficial features while suppressing task-specific noise.
- EADA achieves state-of-the-art adaptation performance on Potsdam and Vaihingen benchmarks, surpassing the success of both single-stage and multi-stage methods. The architecture demonstrates strong extensibility, readily integrating with existing UDA methods to enhance deployability in real-world scenarios.
2. Methods
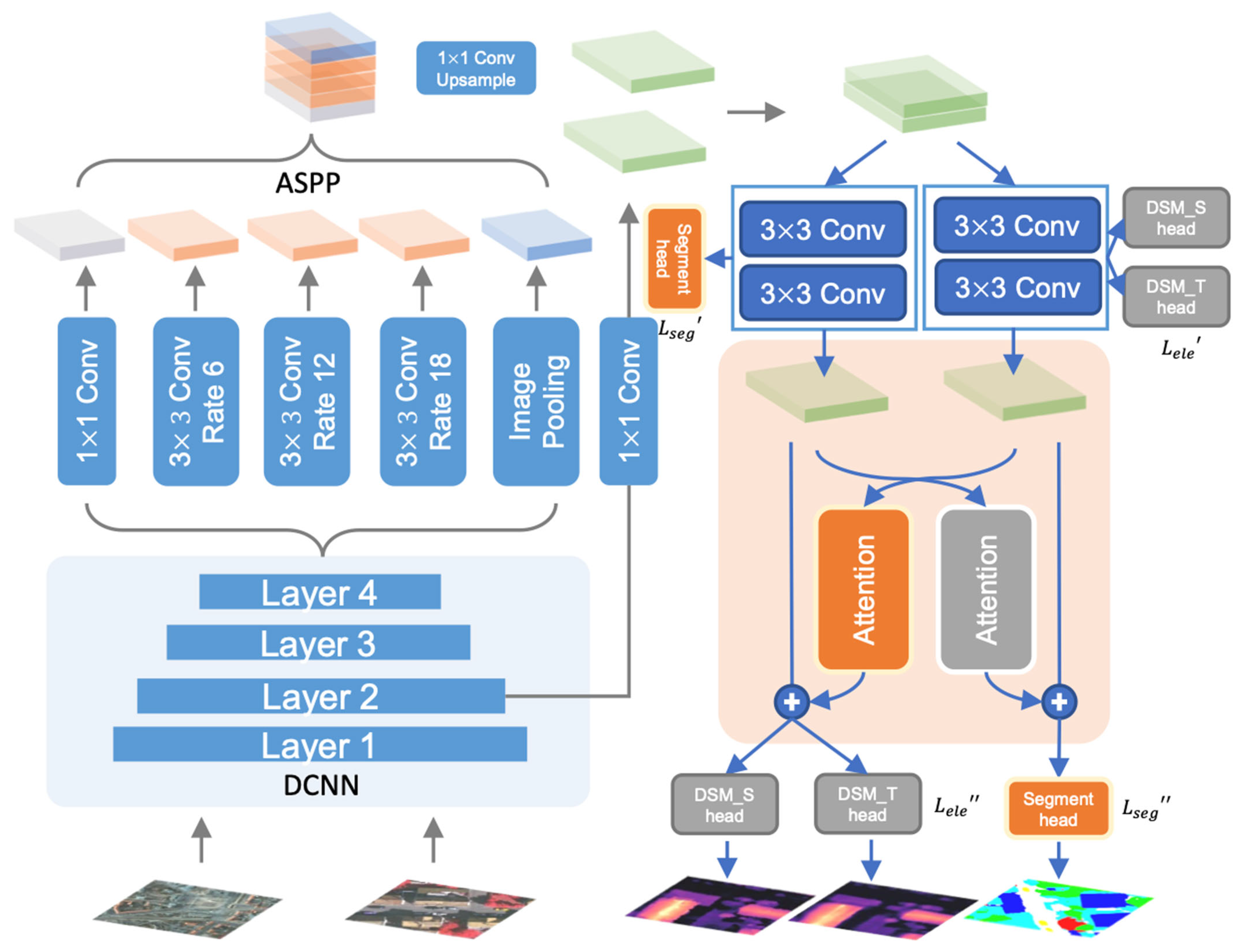
2.1. Overview
2.2. Initial Prediction Module
2.3. Task Feature Correlation Module
2.4. Objective Function Optimization
3. Experiments
3.1. Datasets
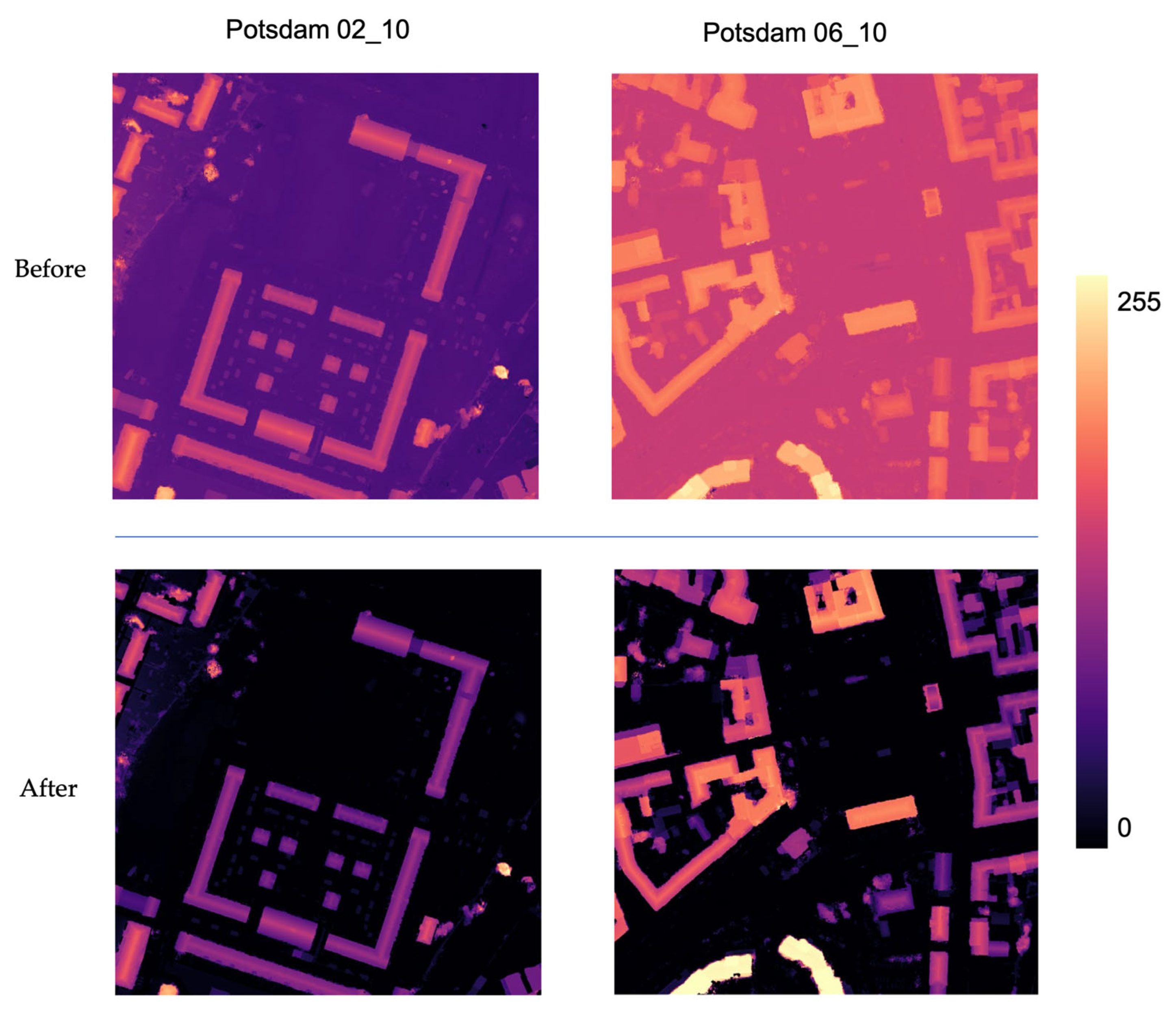
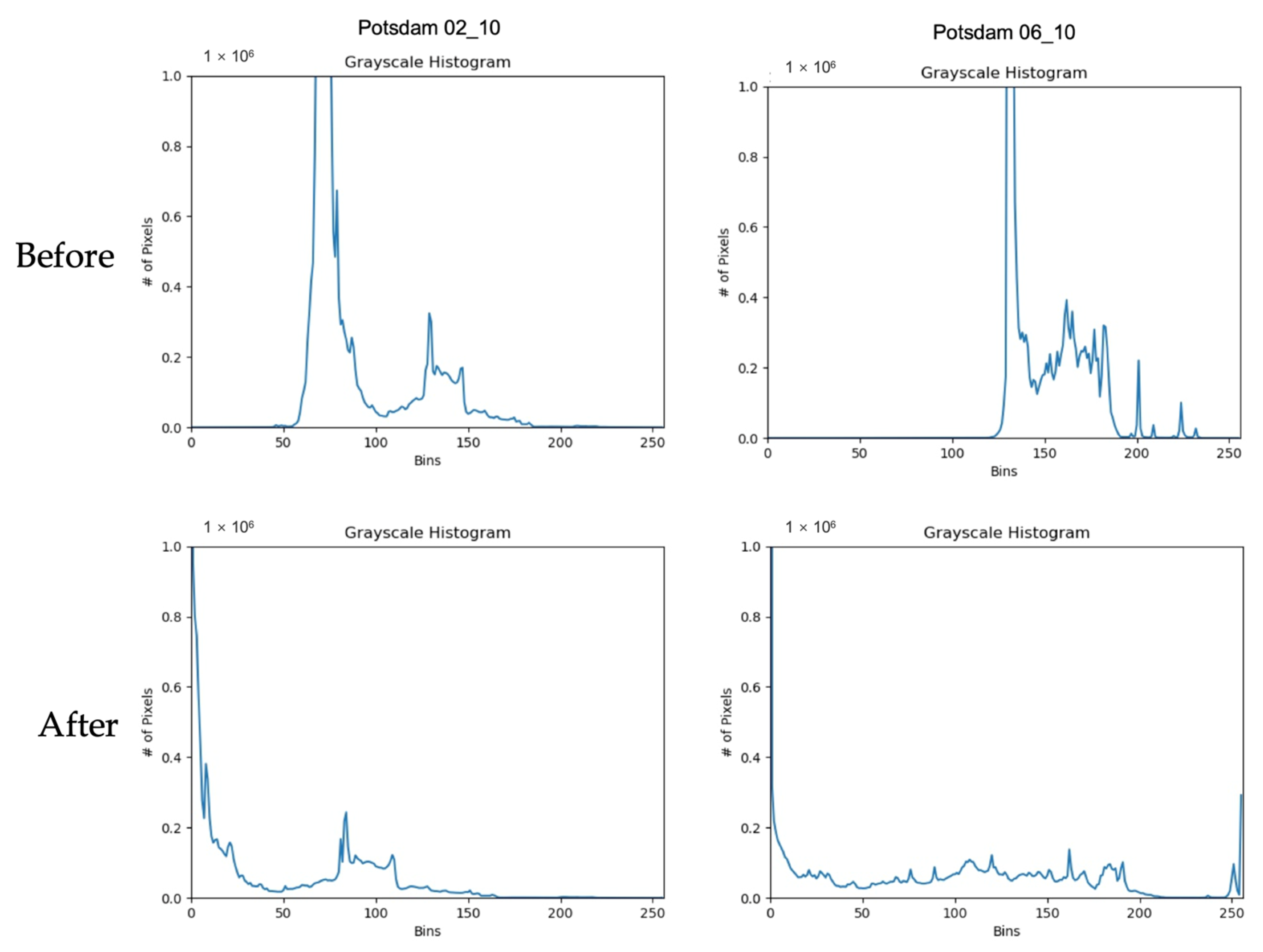
3.2. Elevation Normalization
3.3. Contrast Experiment Setting and Implementation Details
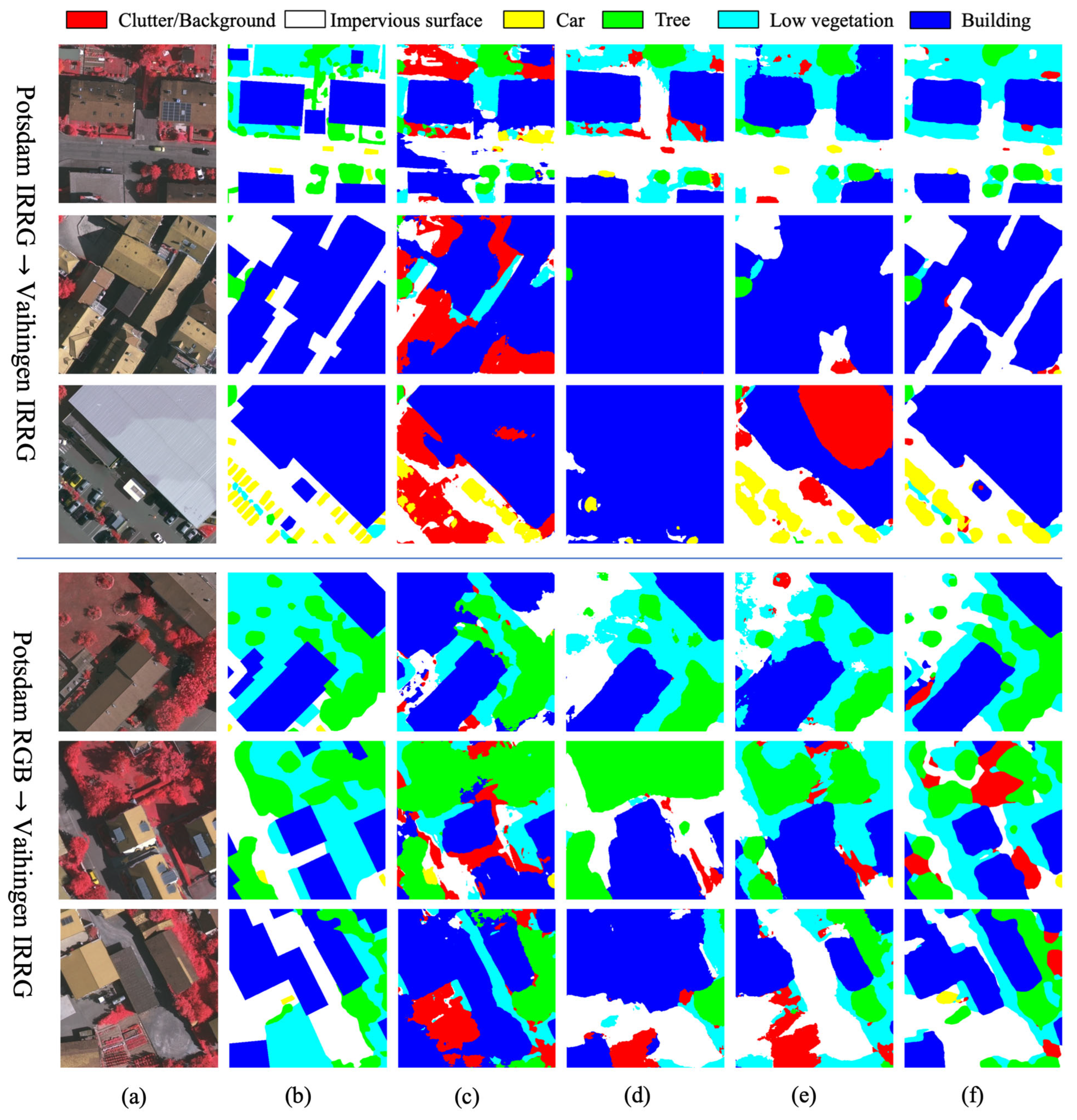
3.4. Results and Comparison
- Single-stage methods
- ii
- Multi-stage methods
- iii
- Results of elevation estimation
4. Discussion
4.1. Auxiliary Tasks of Elevation Estimation
4.2. Extensibility of Multi-Task Learning Models
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chi, M.; Plaza, A.; Benediktsson, J.A.; Sun, Z.; Shen, J.; Zhu, Y. Big data for remote sensing: Challenges and opportunities. Proc. IEEE 2016, 104, 2207–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Di, L.; Du, Q.; Wang, L. Remote sensing big data: Theory, methods and applications. Remote. Sens. 2018, 10, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audebert, N.; Le Saux, B.; Lefèvre, S. Beyond RGB: Very high resolution urban remote sensing with multimodal deep networks. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 140, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Du, B. Advances in Machine Learning for Remote Sensing and Geosciences. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2016, 4, 22–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Volpi, M.; Tuia, D. Joint height estimation and semantic labeling of monocular aerial images with CNNs. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–28 July 2017; pp. 5173–5176. [Google Scholar]
- Mou, L.; Zhu, X.X. IM2HEIGHT: Height estimation from single monocular imagery via fully residual convolutional-deconvolutional network. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.10249. [Google Scholar]
- Amirkolaee, H.A.; Arefi, H. Height estimation from single aerial images using a deep convolutional encoder-decoder network. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 149, 50–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjdira, B.; Bazi, Y.; Koubaa, A.; Ouni, K. Unsupervised domain adaptation using generative adversarial networks for semantic segmentation of aerial images. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Zhang, H.; Tan, P.; Gong, M. Dualgan: Unsupervised dual learning for image-to-image translation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) 2017, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2849–2857. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Guo, P.; Sun, Z.; Chen, X.; Gao, H. ResiDualGAN: Resize-residual DualGAN for cross-domain remote sensing images semantic segmentation. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.-Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) 2017, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2223–2232. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.-H.; Bilen, H. Knowledge distillation for multi-task learning. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision 2020, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 163–176. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert-Lacroix, S.; Zwald, L. The adaptive BerHu penalty in robust regression. J. Nonparametr. Stat. 2016, 28, 487–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markus Gerke, I. Use of the Stair Vision Library within the ISPRS 2D Semantic Labeling Benchmark (Vaihingen); University of Twente: Enschede, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Axelsson, P. DEM generation from laser scanner data using adaptive TIN models. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2000, 33, 110–117. [Google Scholar]
- Paszke, A. Pytorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1912.01703. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.-C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) 2018, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 801–818. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, Y.-H.; Hung, W.-C.; Schulter, S.; Sohn, K.; Yang, M.-H.; Chandraker, M. Learning to adapt structured output space for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) 2018, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 7472–7481. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, H.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, P.; Sun, Z.; Chen, X.; Tang, Y. Cycle and self-supervised consistency training for adapting semantic segmentation of aerial images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shi, T.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Wang, Z.; Li, H. Learning deep semantic segmentation network under multiple weakly-supervised constraints for cross-domain remote sensing image semantic segmentation. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 175, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, T.; Wang, B. Curriculum-style local-to-global adaptation for cross-domain remote sensing image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
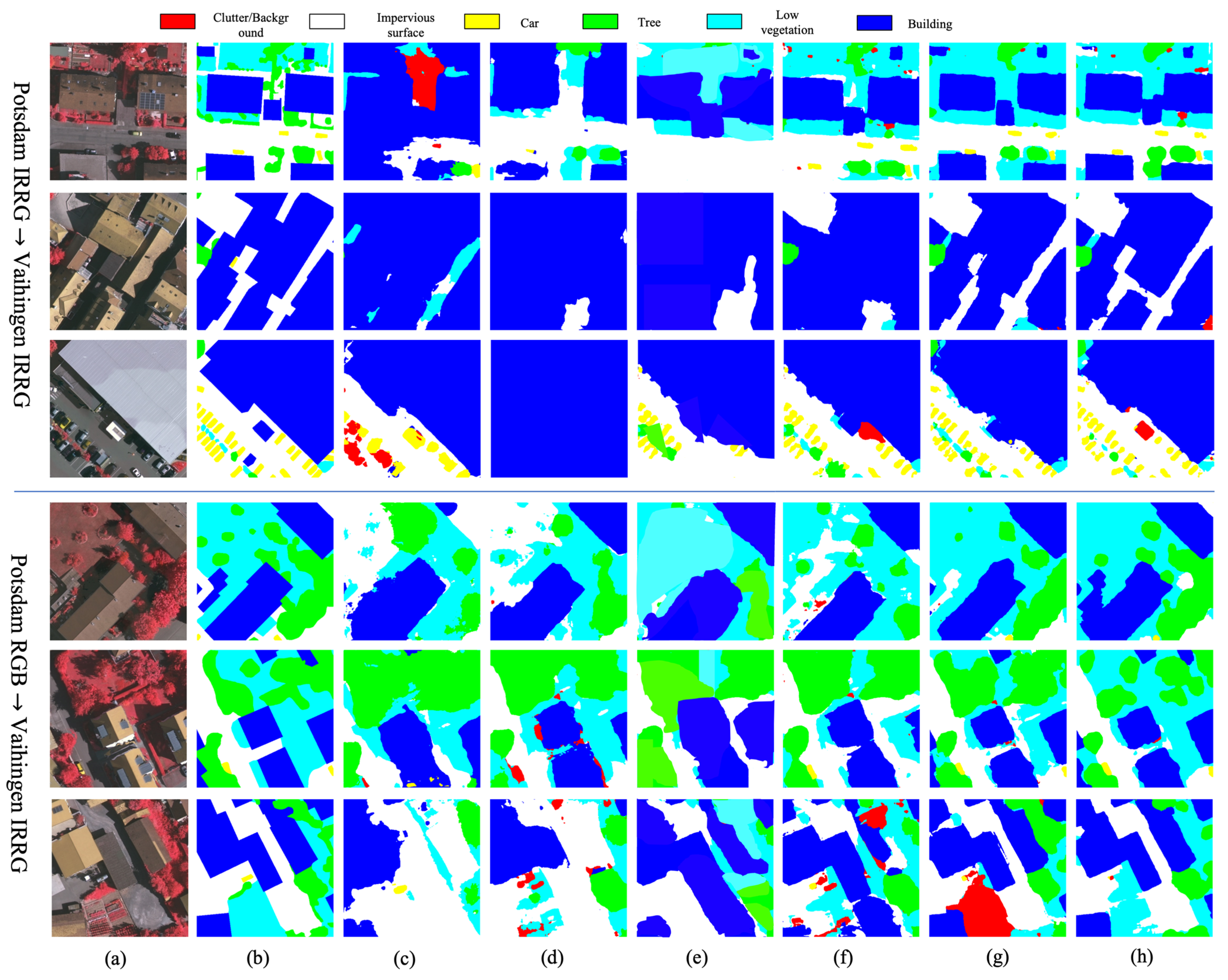
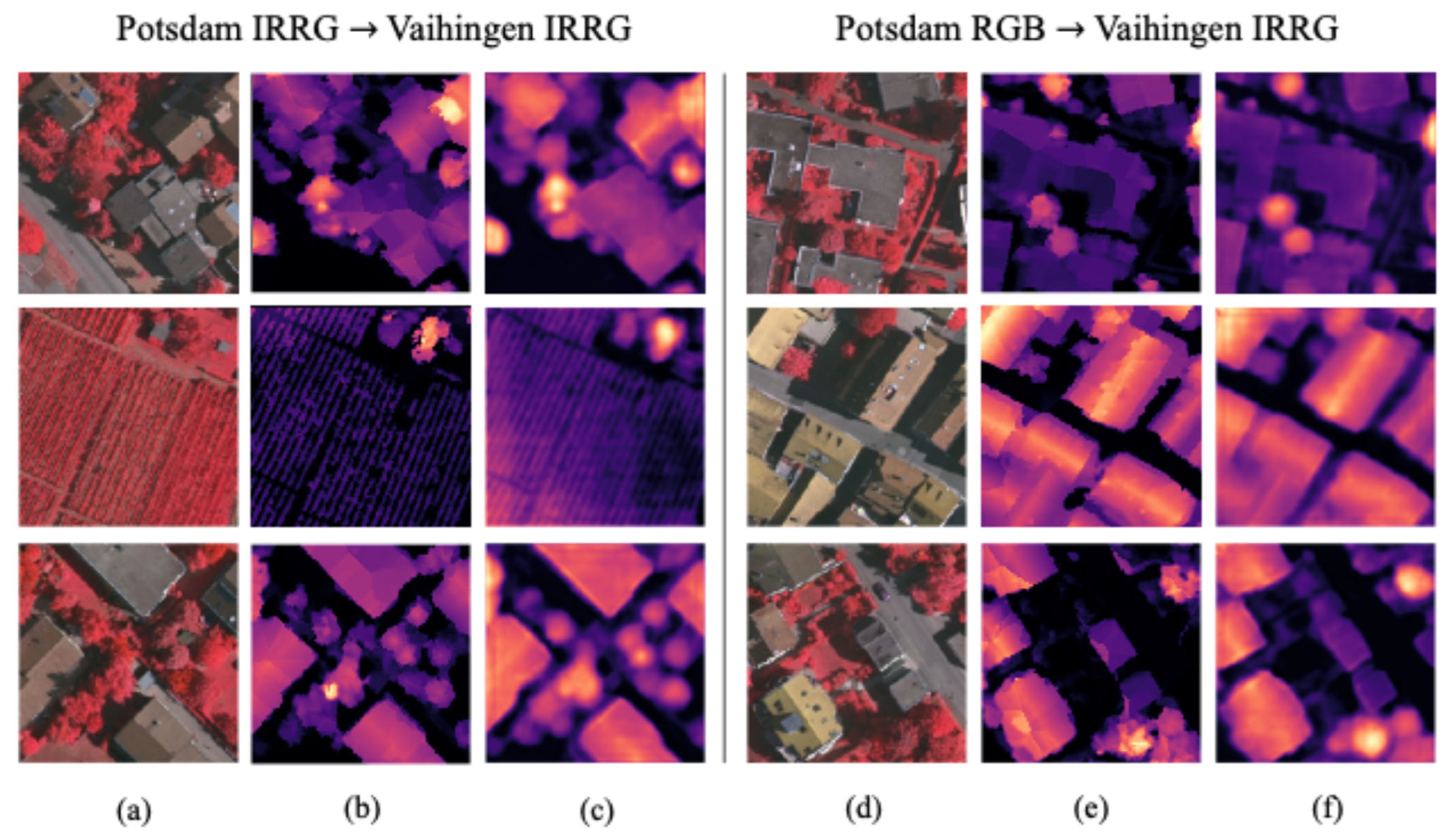
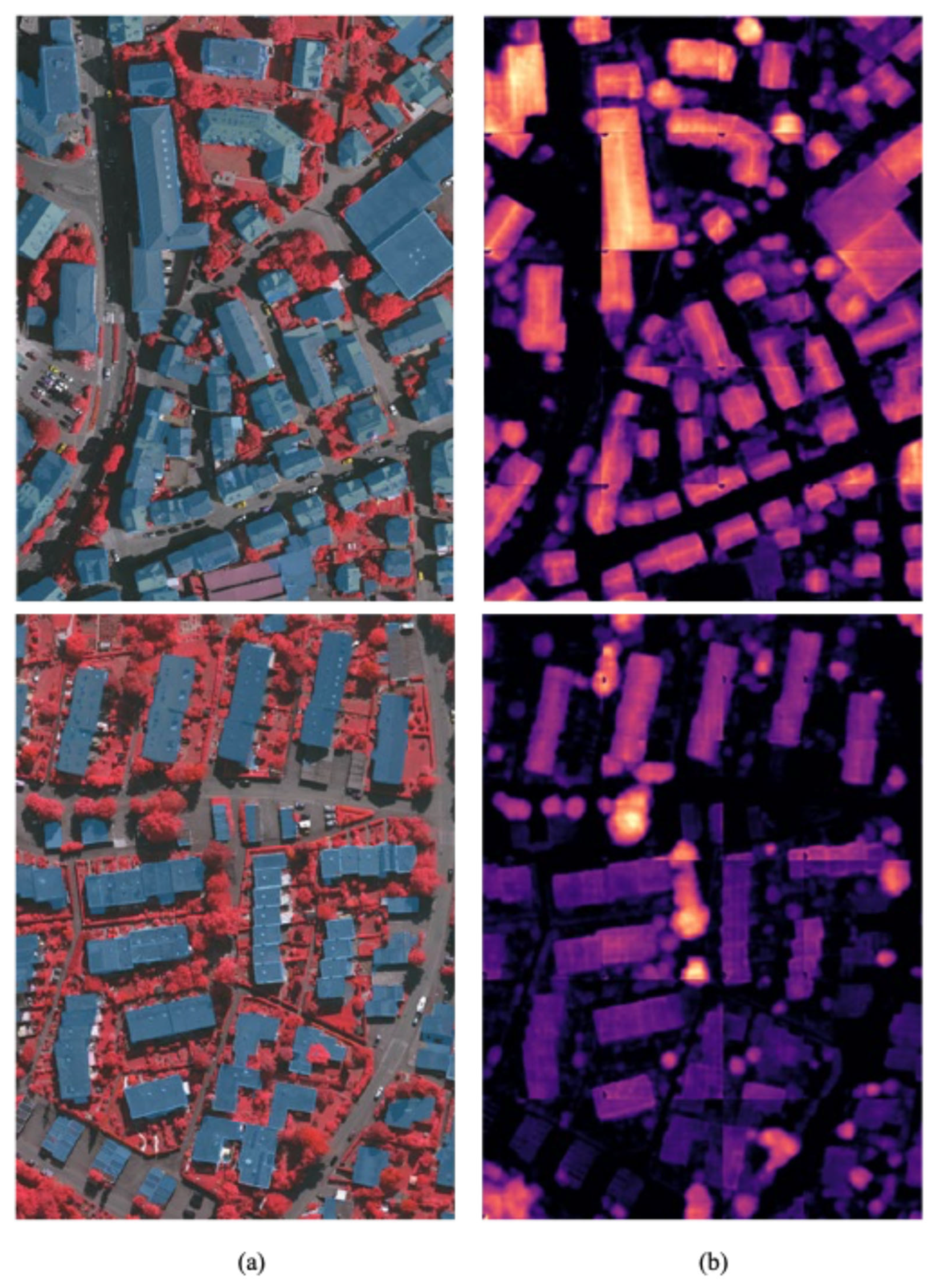
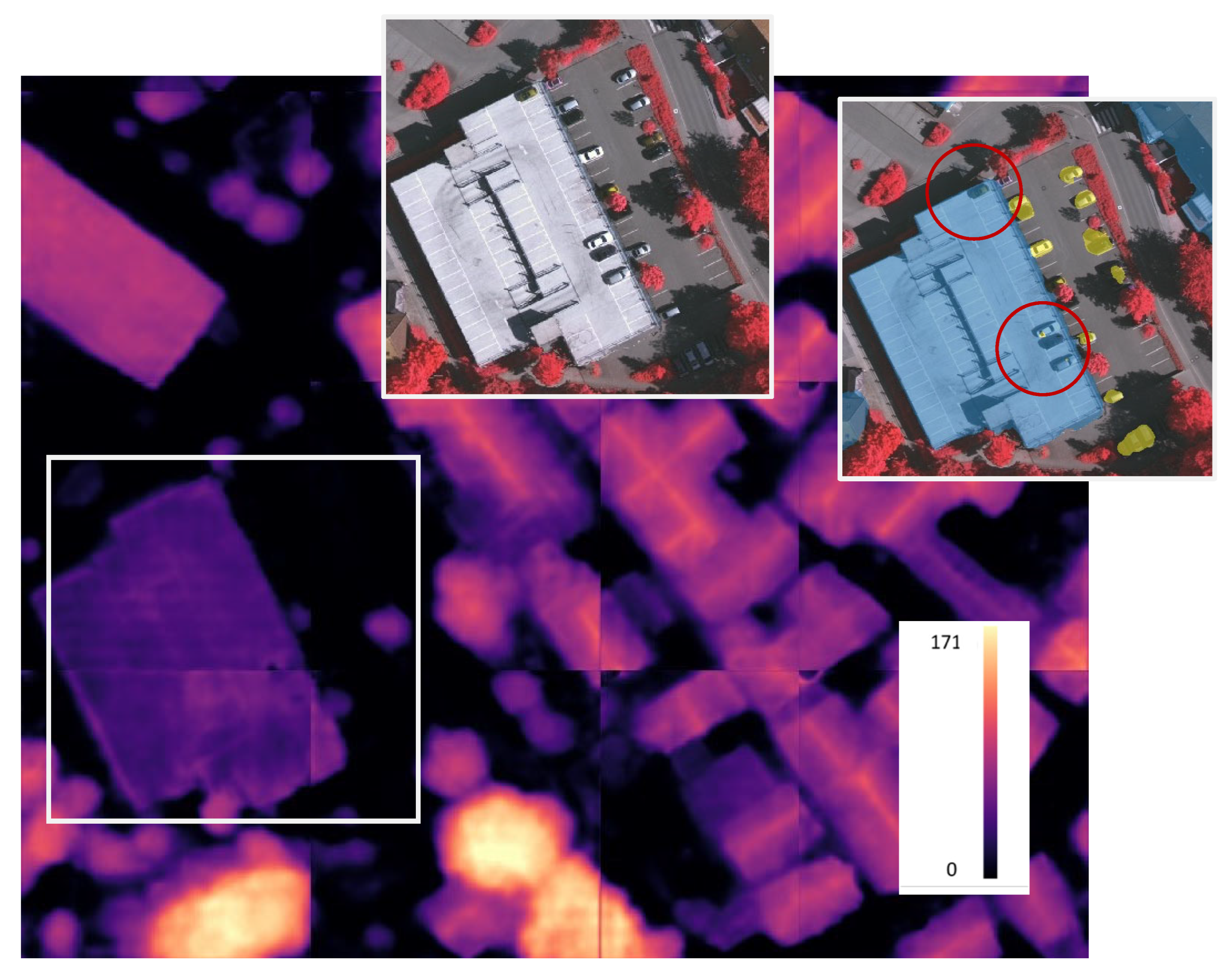
| Method | Metrics | Clutter/ Background | Impervious Surface | Car | Tree | Low Vegetation | Building | Overall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single-stage method | ||||||||
| Baseline (DeepLabv3+) | IoU | 2.99 | 47.88 | 20.82 | 58.74 | 19.57 | 61.37 | 35.23 |
| F1-score | 5.18 | 64.40 | 33.93 | 73.88 | 32.47 | 75.83 | 47.61 | |
| AdaptSegNet | IoU | 6.32 | 62.50 | 29.31 | 55.74 | 40.30 | 70.41 | 44.10 |
| F1-score | 9.67 | 76.66 | 44.81 | 71.36 | 57.01 | 82.50 | 57.00 | |
| CSC-SSO | IoU | 9.76 | 70.03 | 38.18 | 57.27 | 37.23 | 76.15 | 48.10 |
| F1-score | 14.11 | 82.24 | 54.96 | 72.70 | 53.78 | 86.40 | 60.70 | |
| EADA | IoU | 5.06 | 69.69 | 58.07 | 63.20 | 45.58 | 85.66 | 54.62 |
| F1-score | 8.09 | 81.79 | 72.83 | 76.92 | 61.01 | 92.18 | 65.47 | |
| Multi-stage method | ||||||||
| GAN-RSDA | IoU | 7.26 | 57.32 | 20.04 | 44.27 | 35.47 | 65.35 | 38.28 |
| F1-score | 10.32 | 72.60 | 32.53 | 61.04 | 51.99 | 78.84 | 51.22 | |
| MUCSS | IoU | 11.16 | 65.94 | 26.30 | 50.49 | 39.85 | 69.07 | 43.80 |
| F1-score | 14.70 | 79.15 | 40.77 | 66.76 | 56.55 | 81.53 | 56.58 | |
| CCDA | IoU | \ | 58.64 | 28.17 | 53.28 | 30.39 | 60.60 | 46.22 |
| F1-score | \ | 75.13 | 45.81 | 69.52 | 47.62 | 76.89 | 62.99 | |
| RDG-OSA | IoU | 10.70 | 70.31 | 54.04 | 59.22 | 49.03 | 81.20 | 54.08 |
| F1-score | 15.48 | 82.43 | 69.85 | 74.22 | 65.52 | 89.57 | 66.18 | |
| CSC-Aug | IoU | 13.83 | 75.56 | 56.58 | 65.55 | 52.92 | 84.17 | 58.10 |
| F1-score | 19.59 | 86.01 | 72.01 | 79.09 | 68.96 | 91.38 | 69.50 | |
| RDG-EADA | IoU | 7.76 | 76.90 | 56.91 | 67.03 | 59.84 | 85.68 | 59.02 |
| F1-score | 11.95 | 86.80 | 72.22 | 80.15 | 74.72 | 92.23 | 69.68 | |
| Method | Metrics | Clutter/ Background | Impervious Surface | Car | Tree | Low Vegetation | Building | Overall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single-stage method | ||||||||
| Baseline (DeepLabv3+) | IoU | 2.67 | 40.24 | 18.35 | 53.14 | 12.88 | 52.63 | 29.98 |
| F1-score | 4.65 | 56.93 | 30.40 | 69.19 | 22.68 | 68.74 | 42.10 | |
| AdaptSegNet | IoU | 6.26 | 55.91 | 34.09 | 47.56 | 23.18 | 65.97 | 38.83 |
| F1-score | 9.55 | 71.44 | 50.34 | 64.17 | 37.22 | 79.36 | 52.01 | |
| CSC-SSO | IoU | 2.47 | 48.99 | 35.63 | 49.54 | 21.39 | 61.31 | 36.56 |
| F1-score | 4.31 | 65.35 | 52.14 | 66.05 | 35.00 | 75.89 | 49.79 | |
| EADA | IoU | 0.18 | 45.09 | 39.25 | 63.84 | 15.69 | 84.82 | 41.48 |
| F1-score | 0.34 | 60.99 | 55.42 | 77.20 | 26.46 | 91.51 | 51.99 | |
| Multi-stage method | ||||||||
| Baseline | IoU | 2.29 | 48.27 | 25.73 | 42.16 | 23.34 | 64.33 | 34.35 |
| F1-score | 3.50 | 64.79 | 40.20 | 59.03 | 37.55 | 78.13 | 47.20 | |
| GAN-RSDA | IoU | 5.87 | 54.21 | 27.95 | 43.73 | 26.94 | 68.76 | 37.91 |
| F1-score | 8.77 | 70.04 | 42.89 | 60.53 | 42.09 | 81.26 | 50.93 | |
| MUCSS | IoU | 12.38 | 64.47 | 43.43 | 52.83 | 38.37 | 76.87 | 48.06 |
| F1-score | 21.55 | 77.76 | 60.05 | 69.62 | 55.94 | 86.95 | 61.98 | |
| CCDA | IoU | 9.84 | 62.59 | 54.22 | 56.31 | 37.86 | 79.33 | 50.02 |
| F1-score | 14.55 | 76.81 | 70.00 | 71.92 | 54.55 | 88.41 | 62.71 | |
| RDG-OSA | IoU | 8.12 | 68.91 | 57.41 | 65.47 | 48.33 | 81.78 | 55.00 |
| F1-score | 11.23 | 81.48 | 72.76 | 79.04 | 64.78 | 89.94 | 66.54 | |
| CSC-Aug | IoU | 3.80 | 73.50 | 51.22 | 62.62 | 55.32 | 86.57 | 55.51 |
| F1-score | 5.88 | 84.58 | 67.29 | 76.85 | 71.07 | 92.75 | 66.41 | |
| Method | Data Distribution Alignment | Self-Supervision | Elevation Information | mIoU_1 1 | mIoU_2 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 35.23 | 29.98 | |||
| RDG | ✓ | 51.89 | 45.14 | ||
| CSC-SSO | ✓ | 48.10 | 36.56 | ||
| CSC | ✓ | ✓ | 58.10 | 55.00 | |
| EADA | ✓ | ✓ | 54.02 | 65.58 | |
| RDG-EADA | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 59.02 | 55.51 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Z.; Guo, P.; Li, Z.; Chen, X.; Liu, X. Elevation-Aware Domain Adaptation for Sematic Segmentation of Aerial Images. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2529. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17142529
Sun Z, Guo P, Li Z, Chen X, Liu X. Elevation-Aware Domain Adaptation for Sematic Segmentation of Aerial Images. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(14):2529. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17142529
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Zihao, Peng Guo, Zehui Li, Xiuwan Chen, and Xinbo Liu. 2025. "Elevation-Aware Domain Adaptation for Sematic Segmentation of Aerial Images" Remote Sensing 17, no. 14: 2529. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17142529
APA StyleSun, Z., Guo, P., Li, Z., Chen, X., & Liu, X. (2025). Elevation-Aware Domain Adaptation for Sematic Segmentation of Aerial Images. Remote Sensing, 17(14), 2529. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17142529







