The Western North Pacific Monsoon Dominates Basin-Scale Interannual Variations in Tropical Cyclone Frequency
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Datasets and Methods
2.1. Datasets
2.2. Methods
3. Results
3.1. Close Association Between TCF and WNP Monsoon
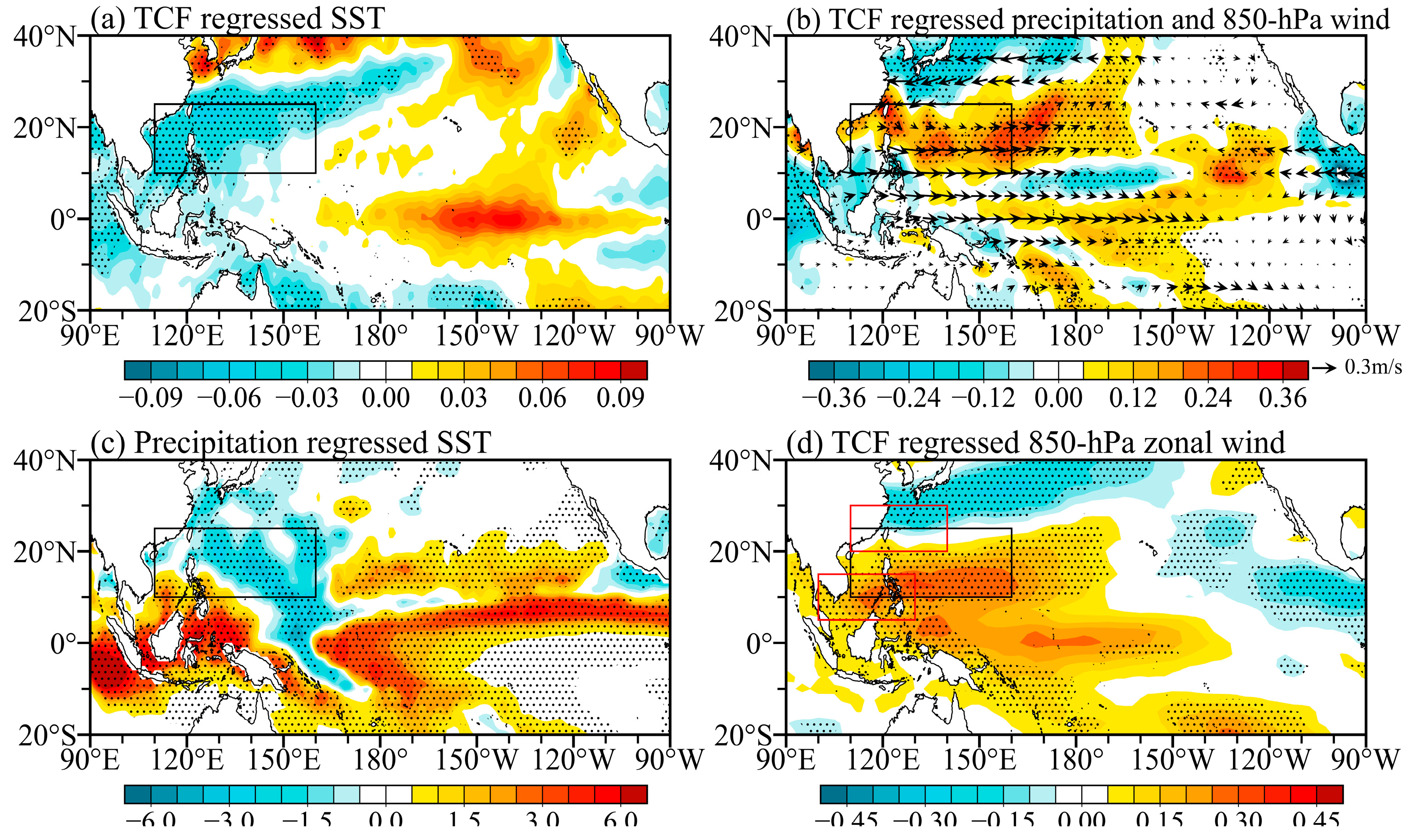
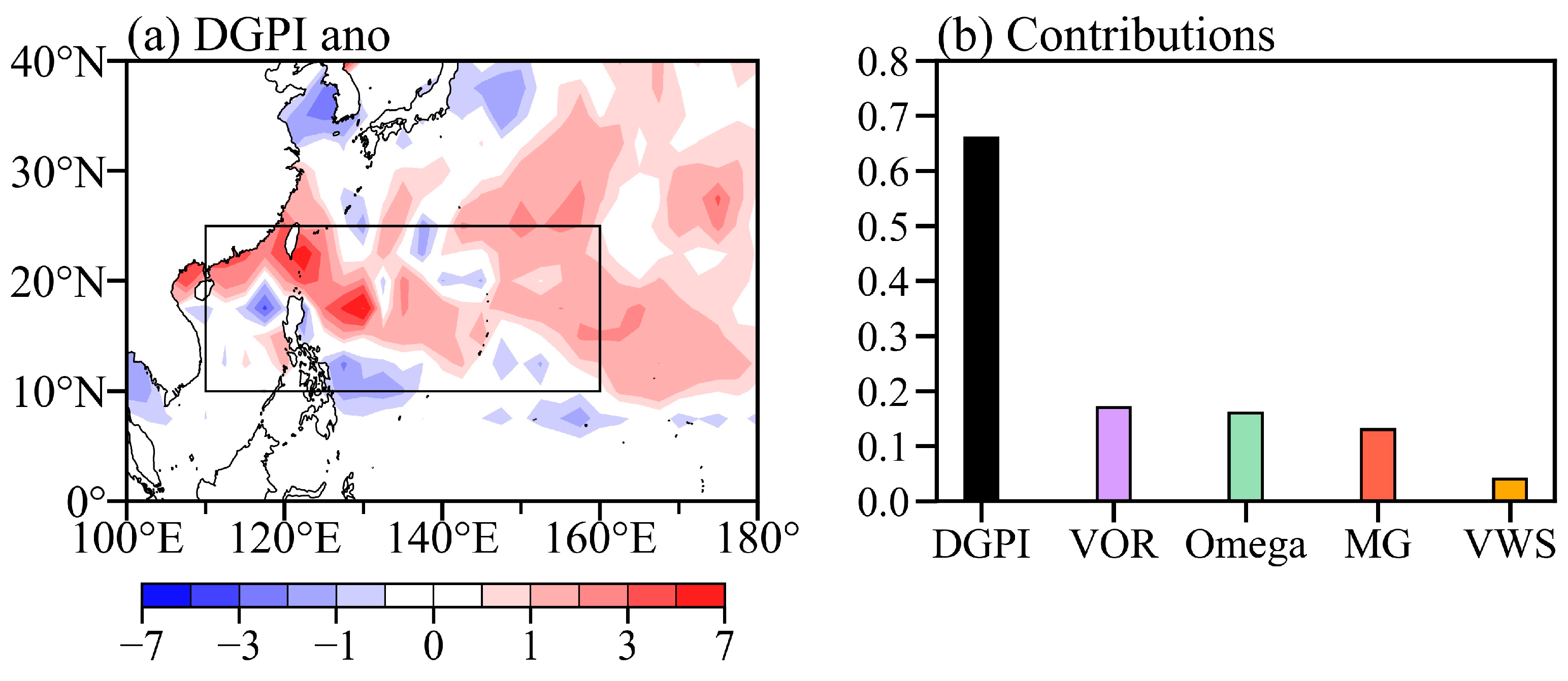
3.2. Key Environmental Factors Determine the Interannual Variation in Basin-Scale TCF
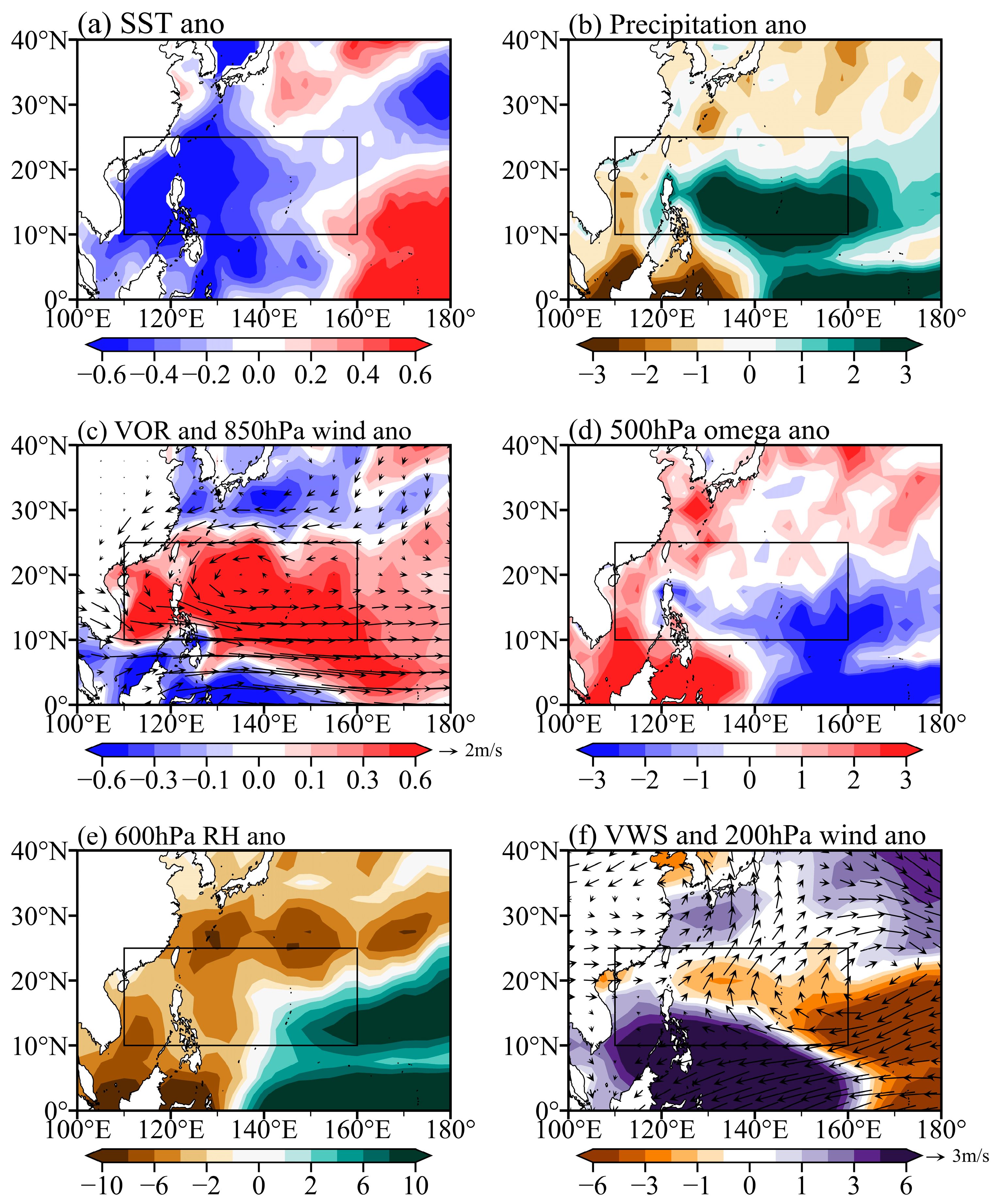
3.3. Dominance of WNP Monsoon on TC Environmental Factors and Frequency
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pielke, R.A., Jr.; Landsea, C.; Mayfield, M.; Layer, J.; Pasch, R. Hurricanes and Global Warming. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2005, 86, 1571–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutson, T.R.; McBride, J.L.; Chan, J.; Emanuel, K.; Holland, G.; Landsea, C.; Held, I.; Kossin, J.P.; Srivastava, A.K.; Sugi, M. Tropical Cyclones and Climate Change. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotzbach, P.J.; Wood, K.M.; Schreck, C.J., III; Bowen, S.G.; Patricola, C.M.; Bell, M.M. Trends in Global Tropical Cyclone Activity: 1990–2021. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2021GL095774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briegel, L.M.; Frank, W.M. Large-Scale Influences on Tropical Cyclogenesis in the Western North Pacific. Mon. Weather Rev. 1997, 125, 1397–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, E.A.; Holland, G.J. Large-Scale Patterns Associated with Tropical Cyclogenesis in the Western Pacific. Mon. Weather Rev. 1999, 127, 2027–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Li, T.; Peng, M.; Chen, W.; Chen, G. Effects of Monsoon Trough Interannual Variation on Tropical Cyclogenesis over the Western North Pacific. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 4332–4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wen, Z.; Wu, R. Influence of the Monsoon Trough on Westward-Propagating Tropical Waves over the Western North Pacific. Part I: Observations. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 7108–7127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wen, Z.; Wu, R. Influence of the Monsoon Trough on Westward-Propagating Tropical Waves over the Western North Pacific. Part II: Energetics and Numerical Experiments. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 9332–9349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landsea, C.W. El Niño/Southern Oscillation and the Seasonal Predictability of Tropical Cyclones. In El Niño and the Southern Oscillation: Multiscale Variability and Global and Regional Impacts; Diaz, H.F., Markgraf, V., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000; pp. 149–182. ISBN 978-0-511-57312-5. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.-C.; Weng, S.-P.; Yamazaki, N.; Kiehne, S. Interannual Variation in the Tropical Cyclone Formation over the Western North Pacific. Mon. Weather Rev. 1998, 126, 1080–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.-C.; Wang, S.-Y.; Yen, M.-C. Interannual Variation of the Tropical Cyclone Activity over the Western North Pacific. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 5709–5720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.C.L. Tropical Cyclone Activity in the Northwest Pacific in Relation to the El Niño/Southern Oscillation Phenomenon. Mon. Weather Rev. 1985, 113, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lander, M.A. An Exploratory Analysis of the Relationship between Tropical Storm Formation in the Western North Pacific and ENSO. Mon. Weather Rev. 1994, 122, 636–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Chan, J.C.L. How Strong ENSO Events Affect Tropical Storm Activity over the Western North Pacific. J. Clim. 2002, 15, 1643–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, S.J.; Sobel, A.H. Western North Pacific Tropical Cyclone Intensity and ENSO. J. Clim. 2005, 18, 2996–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, L.; Zhou, W. Interannual Changes of Tropical Cyclone Intensity in the Western North Pacific. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2011, 89, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, C.; Mu, M.; Duan, W. Seasonal Modulations of Different Impacts of Two Types of ENSO Events on Tropical Cyclone Activity in the Western North Pacific. Clim. Dyn. 2013, 40, 2887–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, H.-Y.; Yu, J.-Y. Contrasting Eastern-Pacific and Central-Pacific Types of ENSO. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 615–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kug, J.-S.; Jin, F.-F.; An, S.-I. Two Types of El Niño Events: Cold Tongue El Niño and Warm Pool El Niño. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 1499–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Tam, C.-Y. Different Impacts of Two Kinds of Pacific Ocean Warming on Tropical Cyclone Frequency over the Western North Pacific. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L01803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-M.; Webster, P.J.; Curry, J.A. Modulation of North Pacific Tropical Cyclone Activity by Three Phases of ENSO. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 1839–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, K.-J.; Yoon, S.-J.; Yun, K.-S.; Kug, J.-S.; Jang, Y.-S.; Chan, J.C.L. Dependency of Typhoon Intensity and Genesis Locations on El Niño Phase and SST Shift over the Western North Pacific. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2012, 109, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, J.C.H.; Vimont, D.J. Analogous Pacific and Atlantic Meridional Modes of Tropical Atmosphere–Ocean Variability. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 4143–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.; Zhang, L.; Saravanan, R.; Vimont, D.J.; Chiang, J.C.H.; Ji, L.; Seidel, H.; Tippett, M.K. Pacific Meridional Mode and El Niño-Southern Oscillation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L16608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Vecchi, G.A.; Murakami, H.; Villarini, G.; Jia, L. The Pacific Meridional Mode and the Occurrence of Tropical Cyclones in the Western North Pacific. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 381–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Z. Strong Modulation of the Pacific Meridional Mode on the Occurrence of Intense Tropical Cyclones over the Western North Pacific. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 7739–7749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Zhou, T.; Li, T. Atmospheric Dynamic and Thermodynamic Processes Driving the Western North Pacific Anomalous Anticyclone during El Niño. Part I: Maintenance Mechanisms. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 9621–9635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Gao, S.; Sun, L.; Chen, G.; Shen, X. Multiscale Mechanisms for the Modulation of the Pacific Meridional Mode on Tropical Cyclone Genesis over the Western North Pacific: A Comparison between 2004 and 2011. Clim. Dyn. 2023, 60, 3241–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.-P.; Hu, K.; Hafner, J.; Tokinaga, H.; Du, Y.; Huang, G.; Sampe, T. Indian Ocean Capacitor Effect on Indo–Western Pacific Climate during the Summer Following El Niño. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 730–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, R.; Wang, Y.; Lei, X. Contributions of ENSO and East Indian Ocean SSTA to the Interannual Variability of Northwest Pacific Tropical Cyclone Frequency. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, R.; Wang, Y.; Tao, L. Intensified Impact of East Indian Ocean SST Anomaly on Tropical Cyclone Genesis Frequency over the Western North Pacific. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 8724–8739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zhao, H.; Klotzbach, P.J.; Wang, C.; Raga, G.B.; Chen, S. Possible Influence of Tropical Indian Ocean Sea Surface Temperature on the Proportion of Rapidly Intensifying Western North Pacific Tropical Cyclones during the Extended Boreal Summer. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 9129–9143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Wu, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J. Influence of Tropical Indian Ocean Warming and ENSO on Tropical Cyclone Activity over the Western North Pacific. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2012, 90, 127–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, P.; Chen, G. Impacts of the Combined Modes of the Tropical Indo-Pacific Sea Surface Temperature Anomalies on the Tropical Cyclone Genesis over the Western North Pacific. Int. J. Climatol. 2019, 39, 2108–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briegel, L.M. The Structure and Variability of the ITCZ of the Western North Pacific; The Pennsylvania State University: University Park, PA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, S.C.; Evans, J.L. Comparison of the Structure of the ITCZ in the West Pacific during the Boreal Summers of 1989–93 Using AMIP Simulations and ECMWF Reanalysis. J. Clim. 2002, 15, 3549–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, T.; Yoshikane, T.; Yasunari, T. Biennial and Lower-Frequency Variability Observed in the Early Summer Climate in the Western North Pacific. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 4254–4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.-C.; Wang, S.-Y.; Yen, M.-C.; Gallus, W.A., Jr. Role of the Monsoon Gyre in the Interannual Variation of Tropical Cyclone Formation over the Western North Pacific. Weather Forecast. 2004, 19, 776–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wu, L.; Wen, Z.; Huang, R.; Wu, R. Possible Linkage between the Monsoon Trough Variability and the Tropical Cyclone Activity over the Western North Pacific. Mon. Weather Rev. 2012, 140, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Chen, G.-H.; Huang, R.-H.; Shen, X.-Y. Large-Scale Circulation Patterns Favourable to Tropical Cyclogenesis over the Western North Pacific and Associated Barotropic Energy Conversions. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, Y.; Wang, C.; Wu, Y.; Wu, L. Emergent Constraint on Projection of the North Pacific Monsoon Trough and Its Implications for Typhoon Activity Using CMIP6 Models. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2024, 129, e2023JD040471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhan, R.; Wen, M. Influence of Monsoon Trough Length on Interannual Variability of Northwest Pacific Multiple Tropical Cyclone Events. Atmos. Res. 2023, 295, 107034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-W.; Kim, B.-J.; Zhang, R.; Park, K.-J.; Kim, J.-Y.; Cha, Y.; Nam, J.-C. Possible Relation of the Western North Pacific Monsoon to the Tropical Cyclone Activity over Western North Pacific. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 3334–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Chen, S.; Chen, W.; Yao, S.; Nath, D.; Yu, B. Interannual Variations of the Rainy Season Withdrawal of the Monsoon Transitional Zone in China. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 53, 2031–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velden, C.; Harper, B.; Wells, F.; Beven, J.L., II; Zehr, R.; Olander, T.; Mayfield, M.; Guard, C.C.; Lander, M.; Edson, R.; et al. The Dvorak Tropical Cyclone Intensity Estimation Technique: A Satellite-Based Method That Has Endured for over 30 Years. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2006, 87, 1195–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, K.R.; Kruk, M.C.; Levinson, D.H.; Diamond, H.J.; Neumann, C.J. The International Best Track Archive for Climate Stewardship (IBTrACS). Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2010, 91, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummerow, C.; Barnes, W.; Kozu, T.; Shiue, J.; Simpson, J. The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) Sensor Package. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1998, 15, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummerow, C.; Simpson, J.; Thiele, O.; Barnes, W.; Chang, A.T.C.; Stocker, E.; Adler, R.F.; Hou, A.; Kakar, R.; Wentz, F.; et al. The Status of the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) after Two Years in Orbit. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2000, 39, 1965–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skofronick-Jackson, G.; Kirschbaum, D.; Petersen, W.; Huffman, G.; Kidd, C.; Stocker, E.; Kakar, R. The Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Mission’s Scientific Achievements and Societal Contributions: Reviewing Four Years of Advanced Rain and Snow Observations. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 144, 27–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, A.Y.; Kakar, R.K.; Neeck, S.; Azarbarzin, A.A.; Kummerow, C.D.; Kojima, M.; Oki, R.; Nakamura, K.; Iguchi, T. The Global Precipitation Measurement Mission. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 701–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, N.A.; Parker, D.E.; Horton, E.B.; Folland, C.K.; Alexander, L.V.; Rowell, D.P.; Kent, E.C.; Kaplan, A. Global Analyses of Sea Surface Temperature, Sea Ice, and Night Marine Air Temperature since the Late Nineteenth Century. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 Global Reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Murakami, H. Dynamic Genesis Potential Index for Diagnosing Present-Day and Future Global Tropical Cyclone Genesis. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 114008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Fan, Z. Choice of South Asian Summer Monsoon Indices. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1999, 80, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Kimoto, M. Atmosphere-Ocean Thermal Coupling in the North Atlantic: A Positive Feedback. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2000, 126, 3343–3369. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, W.M. Tropical Cyclone Genesis; Deptartment of Atmospheric Science, Colorado State University: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Cheung, K.K.W. Large-Scale Environmental Parameters Associated with Tropical Cyclone Formations in the Western North Pacific. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 466–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Ho, C.-H.; Kim, H.-S. Influence of Large-Scale Environments on Tropical Cyclone Activity over the Western North Pacific: A Case Study for 2009. J. Clim. Chang. Res. 2010, 1, 133–145. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, W.M. The Formation of Tropical Cyclones. Meteorl. Atmos. Phys. 1998, 67, 37–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobel, A.H.; Camargo, S.J. Influence of Western North Pacific Tropical Cyclones on Their Large-Scale Environment. J. Atmos. Sci. 2005, 62, 3396–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhao, J.; Zhan, R.; Gao, J. Revisiting the Interannual Impact of the Pacific Meridional Mode on Tropical Cyclone Genesis Frequency in the Western North Pacific. Clim. Dyn. 2021, 56, 1003–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Wang, C.; Wu, L.; Zhao, H. Season-dependent Modulation of Pacific Meridional Mode on Tropical Cyclone Genesis over the Western North Pacific. J. Geophys. Res. 2023, 128, e2022JD037575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Klotzbach, P.J.; Wang, Y.-F.; Duan, Y. Asymmetric Influence of the Pacific Meridional Mode on Tropical Cyclone Formation over the Western North Pacific. Int. J. Climatol. 2023, 43, 6578–6589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchi, G.A.; Soden, B.J. Effect of Remote Sea Surface Temperature Change on Tropical Cyclone Potential Intensity. Nature 2007, 450, 1066–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vecchi, G.A.; Knutson, T.R. On Estimates of Historical North Atlantic Tropical Cyclone Activity. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 3580–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, A.E. Some Simple Solutions for Heat-Induced Tropical Circulation. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1980, 106, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Ding, Q.; Fu, X.; Kang, I.-S.; Jin, K.; Shukla, J.; Doblas-Reyes, F. Fundamental Challenge in Simulation and Prediction of Summer Monsoon Rainfall. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L15711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, L.; Guo, P.; Hameed, S.; Jin, D. The role of tropical Atlantic SST anomalies in modulating western North Pacific tropical cyclone genesis. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 2378–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Li, T.; Tan, Z.; Zhu, Z. Effects of tropical North Atlantic SST on tropical cyclone genesis in the western North Pacific. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 46, 865–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, C. Interdecadal modulation on the relationship between ENSO and typhoon activity during the late season in the western North Pacific. Clim Dyn 2016, 47, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhao, H.; Klotzbach, P.J.; Jiang, X.; Chen, G.; Chen, S. Interannual Variability in the Boreal Summer Intraseasonal Oscillation Modulates the Meridional Migration of Western North Pacific Tropical Cyclone Genesis. J. Clim. 2023, 36, 4543–4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

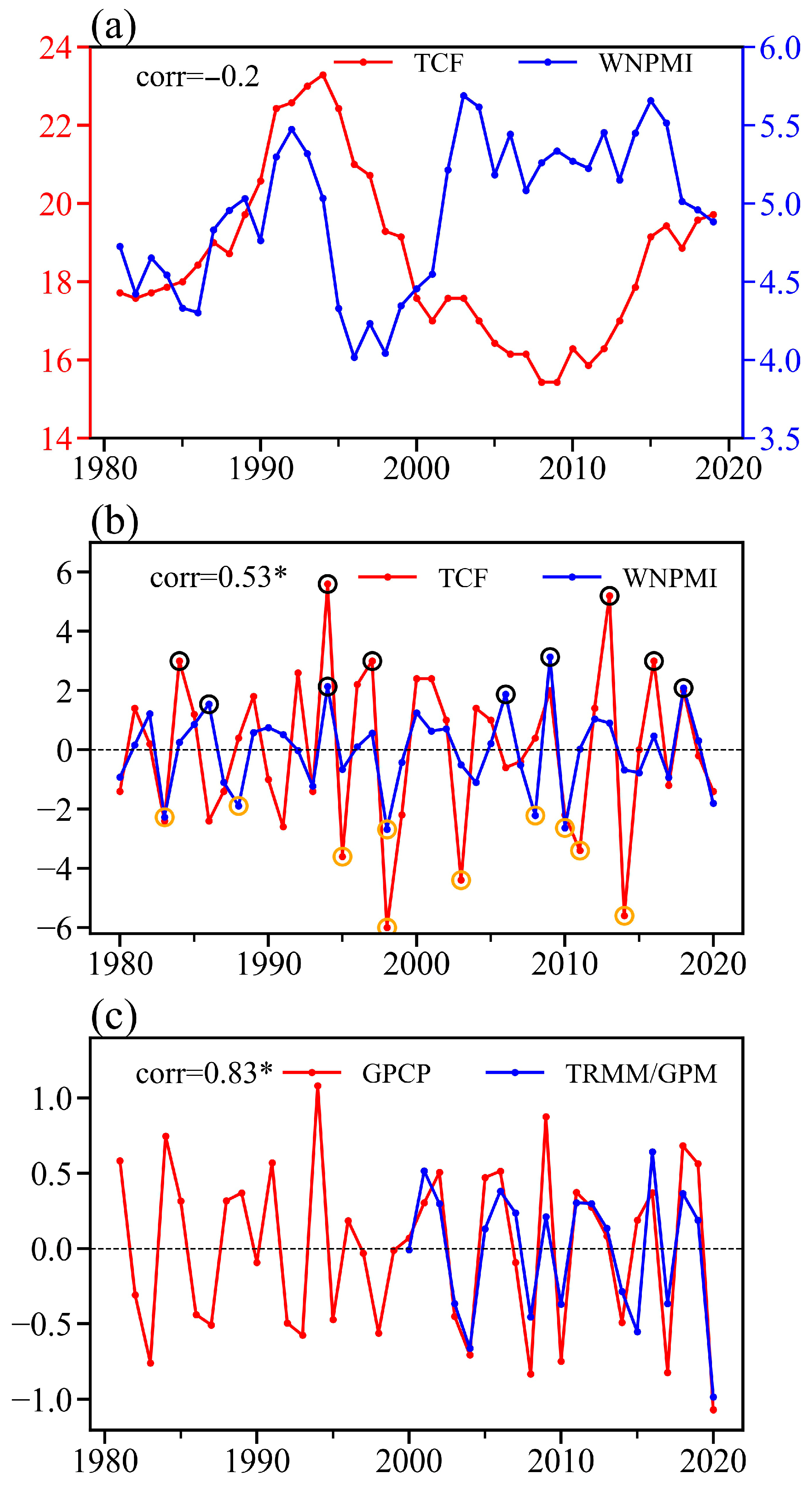


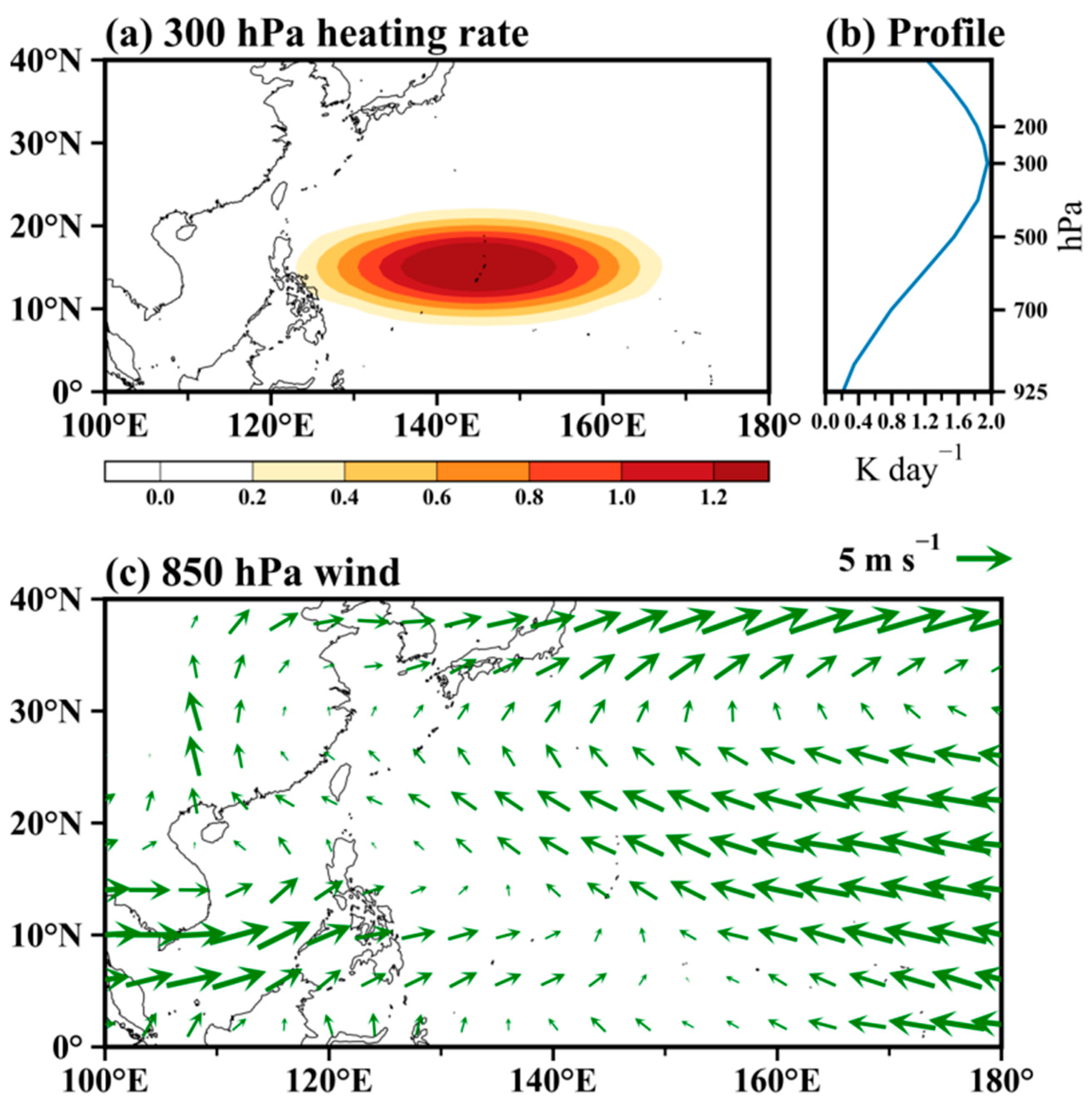
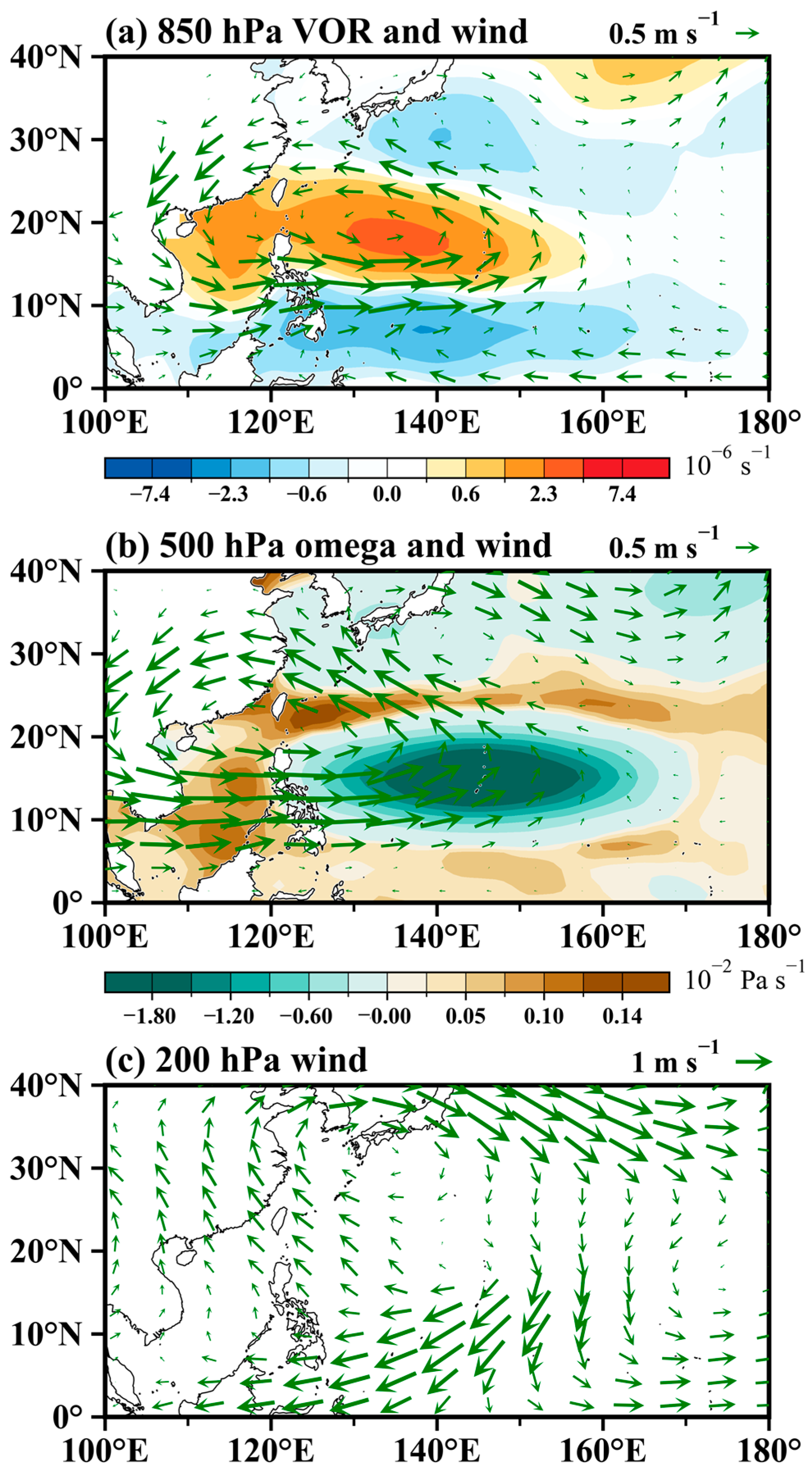
| Correlation | TCF | WNPMI | Pr | SST |
| TCF | / | 0.53 * | 0.53 * | −0.4 * |
| WNPMI | 0.53 * | / | 0.72* | −0.67 * |
| Pr | 0.53 * | 0.72 * | / | −0.4 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Cao, J.; Wang, B.; Feng, J. The Western North Pacific Monsoon Dominates Basin-Scale Interannual Variations in Tropical Cyclone Frequency. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2317. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17132317
Li X, Cao J, Wang B, Feng J. The Western North Pacific Monsoon Dominates Basin-Scale Interannual Variations in Tropical Cyclone Frequency. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(13):2317. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17132317
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xin, Jian Cao, Boyang Wang, and Jiawei Feng. 2025. "The Western North Pacific Monsoon Dominates Basin-Scale Interannual Variations in Tropical Cyclone Frequency" Remote Sensing 17, no. 13: 2317. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17132317
APA StyleLi, X., Cao, J., Wang, B., & Feng, J. (2025). The Western North Pacific Monsoon Dominates Basin-Scale Interannual Variations in Tropical Cyclone Frequency. Remote Sensing, 17(13), 2317. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17132317




