Fault Movement and Uplift Mechanism of Mt. Gongga, Sichuan Province, Constrained by Co-Seismic Deformation Fields from GNSS Observations
Abstract
1. Introduction
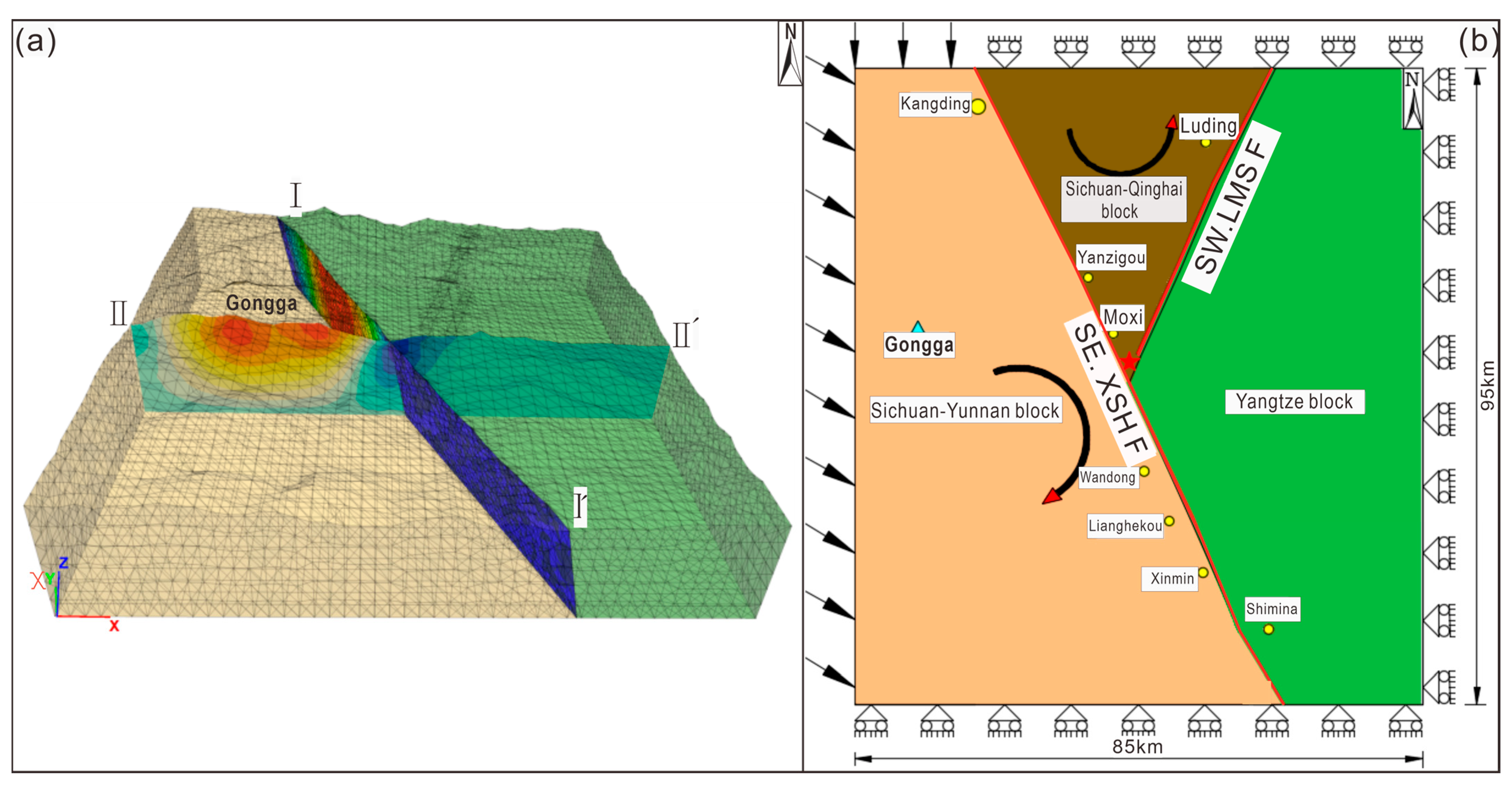
2. Seismic Geologic Conditions in the Mt. Gongga Study Area
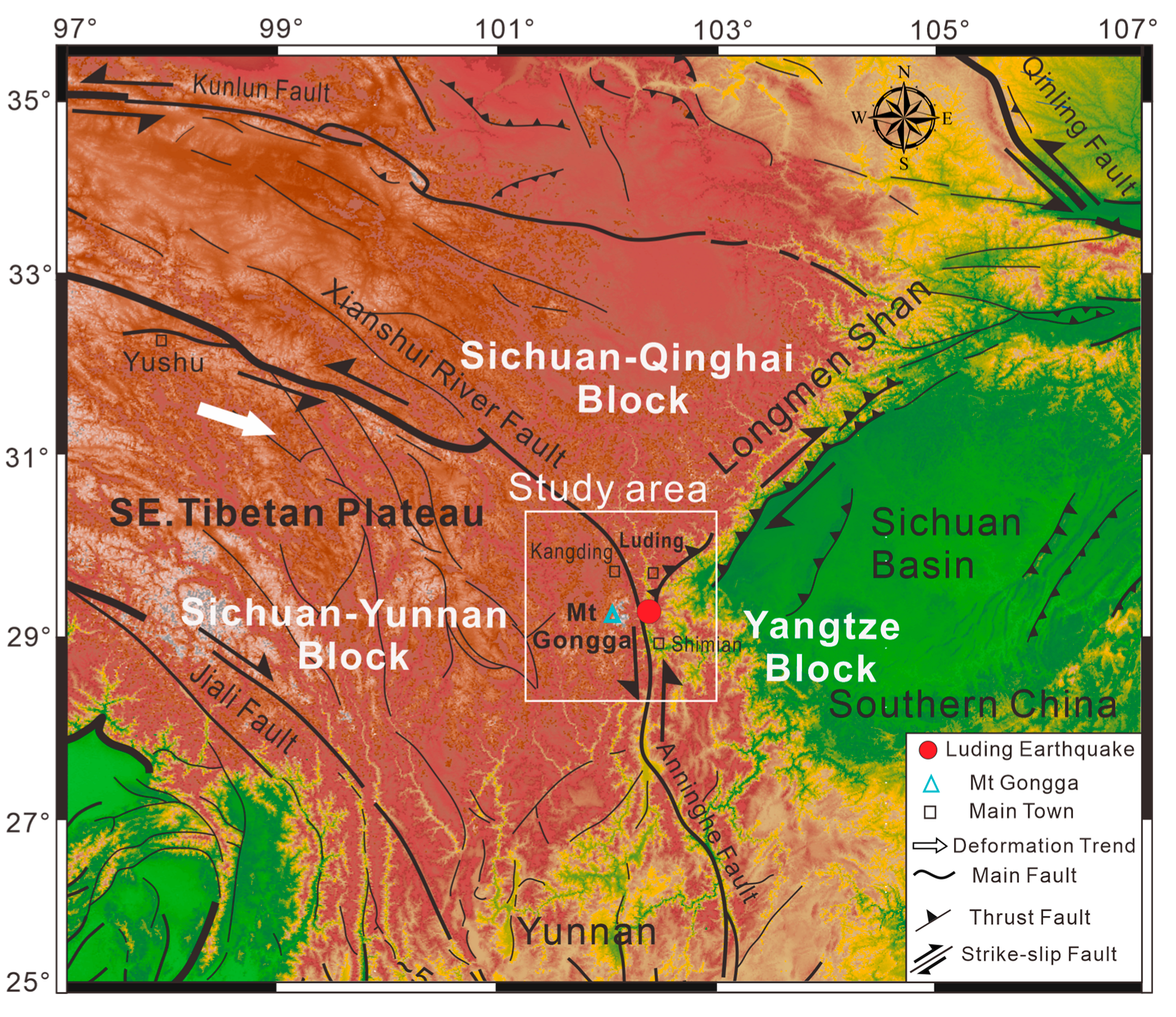
2.1. Regional Tectonic Background
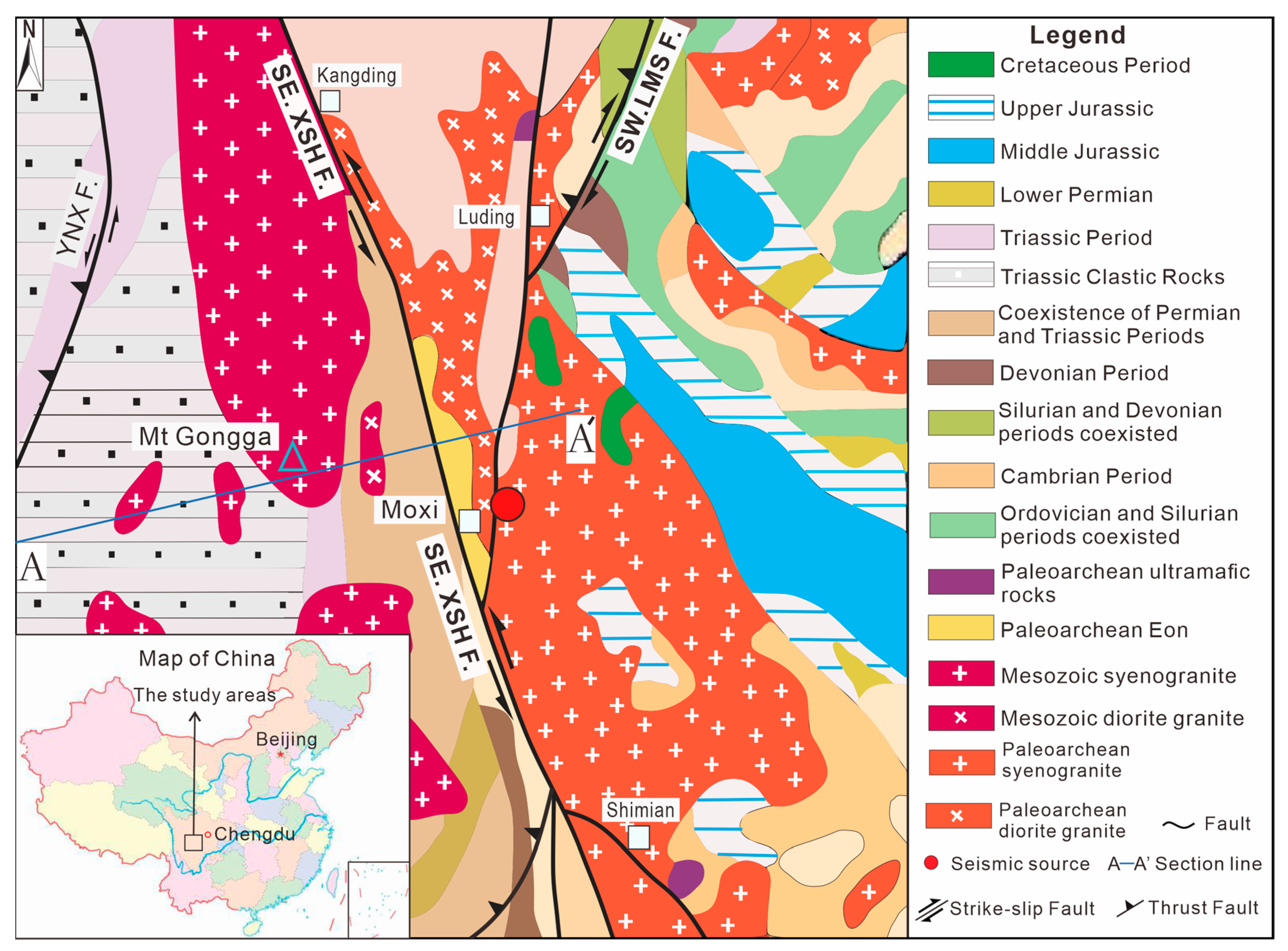
2.2. Seismic Tectonic
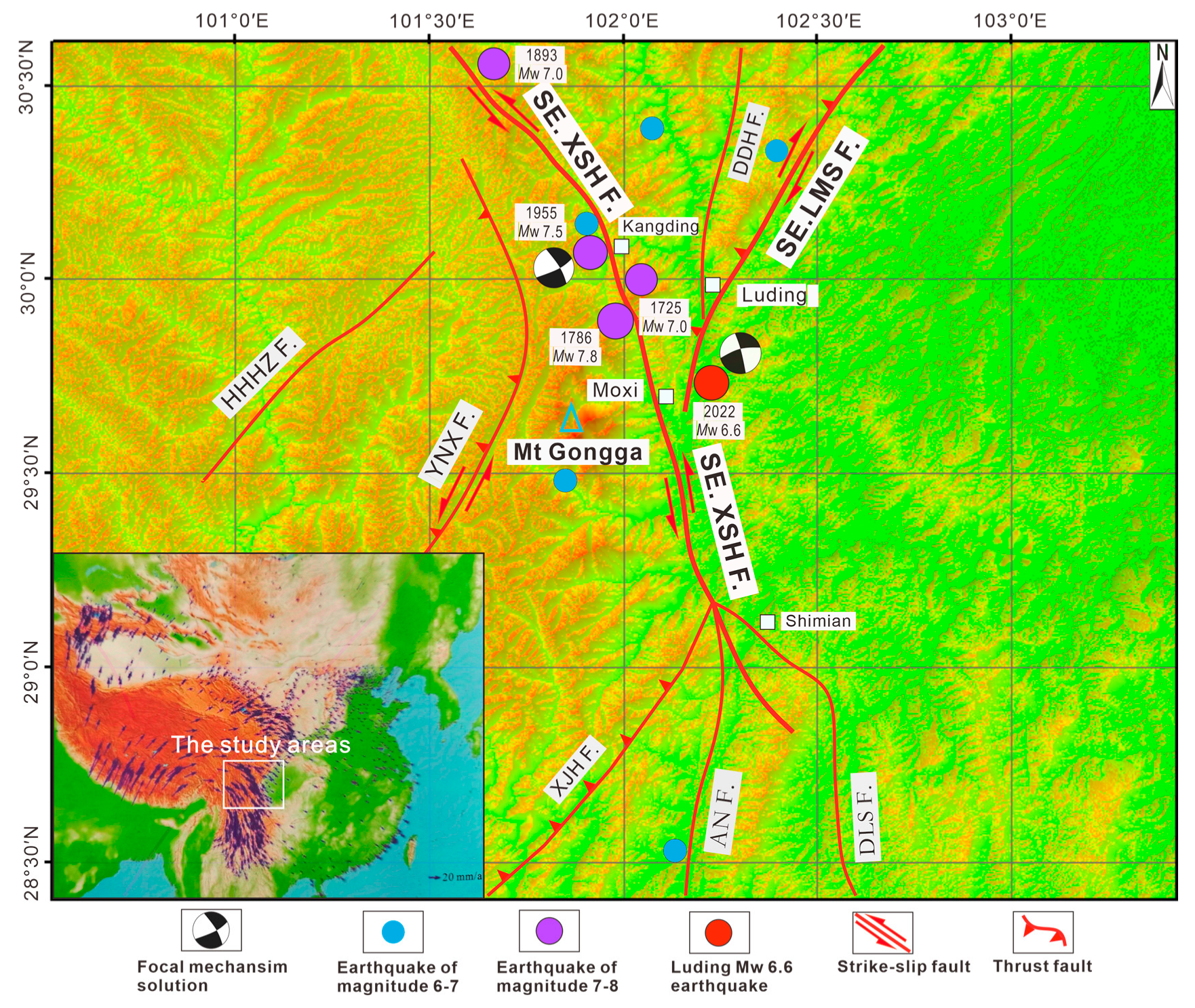
3. Method and Date
3.1. Methodology
3.2. Satellite Observation Data (GNSS)
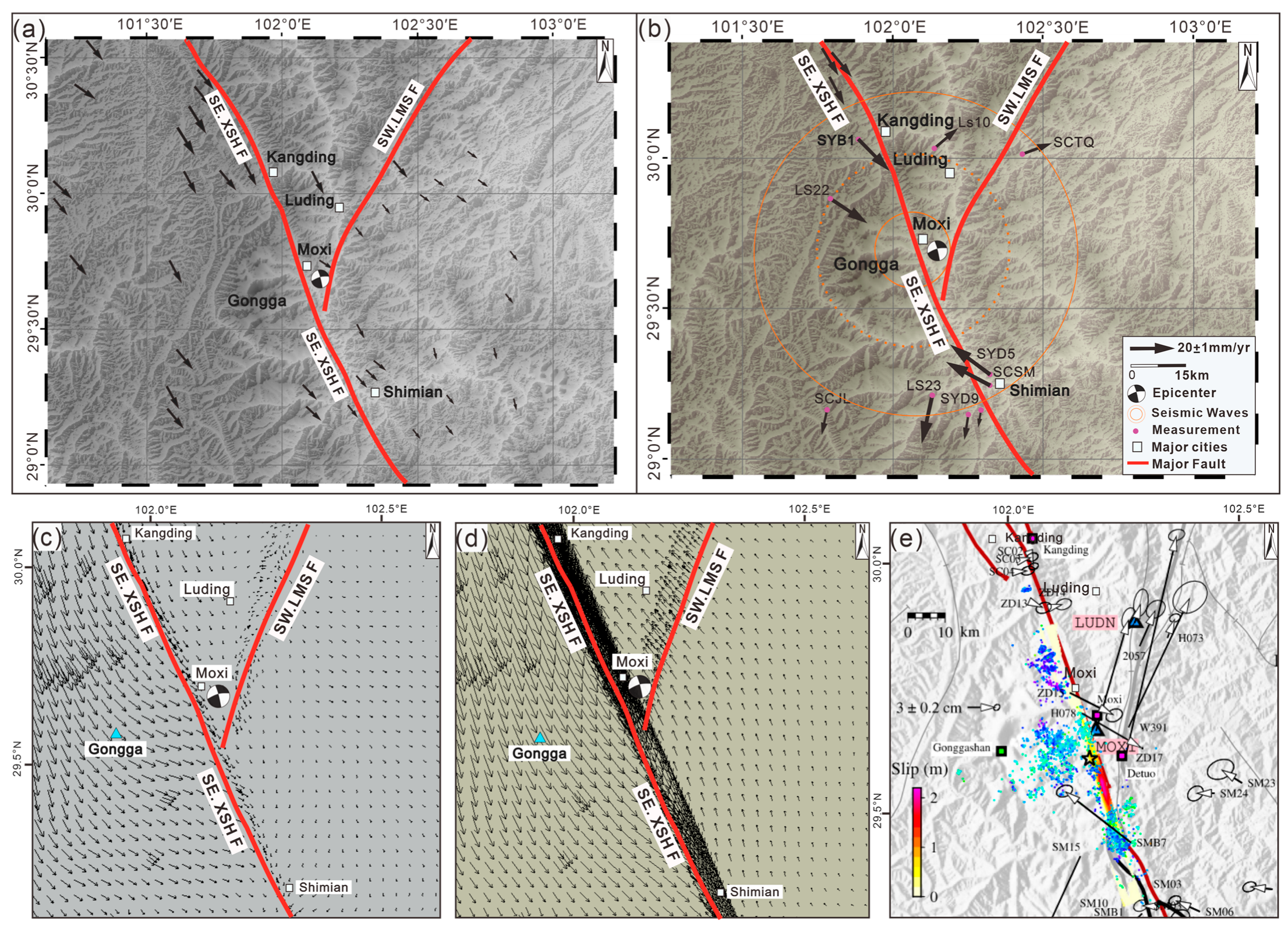
3.3. The Fitting Data Used in the Study
4. Results and Analysis
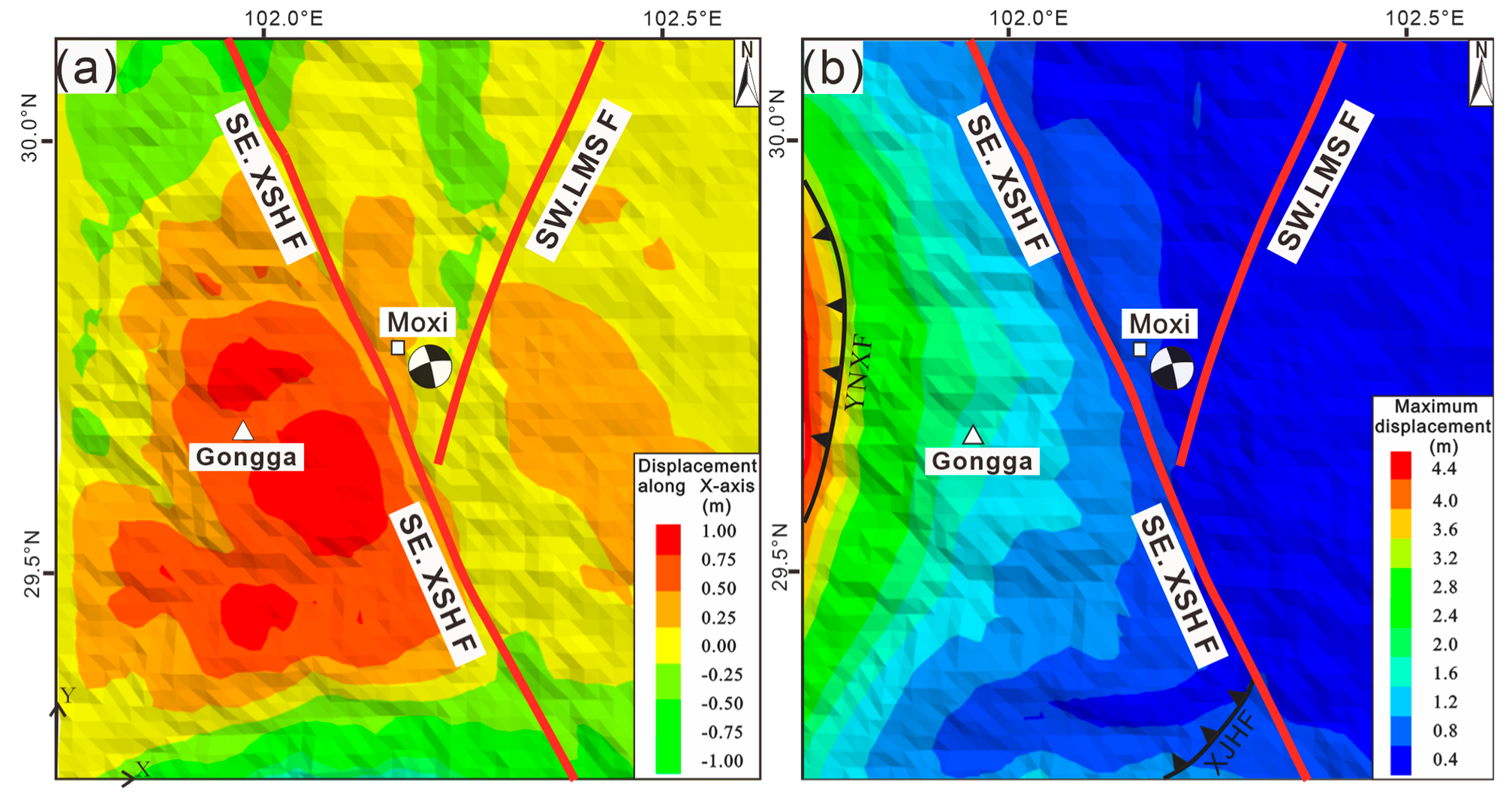
4.1. Characteristics of Pre- and Post-Earthquake Horizontal Displacement Vectors in the Mt. Gongga Region
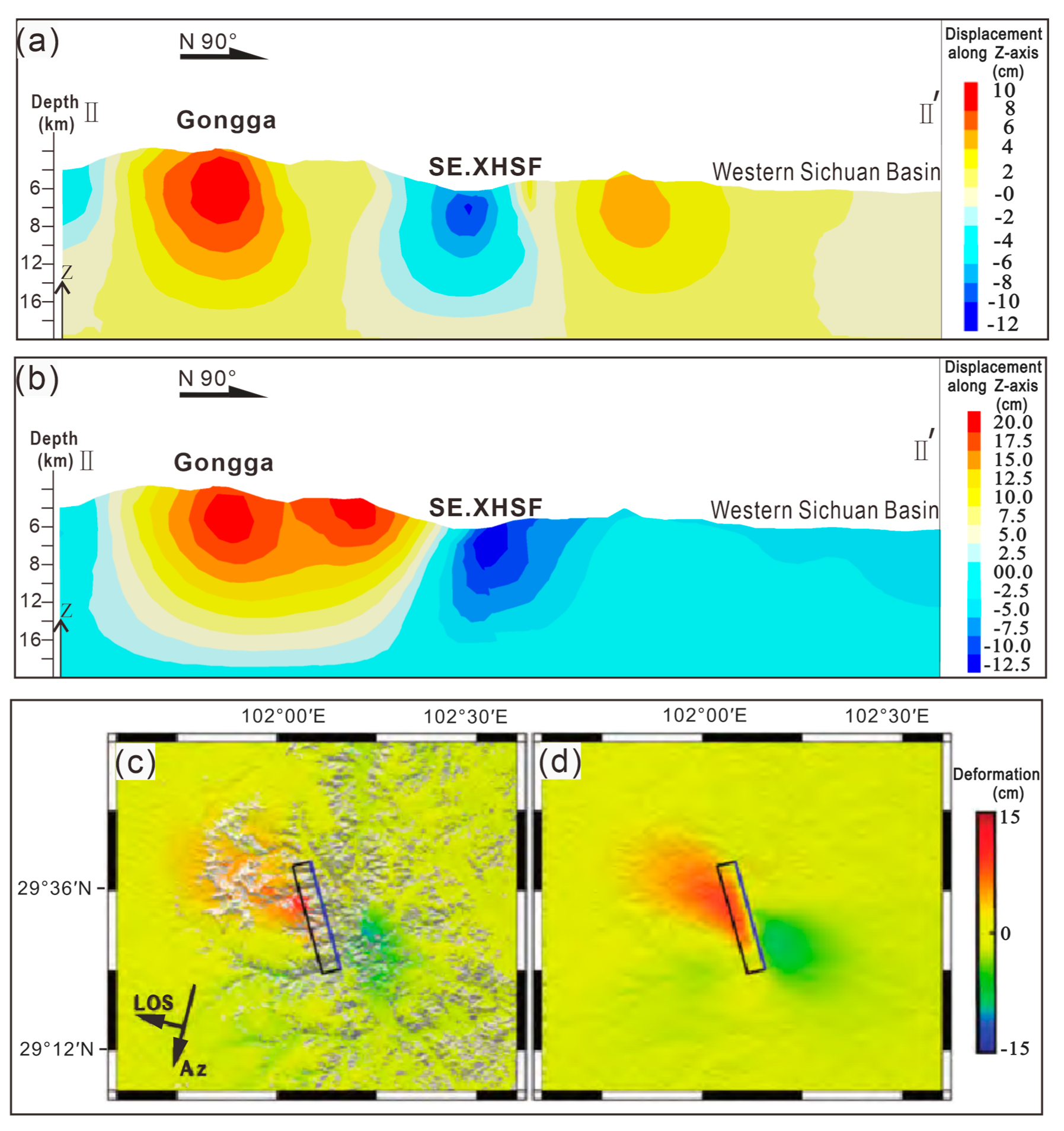
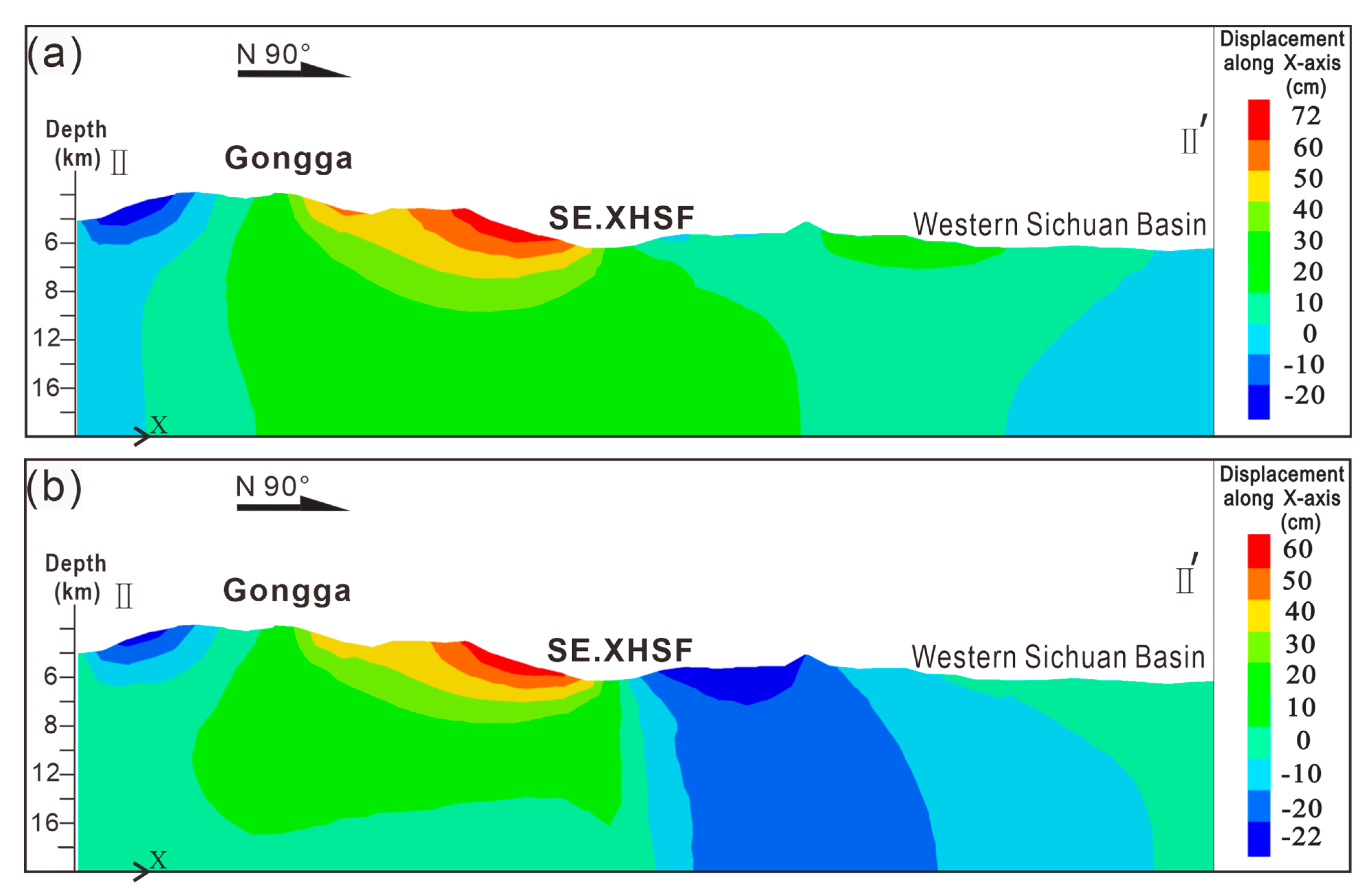
4.2. Pre-Earthquake and Post-Earthquake Uplift the Mt. Gongga Profile and Fault Movement During the Mainshock
5. Discussion
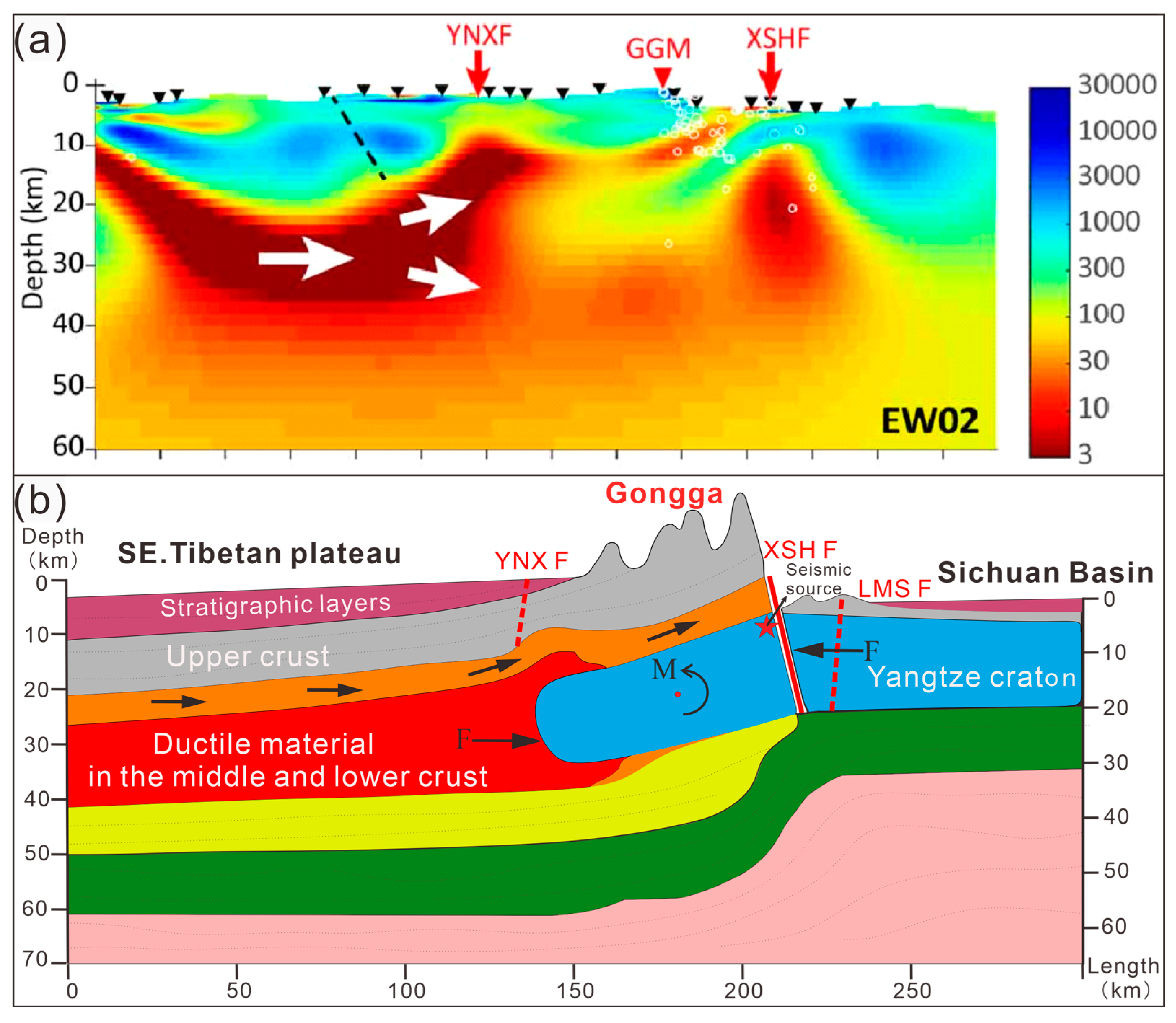
5.1. Discussion on the Deep Uplift Structure of Mt. Gongga
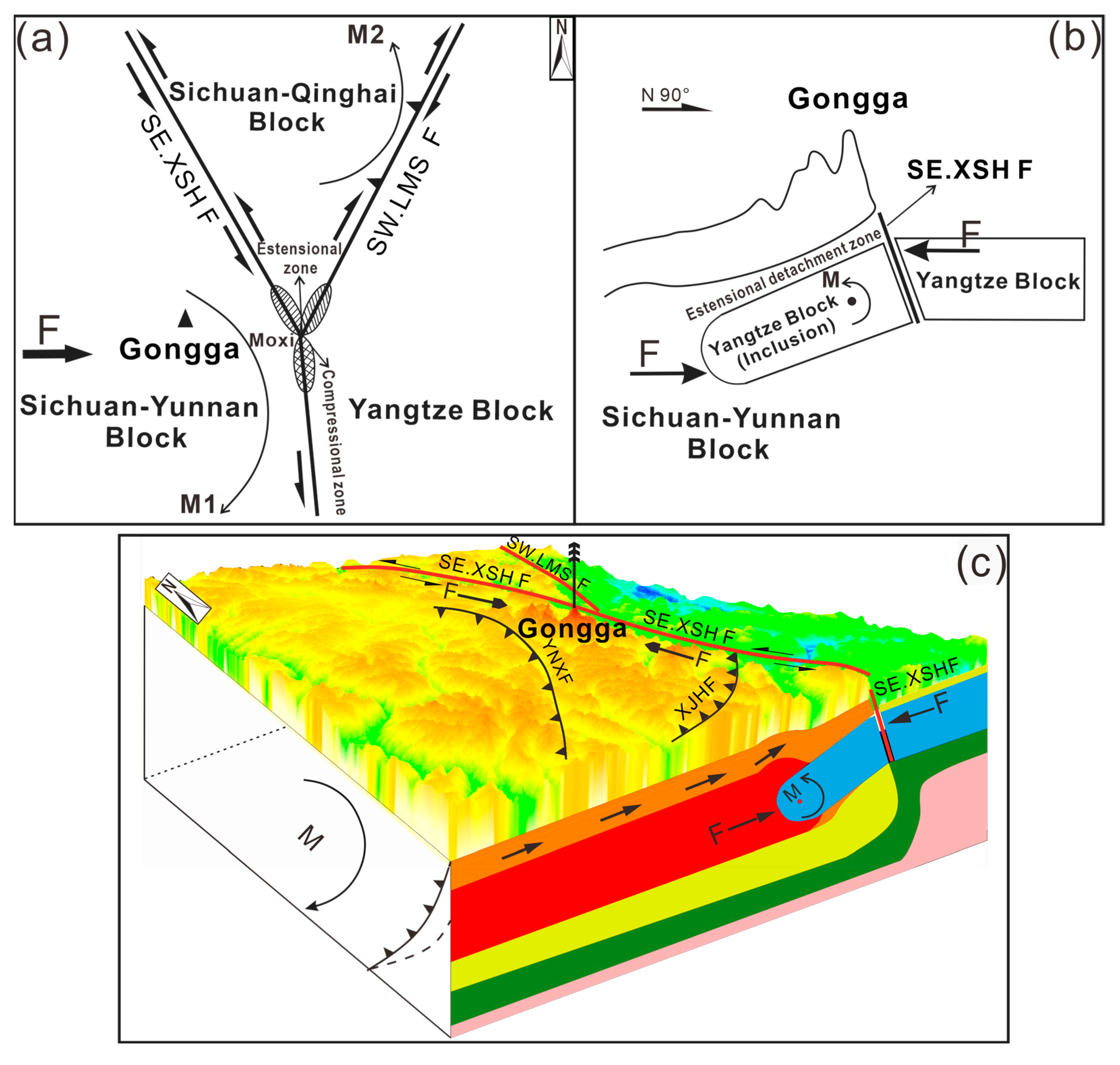
5.2. Analysis of the Uplift Mechanism in Mt. Gongga
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- The seismic source analysis of the earthquake reveals a steep dip angle of the primary fault plane, with a predominant inclination toward the northeast.
- (2)
- Numerical simulations demonstrate a consistent correlation between the horizontal displacement pattern and the arcuate structure of the Sichuan–Yunnan block, promoting the counterclockwise uplift of Mt. Gongga. The vertical displacement pattern indicates that this earthquake accelerated the overall uplift of Mt. Gongga.
- (3)
- Mt. Gongga undergoes a multiple coupling uplift mechanism characterized by “clockwise uplift + rotational flexure + asthenospheric upwelling”.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coleman, M. Evidence for Tibetan plateau uplift before 14My ago from a new minimum ago for east-west extension. Nature 1995, 374, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Li, H.B.; Chevalier, M.L.; Bai, M. A newly discovered active fault on the Selaha-Kangding segment along the Xianshuiher fault belt: The South Mugecuo fault. Acta Geol. Sin. 2020, 94, 3178–3188. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, C.G.; Bozzoni, F.; Conca, D.; Famà, A.; Özcebe, A.G.; Zuccolo, E.; Meisina, C.; Bonì, R.; Bordoni, M.; Cosentini, R.M.; et al. Technical guidelines for the assessment of earthquake induced liquefaction hazard at urban scale. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2021, 19, 4013–4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, R.Z.; Yan, L.; Yan, Z.K.; Ding, H.R.; Shao, C.J. Tectonic Geomorphology and Surface Process of Longmen Shan; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2017; pp. 439–440. [Google Scholar]
- Tapponnier, P.; Zhiqin, X.; Roger, F.; Meyer, B.; Arnaud, N.; Wittlinger, G.; Jingsui, Y. Oblique Stepwise Rise and Growth of the Tibet Plateau. Science 2001, 294, 1671–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, L.H.; Yao, H.J.; Lai, Y.C.; Huang, B.S.; Zhang, P. Crustal structure of southwest China and northern Vietnam from ambient noise tomography: Implication for the large-scale material transport model in SE Tibet. Tectonics 2018, 37, 492–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.Y.; van der Hilst, R.D.; Li, Y.; Yao, H.J.; Chen, J.H.; Guo, B.; Qi, S.H.; Wang, J.; Huang, H.; Li, S.C. Eastward expansion of the Tibetan Plateau by crustal flow and strain partitioning across faults. Nat. Geosci. 2014, 7, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.H. Low wave speed zones in the crust beneath SE Tibet revealed by ambient noise adjoint tomography. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, M.; Li, Y.; Zhuang, W. Crustal movement and strain distribution in east asia revealed by gps observations. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Shen, Z.K. Present-day crustal deformation of continental China derived from GPS and its tectonic implications. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2020, 125, e2019JB018774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Wang, H.; Wright, T.J.; Lou, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, W.; Shi, C.; Huang, J.; Wei, N. Crustal deformation in the india-eurasia collision zone from 25 years of gps measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2017, 122, 9290–9312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Gan, W.; Shen, C.; Xiao, G.; Liu, J.; Chen, W.; Ding, X.; Zhou, D. Three-dimensional velocity field of present–day crustal motion of the tibetan plateau derived from gps measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2013, 108, 5722–5732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.-Z.; Shen, Z.; Wang, M.; Gan, W.; Bürgmann, R.; Molnar, P.; Wang, Q.; Niu, Z.; Sun, J.; Wu, J.; et al. Continuous deformation of the tibetan plateau from global positioning system data. Geology 2004, 32, 809–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, P.-Z.; Freymueller, J.T.; Bilham, R.; Larson, K.M.; Lai, X.; You, X.; Niu, Z.; Wu, J.; Li, Y.; et al. Present-day crustal deformation in china constrained by global positioning system measurements. Science 2001, 294, 574–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.R.; Hergert, T.; Henk, A.; Wang, D.; Zeng, Z.X. Subsurface structure and spatial segmentation of the Longmen Shan fault zone at the eastern margin of Tibetan Plateau: Evidence from focal mechanism solutions and stress field inversion. Tectonophysics 2019, 757, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Dreger, D.; Ge, H.; Xu, P.; Wu, M.; Chiang, A.; Zhao, G.; Yuan, H. Spatial and Temporal Variations in the Moment Tensor Solutions of the 2008 Wenchuan Earthquake Aftershocks and Their Tectonic Implications. Tectonics 2018, 37, 989–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liang, C.T.; Fan, L.H.; Su, J.R.; Hua, Q.A. Comprehensive Analysis on the Stress Field and Seismic Anisotropy in Eastern Tibet. Tectonophysics 2018, 37, 1648–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Zhang, C.Y.; Fan, T.Y. Stress state of the Baoxing segment of the southwestern Longmenshan Fault Zone before and after the Ms 7.0 Lushan earthquake. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2016, 121, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, M.; Qin, X.; Zhang, C. Characteristics and implications of the stress state in the Longmen Shan fault zone, eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Tectonophysics 2015, 656, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roger, F.; Calassou, S.; Lancelot, J.; Malavieille, J.; Mattauer, M.; Zhiqin, X.; Ziwen, H.; Liwei, H. Miocene emplacement and deformation of the Konga Shan granite (Xianshui He fault zone, west Sichuan, China): Geodynamic implications. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1995, 130, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Shan, X.; Qu, C.; Han, Y.; Zhang, G.; Guo, L.; Zhang, G. The characteristics of post-earthquake surface deformation of the Wenchuan MS8.0 earthquake from InSAR. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 July 2010; pp. 1210–1213. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, G.; Xu, X.; Chen, G.; Liu, Y.; Fukahata, Y.; Wang, H.; Yu, G.; Tan, X.; Xu, C. Geodetic imaging of potential seismogenic asperities on the Xianshuihe-Anninghe-Zemuhe fault system, southwest China, with a new 3-D viscoelastic interseismic coupling model. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2015, 120, 1855–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, M.E.; Simons, M.; Rosen, P.A.; Hensley, S.; WEbb, F.H. Co-seismic slip from the 1995 July 30 Mw= 8.1 Antofagasta, Chile, earthquake as constrained by InSAR and GPS observations. Geophys. J. Int. 2002, 150, 362–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.; Zhang, G.; Shan, X.; Zhang, G.; Song, X.; Liu, Y. Coseismic deformation field derived from ENVISAT/ASAR data and fault slip inversion of Ms7.1 Yushu earthquake, China in 2010. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012; pp. 3879–3882. [Google Scholar]
- Zeitler, P.; Meltzer, A.S.; Koons, P.O.; Craw, D.; Hallet, B.; Chamberlain, C.P.; Kidd, W.F.; Park, S.K.; Seeber, L.; Bishop, M.; et al. Erosion, Himalayan geodynamics, and the geomorphology of metamorphism. GSA Today 2021, 11, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.; House, M.; Royden, L.; Whipple, K.; Burchfiel, B.; Zhang, X.; Tang, W. Late cenozoic uplift of southeastern Tibet. Geology 2005, 33, 525–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Su, Z.; Xu, G. A case study on lateral extrusion occurred along some orogenic belts in China. Chin. J. Geol. 2009, 44, 1266–1288. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, F.; Chen, X.B.; Unsworth, M.J.; Cai, J.T.; Han, B.; Wang, L.F.; Dong, Z.Y.; Tengfa, C.; Zhan, Y.; Zhao, G.Z.; et al. Mechanism for the uplift of Mt Gongga in the southeastern Tibetan Plateau constrained by 3D magnetotelluric data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2021GL097394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Ji, L.; Jiang, F. Variations in locking along the east Kunlun fault, Tibetan Plateau, China, using GPS and leveling data. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2020, 177, 231–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.R. 3-D Numerical Modeling of Tectonic Stress Field in the Eastern Tibetan Plateau and the Seismic Hazard Assessment; China University of Geosciences: Wuhan, China, 2020; pp. 1–154. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.Q. Mountain-Cutting Process in Songpan-Ganzi Orogenic Belt, 3rd ed.; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2008; pp. 154–196. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, W.J. The Geologca Tectonic Foundation of Minya Gongkar Clacial And Its Characteristc Claciac Landforms. J. Chengdu Univ. Sci. Technol. 1982, 3, 19–33. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, X.; Ma, S.; Xu, X.; He, Y. Historical pattern and behavior of earthquake ruptures along the eastern boundary of the Sichuan-Yunnan faulted-block, southwestern China. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 2008, 168, 16–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.Z. A review on active tectonics and deep crustal processes of the Western Sichuan region, eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Tectonophysics 2013, 584, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Long, C.; Fan, T.; Zhou, C.; Feng, H.; Yang, Z.; Tong, Y. The arc rotational-shear active tectonic system on the southeastern margin of Tibetan Plateau and its dynamic characteristics and mechanism. Geol. Bull. China 2015, 34, 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Z.K.; Lü, J.; Wang, M.; Bürgmann, R. Contemporary crustal deformation around the southeast borderland of the TibetanPlateau. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, B11409. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, T.; Wang, P.; Deng, H.; Liu, Y.P.; Tang, W.Q. Petrological records of major tectono-magmatic events since Oligocene in the southeastern segment of Xianshuihe fault zone in the eastern margin of Tibetan Plateau. Geol. Bull. China 2022, 41, 1121–1143. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.Z.; Wen, X.Z.; Shen, Z.K.; Chen, J.H. Oblique high-angle listric-reverse faulting and associated straining processes: The Wenchuan earthquake of 12 May 2008, Sichuan, China. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2010, 38, 353–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Meng, K.; Su, Z.; Meng, Q.; Chu, J.J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, G.; Shi, X.; Liang, X. Block rotation: Tectonic response of the Sichuan basin to the southeastward growth of the Tibetan Plateau along the Xianshuihe-Xiaojiang fault. Tectonics 2014, 33, 686–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.Q.; Yang, J.S.; Li, H.B.; Ji, S.C.; Zhang, Z.M.; Liu, Y. On the Tectonics of the India-Asia Collision. Acta Geol. Sin. 2011, 85, 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.M.; Xu, D.P. FLAC Foundation and Engineering Example, 3rd ed.; China Water Resources and Hydropower Press: Beijing, China, 2009; pp. 127–129. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.B.; Xu, Z.; Wang, R.X. Inversion analysis of abrupt change characteristics of in–situ stress field in Wenchuan earthquake region based on seismic fault displacement. J. Eng. Geol. 2016, 24, 760–767. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, D.; Shan, X.; Gao, Z.; Huang, X.; Gong, W. Coseismic slip model of the 2022 Mw 6.7 Luding (Tibet) earthquake: Pre- and post-earthquake interactions with surrounding major faults. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL102043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Li, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, X.; Dai, K.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J. Kinematic slip evolution during the 2022 Ms 6.8 Luding, China, Earthquake: Compatible with the preseismic locked patch. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2023, 50, e2023GL103164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhao, B.; Xu, R.; Qiao, X.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Lin, M.; Zhao, X.; Nie, Z.; Xiong, W.; et al. Gnss constrained rupture kinematics of the 2022 Mw 6.7 Luding, China, earthquake: Directivity pulse during the asymmetrical bilateral rupture. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2024, 95, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.Q.; Liu, Z.J.; Chen, B.; Li, Z.; Yu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, J. Coseismic Deformation and Slip Distribution of the 2022 Luding Mw 6.6 Earthquake Revealed by In SAR Observations; Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University: Wuhan, China, 2023; Volume 48, pp. 36–46. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, A.; Li, B.; Wang, S.; Liang, S.; Jiang, C.; Wu, J.; Li, Y.; et al. 2022 Mw 6.6 Luding, China, Earthquake: A Strong Continental Event Illuminating the Moxi Seismic Gap. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2023, 94, 2129–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, M.; Wang, Q.; Shen, Z.; Cui, D.; Ji, L.; Li, Y.; Qin, S. Present day crustal vertical movement inferred from precise leveling data in eastern margin of Tibetan plateau. Tectonophysics 2014, 632, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, G.H.; Xu, X.W.; Wen, X.Z.; Wang, Y.L. Kinem Atical Transformation And Slippartitioning of Northern Toeastern Active Boundary Belt of Sichuan-Yunnan block. Seismol. Geol. 2008, 30, 58–85. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, J.; Zhao, D. Teleseismic p-wave tomography and mantle dynamics beneath eastern Tibet. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2016, 17, 1861–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.K.; Royden, L.H. Topographic ooze: Building the eastern margin of Tibetan by lower crustal flow. Geology 2000, 28, 703–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, D.; Unsworth, M.J.; Meju, M.A.; Ma, X.; Teng, J.; Kong, X.; Sun, Y.; Sun, J.; Wang, L.; Jiang, C.; et al. Crustal deformation of the eastern Tibetan plateau revealed by magnetotelluric imaging. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Q.; McCaffrey, R.; Zhang, P.Z. Relative motion across the eastern Tibetan Plateau: Contributions from faulting, internal strain and rotation rates. Tectonophysics 2013, 584, 240–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.B.; Pan, J.W.; Sun, Z.M.; Si, J.; Pei, J.L.; Liu, D.L.; Chevalier, M.L.; Wang, H.; Lu, H.J.; Yong, Z.; et al. Continental tectonic deformation and seismic activity: A case study of the Tibetan Plateau. Acta Geol. Sin. 2021, 95, 194–213. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.W.; Wen, X.Z.; Zheng, R.Z.; Ma, W.T.; Song, F.M.; Yu, G.H. Pattern of latest tectonic motion and its dynamics for active blocks in Sichuan-Yunnan region. China Sci. China (Ser D) 2003, 46, 210–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Seismic Sequence | Magnitud (Mw) | Seismic Depth (km) | Fault Plane I/(°) | Data Source | Beach Volleyball | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strike | Dip | Rake | |||||
| ① | 6.64 | 12 | 254 | 73 | 178 | USGS |  |
| 6.70 | 7 | 76 | 66 | −79 | IPG |  | |
| 6.70 | 7 | 74 | 175 | −79 | GFZ |  | |
| ② | 4.0 | 17 | 36 | 86 | −158 | CENC |  |
| ③ | 3.8 | 9 | 120 | 35 | −130 | CENC |  |
| ④ | 3.8 | 10 | 146 | 47 | −93 | CENC |  |
| ⑤ | 4.5 | 9 | 241 | 84 | 163 | CENC |  |
| ⑥ | 3.8 | 8 | 61 | 67 | −178 | CENC |  |
| ⑦ | 3.8 | 8 | 59 | 79 | −175 | CENC |  |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Z.; Li, Y.; Yi, G.; Zhao, S.; Liu, S. Fault Movement and Uplift Mechanism of Mt. Gongga, Sichuan Province, Constrained by Co-Seismic Deformation Fields from GNSS Observations. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2286. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17132286
Xu Z, Li Y, Yi G, Zhao S, Liu S. Fault Movement and Uplift Mechanism of Mt. Gongga, Sichuan Province, Constrained by Co-Seismic Deformation Fields from GNSS Observations. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(13):2286. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17132286
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Zheng, Yong Li, Guixi Yi, Shaoze Zhao, and Shujun Liu. 2025. "Fault Movement and Uplift Mechanism of Mt. Gongga, Sichuan Province, Constrained by Co-Seismic Deformation Fields from GNSS Observations" Remote Sensing 17, no. 13: 2286. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17132286
APA StyleXu, Z., Li, Y., Yi, G., Zhao, S., & Liu, S. (2025). Fault Movement and Uplift Mechanism of Mt. Gongga, Sichuan Province, Constrained by Co-Seismic Deformation Fields from GNSS Observations. Remote Sensing, 17(13), 2286. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17132286






