SFMattingNet: A Trimap-Free Deep Image Matting Approach for Smoke and Fire Scenes
Abstract
1. Introduction
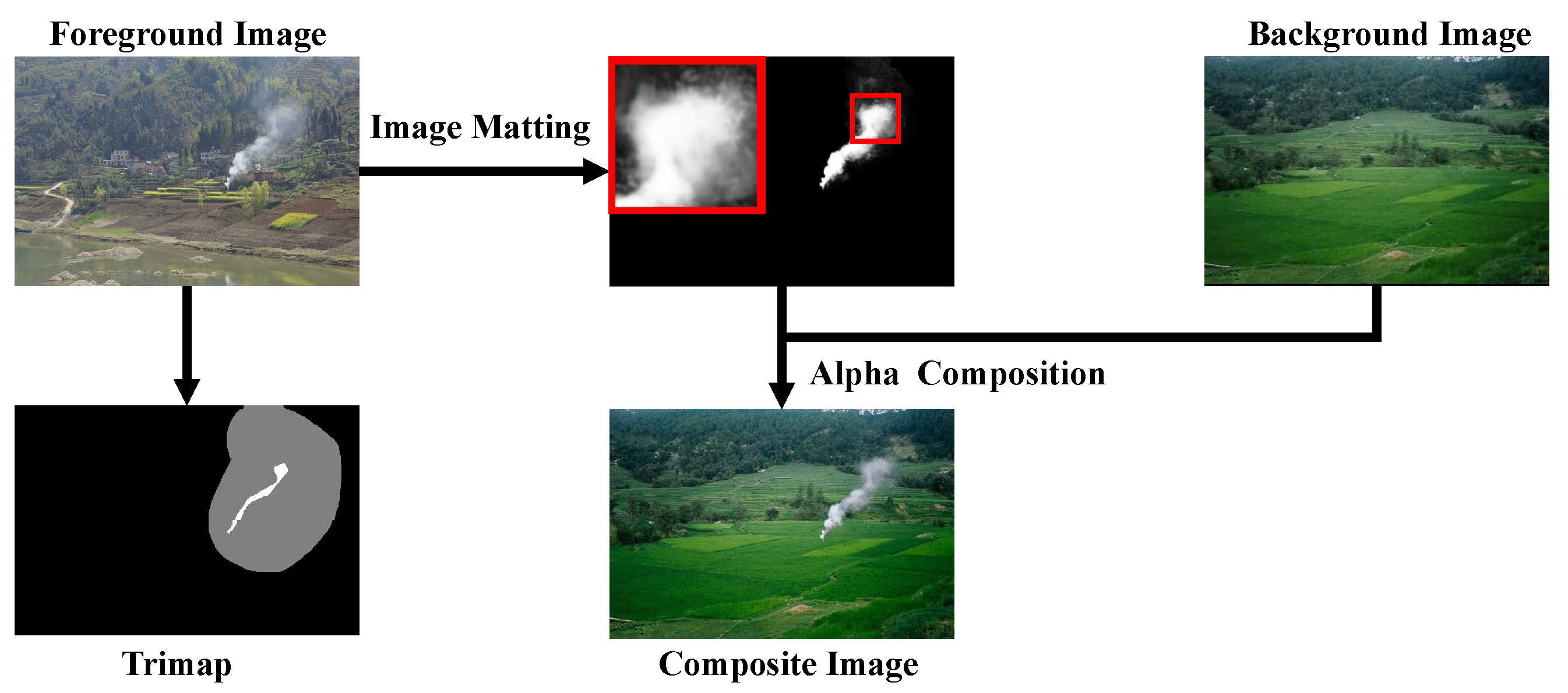
- (1)
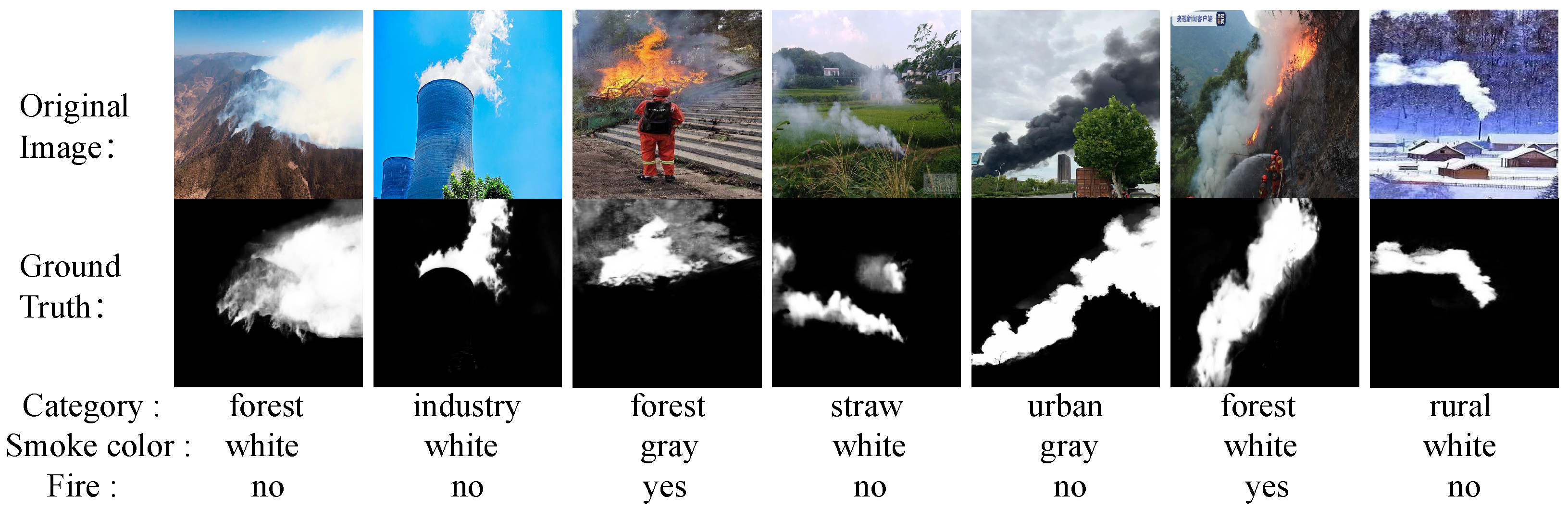
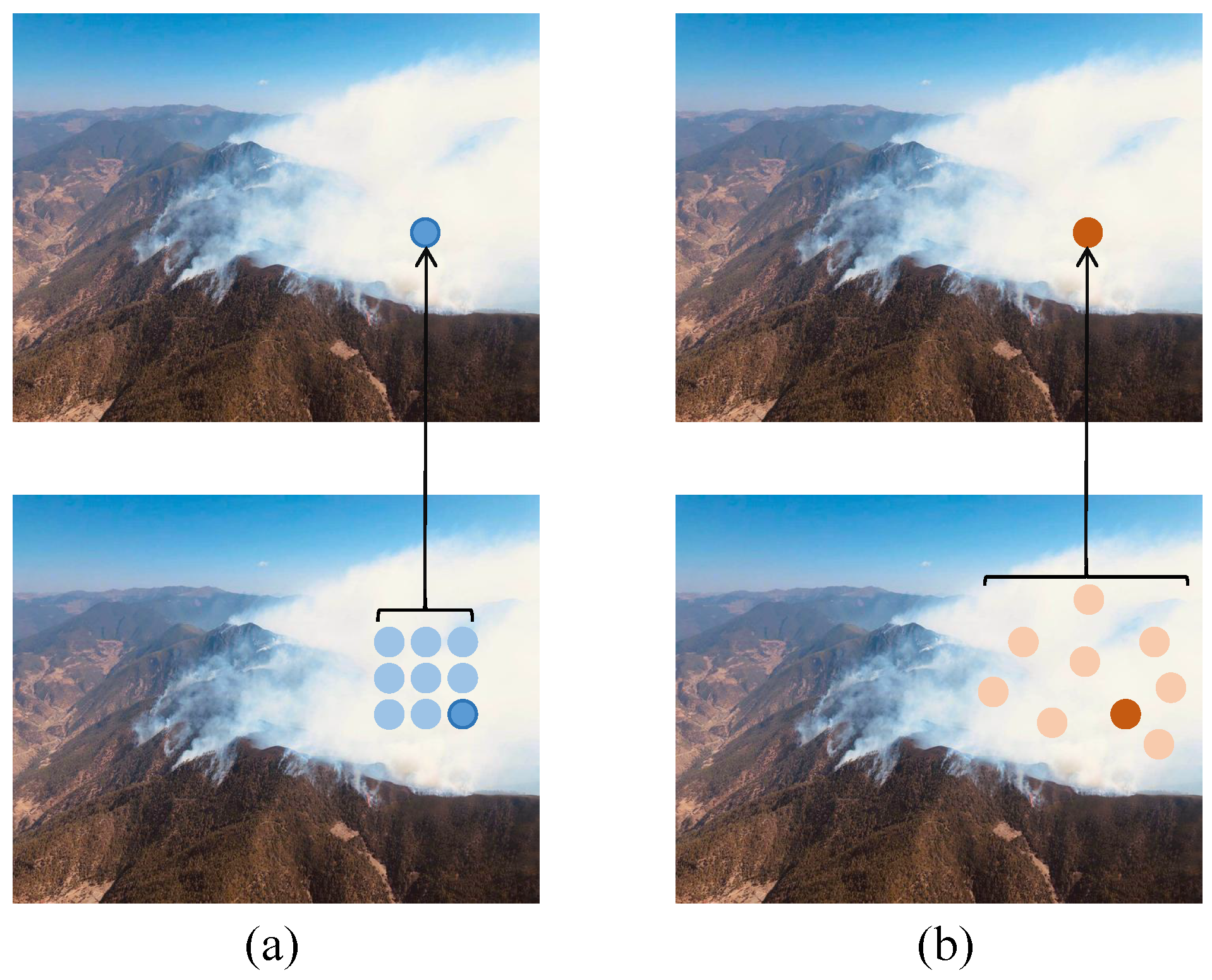
- A high-precision, multi-scene, multi-attribute, and fine-grained smoke and fire image matting dataset, SFMatting-800, was constructed, encompassing factories, rural areas, forests, grasslands, urban environments, etc. This dataset provides precise foreground alpha values and detailed attribute annotations of smoke and fire objects.
- (2)
- Based on the SFMatting-800 dataset, the performance of existing matting methods was evaluated, providing a solid and reliable evaluation benchmark for better model design.
- (3)
- A trimap-free image matting network, SFMattingNet, is proposed, which takes a single image as input without using the trimap. SFMattingNet achieved state-of-the-art performance on the smoke and fire image matting task. Ablation experiments on the SFMatting-800 dataset demonstrated the effectiveness of each module. Compared to other baselines, the proposed SFMattingNet achieves higher accuracy in the alpha value prediction of smoke and fire objects.
2. Related Work
2.1. Image Matting
2.1.1. Traditional Matting Methods
- Propagation-based Image Matting Methods
- Sampling-based Image Matting Methods
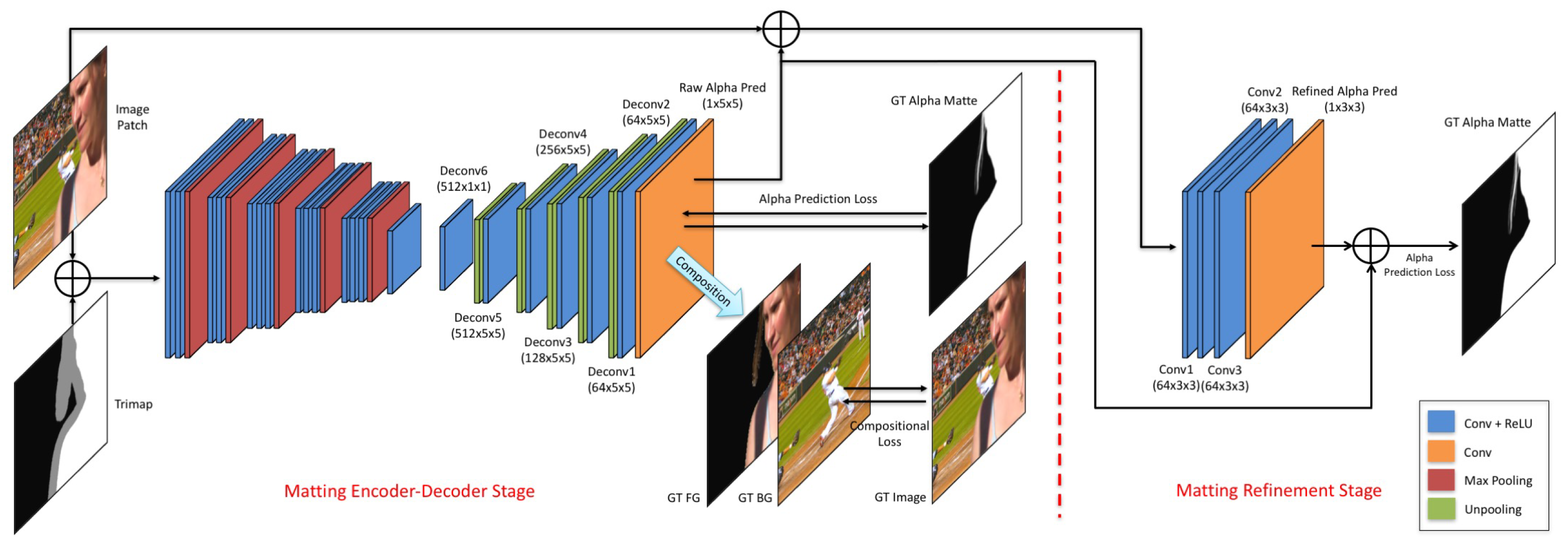
2.1.2. Deep Learning-Based Image Matting Methods
- Methods with Auxiliary Input
- Trimap-Free Methods
2.2. Image Matting Dataset
2.3. Deep Learning-Based Smoke and Fire Detection Methods
2.4. Smoke and Fire Dataset
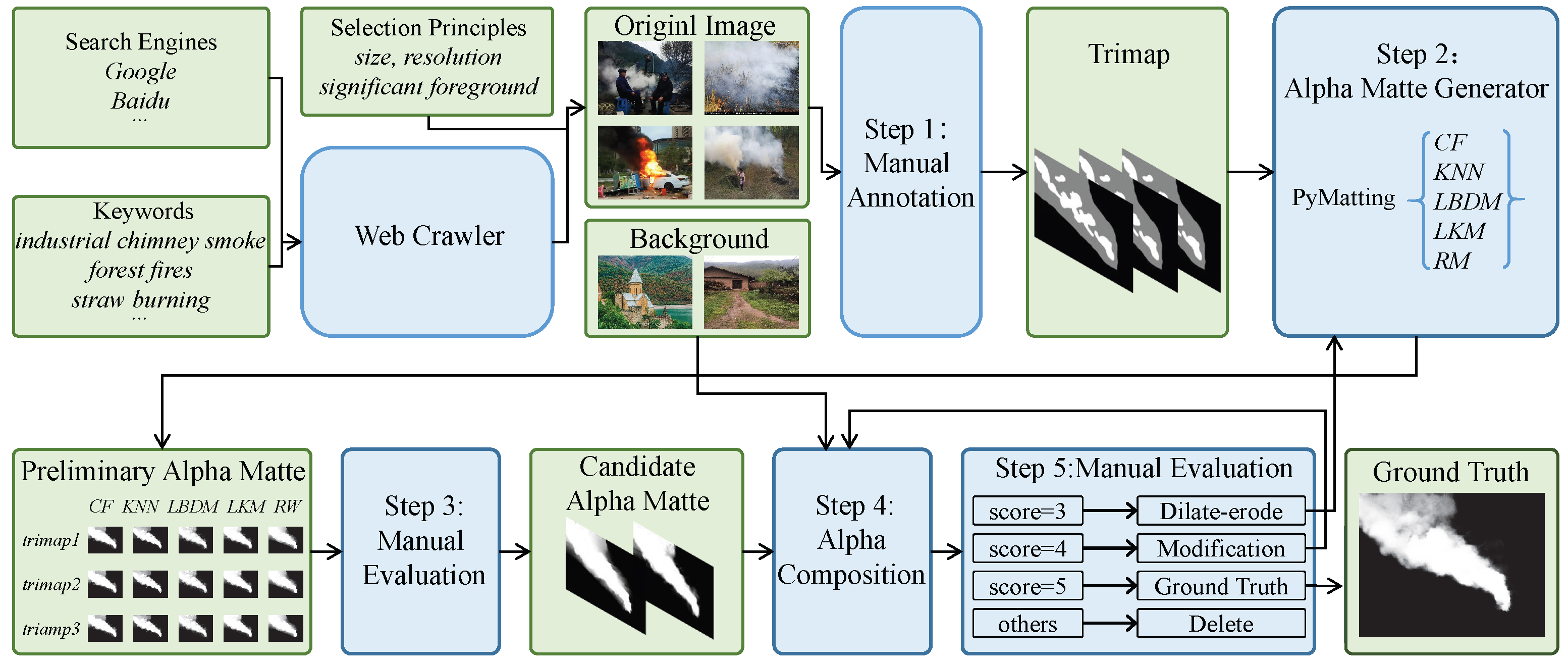
3. Datasets Generation
3.1. Data Collection
3.2. Data Filtering
3.3. Data Annotation
3.4. Data Quality Control
4. Methods
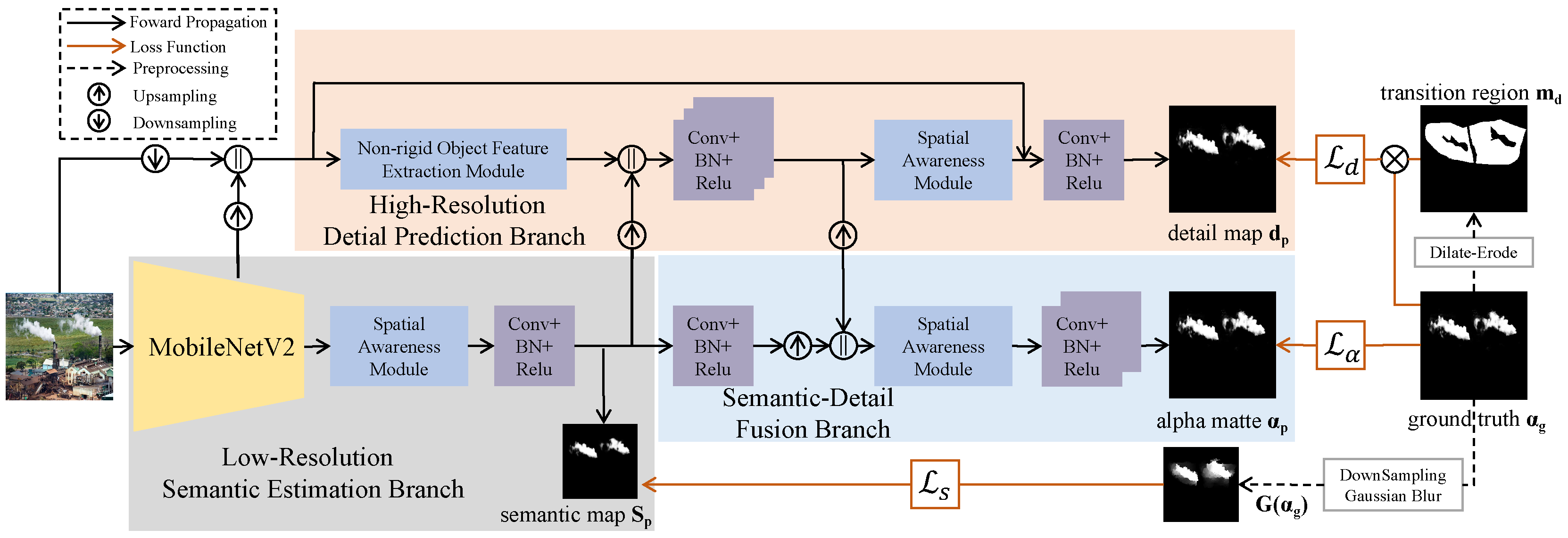
4.1. Framework of SFMattingNet
4.1.1. Low-Resolution Semantic Estimation Branch
4.1.2. High-Resolution Detail Estimation Branch
4.1.3. Semantic-Detail Fusion Branch
4.2. Non-Rigid Object Feature Extraction Module
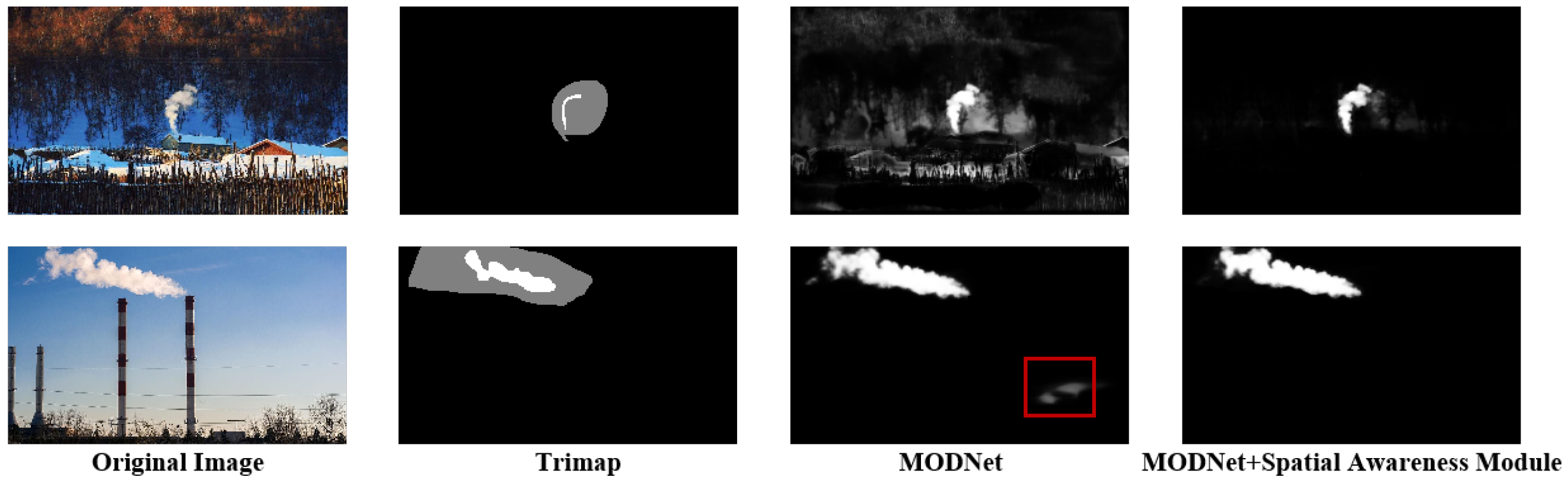
4.3. Spatial Awareness Module
4.4. Loss Function
4.4.1. The Loss Function for Low-Resolution Semantic Estimation Branch
4.4.2. The Loss Function for High-Resolution Detail Estimation Branch
4.4.3. The Loss Function for Semantic-Detail Fusion Branch
5. Experiments
5.1. Evaluation Metrics
5.2. Overall Experiments
5.2.1. Traditional Image Matting Methods
5.2.2. Trimap-Based Deep Image Matting Methods
5.2.3. Trimap-Free Deep Image Matting Methods
5.3. Ablation Experiments
5.3.1. Quantitative Analysis
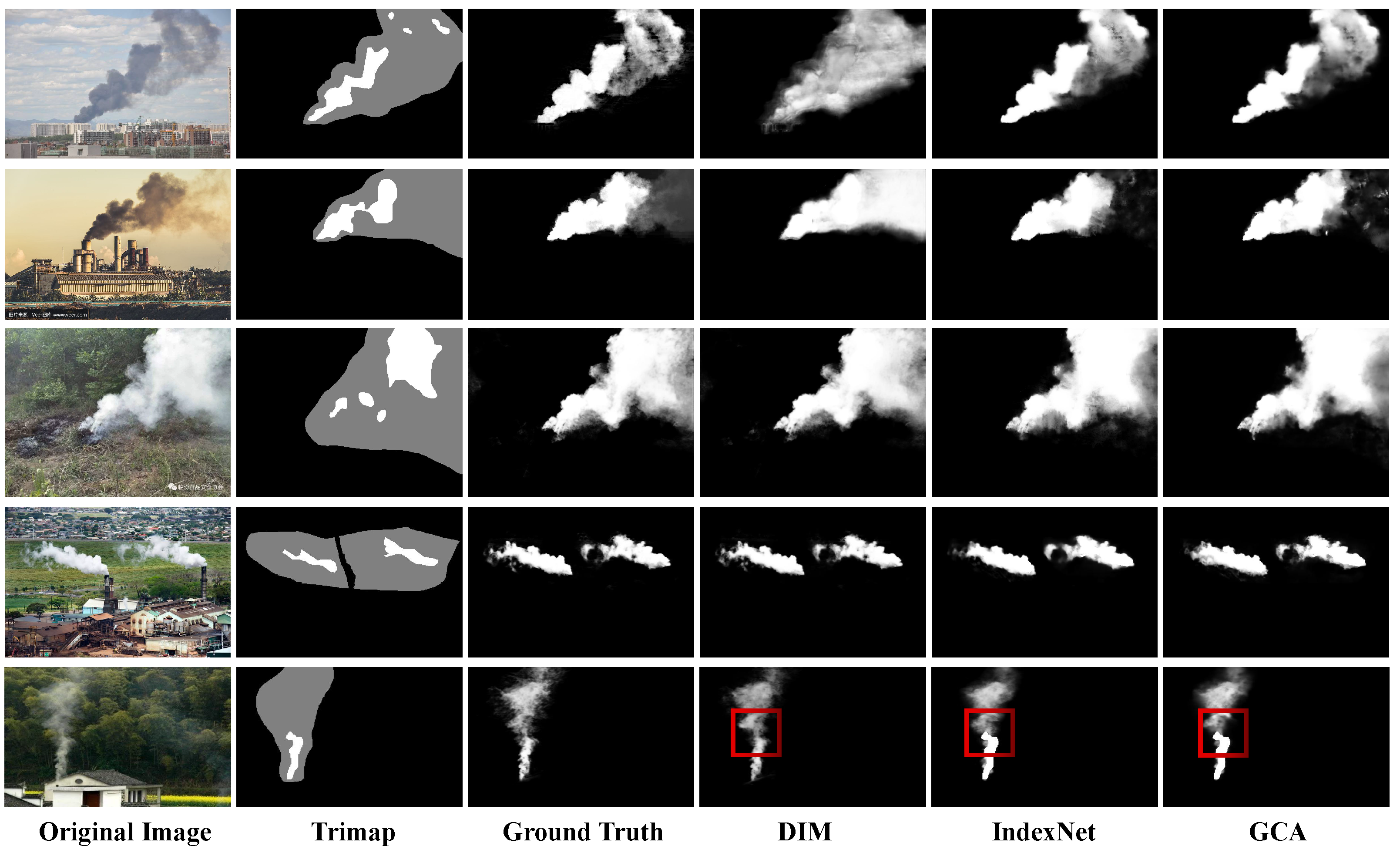
5.3.2. Visual Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, H.; Jin, J.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Shen, Y. FSDF: A high-performance fire detection framework. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 238, 121665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, T. Fast and efficient method for fire detection using image processing. ETRI J. 2010, 32, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunnings, A.J.; Breckon, T.P. Experimentally defined convolutional neural network architecture variants for non-temporal real-time fire detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 1558–1562. [Google Scholar]
- de Venancio, P.V.A.; Lisboa, A.C.; Barbosa, A.V. An automatic fire detection system based on deep convolutional neural networks for low-power, resource-constrained devices. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 15349–15368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Zhang, J.; Barnes, N. Transmission-guided bayesian generative model for smoke segmentation. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Online Conference, 22 February–1 March 2022; pp. 3009–3017. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad, K.; Khan, S.; Elhoseny, M.; Ahmed, S.H.; Baik, S.W. Efficient fire detection for uncertain surveillance environment. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 15, 3113–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaabi, R.; Sayadi, M.; Bouchouicha, M.; Fnaiech, F.; Moreau, E.; Ginoux, J.M. Early smoke detection of forest wildfire video using deep belief network. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Technologies for Signal and Image Processing, Sousse, Tunisia, 21–24 March 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Muhammad, K.; Hussain, T.; Del Ser, J.; Cuzzolin, F.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Akhtar, Z.; de Albuquerque, V.H.C. Deepsmoke: Deep learning model for smoke detection and segmentation in outdoor environments. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 182, 115125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Zhang, L.; Xia, X.; Huang, Q.; Li, X. A gated recurrent network with dual classification assistance for smoke semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 4409–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, Z.; Wu, Q.J.; Liu, C. 3D parallel fully convolutional networks for real-time video wildfire smoke detection. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2018, 30, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Zhang, L.; Xia, X.; Huang, Q.; Li, X. A wave-shaped deep neural network for smoke density estimation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 29, 2301–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lin, G.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, G.; Wang, J. Wildland forest fire smoke detection based on faster R-CNN using synthetic smoke images. Procedia Eng. 2018, 211, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Feng, J. Fire and smoke precise detection method based on the attention mechanism and anchor-free mechanism. Complex Intell. Syst. 2023, 9, 5185–5198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhao, L.; Liu, P.; Huang, D. Fire smoke detection algorithm based on motion characteristic and convolutional neural networks. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2018, 77, 15075–15092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Tao, D. Deep image matting: A comprehensive survey. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.04672. [Google Scholar]
- Zolfi, A.; Kravchik, M.; Elovici, Y.; Shabtai, A. The translucent patch: A physical and universal attack on object detectors. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Online Conference, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 15232–15241. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.; Ding, K.; Yan, H. SFMatting-800: A multi-scene smoke and fire image matting dataset for fine-grained fire detection. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computer Engineering, Dalian, China, 17–19 November 2023; pp. 22–30. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, Z.; Sun, J.; Li, K.; Yan, Q.; Lau, R.W.H. MODNet: Real-Time Trimap-Free Portrait Matting via Objective Decomposition. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Online Conference, 22 February–1 March 2022; pp. 1140–1147. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, H.; Xue, F.; Xu, L.; Guo, L. TransMatting: Tri-token equipped transformer model for image matting. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.06476. [Google Scholar]
- Levin, A.; Lischinski, D.; Weiss, Y. A Closed-Form Solution to Natural Image Matting. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2008, 30, 228–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Li, D.; Tang, C. KNN Matting. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 35, 2175–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grady, L.; Schiwietz, T.; Aharon, S.; Westermann, R. Random walks for interactive alpha-matting. In Proceedings of the ICVIP, Benidorm, Spain, 7–9 September 2005; pp. 423–429. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Jia, J.; Tang, C.K.; Shum, H.Y. Poisson matting. ACM Trans. Graph. 2004, 23, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Rhemann, C.; Rother, C.; Tang, X.; Sun, J. A global sampling method for alpha matting. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 20–25 June 2011; pp. 2049–2056. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Cohen, M.F. Optimized color sampling for robust matting. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 17–22 June 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Shahrian, E.; Rajan, D.; Price, B.; Cohen, S. Improving image matting using comprehensive sampling sets. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 636–643. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.; Liang, X.; Zhang, Z. A cluster sampling method for image matting via sparse coding. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 204–219. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, N.; Price, B.L.; Cohen, S.; Huang, T.S. Deep Image Matting. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 311–320. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Xu, N.; Bai, Y.; Yuille, A. Mask guided matting via progressive refinement network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Online Conference, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 1154–1163. [Google Scholar]
- Sengupta, S.; Jayaram, V.; Curless, B.; Seitz, S.M.; Kemelmacher-Shlizerman, I. Background matting: The world is your green screen. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 2291–2300. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Qiao, Y.; Chen, S.; He, S.; Yin, B.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, X.; Lau, R.W. Smart scribbles for image matting. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl. 2020, 16, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, C.; Jiang, X. Deep interactive image matting with feature propagation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 2421–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; Ramesh, A.; Goh, G.; Agarwal, S.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Mishkin, P.; Clark, J.; et al. Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Online Conference, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 8748–8763. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Lutz, S.; Amplianitis, K.; Smolic, A. Alphagan: Generative adversarial networks for natural image matting. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.10088. [Google Scholar]
- Karras, T.; Laine, S.; Aila, T. A style-based generator architecture for generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 4401–4410. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.; Dai, Y.; Shen, C.; Xu, S. Indices Matter: Learning to Index for Deep Image Matting. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 3265–3274. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Lu, H. Natural Image Matting via Guided Contextual Attention. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; pp. 11450–11457. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Aksoy, Y.; Oztireli, C.; Gross, M.; Aydin, T.O. Learning-based sampling for natural image matting. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3055–3063. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Q.; Liu, F. Context-aware image matting for simultaneous foreground and alpha estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 4130–4139. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, S.; Zhang, X.; Fan, H.; Huang, H.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Sun, J. Disentangled image matting. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 8819–8828. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.; Tao, X.; Gao, H.; Zhou, C.; Jia, J. Deep automatic portrait matting. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 92–107. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Gong, L.; Fan, L.; Ren, P.; Huang, Q.; Bao, H.; Xu, W. A late fusion cnn for digital matting. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 7469–7478. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Maybank, S.J.; Tao, D. Bridging Composite and Real: Towards End-to-End Deep Image Matting. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2022, 130, 246–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Peng, J.; Hao, Y.; Chu, L.; Tang, S.; Wu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Yu, Z.; et al. PP-Matting: High-Accuracy Natural Image Matting. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.09433. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Tao, D. Deep automatic natural image matting. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Online Conference, 19–26 August 2021; pp. 800–806. [Google Scholar]
- Rhemann, C.; Rother, C.; Wang, J.; Gelautz, M.; Kohli, P.; Rott, P. A perceptually motivated online benchmark for image matting. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 1826–1833. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhou, D.; Xu, M.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, X. Attention-guided hierarchical structure aggregation for image matting. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 13676–13685. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Xie, J.; Shi, X.; Qiao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Yang, X. Tripartite information mining and integration for image matting. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision, Online Conference, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 7555–7564. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Ma, S.; Zhang, J.; Tao, D. Privacy-preserving portrait matting. In Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Chengdu, China, 20–24 October 2021; pp. 3501–3509. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, X.; Liu, R.; Li, B. A dataset for fire and smoke object detection. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 6707–6726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chino, D.Y.; Avalhais, L.P.; Rodrigues, J.F.; Traina, A.J. Bowfire: Detection of fire in still images by integrating pixel color and texture analysis. In Proceedings of the Conference on Graphics, Patterns and Images, Salvador, Brazil, 26–29 June 2015; pp. 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Kambhamettu, C. Learning based digital matting. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Kyoto, Japan, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 889–896. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Sun, J.; Tang, X. Fast matting using large kernel matting Laplacian matrices. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; pp. 2165–2172. [Google Scholar]
- Berman, A.; Vlahos, P.; Dadourian, A. Comprehensive Method for Removing From an Image the Background Surrounding a Selected Subject. U.S. Patent 6,134,345, 17 October 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Kendall, A.; Gal, Y.; Cipolla, R. Multi-task learning using uncertainty to weigh losses for scene geometry and semantics. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7482–7491. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.; Qi, H.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y. Deformable convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 764–773. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, X.; Huang, L.; Huang, C.; Wei, Y.; Liu, W. Ccnet: Criss-cross attention for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 603–612. [Google Scholar]
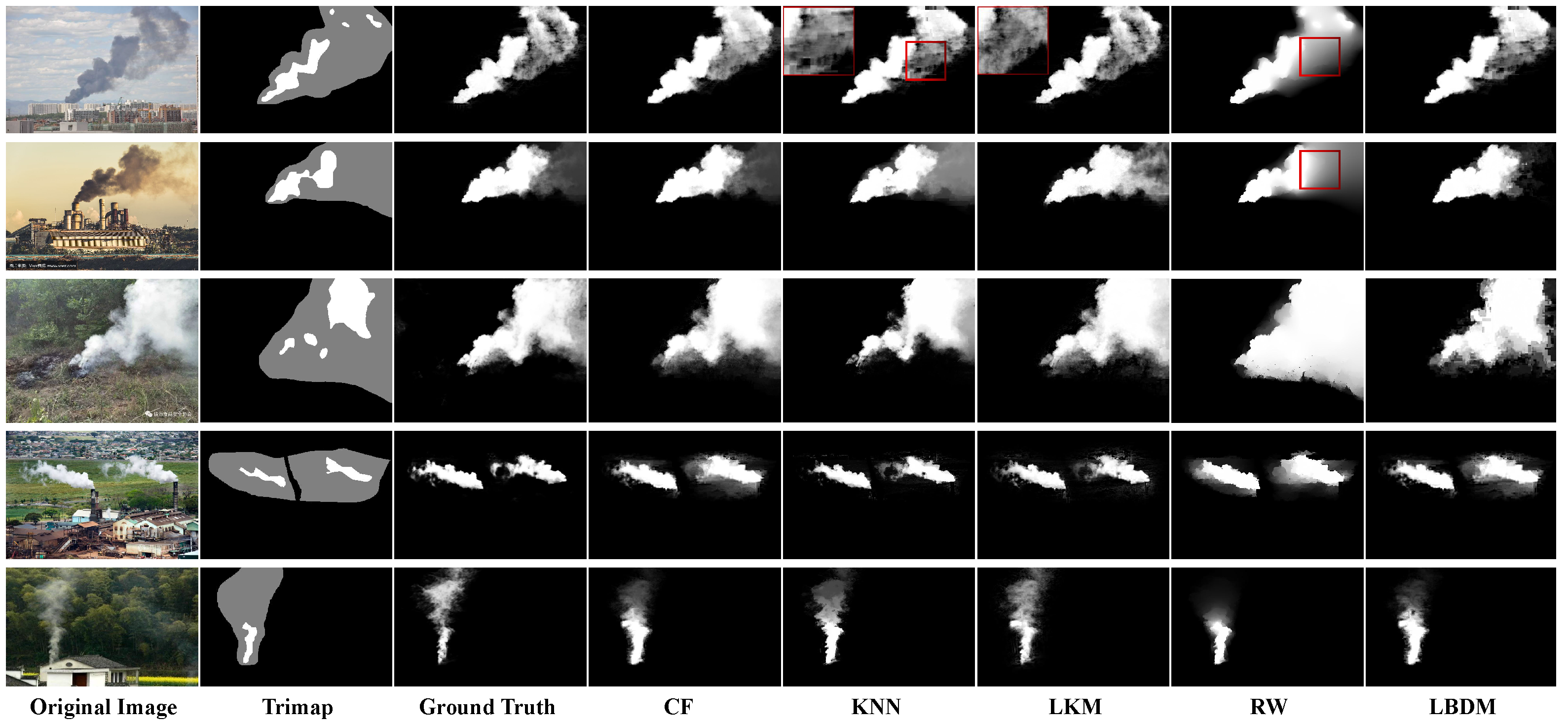





| Method Group | Method | SAD ↓ | MSE ↓ | Grad ↓ | Conn ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Matting Methods | CF Matting [20] | 23.402 | 0.067 | 3.670 | 23.838 |
| KNN Matting [21] | 19.108 | 0.035 | 4.620 | 19.587 | |
| LKM [56] | 21.009 | 0.042 | 3.583 | 21.186 | |
| RW Matting [22] | 35.599 | 0.111 | 6.290 | 37.226 | |
| LBDM [55] | 26.990 | 0.080 | 7.361 | 27.399 | |
| Trimap-based Matting Methods | DIM [28] | 13.038 | 0.034 | 2.189 | 13.051 |
| IndexNet [38] | 18.910 | 0.025 | 2.525 | 18.760 | |
| GCA Matting [39] | 18.571 | 0.024 | 2.170 | 18.426 |
| Method | SAD ↓ | SAD- ALL ↓ | MSE ↓ | MSE- ALL ↓ | Grad ↓ | Grad- ALL ↓ | Conn ↓ | Conn- ALL ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MODNet [18] | 15.131 | 43.881 | 0.031 | 0.013 | 2.231 | 3.697 | 15.046 | 42.704 |
| GFM [46] | 17.746 | 50.658 | 0.049 | 0.025 | 2.558 | 5.744 | 17.966 | 50.224 |
| PP-Matting [47] | 17.256 | 48.853 | 0.058 | 0.026 | 2.699 | 5.141 | 17.111 | 48.470 |
| SFMattingNet (ours) | 13.161 | 33.553 | 0.029 | 0.011 | 2.293 | 3.485 | 12.734 | 32.262 |
| Module1 | Module2 | SAD | SAD-ALL | MSE | MSE-ALL | Grad | Grad-ALL | Conn | Conn-ALL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| × | × | 15.131 | 43.881 | 0.031 | 0.013 | 2.231 | 3.697 | 15.046 | 42.704 |
| ✓ | × | 15.854 | 36.627 | 0.030 | 0.011 | 2.263 | 3.513 | 15.782 | 35.707 |
| × | ✓ | 13.978 | 37.501 | 0.028 | 0.012 | 2.244 | 3.411 | 13.775 | 36.524 |
| ✓ | ✓ | 13.161 | 33.553 | 0.029 | 0.011 | 2.293 | 3.485 | 12.734 | 32.262 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, S.; Xu, Z.; Yan, H. SFMattingNet: A Trimap-Free Deep Image Matting Approach for Smoke and Fire Scenes. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2259. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17132259
Ma S, Xu Z, Yan H. SFMattingNet: A Trimap-Free Deep Image Matting Approach for Smoke and Fire Scenes. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(13):2259. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17132259
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Shihui, Zhaoyang Xu, and Hongping Yan. 2025. "SFMattingNet: A Trimap-Free Deep Image Matting Approach for Smoke and Fire Scenes" Remote Sensing 17, no. 13: 2259. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17132259
APA StyleMa, S., Xu, Z., & Yan, H. (2025). SFMattingNet: A Trimap-Free Deep Image Matting Approach for Smoke and Fire Scenes. Remote Sensing, 17(13), 2259. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17132259





