Abstract
This study integrates the analysis of surface temperature data with natural and anthropogenic factors closely related to the urban thermal environment in Nanjing from 2000 to 2020, exploring the spatiotemporal variation characteristics of the urban heat island effect and the interactive relationships among its influencing factors. The research findings are as follows: (1) Between 2000 and 2020, the urban heat island effect in Nanjing exhibited an expansion trend radiating from the city center to the periphery, with the heat island phenomenon primarily concentrated in the old urban areas characterized by developed commerce, industry, and dense populations. Surface temperatures gradually decreased from the city center to the suburbs, forming a distinct spatial distribution gradient. Both the standard deviation ellipse and the centroid of high-temperature areas showed a southward shift. (2) Significant differences in surface temperatures were observed across different land use types, with built-up areas and arable land maintaining relatively stable and higher surface temperatures, while water bodies and forests exhibited lower and stable surface temperatures. (3) Vegetation coverage, normalized water body index, elevation, dispersion, and the Shannon diversity index were negatively correlated with surface temperature, while the normalized difference bare land index, building index, dispersion index, and patch cohesion index were positively correlated with surface temperature. In Nanjing, the interactive effects of dual factors on the urban heat island effect were found to be greater than those of individual factors, with vegetation coverage identified as the most critical factor affecting surface temperature. Considering multidimensional factors together enhances the understanding of the spatial patterns and causes of the urban heat island effect, clarifies the interrelationships and degrees of influence among natural, socio-economic, and landscape pattern factors, and provides a scientific basis for improving the quality of the living environment in Nanjing.
1. Introduction
Rapid urbanization drives significant fuel consumption through urban transportation, industrial production, and residential activities [1]. However, inefficient energy use and poor management systems lead to the substantial discharge of “three wastes”, a regulatory term referring to industrial wastewater, exhaust gas, and solid waste in China, which may indirectly exacerbate urban heat island effects through multiple pathways. For instance, industrial waste gas emissions contribute to greenhouse gas accumulation [2], while impervious surfaces from urban waste disposal sites alter the surface albedo [3]. These anthropogenic disturbances collectively degrade urban ecosystems and thermal environments. Prolonged exposure to the heat island effect may lead to problems in human cardiovascular and respiratory systems, which has significant implications for building a healthy, comfortable, livable, and sustainable urban living environment [4,5,6,7,8]. Currently, the mechanisms of the heat island effect have become one of the research hotspots in disciplines such as geography, environmental science, urban planning, and architecture [9,10].
The urban heat island (UHI) effect typically refers to the phenomenon where the atmospheric temperature in urban areas is significantly higher than that in surrounding rural regions. In contrast, the surface urban heat island (SU-HI) effect is based on the differences in land surface temperature (LST) between urban and rural areas. Compared with the UHI, the SU-HI exhibits stronger spatial variability and can more directly reflect surface characteristics and human disturbances [11,12]. Extensive research into the surface urban heat island (SUHI) has been conducted both domestically and internationally. In terms of research scale, the existing studies have primarily focused on macroscopic scales at the national or global level [13], regional scales of large urban agglomerations [14], local scales of individual cities [15], and microscopic scales of small areas such as neighborhoods [16]. For instance, Peng et al. [17] analyzed data from 419 global cities to reveal the universal associations between heat island intensity and biophysical factors, but these findings failed to reflect region-specific characteristics. Qin et al. [18] provided a case study of the Beibu Gulf urban agglomeration, capturing regional synergistic effects but downplaying the dynamic details of individual cities. Lin et al. [19] explored the relationship between three-dimensional urban form and heat islands, which is spatially targeted but lacks multi-temporal evolution analysis. While neighborhood-scale microscopic studies can elucidate the mechanisms of local thermal environments, they struggle to support city-level planning decisions.
In terms of data utilization, surface heat islands derived from land surface temperature (LST) data have proven to be highly effective in elucidating the patterns of regional energy flux and in highlighting more pronounced spatiotemporal variations. Such data are particularly adept at reflecting surface characteristics and the impacts of human activities [20]. However, due to challenges such as high observation altitudes and a scarcity of observation stations, many existing studies have had to rely on remotely sensed radiative land-surface temperatures [21]. For instance, Zargari et al. [22] conducted a comparative analysis of data from three distinct satellites and concluded that MODIS data are especially well-suited for examining heat island patterns at medium and large scales. Huang et al. [23] utilized the MOD11A1 data product to investigate the summer heat island effect in China’s seven “furnace cities” over the decade from 2013 to 2023. While their study successfully established a correlation between heat islands and urban expansion, the inherent instantaneous fluctuations in daily data impeded the reliability of the long-term trend analysis. Drawing on these comparative insights, this study opts for the MOD11A2 data product as the land surface temperature dataset. This particular data product, which undergoes an 8-day synthesis process, not only ensures the stability of the time series but also provides the benefit of spatial continuity. It is capable of effectively mitigating the high-frequency noise interference that is characteristic of daily-scale data, while simultaneously preserving the capacity to discern the urban–suburban temperature gradient.
Existing studies on the urban heat island (UHI) effect have employed varying methods depending on the scale and subject of the research. In terms of data acquisition, remote sensing monitoring, leveraging its spatial coverage advantages, has become the mainstream approach for quantifying LST [24,25]. In contrast, meteorological data analysis is more suitable for local climate validation [26]. Regarding analytical methods, correlation analysis can initially identify linear relationships between temperature and factors [27], but it struggles to capture nonlinear interactions. Numerical simulation, although capable of predicting UHI dynamics, is limited by the accuracy of parameterization schemes [28]. For example, Xi et al. [29] combined Pearson correlation analysis with the geographical detector to reveal the spatial heterogeneity of UHI influenced by urban form, but their study did not quantify the synergistic effects of natural and anthropogenic factors. Rajagopal et al. [30] established a temperature–landscape association model using multimodal data but did not consider the moderating role of topographical factors. These limitations indicate that the current research needs to integrate multi-source data and multidimensional analytical methods to systematically parse the compound driving mechanisms of the urban-surface heat island effect. Addressing this gap, this study innovatively proposes an integrated research framework of data quantification–spatial analysis–factor synergy. First, it standardizes the quantification of land surface temperature based on long-term MODIS data. Then, it systematically analyzes the spatial clustering patterns of heat islands by combining spatial autocorrelation and landscape index methods. Finally, it deeply dissects the nonlinear interactions between natural and anthropogenic factors by combining the geographical detector with principal component analysis, thereby improving the single statistical model used by Rajagopal et al. [30].
Based on different research methods, existing studies have conducted in-depth investigations into various factors affecting urban surface heat island effects. For example, Cai [31] analyzed the significant role of urban parks in mitigating the urban heat island effect from the perspective of landscape patterns within parks. Han [32] examined the influence of parks on alleviating the urban heat island effect under extreme heat and normal weather conditions from a weather perspective. Ahmed [33] studied how the heat island effect impacts the use of public spaces in the Rome area from an urban spatial viewpoint and redesigned the sites in Rome accordingly. Muhammad [34] analyzed the impact of land use and land cover (LULC) factors on surface temperature and urban heat island effects based on LULC data from the Nowshera District in Pakistan from 2008 to 2018.
Despite the extensive research conducted by scholars on the spatiotemporal distribution characteristics and influencing mechanisms of the urban heat island effect, there are still several areas requiring improvement in the existing studies. Existing studies have extensively explored the mechanisms of individual influencing factors. However, in terms of the systematic analysis of interactive effects among multiple factors, especially in rapidly urbanizing areas, how to conduct a holistic analysis of the urban surface heat island effect by integrating multidimensional factors such as natural and human elements still needs to be further enriched. Secondly, the existing research often shows a disconnect between temporal and spatial dimensions. Many studies emphasize long-term evolutionary analysis while neglecting spatial heterogeneity. Others focus primarily on spatial pattern analysis without exploring dynamic evolutionary mechanisms in depth.
As a megacity in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, Nanjing provides a distinctive sample for studying the heat island effect. Influenced by the relatively low elevation of the Yangtze River valley and the local impact of surrounding hills, the city faces difficulties in surface heat dissipation, resulting in significantly higher temperatures than surrounding areas, classifying it as one of the “Four Major Oven Cities” in China. Additionally, due to its dense population and tall buildings, the urban heat island effect in Nanjing is pronounced [35,36], making the study of its spatiotemporal differentiation characteristics and influencing factors of great theoretical value and practical significance.
Based on this, this study combines the annual average surface temperature data from Nanjing between 2000 and 2020 to conduct a graded quantification of surface temperatures using the standard deviation method. It analyzes the spatiotemporal variation characteristics of the urban heat island effect in Nanjing through standard deviation ellipses and centroid migration. Furthermore, by employing geographic detectors, principal component analysis, and Pearson correlation coefficient analysis from the perspectives of landscape pattern distribution, socioeconomic conditions, and topography, this research aims to uncover the driving mechanisms behind Nanjing’s urban heat island effect. The findings are expected to provide a reference for Nanjing’s strategies to address summer urban heat island issues and inform future urban planning.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Nanjing is located in eastern China, on the lower reaches of the Yangtze River, adjacent to the river and the sea, with geographical coordinates ranging from 31°14′ to 32°37′N and 118°22′ to 119°14′E (Figure 1). The city experiences a humid subtropical climate with distinct seasons, an annual average temperature of 15.4 °C, and extreme annual temperatures reaching as high as 39.7 °C and as low as −13.1 °C [37]. Nanjing has short spring and autumn seasons, while winter and summer are climatically significant, exhibiting a significant temperature difference between the two, which has categorized it as one of China’s traditional “oven cities.” As early as the Republic of China period, Chongqing, Wuhan, and Nanjing were considered very hot cities in summer, collectively referred to as the “Three Major Ovens.” In Nanjing, summer temperatures are often high and humid, with some years having more than 70 days where the daily maximum temperature exceeds 30 °C, including occurrences of extreme heat above 40 °C [38]. In response to urban heat island effects and to enhance urban habitat quality, Nanjing’s municipal government has integrated thermal environment mitigation strategies into its urban and rural planning framework [39,40].
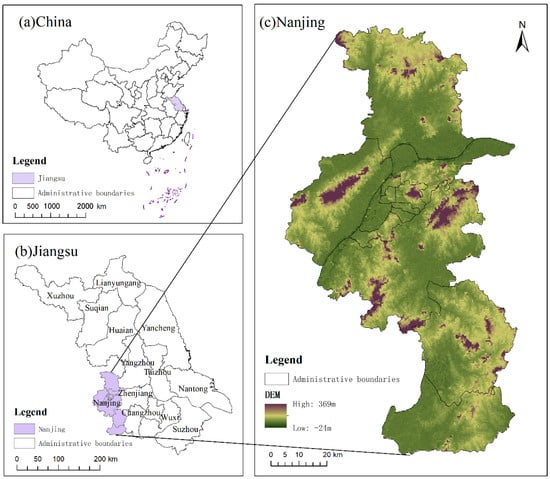
Figure 1.
Study area of Nanjing, China: (a) China; (b) Jiangsu province; (c) topography of Jiangsu Province.
2.2. Data
The surface temperature data for this study were sourced from the Resource and Environment Data Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, specifically selecting the annual 1 km surface temperature LST dataset for Jiangsu Province from 2000 to 2020 [41]. This dataset is derived from the MODIS land surface temperature data product (MOD11A2), which calculates the annual average daytime and night-time LST data, with a spatial resolution of 1 km. For the surface information inversion data, we selected the Landsat 8 multispectral and thermal infrared remote sensing images from 17 June 2020, at 14:20 p.m., which can be accessed via the provided link (http://www.gscloud.cn, accessed on 20 February 2025).Surface information inversion data were derived from Landsat 8 multispectral imagery and represent key surface parameters for analyzing how urban land cover characteristics influence the heat island effect. The remote sensing imaging was conducted at noon during the summer, under clear weather conditions, with less than 1% cloud cover in the study area, providing favorable conditions for remote sensing imaging. The DEM data used in this study were obtained from the Data Center for Resources and Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences. This dataset was generated by resampling the latest SRTM V4.1 data. The data were projected using the WGS84 ellipsoid, and for this study, the 1 km resolution DEM data were selected.
2.3. Method
This study is divided into three core phases (Figure 2). First, we conducted spatial clipping and projection transformation on the annual 1 km land surface temperature (LST) dataset of Jiangsu Province from 2000 to 2020, provided by the Data Center for Resources and Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences. This process yielded a 1 km resolution LST dataset for Nanjing from 2000 to 2020. Additionally, based on Landsat 8 imagery, we extracted vegetation cover and the modified normalized difference water index (MNDWI) to reflect the spatial distribution of vegetation and water bodies on the ground. Second, this study employed the standard deviation method and spatial autocorrelation analysis to investigate the spatiotemporal variations in the urban heat island effect, identifying trends in high-temperature area expansion and aggregation patterns, along with temperature differences across various land use types. Finally, integrating both natural and human factors, Pearson correlation analysis and geographic detectors were utilized to assess the influence of multidimensional factors on surface temperature and their synergistic effects, clarifying the cooling mechanisms involving vegetation coverage, topography, and landscape patterns.
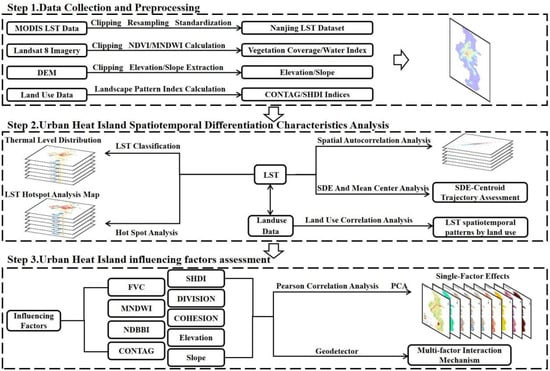
Figure 2.
Research framework.
2.3.1. Urban Heat Island Ratio Index (URI)
URI is a quantitative measure of the intensity of the heat island effect [42,43]. This index provides a basis for the quantitative comparison of urban heat island effects at different time points, allowing for a scientific measurement and comparison of the development degree of urban heat islands over time. The URI has been referenced by the Ministry of Environmental Protection and the Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of China and is widely used in research on urban thermal environment changes.
The index characterizes the development degree of heat islands by calculating the ratio of heat island area to built-up area and assigning weights, enabling a more scientific comparison of urban heat island changes across different years. A larger index value indicates a more severe heat island effect. The URI reflects the proportional relationship between the heat island area and urban built-up area, and its calculation formula is as follows:
where is the weight assigned to the i-th level, with high-temperature zones and sub-high-temperature zones having weight values of 5 and 4, respectively; is the area proportion of the i-th level; m is the normalized number of temperature levels, which is 5 in this study; and n is the number of temperature levels in urban areas that exceed those in suburban areas, which is 2 in this study.
2.3.2. Surface Information Acquisition
Fractional vegetation cover (FVC) refers to the proportion of the vertical projection area of ground vegetation leaves to the total calculated area [44]. The calculation formula is as follows:
Modified Normalized Difference Water Index (MNDWI) is used to normalize the difference of image bands containing water body information [45]. The calculation formula is as follows:
Normalized Difference Bare Soil And Building Index (NDBBI) involves directly removing water body and vegetation information from remote sensing images and normalizing the difference for bare soil and built-up land information:
where Green, Red, NIR, SWIR1, and SWIR2 correspond to bands 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7 of the Landsat 8 remote sensing images, respectively.
Landscape Pattern Indices are comprehensive indicators used to evaluate and analyze the spatial structure, landscape functions, and ecological service capabilities of regional landscapes. Based on landscape ecology theory, these indices reflect the composition, configuration, and environmental functions of landscapes through statistical and quantitative analysis of different categories and types of landscape units. This study prioritizes four types of landscape indices that are widely used and closely related to the changes in heat islands. These include the contagion index, Shannon’s diversity index, interspersion and juxtaposition index, and patch cohesion index. The relevant literature indicates that these indices can reflect the formation mechanisms of the urban thermal environment from the dimensions of landscape aggregation, structural diversity, fragmentation degree, and connectivity. Especially against the backdrop of rapid urban expansion and increasing fragmentation of green spaces, these indices are of great significance in identifying high-incidence areas of heat islands and assessing the optimization of urban structures [46,47,48].
Contagion Index (CONTAG) measures the degree of aggregation or expansion tendency of different patch types in the landscape pattern. The calculation formula is as follows:
where is the proportion of patch type; is the connectivity coefficient between patch types i and k, and was calculated using the landscape pattern analysis software Fragstats 4.2; and m is the number of current patch types, which was extracted from Landsat 8 remote sensing imagery.
Shannon Diversity Index (SHDI) reflects the complexity of the landscape pattern. The calculation formula is as follows:
where n is the number of landscape patches and is the proportion of area of patch type i to the total area of all landscape patches.
Division (DIVISION) measures the dispersion of patches within a particular landscape type. The calculation formula is as follows:
where is the distance of landscape type i and is the area of landscape type i.
Patch Cohesion Index (COHESION) measures the physical connectivity between different patch types. The calculation formula is as follows:
where pij is the proportion of the ij-th patch type; aij is the number of pixels in the ij-th patch; and A is the total number of pixels.
Elevation refers to the vertical distance from a ground point to a reference height. The research indicates a correlation between temperature and elevation, with temperature decreasing by approximately 0.6 °C for every 100 m of elevation gain.
Slope refers to the amplitude of surface undulation in a given area, calculated using the slope analysis tool in ArcGIS 10.3 software.
All the above surface information acquired are shown in Figure 3.
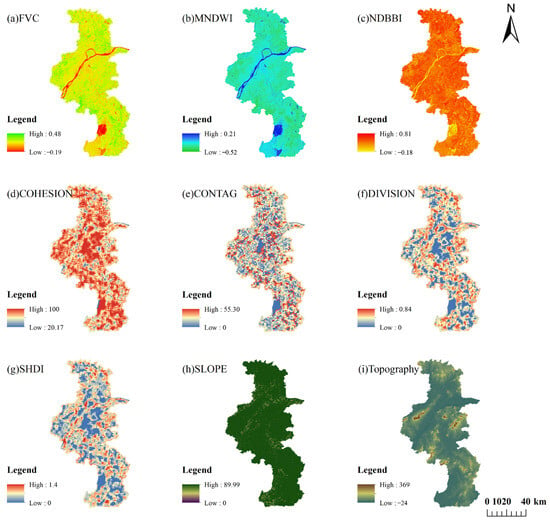
Figure 3.
Surface information of Nanjing: (a) FVC; (b) MNDWI; (c) CONTAG; (d) SIIDI; (e) DIVISION; (f) COHESION; (g) NDBBI; (h) DEM; (i) SLOPE.
2.3.3. Spatial Principal Component Analysis
This study focuses on the natural and human factors influencing the distribution pattern of urban surface temperature, utilizing SPSS Pro and ArcGIS 10.5 software for correlation and spatial principal component analysis. Spatial principal component analysis is a method that transforms multiple indicators into several independent composite indicators through computation. In a multivariate system, each principal component represents an independent indicator, and they are ranked in descending order based on their contribution [49,50].
2.3.4. Geographic Detector Model
The Geographic Detector (GD) model can be employed to explore the impact intensity and direction of various geographic factors and their interactive effects on the research subject. This method integrates spatial analysis from geography with the concept of disease detectors from epidemiology, aiming to reveal how geographical environmental factors influence social, economic, and ecological phenomena [51]. By calculating and comparing the q-values of individual factors and the q-values after the overlay of two factors, the GD can determine whether there is an interaction between the two factors, as well as the strength and direction of the interaction, and whether the interaction is linear or nonlinear. Considering the characteristics of the Geographic Detector and the features of the study area in this research, seven explanatory factors were selected, including ecosystem services, slope, soil, population, GDP, aspect, and topography. The formula is as follows:
where h = 1, …, L represents the stratification of variable Y or factor X, that is, classification or partitioning; Nh and N are the number of units in layer h and the entire area, respectively; and are the variances in Y values in layer h and the entire area, respectively; and SSW and SST represent the sum of within-layer variances and the total sum of squares for the entire area, respectively.
2.3.5. Surface Temperature Classification
This study uses the standard deviation method to classify land surface temperature into five levels: low-temperature zone, sub-low-temperature zone, medium-temperature zone, sub-high-temperature zone, and high-temperature zone. The specific classification criteria are shown in Table 1. Here, Tni is the normalized pixel value, Tmean is the average value of all pixel Tni in the study area after normalization, and S is the standard deviation.

Table 1.
Classification criteria for land surface temperature (LST) grades.
2.3.6. Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis Model
Spatial autocorrelation can be divided into two types, global spatial autocorrelation and local spatial autocorrelation. Global spatial autocorrelation is used to describe the spatial distribution pattern of the entire study area, while local spatial autocorrelation is used to describe the spatial heterogeneity of local areas. The global Moran’s I index is used to measure the global spatial autocorrelation of carbon emissions across regions. The value of the Moran’s I index ranges from −1 to 1. When the value is greater than 0, it indicates positive spatial correlation, meaning that adjacent elements show a “high-high, low-low” clustering trend. When the value is less than 0, it indicates negative spatial correlation, meaning that adjacent elements show a “high-low, low-high” distribution trend. When the value is close to 0, it indicates a random spatial distribution with no correlation. The calculation formula is as follows:
where n is the number of spatial elements; and represent the attribute values of the element i and element j, respectively; denotes the mean of all attribute values; and is the spatial weight between the element i and element j.
3. Results
3.1. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Heat Island
High-temperature areas in Nanjing are primarily concentrated in the central city, particularly along the Yangtze River and within the central urban regions of Luhe, Lishui, and Gaochun Districts (Figure 4). These areas are densely populated with residential zones, industrial areas, and central business districts, featuring a high proportion of impervious surfaces, which contributes to the concentration of high temperatures. Over time, the extent of these high-temperature zones has expanded annually, and their distribution has become more fragmented. In contrast, low-temperature areas are mainly found in forested and water regions, such as the Yangtze River, Xuanwu Lake, and Shihutou Lake, where temperatures are significantly lower than the surrounding areas.
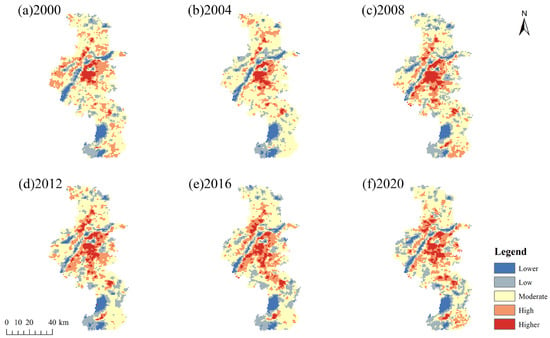
Figure 4.
Thermal grade distribution map from 2000 to 2020: (a) 2000; (b) 2004; (c) 2008; (d) 2012; (e) 2016; (f) 2020.
Figure 5 illustrates the changes in the centroids of different surface temperature grades in Nanjing from 2000 to 2020. The centroids of high-temperature, secondary high-temperature, and medium-temperature zones all migrated southeast, while the centroid of low-temperature zones shifted northeast. Additionally, the centroid of secondary low-temperature zones slightly moved east and south. Nanjing’s development model is characterized by river-oriented growth, with urban expansion primarily concentrated in the southwestern and southeastern parts of the city, exhibiting distinct phases. As the construction of Hexi New City and Xianlin Suburb progresses, development in the southern part of the city has also strengthened significantly. Overall, there is a correlation between changes in Nanjing’s thermal environment and the intensity of urban construction.
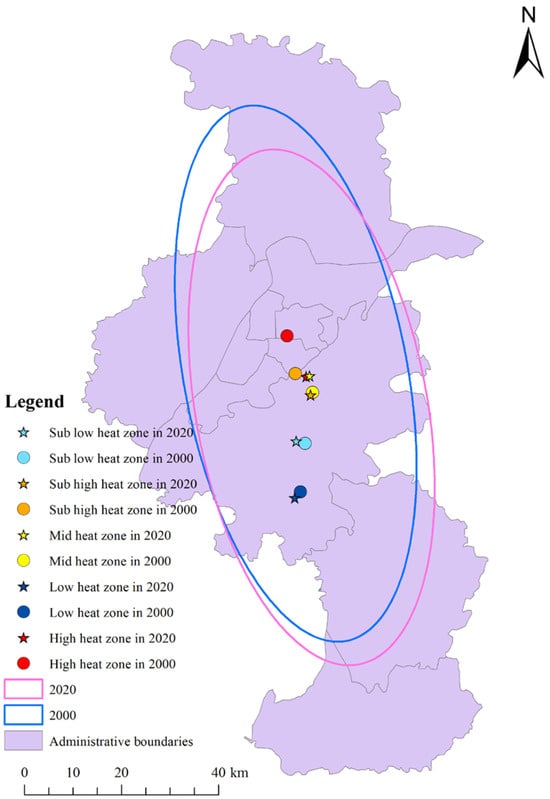
Figure 5.
Standard deviation ellipse and centroid migration distribution map from 2000 to 2020.
The data clearly show significant variations in surface temperatures in Nanjing from 2000 to 2020 (Table 2). The URI index initially declined, then increased, and has since stabilized, decreasing by 0.6 from 2000 to 2004, rising to 0.22, and remaining around 0.23 thereafter. This suggests that the intensity of Nanjing’s urban heat island effect has gradually stabilized.

Table 2.
Proportion of surface temperature area by different levels and URI values.
During this period, the area of low-temperature zones remained relatively constant at about 6% of the total area, while the area of secondary low-temperature zones increased by 5.03% over 20 years (Figure 6). The area of medium-temperature zones rose by 5.66% from 2000 to 2004 but then continuously decreased, resulting in a total reduction of 12.20% by 2020. The area of secondary high-temperature zones decreased by 7.65% from 2000 to 2004, but steadily increased afterward, reaching levels nearly equal to those in 2000 by 2020. The area of high-temperature zones has increased annually since 2000 and then stabilized.
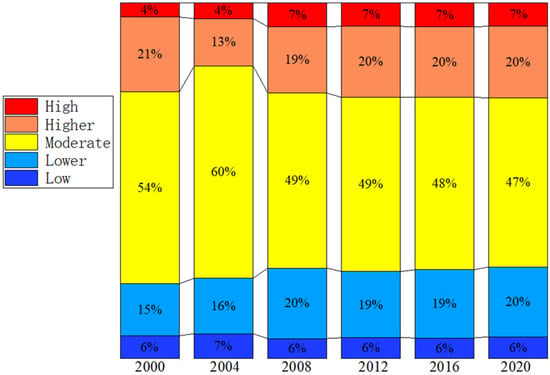
Figure 6.
Percentage area of temperature levels in Nanjing.
Overall, the areas of low- and secondary low-temperature zones in Nanjing show a slow increasing trend, while the areas of high- and secondary high-temperature zones initially decreased before increasing, and the area of medium-temperature zones first increased and then decreased. Changes in the areas of all temperature grades have stabilized since 2012, reflecting the gradual stabilization of Nanjing’s urban heat island effect. This trend is partly attributed to a series of environmental protection measures implemented by the Nanjing municipal government in response to the dual-carbon policy, including restrictions on industrial emissions and encouragement of clean energy use, which help reduce air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, thereby mitigating the urban heat island effect.
3.2. Hotspot of Heat Island
The hotspot analysis of Nanjing’s surface temperature from 2000 to 2020 reveals that cold spots are primarily located in forested and water areas, indicating that large bodies of water and vegetation can create cold aggregation zones, consistent with the actual distribution of land cover types. During this period, the area of low-temperature zones in northern Nanjing showed significant fluctuations, while the southern part experienced little change (Figure 7).
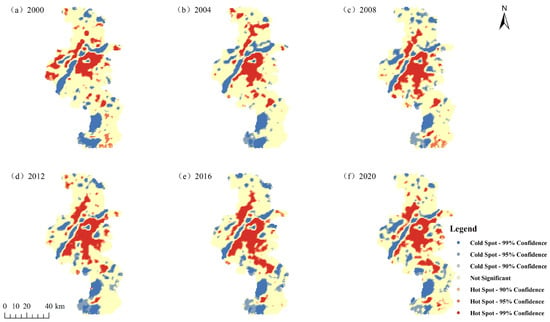
Figure 7.
Hotspot analysis of surface temperature.
The spatial distribution of hotspots exhibits notable aggregation, particularly along the banks of the Yangtze River and in the central areas of Luhe, Lishui, and Gaochun Districts. These regions are densely populated with residential areas, industrial zones, and central business districts. Due to the high proportion of impervious surfaces, high-temperature zones are relatively concentrated.
Analysis of the spatial changes in hotspots from 2000 to 2016 shows a continuous expansion of thermal aggregation areas, especially in the main urban areas. However, by 2020, there was a trend of contraction in these thermal aggregation areas. This change may be linked to the slowdown in the growth rate of built-up areas in Nanjing after 2016, along with a continuous increase in green coverage and green space. Enhancing vegetation coverage can help mitigate the urban heat island effect. Overall, thermal aggregation areas in Nanjing show a trend of shrinking and fragmenting, while cold aggregation areas exhibit fluctuations followed by stabilization.
3.3. Characteristics of Surface Temperature for Different Land Use Types
The urban heat island effect is closely related to land cover types, making its study significant for understanding this phenomenon. In this study, overlay the average surface temperatures of Jiangsu Province for the years 2000, 2004, 2008, 2012, 2016, and 2020 with land use data to obtain statistical results regarding surface temperatures among different land use types. The findings indicate significant differences between various land use categories (Figure 8). During the study period, the average surface temperature for all land use types in Jiangsu Province exhibited fluctuations, which are closely related to annual temperature variations. Notably, the average temperature of built-up areas is significantly higher than that of other land use types. Furthermore, the standard deviation of land surface temperature (LST) for grasslands and unused lands varies annually, indicating that the surface temperatures of these two land use types undergo significant and irregular changes within the study area. This variation is primarily attributed to the relatively small area of grasslands and unused lands in the study region, leading to pronounced differences in surface temperature. In contrast, built-up areas and croplands demonstrate smaller standard deviations in surface temperature, reflecting a stable high-temperature environment, while water bodies and forests maintain a relatively stable low-temperature environment.
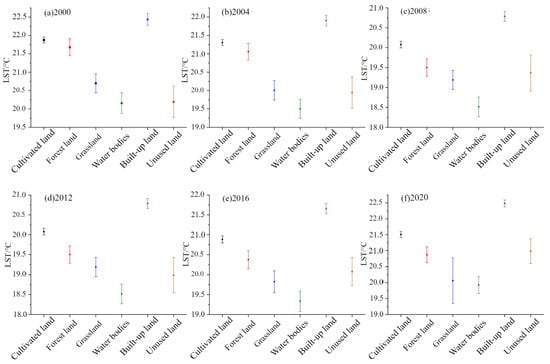
Figure 8.
Temperature distribution map of different land use types in Nanjing.
3.4. Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis
A spatial autocorrelation analysis was conducted on the land surface temperature (LST) of Nanjing from 2000 to 2020. As illustrated in Figure 9, the global Moran’s I index for LST across six time periods all exceeded 0.8, indicating a highly significant global spatial autocorrelation. The LST exhibited a strong positive spatial correlation. From the perspective of local spatial autocorrelation, the number of points in the first and third quadrants were significantly higher than that in the second and fourth quadrants. This suggests that regions with “low–low” and “high–high” LST clusters are more numerous than those with “high–low” and “low–high” clusters. In other words, areas with low (or high) LST in Nanjing are more likely to be spatially aggregated. The geographical location of Nanjing determines its climatic characteristics. The city has a subtropical monsoon climate, with warm springs, cool autumns, hot summers, and cold winters. The four seasons are distinct. The presence of the Yangtze River and numerous lakes and water bodies endows the region with a pronounced humid climate. The southern and eastern parts of the city are characterized by hilly terrain, which makes it difficult for southeast winds to penetrate. Consequently, the heat from ground radiation is not easily dissipated. These factors contribute to the urban heat island effect, making the urban area more susceptible to high temperatures. However, due to the abundance of water bodies and hills, and the relatively low population density, cold islands tend to form around the lakes.
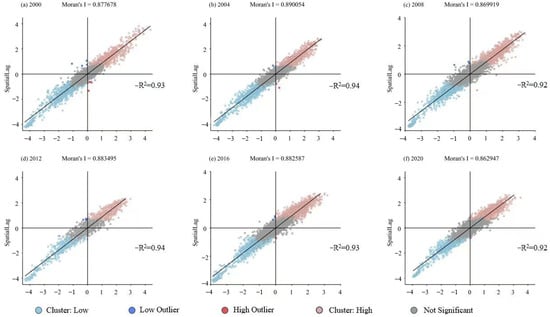
Figure 9.
Scatter plots of spatial autocorrelation for land surface temperature in Nanjing.
3.5. Influencing Factors
3.5.1. Pearson Correlation Analysis
This study selected data from Jiangsu Province in 2020 for the analysis of influencing factors. To analyze the correlation between urban thermal environment influencing factors and land surface temperature (LST), this paper used the sampling tool in ArcGIS 10.3 to randomly select 500 sample points within the scope of Nanjing and obtained the index values and LST values at each point location. The data were then imported into SPSS Pro for Pearson correlation analysis to obtain the Pearson correlation coefficients between each index and LST (Table 3).

Table 3.
Pearson correlation analysis between influencing factors and land surface temperature.
3.5.2. PCA and Geodetector Analysis
The spatial principal component analysis (PCA) combines statistical principles with GIS technology, mapping each spatial variable to a matrix and allocating the degree of influence of related spatial variables on the dependent variable to the corresponding principal component factors [52]. This method allows the results of principal component analysis to be clearly applied to each pixel, thereby intuitively extending the original principal component analysis results into two-dimensional space. According to Table 4, the contribution rate of the first five principal components reaches 91.692%, which justifies the extraction of these five components to reflect the composition of the urban thermal environment spatial pattern in Nanjing. Table 5 presents the information load of the original nine variables contained in each principal component, where a larger coefficient corresponding to a principal component indicates that the component more strongly represents the original variables, providing a basis for a detailed analysis of the composition of each principal component [53].

Table 4.
Eigenvalue and contribution rates of PCA.

Table 5.
Principal component loading matrix.
The analysis results indicate that the main factors influencing the urban thermal environment pattern in Nanjing include landscape complexity, vegetation coverage, landscape aggregation degree, urban construction, and topography. The first principal component primarily reflects the impact of landscape complexity on the thermal environment in Nanjing. The central urban area of Nanjing is characterized by land use types dominated by construction land, forest land, and water bodies, with high scores for dispersion and Shannon diversity indices, at 0.945 and 0.95, respectively. This suggests that the proportion of green landscape types is relatively low, leading to increased surface temperatures. The second principal component summarizes the impact of greening on the urban thermal environment, as vegetation significantly lowers surface temperatures through transpiration and shading effects. Areas with high vegetation coverage can typically mitigate the formation of the urban heat island effect, making the urban environment more comfortable. The third principal component reflects the influence of landscape aggregation degree on the urban thermal environment, which is often correlated with the level of urbanization. Highly urbanized areas tend to have dense buildings and impervious surfaces that absorb and store substantial amounts of solar radiation heat, resulting in elevated local temperatures and the formation of heat islands. The fourth principal component addresses the heat generated by urban construction activities, primarily represented by the building index. Finally, the fifth principal component focuses on the impact of elevation in topography on the thermal environment. The presence of hills and mountainous areas in Nanjing affects airflow, either blocking or guiding it, which alters air circulation within the city. Additionally, the higher vegetation coverage in hilly areas helps alleviate the urban heat island effect. Through this analysis, a more comprehensive understanding of the influencing factors and spatial distribution characteristics of the urban heat island effect in Nanjing can be achieved.
Further analysis using the geographic detector model was conducted to examine the impact of different indicators on the urban heat island effect in Nanjing. The geographic detector is an effective spatial statistical analysis tool designed to reveal the influence and driving mechanisms of various geographic variables on surface phenomena. It quantitatively assesses the strength of various factors’ impacts spatially, helping researchers understand the environmental changes and their dynamic interactions. The results indicate that different interactive types of influencing factors exert varying interactions on the surface temperature of the central urban area of Nanjing. The results indicate that double-factor interactions have the most significant impact, demonstrating that the urban heat island effect in Nanjing is primarily driven by the synergistic action of multiple factors rather than individual influences. However, the geographic detector’s results do not reveal the directional nature of these influencing factors. The presence of significant double-factor enhancement indicates that these factors exhibit spatial synergy, collectively explaining the variations in surface temperature in Nanjing. For instance, the double-factor enhancement interaction between vegetation coverage and elevation or slope reflects the contribution of natural topographic changes in lowering the surface temperature and mitigating the urban heat island effect. Meanwhile, the double-factor enhancement interaction between vegetation coverage and GDP illustrates the potential driving role of economic development in ecological protection and improvement. When vegetation coverage interacts with other factors, it enhances the impacts of these factors on surface temperature. Conversely, the single-factor nonlinear weakening reflects the interaction type between MNDWI and NDBI, indicating that when water bodies interact with built-up or impervious surfaces, the mitigating effect of water on the thermal environment is weakened. In terms of influence, vegetation coverage exhibits the highest impact, with an average influence value of 0.53, significantly higher than the influence of other factors (averaging between 0.18 and 0.37), indicating that vegetation coverage is the primary determinant of surface temperature.
4. Discussion
4.1. Distribution and Influencing of Urban Heat Island Effect
The urban heat island effect is an important indicator of urban living conditions and ecological health. Revealing the spatial and temporal evolution characteristics and driving mechanisms of the urban heat island effect can provide a scientific basis for optimizing green infrastructure, adjusting energy structures, and constructing climate resilience in urban planning. The formation and intensification of urban heat islands is a multiscale coupling process, involving complex interactions between natural geographical contexts and human activities. In this process, rapid urban spatial expansion, increasing population density, and rising impervious surface coverage in Nanjing are identified as core driving factors exacerbating the heat island effect.
First, regarding the temporal and spatial distribution changes in urban surface temperatures, this study observed a clear trend of outward radiation from the center of the urban heat island effect in Nanjing between 2000 and 2020. As a core city in the Yangtze River Delta, Nanjing has seen its urbanization process accelerate since the beginning of the 21st century. Following the implementation of the “Three Concentrations” strategy by the Nanjing municipal government in 2005, the evolution of the city’s spatial pattern has been further propelled [54]. The resident population in Nanjing surged from 6.89 million in 2005 to 9.31 million in 2020, representing a growth rate of 35.1%. During this period, the urbanization rate of the resident population increased from 76% to 86%, and the built-up area expanded to 868.28 square kilometers, with the proportion of construction land in the main urban area exceeding 65% [55]. This phased characteristic of the urbanization process provides essential macro-context for analyzing the evolution of the urban thermal environment. Specifically, the core areas of the heat island are concentrated in the old city and industrial–commercial dense zones. The Xinjiekou commercial district, as one of the first national-level mega-business circles, forms a peak heat area relying on comprehensive commercial complexes such as Deji Plaza and Gold Eagle Center. Although the Gulou area, centered around Nanjing University and Southeast University, constitutes a knowledge economy zone, the high concentration of research institutions, hospitals, and office buildings severely pressures the green space. This heat island spatial expansion pattern, centered around industrial and commercial dense areas, aligns with the observations made by Cai in Beijing on industrial land-centered heat island radiation characteristics and the research conclusions regarding heat island aggregation effects in Wuhan’s industrial and commercial core by Cai [56,57]. The formation of this spatial pattern primarily arises from the interplay of three factors: high-density buildings obstructing air circulation, impervious surfaces limiting evaporation cooling, and concentrated populations generating substantial anthropogenic heat emissions. For instance, after the introduction of the Jiangsu headquarters of Alibaba and the East China headquarters of Xiaomi in Jianye District in 2019, the cluster of high-rise buildings in the Hexi CBD exacerbated heat accumulation, making the area an emerging high-temperature zone. Meanwhile, since the establishment of the national-level development zone in the Jiangbei New Area in 2015, its core area has expanded by 3.6 times in built-up area over the past decade [58]. The densely arranged technology parks and financial centers employ extensive hard-paved surfaces, leading to a decline in the thermal environmental carrying capacity. Notably, the center of the heat island in Nanjing exhibits a gradual southward shift, closely related to the direction of urban expansion. As new industrial parks like the Jiangning Development Zone emerge, adjustments in industrial layout alter the thermal environmental pattern. Xu’s research confirms that the axis of urban expansion often coincides with the direction of heat island extension [59]. Additionally, Nanjing’s topographical features, such as its proximity to the Yangtze River and surrounding hilly areas, also influence the expansion of the heat island effect and the shift in its center to a certain degree.
Secondly, regarding the relationship between land use types and surface temperature, this study revealed long-term stability patterns in the thermal environmental characteristics of different land categories in Nanjing through time-series analysis from 2000 to 2020. The results demonstrate that built-up areas consistently maintained higher average temperatures than other land types (Figure 8). Particularly in commercial–industrial clusters like the Xinjiekou business district, the synergistic effect of glass curtain walls with high heat absorption capacity and anthropogenic heat emissions from subway transportation hubs has formed persistent “thermal core” phenomena. In contrast, the temperatures of bodies of water and forested areas, such as Xuanwu Lake and Purple Mountain, are significantly lower, primarily due to the high heat capacity of water and the transpiration effects of forests, effectively reducing local temperatures. The temperatures of grasslands and unused lands exhibit instability and are significantly influenced by land use changes. Since these types of land are prone to conversion or development for other purposes, their thermal environmental characteristics present a high degree of uncertainty. Conversely, the surface temperatures of cultivated land and built-up areas remain relatively stable, likely due to the long-term stability of land management policies, such as consistent agricultural practices and minimal land use changes. This finding aligns with the conclusions of Ma and Zou on the spatial–temporal coupling relationship between land cover composition and urban heat island effects [60,61]. Based on these findings, we suggest that Nanjing should prioritize the protection of water bodies and forests with a continuous cooling effect during urban renewal. At the same time, it is recommended to focus on the transformation of industrial and commercial areas that have formed stable heat cores. Additionally, based on different vegetation types, we propose that the Nanjing municipal government prioritize the planting of native arbor species such as sycamore and camphor in urban greening. These species have higher canopy shading and transpiration efficiency compared to lawns.
Furthermore, in terms of the multifactorial driving mechanisms influencing urban thermal environments, the existing research has revealed the pathways through which various factors, including socio-economics, surface morphology, and climatic elements, affect the heat island effect from multidimensional perspectives. For instance, Shao analyzed the impacts of surface characteristics and climatic contexts on urban heat islands [62], while Stache et al. examined the extent to which building materials and vegetation influence urban heat islands [63]. This study finds that vegetation coverage and landscape aggregation are among the most critical factors in alleviating the urban heat island effect, consistent with findings by Calhoun regarding vegetation and Ribeiro concerning landscape patterns [64,65]. The results of this study reveal a significant negative correlation between vegetation coverage and surface temperature, indicating the essential role that vegetation plays in lowering urban temperatures. By providing shade and promoting transpiration, vegetation can significantly reduce the accumulation of heat on the surface. This principle is particularly evident in the renovation of the Qinhuai River Ecological Corridor, where the systematic planting of native species, such as plane trees and camphor trees, has created a continuous green network. After completion, the corridor notably reduced average summer temperatures, forming a stable microclimate environment [66]. Therefore, urban planning should prioritize the increase in urban green spaces and vegetation cover, especially in high-temperature areas, to effectively alleviate the thermal pressure on urban environments. Additionally, landscape aggregation has also been proven to be an essential factor affecting urban thermal environments. According to research by Peng [67], higher landscape aggregation corresponds to more pronounced spatial differences in surface temperatures, closely related to the thermal environments of different landscape types. A rational layout of built-up areas, forests, and water bodies helps to reduce the spatial diffusion of heat island effects. Moreover, within the specific topographical conditions of Nanjing, topographical factors (such as elevation and slope) play a significant role in regulating the thermal environment; mountainous and hilly areas can alleviate local heat island effects to some extent due to their topographical barriers.
Finally, in terms of the synergistic mechanisms of multiple factors, this study further explored the synergistic mechanisms of multiple factors on the heat island effect using the geographical detector. The results show that in most cases, the explanatory power of the heat island effect in Nanjing by the interaction of two factors is significantly higher than that of a single factor, indicating the presence of a nonlinear enhancement effect. Further analysis revealed that there may be certain correlations between these factors in terms of physical mechanisms and spatial distribution. For example, there is a certain spatial coupling between vegetation cover (NDVI) and topographic factors (DEM), with higher-altitude areas often accompanied by higher green space coverage. This co-occurrence amplifies the regulatory effect on the urban thermal environment. Similarly, there is a strong correlation between construction density and landscape aggregation. The high-density distribution of construction land usually leads to the fragmentation of landscape patches, increasing the complexity of local heat accumulation and diffusion. The interaction analysis of the geographical detector also shows that there are significant hierarchical differences in the synergistic effects of different factors on the heat island effect (Table 6). Vegetation cover (FVC) acts as a core regulatory factor, with a q-value of 0.45–0.47 when interacting with topographic factors such as elevation and slope. It dominates the mitigation of heat islands through the synergistic effects of evaporative cooling and topographic ventilation. When interacting with landscape aggregation (CONTAG), the q-value is 0.52, reflecting the secondary enhancement of ecological connectivity on heat diffusion. In contrast, human activity-related factors (such as NDBBI) only produce nonlinear enhancement when combined with other natural factors (q-values of 0.26–0.40). For example, the interaction between water bodies (MNDWI) and the construction index (NDBBI) actually weakens the cooling effect (q-value of 0.26), confirming the suppression of hydrological regulation capacity by urban impervious surfaces. This hierarchical relationship indicates that future urban planning should prioritize the synergistic design of vegetation cover and topographic ventilation and then regulate construction density and landscape fragmentation.

Table 6.
Results of synergistic influence factors of habitat quality.
4.2. Recommendation for Future Policy
By analyzing the spatial and temporal differentiation characteristics of the urban heat island effect in Nanjing and the interrelationships of its influencing factors, significant coupling relationship was revealed between the evolution of the urban thermal environment and land use, landscape patterns, and human activities. As urban space continues to expand and the intensity of land development increases, the contradiction between high-temperature areas and ecological spaces will become increasingly prominent. To effectively mitigate the trend of worsening thermal environments, the following strategic recommendations are proposed.
Optimize the Layout of Urban Ecological Spaces: For high-temperature areas with frequent commercial activities in Nanjing, such as the Xinjiekou business district and Gulou commercial area, the government should focus on increasing the green space in these regions. This can be accomplished by connecting parks, street greenery, and tree-lined avenues to create a citywide “green network.” Key areas capable of natural cooling, such as Xuanwu Lake, Shijiuhu Lake, and the Yangtze River, should be protected. By utilizing rivers and lakes to link scattered green spaces, contiguous cooling areas can be formed. Considering the trend of the heat island effect extending southward, it is recommended that a linear green belt be constructed in the southern region to block the path of heat dispersion.
Regulate Urban Spatial Structure Density: Based on this study, landscape aggregation (CONTAG) in Nanjing is positively correlated with land surface temperature (LST) (r = 0.103), indicating that contiguous high-rise building clusters have a heat-trapping effect, inhibiting heat dissipation. Consequently, for areas with concentrated, old urban districts, the government should control the unregulated densification of high-rise buildings and prioritize measures such as vertical greening. For new urban areas, it is recommended that the government reserve ventilation corridors during the planning phase and adopt a stepped building height design to balance development intensity with microclimate regulation.
Implement Differentiated Land Use Management: Addressing the concentration of the urban heat island effect in built-up areas, the government should prioritize the revitalization of small micro-greens and green spaces under bridges in old communities. Simultaneously, roof greening should be promoted in commercial areas, along with implementing shading greenery on residential building walls and permeable pavement to reduce heat radiation from hard surfaces. For natural systems like Purple Mountain and Xuanwu Lake, the government can plan ventilation corridors to reduce the number of surrounding high-rise buildings, thereby improving local high-temperature issues.
Enhance Public Environmental Awareness: The government should disseminate knowledge about the urban heat island effect through community outreach and educational programs in schools, promoting a “walking + biking + public transport” green travel model. Incentives, such as parking fee reductions and public transport card top-up discounts, can be offered to citizens using shared bicycles or new energy vehicles. Additionally, in communities, the government can grant identification to merchants who adopt shading canopies and vertical greening, as well as reduce their property fees, fostering a network of sustainable cooling through community participation.
4.3. Limitations
Despite providing significant insights into the spatial and temporal variations in the urban heat island effect and its driving mechanisms in Nanjing, this study has several limitations. First, the MODIS data used in this research have a relatively low spatial resolution and a lengthy time span, making it challenging to capture subtle variations in surface temperature at a fine scale. This may lead to discrepancies in analyzing the complex thermal characteristics within the urban area. Future research could employ higher-resolution remote sensing data in conjunction with vegetation classification information to analyze the differential impacts of various vegetation types on the urban thermal environment. This approach would provide more targeted recommendations for refined urban green space planning. Additionally, while various research methods were employed to analyze the changes in and causes of the urban heat island effect, these methods still have inherent limitations in data processing and spatial analysis. Therefore, future research could consider utilizing higher-resolution remote sensing data and employing more diverse analytical approaches to explore additional factors influencing the urban heat island effect, such as anthropogenic heat sources and traffic density.
5. Conclusions
This study addresses the influencing factors on urban heat island effects, focusing on Nanjing, a city experiencing rapid urbanization. Utilizing annual average surface temperature data from 2000 to 2020, the research employs methods such as centroid analysis and standard deviation ellipses to examine the temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of surface temperature in Nanjing. Three categories of influencing factors closely related to the urban heat island effect—natural, landscape, and human factors—are selected to explore the mechanisms and driving forces behind the heat island effect in Nanjing, thereby providing decision support for urban planning, mitigation of heat island effects, summer heat disaster management, and urban emergency response.
(1) From 2000 to 2020, the urban heat island effect in Nanjing has exhibited a trend of radiating outward from the center. The heat island areas are primarily concentrated in established zones, such as densely populated old towns and commercial centers, with a spatial distribution pattern of surface temperature that gradually decreases from the city center to the suburbs. Multiple high-temperature centers have emerged, including the Xinjiekou business district, the Qinhuai River scenic area, and the Gulou commercial area. The standard deviation ellipses and the centroid of high-temperature areas also demonstrate a southward shift.
(2) Significant differences exist in surface temperatures among different land use types. The average temperature of built-up areas is notably higher than that of other land use types. Grasslands and unused lands are small in area and unstable, making them susceptible to conversion, which results in a larger standard deviation in surface temperature. In contrast, built-up areas and cultivated lands exhibit smaller standard deviations in surface temperature, indicating a stable high-temperature environment, while water bodies and forests maintain a relatively stable low-temperature environment due to their high specific heat capacity and the cooling effects of transpiration.
(3) Correlation analysis reveals that vegetation coverage, normalized difference water index, elevation, landscape fragmentation, and Shannon diversity index are negatively correlated with surface temperature, while normalized difference bare soil, building index, dispersion index, and patch cohesion index are positively correlated. Principal component analysis identifies landscape complexity, vegetation coverage, landscape aggregation, urban development, and topography as the main factors influencing the urban thermal environment pattern in Nanjing, with landscape and vegetation being the most significant influencing factors. Geographic detector results indicate that, in most cases, the interaction of dual factors in Nanjing’s heat island effect exerts a greater influence than that of individual factors, with vegetation coverage being the primary determinant of surface temperature.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: G.S.; methodology: G.S., C.C. and Q.A.; data processing: J.L., Z.T., X.L. and X.T.; writing-original draft: G.S. and Q.A.; writing-review and editing: Y.Z. and C.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscripts.
Funding
This research was funded by the research project of Observation Research Station of Land Ecology and Land Use in the Yangtze River Delta, Ministry of Natural Resources (No.2023YRDLELU05); the 2024 Philosophy and Social Science Research in Colleges and Universities Program in Jiangsu Province (No. 2024SJYB0167).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
Acknowledgement for the data support from “National Earth System Science Data Center, National Science & Technology Infrastructure of China. (http://www.geodata.cn, accessed on 20 February 2025)”. Acknowledgement for the policy consulting support from Institute for Emergency Governance and Policy in Nanjing Tech University. Acknowledgement for the valuable assistance in data visualization from Wang Yutong. Ge Shi, the corresponding author of this paper, served as Quan An’s academic supervisor during this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Liu, C.X.; Wang, L.Q.; Xu, H.; Zhang, S.H.; Zhang, Z.Q. Impact of Vegetation Cover on Summer Urban Heat Island Effects in China from 2001 to 2021. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 11020–11034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Zeeshan, Z.; Talpur, B.A.; Sadiq, T.; Bhatti, U.A.; Awwad, E.M.; Al-Razgan, M.; Ghadi, Y.Y. Studying Long Term Relationship Between Carbon Emissions, Soil, and Climate Change: Insights from a Global Earth Modeling Framework. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinform. 2024, 130, 103902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, K.C.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Othman, M.H.D.; Anouzla, A.; Aziz, F.; Ali, I.; Casila, J.C.C.; Khan, M.I.; Zhang, D.; Dai, W.; et al. Reinforcing Urban Resilience Through Sound Landfill Management: Addressing Global Climatic Challenges with Novel Solutions. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2025, 195, 106789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.L.; Wang, J.; Zhou, W.Q. Impacts of Urban Agglomeration Development on the Spatial Evolution of Regional Heat Islands. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 11035–11048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.H.; Gu, K.K.; Ma, Q. Construction and Efficiency Evaluation of Urban Ventilation Corridors Based on Multi-source Data: A Case Study of Hefei Main Urban Area. Prog. Geogr. 2024, 43, 1597–1608. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, Y.; Liu, W. Spatiotemporal Evolution Characteristics and Spatial Heterogeneity of Driving Factors of Surface Urban Heat Island Intensity in Beijing Main Urban Area. Environ. Sci. 2024, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, S.P.; Yang, Q.W. Spatiotemporal Evolution Characteristics of Heat Island Effects in Mountainous New Urbanization Processes. J. China Agric. Univ. 2024, 29, 290–304. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, J.D.; Zhang, J.H.; Huang, B. A Review on the Impact of Urban Heat Island Effect on Human Health. Ecol. Sci. 2021, 40, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zeng, S.-P.; Lu, J.-M.; Aihemaiti, N.; Zeng, J. Gradient Differences in the Impact of Urban Morphology on Heat Island Intensity During Zhengzhou’s Urban Development. Environ. Sci. 2025, 46, 1924–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Xie, X.Y.; Yang, Y.F. Cooling Benefits of Urban Parks Based on Landscape Patterns and Cumulative Impacts: A Case Study of Nanjing. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2024, 33, 1055–1065. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, C.C. Multi-scale Impacts of Mining and Industrial Land Use on Urban Heat Island Effects in Mining Cities. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences (Beijing), Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, L.; Tang, X.; You, H.; Gu, Q.; Hu, H. Comparison of the Urban Heat Island Intensity Quantified by Using Air Temperature and Landsat Land Surface Temperature in Hangzhou, China. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 72, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, M. Study on Global Urban Heat Island Effects Under Different City Sizes and Background Climates. Ph.D. Thesis, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Q.; Yang, L.; Mu, K.; Zhang, M.; Liu, J. Urban Heat Island Effects of Various Urban Morphologies under Regional Climate Conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 743, 140589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Chen, Y.; He, H.; Wang, J.; Zhao, L.; Cai, Y. Assessing the Synergies Between Heat Waves and Urban Heat Islands of Different Local Climate Zones in Guangzhou, China. Build. Environ. 2023, 240, 110434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, C.; Han, L.; Wang, J.; Feng, Z.; Kumar, P.; Cao, S.-J. How Can Greenery Space Mitigate Urban Heat Island? An Analysis of Cooling Effect, Carbon Sequestration, and Nurturing Cost at the Street Scale. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 419, 138230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Piao, S.; Ciais, P.; Friedlingstein, P.; Ottle, C.; Bréon, F.-M.; Nan, H.; Zhou, L.; Myneni, R.B. Surface Urban Heat Island Across 419 Global Big Cities. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, M.; Ouyang, H.; Jiang, H.; Luo, T.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y. Spatiotemporal Evolution Characteristics and Driving Factors of Heat Island Effect Based on Territorial Perspective: A Case Study of Beibu Gulf Urban Agglomeration, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Xu, H.; Hu, X.; Liu, Z.; Yao, X.; Zhu, Z. Characterizing the Seasonal Relationships Between Urban Heat Island and Surface Energy Balance Fluxes Considering the Impact of Three-Dimensional Urban Morphology. Build. Environ. 2024, 265, 112017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, K.P.; Owen, T.W. Satellite-Based Adjustments for the Urban Heat Island Temperature Bias. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 1999, 38, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, K.; Tarpley, J.; McNab, A.; Karl, T. Assessment of Urban Heat Islands: A Satellite Perspective. Atmos. Res. 1995, 37, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargari, M.; Mofidi, A.; Entezari, A.; Baaghideh, M. Climatic Comparison of Surface Urban Heat Island Using Satellite Remote Sensing in Tehran and Suburbs. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Zhong, S.; Mei, X.; He, J. Spatiotemporal Patterns in the Urban Heat Island Effect of Several Contemporary and Historical Chinese “Stove Cities”. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Huang, L.; Zhang, L.; Wu, P.; Zeng, C. Long-term and Fine-scale Satellite Monitoring of the Urban Heat Island Effect by the Fusion of Multi-temporal and Multi-sensor Remote Sensed Data: A 26-year Case Study of the City of Wuhan in China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 172, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rech, B.; Moreira, N.R.; Mello, G.A.T.; Klouček, T.; Komárek, J. Assessment of Daytime and Nighttime Surface Urban Heat Islands Across Local Climate Zones—A Case Study in Florianópolis, Brazil. Urban Clim. 2024, 55, 101954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandel, H.; Melesse, A.; Whitman, D. An Analysis on the Urban Heat Island Effect Using Radiosonde Profiles and Landsat Imagery with Ground Meteorological Data in South Florida. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 2313–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Xie, X.; Li, S. Correlation Analysis of the Urban Heat Island Effect and the Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Atmospheric Particulates Using TM Images in Beijing. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 178, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.K.; Bhati, S.; Mohan, M.; Sahoo, N.R.; Dash, S. Numerical Simulation of the Impact of Urban Canopies and Anthropogenic Emissions on Heat Island Effect in an Industrial Area: A Case Study of Angul-Talcher Region in India. Atmospheric Res. 2022, 277, 106320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Wang, S.; Zou, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y. Seasonal Surface Urban Heat Island Analysis Based on Local Climate Zones. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 159, 111669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, P.; Priya, S.R. Comprehensive Analysis of the Impact of Elevated Metro Line Infrastructure on the Urban Heat Island Effect in Chennai: A Multi-model Approach. Energy Build. 2024, 319, 114541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Xia, J. Cooling Island Effect in Urban Parks from the Perspective of Internal Park Landscape. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2023, 10, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Xu, X.; Qiao, Z.; Wang, F.; Cai, H.; An, H.; Jia, K.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Z.; Wang, S.; et al. The Roles of Surrounding 2D/3D Landscapes in Park Cooling Effect: Analysis from Extreme Hot and Normal Weather Perspectives. Build. Environ. 2023, 231, 110053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.M.; Altamura, P.; Giampaoletti, M.; Hemeida, F.A.; Mohamed, A.F.A. Optimizing Human Thermal Comfort and Mitigating the Urban Heat Island Effect on Public Open Spaces in Rome, Italy Through Sustainable Design Strategies. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 19931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad, I.; Jamal, M.N. Unraveling the Complexities of Land-Use–Land Cover Transformation and Its Impact on Land Surface Temperature and Urban Heat Island Effect: A Study of Nowshera District, Pakistan. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2024, 4, 150. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.F.; Wang, H.; Qin, S.H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y. Research on Cooling Effects of Urban Parks in Nanjing Based on Multi-source Data. J. Nanjing For. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2024, 48, 285–294. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.F.; Ma, M.M.; Geng, L.Y. Spatiotemporal Evolution Analysis of Urban Heat Islands in Nanjing Based on Remote Sensing Indices. Geomat. World 2021, 28, 52–57. [Google Scholar]
- Nanjing Municipal People’s Government. Natural Conditions. 2019. Available online: https://www.nanjing.gov.cn/zjnj/zrzk/201910/t20191014_1676314.html (accessed on 11 September 2024).
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2024. Available online: http://www.stats.gov.cn/ (accessed on 23 March 2025).
- Nanjing Municipal Bureau of Ecology and Environment. Notice on Issuing the “14th Five-Year Plan” for Ecological Environmental Protection in Nanjing [EB/OL]. 2022. Available online: https://sthjj.nanjing.gov.cn/njshjbhj/202202/t20220209_3285947.html (accessed on 23 March 2024).
- Nanjing Municipal Bureau of Planning and Natural Resources. Detailed Planning of Greenways in Nanjing (2020–2035) [EB/OL]. 2022. Available online: https://ghj.nanjing.gov.cn/ghbz/zxgh/202206/P020241127550610603822.pdf (accessed on 23 March 2024).
- Xu, X.L. Annual 1-km Land Surface Temperature Dataset of China. Resour. Environ. Sci. Data Cent. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q.; Firozjaei, M.K.; Sedighi, A.; Kiavarz, M.; Alavipanah, S.K. Statistical Analysis of Surface Urban Heat Island Intensity Variations: A Case Study of Babol City, Iran. GISci. Remote Sens. 2019, 56, 576–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Brown, R.D. Urban Heat Island (UHI) Intensity and Magnitude Estimations: A Systematic Literature Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 779, 146389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Wang, X.; Johnson, B.A.; Tian, Q.; Wang, Y.; Verrelst, J.; Mu, X.; Gu, X. Remote Sensing Algorithms for Estimation of Fractional Vegetation Cover Using Pure Vegetation Index Values: A Review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 159, 364–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelkan, E. Water Body Detection Analysis Using NDWI Indices Derived from Landsat-8 OLI. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 29, 1759–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, J. The Correlation Analysis on the Landscape Pattern Index and Hydrological Processes in the Yanhe Watershed, China. J. Hydrol. 2015, 524, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Tang, L.; Xu, M.; Yang, X. Landscape Pattern Indices for Evaluating Urban Spatial Morphology—A Case Study of Chinese Cities. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 99, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, S. Investigating Landscape Pattern and Its Dynamics in Daqing, China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 2259–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, S.; Pramanik, M.; Chaudhary, S.; Maurya, A.K.; Kumar, M. Watershed Prioritization for Soil Erosion Mapping in the Lesser Himalayan Indian Basin Using PCA and WSA Methods in Conjunction with Morphometric Parameters and GIS-Based Approach. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 24, 3723–3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, J.; Gupta, G.; Singh, N.K.; Bhave, V.N.; Bhardwaj, V.; Upreti, P.; Singh, R.; Sinha, A.K. Geophysical and Geostatistical Assessment of Groundwater and Soil Quality Using GIS, VES, and PCA Techniques in the Jaipur Region of Western India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 77713–77728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhao, X.; Liu, B.; Yi, L. Urban Expansion Monitoring and Driving Forces Analysis: A Case Study of Jiangsu Province, China. In Proceedings of the 2009 Joint Urban Remote Sensing Event, Shanghai, China, 20–22 May 2009; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Philippe, P.J.; Malet-Damour, B.; Radanielina, M.H.; Fontaine, L.; Rivière, G. GIS-Based Approach to Identify Climatic Zoning: A Hierarchical Clustering on Principal Component Analysis. Build. Environ. 2019, 164, 106330. [Google Scholar]
- Richmond, A.; Peng, C.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Guo, Z.; Xiao, X. Identifying Sources and Transport Routes of Heavy Metals in Soil with Different Land Uses Around a Smelting Site by GIS Based PCA and PMF. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 823, 153759. [Google Scholar]
- Nanjing Municipal People’s Government. Implementation Opinions on the Concentration of Farmers in Suburban Counties to Towns and Rural Residential Areas. 2005. Available online: https://www.nanjing.gov.cn/zdgk/200805/t20080528_1054465.html (accessed on 23 March 2024).
- Nanjing Municipal Bureau of Statistics. Nanjing Statistical Yearbook; Nanjing Statistical Press: Nanjing, China, 2024. Available online: https://tjj.nanjing.gov.cn (accessed on 23 March 2024).
- Cai, G.; Du, M.; Xue, Y. Monitoring of Urban Heat Island Effect in Beijing Combining ASTER and TM Data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 1213–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Tang, Y.; Zhan, Q. A Cooled City? Comparing Human Activity Changes on the Impact of Urban Thermal Environment Before and After City-Wide Lockdown. Build. Environ. 2021, 195, 107729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiangsu Provincial People’s Government. Approval of the Master Plan for the Development of Nanjing Jiangbei New District; Jiangsu Provincial People’s Government: Nanjing, China, 2017. Available online: https://www.jiangsu.gov.cn/art/2017/8/25/art_46143_5585095.html (accessed on 23 March 2024).
- Xu, Y.; Jia, R.; Liu, J.; Han, D.; He, T.; Xu, X.; Liu, L.; Sun, Z.; Qiao, Z. The Population Exposure Risk of Urban Heat Island Effect: From the Perspective of Urban Spatial Expansion in China. Build. Environ. 2024, 258, 111565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Peng, S. Research on the Spatiotemporal Coupling Relationships Between Land Use/Land Cover Compositions or Patterns and the Surface Urban Heat Island Effect. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 39723–39742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Yan, C.; Yu, L.; Jiang, X.; Ding, J.; Qin, L.; Wang, B.; Qiu, G. Impacts of Land Use/Land Cover Types on Interactions Between Urban Heat Island Effects and Heat Waves. Build. Environ. 2021, 204, 108138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Liao, W.; Li, P.; Luo, M.; Xiong, X.; Liu, X. Drivers of Global Surface Urban Heat Islands: Surface Property, Climate Background, and 2D/3D Urban Morphologies. Build. Environ. 2023, 242, 110581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stache, E.; Schilperoort, B.; Ottelé, M.; Jonkers, H. Comparative Analysis in Thermal Behaviour of Common Urban Building Materials and Vegetation and Consequences for Urban Heat Island Effect. Build. Environ. 2022, 213, 108489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calhoun, Z.D.; Willard, F.; Ge, C.; Rodriguez, C.; Bergin, M.; Carlson, D. Estimating the Effects of Vegetation and Increased Albedo on the Urban Heat Island Effect with Spatial Causal Inference. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.P.; Bollmann, H.A.; de Oliveira, A.; Rakauskas, F.; Cortese, T.T.P.; Rodrigues, M.S.C.; Quaresma, C.C.; Ferreira, M.L. The Role of Tree Landscape to Reduce Effects of Urban Heat Islands: A Study in Two Brazilian Cities. Trees 2023, 37, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiangsu Provincial People’s Government. Approval on the Adjustment of Water Function Zoning in the Jiangning Section of the Qinhuai River; Jiangsu Provincial People’s Government: Nanjing, China, 2016. Available online: https://www.jiangsu.gov.cn/art/2016/11/21/art_46143_2543249.html (accessed on 23 March 2024).
- Peng, J.; Cheng, X.; Hu, Y.; Corcoran, J. A Landscape Connectivity Approach to Mitigating the Urban Heat Island Effect. Landsc. Ecol. 2022, 37, 1707–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).