GNSS Precipitable Water Vapor Prediction for Hong Kong Based on ICEEMDAN-SE-LSTM-ARIMA Hybrid Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
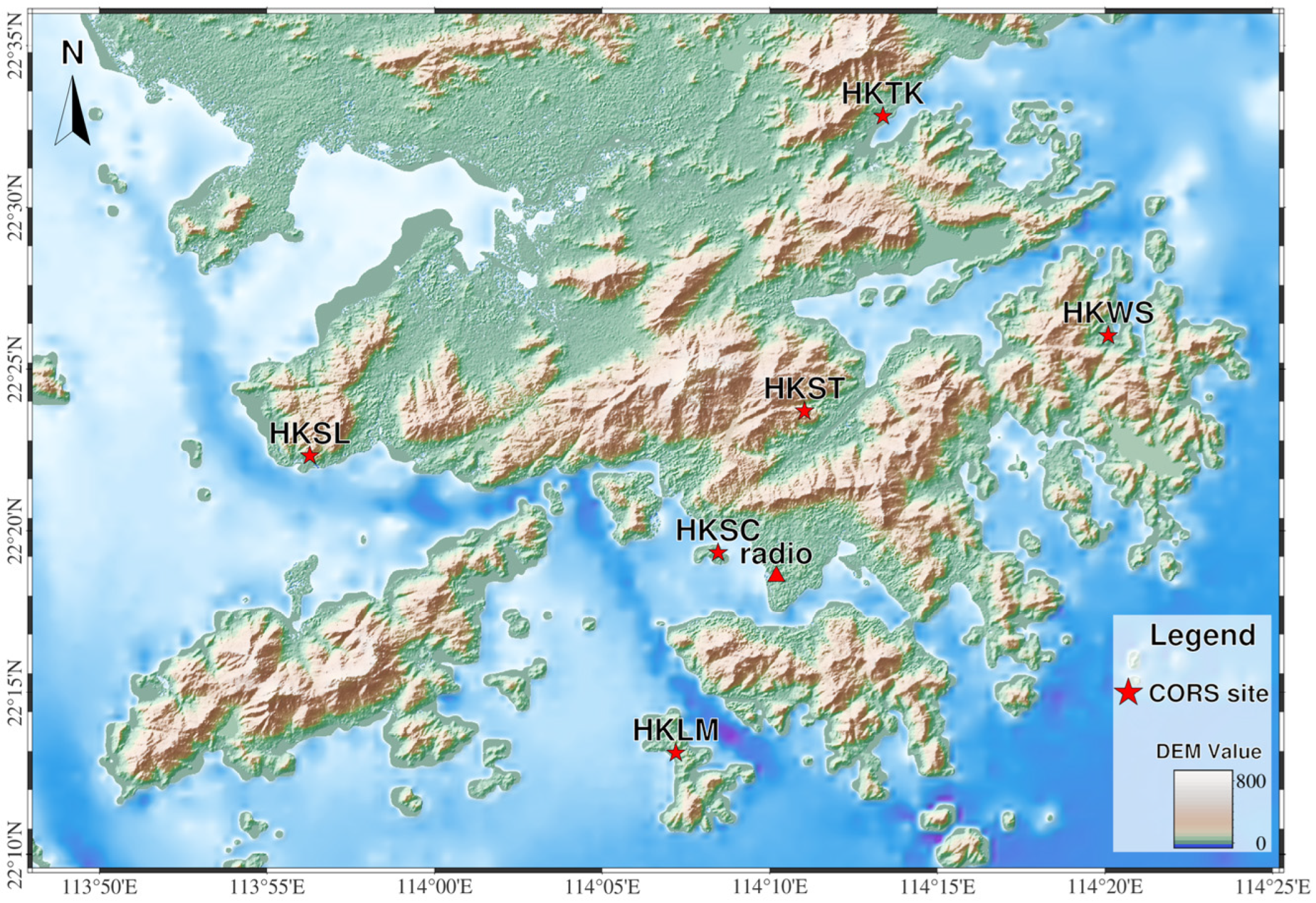
2.1. Study Area and Data Description
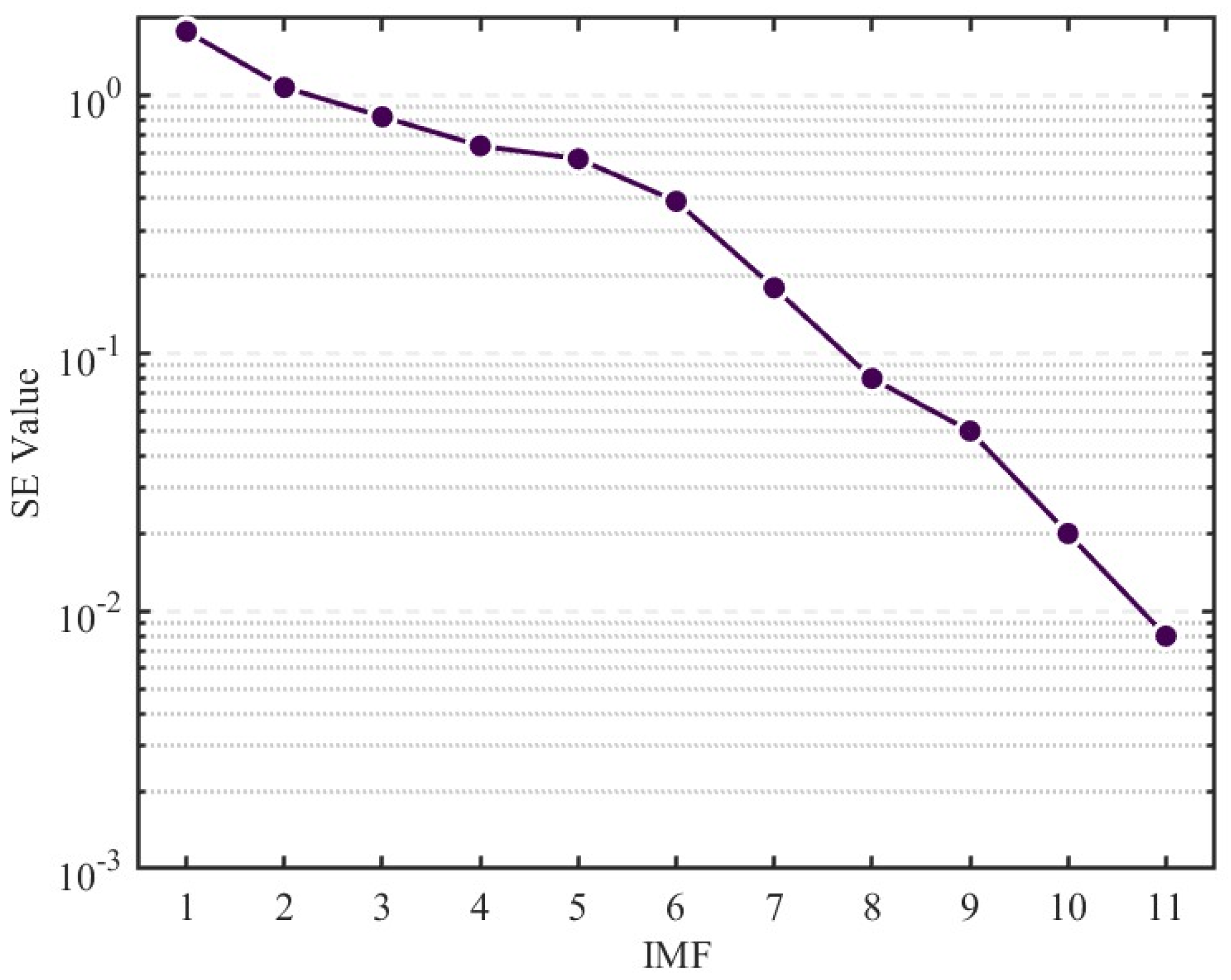
2.2. Data Preprocessing
3. Methodology
3.1. IS-LA Model Construction
3.2. Evaluation Indicators
4. Results
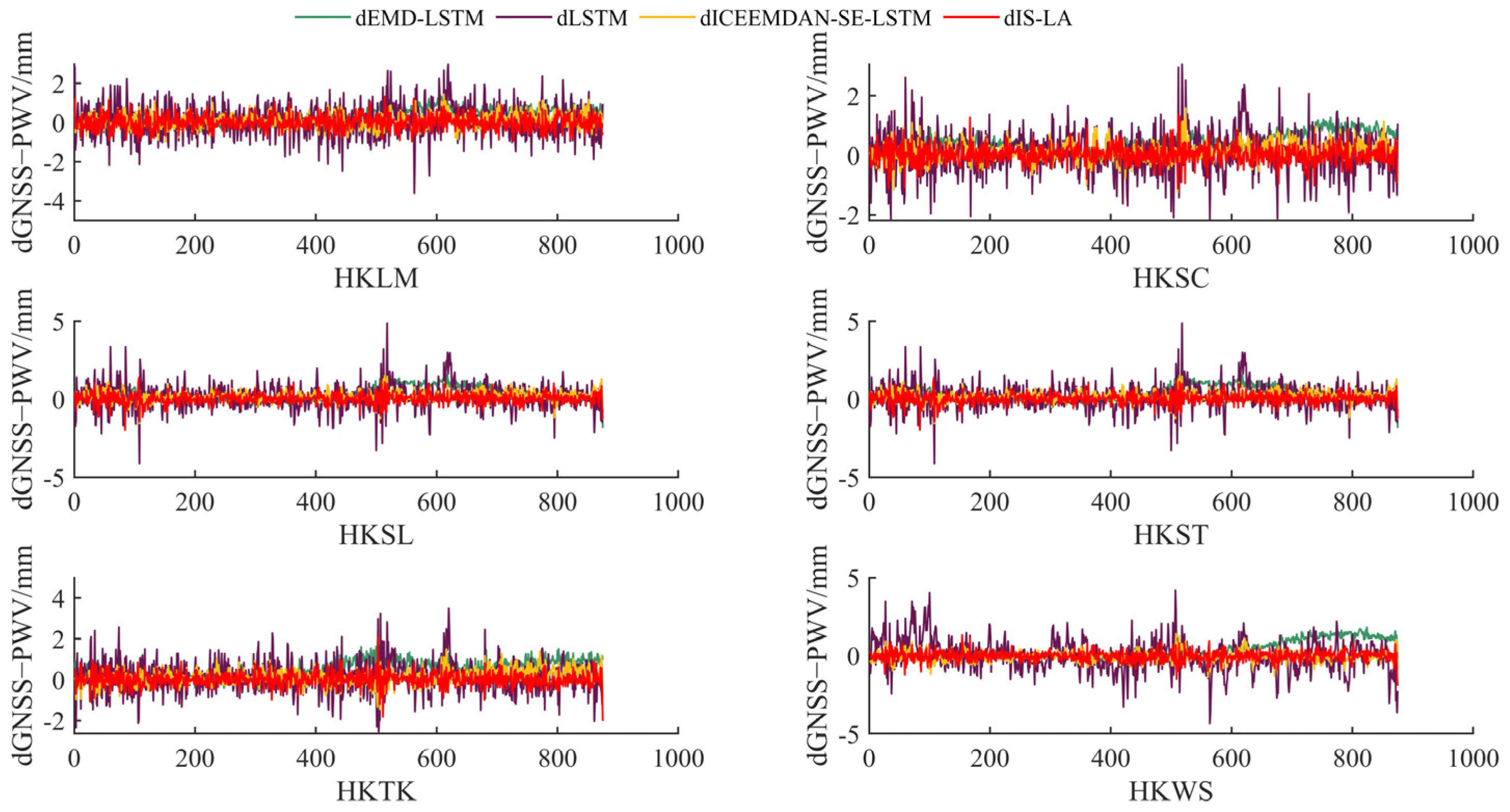
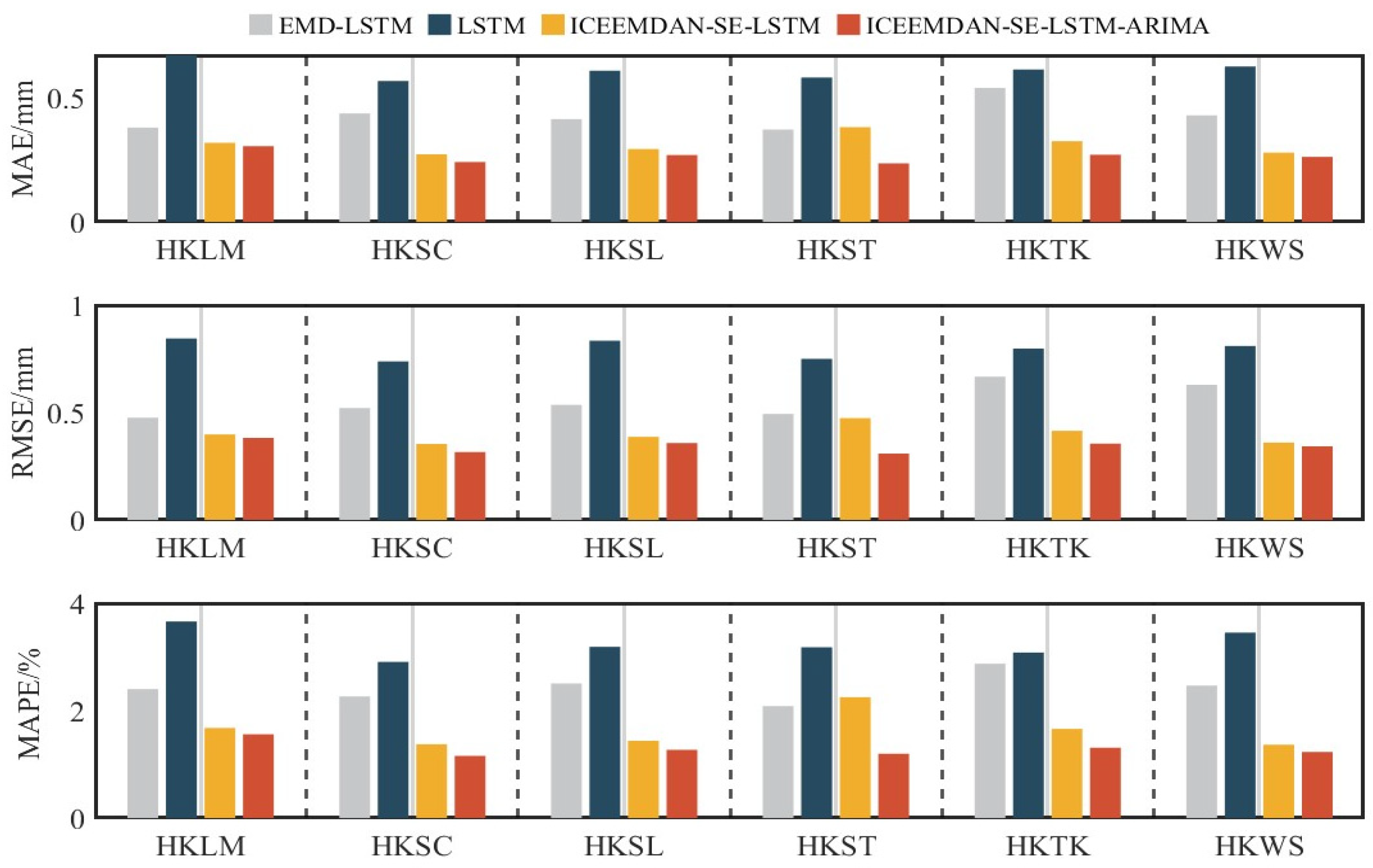
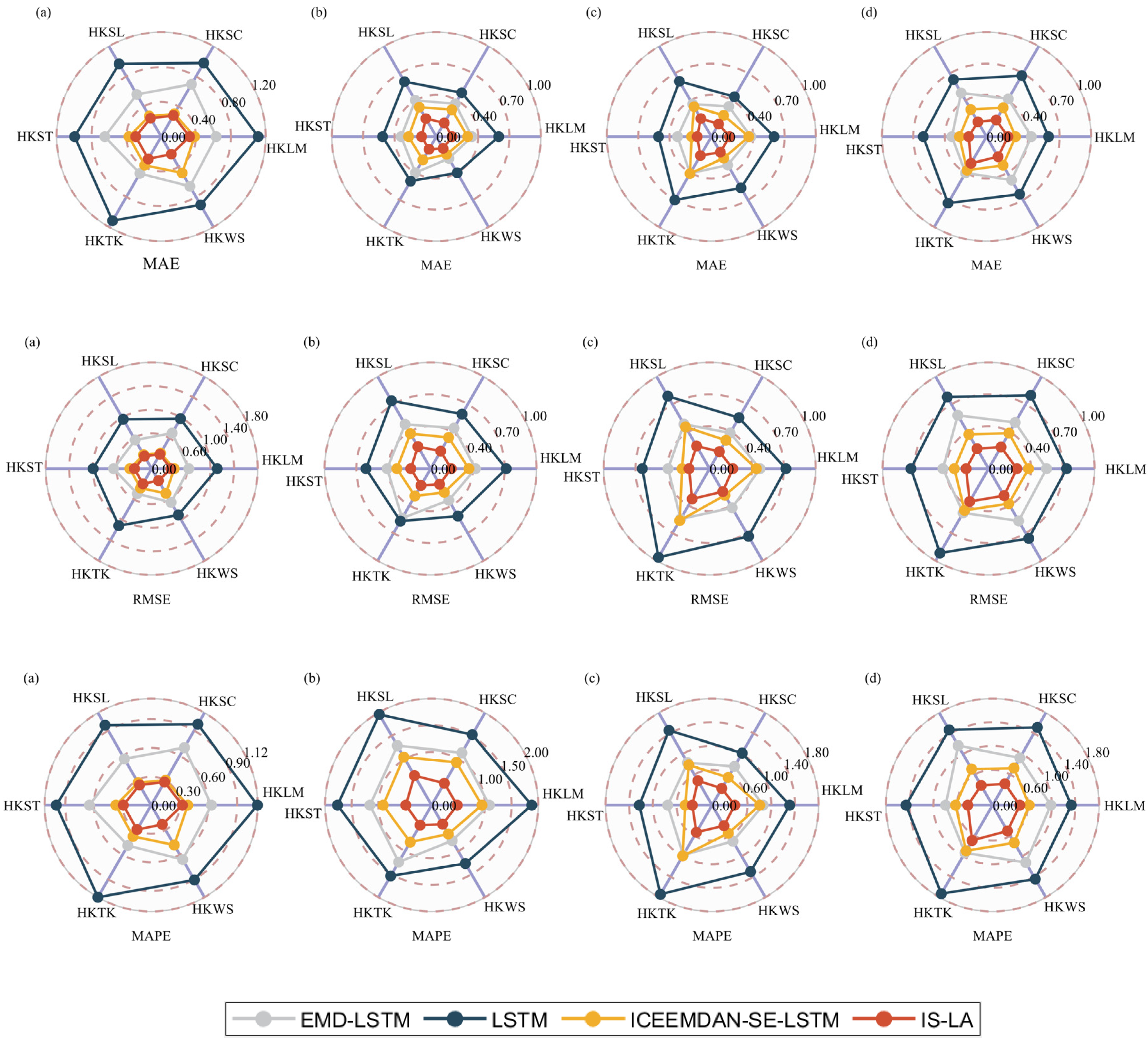
4.1. GNSS-PWV Forecasts for Different Sites
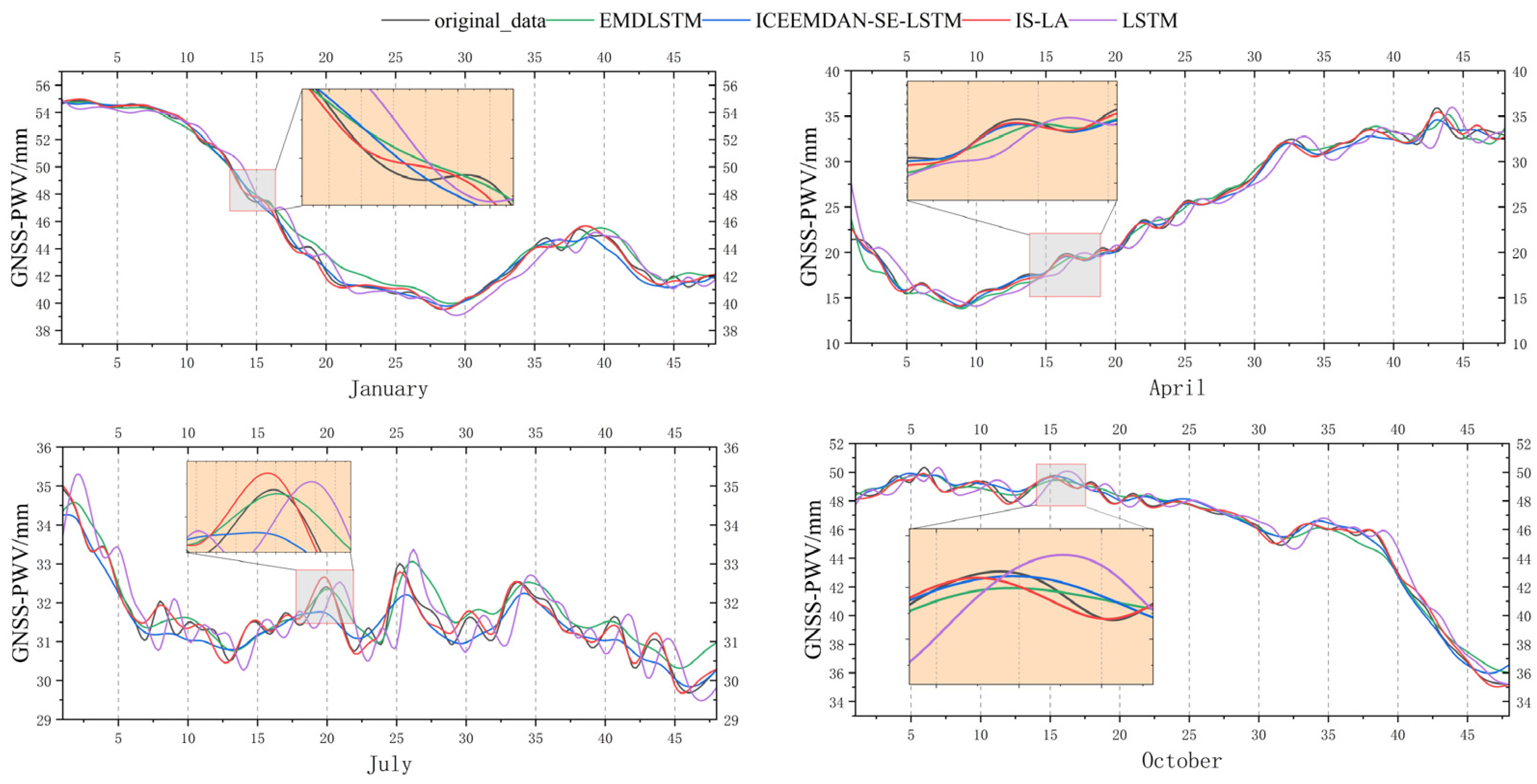
4.2. GNSS-PWV Forecasts for Different Months
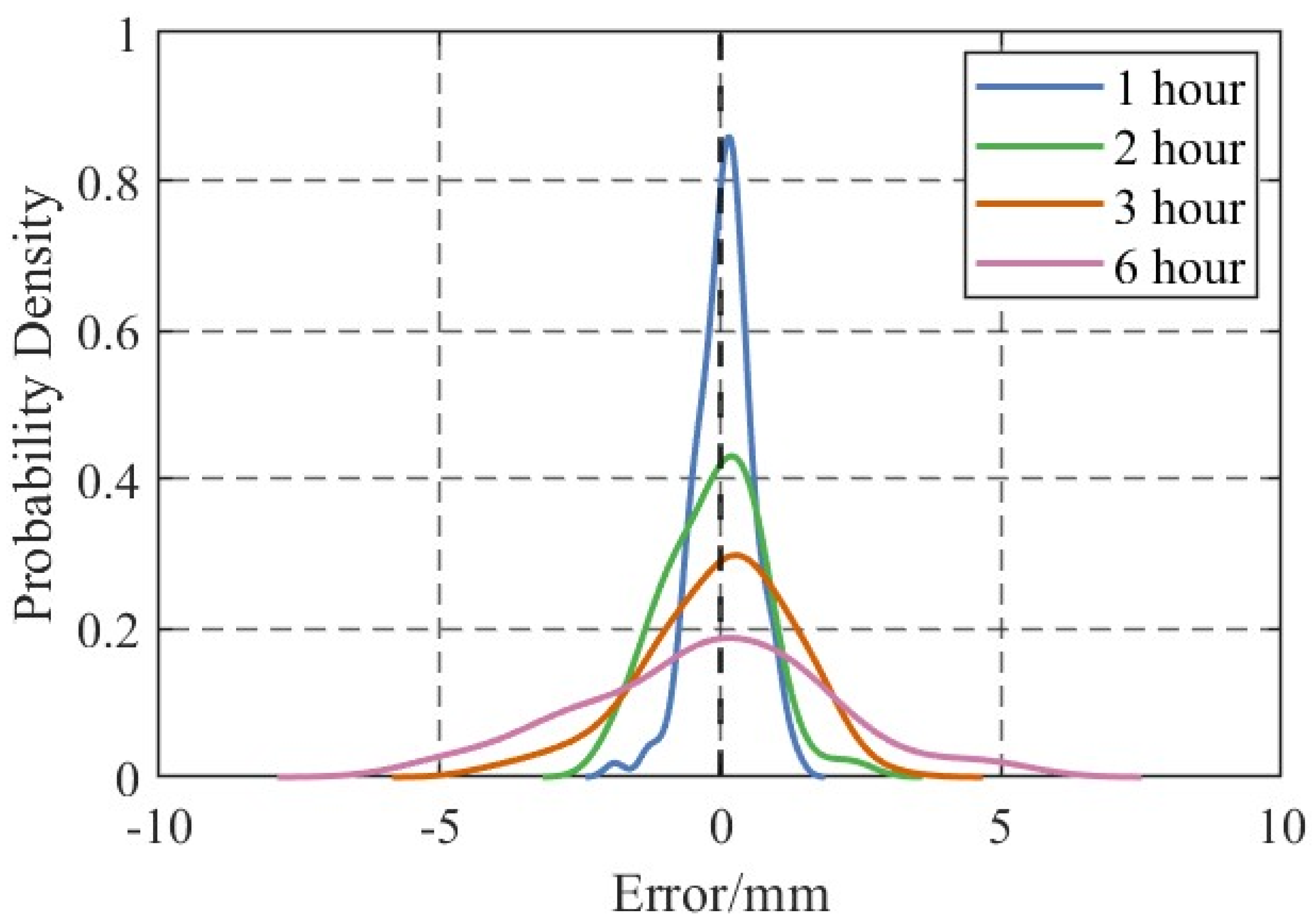
4.3. GNSS-PWV Forecasts for Different Steps
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PWV | Precipitable Water Vapor |
| GNSS | Global Navigation Satellite System |
| CORSs | Continuously Operating Reference Stations |
| EMD | Empirical Mode Decomposition |
| CEEMDAN | Complete Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition with Adaptive Noise |
| ICEEMDAN | Improved Complete Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition with Adaptive Noise |
| SE | Sample Entropy |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| ARIMA | Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average model |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| MAPE | Mean Absolute Percentage Error |
| ZTD | Zenith Tropospheric delay |
| ZHD | Zenith Hydrostatic Delay |
| ZWD | Zenith Wet Delay |
| IMF | Intrinsic Mode Function |
| AIC | Akaike Information Criterion |
| BIC | Bayesian Information Criterion |
| ADF | Augmented Dickey–Fuller Test |
| BDS | Binary Decision Diagrams Test |
Appendix A. Appendix Information and Missing Data Rates for Seven Sites in the Hong Kong Region
| Stations | Latitude | Longitude | Elevation (m) | Missing Data Rates |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HKLM | 22.219 | 114.120 | 11.245 | 0.27% |
| HKSC | 22.322 | 114.141 | 23.119 | 0.27% |
| HKSL | 22.372 | 113.938 | 99.264 | 0.27% |
| HKST | 22.395 | 114.184 | 261.534 | 0.58% |
| HKTK | 22.547 | 114.223 | 25.462 | 0.82% |
| HKWS | 22.434 | 114.335 | 66.107 | 0.58% |
| Radio | 22.310 | 114.170 | 66.000 | 0.19% |
References
- Liu, Z.; Fan, Q.; Lv, Q.; Wang, M.; Wu, J.; Liu, Y.; Xu, C. A Novel Linear Rainfall Forecast Model Based on GNSS Observations and CAPE. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Ma, X.; Yao, W.; Liu, Y.; Yao, Y. A Drought Monitoring Method Based on Precipitable Water Vapor and Precipitation. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 10727–10741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Yao, Y.; Yao, W. GPS-based PWV for precipitation forecasting and its application to a typhoon event. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2018, 167, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Lu, C.; Han, X.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y. Real-time shipborne multi-GNSS atmospheric water vapor retrieval over the South China Sea. GPS Solut. 2023, 27, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Liu, R.; Huo, Y.; Wu, Y.; Ye, S.; Wang, S.; Mu, X.; Zhu, L. Retrieving the Atmospheric Water Vapor Profile Combining FY-4A/GIIRS and Ground-Based GNSS PWV in Hong Kong Region. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 63, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Zhang, K.; Wu, S.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, X.; Shen, Z.; Li, L.; Wan, M.; Liu, X. Real-Time GNSS-Derived PWV for Typhoon Characterizations: A Case Study for Super Typhoon Mangkhut in Hong Kong. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, D.; He, Q.; Li, L.; Fu, E.; Zhang, K. Accuracy Assessment of ERA5-ZTD/PWV and Response of Typhoon Events in China. J. Catastrophology 2024, 39, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.B.; Wang, X.M.; Wu, S.Q.; Zhang, K.F.; Chen, X.L.; Qiu, C.; Zhang, S.T.; Zhang, J.L.; Xie, M.Q.; Li, L. Development of an Improved Model for Prediction of Short-Term Heavy Precipitation Based on GNSS-Derived PWV. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Yang, W.; Gao, M.; Ding, N.; Zhang, W.; Li, L.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, K. The WOA-CNN-LSTM-Attention Model for Predicting GNSS Water Vapor. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, M.A.; Souri, A.H. A hybrid LS-HE and LS-SVM model to predict time series of precipitable water vapor derived from GPS measurements. Arab. J. Geosci. 2015, 8, 7257–7272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffari-Razin, S.R.; Majd, R.D.; Hooshangi, N. Regional modeling and forecasting of precipitable water vapor using least square support vector regression. Adv. Space Res. 2023, 71, 4725–4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acheampong, A.; Obeng, K. Application of GNSS derived precipitable water vapour prediction in West Africa. J. Geod. Sci. 2019, 9, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffari Razin, M.-R.; Voosoghi, B. Modeling of precipitable water vapor from GPS observations using machine learning and tomography methods. Adv. Space Res. 2022, 69, 2671–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, Q. Precipitable water vapor estimation from Himawari-8/AHI observations using a stacking machine learning model. Atmos. Res. 2024, 301, 107281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Ye, T. Predicting precipitable water vapor by using ANN from GPS ZTD data at Antarctic Zhongshan Station. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2019, 191, 105059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkal, O.; Yildiz, B.Y.; Sahin, M.; Pestemalci, V. Precipitable water modelling using artificial neural network in Cukurova region. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffari-Razin, S.R.; Davari Majd, R.; Hooshangi, N. Estimation of precipitable water vapor (PWV) using generalized regression neural network (GRNN) and comparison against tomography, ECMWF, Saastamoinen, GPT3 and ANN models. J. Water Health 2023, 49, 243–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.; Manandhar, S.; Lee, Y.H.; Winkler, S.; Dev, S. Forecasting Precipitable Water Vapor Using LSTMs. In Proceedings of the IEEE AP-S Symposium on Antennas and Propagation and CNC/USNC-URSI Joint Meeting, Montréal, QC, Canada, 5–10 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Wei, G.; Ren, R. Improved BP neural network model for prediction of atmospheric precipitable water vapor. J. Navig. Position. 2020, 8, 63–67, 110. [Google Scholar]
- Kou, M.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, W.; Ma, J.; Ren, J.; Wang, G. Application research of combined model based on VMD and MOHHO in precipitable water vapor Prediction. Atmos. Res. 2023, 292, 106841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.P.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z. RBF Prediction Model Based on EMD for Forecasting GPS Precipitable Water Vapor and Annual Precipitation. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 765–767, 2830–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shangguan, M.; Dang, M.; Yue, Y.; Zou, R. A Combined Model to Predict GNSS Precipitable Water Vapor Based on Deep Learning. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 4713–4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.D.; Lin, X.; Xu, Y.S.; Dai, R.T.; Yang, C.; Zhao, L.W.; Han, Y.K. The VMD-Informer-BiLSTM-EAA Hybrid Model for Predicting Zenith Tropospheric Delay. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wu, L.; Sun, M.; Lu, Y.N.; Han, Y.H. Application of Boundary Local Feature Scale Adaptive Matching Extension EMD Endpoint Effect Suppression Method in Blasting Seismic Wave Signal Processing. Shock Vib. 2021, 2021, 2804539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liu, S.; Zhang, H. Adaptive estimation of VMD modes number based on cross correlation coefficient. J. Vibroengineering 2017, 19, 1185–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Suganthan, P.N.; Srikanth, N. A Comparative Study of Empirical Mode Decomposition-Based Short-Term Wind Speed Forecasting Methods. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2015, 6, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Lu, Q. Forecasting gold price using a novel hybrid model with ICEEMDAN and LSTM-CNN-CBAM. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 206, 117847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, M.; Zhang, W.; Ren, J.; Zhang, X. A combined model based on data decomposition and multi-model weighted optimization for precipitable water vapor forecasting. Earth Sci. Inform. 2022, 15, 2213–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Lv, W.; Han, Y.; Lu, F.; Liu, J. Prediction of CORS Water Vapor Values Based on the CEEMDAN and ARIMA-LSTM Combination Model. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevis, M.; Businger, S.; Herring, T.A.; Rocken, C.; Anthes, R.A.; Ware, R.H. GPS Meteorology: Remote Sensing of Atmospheric Water Vapor Using the Global Positioning System. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1992, 97, 15787–15801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colominas, M.A.; Schlotthauer, G.; Torres, M.E. Improved complete ensemble EMD: A suitable tool for biomedical signal processing. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2014, 14, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, A.; Schmidhuber, J. Framewise phoneme classification with bidirectional LSTM and other neural network architectures. Neural Netw. 2005, 18, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.M.; Shen, Z.; Wan, M.F.; Li, L.J. Precipitable Water Vapor Converted from GNSS-ZTD and ERA5 Datasets for the Monitoring of Tropical Cyclones. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 87275–87290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
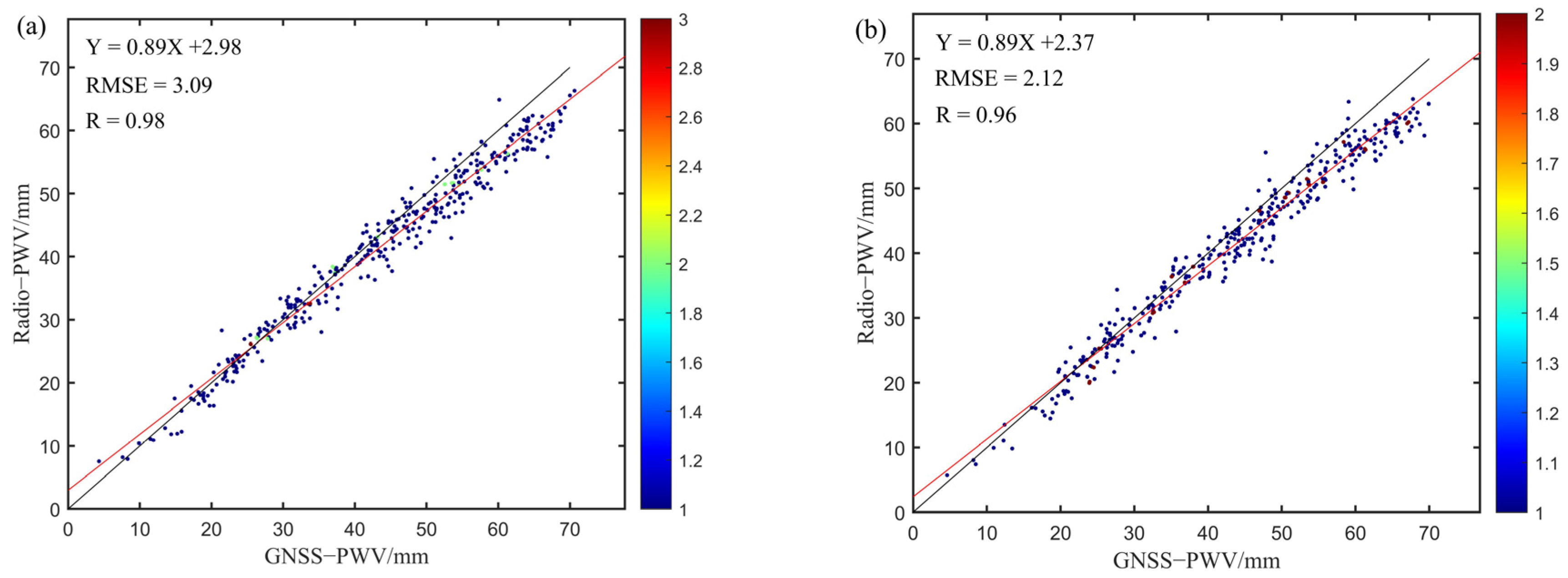


| Time | BIAS/mm | RMSE/mm | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum | Minimum | Average | ||
| 12 moments | 11.05 | −6.86 | 1.98 | 3.09 |
| 0 moment | 11.21 | −7.70 | 1.16 | 2.12 |
| Models | Mean-MAE/mm | Mean-RMSE/mm | Mean-MAPE/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| LSTM | 0.61 | 0.80 | 3.25% |
| EMD-LSTM | 0.43 | 0.55 | 2.43% |
| ICEEMDAN-SE-LSTM | 0.31 | 0.40 | 1.46% |
| IS-LA | 0.26 | 0.34 | 1.29% |
| Models | January | April | July | October | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | RMSE | MAPE | MAE | RMSE | MAPE | MAE | RMSE | MAPE | MAE | RMSE | MAPE | |
| LSTM | 1.11 | 1.52 | 4.83% | 0.60 | 0.71 | 1.88% | 0.60 | 0.72 | 1.31% | 0.59 | 0.74 | 1.33% |
| EMD-LSTM | 0.63 | 0.84 | 2.72% | 0.34 | 0.42 | 1.08% | 0.38 | 0.48 | 0.86% | 0.43 | 0.55 | 0.98% |
| ICEEMDAN-SE-LSTM | 0.38 | 0.50 | 1.53% | 0.30 | 0.36 | 0.94% | 0.33 | 0.44 | 0.80% | 0.28 | 0.38 | 0.62% |
| IS-LA | 0.33 | 0.43 | 1.37% | 0.15 | 0.19 | 0.48% | 0.17 | 0.22 | 0.38% | 0.21 | 0.27 | 0.46% |
| Predicted Steps | Mean-MAE/mm | Mean-RMSE/mm | Mean-MAPE/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 h | 0.40 | 0.51 | 1.85% |
| 2 h | 0.77 | 0.98 | 3.67% |
| 3 h | 0.92 | 1.16 | 4.31% |
| 6 h | 1.73 | 2.19 | 7.74% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, J.; Lin, X.; Yuan, Z.; Du, N.; Cai, X.; Yang, C.; Zhao, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, L. GNSS Precipitable Water Vapor Prediction for Hong Kong Based on ICEEMDAN-SE-LSTM-ARIMA Hybrid Model. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1675. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101675
Zhao J, Lin X, Yuan Z, Du N, Cai X, Yang C, Zhao J, Xu Y, Zhao L. GNSS Precipitable Water Vapor Prediction for Hong Kong Based on ICEEMDAN-SE-LSTM-ARIMA Hybrid Model. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(10):1675. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101675
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Jie, Xu Lin, Zhengdao Yuan, Nage Du, Xiaolong Cai, Cong Yang, Jun Zhao, Yashi Xu, and Lunwei Zhao. 2025. "GNSS Precipitable Water Vapor Prediction for Hong Kong Based on ICEEMDAN-SE-LSTM-ARIMA Hybrid Model" Remote Sensing 17, no. 10: 1675. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101675
APA StyleZhao, J., Lin, X., Yuan, Z., Du, N., Cai, X., Yang, C., Zhao, J., Xu, Y., & Zhao, L. (2025). GNSS Precipitable Water Vapor Prediction for Hong Kong Based on ICEEMDAN-SE-LSTM-ARIMA Hybrid Model. Remote Sensing, 17(10), 1675. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101675











