Variability Assessment of Global Extreme Coastal Sea Levels Using Altimetry Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
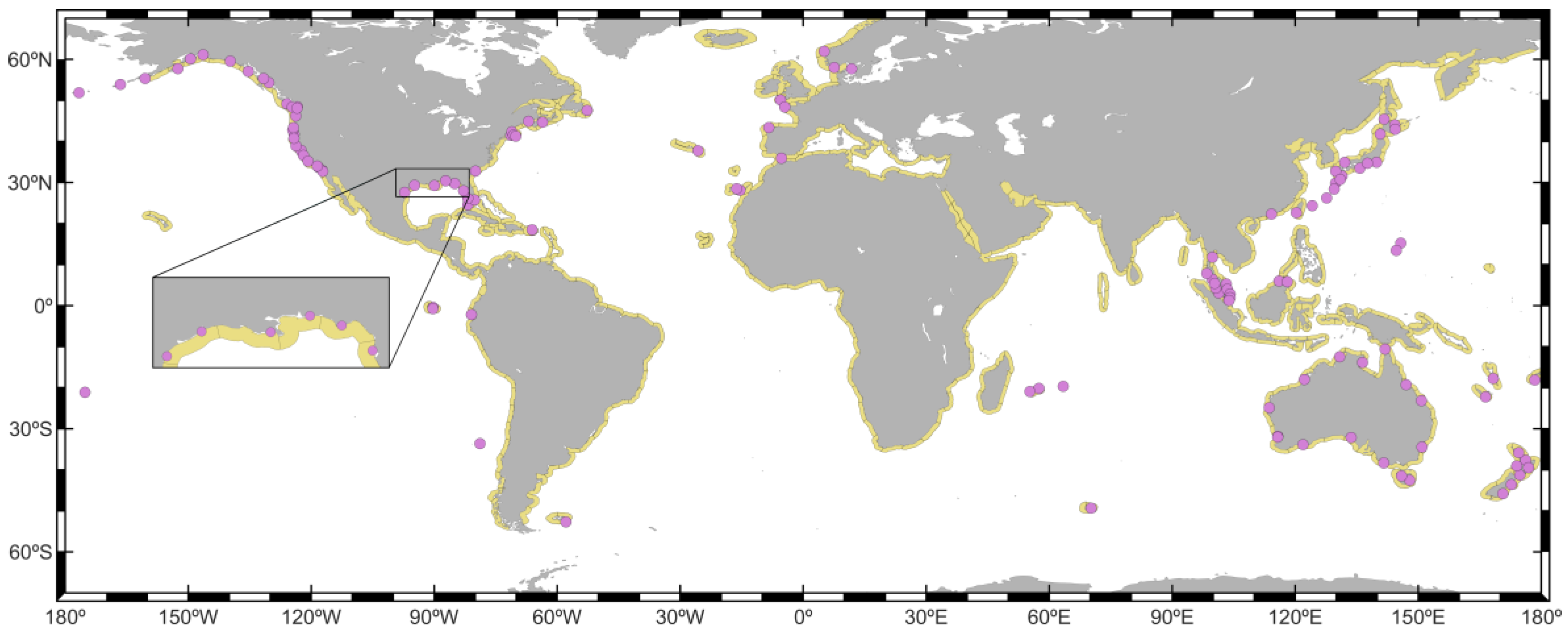
2.1. Sea Level Altimetry Data
2.2. In Situ Data for Validation
2.3. Climate Teleconnection Indices Data
2.4. Statistical Extreme Model
2.5. Non-Tidal Residual Coastal Extreme Sample
2.6. Extreme Variability Assessment
2.6.1. Intra-Annual Variability
2.6.2. Long-Term Trends
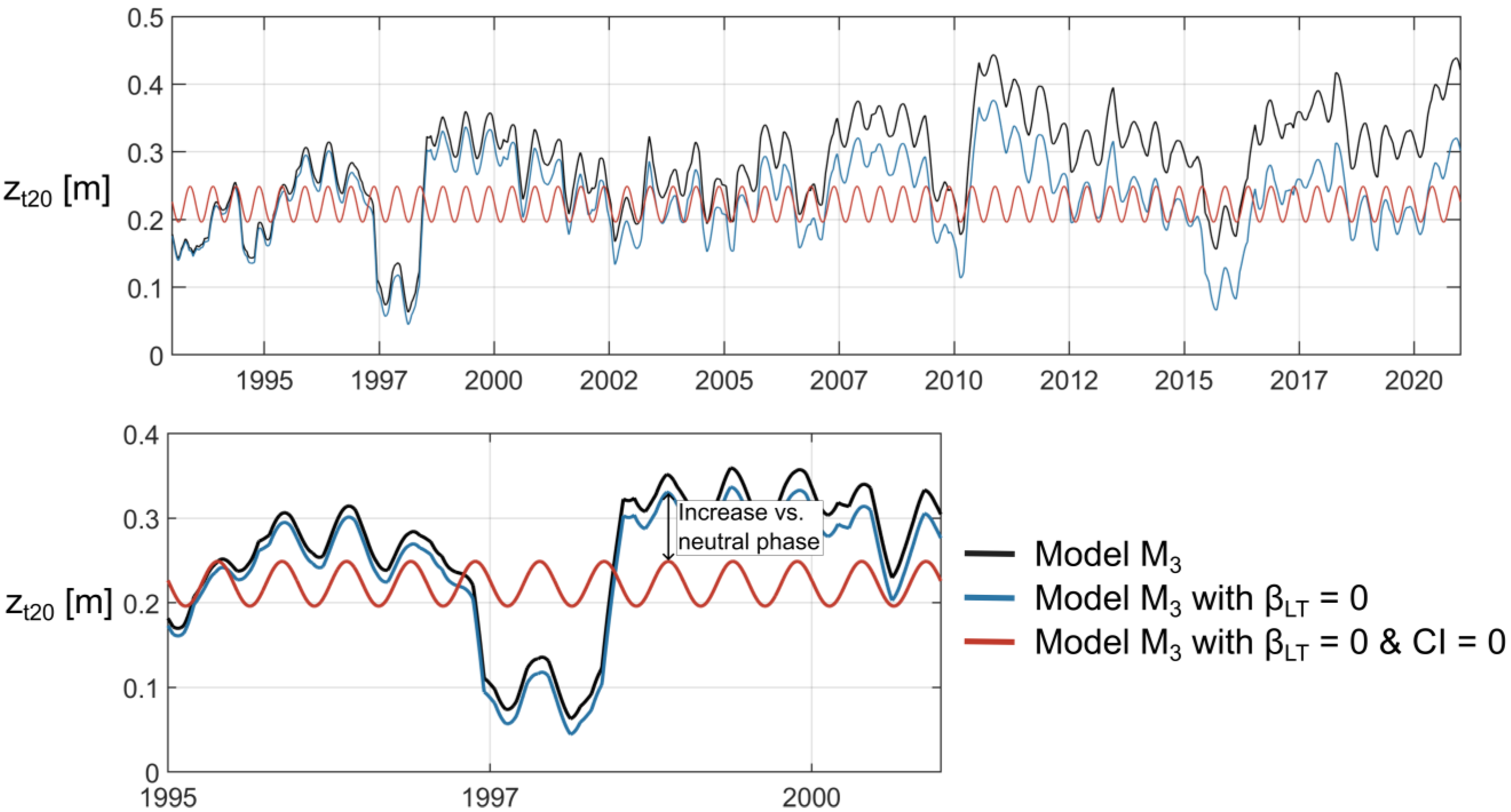
2.6.3. Inter-Annual Variability
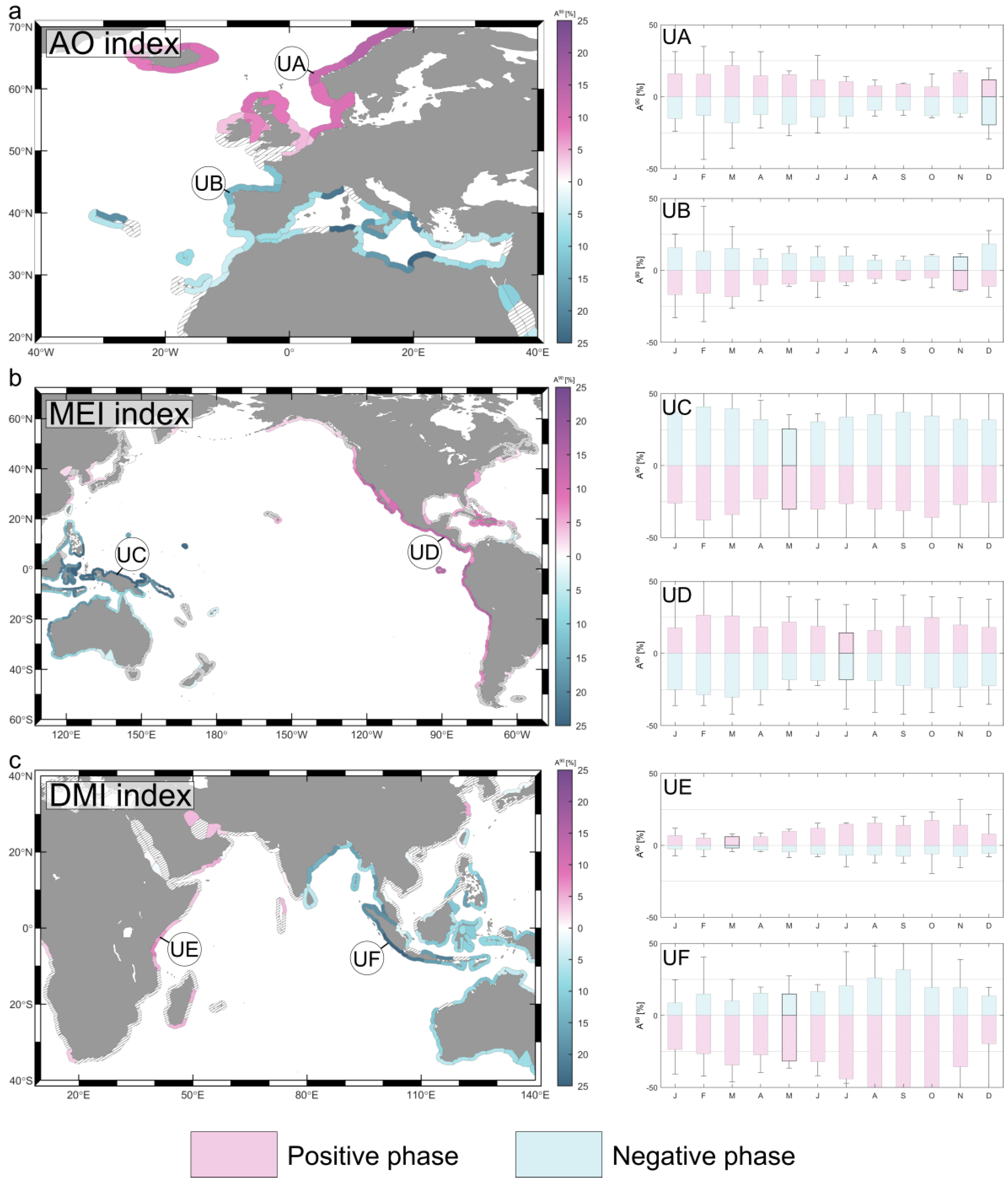
2.6.4. Extreme Variability Dominance
3. Results
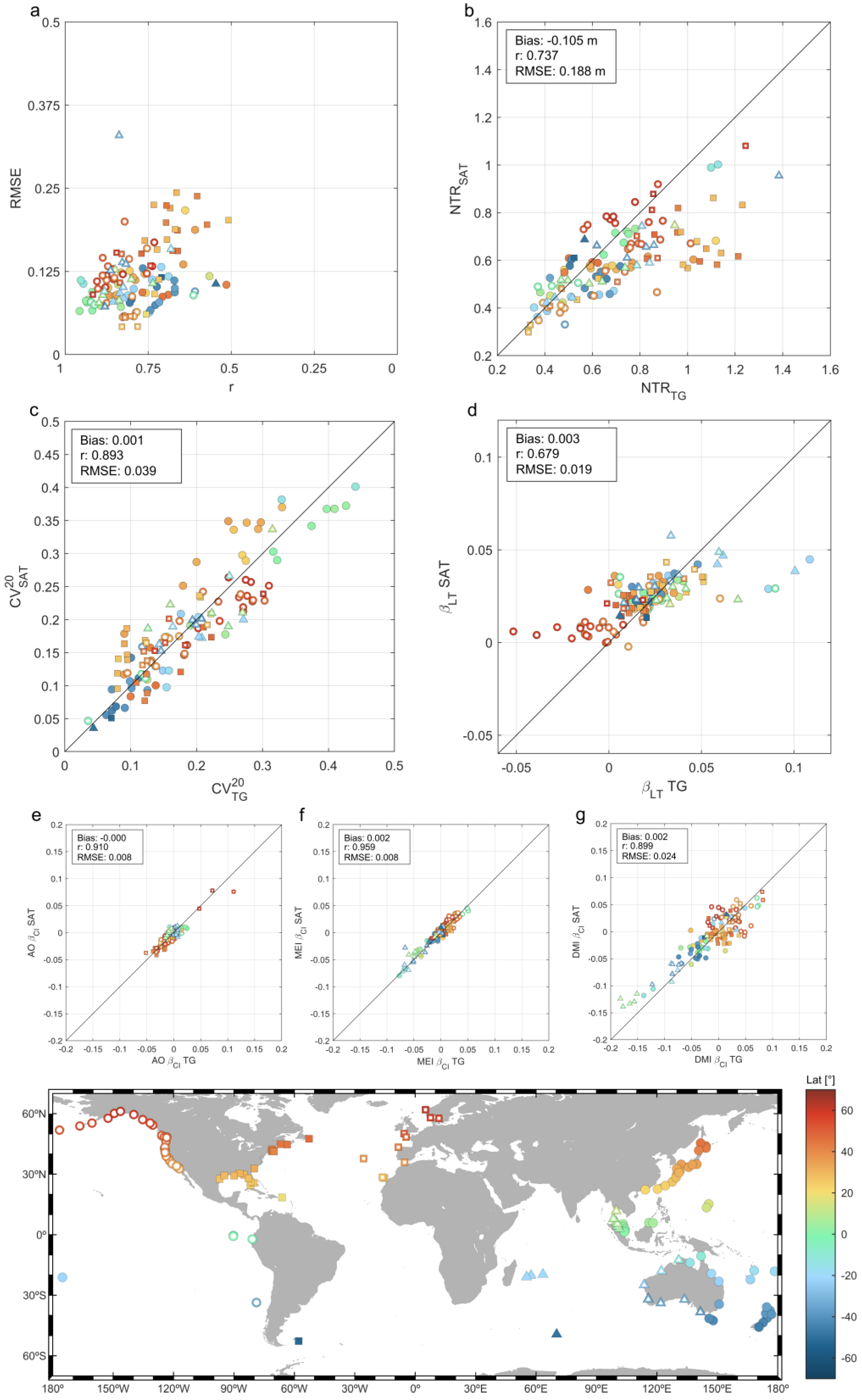
3.1. Validation of NTRSAT
3.1.1. Selection of the Validation Extreme Sample
3.1.2. Validation Results
3.2. Intensity of Coastal NTR Extremes
3.3. Climate Variability of Coastal ESLs
3.3.1. Intra-Annual Variability
3.3.2. Long-Term Trends
3.3.3. Inter-Annual Variability
3.3.4. Extreme Variability Dominance
4. Conclusions and Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Losada, I.J.; Toimil, A.; Muñoz, A.; Garcia-Fletcher, A.P.; Diaz-Simal, P. A Planning Strategy for the Adaptation of Coastal Areas to Climate Change: The Spanish Case. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2019, 182, 104983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueda, A.; Vitousek, S.; Camus, P.; Tomás, A.; Espejo, A.; Losada, I.J.; Barnard, P.L.; Erikson, L.H.; Ruggiero, P.; Reguero, B.G.; et al. A Global Classification of Coastal Flood Hazard Climates Associated with Large-Scale Oceanographic Forcing /704/106/829/2737/704/4111/141/129 Article. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bromirski, P.D.; Cayan, D.R.; Helly, J.; Wittmann, P. Wave Power Variability and Trends across the North Pacific. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2013, 118, 6329–6348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Q.; Yue, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z.; Xu, S.; Yang, Y.; Chu, S. Characteristics Analysis and Risk Assessment of Extreme Water Levels Based on 60-Year Observation Data in Xiamen, China. J. Ocean. Univ. China 2022, 21, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.; Muñoz, D.F.; Bakhtyar, R.; Xue, Z.G.; Moftakhari, H.; Ferreira, C.; Mandli, K. Extreme Water Level Simulation and Component Analysis in Delaware Estuary during Hurricane Isabel. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2022, 58, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kates, R.W.; Colten, C.E.; Laska, S.; Leatherman, S.P. Reconstruction of New Orleans after Hurricane Katrina: A Research Perspective. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 14653–14660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toimil, A.; Losada, I.J.; Hinkel, J.; Nicholls, R.J. Using Quantitative Dynamic Adaptive Policy Pathways to Manage Climate Change-Induced Coastal Erosion. Clim. Risk Manag. 2021, 33, 100342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coles, S. An Introduction to Statistical Modeling of Extreme Values, 1st ed.; Springer: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Alves, B.; Angnuureng, D.B.; Morand, P.; Almar, R. A Review on Coastal Erosion and Flooding Risks and Best Management Practices in West Africa: What Has Been Done and Should Be Done. J. Coast. Conserv. 2020, 24, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toimil, A.; Losada, I.J.; Nicholls, R.J.; Dalrymple, R.A.; Stive, M.J.F. Addressing the Challenges of Climate Change Risks and Adaptation in Coastal Areas: A Review. Coast. Eng. 2020, 156, 103611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menéndez, M.; Woodworth, P.L. Changes in Extreme High Water Levels Based on a Quasi-Global Tide-Gauge Data Set. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, T.; Haigh, I.D.; Nicholls, R.J.; Arns, A.; Dangendorf, S.; Hinkel, J.; Slangen, A.B.A. Understanding Extreme Sea Levels for Broad-Scale Coastal Impact and Adaptation Analysis. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 16075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cid, A.; Menéndez, M.; Castanedo, S.; Abascal, A.J.; Méndez, F.J.; Medina, R. Long-Term Changes in the Frequency, Intensity and Duration of Extreme Storm Surge Events in Southern Europe. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 46, 1503–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Männikus, R.; Soomere, T.; Viška, M. Variations in the Mean, Seasonal and Extreme Water Level on the Latvian Coast, the Eastern Baltic Sea, during 1961–2018. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2020, 245, 106827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcos, M.; Woodworth, P.L. Spatiotemporal Changes in Extreme Sea Levels along the Coasts of the North Atlantic and the Gulf of Mexico. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2017, 122, 7031–7048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez, F.J.; Menéndez, M.; Luceño, A.; Losada, I.J. Analyzing Monthly Extreme Sea Levels with a Time-Dependent GEV Model. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2007, 24, 894–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menendez, M.; Mendez, F.J.; Losada, I.J. Forecasting Seasonal to Interannual Variability in Extreme Sea Levels. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2009, 66, 1490–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yan, Y.; Zheng, J.; Li, L.; Dong, X.; Cai, H. Temporal and Spatial Variability of Annual Extreme Water Level in the Pearl River Delta Region, China. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2009, 69, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, P.R.; Mitchum, G.T.; Vonesch, C.; Li, J. Variability of Winter Storminess in the Eastern United States during the Twentieth Century from Tide Gauges. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 9713–9726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wahl, T.; Chambers, D.P. Evidence for Multidecadal Variability in US Extreme Sea Level Records. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2015, 120, 1527–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, B.F.; Landsea, C.W. Assessing the Skill of Operational Atlantic Seasonal Tropical Cyclone Forecasts. Weather. Forecast. 2003, 18, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, D.; Tsirkunov, V. Costs and Benefits of Early Warning Systems. 2011. Available online: https://www.preventionweb.net/english/hyogo/gar/2011/en/bgdocs/Rogers_&_Tsirkunov_2011.pdf (accessed on 30 January 2024).
- Madireddy, M.; Kumara, S.; Medeiros, D.J.; Shankar, V.N. Leveraging Social Networks for Efficient Hurricane Evacuation. Transp. Res. Part. B Methodol. 2015, 77, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamy, R.; Kang, J.E.; Batta, R.; Chung, Y. Hurricane Evacuation Planning Using Public Transportation. Socioecon. Plann Sci. 2017, 59, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semedo, A.; Vettor, R.; Breivik; Sterl, A.; Reistad, M.; Soares, C.G.; Lima, D. The Wind Sea and Swell Waves Climate in the Nordic Seas. Ocean. Dyn. 2015, 65, 223–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillett, N.P.; Kell, T.D.; Jones, P.D. Regional Climate Impacts of the Southern Annular Mode. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Zhang, W.; Feng, X.; Guo, Y.; Hoitink, A.J.F. Storm Surge Variability and Prediction from ENSO and Tropical Cyclones. Environ. Res. Lett. 2023, 18, 024016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson-Delmotte, V.; Zhai, P.; Pirani, A.; Connors, S.L.; Péan, C.; Berger, S.; Caud, N.; Chen, Y.; Goldfarb, L.; Gomis, M.I.; et al. IPCC, 2021: Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cazenave, A.; Dieng, H.B.; Meyssignac, B.; Von Schuckmann, K.; Decharme, B.; Berthier, E. The Rate of Sea-Level Rise. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 358–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, R.J.; Cazenave, A. Sea-Level Rise and Its Impact on Coastal Zones. Science (1979) 2010, 328, 1517–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vousdoukas, M.I.; Mentaschi, L.; Voukouvalas, E.; Verlaan, M.; Feyen, L. Extreme Sea Levels on the Rise along Europe’s Coasts. Earths Future 2017, 5, 304–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vousdoukas, M.I.; Mentaschi, L.; Voukouvalas, E.; Verlaan, M.; Jevrejeva, S.; Jackson, L.P.; Feyen, L. Global Probabilistic Projections of Extreme Sea Levels Show Intensification of Coastal Flood Hazard. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muis, S.; Apecechea, M.I.; Dullaart, J.; de Lima Rego, J.; Madsen, K.S.; Su, J.; Yan, K.; Verlaan, M. A High-Resolution Global Dataset of Extreme Sea Levels, Tides, and Storm Surges, Including Future Projections. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muis, S.; Aerts, J.C.J.H.; José, J.A.; Dullaart, J.C.; Duong, T.M.; Erikson, L.; Haarsma, R.J.; Apecechea, M.I.; Mengel, M.; Le Bars, D.; et al. Global Projections of Storm Surges Using High-Resolution CMIP6 Climate Models. Earths Future 2023, 11, e2023EF003479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirezci, E.; Young, I.R.; Ranasinghe, R.; Muis, S.; Nicholls, R.J.; Lincke, D.; Hinkel, J. Projections of Global-Scale Extreme Sea Levels and Resulting Episodic Coastal Flooding over the 21st Century. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arns, A.; Wahl, T.; Haigh, I.D.; Jensen, J.; Pattiaratchi, C. Estimating Extreme Water Level Probabilities: A Comparison of the Direct Methods and Recommendations for Best Practise. Coast. Eng. 2013, 81, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haigh, I.D.; MacPherson, L.R.; Mason, M.S.; Wijeratne, E.M.S.; Pattiaratchi, C.B.; Crompton, R.P.; George, S. Estimating Present Day Extreme Water Level Exceedance Probabilities around the Coastline of Australia: Tropical Cyclone-Induced Storm Surges. Clim. Dyn. 2014, 42, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, E.; Rohmer, J.; Le Cozannet, G.; Van De Wal, R.S.W. Adaptation Time to Magnified Flood Hazards Underestimated When Derived from Tide Gauge Records. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 074015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebisi, N.; Balogun, A.L.; Min, T.H.; Tella, A. Advances in Estimating Sea Level Rise: A Review of Tide Gauge, Satellite Altimetry and Spatial Data Science Approaches. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2021, 208, 105632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denys, P.H.; Beavan, R.J.; Hannah, J.; Pearson, C.F.; Palmer, N.; Denham, M.; Hreinsdottir, S. Sea Level Rise in New Zealand: The Effect of Vertical Land Motion on Century-Long Tide Gauge Records in a Tectonically Active Region. J. Geophys. Res. Solid. Earth 2020, 125, e2019JB018055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebaldi, C.; Strauss, B.H.; Zervas, C.E. Modelling Sea Level Rise Impacts on Storm Surges along US Coasts. Environ. Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 014032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muis, S.; Verlaan, M.; Winsemius, H.C.; Aerts, J.C.J.H.; Ward, P.J. A Global Reanalysis of Storm Surges and Extreme Sea Levels. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sheng, J. Examination of Extreme Sea Levels Due to Storm Surges and Tides over the Northwest Pacific Ocean. Cont. Shelf Res. 2015, 93, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, D.; Li, J.; Hou, Y.; Hu, P. Modeling the Sea Level Response of the Northern East China Sea to Different Types of Extratropical Cyclones. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2023, 128, e2022JC018728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipollini, P.; Calafat, F.M.; Jevrejeva, S.; Melet, A.; Prandi, P. Monitoring Sea Level in the Coastal Zone with Satellite Altimetry and Tide Gauges. Surv. Geophys. 2017, 38, 33–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valle-Rodríguez, J.; Trasviña-Castro, A. Sea Level Anomaly Measurements from Satellite Coastal Altimetry and Tide Gauges at the Entrance of the Gulf of California. Adv. Space Res. 2020, 66, 1593–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stammer, D.; Ray, R.D.; Andersen, O.B.; Arbic, B.K.; Bosch, W.; Carrère, L.; Cheng, Y.; Chinn, D.S.; Dushaw, B.D.; Egbert, G.D.; et al. Accuracy assessment of global barotropic ocean tidemodels. Rev. Geophys. 2014, 52, 243–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamlington, B.D.; Willis, J.K.; Vinogradova, N. The Emerging Golden Age of Satellite Altimetry to Prepare Humanity for Rising Seas. Earths Future 2023, 11, e2023EF003673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legeais, J.F.; Meyssignac, B.; Faugère, Y.; Guerou, A.; Ablain, M.; Pujol, M.I.; Dufau, C.; Dibarboure, G. Copernicus Sea Level Space Observations: A Basis for Assessing Mitigation and Developing Adaptation Strategies to Sea Level Rise. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 704721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazenave, A.; Palanisamy, H.; Ablain, M. Contemporary Sea Level Changes from Satellite Altimetry: What Have We Learned? What Are the New Challenges? Adv. Space Res. 2018, 62, 1639–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prandi, P.; Meyssignac, B.; Ablain, M.; Spada, G.; Ribes, A.; Benveniste, J. Local Sea Level Trends, Accelerations and Uncertainties over 1993–2019. Sci Data 2021, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Qi, Y. Trends of Sea Level Variations in the South China Sea from Merged Altimetry Data. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2007, 57, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handoko, E.Y.; Richasari, D.S.; Pratomo, D.G. Seasonal and Interannual of Sea Level Variability in the Indonesian Seas Using Satellite Altimetry. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing Ltd.: Bristol, UK, 2021; Volume 731, p. 012004. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J.; Guo, J.; Zhu, C.; Hwang, C.; Yu, D.; Sun, M.; Mu, D. High-Resolution Sea Level Change around China Seas Revealed through Multi-Satellite Altimeter Data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 102, 102433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Montillet, J.P.; Fernandes, R.; Melbourne, T.I.; Jiang, W.; Huang, Z. Sea Level Rise Estimation on the Pacific Coast from Southern California to Vancouver Island. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, D.T.; Llovel, W.; Nguyen, T.M.; Le, H.Q.; Le, M.N.; Ha, H.T. Sea-Level Trends and Variability along the Coast of Vietnam over 2002–2018: Insights from the X-TRACK/ALES Altimetry Dataset and Coastal Tide Gauges. Adv. Space Res. 2023, 73, 1630–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benveniste, J.; Birol, F.; Calafat, F.; Cazenave, A.; Dieng, H.; Gouzenes, Y.; Legeais, J.F.; Léger, F.; Niño, F.; Passaro, M.; et al. Coastal Sea Level Anomalies and Associated Trends from Jason Satellite Altimetry over 2002–2018. Sci Data 2020, 7, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazenave, A.; Gouzenes, Y.; Birol, F.; Leger, F.; Passaro, M.; Calafat, F.M.; Shaw, A.; Nino, F.; Legeais, J.F.; Oelsmann, J.; et al. Sea Level along the World’s Coastlines Can Be Measured by a Network of Virtual Altimetry Stations. Commun. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazenave, A.; Gouzenes, Y.; Lancelot, L.; Birol, F.; Legér, F.; Passaro, M.; Calafat, F.M.; Shaw, A.; Niño, F.; Legeais, J.F.; et al. New Network of Virtual Altimetry Stations for Measuring Sea Level along the World Coastlines. SEOANE 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, R.J.; Cuttler, M.V.W.; Hansen, J.E. Climatic Drivers of Extreme Sea Level Events Along the Coastline of Western Australia. Earths Future 2021, 9, e2020EF001620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korotaev, G.K.; Saenko, O.A.; Koblinsky, C.J. Satellite Altimetry Observations of the Black Sea Level. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2001, 106, 917–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Ma, Z.; Chen, N.; Chen, N.; Yang, J.; Chen, D. Hurricane Isaac Storm Surges off Florida Observed by Jason-1 and Jason-2 Satellite Altimeters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 198, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobeto, H.; Menendez, M.; Losada, I.J. Toward a Methodology for Estimating Coastal Extreme Sea Levels From Satellite Altimetry. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2018, 123, 8284–8298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujol, M.I.; Faugère, Y.; Taburet, G.; Dupuy, S.; Pelloquin, C.; Ablain, M.; Picot, N. DUACS DT2014: The New Multi-Mission Altimeter Data Set Reprocessed over 20 Years. Ocean. Sci. 2016, 12, 1067–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignudelli, S.; Kostianoy, A.G.; Cipollini, P.; Benveniste, J. (Eds.) Coastal Altimetry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; ISBN 978-3-642-12795-3. [Google Scholar]
- Codiga, D.L. Unified Tidal Analysis and Prediction Using the UTide Matlab Functions; Technical Report. 2011.01; Graduate School of Oceanography, University of Rhose Island: Narragansett, RI, USA, 2011; p. 59. [Google Scholar]
- Antony, C.; Testut, L.; Unnikrishnan, A.S. Observing Storm Surges in the Bay of Bengal from Satellite Altimetry. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2014, 151, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Andersen, O.B.; Knudsen, P. Integrating Non-Tidal Sea Level Data from Altimetry and Tide Gauges for Coastal Sea Level Prediction. Adv. Space Res. 2012, 50, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, T.; Li, G.; Zhang, Y. Observing Storm Surges in China’s Coastal Areas by Integrating Multi-Source Satellite Altimeters. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 225, 106224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, L.P.M.; Almar, R.; Meyssignac, B.; Viet, N.T. Contributions to Coastal Flooding Events in Southeast of Vietnam and Their Link with Global Mean Sea Level Rise. Geosciences 2018, 8, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, O.B.; Cheng, Y. Long Term Changes of Altimeter Range and Geophysical Corrections at Altimetry Calibration Sites. Adv. Space Res. 2013, 51, 1468–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R.A. Statistical Methods for Research Workers. In Breakthroughs in Statistics: Methodology and Distribution; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1970; pp. 66–70. [Google Scholar]
- Hodson, T.O. Root-Mean-Square Error (RMSE) or Mean Absolute Error (MAE): When to Use Them or Not. Geosci. Model. Dev. 2022, 15, 5481–5487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, C.F.; Motyka, R.J.; Freymueller, J.T.; Echelmeyer, K.A.; Ivins, E.R. Rapid Uplift of Southern Alaska Caused by Recent Ice Loss. Geophys. J. Int. 2004, 158, 1118–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, J.C.; Plafker, G. Tide Gage Measurements of Uplift along the South Coast of Alaska. J. Geophys. Res. 1991, 96, 4325–4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodet, G.; Castelle, B.; Masselink, G.; Scott, T.; Davidson, M.; Floc’h, F.; Jackson, D.; Suanez, S. Beach Recovery from Extreme Storm Activity during the 2013–14 Winter along the Atlantic Coast of Europe. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2019, 44, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettle, A.J. Storm Xaver over Europe in December 2013: Overview of Energy Impacts and North Sea Events. Adv. Geosci. 2020, 54, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Douglas, B.C.; Leatherman, S.P. Twentieth-Century Storm Activity along the U.S. East Coast. J. Clim. 2000, 13, 1748–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogi, M.; Tachibana, Y.; Yamazaki, K. Impact of the Wintertime North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO) on the Summertime Atmospheric Circulation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boumis, G.; Moftakhari, H.R.; Moradkhani, H. Coevolution of Extreme Sea Levels and Sea-Level Rise Under Global Warming. Earths Future 2023, 11, e2023EF003649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lobeto, H.; Menendez, M. Variability Assessment of Global Extreme Coastal Sea Levels Using Altimetry Data. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1355. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16081355
Lobeto H, Menendez M. Variability Assessment of Global Extreme Coastal Sea Levels Using Altimetry Data. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(8):1355. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16081355
Chicago/Turabian StyleLobeto, Hector, and Melisa Menendez. 2024. "Variability Assessment of Global Extreme Coastal Sea Levels Using Altimetry Data" Remote Sensing 16, no. 8: 1355. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16081355
APA StyleLobeto, H., & Menendez, M. (2024). Variability Assessment of Global Extreme Coastal Sea Levels Using Altimetry Data. Remote Sensing, 16(8), 1355. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16081355





