Laser Backscattering Analytical Model of Doppler Power Spectra about Convex Quadric Bodies of Revolution during Precession
Abstract
1. Introduction
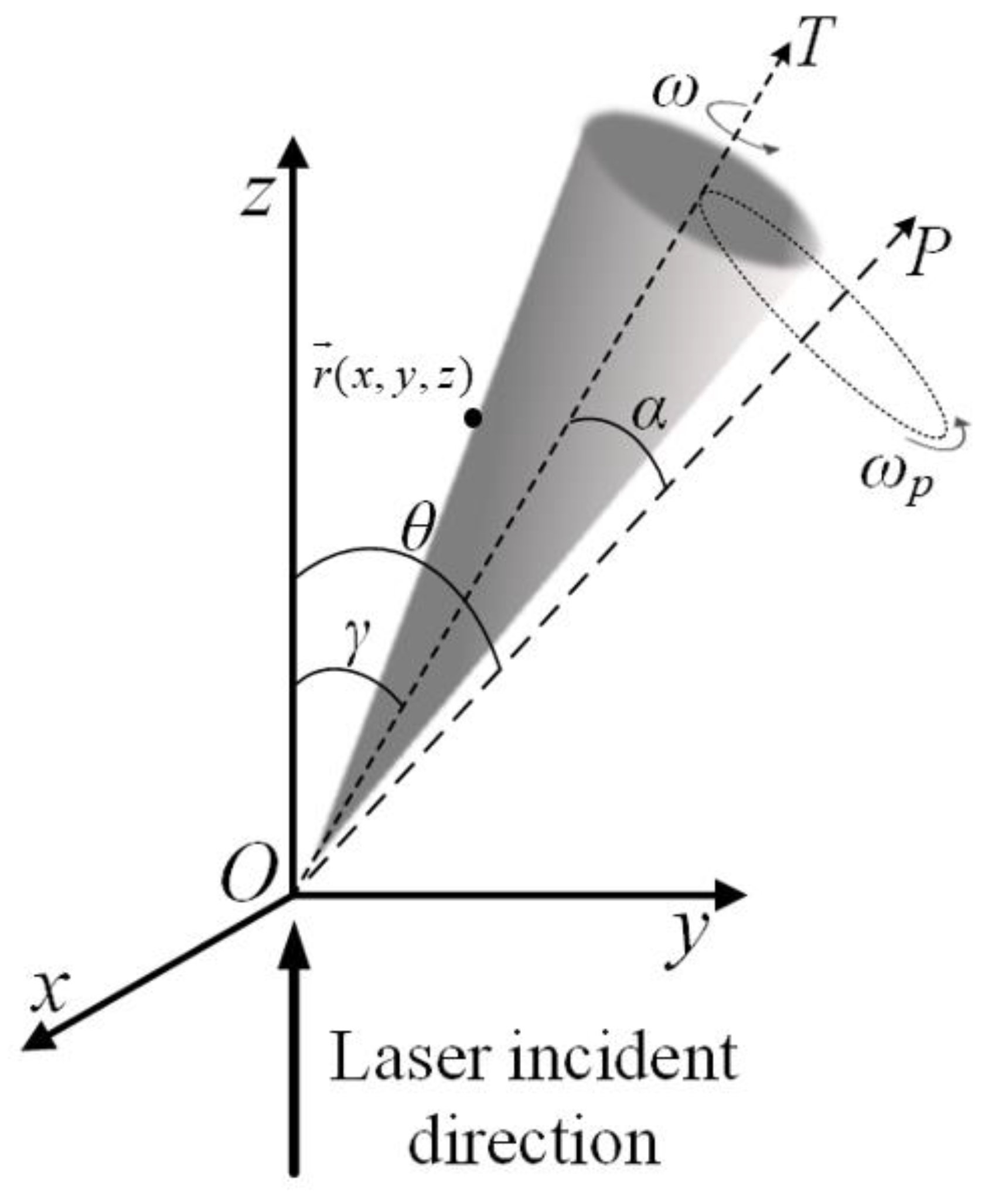
2. Model of Space Precession Target
3. Simulations and Discussion
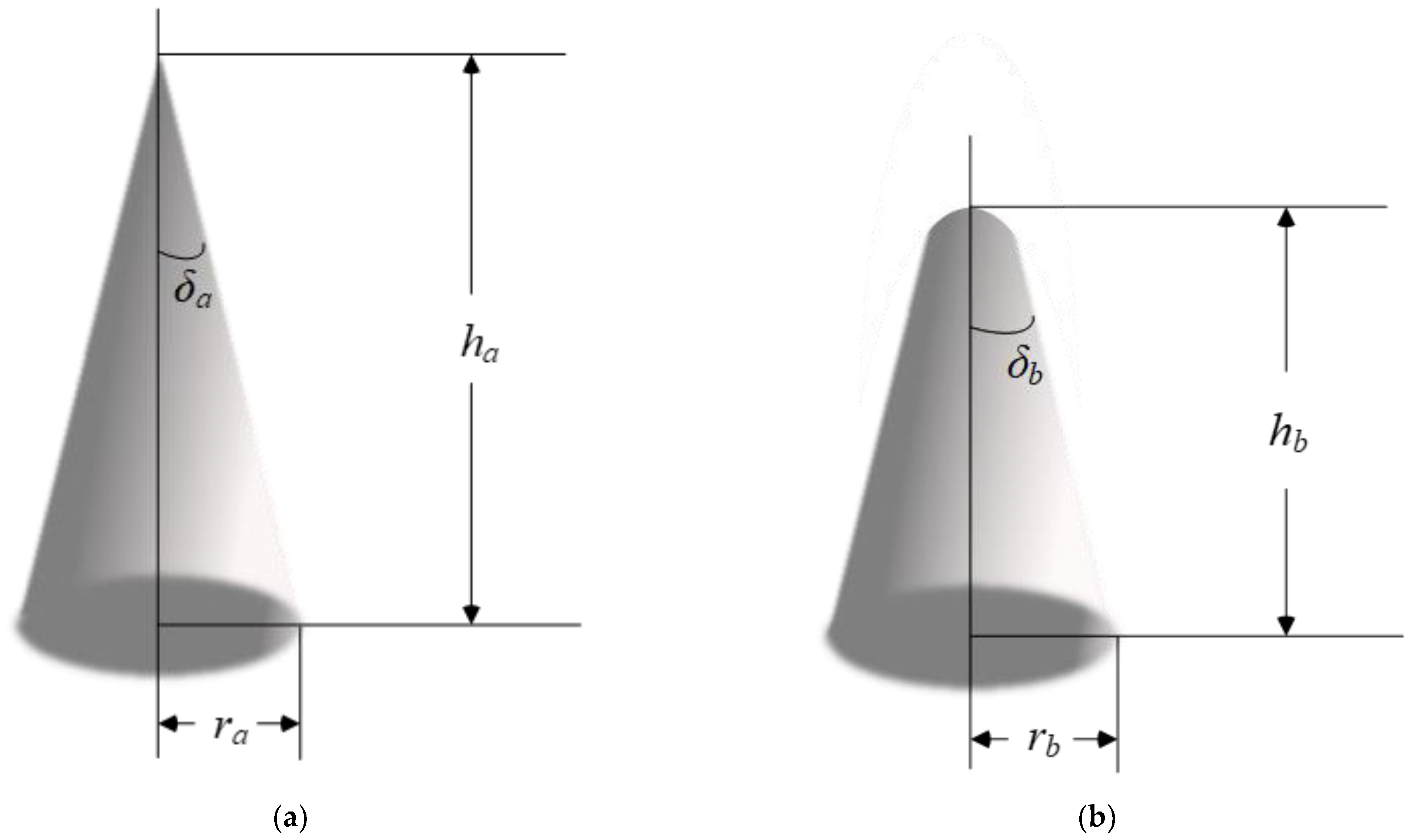
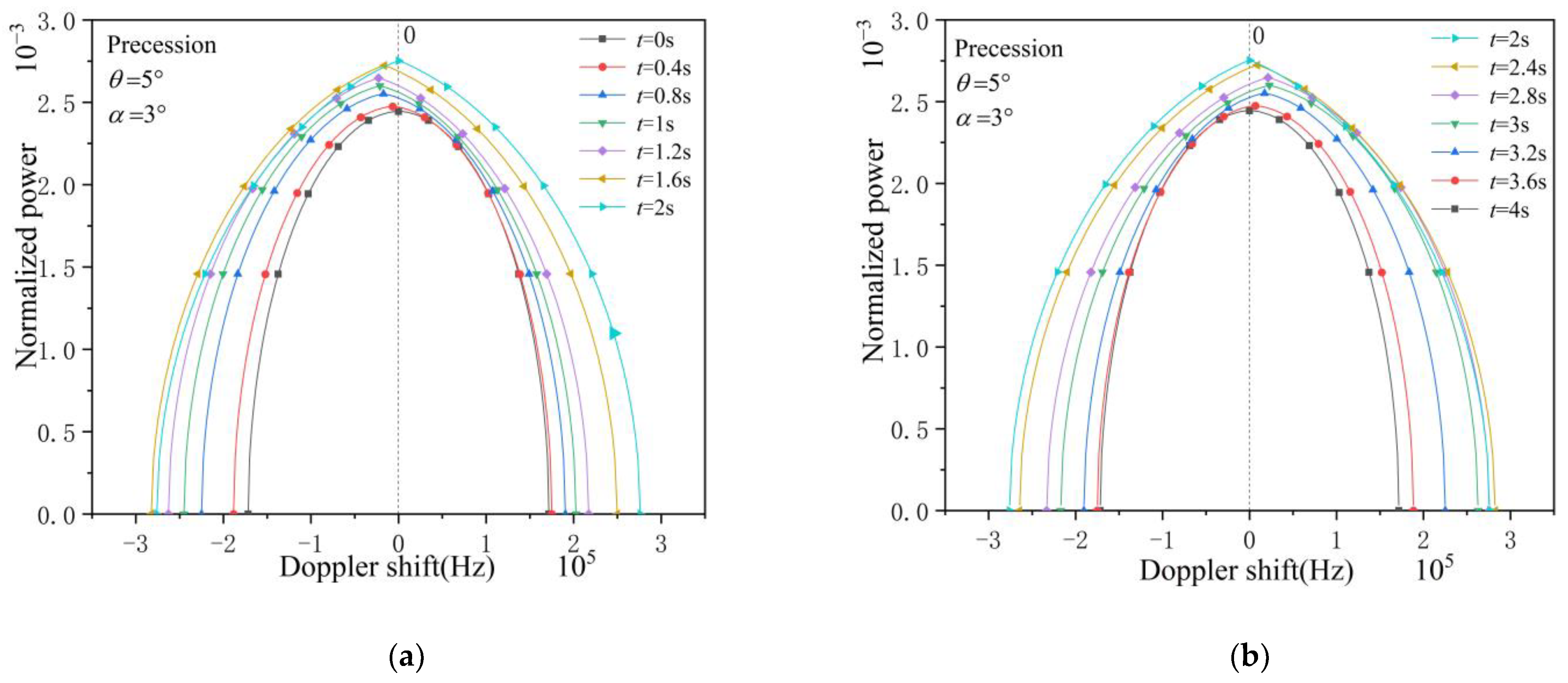
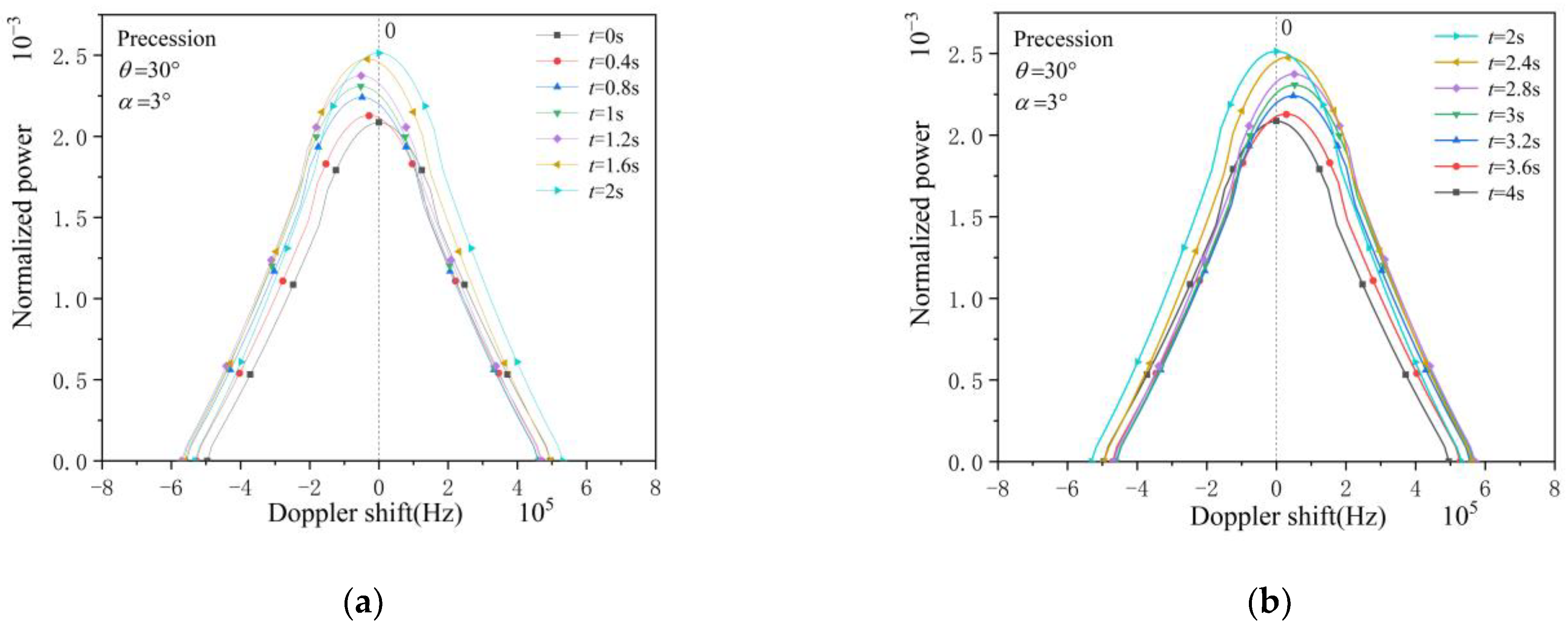
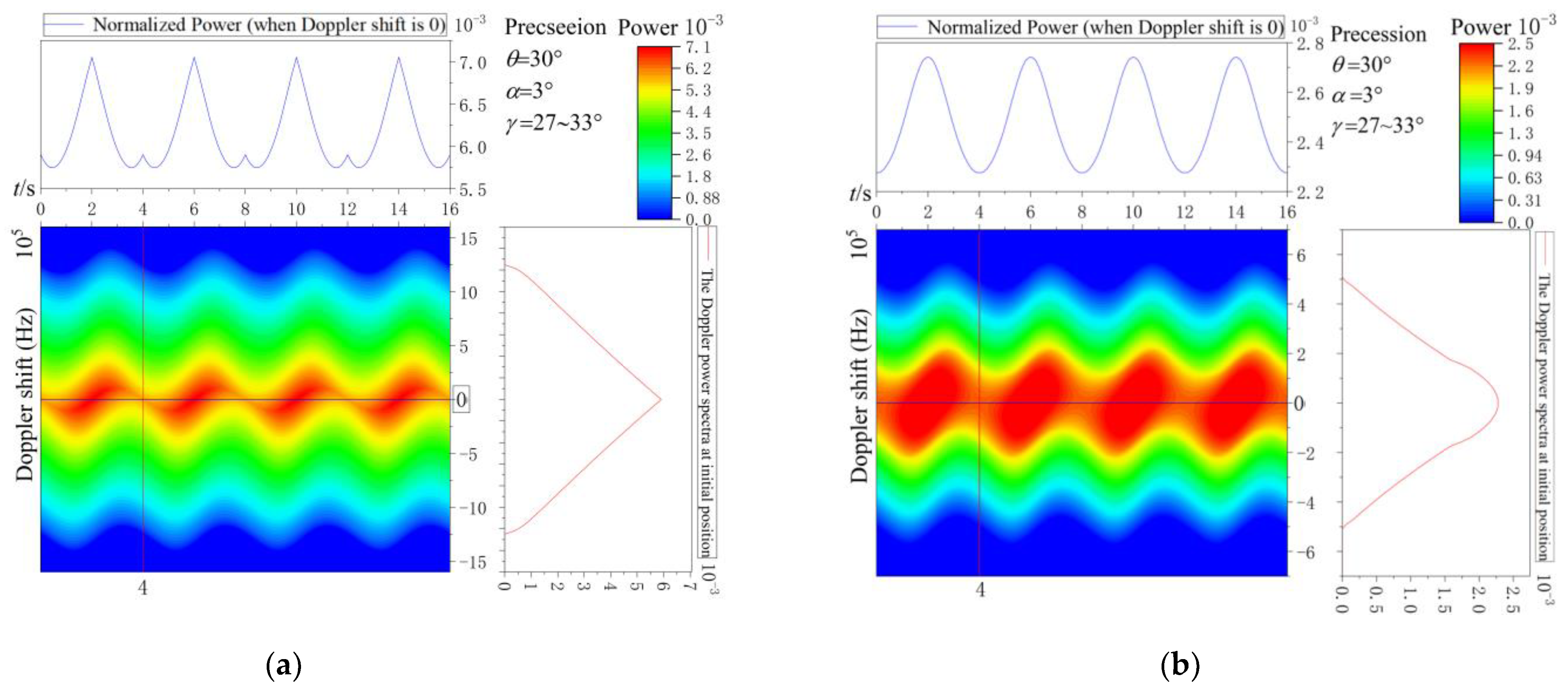
3.1. Precession Cone and Sphere–Cone Combination
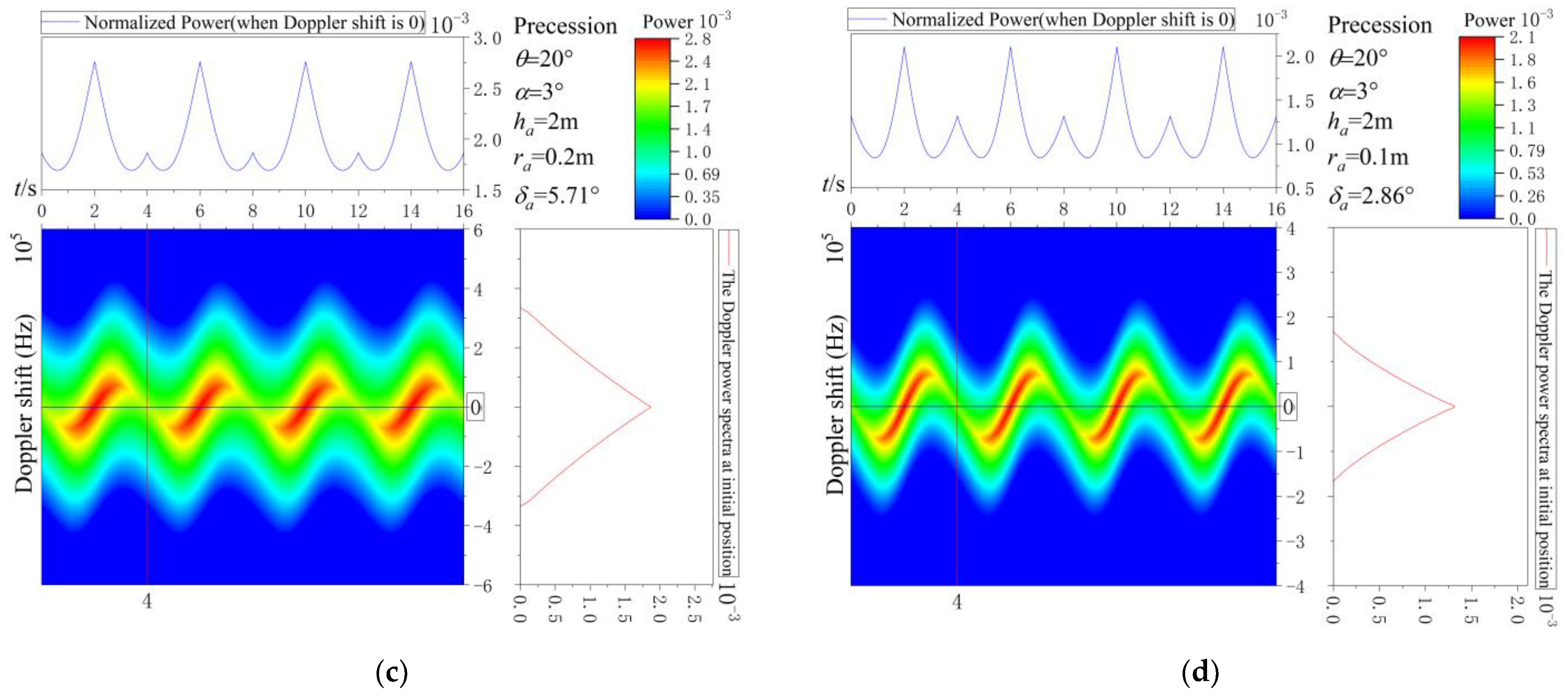
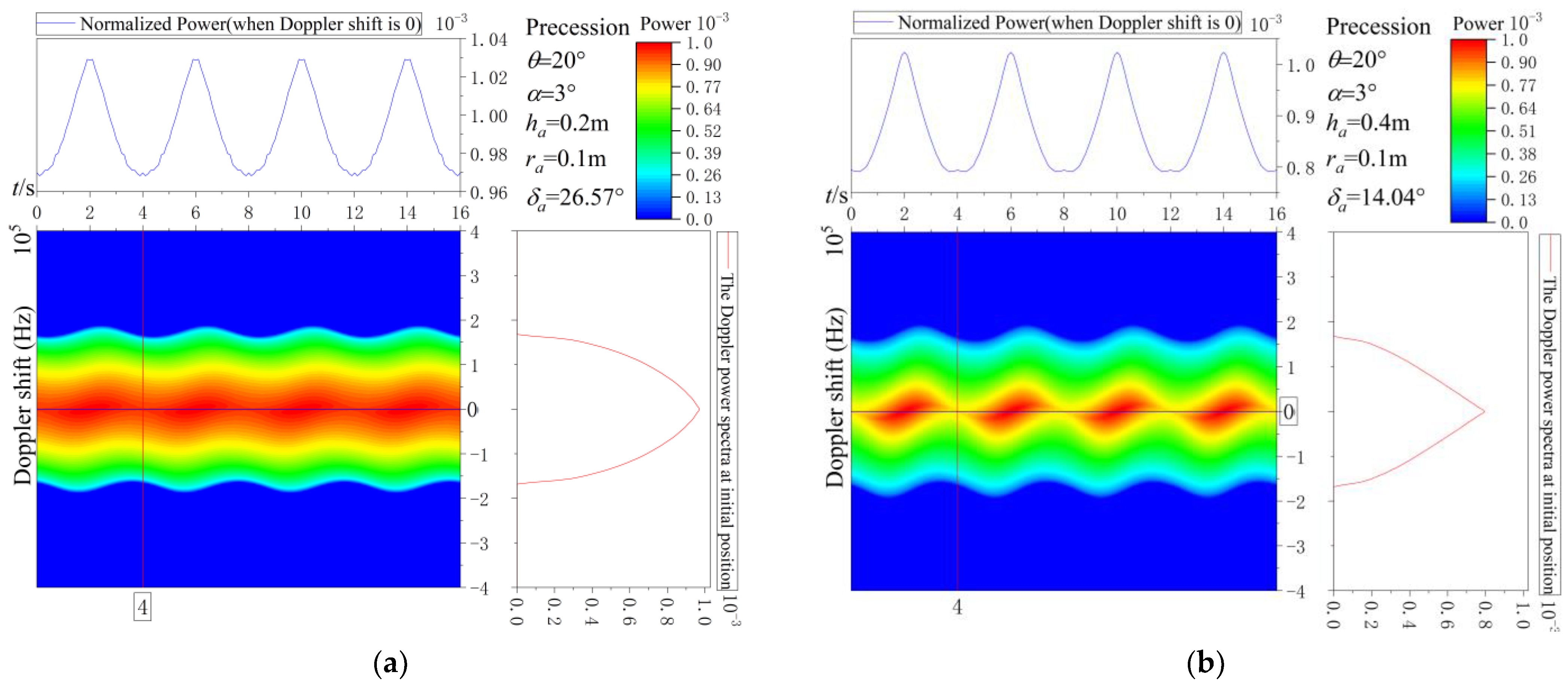
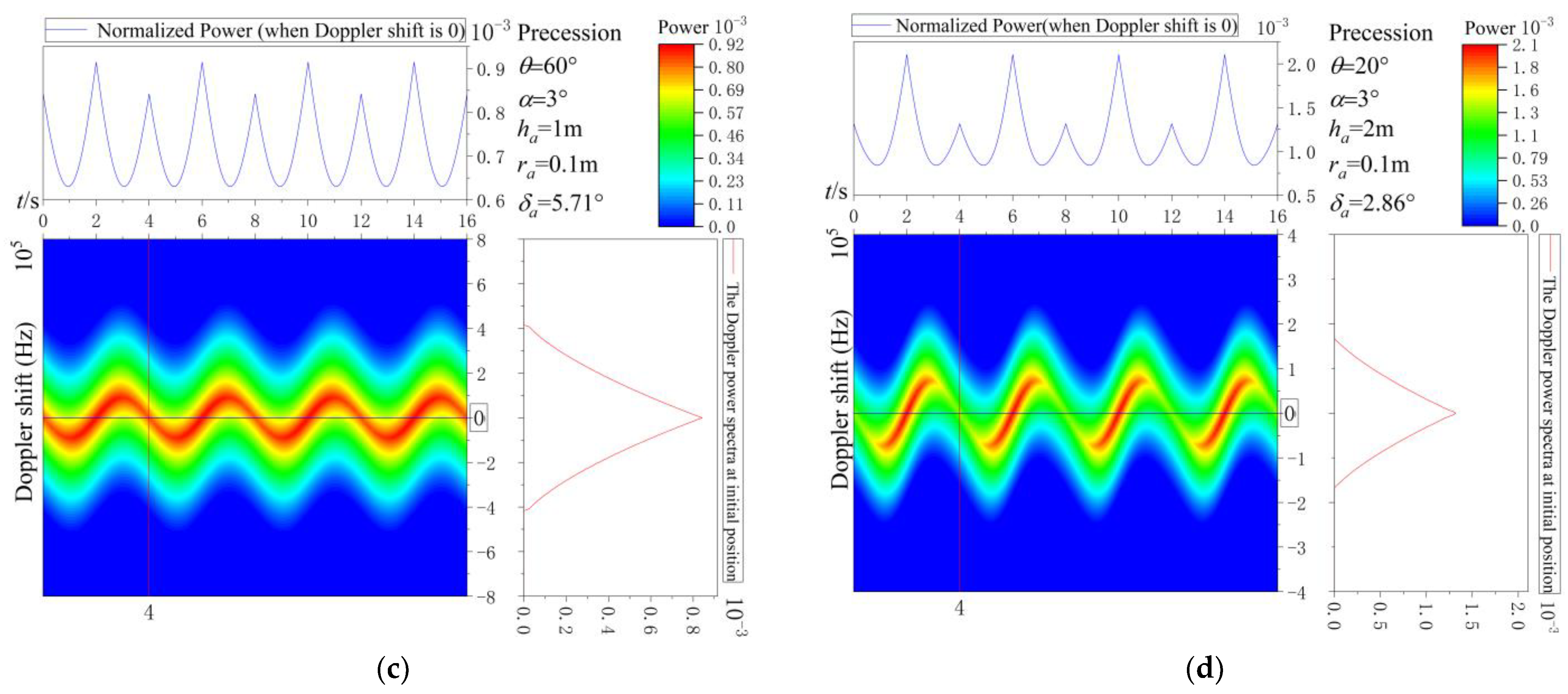
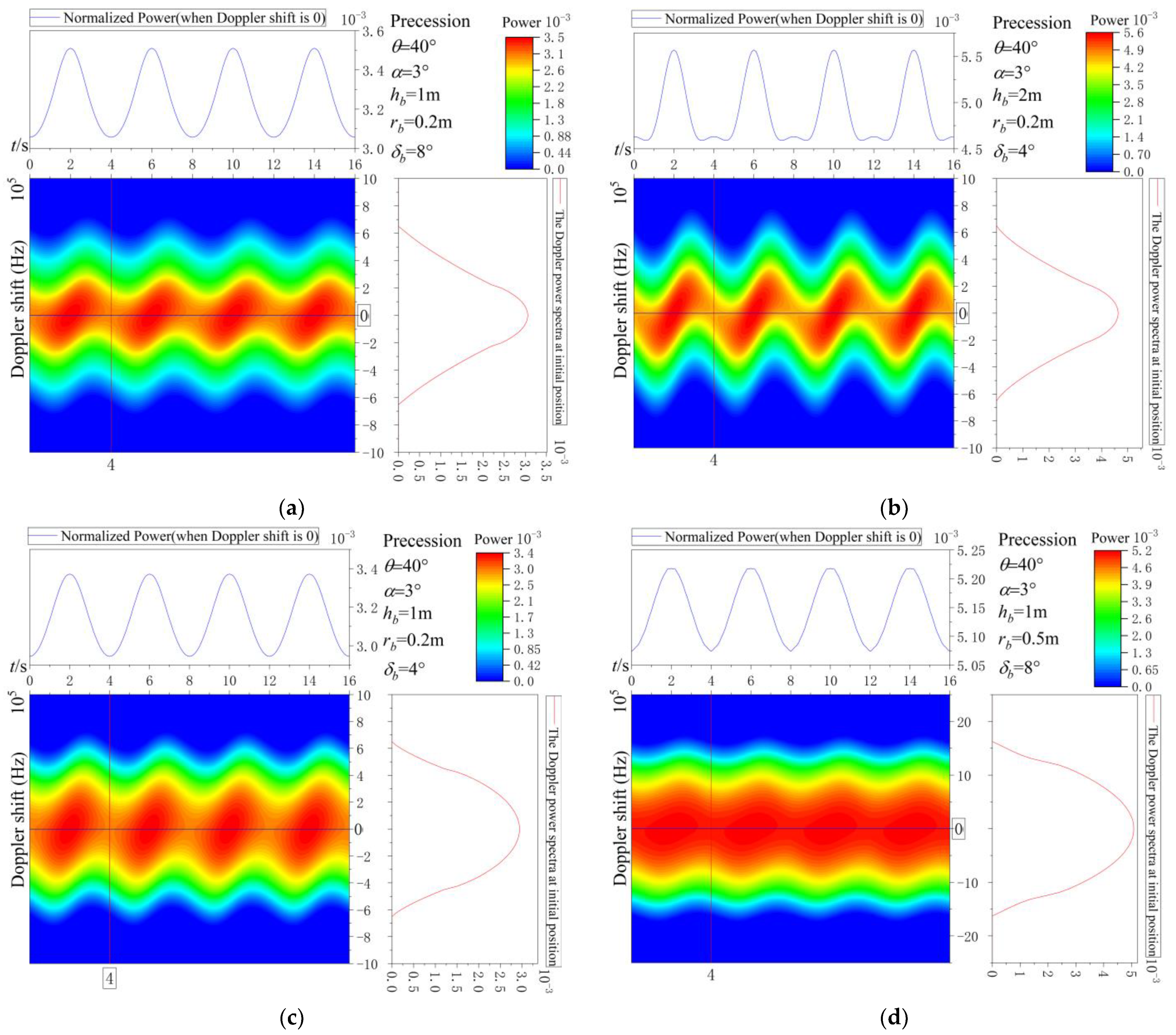
3.2. The Influence of Geometric Parameters on Doppler Spectra
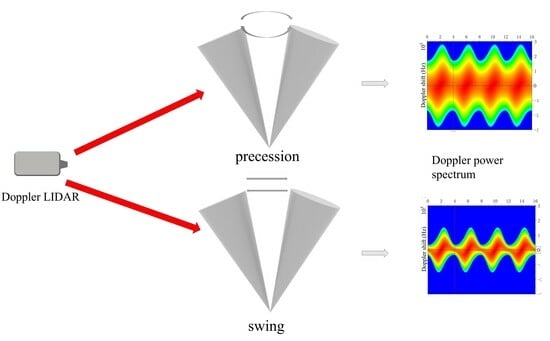
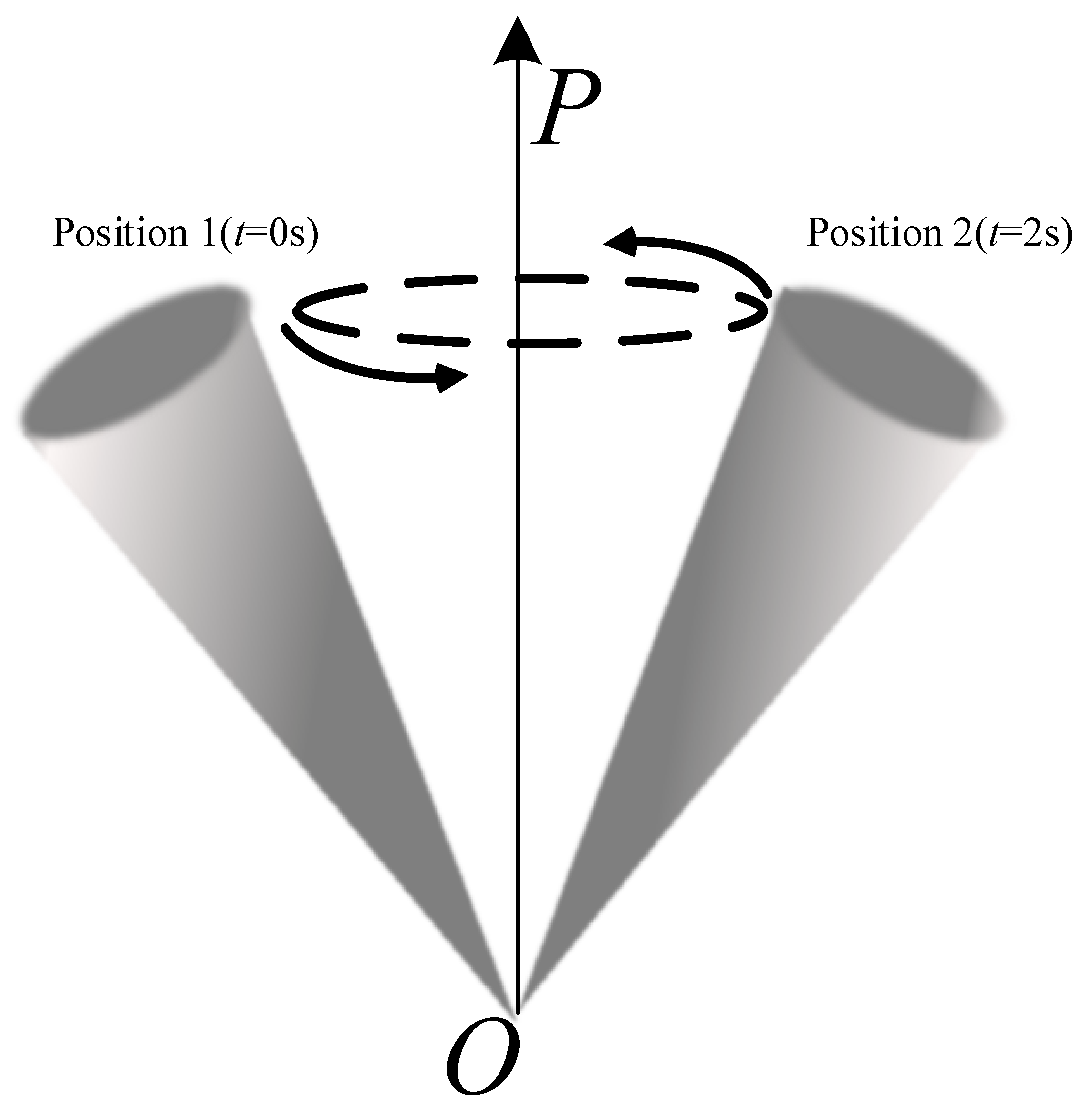
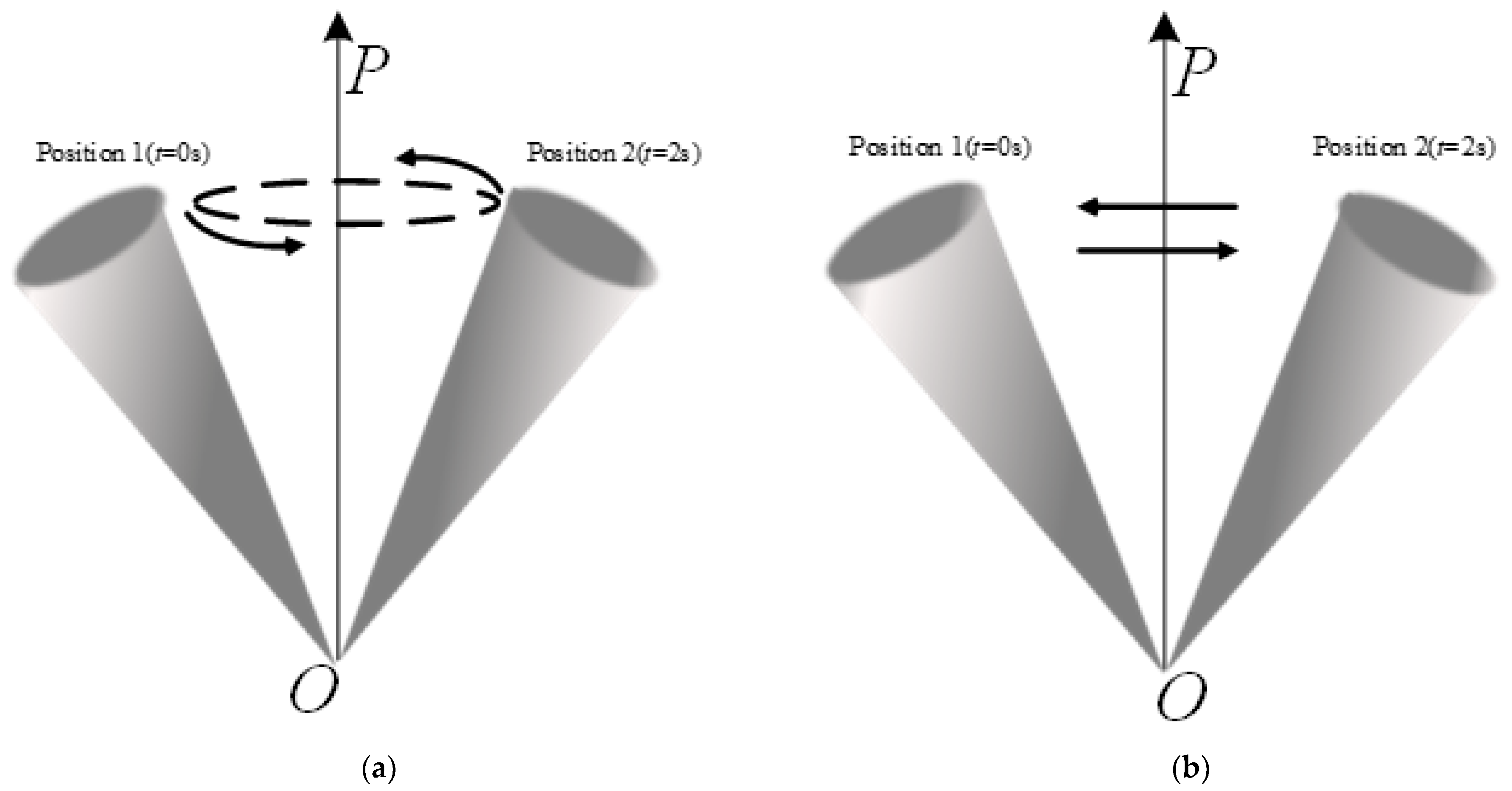
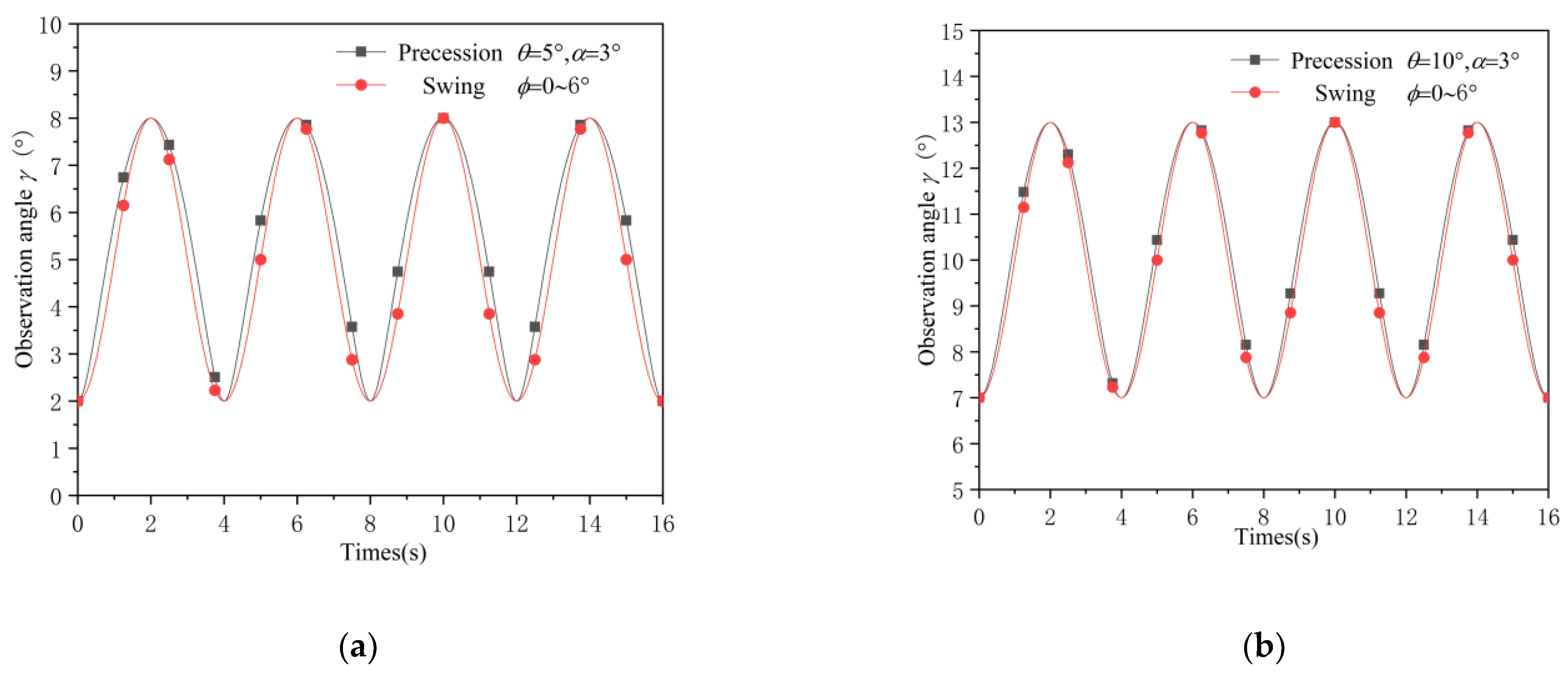
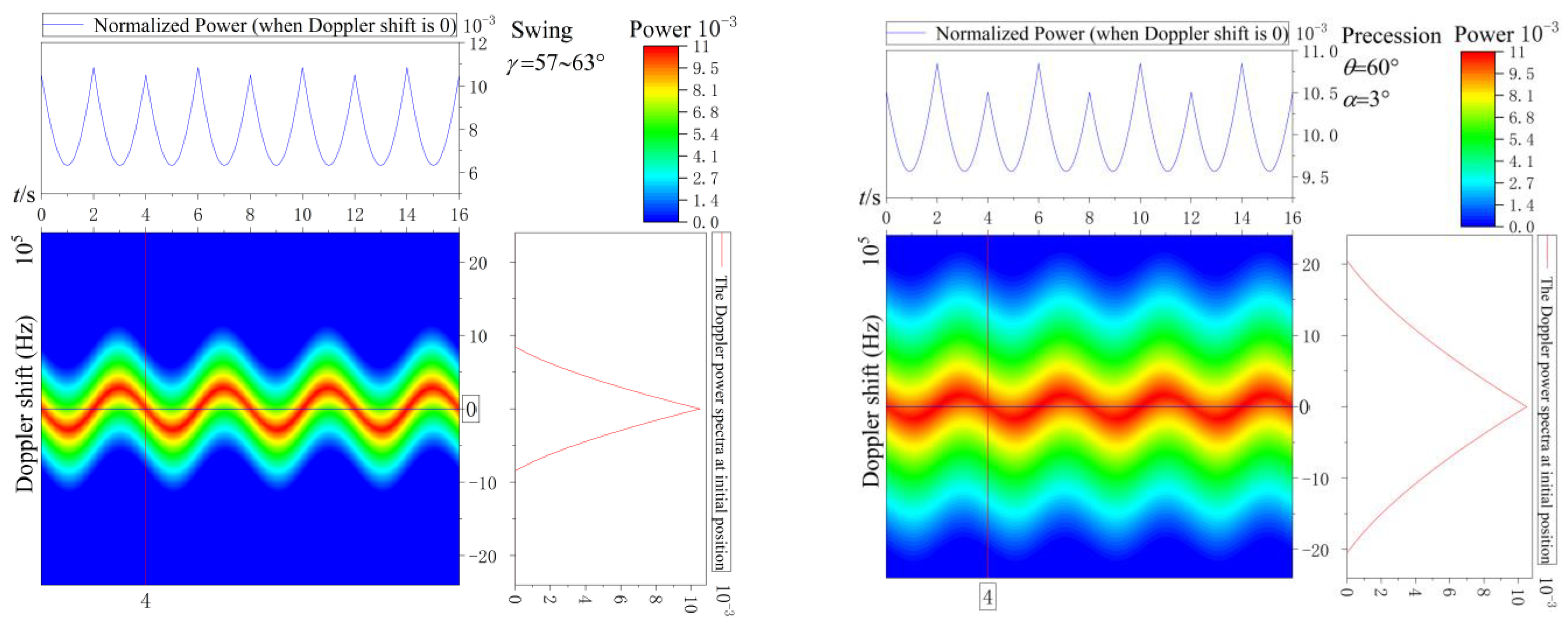
3.3. Precession Cone and Swing Cone
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Verly, J.G.; Delanoy, R.L. Model-based automatic target recognition (ATR) system for forward-looking ground based and airborne imaging laser radars (LIDAR). Proc. IEEE 1996, 84, 126–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelalian, A.V. Laser Radar Systems; Artech House: Boston, MA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Pearson, G.; Davies, F.; Collier, C. Remote Sensing of the Tropical Rain Forest Boundary Layer Using Pulsed Doppler Lidar. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 5891–5901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollias, P.; Rémillard, J.; Luke, E.; Szyrmer, W. Cloud Radar Doppler Spectra in Drizzling Stratiform Clouds: 1. Forward Modeling and Remote Sensing Applications. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, D13201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, V.C. Analysis of radar micro-Doppler with time-frequency transform. In Proceedings of the Tenth IEEE Workshop on Statistical Signal and Array Processing (Cat. No.00TH8496), Pocono Manor, PA, USA, 16 August 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, V.C. The Micro-Doppler Effect in Radar; Artech House: Boston, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yura, H.T.; Hanson, S.G.; Lading, L. Laser doppler velocimetry: Analytical solution to the optical system including the effects of partial coherence of the target. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1995, 12, 2040–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youmans, D.G. Cylindrical target Doppler and Doppler-spread feature estimation using coherent mode-locked pulse laser radars with long observation times. Proc. SPIE Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 2001, 4377, 272–283. [Google Scholar]
- Bankman, I.N. Model of laser radar signatures of ballistic missile warheads. Proc. SPIE Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 1999, 3699, 133–137. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Y.; Wu, Z.; Wang, M.; Cao, Y. Laser backscattering analytical model of Doppler power spectra about rotating convex quadric bodies of revolution. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2010, 48, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manninen, A.J.; Marke, T.; Tuononen, M.J.; O’Connor, E.J. Atmospheric boundary layer classification with Doppler lidar. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 8172–8189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Shan, J. Detection and Tracking of Pedestrians Using Doppler LiDAR. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankman, I. Analytical model of Doppler spectra of coherent light backscattered from rotating cone and cylinders. J. Opt. Soc. Am. Opt. Image Sci. Vis. 2000, 17, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; McLernon, D.; Ghogho, M.; Hu, W.; Huang, J. Ballistic missile detection via micro-Doppler frequency estimation from radar return. Digit. Signal Process. 2012, 22, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Xie, L.; Wen, S.; Kuang, Y. Micro-Doppler Signature Extraction from Ballistic Target with Micro-Motions. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. IEEE Trans. 2010, 46, 1969–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, V.C. Doppler signatures of radar backscattering from objects with micro-motions. IET Signal Process. 2008, 2, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Du, L.; Liu, H.W.; Shao, C.Y. Classification of micro-motion form of space cone-shaped objects based on time-frequency distribution. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2013, 35, 684–691. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Mo, D.; Song, Z.; Wang, R.; Wu, Y. Feature extraction algorithm of a precession target based on a Doppler frequency profile of dual-aspect observation. Appl. Opt. 2019, 58, 4695–4700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Hu, J.; Luo, Y.; Chen, Y. Research progresses in radar feature extraction, imaging, and recognition of target with micro-motions. J. Radars 2018, 7, 531–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| λ | 1 μm |
| KL | 1 |
| ω | 1 rad/s |
| ωp | 0.5π rad/s |
| α | 3° |
| ra | 0.5 m |
| rb | 0.2 m |
| ha | 2 m |
| hb | 1 m |
| δa | 14.04° |
| δb | 8° |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Tn | 4 s |
| ϕ1 | 3° |
| Ψ1 | −0.5π rad/s |
| ϕ2 | 3° |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Zhao, H.; Huang, R.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, H.; Han, C.; Bai, L. Laser Backscattering Analytical Model of Doppler Power Spectra about Convex Quadric Bodies of Revolution during Precession. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16061104
Li Y, Zhao H, Huang R, Zhang G, Zhou H, Han C, Bai L. Laser Backscattering Analytical Model of Doppler Power Spectra about Convex Quadric Bodies of Revolution during Precession. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(6):1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16061104
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yanhui, Hua Zhao, Ruochen Huang, Geng Zhang, Hangtian Zhou, Chenglin Han, and Lu Bai. 2024. "Laser Backscattering Analytical Model of Doppler Power Spectra about Convex Quadric Bodies of Revolution during Precession" Remote Sensing 16, no. 6: 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16061104
APA StyleLi, Y., Zhao, H., Huang, R., Zhang, G., Zhou, H., Han, C., & Bai, L. (2024). Laser Backscattering Analytical Model of Doppler Power Spectra about Convex Quadric Bodies of Revolution during Precession. Remote Sensing, 16(6), 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16061104