Effects of Geomorphic Spatial Differentiation on Vegetation Distribution Based on Remote Sensing and Geomorphic Regionalization
Abstract
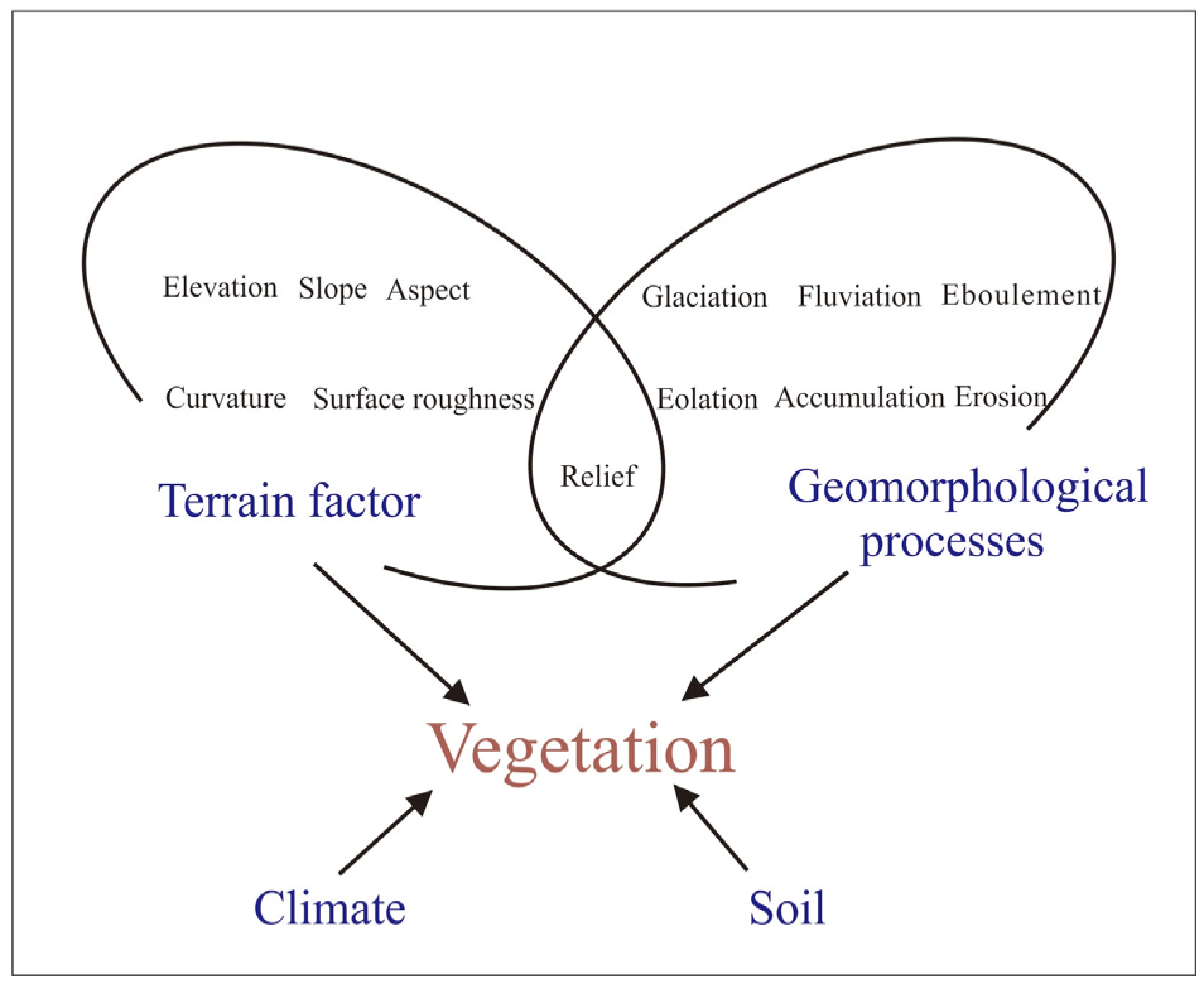
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
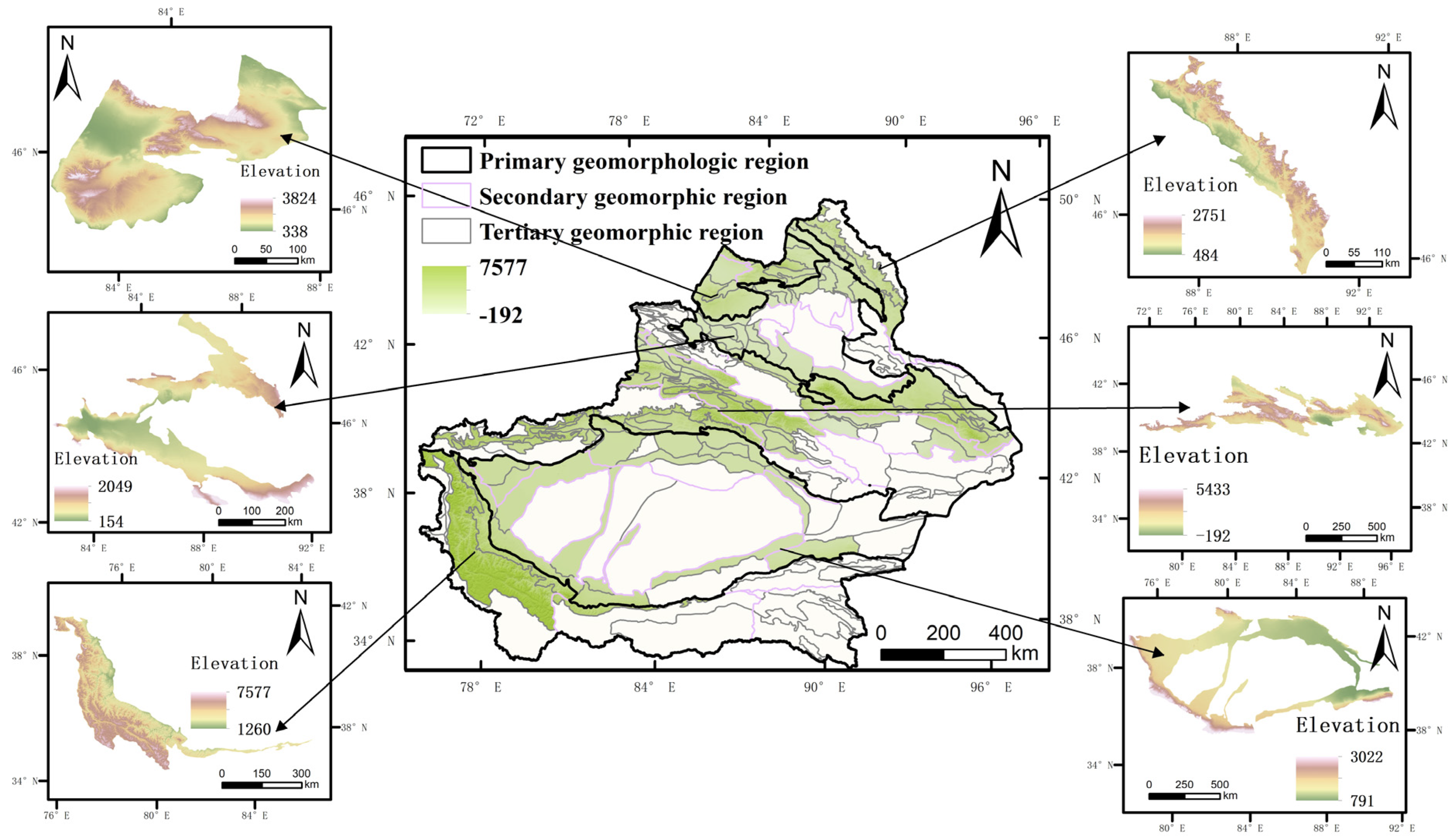
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources and Preprocessing
2.3. Methods
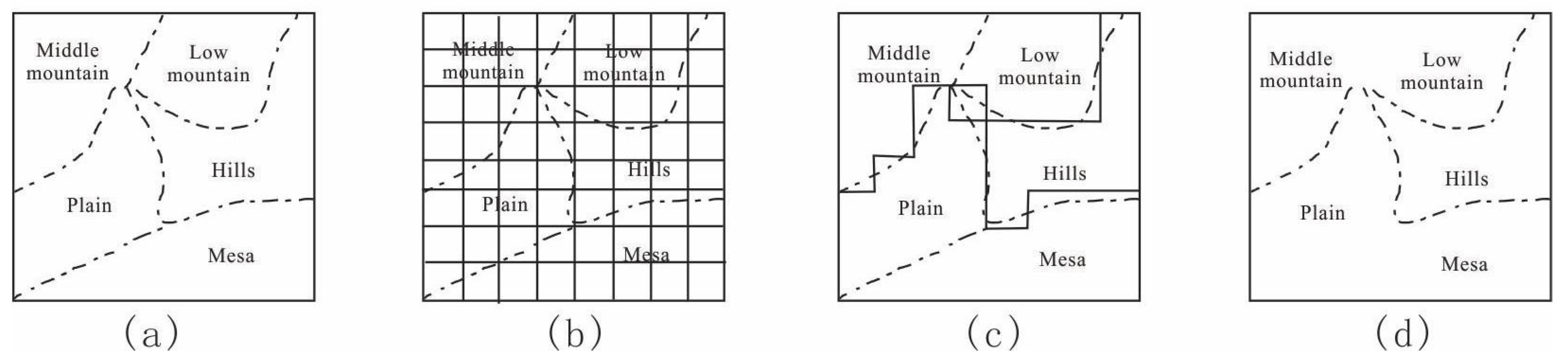
2.3.1. Geomorphic Regionalization
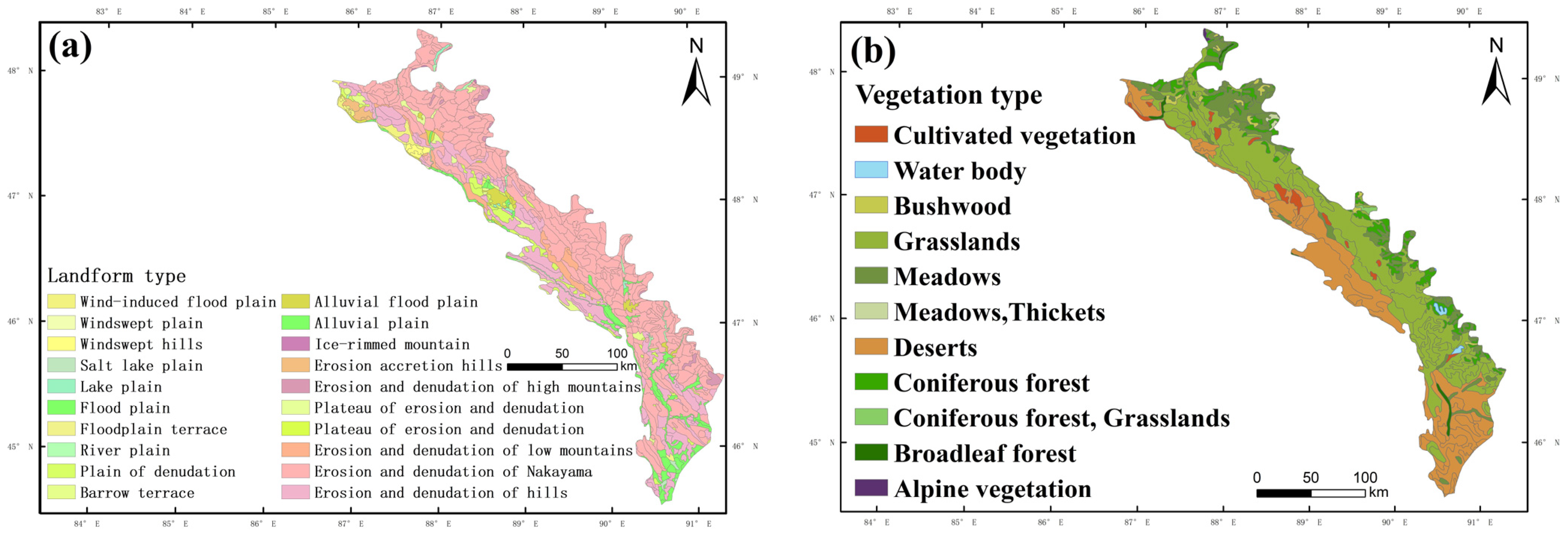
2.3.2. Landform Classification
2.3.3. Vegetation Coverage
2.3.4. Geodetector
- (1)
- Factor detection
- (2)
- Interaction detection
- (3)
- Ecological detection
3. Results
3.1. Study of the Influence of Geomorphic Spatial Differentiation on Vegetation Distribution
3.2. Coupling Study of Landform Types with Vegetation and Cover Based on Geomorphologic Zoning
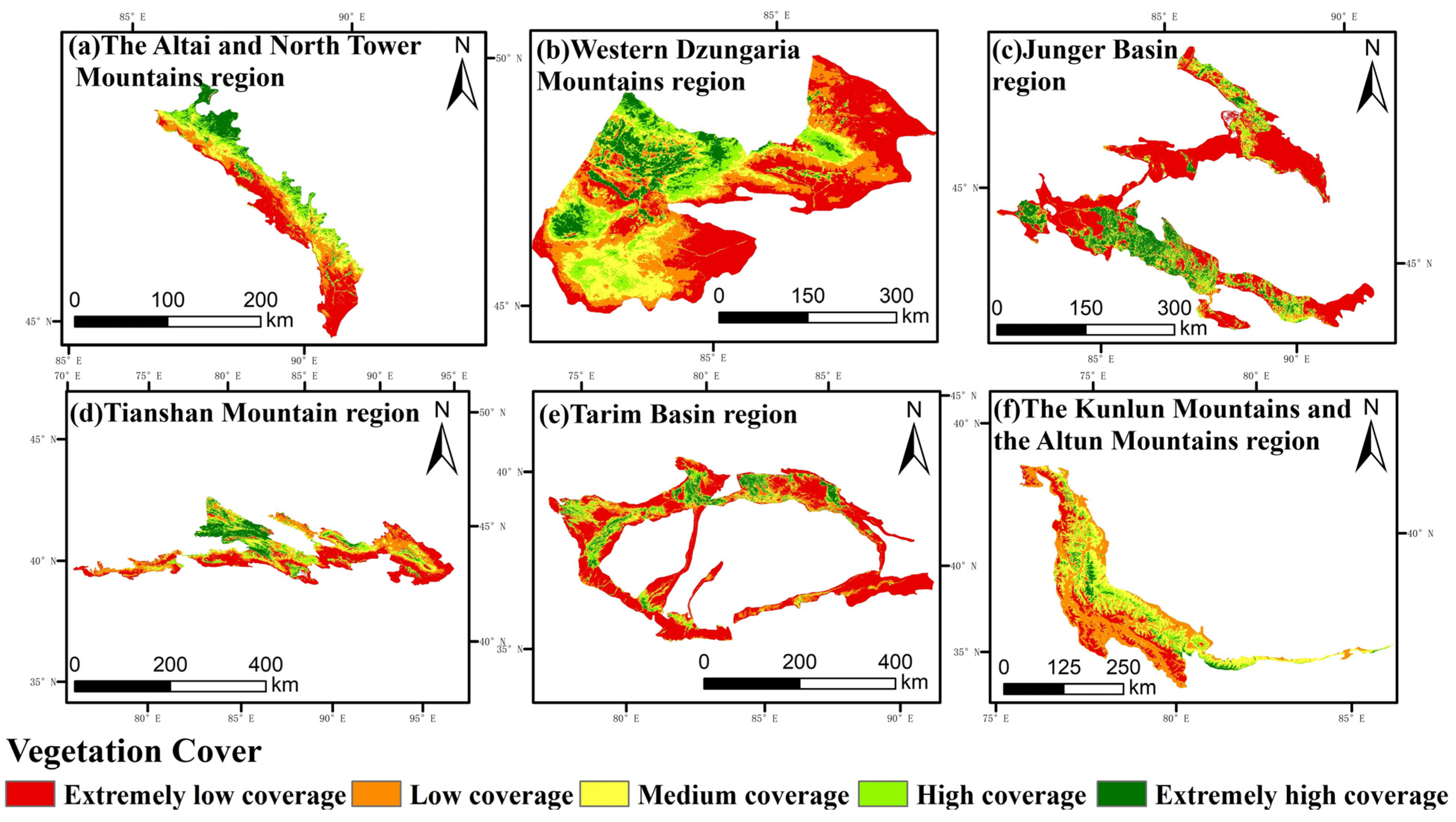
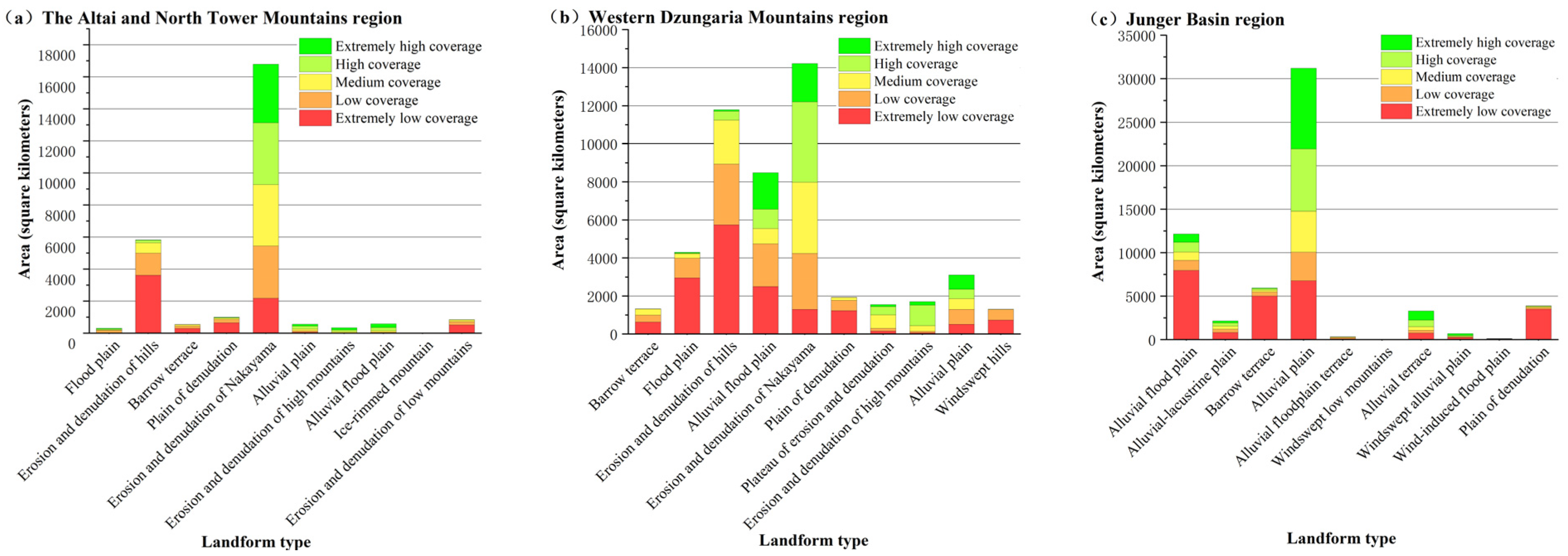
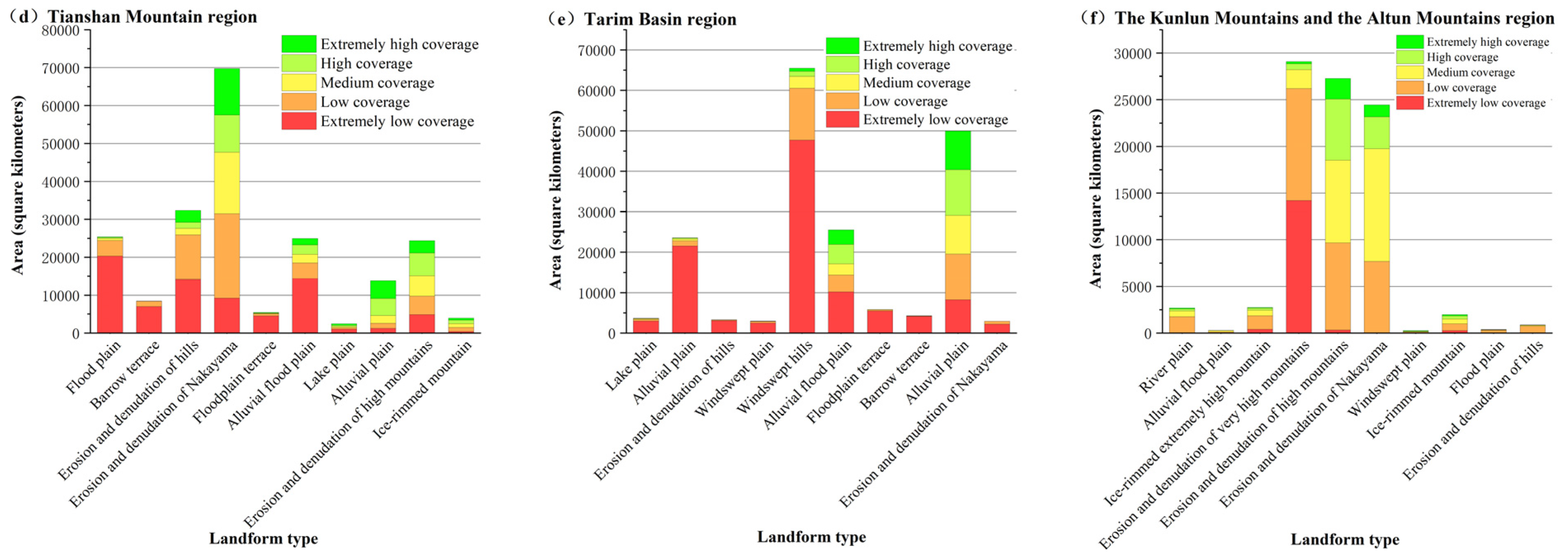
3.2.1. Patterns of Vegetation Distribution within the Six Geomorphic Zones of the Hilly Oasis Zone
3.2.2. Response of Vegetation Cover to Spatial Differentiation of Landforms
3.2.3. Correlation between Vegetation Cover and Spatial Differentiation of Landforms
3.3. Key Environmental Drivers of Vegetation Cover
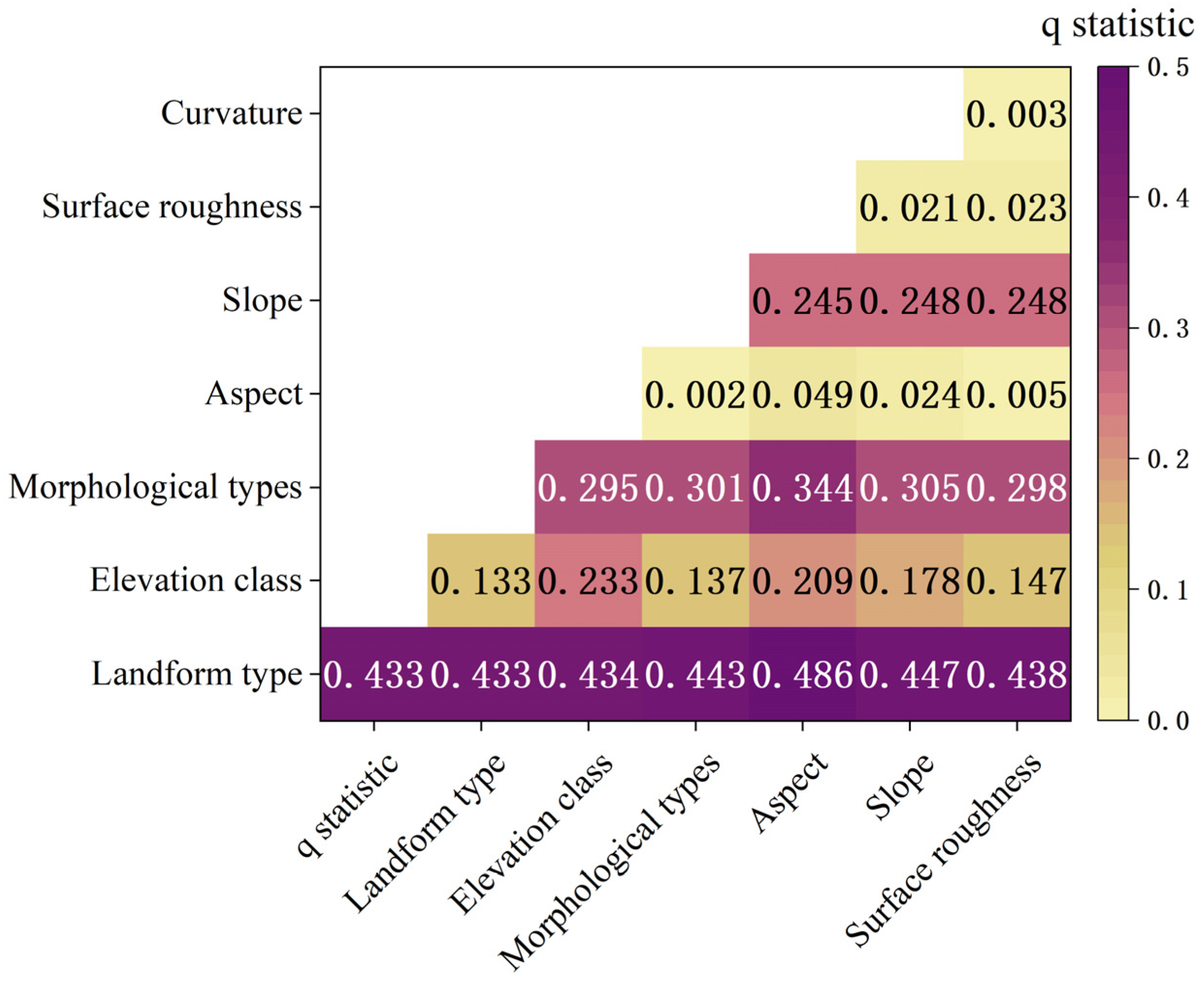
3.3.1. Factor Detection
3.3.2. Interaction Detection
3.3.3. Ecological Detection
4. Discussion
4.1. Influence of Detailed Geomorphic Type on Vegetation Distribution in the Hilly Oasis Zone
4.2. Geodetector Analysis
4.3. Limitations and Future Research Directions
4.4. Recommendations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arruda, D.M.; Schaefer, C.E.; Corrêa, G.R.; Rodrigues, P.M.; Duque-Brasil, R.; Ferreira-JR, W.G.; Oliveira-Filho, A.T. Landforms and soil attributes determine the vegetation structure in the Brazilian semiarid. Folia Geobot. 2015, 50, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baartman, J.E.; Temme, A.J.; Saco, P.M. The effect of landform variation on vegetation patterning and related sediment dynamics. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2018, 43, 2121–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentini, E.; Taramelli, A.; Cappucci, S.; Filipponi, F.; Nguyen Xuan, A. Exploring the dunes: The correlations between vegetation cover pattern and morphology for sediment retention assessment using airborne multisensor acquisition. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokarram, M.; Sathyamoorthy, D. Relationship between landform classification and vegetation (case study: Southwest of Fars province, Iran). Open Geosci. 2016, 8, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Smith, M.; Pain, C. Applications of remote sensing in geomorphology. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2009, 33, 568–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, S.J.; Butler, D.R.; Malanson, G.P. An overview of scale, pattern, process relationships in geomorphology: A remote sensing and GIS perspective. Geomorphology 1998, 21, 183–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Xu, Y.; Ge, H.; Yang, W. Vegetation growth variation in relation to topography in Horqin Sandy Land. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 113, 106215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Dong, G.; Jiang, X.; Nie, T.; Yin, H.; Guo, X. Quantification of natural and anthropogenic driving forces of vegetation changes in the Three-River Headwater Region during 1982–2015 based on geographical detector model. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Guo, D. A GIS-based research on vegetation landscape pattern. In Proceedings of the Geoinformatics 2007: Geospatial Information Science, Nanjing, China, 25–27 May 2007; pp. 497–509. [Google Scholar]
- Shaheen, H.; Qureshi, R.A. Vegetation types of sheosar lake and surrounding landscape in deosai plains of North Pakistan, Western Himalayas. J. Med. Plants Res. 2011, 5, 599–603. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Chang, S.X.; Liu, J.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, X. Topography-soil relationships in a hilly evergreen broadleaf forest in subtropical China. J. Soils Sediments 2017, 17, 1101–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Qiao, Y.-P.; Wang, L.-J.; Zhang, J.-C. Terrain gradient variations in ecosystem services of different vegetation types in mountainous regions: Vegetation resource conservation and sustainable development. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 482, 118856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Song, X.; Mu, X.; Gao, P.; Wang, F.; Zhao, G. Spatiotemporal vegetation cover variations associated with climate change and ecological restoration in the Loess Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 209, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Fu, D.; Lu, C.; Xu, X.; Tang, Q. Positive effects of ecological restoration policies on the vegetation dynamics in a typical ecologically vulnerable area of China. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 159, 106087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, D.; Yan, J.; Ma, X.; Gao, F.; Wang, F.; Wen, L.; Bai, J.; Cui, B. How vegetation influence the macrobenthos distribution in different saltmarsh zones along coastal topographic gradients. Mar. Environ. Res. 2019, 151, 104767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zha, T.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Ji, X. Functional vegetation community responses to soil and topographic factors in the Loess Plateau of China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 5355–5372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesse, R. Spatial distribution of and topographic controls on Tillandsia fog vegetation in coastal southern Peru: Remote sensing and modelling. J. Arid Environ. 2012, 78, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, A.; Guo, Z.; Wu, H.; Li, Q.; Yu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Jiang, W.; Li, X. Reconstruction of the vegetation distribution of different topographic units of the Chinese Loess Plateau during the Holocene. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2017, 173, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, H.; Meng, L.; Liu, M.; Wu, Z.; Liu, T.; Labat, D. Spatial-temporal evolution of vegetation coverage and its relationship with terrain and human factors in the upper reaches of Ganjiang River Basin, China. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 10, 1043403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.; Xiong, S.; Wu, G.; Deng, O. Multi-scale spatial correlation between vegetation index and terrain attributes in a small watershed of the upper Minjiang River. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 126, 107610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Li, S.; Tan, Z.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Huang, G.; Huang, Z. Understanding the modifiable areal unit problem in dockless bike sharing usage and exploring the interactive effects of built environment factors. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2021, 35, 1905–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zuo, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X. Driving forces and their interactions of built-up land expansion based on the geographical detector—A case study of Beijing, China. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2016, 30, 2188–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, J.; Ge, Y.; Xu, C. An optimal parameters-based geographical detector model enhances geographic characteristics of explanatory variables for spatial heterogeneity analysis: Cases with different types of spatial data. GISci. Remote Sens. 2020, 57, 593–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Qian, Y.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Z. Vegetation-environment relationships between northern slope of Karlik Mountain and Naomaohu Basin, East Tianshan Mountains. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2012, 22, 288–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, B.; Cheng, W. Sustainable land-use patterns for arid lands: A case study in the northern slope areas of the Tianshan Mountains. J. Geogr. Sci. 2010, 20, 510–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aili, A.; Xu, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, P.; Yang, R. Dynamics of vegetation productivity in relation to surface meteorological factors in the Altay Mountains in Northwest China. Forests 2022, 13, 1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yan, J.; Zhu, X.; Ling, H.; Xu, H. Spatio-temporal variation in grassland degradation and its main drivers, based on biomass: Case study in the Altay Prefecture, China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2019, 20, e00723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, H.; Ou, Y.; Chen, X.; Cheng, W.; Zhou, C. A new schem a of Xinjiang geomorhpologic regionalization. Arid. Land Geogr. 2009, 32, 95–106. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, H.; Zhou, C.; Chen, X.; Cheng, W. Digital regionalization of geomorphology in Xinjiang. J. Geogr. Sci. 2009, 19, 600–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, M.; Sun, G. Impacts of climatic change on river runoff in northern Xinjiang of China over last fifty years. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2010, 20, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Mao, W.; Chen, J.; Dilinuer, T. Recent signal and impact of wet-to-dry climatic shift in Xinjiang, China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2021, 31, 1283–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Lu, G.; Pan, X.; Anabiek, S.; Zhou, C.; Chang, S. Remote sensing classification method for divided areas applied to Xinjiang vegetation classification. In Proceedings of the Ecosystems Dynamics, Ecosystem-Society Interactions, and Remote Sensing Applications for Semi-Arid and Arid Land, Hangzhou, China, 23–27 October 2003; pp. 254–261. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Guo, J.; Liang, T.; Feng, Q. Grassland vegetation phenological variations and responses to climate change in the Xinjiang region, China. Quat. Int. 2019, 513, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S. Big Earths of China: Remotely Sensing Xinjiang along the Belt and Road. Crit. Inq. 2022, 49, 77–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Li, G. Retracted: The Silk Road Economic Belt-Urumqi Construction for Regional Financial Center Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Smart City and Systems Engineering (ICSCSE), Changsha, China, 11–12 November 2017; pp. 100–103. [Google Scholar]
- XiaoMing, C.; Xi, C.; AnMing, B.; Quan, W. Response of vegetation to temperature and precipitation in Xinjiang during the period of 1998–2009. J. Arid Land 2011, 3, 94–103. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, J.; Hu, W.; Chen, Y.; Huo, W.; Zhao, Y.; Mao, W.; Yang, Q. Hydro-climatic changes and their impacts on vegetation in Xinjiang, Central Asia. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Ju, W.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, J.; He, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, H.; Guan, D.; Yan, J.; Li, Y. Development of a two-leaf light use efficiency model for improving the calculation of terrestrial gross primary productivity. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 173, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Pan, B.; Cheng, W.; Han, J.; Qi, D.; Zhu, C. Research on geomorphological regionalization of China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2013, 68, 291–306. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, W.; Zhou, C.; Chai, H.; Zhao, S.; Li, B. Ouantitative Extraction and Analysis of Basic Morphological Types of Land Geomorphology in China. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2009, 11, 725–736. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, W.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, S.; Gao, X.; Wang, N. Research and perspectives on geomorphology in China: Four decades in retrospect. J. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 1283–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cheng, W.; Chai, H.; Zhou, C.; Chen, X. The spatial distribution patterns of digital geomorphlolgy inXinjiang. Geogr. Res. 2009, 28, 1157–1169. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, H.; Li, L.; Wu, Y.; Feng, G.; Gong, Z.; Sun, G. Identifying Critical Meteorological elements for vegetation coverage change in China. Front. Phys. 2022, 10, 834094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Jia, Z.; Li, Q.; Zhao, A.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Z. Spatiotemporal change of sparse vegetation coverage in northern China. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2019, 47, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.Z.; Zhu, J.G.; Qian, Y.L. Analysis on terrain effects to vegetation coverage by quantitative remote sensing. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 518, 5673–5677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Lyu, A. Investigating natural drivers of vegetation coverage variation using MODIS imagery in Qinghai, China. J. Arid Land 2016, 8, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Xu, C. Geodetector: Principle and prospective. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.-F.; Zhang, T.-L.; Fu, B.-J. A measure of spatial stratified heterogeneity. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 67, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Zhang, N.; He, B.; Liu, C.-Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Chen, X.-Y.; Lin, H. Construction of a GeogDetector-based model system to indicate the potential occurrence of grasshoppers in Inner Mongolia steppe habitats. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2015, 105, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.F.; Li, X.H.; Christakos, G.; Liao, Y.L.; Zhang, T.; Gu, X.; Zheng, X.Y. Geographical detectors-based health risk assessment and its application in the neural tube defects study of the Heshun Region, China. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, W. Landslide susceptibility mapping using hybrid random forest with GeoDetector and RFE for factor optimization. Geosci. Front. 2021, 12, 101211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Yang, L.; Wu, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, G.; Bian, J.; Zeng, J.; Liu, Z. Spatio-temporal characteristics and influencing factors of traditional villages in the Yangtze River Basin: A Geodetector model. Herit. Sci. 2023, 11, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Valle Villalonga, L.; Timar-Gabor, A.; Fornós, J.J. Geomorphological Processes and Environmental Interpretation at Espalmador islet (Western Mediterranean). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liucci, L.; Melelli, L. The fractal properties of topography as controlled by the interactions of tectonic, lithological, and geomorphological processes. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2017, 42, 2585–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemppinen, J.; Niittynen, P.; Happonen, K.; le Roux, P.C.; Aalto, J.; Hjort, J.; Maliniemi, T.; Karjalainen, O.; Rautakoski, H.; Luoto, M. Geomorphological processes shape plant community traits in the Arctic. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2022, 31, 1381–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Q.; Liu, M.; Zhang, M.; Cheng, W. Vegetation Dynamic Change and lts Response to Climate and Topography in Altay Region of Xinjiang in Recent 20 Years. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2023, 48, 1522–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Xie, H.; Liu, H.; Wen, G.; Li, Y. Relations of Vegetation with Topography and Groundwater in Yili River Valley of Xinjiang. J. Yangtze River Sci. Res. Inst. 2018, 35, 54–57. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wei, X.; Ni, P.; Dong, J. Preliminary investigalion on weathering proess and vertical zoning characleristics of clinosol in TiansnanMounains. J. Eng. Geol. 2023, 32, 1235–1246. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Qiao, H.; Feng, S.; Xi, L.; Qi, Z.; Lan, L. A dataset of temporal-spatial FVC in the Ring Tarim Basin from 1990 to 2021. China Sci. Data 2023, 8, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Ouyang, W.; Lyu, F.; Song, Y.; Hao, R. Variation of Vegetation Cover and Its Correlation of Topographic Factors in Guandu River Basin. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2019, 26, 135–140, 147. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.-M.; Pan, Y.-C.; Xu, Y.; Cuo, Z.-D.; Zheng, Z.-W.; Dai, O.-Y. Spatio-temporal variation of fractional vegetation cover and its relationshipwith climate and topographic factors in southwest China. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2023, 36, 1307–1317. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Xi, G.; Ji, F.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Xie, Y. Spatial and Temporal Variation in Vegetation Cover and Its Response to Topography in the Selinco Region of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
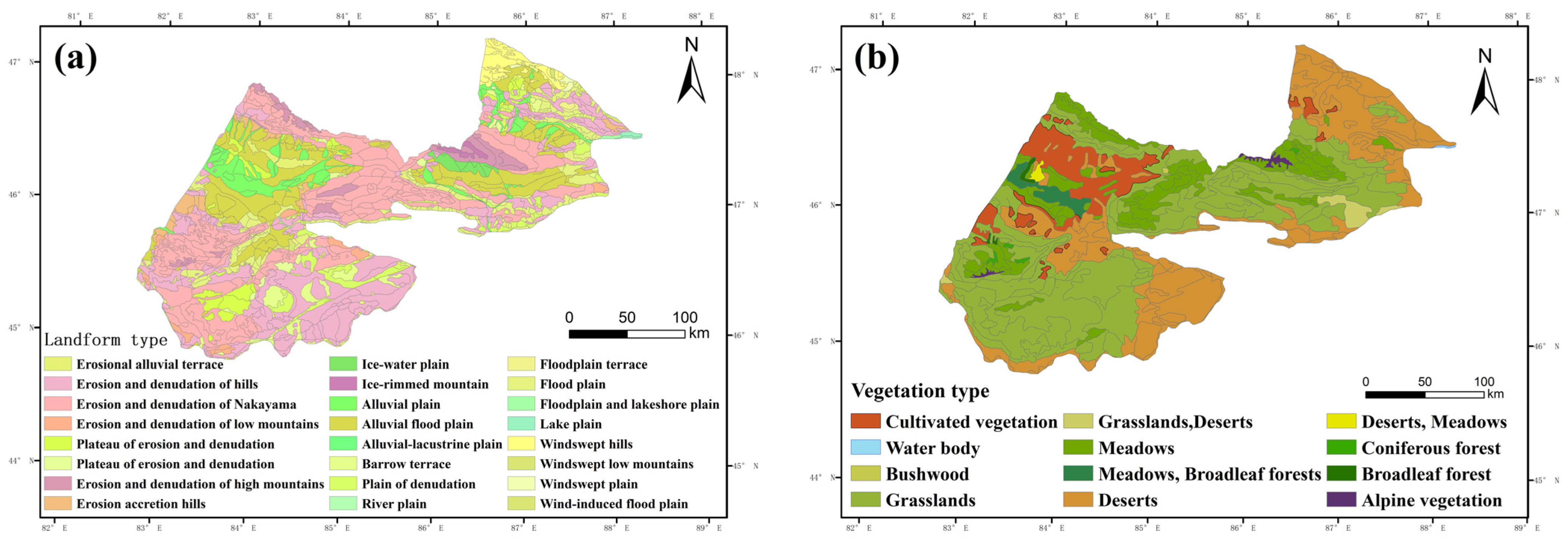

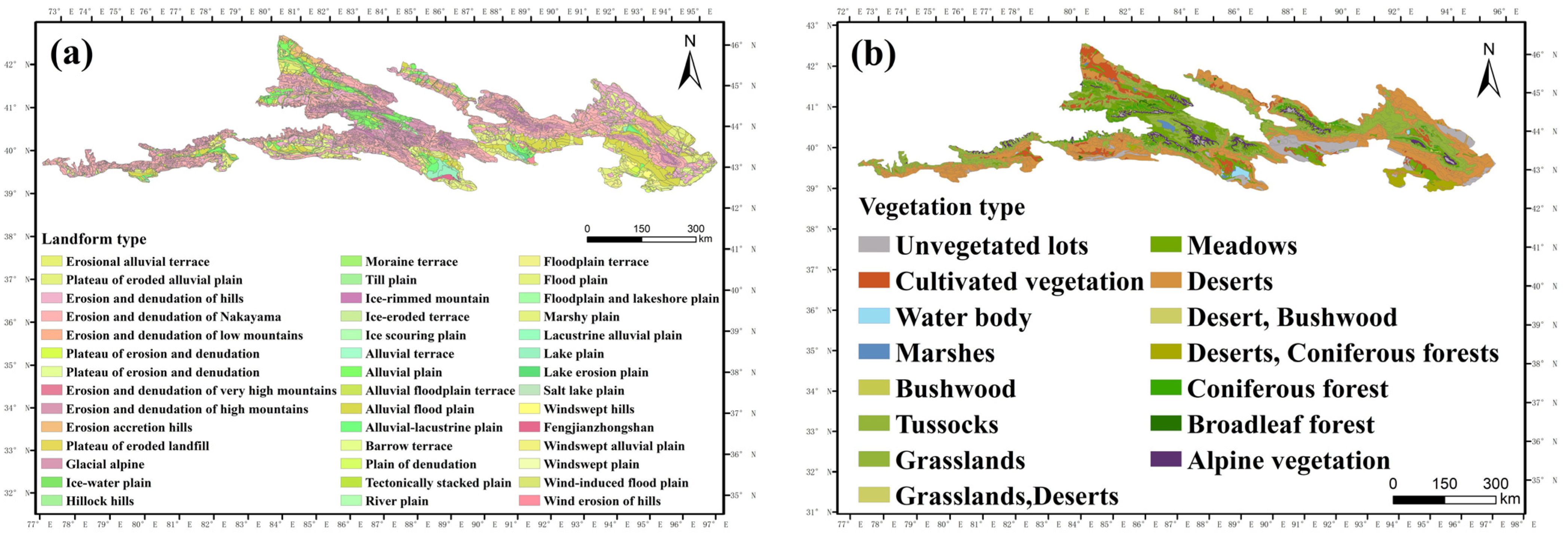
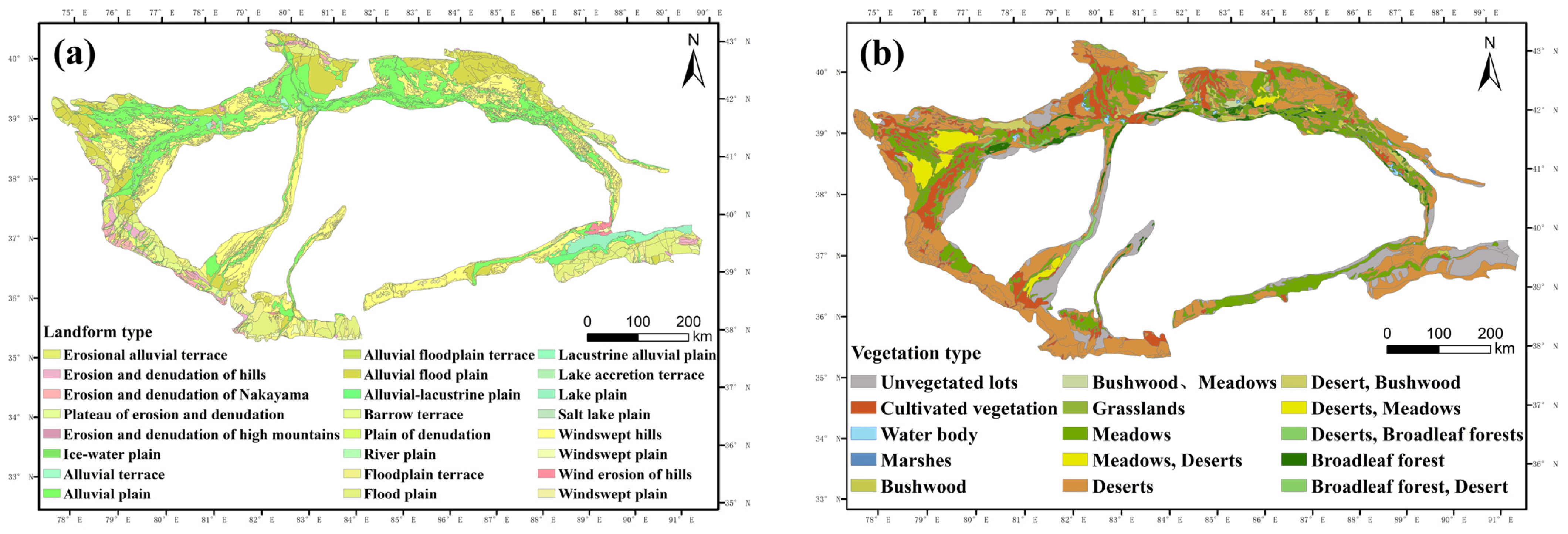
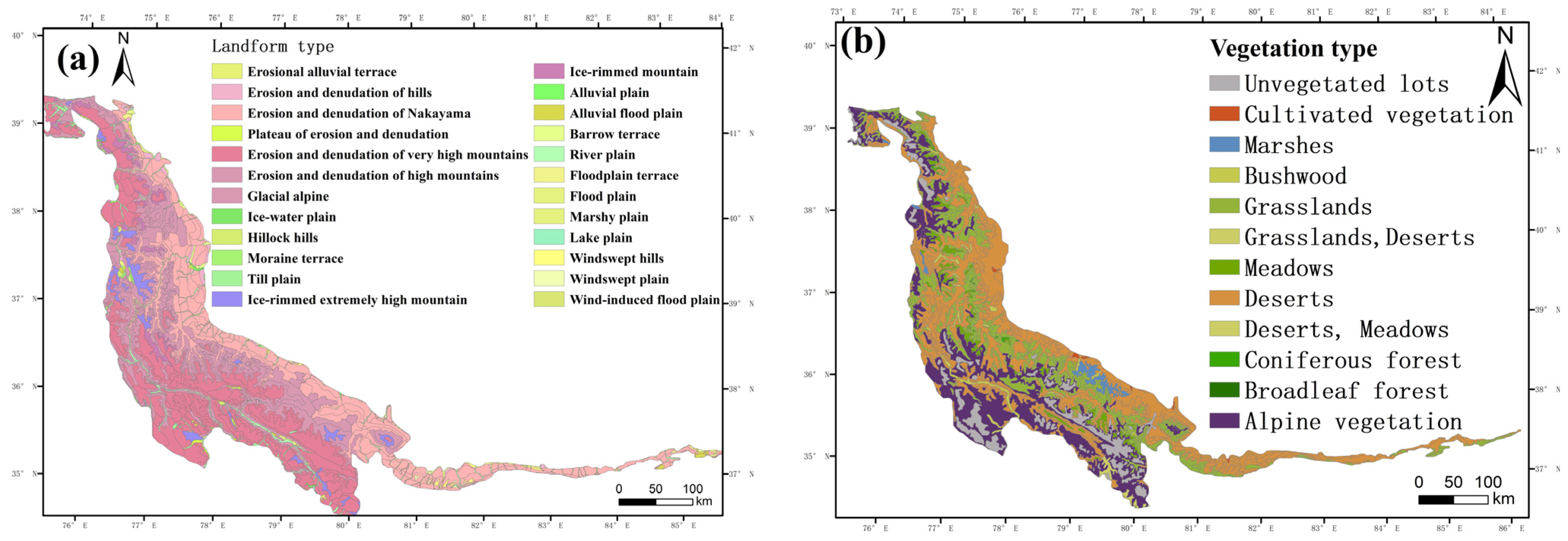
| Factors | Topographic and Geomorphologic Factors | Detecting the Impact Factor | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Geomorphic factors | Landform type | X1 | 54 |
| Elevation class | X2 | 4 | |
| Morphological types | X3 | 7 | |
| Terrain factors | Aspect | X4 | 9 |
| Slope | X5 | 9 | |
| Surface roughness | X6 | 6 | |
| Curvature | X7 | 6 |
| Types of Interactions | Interaction Types |
|---|---|
| Nonlinear weakened | |
| Univariate weakened | |
| Bivariate enhanced | |
| Independent | |
| Nonlinear enhanced |
| Factors | Landform Type | Elevation Class | Morphological Types | Aspect | Slope | Surface Roughness | Curvature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| q statistic | 0.433 | 0.133 | 0.295 | 0.002 | 0.245 | 0.021 | 0.003 |
| p value | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Factors | Landform Type | Elevation Class | Morphological Types | Aspect | Slope | Surface Roughness | Curvature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Landform type | |||||||
| Elevation class | Y | ||||||
| Morphological types | Y | Y | |||||
| Aspect | Y | Y | Y | ||||
| Slope | Y | N | Y | Y | |||
| Surface roughness | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | ||
| Curvature | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, H.; Cheng, W.; Wang, B.; Song, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, R.; Bao, A. Effects of Geomorphic Spatial Differentiation on Vegetation Distribution Based on Remote Sensing and Geomorphic Regionalization. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16061062
Xu H, Cheng W, Wang B, Song K, Zhang Y, Wang R, Bao A. Effects of Geomorphic Spatial Differentiation on Vegetation Distribution Based on Remote Sensing and Geomorphic Regionalization. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(6):1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16061062
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Hua, Weiming Cheng, Baixue Wang, Keyu Song, Yichi Zhang, Ruibo Wang, and Anming Bao. 2024. "Effects of Geomorphic Spatial Differentiation on Vegetation Distribution Based on Remote Sensing and Geomorphic Regionalization" Remote Sensing 16, no. 6: 1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16061062
APA StyleXu, H., Cheng, W., Wang, B., Song, K., Zhang, Y., Wang, R., & Bao, A. (2024). Effects of Geomorphic Spatial Differentiation on Vegetation Distribution Based on Remote Sensing and Geomorphic Regionalization. Remote Sensing, 16(6), 1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16061062








