Investigating a Possible Correlation between NOAA-Satellite-Detected Electron Precipitations and South Pacific Tectonic Events
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
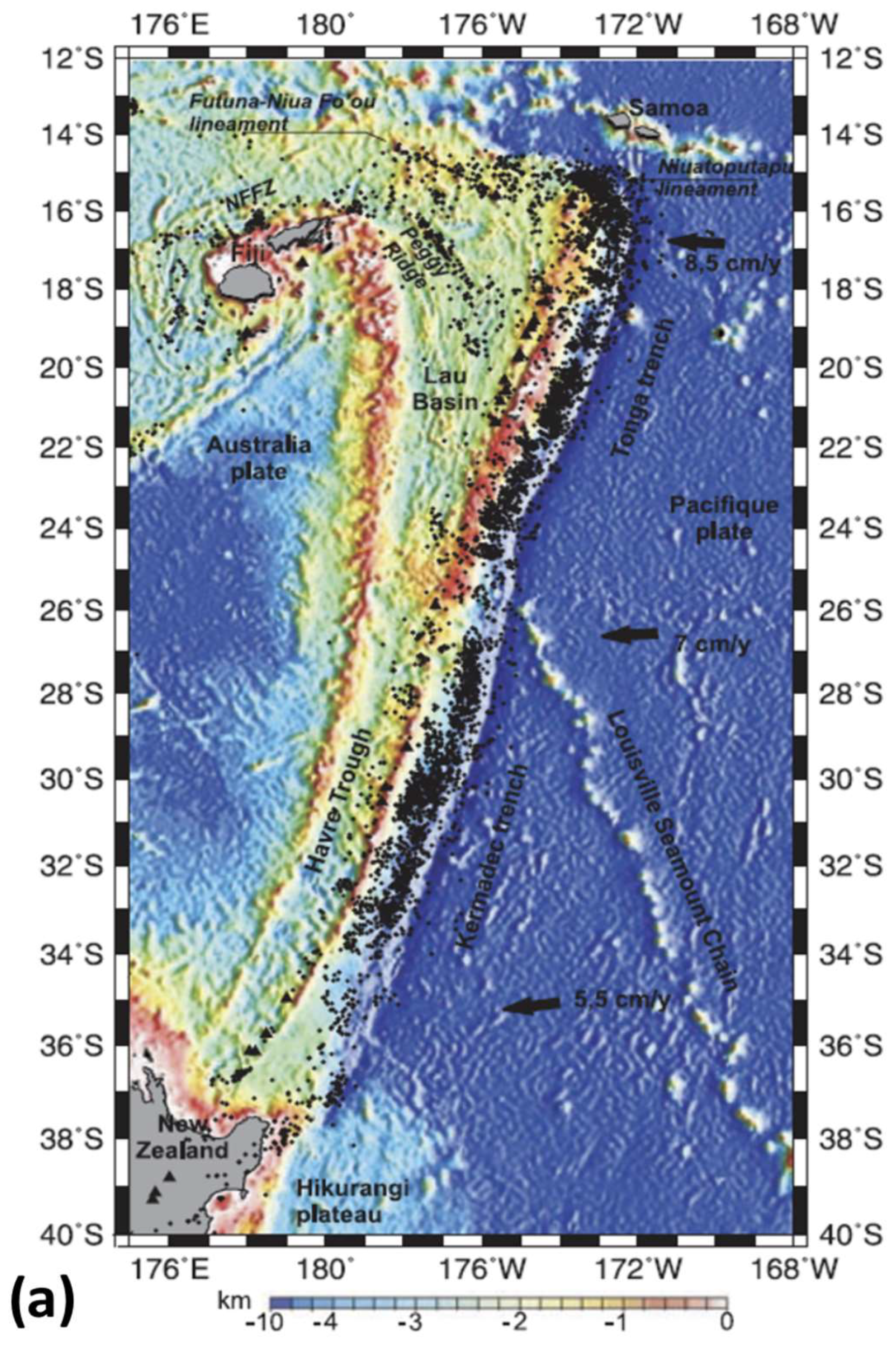
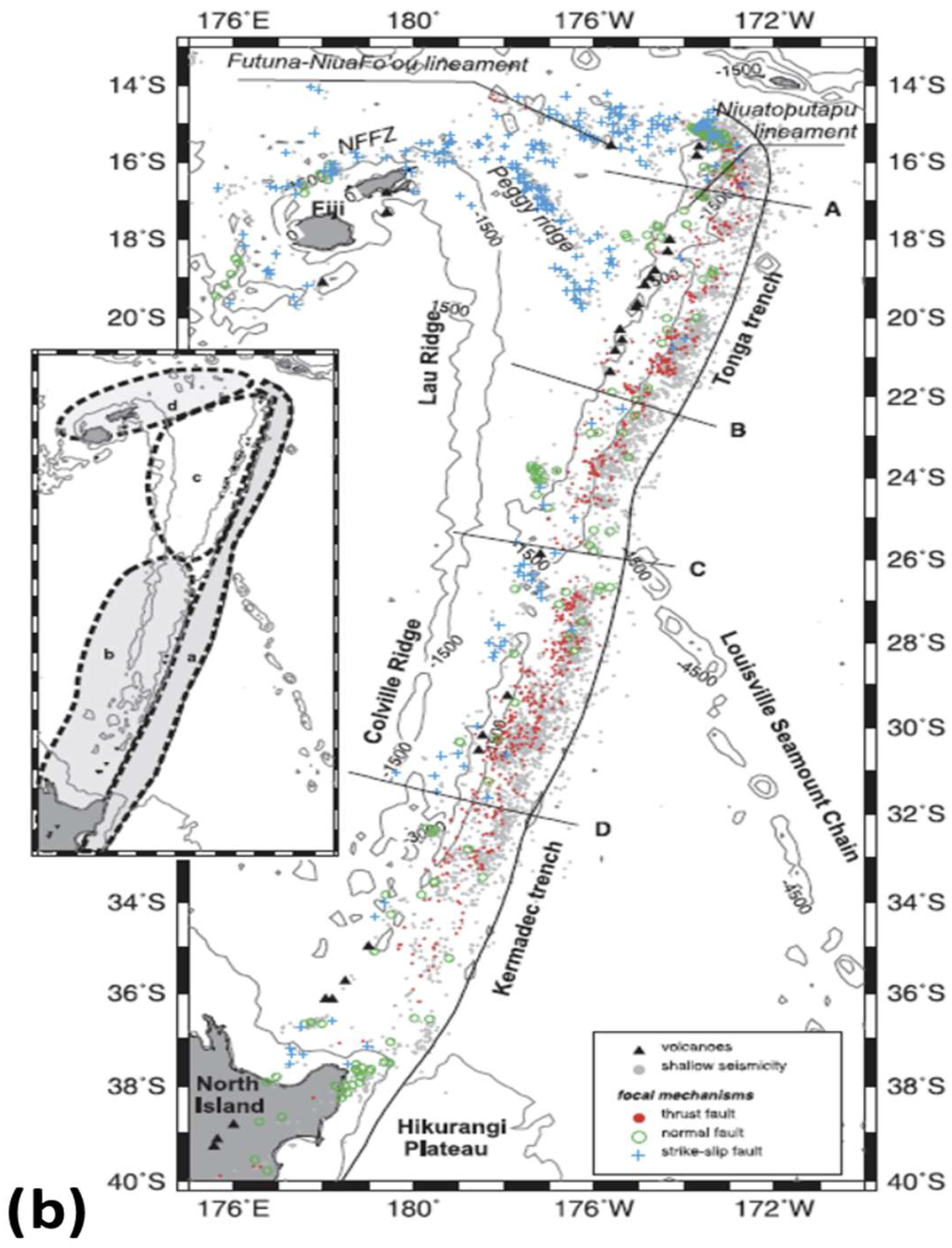
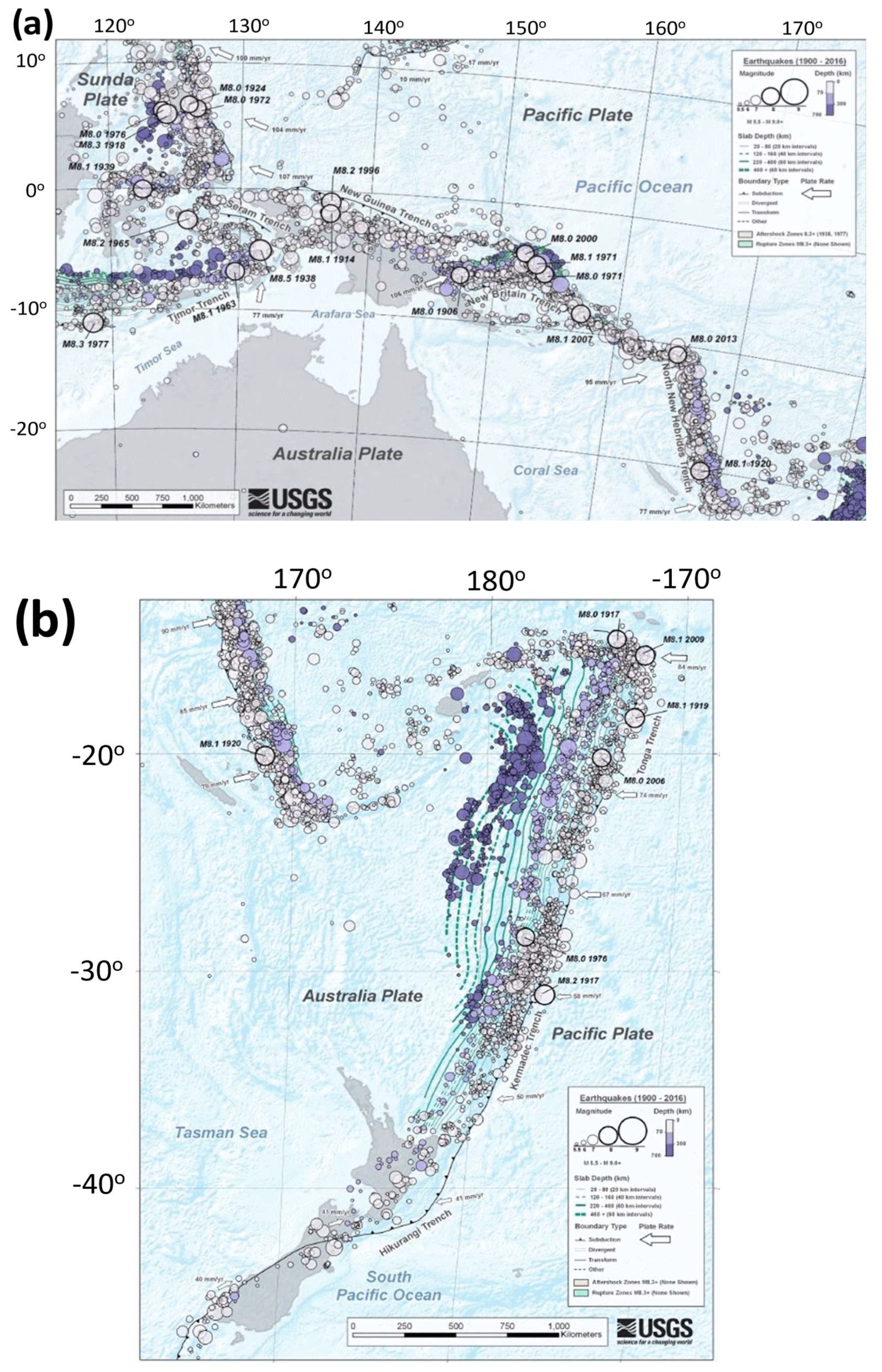
2.1. Tectonics
2.2. NOAA Data
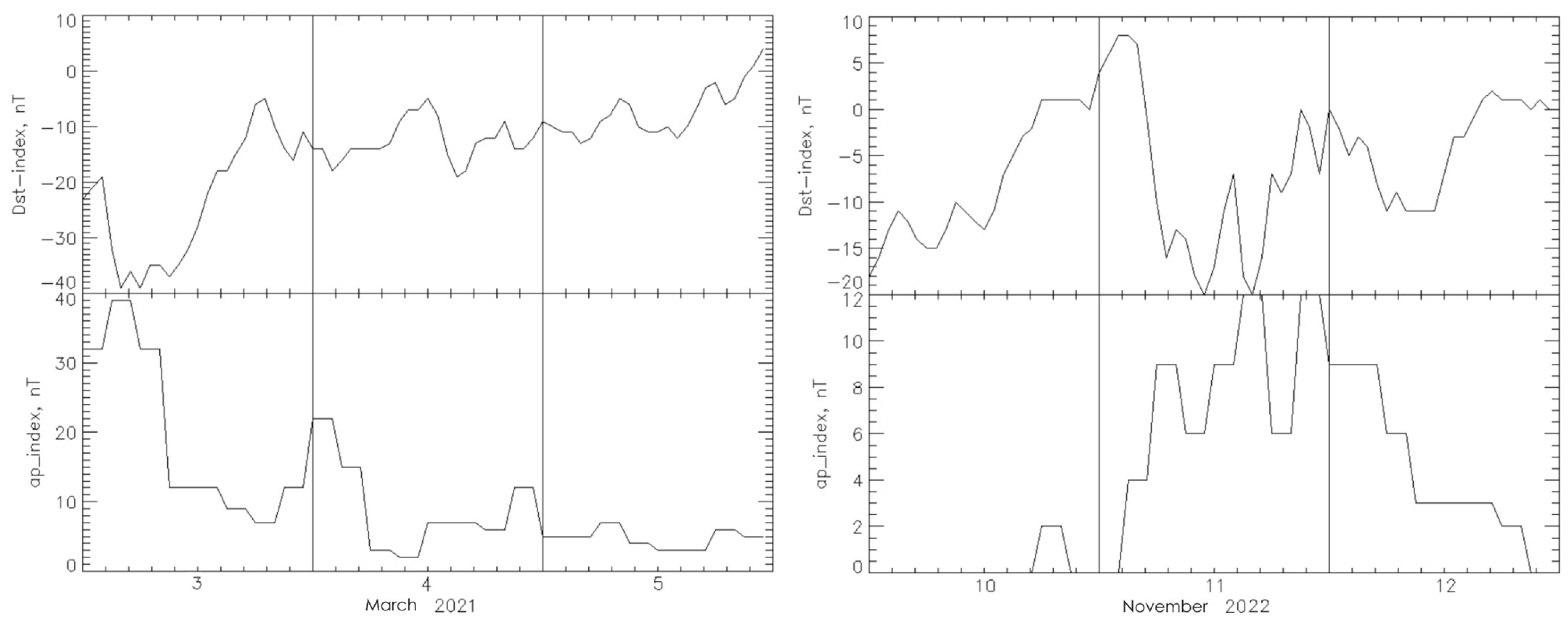
2.3. Selections of Seismic Events and Electron Events for a Comparison
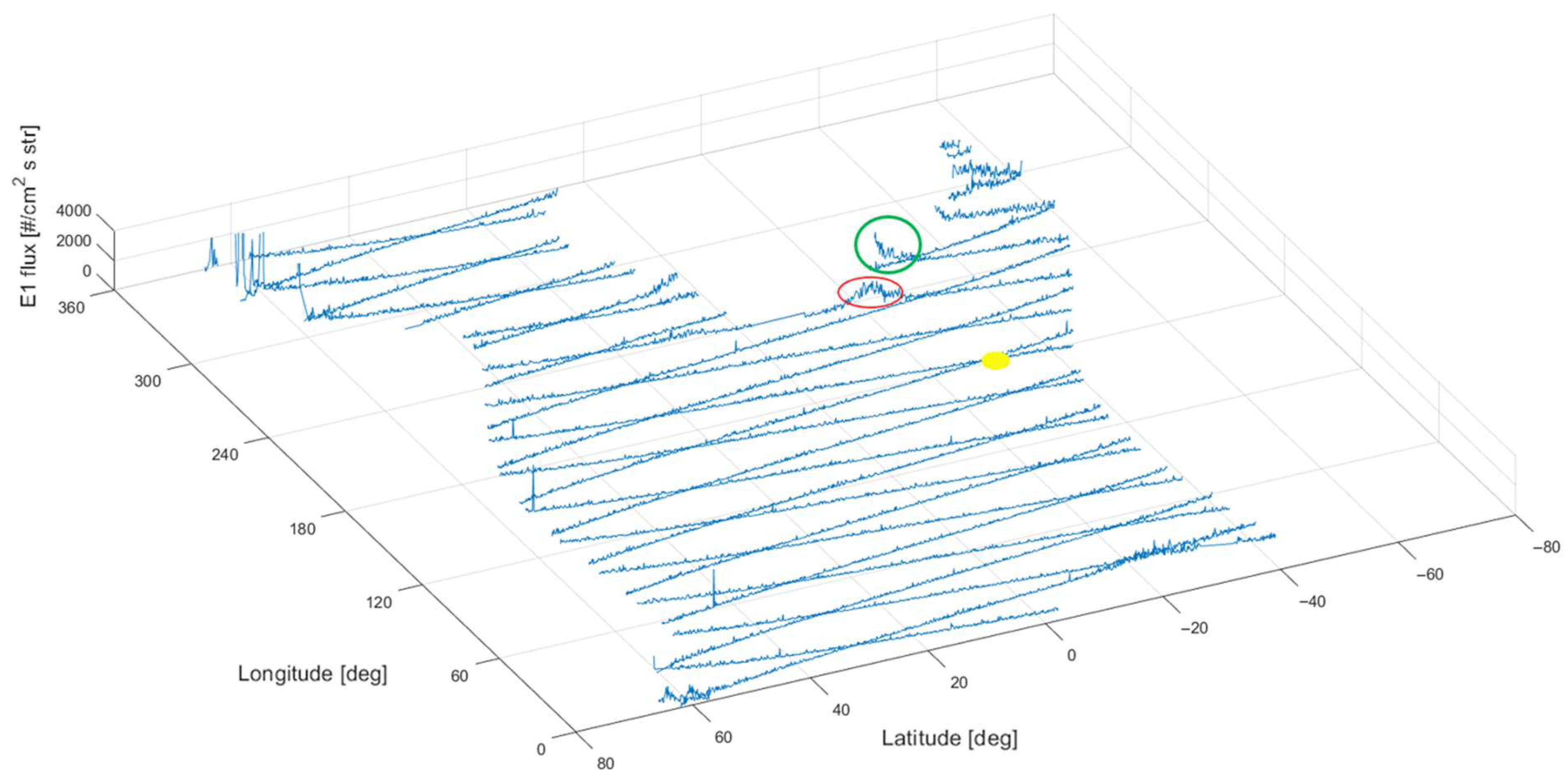
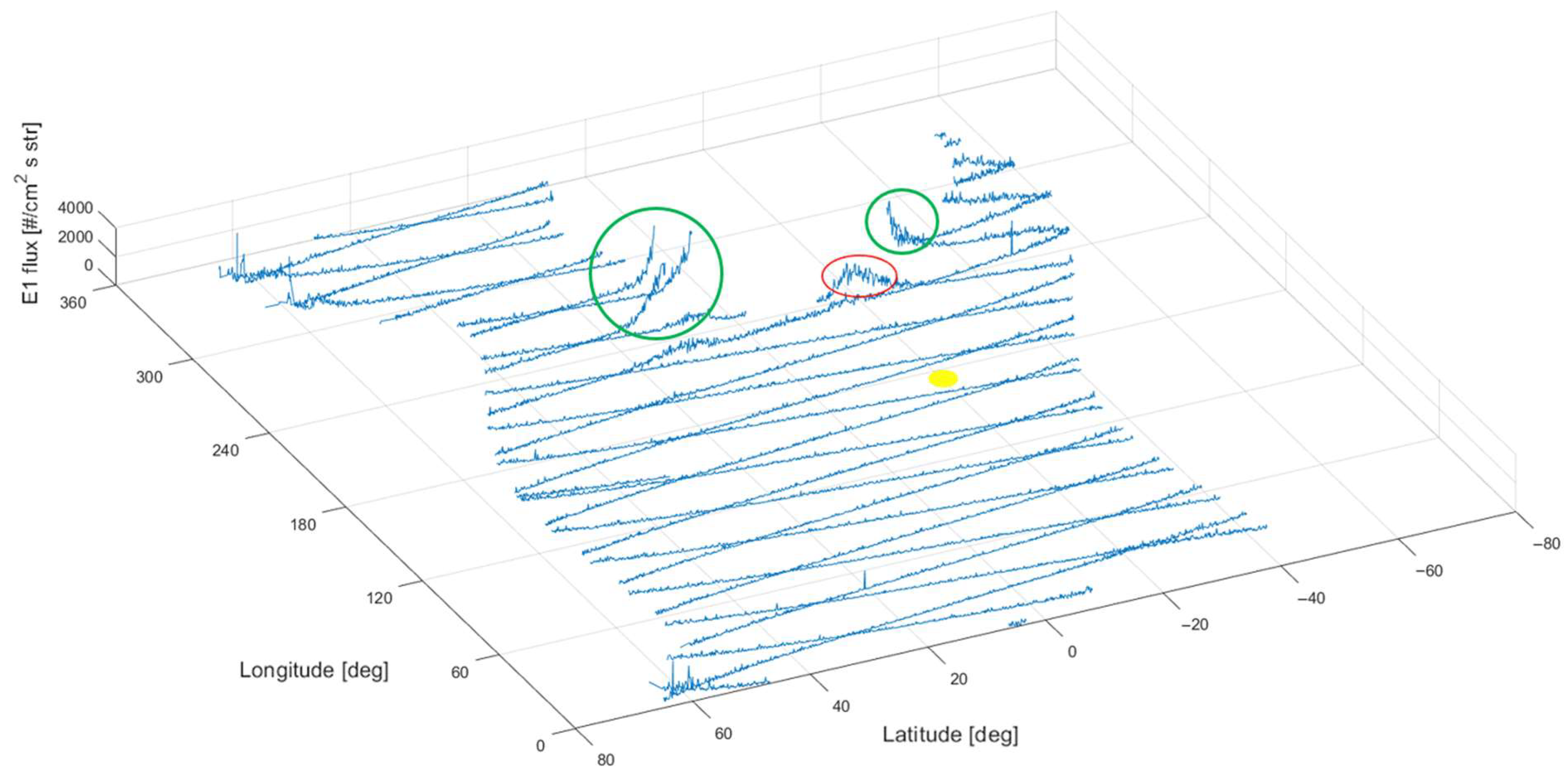
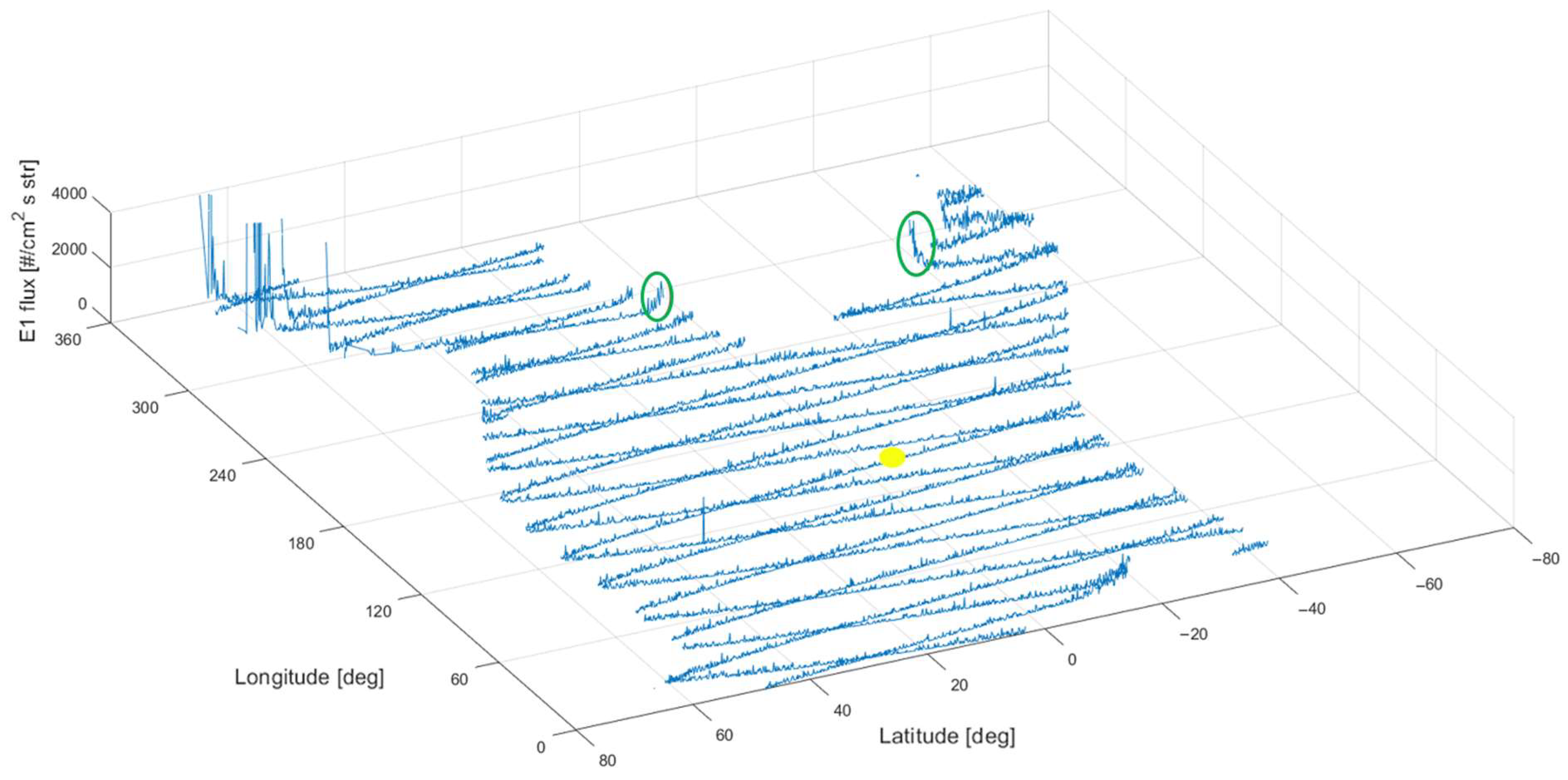
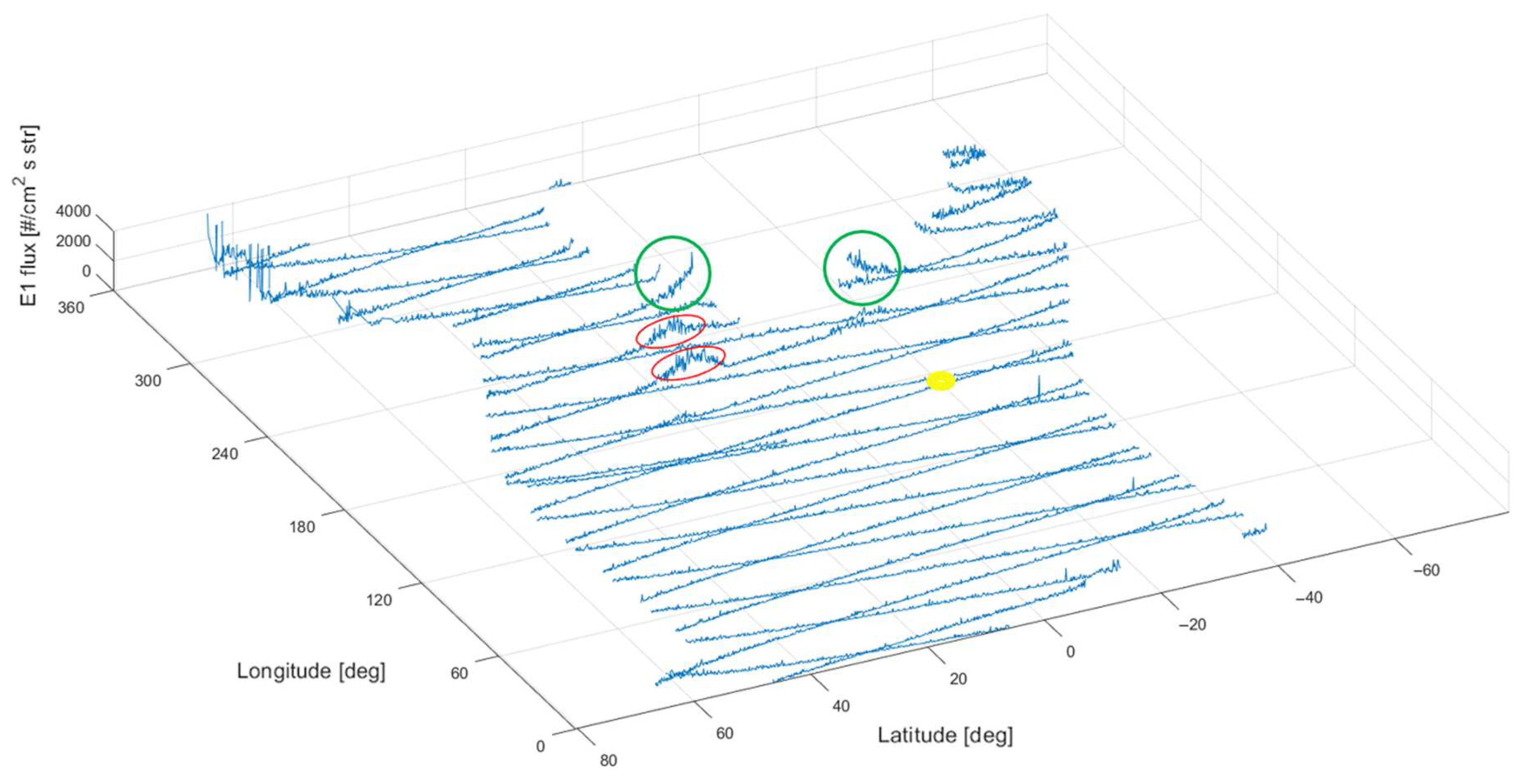
3. Results
3.1. Electron Perturbations of Kermadec and Tonga EQs
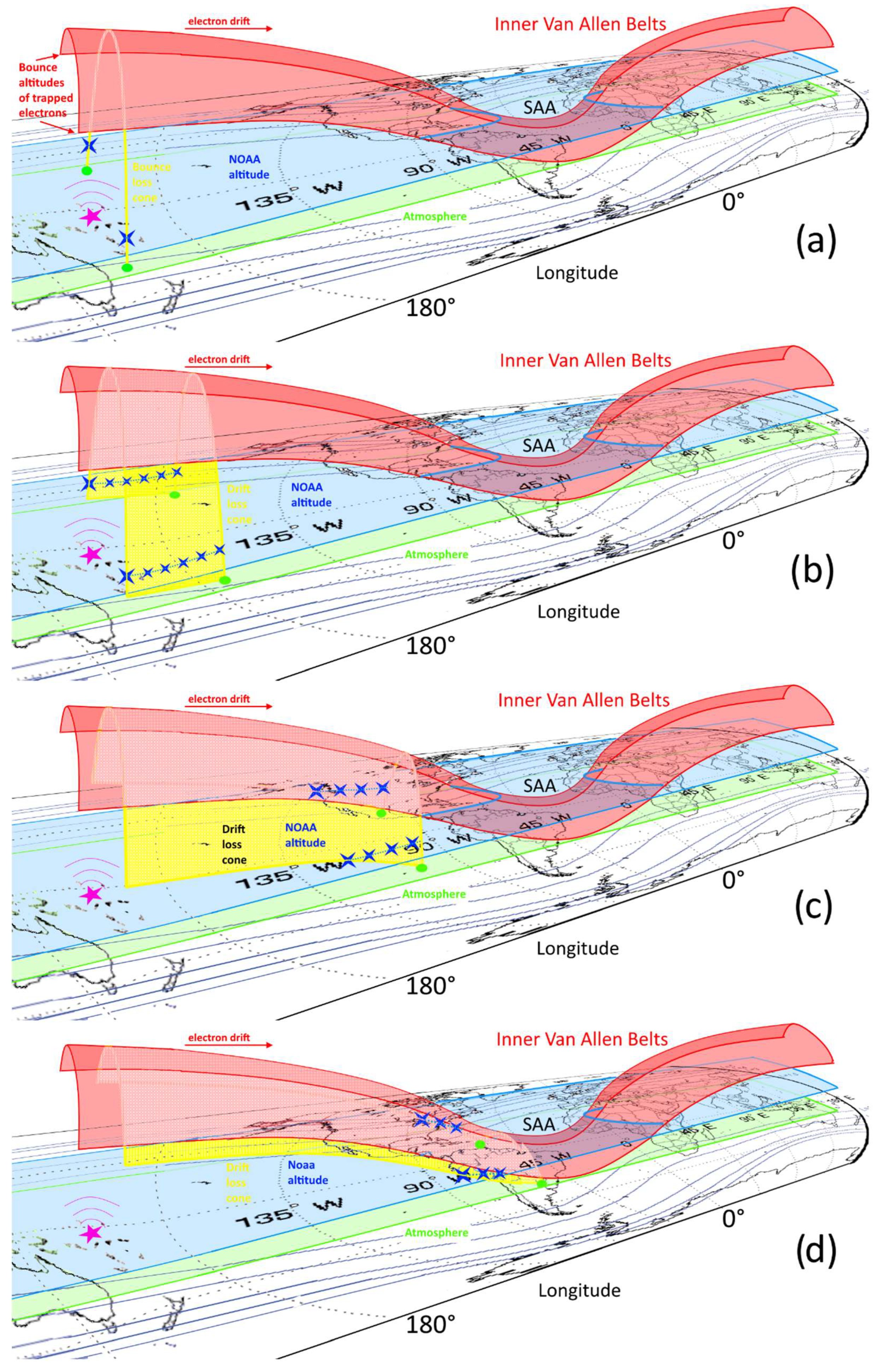
3.2. Types of Electron Perturbations
3.3. A Comparison between Losses Observed with and without EQs
3.4. The Coincidences between PELs and EQs
× cos(0.0172 × (D − 29,612 − 365 × (A − 2013))),
4. Discussion
4.1. The Physical Model of Possible Long-Distance Coincidences between PELs and EQs
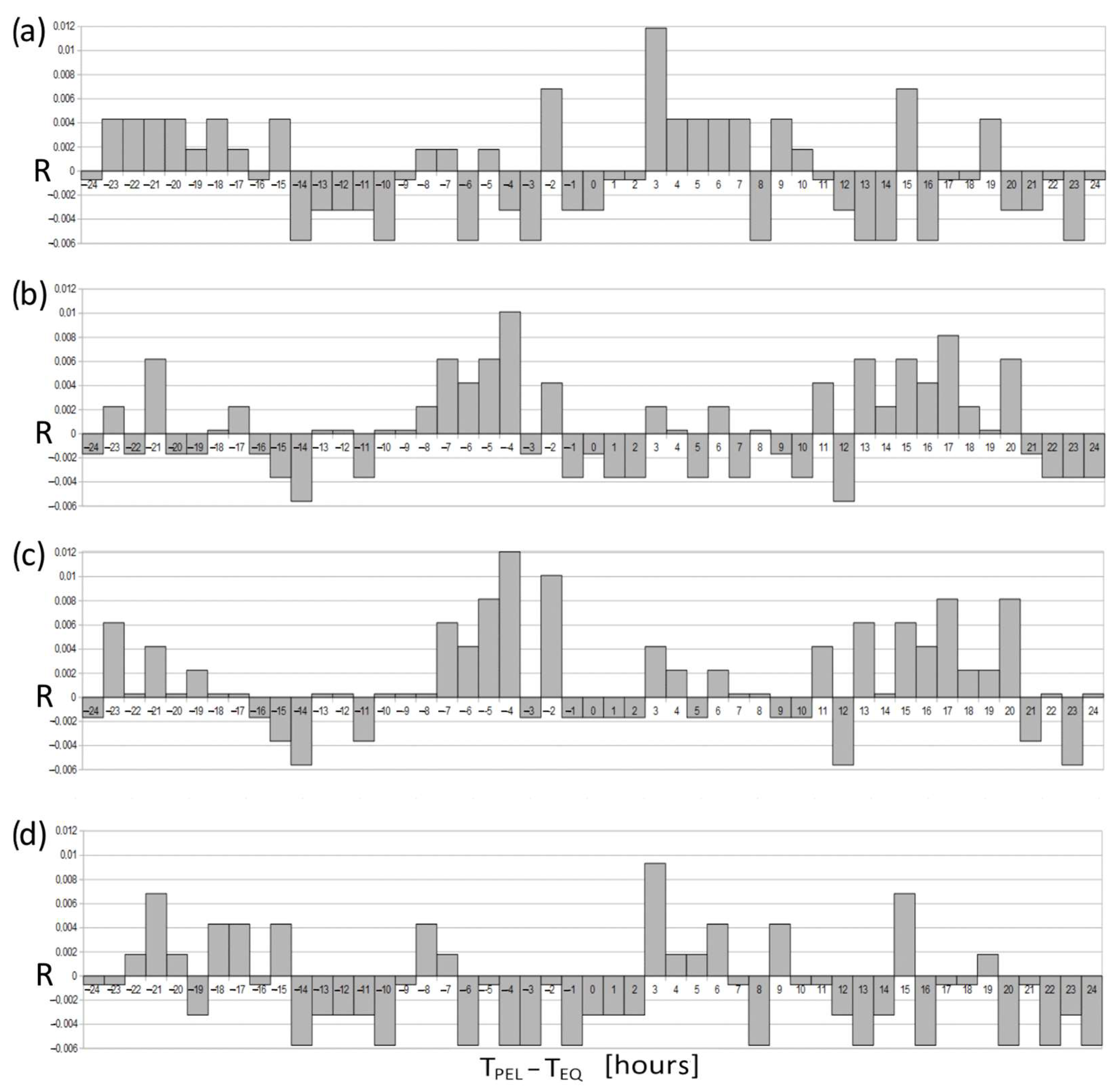
4.2. Pearson Correlations between PELs and EQs
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Imhof, W.L.; Gaines, E.E.; Reagan, J.B. High-Resolution Spectral Features Observed in the Inner Radiation Belt Trapped Electron Population. J. Geophys. Res. 1981, 86, 2341–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Allen, J.A. The Geomagnetically Trapped Corpuscular Radiation. J. Geophy. Res. 1959, 64, 1683–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badhwar, G.D. Radiation Measurements in Low Earth Orbit: U.S. and Russian Results. Health Phys. Radiat. Saf. J. 2000, 79, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datlowe, D.W.; Imhof, W.L.; Gaines, E.E.; Voss, H.D. Multiple Peaks in the Spectrum of Inner Belt Electrons. J. Geophys. Res. 1985, 90, 8333–8342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voronov, S.A.; Galper, A.M.; Koldashov, S.V. Observation of high-energy charged particle flux increases in SAA region in 10 September 1985. Cosmic Res. 1989, 27, 629–631. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, G. History of the NOAA satellite program. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2007, 1, 012504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandrin, S.Y.; Galper, A.M.; Grishantzeva, L.A.; Koldashov, S.V.; Maslennikov, L.V.; Murashov, A.M.; Picozza, P.; Sgrigna, V.; Voronov, S.A. High-energy charged particle bursts in the near-Earth space as earthquake precursors. Ann. Geophys. 2003, 21, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgrigna, V.; Carota, L.; Conti, L.; Corsi, M.; Galper, A.; Koldashov, S.; Murashov, A.; Picozza, P.; Scrimaglio, R.; Stagni, L. Correlations between Earthquakes and Anomalous Particle Bursts from SAMPEX/PET Satellite Observations. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 2005, 67, 1448–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidani, C.; Battiston, R.; Burger, W.J. A study of the correlation between earthquakes and NOAA satellite energetic particle bursts. Remote Sens. 2010, 2, 2170–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Sasmal, S.; Basak, T.; Chakrabarti, S.K. Comparative study of charged particle precipitation from Van Allen radiation belts as observed by NOAA satellites during a land earthquake and an ocean Earthquake. Adv. Space Res. 2019, 64, 719–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhima, Z.; Shen, X.; Chu, W.; Yan, R.; Guo, F.; Zhou, N.; Chen, H.; Wei, D. Statistical Analysis of High–Energy Particle Perturbations in the Radiation Belts Related to Strong Earthquakes Based on the CSES Observations. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidani, C. Particle precipitation prior to large earthquakes of both the Sumatra and Philippine Regions: A statistical analysis. J. Southeast Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 114, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz-Schampera, U.; Botz, R.; Hannington, M.; Adamson, R.; Anger, V.; Cormany, D.; Evans, L.; Gibson, H.; Haase, K.; Hirdes, W.; et al. Cruise Report SONNE 192/2—MANGO—Marine Geoscientific Research on Input and Output in the Tonga-Kermadec Subduction Zone (Marine Geowissenschaftliche Untersuchungen zum In- und Output der Tonga-Kermadec Subduktionszone); EPIC: Auckland, New Zealand, 2007; p. 92. [Google Scholar]
- D’Arcangelo, S.; Bonforte, A.; De Santis, A.; Maugeri, S.R.; Perrone, L.; Soldani, M.; Arena, G.; Brogi, F.; Calcara, M.; Campuzano, S.A.; et al. A multi-parametric and multi-layer study to investigate the largest 2022 Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai eruptions. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnardot, M.A.; Régnier, M.; Ruellan, E.; Christova, C.; Tric, E. Seismicity and state of stress within the overriding plate of the Tonga-Kermadec subduction zone. Tectonics 2007, 26, TC5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genzano, N.; Filizzola, C.; Hattori, K.; Pergola, N.; Tramutoli, V. Statistical correlation analysis between thermal infrared anomalies observed from MTSATs and large earthquakes occurred in Japan (2005–2015). J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2021, 126, e2020JB020108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schekotov, A.; Molchanov, O.; Hattori, K.; Fedorov, E.; Gladyshev, V.A.; Belyaev, G.G.; Chebrov, V.; Sinitsin, V.; Gordeev, E.; Hayakawa, M. Seismo-ionospheric depression of the ULF geomagnetic fluctuations at Kamchatka and Japan. Phys. Chem. Earth 2006, 31, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Hattori, K.; Hirokawa, M.; Zhuang, J.; Chen, C.-H.; Febriani, F.; Yamaguchi, H.; Yoshino, C.; Liu, J.-Y.; Yoshida, S. Statistical analysis of ULF seismo magnetic phenomena at Kakioka, Japan, during 2001–2010. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2014, 119, 4998–5011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierotti, L.; Fidani, C.; Facca, G.; Gherardi, F. Local earthquake conditional probability based on long term CO2 measurements. In Proceedings of the 40th GNGTS, Trieste, Italy, 27–29 June 2022; pp. 297–300. [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa, M.; Kasahara, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Muto, F.; Horie, T.; Maekawa, S.; Hobara, Y.; Rozhnoi, A.A.; Solovieva, M.; Molchanov, O.A. A statistical study on the correlation between lower ionospheric perturbations as seen by subionospheric VLF/LF propagation and earthquakes. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, A09305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrot, M. The micro-satellite DEMETER. J. Geodyn. 2002, 33, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulinets, S.A. Space technologies for short-term earthquake warning. Adv. Space Res. 2006, 37, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemec, F.; Santolík, O.; Parrot, M. Decrease of intensity of ELF/VLF waves observed in the upper ionosphere close to earthquakes: A statistical study. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, A4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Parrot, M. Statistical Analysis of an Ionospheric Parameter as a Base for Earthquake Prediction. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2013, 118, 3731–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.; Jin, S. Statistical characteristics of seismo ionospheric GPS TEC disturbances prior to global Mw ≥ 5.0 earthquakes (1998–2014). J. Geodyn. 2015, 92, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Nayak, K.; Romero-Andrade, R.; Mohammed-Aslam, M.A.; Sarma, K.K.; Aggarwal, S.P. Low Ionosphere Density Above the Earthquake Epicentre Region of Mw 7.2, El Mayor–Cucapah Earthquake Evident from Dense CORS Data. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, S.F.; Shah, M.; Li, B.; Jamjareegulgarn, P.; de Oliveira-Júnior, J.F.; Zhou, C. Synchronized and Co-Located Ionospheric and Atmospheric Anomalies Associated with the 2023 Mw 7.8 Turkey Earthquake. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.C.; Lee, L.C.; Ouzounov, D.; Jan, J.C. Earth’s outgoing longwave radiation variability prior to M ≥ 6.0 earthquakes in the Taiwan area during 2009–2019. Front. Earth Sci. 2020, 8, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, D.; De Santis, A.; Campuzano, S.A.; Zhu, K.; Soldani, M.; D’Arcangelo, S.; Orlando, M.; Wang, T.; Cianchini, G.; Di Mauro, D.; et al. Worldwide statistical correlation of eight years of Swarm satellite data with M5.5+ earthquakes: New hints about the pre seismic phenomena from space. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freund, F. Pre-earthquake signals: Underlying physical processes. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2011, 41, 383–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokin, V.M.; Chmyrev, V.M.; Yaschenko, A.K. Electrodynamic Model of the Lower Atmosphere and the Ionosphere Coupling. J. Atmos. Solar-Terrestrial Phys. 2001, 63, 1681–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulinets, S.; Ouzounov, D. Lithosphere-Atmosphere-Ionosphere Coupling (LAIC) model—An unified concept for earthquake precursors validation. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2011, 41, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, M.; Molchanov, O.A.; NASDA/UEC Team. Summary report of NASDA’s earthquake remote sensing frontier project. Phys. Chem. Earth 2004, 29, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molchanov, O.A.; Hayakawa, M. Electromagnetics and Related Phenomena: History and Latest Results; Terra Scientific Publishing: Tokyo, Japan, 2008; p. 189. [Google Scholar]
- Korepanov, V.; Hayakawa, M.; Yampolski, Y.; Lizunov, G. AGW as a seismo-ionospheric coupling responsible agent. Phys. Chem. Earth 2009, 34, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidani, C. West Pacific Earthquake Forecasting Using NOAA Electron Bursts With Independent L-Shells and Ground-Based Magnetic Correlations. Front. Earth Sci. Sect. Environ. Inform. Remote Sens. 2021, 9, 673105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.S.; Greer, M.S. Polar Orbiting Environmental Satellite Space Environment Monitor—2: Instrument Descriptions and Archive Data Documentation; Version 1.4; NOAA Technical Memorandum: Boulder, CO, USA, 2004; p. 155. [Google Scholar]
- Battiston, R.; Fidani, C. Correlations between NOAA Satellite Particle Bursts and Strong Earthquakes; EGU: Vienna, Austria, 2010; Volume 12, NH4.3. [Google Scholar]
- Fidani, C. Positive Correlation between Strong Indonesian and Philippine Region Earthquakes and NOAA Satellite Low L-shell Electron Bursts. In Proceedings of the 33th GNGTS, Bologna, Italy, 25–27 November 2014; pp. 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Fidani, C. Improving Earthquake Forecasting by Correlations Between Strong Earthquakes and NOAA Electron Bursts. TAO 2018, 29, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yando, K.; Millan, R.M.; Green, J.C.; Evans, D.S. A Monte Carlo simulation of the NOAA POES medium energy proton and electron detector instrument. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, A10231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidani, C. The Conditional Probability of Correlating East Pacific Earthquakes with NOAA Electron Bursts. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krunglanski, M. UNILIB Reference Manual, Belgisch Instituut Voor Ruimte–Aeronomie, Which Can Be Downloaded Together to the Library from. 2003. Available online: http://www.oma.be/NEEDLE/unilib.php/ (accessed on 11 March 2024).
- Asikainen, T.; Mursula, K. Energetic electron flux behaviour at low L-shells and its relation to the South Atlantic Anomaly. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2008, 70, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galper, A.M.; Koldashov, S.V.; Voronov, S.A. High Energy Particle Flux Variations as Earthquake Predictors. Adv. Space Res. 1995, 15, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walt, M. Introduction to Geomagnetically Trapped Radiation; Cambridge University: Cambridge, UK, 1994; p. 168. [Google Scholar]
- Bošková, J.; Šmilauer, J.; Tříska, P.; Kudela, K. Anomalous behaviour of plasma parameters as observed by the intercosmos 24 satellite prior to the Iranian earthquake of 20 June 1990. Stud. Geophys. Geod. 1994, 38, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Daily Results | PEL Average without EQs | PEL STD without EQs | PEL Average with EQs | PEL STD with EQs | t-Statistic (T-Test 0.05 tc = 1.645) | T-Test p-Value | Chi-Square 0.05 (DF) (χc) | Chi-Square p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending semi-orbits | 0.30 | 0.56 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 3.97 | 0.000049 | (3) (7.81) 18.16 | 0.000407 |
| Descending semi-orbits | 0.58 | 0.87 | 1.18 | 0.95 | 4.21 | 0.000019 | (4) (9.49) 26.44 | 0.000026 |
| Southern latitudes | 1.51 | 1.18 | 2.18 | 1.23 | 3.60 | 0.000198 | (5) (11.07) 15.53 | 0.008322 |
| Northern latitudes | 0.90 | 1.00 | 0.87 | 1.00 | - | - | - | - |
| Ascending around SAA | 0.60 | 0.66 | 0.35 | 0.52 | - | - | - | - |
| Descending around SAA | 0.93 | 0.58 | 0.83 | 0.60 | - | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fidani, C.; D’Arcangelo, S.; De Santis, A.; Perrone, L.; Soldani, M. Investigating a Possible Correlation between NOAA-Satellite-Detected Electron Precipitations and South Pacific Tectonic Events. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1059. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16061059
Fidani C, D’Arcangelo S, De Santis A, Perrone L, Soldani M. Investigating a Possible Correlation between NOAA-Satellite-Detected Electron Precipitations and South Pacific Tectonic Events. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(6):1059. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16061059
Chicago/Turabian StyleFidani, Cristiano, Serena D’Arcangelo, Angelo De Santis, Loredana Perrone, and Maurizio Soldani. 2024. "Investigating a Possible Correlation between NOAA-Satellite-Detected Electron Precipitations and South Pacific Tectonic Events" Remote Sensing 16, no. 6: 1059. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16061059
APA StyleFidani, C., D’Arcangelo, S., De Santis, A., Perrone, L., & Soldani, M. (2024). Investigating a Possible Correlation between NOAA-Satellite-Detected Electron Precipitations and South Pacific Tectonic Events. Remote Sensing, 16(6), 1059. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16061059







