Satellite-Based Water Quality Assessment of the Beijing Section of the Grand Canal: Implications for SDG11.4 Evaluation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Acquisition
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Acquisition
2.2.1. In Situ Data Acquisition
2.2.2. Satellite Data Acquisition
3. Methods
3.1. Satellite Data Preprocessing
3.1.1. Data Resampled
3.1.2. Water Mask Extraction
3.1.3. Rrs Correction of Sentinel-2 MSI L2A Products
3.2. Inversion and Evaluation Methods for Water Quality Parameters
3.2.1. Inversion Modelling of Chl-a
3.2.2. Zsd Estimation
3.2.3. Evaluation of the Accuracy of Chl-a and Zsd Inversion
3.3. Method for Calculating TLI and Evaluating Water Quality
3.3.1. Method for Calculating TLI
3.3.2. Evaluation Methods for Good Water Quality
3.4. Spatiotemporal Analysis Method of TLI and Good Ambient Water Quality
4. Results
4.1. Calibration and Validation of Water Quality Estimation Model
4.1.1. Calibration and Validation of Chl-a Estimation Model
4.1.2. Calibration and Validation of Zsd Estimation Model
4.2. Spatiotemporal Analysis of the Comprehensive Trophic Level Index
5. Discussion
5.1. Influencing Factors Analysis of the Annual Change of Water Quality of BGC
5.1.1. Meteorological Factors
5.1.2. Human Activities Factors
5.1.3. Water Environment Protection Policies
5.2. Implications for the SDG 11.4 Evaluation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BGC | Beijing section of the Grand Canal |
| TLI | Comprehensive Trophic Level Index |
| SDG | Sustainable Development Goal |
| Chl-a | Chlorophyll-a concentration |
| Zsd | Transparency |
| Rrs | Remote sensing reflectance |
| ASD | Analytical Spectral Devices |
| Stdv | Standard Deviation |
| Min | Minimum |
| Max | Maximum |
| ESA | European Space Agency |
| QAA | Quasi-Analytical Algorithm |
| NIR | Near-Infrared |
| SWIR | Short-Wave Infrared |
| SL | Slope Index |
| FLH | Fluorescence Line Height |
| MCI | Maximum Chlorophyll Index |
| NDCI | Normalized Difference Chlorophyll-a Index |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| MRE | Mean Relative Error |
References
- Pan, X.T. Millennium Canal Welcomes Century Revival. People’s Daily Overseas Edition, 26 May 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J. Study on the Ecological Environmental Change of the Jing-Hang Grand Canal; Nanjing Forestry University: Nanjing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, W.X.; Zhu, X.K.; Zhang, Y.R.; Ding, Y.; Qi, J.Y. Land Cover Change and Landscape Pattern Evolution in Beiing Section of the Grand Canal. Beijing Surv. Mapp. 2021, 35, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, N.; Cui, Q. Present the Culture the Preservation Plan of JingHang Grand Canna (BeiJing Part). China Anc. City 2011, 5, 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.F.; Zhao, Y.W.; Peng, K.Y.; Wang, J.; Ren, S.Y. Phytoplankton Evaluation and Cluster Analysis of 5 Landscape-lakes in Beijing. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2009, 16, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.J. Current Situation Existing Problems and Improvement Path of Water Environment Governance in Beijing; Beijing University of Technology: Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H. Landscape Changes and Heritage Protection of the Beijing Section of the Grand Canal. Yanhuang Geogr. 2020, 4, 86–89. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.W. Study on the Spatial Characteristics of the Traditional Settlement in the BeijingSection of the Grand Canal; Beijing University of Architecture: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.Y.; Ren, H.G.; Wang, P.; Yang, R.X.; Cheng, F.L. A preliminary study on target 11.4 for UN Sustainable Development Goals. Int. J. Geoherit. Parks 2018, 6, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.Y. Grand Canal heritage protection and utilization under the background of applying for world heritage. Soc. Sci. Beijing 2012, 5, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. The Grand Canal steps into the world heritage. Openings 2014, 28, 14–15. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. Transforming our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.Y.; Liu, C.Q.; Shi, X.L.; Li, Y.; Fan, Z.W.; Jia, B.Y.; Liao, Y.P. Ten-year Trend Analysis of Eutrophication Status and the Related Causes in Lake Hongze. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 3523–3531. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.C.; Wang, C.; Wang, M.Q.; Zhao, H.; Yan, K.; Mu, Y.C.; Zhang, W.Z.; Zhang, F.F.; Wang, S.L.; Li, J.S. Spatiotemporal variation of cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms in China based on literature and media information. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2023, 16, 3905–3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadollah, S.B.H.S.; Sharafati, A.; Motta, D.; Yaseen, Z.M. River water quality index prediction and uncertainty analysis: A comparative study of machine learning models. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Zhang, C. Eutrophication of Wetland Water in Fenhe River Scenic Area Based on Comprehensive Nutritional State Index. Soil Water Conserv. China 2023, 4, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.P.; Yang, W.J.; Sha, J.; Shang, Y.T.; Li, X. Spatial characteristics of nutrient status in Danjiangkou Reservoir. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 43, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Zhu, G.W.; Cai, Y.J.; Xu, H.; Zhu, M.Y.; Gong, Z.J.; Zhang, Y.L.; Qin, B.Q. The limitations of comprehensive trophic level index (TLI) in the eutrophication assessment of lakes along the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River during summerseason and recommendation for its improvement. J. Lake Sci. 2020, 32, 36–47. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Zhou, C.; Wang, X.X.; Meng, Q.H.; Chen, Y.L. Remote sensing quantitative retrieval of Chlorophyll a and trophie level index in main sagoing rivers of Lianyungang. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2023, 43, 3314–3320. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.C.; Liu, X.Q.; Zhang, J.H. Evaluate method and classification standard on lake eutrophication. Environ. Monit. China 2002, 18, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Q. Remote Sensing Study on the Spatio-Temporal Variation of Water Quality Distribution in the Jing-Hang Grand Canal over the Past Forty Years; Jiangsu Normal University: Xuzhou, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Naimaee, R.; Kiani, A.; Jarahizadeh, S.; Haji Seyed Asadollah, S.B.; Melgarejo, P.; Jodar-Abellan, A. Long-Term Water Quality Monitoring: Using Satellite Images for Temporal and Spatial Monitoring of Thermal Pollution in Water Resources. Sustainability 2024, 16, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehri, R.; Khlifi, S.; Vanclooster, M. Disaggregating SDG-6 water stress indicator at different spatial and temporal scales in Tunisia. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 694, 133766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Li, J.S.; Shen, Q.; Wu, Y.H.; Zhang, F.F.; Wang, S.L.; Yao, Y.; Guo, L.N.; Yin, Z.Y. Recent research progress on long time series and large scale optical remote sensing of inland water. Nat. Remote Sens. Bull. 2021, 25, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Schalles, J.F.; Hladik, C.M. Remote chlorophyll-a retrieval in turbid, productive estuaries: Chesapeake Bay case study. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 109, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmanson, L.G.; Brezonik, P.L.; Bauer, M.E. Airborne hyperspectral remote sensing to assess spatial distribution of water quality characteristics in large rivers: The Mississippi River and its tributaries in Minnesota. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 130, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Guo, H.; Xu, W.; Zhu, X.; Wang, B.; Zeng, Q.; Huang, J.J. Remote sensing retrieval of inland water quality parameters using Sentinel-2 and multiple machine learning algorithms. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 18617–18630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quang, N.H.; Dinh, N.T.; Dien, N.T.; Son, L.T. Calibration of Sentinel-2 Surface Reflectance for Water Quality Modelling in Binh Dinh’s Coastal Zone of Vietnam. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.F. Analysis and Optimization Strategy of Typical Waterfront and Water front Landscape of Grand Canal (Beijing Section); Tianjin University of Technology: Tianjin, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, J.L.; Morel, A.; Frouin, R.; Davis, C.; Arnone, R.; Carder, K.; Lee, Z.P. Ocean Optics Protocols for Satellite Ocean Color Sensor Validation, Revision 4. In Volume III: Radiometric Measurements and Data Analysis Protocols; Goddard Space Flight Space Centre: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.W.; Tian, G.L.; Wang, X.Y.; Wang, X.M.; Song, Q.J. The methods of water spectra measurement and analysis I: Above-water method. Nat. Remote Sens. Bull. 2004, 8, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Sartory, D.P.; Grobbelaar, J.U. Extraction of chlorophyll a from freshwater phytoplankton for spectrophotometric analysis. Hydrobiologia 1984, 114, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Qin, B.Q.; Liu, M.L. Temporal–spatial variations of chlorophyll a and primary production in Meiliang Bay, Lake Taihu, China from 1995 to 2003. J. Plankton Res. 2007, 29, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.Y.; Li, J.S.; Huang, J.; Wang, S.L.; Zhang, F.F.; Zhang, B. Steady increase in water clarity in Jiaozhou Bay in the Yellow Sea from 2000 to 2018: Observations from MODIS. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2020, 39, 800–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, R.T.; Wang, S.L.; Shi, J.K.; Shen, W.; Zhang, W.Z.; Zhang, F.F.; Li, J.S. Sentinel-2 MSI Observations of Water Clarity in Inland Waters across Hainan Island and Implications for SDG 6.3.2 Evaluation. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanda, A.; Šerić, L.; Žagar, D.; Oštir, K. An application of 1D convolution and deep learning to remote sensing modelling of Secchi depth in the northern Adriatic Sea. Big Earth Data 2023, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Xiang, C.C. Extraction of Rivers and Lakes Based on Sentinel-2 Remote Sensing lmages. Geomat. Spatial Inf. Tech. 2023, 46, 120–123. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Zhao, H.L.; Li, J.S.; Zhang, F.F.; Wang, S.L.; Yin, Z.Y.; Shen, W. Phytoplankton biomass variation after cage aquaculture removal from the Daheiting Reservoir, China: Observations from satellite data. Hydrobiologia 2022, 849, 4759–4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.P.; Shang, S.L.; Hu, C.M.; Du, K.P.; Weidemann, A.; Hou, W.L.; Lin, J.F.; Lin, G. Secchi disk depth: A new theory and mechanistic model for underwater visibility. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 169, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitarch, J.; Vanhellemont, Q. The QAA-RGB: A universal three-band absorption and backscattering retrieval algorithm for high resolution satellite sensors. Development and implementation in ACOLITE. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 265, 112667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.L.; Li, J.S.; Zhang, B.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, F.F. Monitoring cyanobacteria-dominant algal blooms in eutrophicated Taihu Lake in China with synthetic aperture radar images. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2015, 33, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.J.; Feng, L.; Duan, H.T.; Chen, X.L.; Sun, D.Y.; Shi, K. Fifteen-year monitoring of the turbidity dynamics in large lakes and reservoirs in the middle and lower basin of the Yangtze River, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 190, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller-Wilm, U.; Devignot, O.; Pessiot, L. Sen2Cor Configuration and User Manual; European Space Agency: Paris, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.L.; Li, J.S.; Bing, Z.; Qian, S.; Zhang, F.; Iu, Z. A simple correction method for the MODIS surface reflectance product over typical inland waters in China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 6076–6096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, C.F.; Hu, C.M.; Cannizzaro, J.; English, D.; Muller-Karger, F.; Lee, Z.P. Evaluation of chlorophyll-a remote sensing algorithms for an optically complex estuary. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 129, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, F.; AlcÂNtara, E.; Rodrigues, T.; Rotta, L.; Bernardo, N.; Imai, N. Remote sensing of the chlorophyll-a based on OLI/Landsat-8 and MSI/Sentinel-2A (Barra Bonita reservoir, Brazil). An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2018, 90, 1987–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gons, H.J.; Rijkeboer, M.; Ruddick, K.G. Effect of a waveband shift on chlorophyll retrieval from MERIS imagery of inland and coastal waters. J. Plankton Res. 2005, 27, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, D.R.; Mishra, S. Plume and bloom: Effect of the Mississippi River diversion on the water quality of Lake Pontchartrain. Geocarto Int. 2010, 25, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letelier, R.M.; Abbott, M.R. An analysis of chlorophyll fluorescence algorithms for the moderate resolution imaging spectrometer (MODIS).pdf. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 58, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gower, J.; King, S.; Borstad, G.; Brown, L. Detection of intense plankton blooms using the 709 nm band of the MERIS imaging spectrometer. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 2005–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Mishra, D.R. Normalized difference chlorophyll index: A novel model for remote estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration in turbid productive waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmanson, L.G.; Brezonik, P.L.; Bauer, M.E. Evaluation of medium to low resolution satellite imagery for regional lake water quality assessments. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiawan, F.; Matsushita, B.; Hamzah, R.; Jiang, D.; Fukushima, T. Long-Term Change of the Secchi Disk Depth in Lake Maninjau, Indonesia Shown by Landsat TM and ETM+ Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.P.; Shang, S.L.; Qi, L.; Yan, J.; Lin, G. A semi-analytical scheme to estimate Secchi-disk depth from Landsat-8 measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 177, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, S.L.; Lee, Z.P.; Shi, L.H.; Lin, G.; Wei, G.M.; Li, X.D. Changes in water clarity of the Bohai Sea: Observations from MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 186, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Hou, X.J.; Zheng, Y. Monitoring and understanding the water transparency changes of fifty large lakes on the Yangtze Plain based on long-term MODIS observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 221, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.Y.; Li, J.S.; Liu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, F.F.; Wang, S.L.; Sun, X.; Zhang, B. Water clarity changes in Lake Taihu over 36 years based on Landsat TM and OLI observations. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2021, 102, 102457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Wang, M.H.; Li, J.S. Water property in high-altitude Qinghai Lake in China. Sci. Remote Sens. 2020, 2, 100012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.T.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Shi, K. Research progress on remote sensing assessment of lake nutrient status and retrieval algorithms ofcharacteristic parameters. Nat. Remote Sens. Bull. 2022, 26, 77–91. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Lu, Q.; Fan, Z.P.; Li, F.Y. Eutrophication and spatial distribution of N, P and chlorophyl-a in the Taizihe River Basin, LiaoheRiver Catchment. J. Lake Sci. 2017, 29, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.P.; Wang, Q.; Xiao, Q. Eutrophication evaluation of Taihu Lake based on quantitative remotesensing inversion. Geogr. Geoinf. Sci. 2007, 23, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.C. Chinese Lake Environment Volume One; Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 1995; pp. 275–278. [Google Scholar]
- Bigham Stephens, D.L.; Carlson, R.E.; Horsburgh, C.A.; Hoyer, M.V.; Bachmann, R.W.; Canfield, D.E. Regional distribution of Secchi disk transparency in waters of the United States. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2015, 31, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.D. Big Earth Data in Support of the Sustainable Development Goals (2020); EDP Sciences: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.; Li, J.S.; Hu, R.M.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, F.F. Landsat-satellite-based analysis of spatial–temporal dynamics and drivers of CyanoHABs in the plateau Lake Dianchi. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 8552–8571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansper, A.; Alikas, K. Retrieval of Chlorophyll a from Sentinel-2 MSI Data for the European Union Water Framework Directive Reporting Purposes. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrose-Igho, G.; Seyoum, W.M.; Perry, W.L.; O’Reilly, C.M. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Water Quality Indicators in Small Lakes Using Sentinel-2 Satellite Data: Lake Bloomington and Evergreen Lake, Central Illinois, USA. Environ. Prog. 2021, 8, 637–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhag, M.; Gitas, I.; Othman, A.; Bahrawi, J.; Gikas, P. Assessment of Water Quality Parameters Using Temporal Remote Sensing Spectral Reflectance in Arid Environments, Saudi Arabia. Water 2019, 11, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; Wang, X.D.; Luo, F.; Xu, D.D.; Wu, B.W.; Xue, Y.H.; Ju, X.H.; Wen, X.L. Application limitations and improvement recommendations of trophic state indices in theeutrophication level assessment of small shallow lakes along the lower reach of the Yangtze. J. Lake Sci. 2023, 35, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar]
- An, G.Y.; Guo, Z.C.; Ye, P. Climatic Changes and Impacts on Water Quality of Erhai Lake in Dali Area, Yunnan Province over the Period from 1989 to 2019. Geoscience 2022, 36, 406. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.H.; Liu, J.Q.; Wang, J.R.; Tian, L.Q.; Zhou, Q.; Li, J. Integrated monitoring of lakes’ turbidity in Wuhan, China during the COVID-19 epidemic using multi-sensor satellite observations. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2020, 14, 443–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.T.; Ma, R.H.; Xu, X.F.; Kong, F.X.; Zhang, S.X.; Kong, W.J.; Hao, J.Y.; Shang, L.L. Two-Decade Reconstruction of Algal Blooms in China’s Lake Taihu. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3522–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, G.; Yu, G. A Numerical Simulation of Nutrient Transport in Taihu Basin. In Hydrology and Management of Forested Wetlands, Proceedings of the International Conference, New Bern, NC, USA, 8–12 April 2006; American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State Council. Water Pollution Prevention and Control Action Plan. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2015-04/16/content_9613.htm (accessed on 16 April 2015).
- Qiu, J. Safeguarding China’s water resources. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2018, 5, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beijing Municipal Ecology and Environment Bureau. Opinions on Strengthening Ecological Environment Protection and Combating Pollution in Beijing. Available online: https://sthjj.beijing.gov.cn/bjhrb/index/xxgk69/sthjlyzwg/wrfzgjz/1707132/ (accessed on 14 July 2018).
- State Council. Outline of the Plan for Cultural Protection, Inheritance, and Utilization of the Grand Canal. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/2019-05/09/content_5390046.htm?eqid=c4a5704700006a04000000046486b5a3 (accessed on 9 May 2019).
- Standing Committee of Beijing Municipal People’s Congress. Regulations on the Protection and Management of Rivers and Lakes in Beijing. Available online: https://www.beijing.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengcefagui/201907/t20190729_102510.html (accessed on 29 July 2019).
- Xu, B.; Yang, Y.; Sun, C.Y.; Huang, Z.F.; Wang, J.Y.; Zhao, H.L. Quality and quantity characteristics of the middle route of South-to-North Water Diversion Projectin Beijing area and its effect on the local rivers and lakes. J. China Hydrol. 2023, 43, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M. Analysis on spatial-temporal differences and influencing factors of industrial water resourcesreen efficiency in the South-to-North Water Diversion Project’s Central Route. Ecol. Econ. 2023, 39, 174–181. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.L. Release of the Construction and Protection Plan for the Grand Canal National Cultural Park in Beijing. China Cultural Relics Daily, 12 October 2021; p. 002. Available online: https://en.planning.org.cn/nua/view?id=506 (accessed on 29 July 2019).
- Beijing Municipal Water Bureau. Beijing Water Resources Guarantee Plan (2020–2035). Available online: https://swj.beijing.gov.cn/swdt/tzgg/202209/t20220916_2816811.html (accessed on 16 September 2022).
- Cai, Y. The Evaluation Index System of Water-Saving Society Construction Researchof Beijing; Beijing University of Civilengineering and Architecture: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Transforming Tourism. 2023-SDG Midterm Stocktaking. Available online: http://www.transforming-tourism.org/2023-sdg-midterm-stocktaking.html (accessed on 19 February 2023).

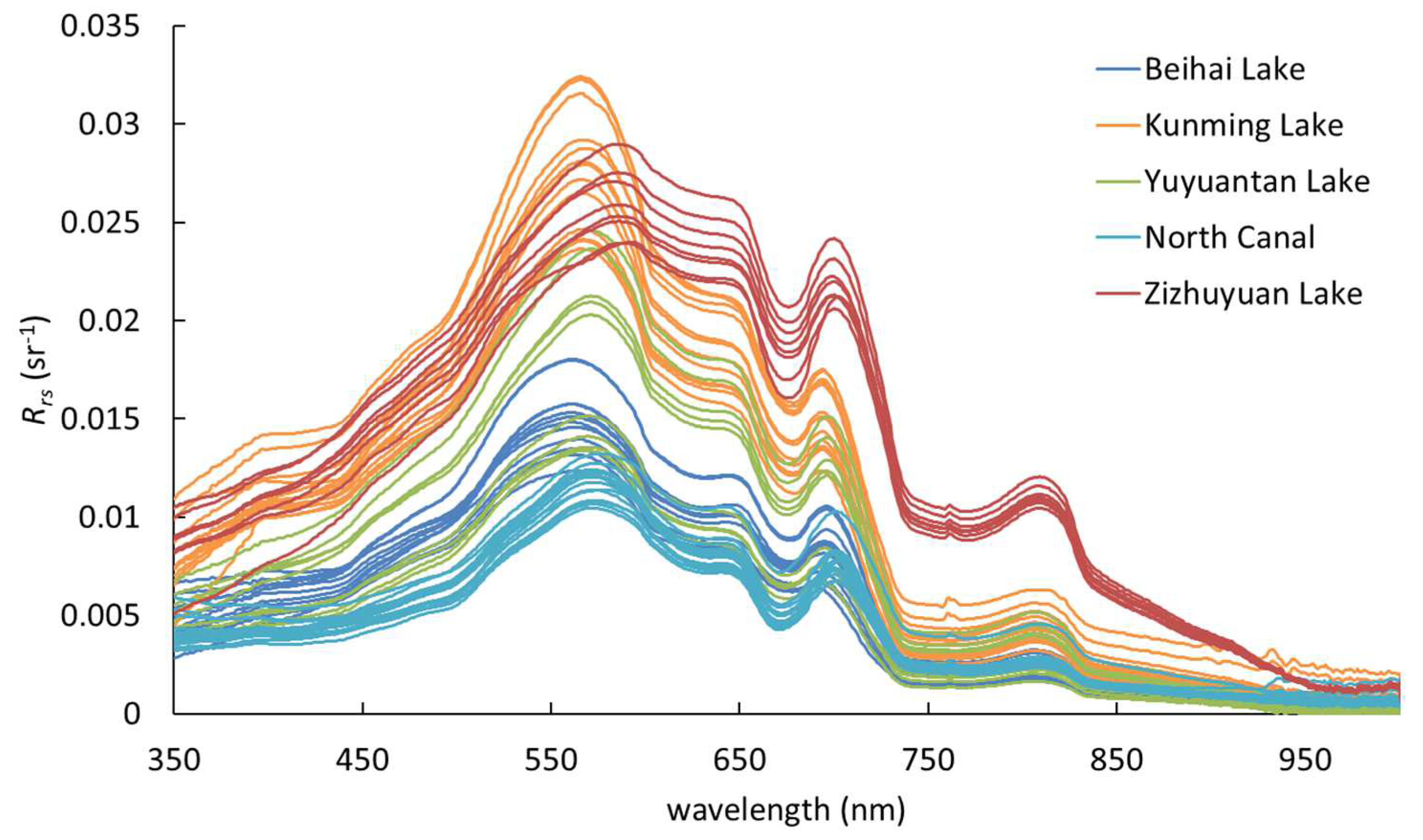
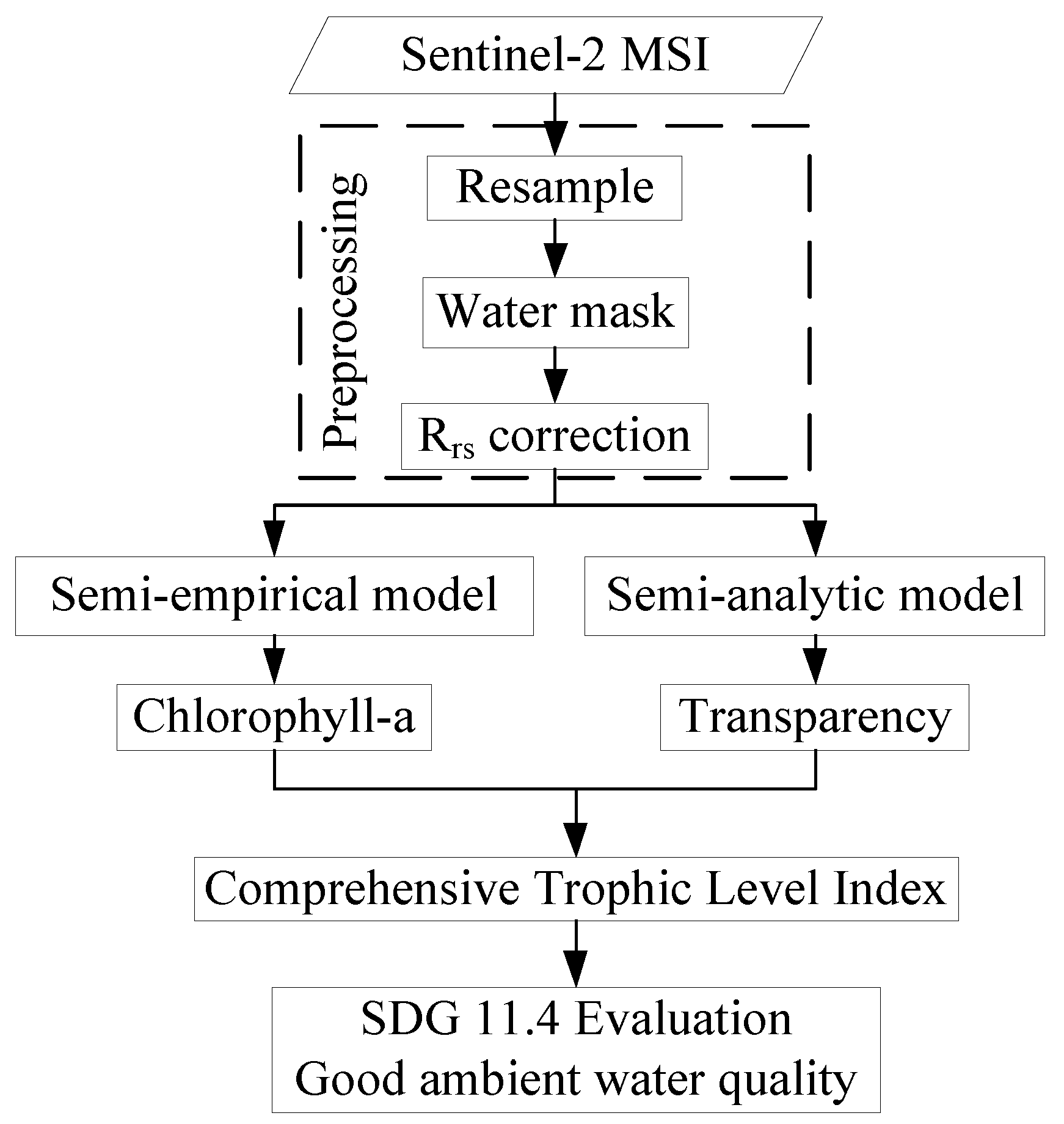
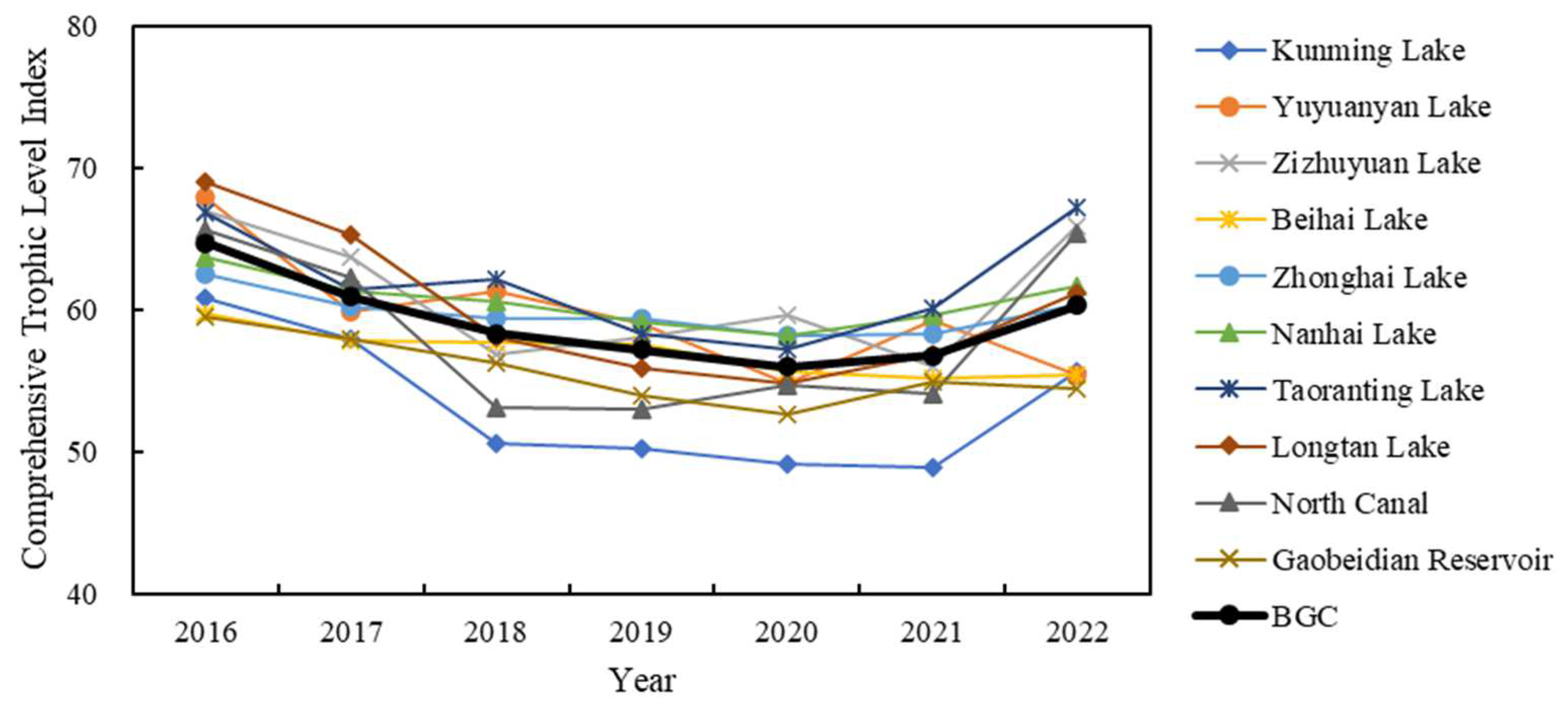
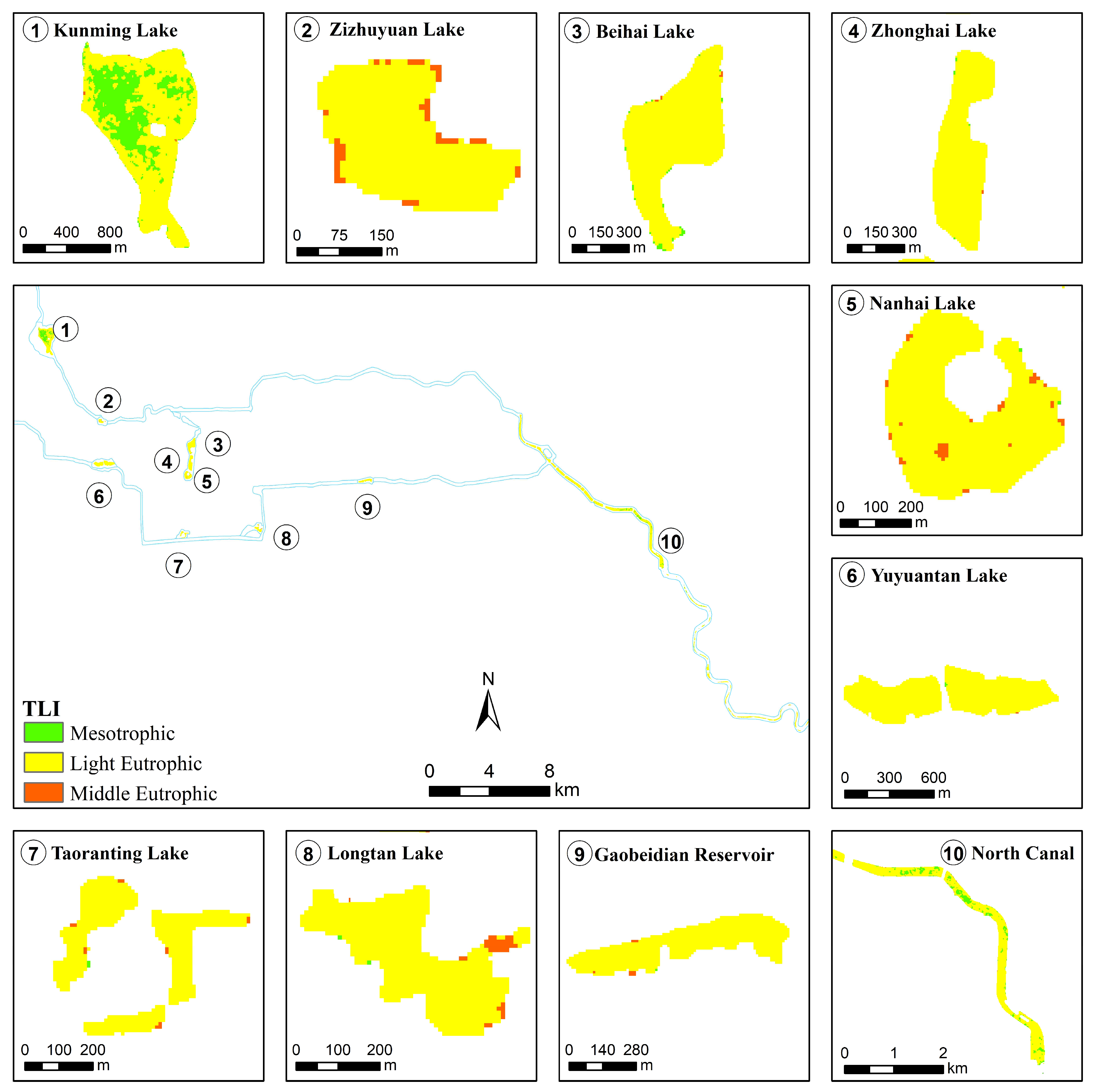


| Study Area | Experiment Date | Sampling Points | Chl-a (mg/m3) | Zsd (m) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max | Min | Mean | Stev | Max | Min | Mean | Stev | |||
| Yuyuantan Lake | 21 August | 9 | 26.65 | 14.35 | 21.18 | 0.20 | 0.94 | 0.40 | 0.62 | 0.20 |
| Kunming Lake | 16 September | 14 | 14.60 | 10.14 | 12.88 | 1.13 | 0.58 | 0.48 | 0.53 | 0.04 |
| Beihai Lake | 18 September | 12 | 18.88 | 5.05 | 13.97 | 4.30 | 1.05 | 0.55 | 0.73 | 0.18 |
| North Canal | 15 October | 15 | 68.47 | 38.73 | 47.99 | 7.82 | 0.80 | 0.58 | 0.66 | 0.06 |
| Zizhuyuan Lake | 25 October | 8 | 37.39 | 15.36 | 22.78 | 6.75 | 0.25 | 0.20 | 0.22 | 0.02 |
| Reference | Spectra Index Abbreviation | Spectra Index Formula |
|---|---|---|
| [48] | SL | X = (Rrs (705) − Rrs (665))/(705 − 665) |
| [49] | FLH | X = Rrs (665) − Rrs (560) − ((665 − 560)/(705 − 560)) × (Rrs (705) − Rrs (665)) |
| [50] | MCI | X = Rrs (705) − Rrs (665) − ((705 − 665)/(740 − 665)) × (Rrs (740) − Rrs (665)) |
| [51] | NDCI | X = (Rrs (705) –Rrs (665))/(Rrs (705) + Rrs (665)) |
| Step | Property | Calculation Formula | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | |||
| 2 | , g0 = 0.089, g1 = 0.1245 | ||
| 3 | If (665) < 0.02 sr−1 P = −1.085 − 1.110 − 0.2342 − 0.1023 | Else | |
| 4 | |||
| 5 | |||
| 6 | |||
| 7 | |||
| 8 | |||
| 9 | |||
| Index (X) | Optimized Chl-a Model | Calibration | Validation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R² | R² | RMSE (mg/m³) | MRE (%) | ||
| SL | 10^ (35,748,887,305.13X3 − 28,085,209.05X2 + 6714.07X + 1.37) | 0.84 | 0.16 | 13.83 | 42.8 |
| FLH | 10^ (−3,190,137.93X3 − 77,772.4X2 − 588.52X + 0.48) | 0.78 | 0.08 | 14.85 | 40.1 |
| MCI | 10^ (28.19X3 − 9.17 X2 + 2.07X + 1.69) | 0.84 | 0.04 | 17.57 | 54.0 |
| NDCI | 10^ (3.37X + 1.34) | 0.85 | 0.73 | 11.54 | 32.1 |
| Reference | Band or Spectral Index | Zsd Model | Calibration | Validation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R² | R² | RMSE (m) | MER (%) | |||
| [52] | X1 = Rrs (560) | 1.941 − 11.069X1 − 1.27X2 | 0.81 | 0.83 | 0.1 | 18.2 |
| X2 = Rrs (665)/Rrs (490) | ||||||
| [53] | X1 = Rrs (490)/Rrs (560) | 0.913 − 2.069X1 + 1.378X2 | 0.71 | 0.8 | 0.11 | 20.8 |
| X2 = Rrs (665)/Rrs (560) | ||||||
| [40] | QAA_RGB | 0.87 | 0.09 | 18.1 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Xiao, X.; Chen, F.; Huang, Y.; Kang, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, F.; Gao, M.; Du, Y.; et al. Satellite-Based Water Quality Assessment of the Beijing Section of the Grand Canal: Implications for SDG11.4 Evaluation. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 909. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16050909
Xie Y, Zhou Q, Xiao X, Chen F, Huang Y, Kang J, Wang S, Zhang F, Gao M, Du Y, et al. Satellite-Based Water Quality Assessment of the Beijing Section of the Grand Canal: Implications for SDG11.4 Evaluation. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(5):909. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16050909
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Ya, Qing Zhou, Xiao Xiao, Fulong Chen, Yingchun Huang, Jinlong Kang, Shenglei Wang, Fangfang Zhang, Min Gao, Yichen Du, and et al. 2024. "Satellite-Based Water Quality Assessment of the Beijing Section of the Grand Canal: Implications for SDG11.4 Evaluation" Remote Sensing 16, no. 5: 909. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16050909
APA StyleXie, Y., Zhou, Q., Xiao, X., Chen, F., Huang, Y., Kang, J., Wang, S., Zhang, F., Gao, M., Du, Y., Shen, W., & Li, J. (2024). Satellite-Based Water Quality Assessment of the Beijing Section of the Grand Canal: Implications for SDG11.4 Evaluation. Remote Sensing, 16(5), 909. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16050909







