Abstract
Aquatic vegetation is an important component of aquatic ecosystems; therefore, the classification and mapping of aquatic vegetation is an important aspect of lake management. Currently, the decision tree (DT) classification method based on spectral indices has been widely used in the extraction of aquatic vegetation data, but the disadvantage of this method is that it is difficult to fix the threshold value, which, in turn, affects the automatic classification effect. In this study, Sentinel-2 MSI data were used to produce a sample set (about 930 samples) of aquatic vegetation in four inland lakes (Lake Taihu, Lake Caohai, Lake Honghu, and Lake Dongtinghu) using the visual interpretation method, including emergent, floating-leaved, and submerged vegetation. Based on this sample set, a DL model (Res-U-Net) was used to train an automatic aquatic vegetation extraction model. The DL model achieved a higher overall accuracy, relevant error, and kappa coefficient (90%, 8.18%, and 0.86, respectively) compared to the DT method (79%, 23.07%, and 0.77) and random forest (78%,10.62% and 0.77) when utilizing visual interpretation results as the ground truth. When utilizing measured point data as the ground truth, the DL model exhibited accuracies of 59%, 78%, and 91% for submerged, floating-leaved, and emergent vegetation, respectively. In addition, the model still maintains good recognition in the presence of clouds with the influence of water bloom. When applying the model to Lake Honghu from January 2017 to October 2023, the obtained temporal variation patterns in the aquatic vegetation were consistent with other studies. The study in this paper shows that the proposed DL model has good application potential for extracting aquatic vegetation data.
1. Introduction
Aquatic vegetation is an important part of the ecosystem and plays an important role in climate regulation, carbon sequestration and emission reduction, the purification of water bodies, the protection of biodiversity, and the maintenance of ecosystem balance [1,2]. According to their morphological characteristics and ecological habits, species of aquatic vegetation can be generally categorized into three types—emergent vegetation, floating-leaved vegetation, and submerged vegetation—and are widely distributed in coastal and inland lakes [3].
Compared with traditional methods, remote sensing technology has the advantages of timeliness, low cost, fast monitoring speeds, and a wide range and has become an important means of monitoring aquatic vegetation [4,5,6]. The apparent spectral reflectance of vegetation is influenced by a combination of the physiological characteristics of the plant itself and the environment in which it grows [7]. Aquatic vegetation in remotely sensed images can be classified and extracted based on its reflectance and combined with texture features. Currently, the remote sensing techniques used for monitoring aquatic vegetation are mainly based on methods such as unsupervised classification [8,9], supervised classification [10,11], decision trees [12,13], and bio-optical models [14]. There are also intelligent methods that utilize machine learning [15,16], such as support vector machines [11,17], random forests [18,19], and deep learning [20,21]; among them, the decision tree classification method is the most mainstream approach for classifying aquatic vegetation. Meanwhile, deep learning is increasingly being used for the classification of aquatic vegetation because of its high accuracy, ease of use, and lower susceptibility to noise. With the continuous improvements in computer hardware and software, the increase in the availability of remote sensing image data provides a solid foundation for deep learning in the field of aquatic vegetation extraction.
The decision tree classification method has been the mainstream method for aquatic vegetation classification for a long time due to its simplicity, efficiency, and ease of expression [6]. This method analyzes the spectral characteristics of different types of vegetation, establishes spectral indices to construct a decision tree, and adjusts the thresholds in order to achieve aquatic vegetation classification [22,23,24]. However, determining a suitable threshold for the automatic extraction of aquatic vegetation has been a challenging problem due to a variety of factors such as the shooting time, shooting angle, weather conditions, water turbidity, and water surface conditions [25]. Typically, false-color composite images are used to determine the optimal segmentation thresholds [26], but this method is subject to large errors due to subjective judgments and is time consuming when performing long-time-series monitoring. In order to reduce humans’ subjective influence and achieve fast extraction, researchers usually use fixed-threshold methods. For example, Oyama [27] and Luo et al. [28] classified and extracted the aquatic vegetation from their selected regions using fixed-threshold approaches; however, significant errors are still produced in the practical application of these methods. Therefore, researchers have attempted to automatically obtain thresholds for different images using various methods, such as gradient descent [29], bimodal thresholding [19], and the Otsu method [30]. In addition, researchers have made use of bio-optical models to extract aquatic vegetation data. This type of model simulates the transmission process of light in aquatic plants and their surrounding media, and analyzes the influence of environmental factors, such as water depth, water quality, and plant biomass, on the spectral characteristics of aquatic plants, thereby improving the accuracy of remote sensing monitoring. For example, Rotta et al. [31] revealed the relationship between submerged plants and light radiation through field investigation, remote sensing technology, and a bio-optical model and provided valuable information for water management. However, these methods have limitations and are unable to address all of the challenges of image thresholding when confronted with images such as clouds, fog, and shadows, resulting in low accuracy in the results.
Researchers are much less interested in aquatic vegetation in lakes compared to marine plants [32] and wetland vegetation [33,34]. In addition, marine vegetation is located in a body of water that is clearer than inland lakes, making the extraction of marine vegetation less difficult than that of aquatic vegetation in inland lakes. The remote sensing characteristics of wetland vegetation are very similar to those of water-supported vegetation, so the existing remote sensing extraction methods for wetland vegetation can generally be directly migrated to water-supported vegetation extraction. However, floating-leaved vegetation floats on the surface of the water and is subject to the neighboring effect of the water surface, while submerged vegetation is completely immersed within the water body. The reflectance of these two types of aquatic vegetation is quite different from the performance characteristics of wetland vegetation/terrestrial vegetation on remote sensing images, and the extraction of these two types of aquatic vegetation via remote sensing is difficult. For this reason, the existing remote sensing extraction methods used for wetland vegetation cannot be applied. Zhang et al. [35], Wang et al. [36] classified and extracted emergent vegetation, floating-leaved foliage vegetation, and submerged vegetation in the study area.
Obviously, the extraction of aquatic vegetation data from inland lakes is more complex. Some scholars try to use artificial intelligence methods, such as machine learning algorithms and deep learning algorithms, to extract aquatic vegetation. Machine learning is a broad approach to artificial intelligence that covers various techniques for learning patterns and regularities from data to make predictions or decisions. Some researchers try to use machine learning to classify and extract aquatic vegetation. For example, Huber et al. [32] conducted large-scale monitoring of aquatic vegetation in Sweden through machine learning algorithms. However, due to the weak generalization ability and feature learning ability of the machine learning model, the existing research has not applied the model to multiple regions. At the same time, machine learning models performed relatively poorly on complex tasks, and the researchers did not assess the robustness of their respective models under disturbed conditions (e.g., clouds, water blooms). Deep learning, as a subfield of machine learning, focuses on using deep neural networks to learn complex features and representations, and although it requires more computational resources, it has more powerful feature learning capabilities than traditional machine learning methods. For example, Zac Yung-Chun Liu et al. [37] used deep learning technology to conduct the semantic segmentation of satellite images and identify freshwater vegetation in Senegal. Chen et al. [38] extracted aquatic vegetation in Heilongjiang Basin in China through the DeepPlabv 3+ network. However, the above studies did not perform a more detailed division of the types of aquatic vegetation. In summary, due to the difficulty in distinguishing aquatic vegetation, the low attention, and the high computational resource requirements of deep learning methods, there are few studies on the classification extraction of aquatic vegetation in inland lakes based on deep learning.
In this study, with the goal of developing a set of widely applicable and robust automatic classification and extraction models for aquatic vegetation, we propose the use of Sentinel-2 satellite Multispectral Imager(MSI) launched by the European Space Agency (ESA) as the remote sensing data source and construct a set of sample datasets containing three types of aquatic vegetation, covering the image data from four inland lakes (Lake Taihu, Lake Caohai, Lake Honghu, and Poyanghu Lake) in different growing seasons. We use these datasets to train a model based on a deep learning semantic partitioning network (Res-U-Net), apply the model to the extraction of three types of aquatic vegetation data, and share the results. In addition, we use the model to test images that contain the effects of clouds and water blooms to explore the applicability of the model under complex conditions.
2. Study Area and Data
2.1. Study Area
The lakes concerned in this study are shown in Figure 1: Lake Honghu (39°29′~30° 12′N, 113°7′–114°5′E), Lake Taihu (30°55′~31°32′N, 119°52′~120°36′E), Lake Caohai (26°49′N~53′, 104°12′~104°18′E), and Lake Dongtinghu (27°39′~29°51′N, 111°19′~113°34′E). These four lakes belong to the Yangtze River system, are rich in ecological resources, play important ecological, economic, and social roles, and need continuous attention and protection.
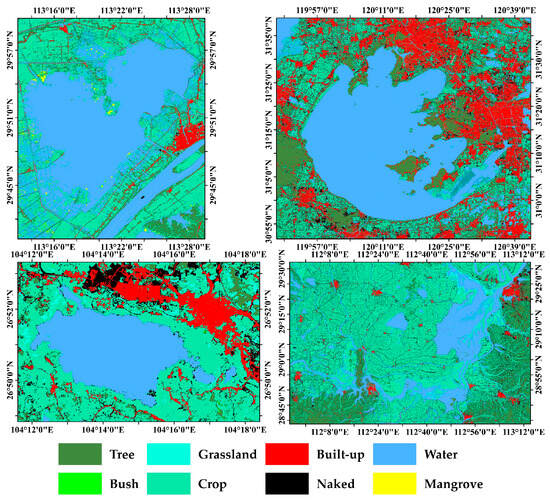
Figure 1.
Land use of the study area. Downloaded from ESA.
2.2. Data
2.2.1. Remote Sensing Image Data
The data source for this study is the Sentinel-2 imagery data from the European Space Agency (ESA) (https://scihub.copernicus.eu/dhus/#/home, accessed on 15 October 2023), which provides multiband high-resolution Earth observation data in 13 bands. In addition to the visible, near-infrared, and short-wave infrared bands common to optical remote sensing satellites, the Sentinel-2 image data contain three “red-edge” bands used in vegetation monitoring and an enhanced narrow near-infrared band. Sentinel-2’s satellites make observations of a specific area every five days. The spatial resolution of each band varies from 10 to 60 m, but can be uniformly upgraded to 10 m after resampling. The higher spatial resolution can clearly show the distribution and texture characteristics of different types of aquatic vegetation and is particularly suitable for monitoring large lakes. It has sufficient potential for aquatic vegetation data extraction.
Some of the raw data used in this study are geometrically corrected L1C-level top-of-atmosphere reflectance data only, which need to be atmospherically corrected using the Sen2corV02.08.00 model provided by ESA to obtain L2A-level surface reflectance data. The nearest neighbor interpolation method was used to resample the L2A level data to 10 m in SNAP 5.0 software, and the resampled L2A level data were spliced, band-synthesized, and cropped with the support of SNAP5.0 software and ENVI5.3 software.
2.2.2. Measured Data
The remote sensing classification and validation of aquatic vegetation requires reference to ground-truthed spectral information and sample point location information. The measured spectral data for aquatic vegetation and water bodies used in this study, as well as the location information of the sample sites, were obtained from four field observation experiments: the April 2023 Lake Dongtinghu and Poyang Lake experiment, the August 2023 Lake Honghu experiment, the September 2023 Lake Taihu experiment, and the October 2023 Caohai experiment. Data were obtained for 178 locations, including 29 submerged locations, 23 floating-leaved locations, 97 emergent locations, and 29 water locations. A total of 80 valid spectral data were collected. Each point was delineated in an area of 10 m * 10 m, and an experienced staff member was used to make a comprehensive on-site judgment of the coverage of aquatic vegetation, including the presence of four types of aquatic vegetation, in ranges of (0–25%), (25–50%), (50–75%), and (75–100%).
The spectra of the water bodies and aquatic vegetation were measured using an ASD portable spectrometer (wavelength range: 350 nm to 2500 nm) using the abovementioned surface spectroscopic measurements (ASD) [39]. The upward water column radiation (Lu), and gray-slab radiation (Lblank) are measured uniformly to facilitate reader understanding and be consistent with the atmospheric correction evaluation and model data input. The measured results are calculated via Formula (1) as the surface reflectance of the target. Affected by the measurement conditions, after removing the invalid data, the surface reflectance curves of the four types of target objects are shown in Figure 2.
where is the Fresnel reflection of the water surface, which is usually taken to be 0.022 for calm water surfaces, and in Equation (1) is the standard reflectance of the whiteboard, which is provided by its manufacturer.
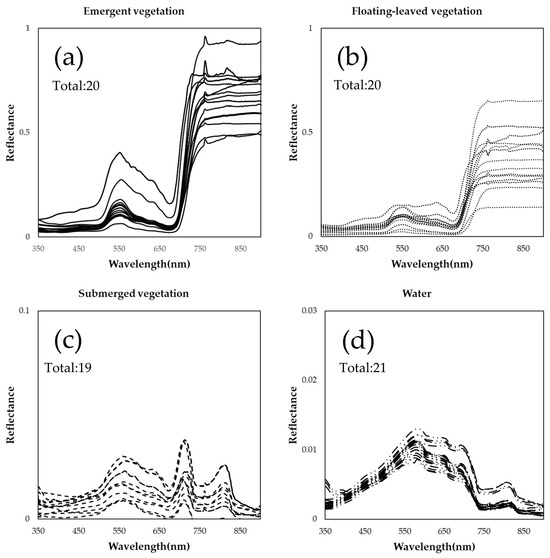
Figure 2.
Different types of aquatic vegetation with their spectral characteristics: (a) emergent vegetation; (b) floating-leaved vegetation; (c) submerged vegetation; (d) water.
3. Method
3.1. Overall Technical Process
The workflow of this study is shown in Figure 3. First, the Sentinel-2 MSI raw data were preprocessed to obtain surface reflectance data with a 10 m resolution. Then, cloud detection was carried out using the visual interpretation method to exclude the influence of the cloud level and mask the water body. By combining the spectral index and visual interpretation, the aquatic vegetation data in each image were accurately extracted to construct the aquatic vegetation dataset. Then, the images were cut into 512 × 512 sub-images, and the dataset was divided into a training set and a validation set according to the ratio of 8:2; these sets were used for the training of the deep learning network model. Finally, based on the validation set, the precision of the prediction results of the deep learning network model was evaluated to verify its performance and effectiveness.
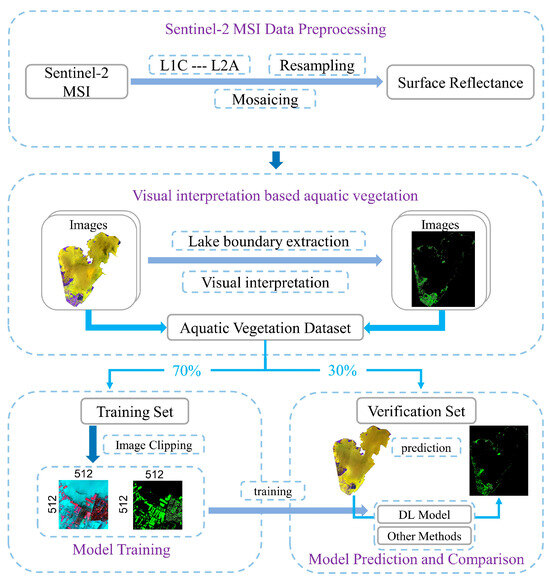
Figure 3.
Overall workflow of the aquatic vegetation data extraction process.
3.2. Sentinel-2 MSI Data Preprocessing
In order to obtain band surface spectral reflectance data at a 10 m spatial resolution, we preprocessed the raw Sentinel-2 MSI data: first, atmospheric corrections were performed on the L1C data; second, band resampling and image stitching were conducted on the L2A data.
3.2.1. Atmospheric Correction of Sentinel-2 MSI Data
Since the European Space Agency has only provided L1C-class products for data up to 2018, we performed an atmospheric correction process on these early L1C-class data. This correction process was implemented using the official Sen2Cor plugin, which relies on the LlibRadtran Laboratory’s theoretical model of atmospheric radiative transfer, as well as the parameter information associated with the MSI sensor, based on the L2A_Process command line tool. The reflectance data for the atmosphere and ground objects collected in the field were compared with the remote sensing images. Since not all of the band data from the Sentinel-2 remote sensing data were required in this study, only the accuracy of the atmospheric corrections from Band 1 to Band 9 was evaluated.
3.2.2. Lake Boundary Data Extraction
Since terrestrial vegetation and emergent vegetation show a high similarity in terms of spectral features, this similarity is very close in remote sensing images, which can easily lead to the misclassification of the two types of vegetation. In order to facilitate the subsequent extraction of aquatic vegetation data, we delineated the boundary of the study area. Based on the lake shoreline boundary range, the lake water range, and aquatic vegetation growth area in the current high-spatial-resolution remote sensing images, the islands, buildings, farmland, fish ponds, and other elements in the lake area in the images were maximally eliminated in order to obtain a more complete representation of the lake watershed covering the area of aquatic vegetation growth, as shown in Figure 4 [40].
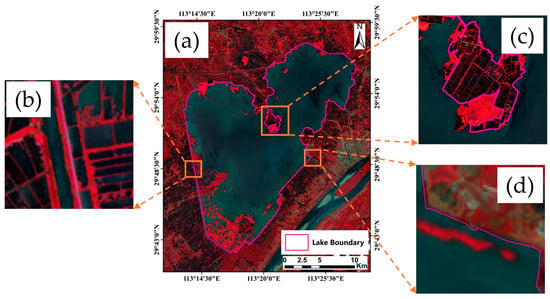
Figure 4.
The boundary of Lake Honghu. (a) The finalized extent of the lake; (b) using the inner side of the surrounding canals as the boundary in the absence of a natural shoreline; (c) excluding the islands and paddy fields in the lake; (d) the natural shoreline.
3.2.3. Visual Interpretation of Aquatic Vegetation Characteristics
Obtaining information regarding the actual distribution of aquatic vegetation is a prerequisite for deep learning model training and evaluation. Aquatic vegetation can show different spectral and textural characteristics from water in images, so the visual interpretation of remote sensing images is usually used to determine a more accurate distribution of aquatic vegetation [41,42,43]. As shown in Figure 5a, the emergent vegetation appeared as red and pink on the false-color (N-G-R) images, and dark green and grass green on the real-color (R-G-B) images, as shown in Figure 5b, mainly in the lake shore area in a facultative distribution. As shown in Figure 5c, the floating-leaved vegetation appeared as pink and bright pink on the false-color image, and bright green on the real-color image (as shown in Figure 5d), mainly in the center of the lake and the area around the lake shore in a patchy distribution. As shown in Figure 5e, the submerged vegetation was shown as dark red and light pink on the false-color image. As shown in Figure 5f, the water was shown as dark green and blue–green on the real-color image in a flocculent distribution.
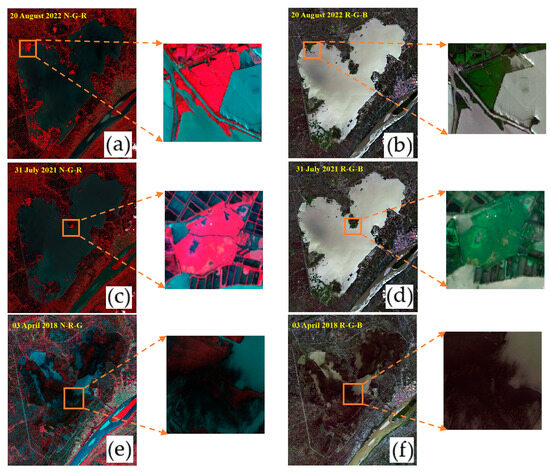
Figure 5.
Distinction between different types of aquatic vegetation and background water bodies under different waveband synthesis methods. Panels (a,c,e) show the effect of the false-color image display, and panels (b,d,f) show the effect of the true-color image display. Comparing the magnified images of local areas reveals that the spectral and textural features of aquatic vegetation are more obvious under false-color compositing (N-R-G). R: red; G: green; B: blue; N: near-infrared.
3.2.4. Sample Production
Based on the final generated aquatic vegetation results, the submerged vegetation, floating-leaved vegetation, and emergent vegetation pixel values were assigned as 1, 2, and 3, respectively, and the non-aquatic vegetation pixels were designated as 0. The results extracted through visual interpretation were then used as the real dataset for the training and validation of the extraction method. The image data from this dataset were obtained from the Sentinel-2 false-color dataset (Green(Band3)–Red(Band4)–NIR(Band8)). We randomly divided the dataset into training and validation sets in a ratio of 8:2. The training set was used to train the aquatic vegetation extraction deep learning model and the validation set was used for precision evaluation and method comparison.
The original images and their corresponding labels from the training dataset were converted to obtain images with 24-bit and 8-bit depths, respectively. The converted images were cropped into multiple images and corresponding labels with a size of 512 × 512 pixels. These images and labels were used as the input data for model training. Given the relatively small amount of submerged vegetation in the Lake Honghu area, it was difficult to meet the requirements for establishing a sample library of this type of vegetation, which may have led to a significant reduction in the model training effect. Thus, we added the data from Lake Taihu and Lake Caohai to satisfy the requirements for establishing a sample library.
After removing invalid images and labels, a total of 930 sets of image–label pairs were selected, of which 7 typical examples are shown below. In deep learning, sample balancing is crucial for improving the stability and generalization ability of the model. A balanced sample set ensures that each category is adequately learned and prevents the model from overly focusing on a large number of categories, resulting in the misclassification of a small number of categories. The proportion of pixels of the different samples in the sample set selected in this study is shown in Figure 6. In order to meet the requirements for sample balance and model follow-up training [44], in this experiment, the sample set was divided into a training set and test set and the division ratio was 8:2. After division, the training set contains 20,597,613 pixels of emergent vegetation, 16,489,963 pixels of floating-leaved vegetation, and 15,901,538 pixels of submerged vegetation. The number of pixels for all categories in the sample set is indicated below the picture sample scale.
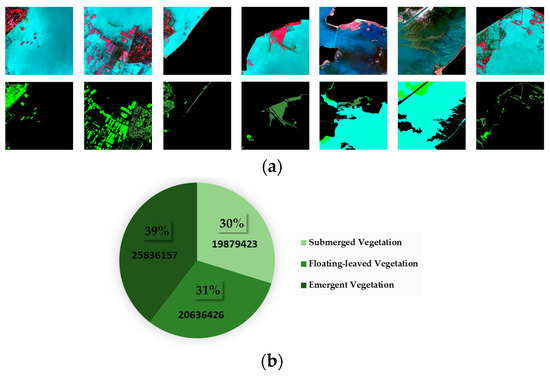
Figure 6.
Schematic diagram of the sample display and sample proportion. (a) Example images from the aquatic vegetation training set. (b) The proportion of the number of pixels in the sample pool for each category; the number of pixels in this category is marked below.
3.3. Deep-Learning-Based Training of Aquatic Vegetation Models
Res-U-Net (Residual U-Net, as shown in Figure 7) is a deep learning neural network model used for image segmentation tasks that is capable of both capturing the local features of an image and overcoming the problem of gradient vanishing in deep network training [45]. This network can improve the performance of image segmentation tasks, which is especially effective when facing large-scale datasets and complex tasks [46,47]. We also used an adaptive moment estimation (Adam) optimizer [48] for model optimization. Adam is a popular stochastic gradient descent optimization algorithm that combines the advantages of momentum and the adaptive learning rate and has shown a good performance and convergence speed in many deep learning tasks.
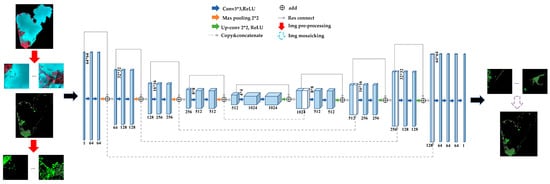
Figure 7.
Schematic diagram of the Res-U-Net network model.
Res-U-Net usually uses a pixel-level loss function to measure the segmentation performance of the model, and in this study, dice loss was used [49]. The mathematical expression for dice loss is as follows:
where |X∩Y| denotes the number of elements in the intersection between X and Y, and |X| and |Y| denote the number of elements in X and Y, respectively.
In this study, we set the initial learning rate to 0.0001 and gradually decreased the learning rate via cosine annealing [50]. The training and prediction in this study were performed on a computer equipped with an Intel Core i5-13400F CPU and an Nvidia GeForce RTX 3060 GPU.
3.4. Precision Evaluation
3.4.1. Atmospheric Correction Precision
The mean relative error (MRE) is an indicator commonly used to evaluate the accuracy of a prediction model, measuring the average relative deviation between the predicted value and the actual observed value. It is usually calculated by summing the relative error between each predicted value and the corresponding actual observed value, and then averaging it.
where n is the number of samples; is the true value; and is the predicted value.
The root mean square error (RMSE) is the square root of the mean square error with the formula:
where n is the number of samples; is the true value; and is the predicted value.
R-squared (R2) is a statistical measure used to evaluate the goodness of fit of a regression model. The formula for calculating R2 is as follows:
where is the true value; is the predicted value; and is the average of the true observed values.
3.4.2. Model Training Precision
In image segmentation tasks, it is common to use the mean intersection over union (MIoU) measure to evaluate the precision of the model’s prediction results for each category [51]. The MIoU is the average of the intersection over union (IoU) of all of the categories and can be used to evaluate the model’s prediction performance for the entire dataset. The MIoU is calculated using the following formula:
where IoU1, IoU2,…, IoUn denote the IoUs of each category, respectively, and N denotes the total number of categories.
The IoU is calculated by calculating the ratio of overlapping and concatenated regions between the predicted results and the true labels for each category. For each category, the IoU is calculated as follows:
where the intersection area is the number of pixels in the intersection area of the prediction result and the real label, and the union area is the number of pixels in the concatenation area of the prediction result and the real label.
The kappa coefficient is a metric used for consistency testing. In classification problems, it tests whether the predicted results of the model are consistent with the actual classification results. The closer it is to 1, the more accurate the model is. For multivariate classification tasks, it can be expressed as
where is the sum of the number of correctly classified samples in each category divided by the total number of samples, which is the overall classification precision. Suppose the true number of samples in each category is , ,…, , and the predicted number of samples in each category is , ,…, and the total number of samples is n; then, can be expressed as
3.4.3. Model Prediction Precision
The optimization model was used to predict the aquatic vegetation in the set of validation images, and the precision of the extraction results was assessed based on the pixel-level-based precision assessment metrics, including precision (P), recall, F1 coefficient (F1), and relative error (RE).
where TP (true positive) is the number of correctly predicted aquatic vegetation pixels; FP (false positive) is the number of incorrectly predicted aquatic vegetation pixels; FN (false negative) is the number of incorrectly predicted non-aquatic vegetation pixels; T is the number of aquatic vegetation pixels in the real dataset; and P is the number of aquatic vegetation pixels in the prediction results. In F1, P denotes the precision rate, and R denotes the recall rate. It is important to note that we can calculate a set of precision assessment indices based on each image, but for images with few or no pixels of aquatic vegetation, the assessment indices will show large errors. Therefore, to avoid this problem, we used the number of pixels in all validation images within the validation set to calculate the total precision assessment index.
4. Results
4.1. Evaluation of Atmospheric Correction Precision
Problems can be encountered during the atmospheric correction of Sentinel-2 MSI data for aquatic environments, and the relationship between errors in aquatic classification and poor atmospheric correction quality needs to be eliminated. Thus, the atmospheric correction accuracy was evaluated by using each category index listed in Section 3.4.1, and the results are shown in Table 1. The accuracy of the atmospheric correction varied from high to low for emergent vegetation, floating-leaved vegetation, and submerged vegetation. The R2 of all vegetation types was above 0.60, which met the requirements for follow-up treatment.

Table 1.
Results of atmospheric correction evaluation for various aquatic vegetation types.
4.2. Model Training and Prediction Precision
We trained 930 pairs of images and labels according to the method presented in Section 3.4 and performed 300 iterations. In order to ensure that the model did not overfit during the training and testing, the fivefold k-fold cross-validation method was used for verification. The average IoU of the final model was 0.70 for submerged vegetation, 0.67 for floating-leaved vegetation, 0.77 for emergent vegetation, and 0.99 for background categories. The MIoU of the model training was 0.79, and the kappa was 0.87. In general, the model exhibited high training accuracy and is therefore suitable for the prediction of aquatic vegetation.
Since the growth of different types of aquatic vegetation in Lake Honghu is strongly influenced by seasons, with floating-leaved and emergent vegetation dominating in summer and submerged and emergent vegetation dominating in spring, we used images of two views of Lake Honghu in summer and spring for the prediction accuracy assessment. Figure 8 and Table 2 show the extraction results and prediction accuracies for each type of aquatic vegetation in Lake Honghu based on the DL model, respectively. In terms of the total area extraction, for 31 July 2021, the difference between the two is large at approximately 2.9 km2; for 28 April 2017, the difference between the two is relatively small at approximately 1.01 km2. The kappa coefficients for the two view images are 0.83 and 0.85, respectively. In terms of visual interpretation data validation, by comparing the prediction accuracy of different types of aquatic vegetation, it can be found that the prediction accuracy of submerged vegetation is slightly lower.
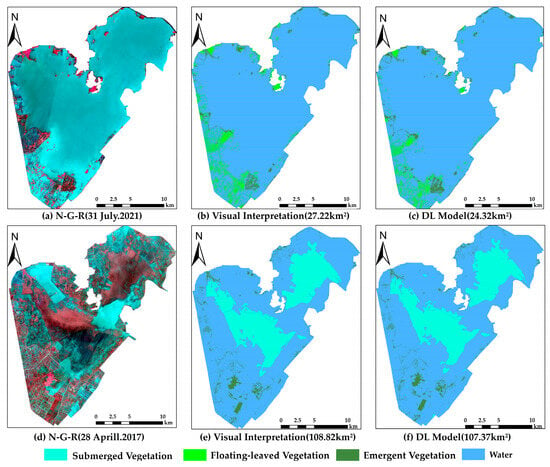
Figure 8.
Aquatic vegetation visual interpretation results and DL prediction results. (a) The (N-R-G) band synthetic image; (b) the visual interpretation results; (c) the DL model results; (d) the (N-R-G) band synthetic image; (e) the visual interpretation results; (f) the DL model results (parentheses represent the total area extracted by aquatic vegetation; N: near-infrared; R: red; G: green).

Table 2.
Evaluation of the certainty of the prediction results of Lake Honghu.
4.3. Evaluation of Model Precision Based on Measured Data
To verify the classification accuracy of the model, we conducted five field investigations in April 2023 and between August and October 2023, covering Lake Caohai, Poyanghu Lake, Lake Dongtinghu, Lake Taihu, and Lake Honghu, respectively. The experimental sites were laid out prior to the expedition using the DL model identification results and historical documentation, as well as point accessibility. Visual, photographic, and salvage methods were used to estimate the aquatic vegetation cover upon arrival at the point. A total of 29 waterbody sites, 29 submerged vegetation sites, 23 floating-leaved vegetation sites, and 97 emergent vegetation sites were assessed, as shown in Figure 9a–e. The classification results were objectively evaluated using the confusion matrix, as shown in Figure 9f, with a kappa coefficient of 0.78, and the accuracy of the extracted results in each category was 100% (background/water body), 59% (submerged vegetation), 78% (floating-leaved vegetation), and 91% (emergent vegetation), respectively. The submerged vegetation had the lowest accuracy for each category compared to the emergent and floating-leaved vegetation.
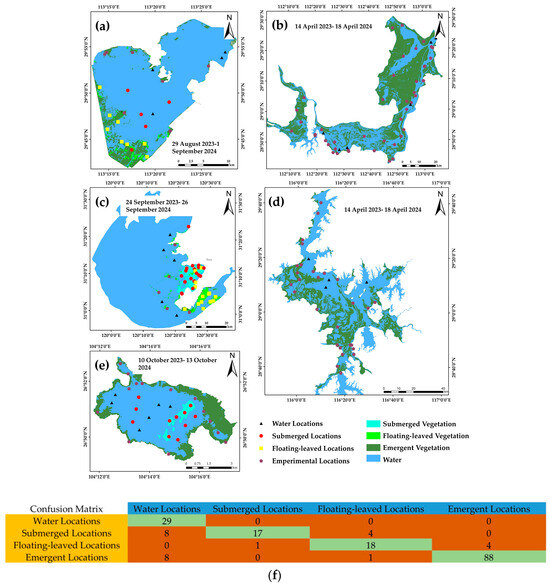
Figure 9.
Results for the verification of field sites in each lake. (a–e) Distribution of verified sites in each lake, with the date of the experiment and the name of the experimental lake in the margins; (f) confusion matrix of the verified sites, with each column denoting the predicted category, and each row denoting the true number of that category.
In the field experiments conducted on Lake Caohai and Lake Taihu, the amount of submerged vegetation was found to be the lowest compared to the emergent vegetation and floating-leaved vegetation. Here, 17 of the 29 submerged vegetation sites were correctly categorized; 8 of the 12 sites were incorrectly categorized as background (water body), and the remaining 4 were incorrectly categorized as other types of aquatic vegetation. In this regard, we investigated the causes of misclassification through field experiments in the more typical Lake Caohai and Lake Taihu.
During our field experiments at Lake Caohai, we found that, as shown in Figure 10, there were six points where the submerged vegetation was misclassified as a water body, and the vegetation coverage of these points was 0–25%. The more sparse submerged vegetation did not occupy a full image element in the remote sensing image, making recognition difficult [52]. The five correctly identified submerged vegetation points had a vegetation coverage of 75–100%; the submerged vegetation at these locations grows closely together and has more obvious spatial continuity in the image, making recognition easier.
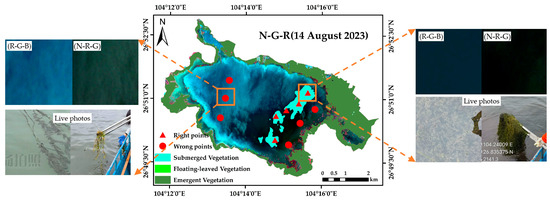
Figure 10.
Submerged vegetation in Lake Caohai that cannot be effectively identified using remote sensing (left) and that can be effectively identified (right).
In Lake Taihu, as shown in Figure 11, we conducted a field experiment on 18 submerged vegetation sites. A total of four sites were misclassified: one was misclassified as background/water body due to low submerged vegetation cover, and the other three were misclassified as floating-leaved vegetation. The misclassification of the water body was due to the coverage of submerged vegetation, similar to the case of Lake Caohai. The other three were misclassified as floating-leaved vegetation mainly because Lake Taihu regularly salvages and clears submerged vegetation to ensure the quality of the water body; some of the cleared vegetation floats on the surface of the water and resembles floating-leaved vegetation in the remote sensing images, thus causing the misclassification.
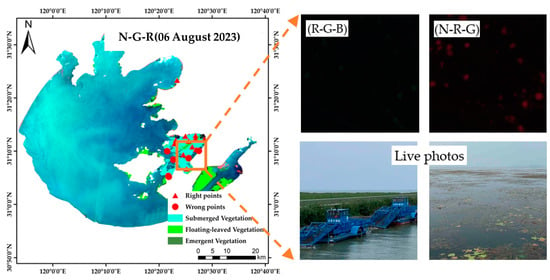
Figure 11.
Remote sensing images of Lake Taihu, from which vegetation cannot be effectively identified.
4.4. Spatial and Temporal Changes in Aquatic Vegetation in Lake Honghu, 2017–2023
In order to analyze the spatial and temporal distribution patterns in aquatic vegetation in Lake Honghu, we extracted aquatic vegetation classification information from all available Sentinel-2 images in the Lake Honghu area from 2017 to 2023, as shown in Figure 12.
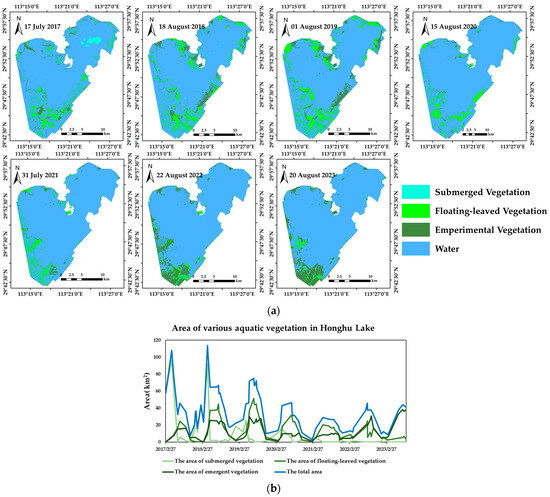
Figure 12.
Spatial and temporal changes in aquatic vegetation in Lake Honghu. (a) Spatial distribution of aquatic vegetation in Lake Honghu from 2017 to 2023; (b) trend in aquatic vegetation area change in Lake Honghu from 2017 to 2023.
The temporal distribution pattern in the aquatic vegetation in Lake Honghu is quite obviously affected by the season, especially the submerged vegetation. As shown in Figure 12b, the submerged vegetation can be monitored over a large area from November to April each year, with the maximum value during our monitoring period being 96.49 km2 on 28 April 2017; however, outside of this timeframe, i.e., from May to October, it is difficult to monitor the distribution of submerged vegetation over a large area due to the influence of the rise in the water level of Lake Honghu and the increase in the turbidity of the water body [53]. In contrast to the submerged vegetation, the most vigorous growth period for the aquatic and floating-leaved vegetation was from May to October each year, with maximum values of 38.05 km2 (9 September 2023; aquatic vegetation) and 51.24 km2 (22 July 2019; floating-leaved vegetation), respectively. Overall, the amount of aquatic vegetation in Lake Honghu showed a clear downward trend from 2017 to 2021, decreasing from the mean value of 45.68 km2 in 2017 to 21.40 km2 in 2021. After 2022, a slow growth trend was observed for aquatic vegetation; however, the recovery trend for the submerged vegetation was still not optimistic, with its area decreasing from the mean value in 2017 of 29.71km2 to 0.8km2 in 2022 and 0.31km2 in 2023. Thus, it can be seen that more time and energy need to be invested in the recovery of submerged vegetation in Lake Honghu.
The vegetation examined in this study first decreased from 2017 to 2021, and later showed a slowly increasing trend in the period 2022–2023. This result is more consistent with other research findings: for example, Song [54] conducted a multi-year study of submerged vegetation in Lake Honghu from 2006 to 2016 and concluded that this vegetation type would decline. Since 2022, the Chinese government has initiated a pilot water ecology assessment program in the Yangtze River Basin [55]. This also indirectly explains the positive trend in water-supporting vegetation and floating-leaved vegetation in Lake Honghu since 2022, as it could be due to this policy.
5. Discussion
5.1. Applicability of the Model
5.1.1. Applicability of Single-Aquatic-Vegetation-Type Lakes
Lake Dongtinghu mainly contains a single vegetation type and is not affected by cyanobacterial blooms, so we used this lake to test the extraction of a single type of aquatic vegetation. The kappa coefficient of the recognition result was 0.91, and the precision was 96%, indicating that the model shows good recognition performance for Lake Dongtinghu; the results are shown in Table 3. This model can be used to assess the generalization ability when migrating from lakes with complex vegetation types to lakes with a single vegetation type.

Table 3.
Evaluation of the certainty of the prediction results for Lake Dongtinghu.
5.1.2. Applicability in Complex Situations
The situation for Lake Taihu is more complicated than for the other lakes. The aquatic vegetation types found in Lake Taihu are rich; moreover, as a lake with high eutrophication, Lake Taihu has often experienced cyanobacterial blooms over recent years, and as the spectral features of cyanobacterial blooms and aquatic vegetation are similar, misjudgments can easily occur. In order to verify the model’s effectiveness in recognizing aquatic vegetation in more complex situations, we selected a remote sensing image of Lake Taihu for testing. The kappa coefficient of the Lake Taihu recognition result was 0.86, and the extraction precision of each category was above 80%, indicating that the model is suitable for dealing with the more complex Lake Taihu. The specific recognition results are shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
Evaluation of the results for the Lake Taihu predictions.
Unlike other lakes, Lake Taihu, as a eutrophic lake, has been seriously affected by water bloom [56], resulting in changes in the optical properties of the water body including an increase in turbidity, a change in water color, a decrease in transparency, and a change in spectral reflectance, ultimately leading to color confusion and spatial information distortion in remote sensing data [57,58]. This situation makes it difficult to effectively segment the water color and aquatic vegetation of Lake Taihu using traditional decision tree methods. On the other hand, cloud occlusion also increases the difficulty of aquatic vegetation data extraction. Cloud cover causes the loss or distortion of information in remote sensing images, which limits the feasibility of aquatic vegetation data extraction. To overcome this difficulty, cloud masking algorithms are usually employed to remove cloudy pixels [59], multi-temporal data are utilized to expand the effective observation time window, and data fusion or synthetic image techniques are used to mitigate the effects of clouds. Although these strategies help to improve the precision and reliability of aquatic vegetation information, they usually require large amounts of time and computational resources.
We selected the remote sensing image of Lake Taihu taken on 30 September 2021 to verify the performance of the model in terms of aquatic vegetation recognition under complex environmental conditions. The model did not misclassify the bloom region and performed well in the cloud-obscured region. Although the characteristics of aquatic vegetation are similar to those of water bloom, the model did not make any misclassifications in this region; when facing the influence of clouds, the model was able to effectively classify along the edges of the cloud obscuration.
5.2. Comparison with Other Methods
We select a Sentinel-2 remote sensing image of Lake Honghu that was not affected by clouds or water blooms for the evaluation of the aquatic vegetation data extraction results. The results showed that the deep learning method demonstrated higher precision and reliability in the aquatic vegetation data extraction task. As shown in Figure 13, the recognition accuracies of the DL model for the three vegetation types were 90% (submerged vegetation), 83% (floating-leaved vegetation), and 71% (emergent vegetation), which were better than those of the decision tree, which were 84% (submerged vegetation), 63% (floating-leaved vegetation), and 67% (emergent vegetation). In addition, the kappa coefficients of the DL results (0.84) were better than those of the decision tree (0.70). Compared with the random forest model, it was found that the accuracies for the submerged vegetation (91%) and floating-leaved vegetation (96%) were slightly higher than that of the DL model, while the accuracy of recall was lower than that of the DL model. These results indicate that random forest performs well in the classification of negative samples when classifying aquatic vegetation, but may be less effective in the identification of true positive samples. This indicates that the DL model has a significant advantage in terms of recognizing aquatic vegetation in complex environments.
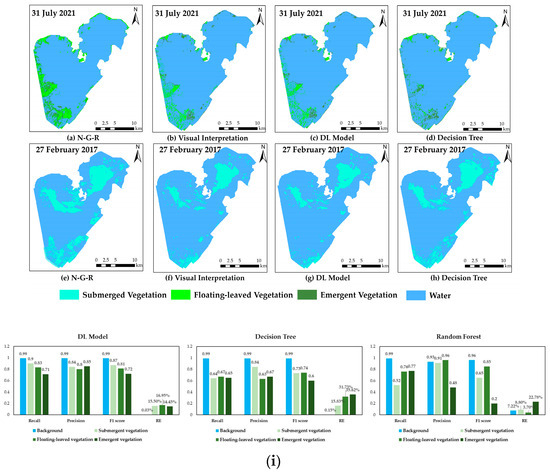
Figure 13.
Comparison of DL model and decision tree and random forest. (a–h) The result of different interpretation methods; (i) precision comparison of the results of different interpretation methods.
6. Conclusions
In this study, a sample set containing the distribution of various types of aquatic vegetation was established for Lake Honghu, Lake Taihu, Lake Caohai, and Poyanghu Lake by utilizing Sentinel-2 MSI data. The sample set was generated through visual interpretation using cloud-free and cloudless reflectance images of the inland lakes. The sample sets were divided into a training set (70%) and a validation set (30%); the aquatic vegetation extraction model constructed based on Res-U-Net was trained using the training set in order to automatically extract and classify the aquatic vegetation data, and the following research results were obtained.
We evaluated the accuracy of the DL model in terms of training accuracy, prediction accuracy, and measured accuracy using visual interpretation and measured data as true values. In terms of the training accuracy, the average IoU of the submerged vegetation was 0.70, the average IoU of the floating-leaved vegetation was 0.67, the average IoU of the emergent vegetation was 0.77, and the IoU of the background category was 0.99. The MIoU of the model training was 0.79, with a kappa of 0.87. In terms of the prediction accuracy, the average accuracy of the DL model’s extracted results was 0.80 with a relative error (RE) of 0.87. The average kappa coefficient was 0.86. In terms of the measured accuracy, the accuracies of the verified points for each category were 59% (submerged vegetation), 78% (floating-leaved vegetation), and 91% (emergent vegetation).
We applied the DL model to Lake Honghu and obtained and analyzed the trend of aquatic vegetation from 2017 to 2023. The results showed that the type of aquatic vegetation in Lake Honghu was greatly influenced by the season: the most dominant vegetation type from November to April each year was submerged vegetation, and from May to October each year, the dominant types were emergent and floating-leaved vegetation. In terms of the area covered by aquatic vegetation in Lake Honghu, there was a decreasing trend from 2017 to 2021, and the overall area has rebounded since 2022. This shows the great potential of the DL model in classifying and extracting aquatic vegetation data from lakes.
Regarding the applicability of the model, we used images of Lake Dongtinghu, which has a single vegetation type, and Lake Taihu, which is rich in vegetation types and has interference from submerged vegetation, for the classification and extraction analysis. We found that the DL model could avoid the interference of submerged vegetation and part of the clouds to a large extent, which is difficult to achieve using traditional methods. However, the model also has some limitations, and some submerged vegetation has no obvious features in the remote sensing image due to its low density, so the ideal extraction effect for this type of aquatic vegetation is not achieved.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.S.; methodology, H.G.; software, Y.S.; validation, H.G.; formal analysis, Q.S. and Y.Y.; investigation, H.G.; resources, Y.Z. (Yuting Zhou); data curation, W.L.; writing—original draft preparation, H.G.; writing—review and editing, R.L., Q.S. and Y.Y.; visualization, Y.Z. (Yuting Zhang); supervision, J.L. and Q.S.; project administration, M.L. and Q.S.; funding acquisition, Q.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China, grant number 2021YFB3901101.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Qian Shen from the Key Laboratory of Digital Earth Science, Aerospace Information Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences, for the help with writing. We are also thankful to all of the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments on the study. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Zhang, Y.; Jeppesen, E.; Liu, X.; Qin, B.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Y.; Thomaz, S.M.; Deng, J. Global Loss of Aquatic Vegetation in Lakes. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 173, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, J.; Song, K.; Lv, Y.; Liu, G.; Fang, C.; Hou, J.; Wen, Z. Distinguishing Algal Blooms from Aquatic Vegetation in Chinese Lakes Using Sentinel 2 Image. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, C.; Li, H.; Liu, J.; Jiang, T.; Yan, D.; Tong, J.; Dong, L. Review on Ecological Response of Aquatic Plants to Balanced Harvesting. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.H.; Xin, C.L.; Sun, Z.; Luo, J.H.; Ma, R.H. Automatic Extraction Method of Aquatic Vegetation Types in Small Shallow Lakes Based on Sentinel-2 Data: A Case Study of Cuiping Lake. Remote Sens. Inf. 2019, 34, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, L. Analyzing the Spectral Response of Submerged Aquatic Vegetation in a Eutrophic Lake, Shanghai, China. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 57, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Yang, J.; Duan, H.; Sun, Z.; Xin, Y. Research progress of aquatic vegetation remote sensing in shallow lakes. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2022, 26, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.S.F.; Costa, M.P.F.; Melack, J.M.; Novo, E.M.L.M. Remote Sensing of Aquatic Vegetation: Theory and Applications. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 140, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albright, T.P.; Ode, D.J. Monitoring the Dynamics of an Invasive Emergent Macrophyte Community Using Operational Remote Sensing Data. Hydrobiologia 2011, 661, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackleson, S.; Klemas, V. Remote Sensing of Submerged Aquatic Vegetation in Lower Chesapeake Bay: A Comparison of Landsat MSS to TM Imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 1987, 22, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheruiyot, E.K.; Mito, C.; Menenti, M.; Gorte, B.; Koenders, R.; Akdim, N. Evaluating MERIS-Based Aquatic Vegetation Mapping in Lake Victoria. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 7762–7782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, P.D.; Gilvear, D.J.; Tyler, A.N.; Willby, N.J.; Kelly, A. Mapping Macrophytic Vegetation in Shallow Lakes Using the Compact Airborne Spectrographic Imager (CASI). Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2010, 20, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Hou, X.; Liu, J.; Zheng, C. Unrealistic Phytoplankton Bloom Trends in Global Lakes Derived from Landsat Measurements. EarthArXiv 2020, preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Feng, L.; Hou, X.; Tang, J. An automatic Classification Algorithm for Submerged Aquatic Vegetation in Shallow Lakes Using Landsat Imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 260, 112459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malthus, T. Chapter 9. Bio-Optical Modeling and Remote Sensing of Aquatic Macrophytes. In Bio-optical Modeling and Remote Sensing of Inland Waters; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piaser, E.; Villa, P. Evaluating Capabilities of Machine Learning Algorithms for Aquatic Vegetation Classification in Temperate Wetlands Using Multi-Temporal Sentinel-2 Data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinform. 2023, 117, 103202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, R.M.; Collier, C.J.; Brown, C.J.; Rasheed, M.A.; Bourner, J.; Turschwell, M.P.; Sievers, M.; Connolly, R.M. Remote estimation of aquatic light environments using machine learning: A new management tool for submerged aquatic vegetation. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 782, 146886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pande-Chhetri, R.; Abd-Elrahman, A.; Jacoby, C. Classification of Submerged Aquatic Vegetation in Black River Using Hyperspectral Image Analysis. GEOMATICA 2014, 68, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Santos, P.; Aristizábal, H.; Díaz-Alcaide, S.; Gómez-Escalonilla, V. Predictive mapping of aquatic ecosystems by means of support vector machines and random forests. J. Hydrol. 2021, 595, 126026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Reynolds, C.; Byrne, M.; Rosman, B. A Remote Sensing Method to Monitor Water, Aquatic Vegetation, and Invasive Water Hyacinth at National Extents. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Jernigan, S.; Richardson, R.; Ferguson, S.; Buckner, G. Autonomous Robotics for Identification and Management of Invasive Aquatic Plant Species. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piaser, E.; Villa, P. Comparing Machine Learning Techniques for Aquatic Vegetation Classification Using Sentinel-2 Data. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 21st Mediterranean Electrotechnical Conference (MELECON), Palermo, Italy, 14–16 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, F.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Crétaux, J.-F. Constructing Long-Term High-Frequency Time Series of Global Lake and Reservoir Areas Using Landsat Imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 232, 111210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowan, G.S.L.; Kalacska, M. A Review of Remote Sensing of Submerged Aquatic Vegetation for Non-Specialists. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, R.; Haas, J.; Deering, D.W. ’aper A 20 Monitoring Vegetation Systems in The Great Plains with ERTS. 1974. Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:133358670 (accessed on 23 February 2024).
- Xu, L.; Zhang, S.; He, Z.; Guo, Y. The comparative study of three methods of remote sensing image change detection. In Proceedings of the 2009 17th International Conference on Geoinformatics, Fairfax, VA, USA, 12–14 August 2009; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Valta-Hulkkonen, K.; Partanen, S.; Kanninen, A. Remote Sensing as a Tool in the Aquatic Macrophyte Mapping of a Eutrophic Lake: A Comparison Between Visual and Digital Classification. In Proceedings of the ScanGIS’2003—The 9th Scandinavian Research Conference on Geographical Information Science, Espoo, Finland, 4–6 June 2003. Proceedings DBLP, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Oyama, Y.; Matsushita, B.; Fukushima, T. Distinguishing surface cyanobacterial blooms and aquatic macrophytes using Landsat/TM and ETM + shortwave infrared bands. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 157, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Ni, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, K.; Shen, M.; Cao, Z.; Qi, T.; Xiao, Q.; Qiu, Y.; Cai, Y.; et al. A New Technique for Quantifying Algal Bloom, Floating/Emergent and Submerged Vegetation in Eutrophic Shallow Lakes Using Landsat Imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 287, 113480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Li, X.; Ma, R.; Li, F.; Duan, H.; Hu, W.; Qin, B.; Huang, W. Applying Remote Sensing Techniques to Monitoring Seasonal and Interannual Changes of Aquatic Vegetation in Taihu Lake, China. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 60, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, C.; Duan, Q. Estimating the Aquatic-Plant Area on a Pond Surface Using a Hue-saturation-Component Combination and an Improved Otsu Method. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 188, 106372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotta, L.H.D.S. Estimation of Submerged Aquatic Vegetation Height and Distribution in Nova Avanhandava Reservoir (São Paulo State, Brazil) Using Bio-Optical Modeling. 2015. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/11449/123843 (accessed on 23 February 2024).
- Huber, S.; Hansen, L.B.; Nielsen, L.T.; Rasmussen, M.L.; Sølvsteen, J.; Berglund, J.; von Friesen, C.P.; Danbolt, M.; Envall, M.; Infantes, E.; et al. Novel Approach to Large-Scale Monitoring of Submerged Aquatic Vegetation: A Nationwide Example from Sweden. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2022, 18, 909–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faza, S.; Nababan, E.B.; Efendi, S.; Basyuni, M.; Rahmat, R.F. An Initial Study of Deep Learning for Mangrove Classification. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 420, 012093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Yu, Z.; Xu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, C. ME-Net: A Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Extracting Mangrove Using Sentinel-2A Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, F.; Li, J.; Xle, Y.; Zhang, B. Aquatic vegetation extraction of Yugiao Reservoir Based on Sentinel-2 image feature optimizati. Ecol. Sci. 2023, 42, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Z. Classification of Honghe Wetland Remote Sensing lmage Based on Random Forests. Geomat. Spat. Inf. Technol. 2014, 37, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.Y.-C.; Chamberlin, A.J.; Tallam, K.; Jones, I.J.; Lamore, L.L.; Bauer, J.; Bresciani, M.; Wolfe, C.M.; Casagrandi, R.; Mari, L.; et al. Deep Learning Segmentation of Satellite Imagery Identifies Aquatic Vegetation Associated with Snail Intermediate Hosts of Schistosomiasis in Senegal, Africa. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhang, R.; Jia, M.; Cheng, L.; Zhao, C.; Li, H.; Wang, Z. Accurate and Rapid Extraction of Aquatic Vegetation in the China Side of the Amur River Basin Based on Landsat Imagery. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Tang, J.W.; Li, T.J.; Zhou, H. Key Technologies of water spectra measurements with above-water method. Ocean. Technol 2012, 31, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merwade, V.M. An Automated GIS Procedure for Delineating River and Lake Boundaries. Trans. GIS 2007, 11, 213–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Qing, S.; Jin, E.; Hao, Y.; Zhao, W. A Spectral Index for the Detection of Algal Blooms Using Sentinel-2 Multispectral Instrument (MSI) Imagery: A Case Study of Hulun Lake, China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 42, 4514–4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Sha, Z.; Yu, M. Remote Sensing Imagery in Vegetation Mapping: A Review. J. Plant Ecol. 2008, 1, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. On the Estimation of Biomass of Submerged Vegetation Using Landsat Thematic Mapper (TM) Imagery: A Case Study of the Honghu Lake, PR China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 19, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Weng, J.; Luo, W.; Lu, W.; Wu, H.; Xu, J.; Tian, Q. Sample Balancing for Deep Learning-Based Visual Recognition. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks Learn. Syst. 2020, 31, 3962–3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, A.; Mahdipour, H.; Moradi, E.; Tariq, A. Agricultural Field Extraction with Deep Learning Algorithm and Satellite Imagery. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2022, 50, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Feng, R.; Wang, L.; Zhong, Y.; Cao, L. D-Resunet: Resunet and Dilated Convolution for High Resolution Satellite Imagery Road Extraction. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2019—2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 28 July–2 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sun, X.; Meng, Y.; Liang, J.; Wu, F.; Li, J. Dice Loss for Data-Imbalanced NLP Tasks. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Online, 5–10 July 2020; pp. 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loshchilov, I.; Hutter, F. SGDR: Stochastic Gradient Descent with Warm Restarts. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, San Juan, Puerto Rico, 2–4 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Loshchilov, I.; Hutter, F. Decoupled Weight Decay Regularization. arXiv 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Ma, R.; Duan, H.; Hu, W.; Zhu, J.; Huang, W.; Lin, C. A New Method for Modifying Thresholds in the Classification of Tree Models for Mapping Aquatic Vegetation in Taihu Lake with Satellite Images. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 7442–7462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Han, H.; Zhi, Y.; Deng, Z.; Zhou, J.; Li, W.; Yuan, L.; Cao, Y. Enclosure study on the limiting factors of submerged macrophyte growth in restored sites of Lake Honghu. Plant Sci. J. 2023, 41, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xinxin, S.; Xiaobin, C.; Zhi, W.; Enhua, L.; Xuelei, W. Community change of dominant submerged macrophyte in Lake Honghu since 1950s. J. Lake Sci. 2016, 28, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Four departments jointly issued assessment index scoring rules for the Yangtze River Basin water ecology “score”. Environ. Monit. Manag. Technol. 2023, 35, 6.
- Wang, S.; Wang, W.; Chen, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, L.; Jiang, X. Characteristics of Dissolved Organic Matter and Its Role in Lake Eutrophication at the Early Stage of Algal Blooms—A Case Study of Lake Taihu, China. Water 2020, 12, 2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Xu, H.; Guo, X. Satellite Remote Sensing of Harmful Algal Blooms (HABs) and a Potential Synthesized Framework. Sensors 2012, 12, 7778–7803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warner, R.A.; Fan, C. Optical Spectra of Phytoplankton Cultures for Remote Sensing Applications: Focus on Harmful Algal Blooms. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev. 2013, 4, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Baetens, L.; Desjardins, C.; Hagolle, O. Validation of Copernicus Sentinel-2 Cloud Masks Obtained from MAJA, Sen2Cor, and FMask Processors Using Reference Cloud Masks Generated with a Supervised Active Learning Procedure. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).