Towards Improved Satellite Data Utilization in China: Insights from an Integrated Evaluation of GSMaP-GNRT6 in Rainfall Patterns
Abstract
1. Introduction
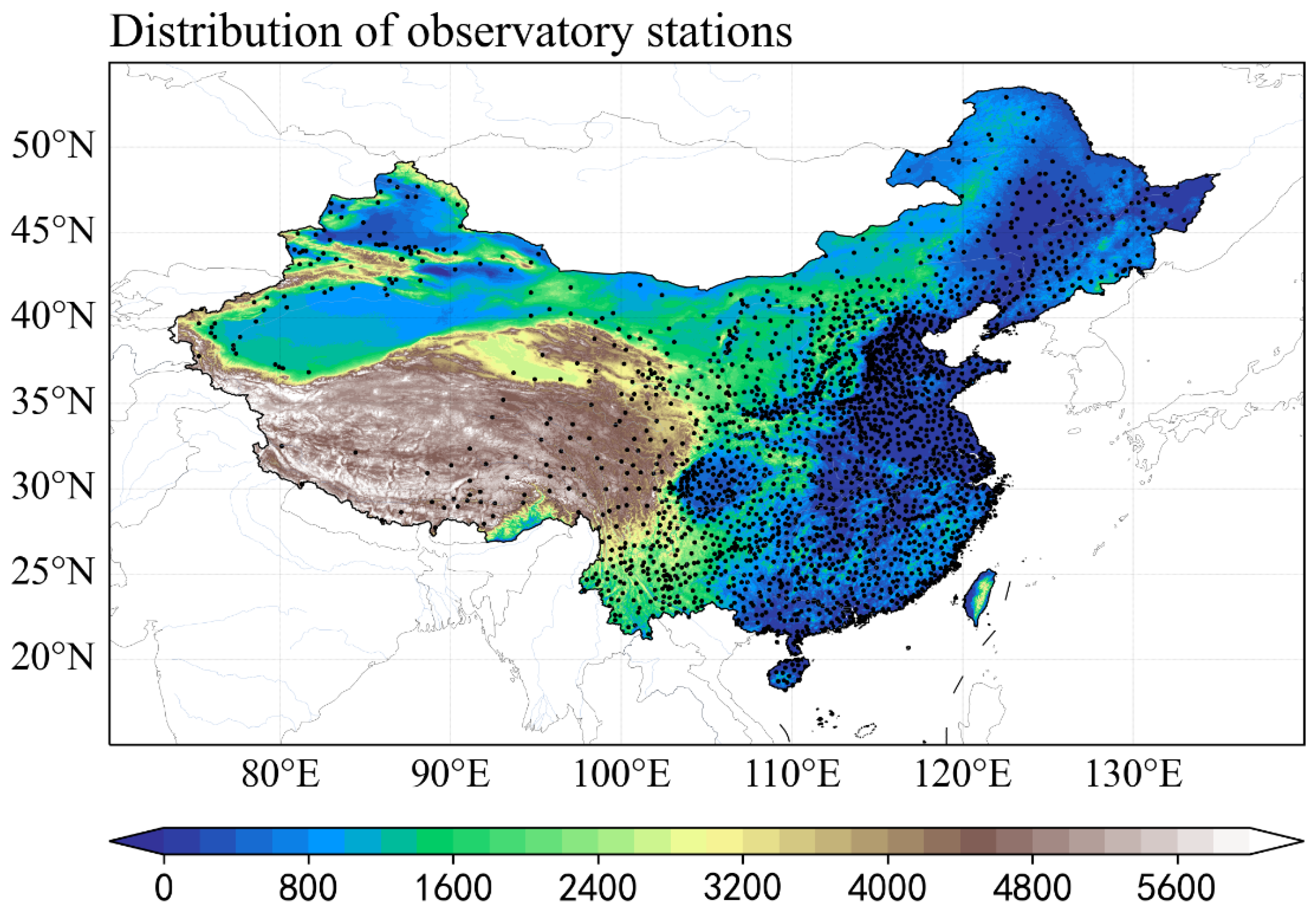
2. Data and Methods
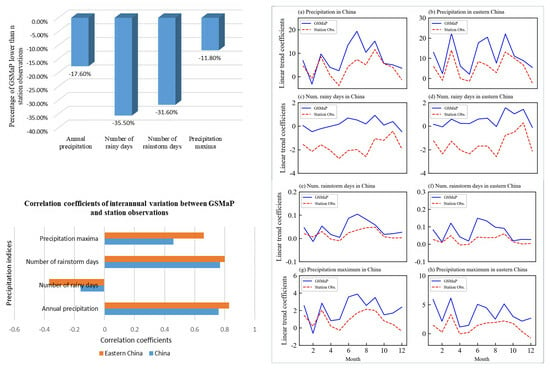
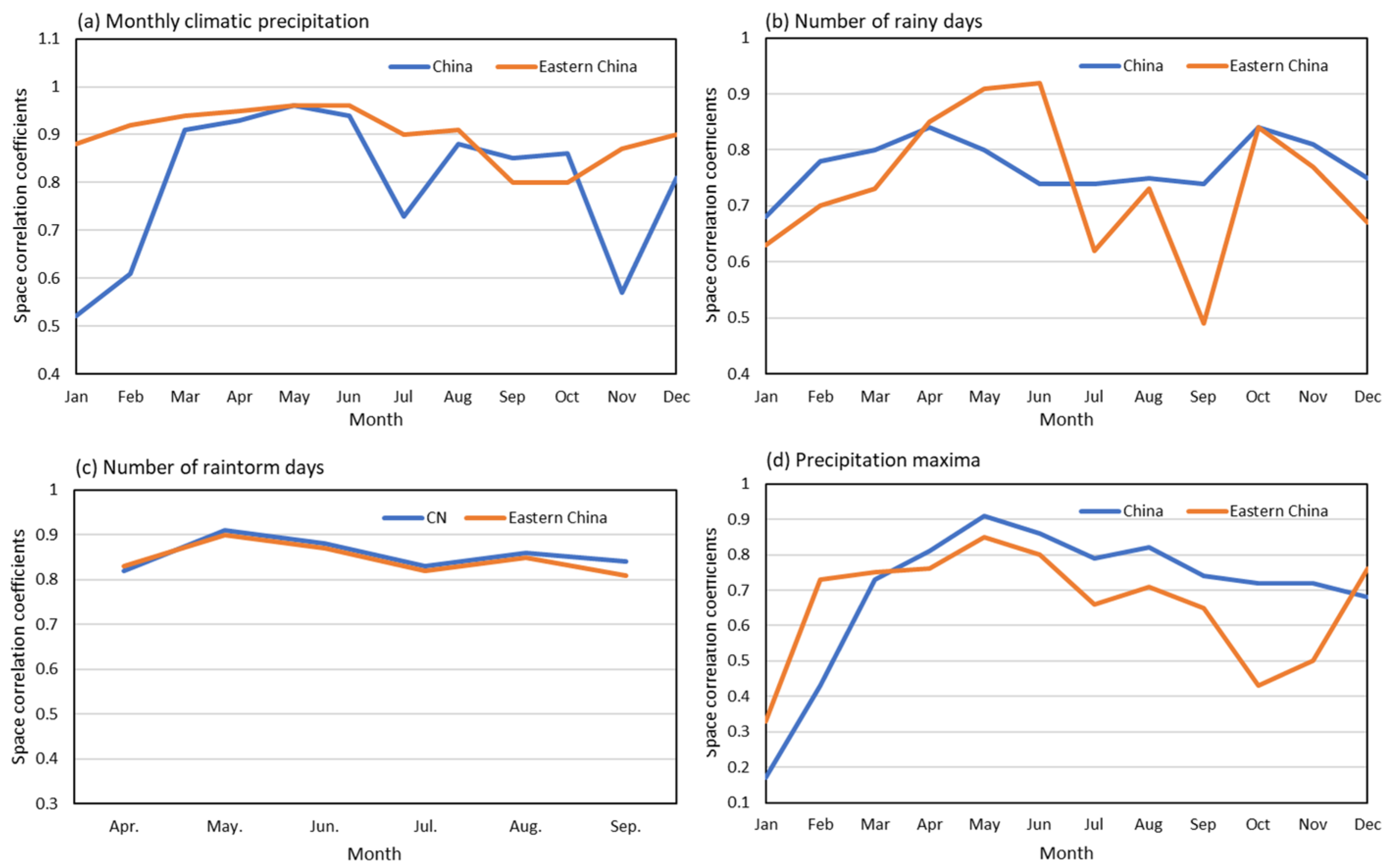
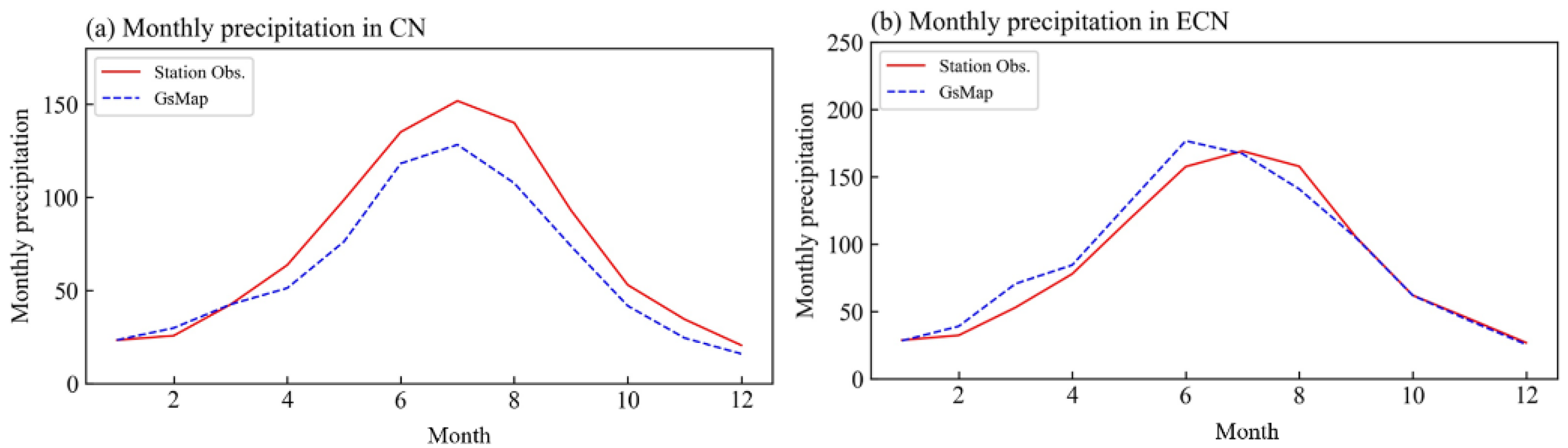
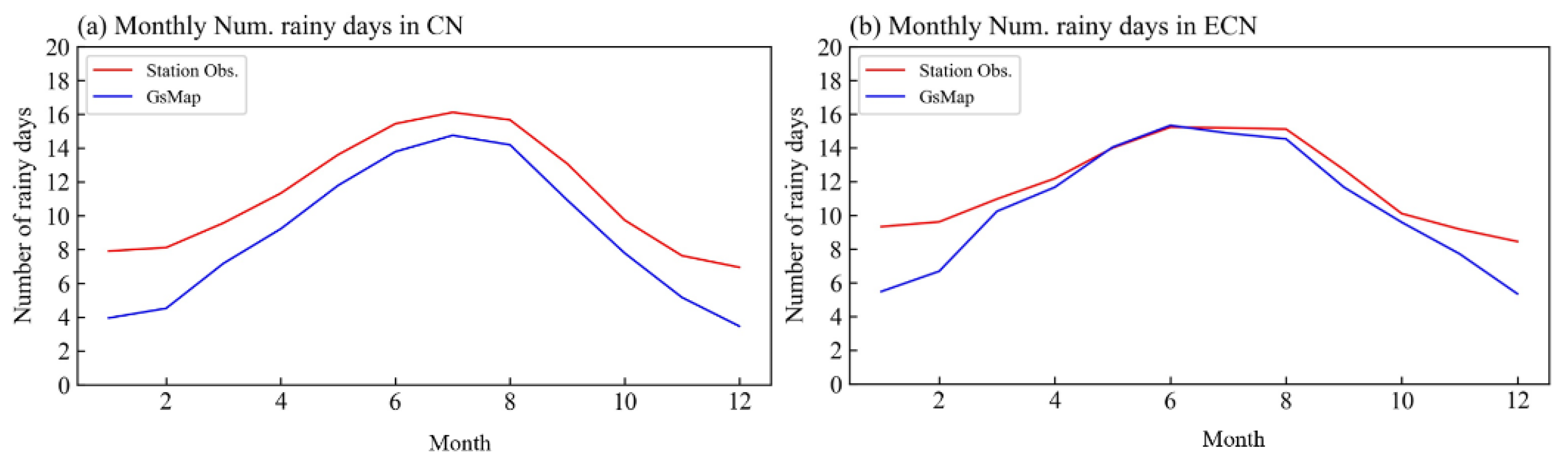
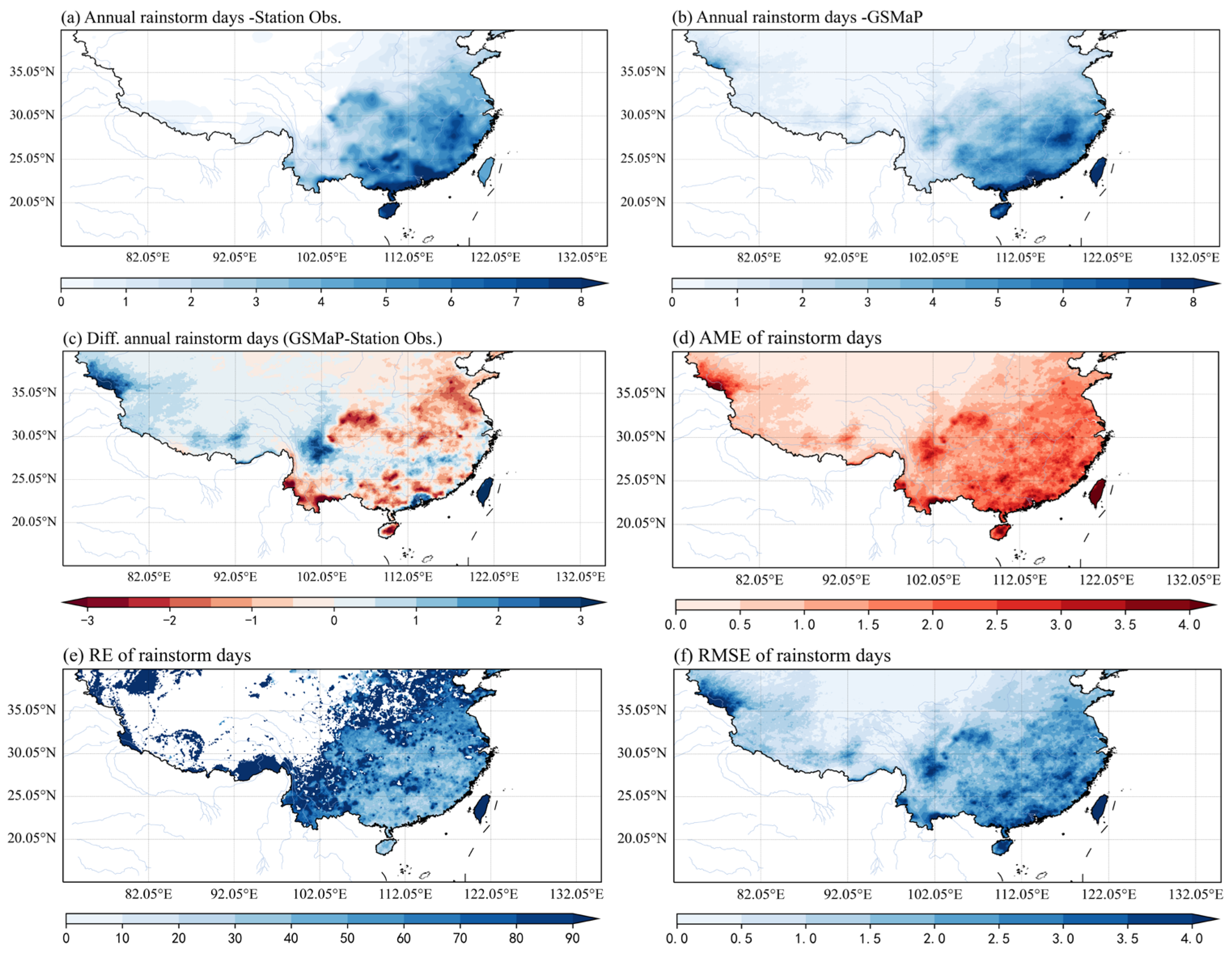
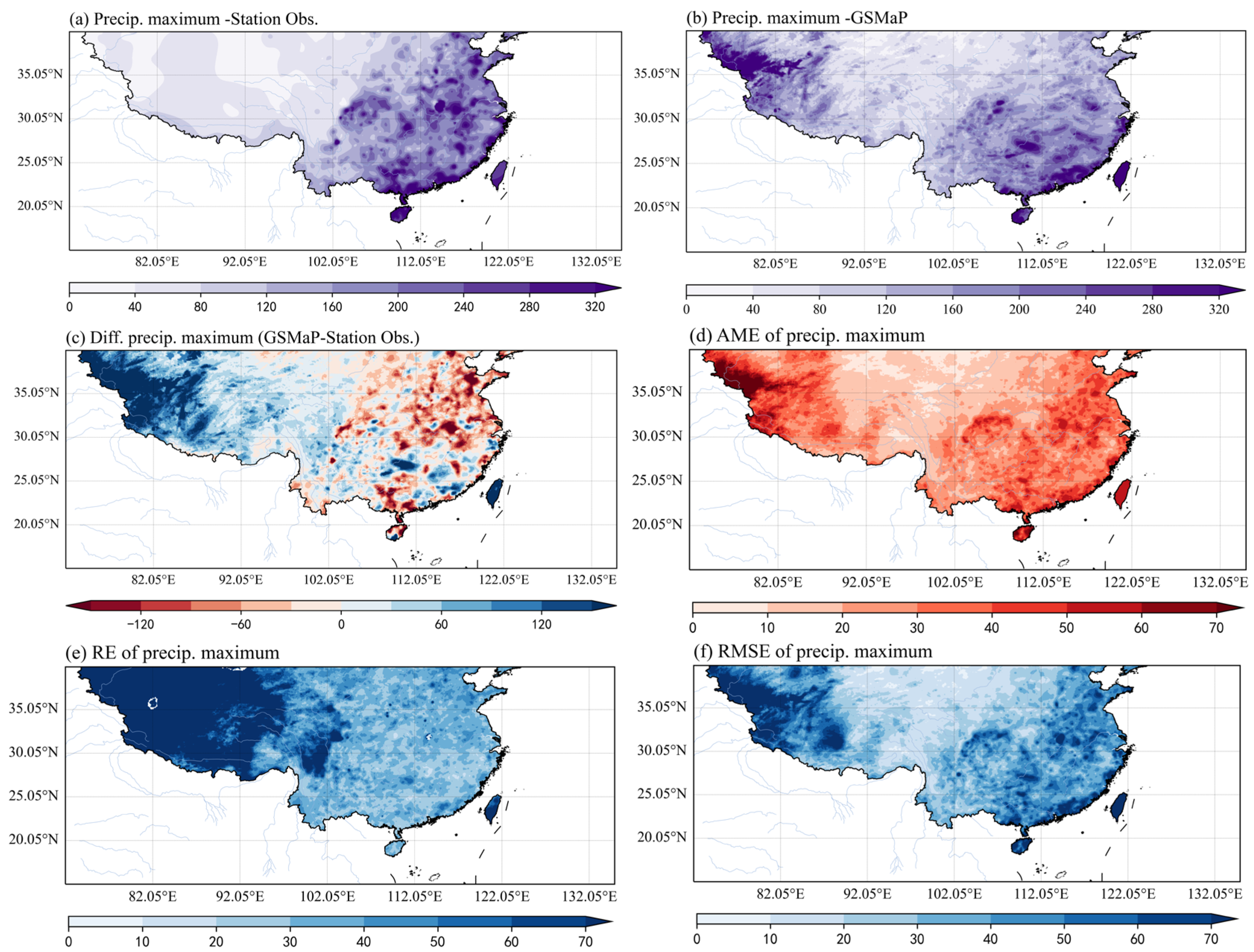
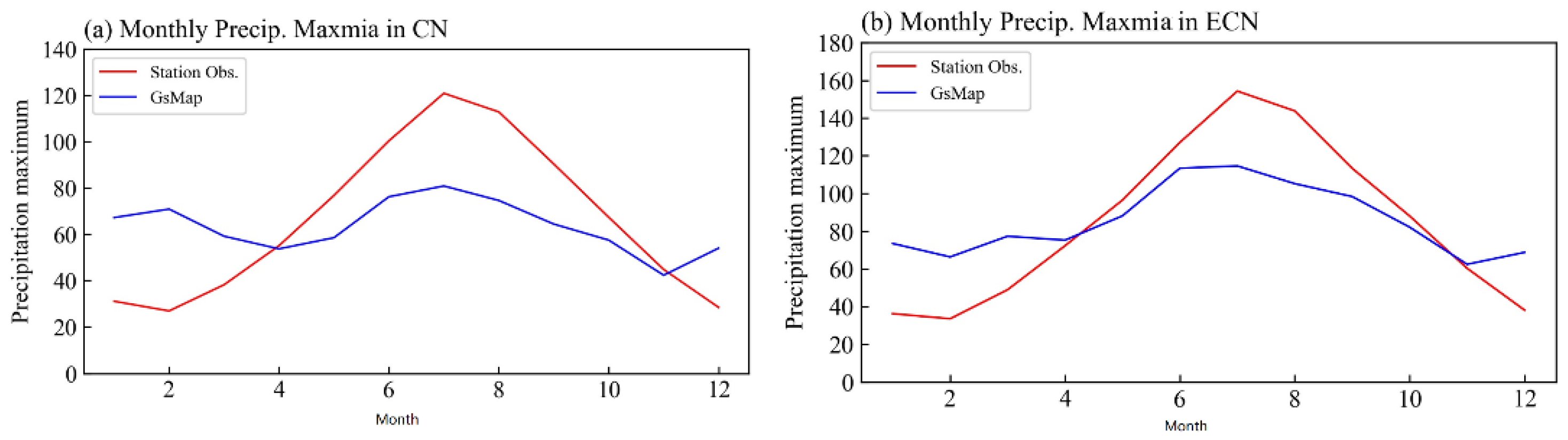
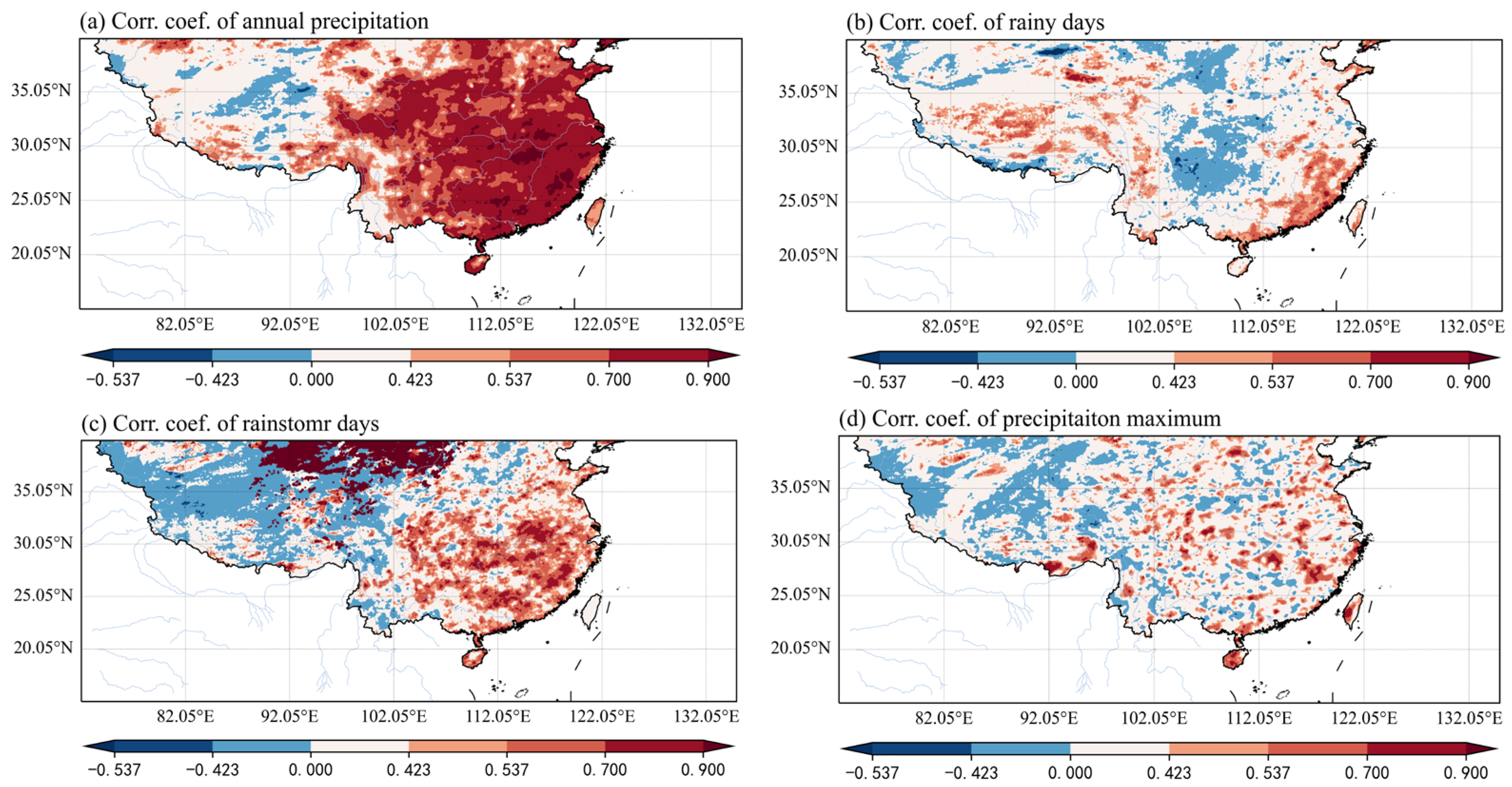
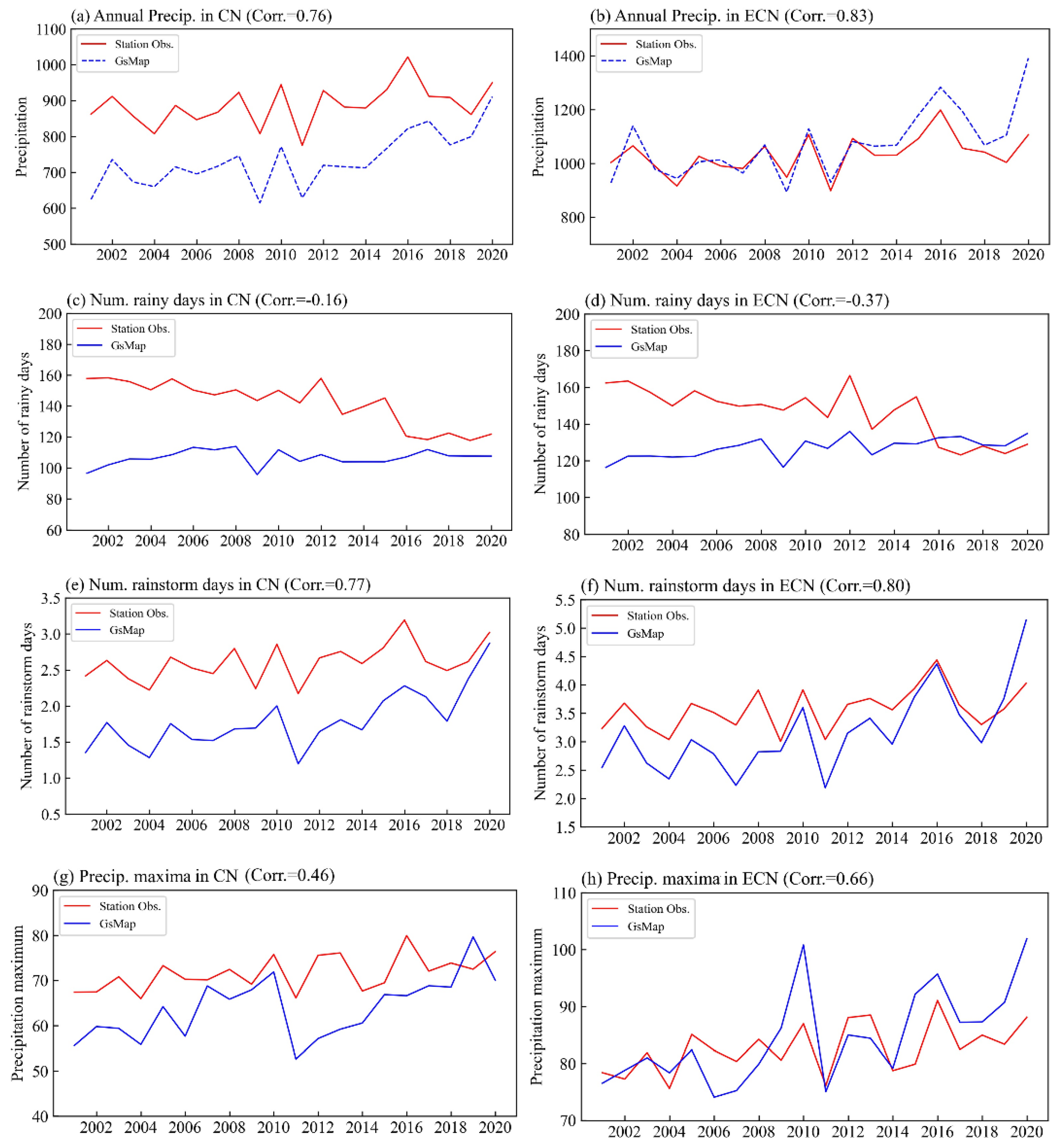
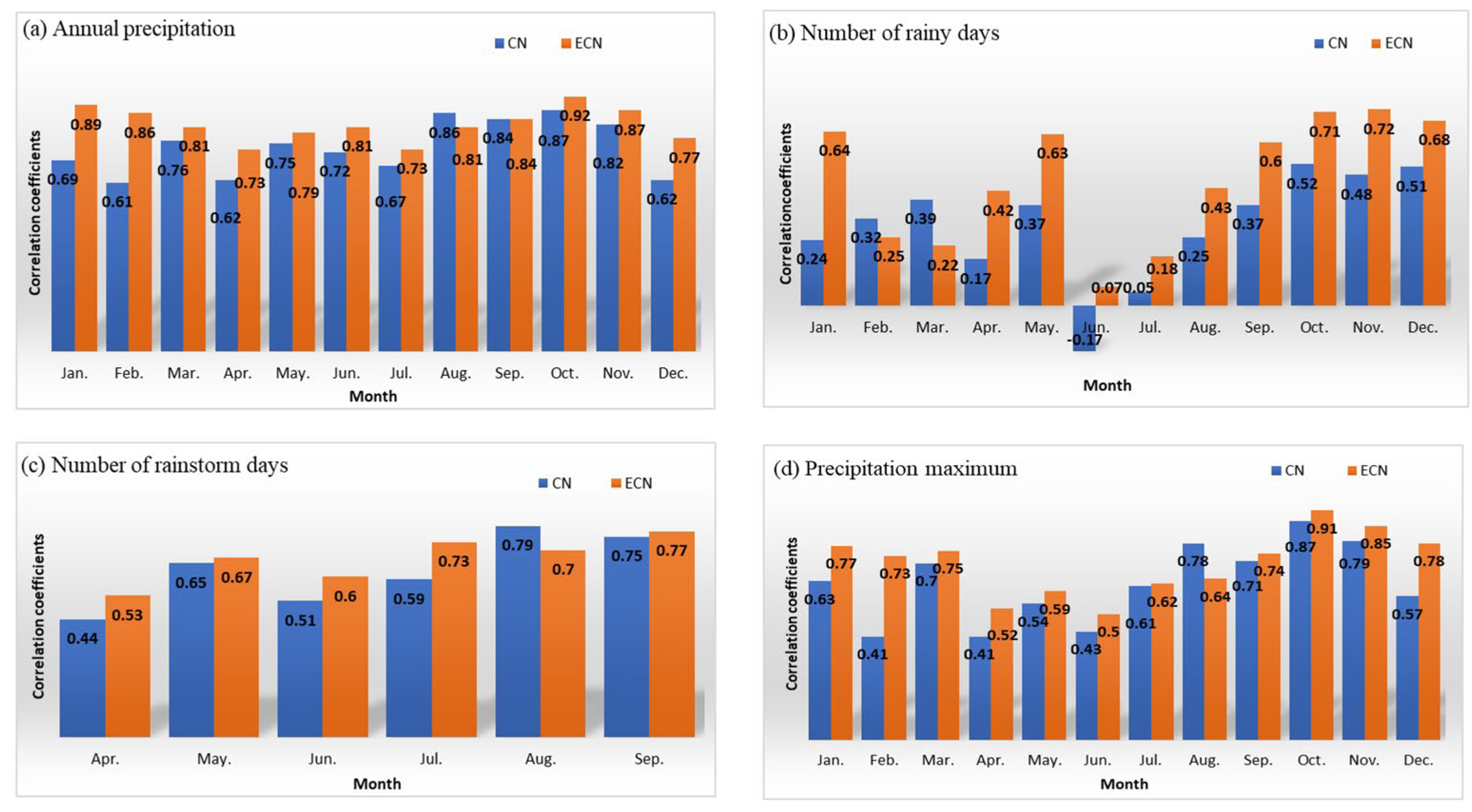
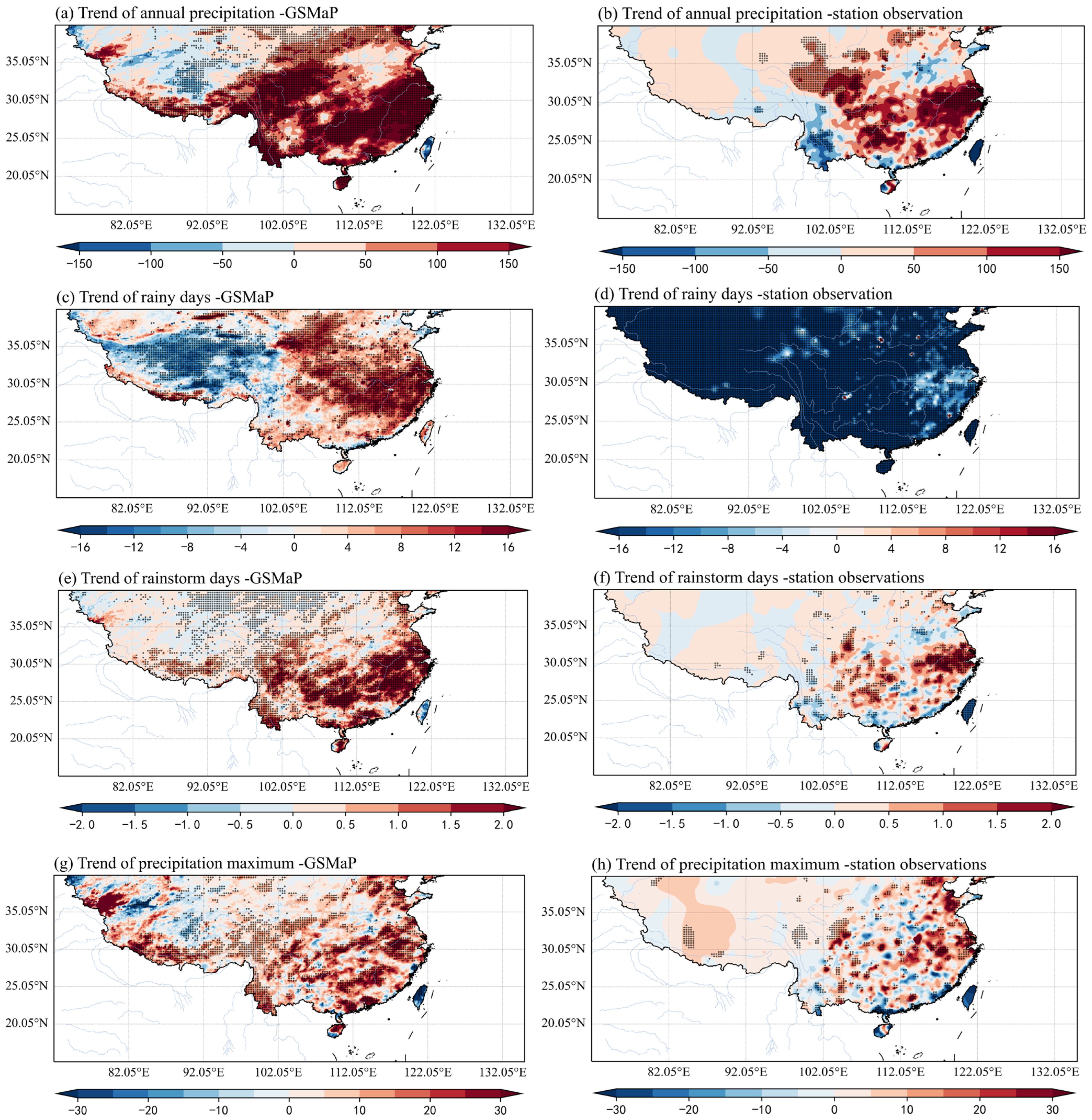
3. Results
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schär, C.; Frei, C. Orographic precipitation and climate change. Glob. Change Mt. Reg. Overv. Curr. Knowl. 2005, 23, 255–266. [Google Scholar]
- Douben, K.J. Characteristics of river floods and flooding: A global overview, 1985–2003. Irrig. Drain. 2006, 55, S9–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petley, D. Global patterns of loss of life from landslides. Geology 2012, 40, 927–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirabayashi, Y.; Mahendran, R.; Koirala, S.; Konoshima, L.; Yamazaki, D.; Watanabe, S.; Kim, H.; Kanae, S. Global flood risk under climate change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowling, C.A.; Santi, P.M. Debris flows and their toll on human life: A global analysis of debris-flow fatalities from 1950 to 2011. Nat. Hazards 2014, 71, 203–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.H.; Gong, D.H.; Chin, C.T.; Jui, Y.H. Using rainfall thresholds and ensemble precipitation forecasts to issue and improve urban inundation alerts. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 4731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Rankin, C.; Gangrade, S.; Zhao, G.; Lander, K.; Voisin, N.; Shao, M.; Morales-Hernández, M.; Kao, S.C.; Gao, H. Evaluating precipitation, streamflow, and inundation forecasting skills during extreme weather events: A case study for an urban watershed. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 127126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.E. The impact of climate change and variability on heavy precipitation, floods, and droughts. In Encyclopedia of Hydrological Sciences; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; Volume 17, pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, A. Drought under global warming: A review. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Clim. Chang. 2011, 2, 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Mishra, A.; Trenberth, K.E. Climate change and drought: A perspective on drought indices. Curr. Clim. Chang. Rep. 2018, 4, 145–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, A.; Zhao, T.; Chen, J. Climate Change and Drought: A Precipitation and Evaporation Perspective. Curr. Clim. Chang. 2018, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, S.; Wang, P. Interdecadal variation of the number of days with drought in China based on the standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index (SPEI). J. Clim. 2022, 35, 2003–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebaldi, C.; Hayhoe, K.; Arblaster, J.M.; Meehl, G.A. Going to the extremes. Clim. Chang. 2006, 79, 185–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S.; Kemfert, C.; Höppe, P. The impact of socio-economics and climate change on tropical cyclone losses in the USA. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2010, 10, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, T.; Qin, D.; Plattner, G.; Tignor, M.; Allen, S.; Boschung, J.; Nauels, A.; Xia, Y.; Bex, V.; Midgley, P. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis: Working Group I Contribution to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013; pp. 167–178. [Google Scholar]
- Mullan, D.; Favis-Mortlock, D.; Fealy, R. Addressing key limitations associated with modelling soil erosion under the impacts of future climate change. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2012, 156, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, G.; Bonada, N.; Brown, L.E.; Death, R.G.; Durance, I.; Gray, C.; Hladyz, S.; Ledger, M.E.; Milner, A.M.; Ormerod, S.J. The effects of climatic fluctuations and extreme events on running water ecosystems. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2016, 371, 20150274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paerl, H.W.; Crosswell, J.R.; Van, D.B.; Hall, N.S.; Rossignol, K.L.; Osburn, C.L.; Hounshell, A.G.; Sloup, R.S.; Harding, L.W. Two decades of tropical cyclone impacts on North Carolina’s estuarine carbon, nutrient and phytoplankton dynamics: Implications for biogeochemical cycling and water quality in a stormier world. Biogeochemistry 2018, 141, 307–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.R.; Ingram, W.J. Constraints on future changes in climate and the hydrologic cycle. Nature 2002, 419, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santer, B.D.; Mears, C.; Wentz, F.; Taylor, K.; Gleckler, P.; Wigley, T.; Barnett, T.; Boyle, J.; Brüggemann, W.; Gillett, N. Identification of human-induced changes in atmospheric moisture content. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 15248–15253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, S.K.; Zhang, X.; Zwiers, F.W.; Hegerl, G.C. Human contribution to more-intense precipitation extremes. Nature 2011, 470, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roderick, T.P.; Wasko, C.; Sharma, A. Atmospheric moisture measurements explain increases in tropical rainfall extremes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 1375–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Wu, X.; Liu, B. Global changes in the spatial extents of precipitation extremes. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 054017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkin, P.A.; Ardanuy, P.E. Estimating climatic-scale precipitation from space: A review. J. Clim. 1989, 2, 1229–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Dai, A.; Rasmussen, R.M.; Parsons, D.B. The Changing Character of Precipitation. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2003, 84, 1205–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, C.; Halbleib, M.; Smith, J.I.; Gibson, W.P.; Doggett, M.K.; Taylor, G.H.; Curtis, J.; Pasteris, P.P. Physiographically sensitive mapping of climatological temperature and precipitation across the conterminous United States. Int. J. Climatol. 2008, 28, 2031–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelides, S.; Levizzani, V.; Anagnostou, E.; Bauer, P.; Kasparis, T.; Lane, J.E. Precipitation: Measurement, remote sensing, climatology and modeling. Atmos. Res. 2009, 94, 512–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, G.L.; L’Ecuyer, T.; Forbes, R.; Gettelmen, A.; Golaz, J.C.; Bodas-Salcedo, A.; Suzuki, K.; Gariel, P.; Haynes, J. Dreary state of precipitation in global models. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, C.; Levizzani, V. Status of satellite precipitation retrievals. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapiador, F.J.; Turk, F.J.; Petersen, W.; Hou, A.Y.; García-Ortega, E.; Machado, L.A.T.; Angelis, C.F.; Salio, P.; Kidd, C.; Huffman, G.J.; et al. Global precipitation measurement: Methods, datasets and applications. Atmos. Res. 2012, 104, 70–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Miao, C.; Duan, Q.; Ashouri, H.; Sorooshian, S.; Hsu, K.L. A review of global precipitation data sets: Data sources, estimation, and intercomparisons. Rev. Geophys. 2018, 56, 79–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.E.; Vergopolan, N.; Pan, M.; Levizzani, V.; Dijk, A.I.J.M.; Weedon, G.P.; Brocca, L.; Pappenberger, F.; Huffman, G.J.; Wood, E.F. Global-scale evaluation of 22 precipitation datasets using gauge observations and hydrological modeling. Satell. Precip. Meas. 2020, 2, 625–653. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, P.; Arkin, P.A. Global precipitation: A 17-year monthly analysis based on gauge observations, satellite estimates, and numerical model outputs. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1997, 78, 2539–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, C. Satellite rainfall climatology: A review. Int. J. Climatol. 2001, 21, 1041–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturaro, G. A Closer look at the climatological discontinuities present in the NCEP/NCAR reanalysis temperature due to the introduction of satellite data. Clim. Dyn. 2003, 21, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, L.; Hagemann, S.; Hodges, K.I. Can climate trends be calculated from reanalysis data? J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, D11111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnay, E.; Kanamitsu, M.; Kistler, R.; Collins, W.; Deaven, D.; Gandin, L.; Iredell, M.; Saha, S.; White, G.; Woollen, J.; et al. The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1996, 77, 437–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanamitsu, M.; Ebisuzaki, W.; Woolen, J.; Yang, S.K.; Hnilo, J.J.; Fiorino, M.; Potter, G.L. NCEP–DOE AMIP-II Reanalysis (R-2). Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2002, 83, 1631–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppala, S.M.; KÅllberg, P.W.; Simmons, A.J.; Andrae, U.; Bechtold, V.D.C.; Fiorino, M.; Gibson, J.K.; Haseler, J.; Hernandez, A.; Kelly, G.A.; et al. The ERA-40 re-analysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2005, 131, 2961–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, P.; et al. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, B.; Hersbach, H.; Simmons, A.; Berrisford, P.; Dahlgren, P.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nocolas, J.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis: Preliminary extension to 1950. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2021, 147, 4186–4227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Moorthi, S.; Pan, H.L.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Nadiga, S.; Tripp, P.; Kistler, R.; Woollen, J.; Behringer, D.; et al. The NCEP climate forecast system reanalysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2010, 91, 1015–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Moorthi, S.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Nadiga, S.; Tripp, P.; Behringer, D.; Hou, Y.T.; Chuang, H.; Iredell, M.; et al. The NCEP climate forecast system version 2. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 2185–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebita, A.; Kobayashi, S.; Ota, Y.; Moriya, M.; Kumabe, R.; Onogi, K.; Harada, Y.; Yasui, S.; Miyaoka, K.; Takahashi, K.; et al. The Japanese 55-year Reanalysis “JRA-55”: An interim report. SOLA 2011, 7, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashima, T.; Kubota, T.; Mega, T.; Ushio, T.; Oki, R. Precipitation Extremes Monitoring Using the Near-Real-Time GSMaP-GNRT6 Product. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 5640–5651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, R.J.; Janowiak, J.E.; Arkin, P.A.; Xie, P. CMORPH: A method that produces global precipitation estimates from passive nicrowave and infrared data at high spatial and temporal resolution. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J.; Wolff, D.B.; Adler, R.F.; Gu, G.; Hong, Y.; Bowman, K.P.; Stocker, E.F. The TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA): Quasi-global, multiyear, combined-sensor precipitation estimates at fine scales. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Hsu, K.L.; Sorooshian, S.; Gao, X.G. Precipitation estimation from remotely sensed imagery using an artificial neural network cloud classification system. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2004, 43, 1834–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, K.L.; Gao, X.G.; Sorooshian, S.; Gupta, H.V. Precipitation estimation from remotely sensed information using artificial neural networks. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1997, 36, 1176–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorooshian, S.; Hsu, K.L.; Gao, X.; Gupta, H.V.; Imam, B.; Braithwaite, D. Evaluation of PERSIANN system satellite-based estimates of tropical rainfall. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2000, 81, 2035–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushio, T.; Kachi, M. Kalman filtering applications for global satellite mapping of precipitation (GSMaP). In Satellite Rainfall Applications for Surface Hydrology; Gebremichael, M., Hossain, F., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 105–123. [Google Scholar]
- Kubota, T.; Aonashi, K.; Ushio, T.; Shige, S.; Takayabu, Y.N.; Kachi, M.; Arai, Y.; Tashima, T.; Makaki, T.; Kawamoto, N.; et al. Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation (GSMaP) products in the GPM era. Satell. Precip. Meas. 2020, 1, 355–373. [Google Scholar]
- Herold, N.; Behrangi, A.; Alexander, L.V. Large uncertainties in observed daily precipitation extremes over land. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 668–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekaranom, A.B.; Masunaga, H. Origins of heavy precipitation biases in the TRMM PR and TMI products assessed with CloudSat and reanalysis data. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2019, 58, 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masunaga, H.; Schröder, M.; Furuzawa, F.A.; Kummerow, C.; Rustemeier, E.; Schneider, U. Inter-product biases in global precipitation extremes. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 125016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, A.Y.; Kakar, R.K.; Neeck, S.; Azarbarzin, A.A.; Kummerow, C.D.; Kojima, M.; Oki, R.; Nakamura, K.; Iguchi, T. The global precipitation measurement mission. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 701–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skofronick-Jackson, G.; Petersen, W.A.; Berg, W.; Kidd, C.; Stocker, E.F.; Krischbaum, D.B.; Kakar, R.; Braun, S.A.; Huffman, G.J.; Iguchi, T.; et al. The Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) mission for science and society. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 98, 1679–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setiawati, M.D.; Miura, F.; Aryastana, P. Validation of Hourly GSMaP and ground base estimates of precipitation for flood monitoring in Kumamoto, Japan. In Geospatial Technology for Water Resource Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 130–143. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Peters-Lidard, C.D.; Adler, R.F.; Kubota, T.; Ushio, T. Evaluation of GSMaP precipitation estimates over the contiguous United States. J. Hydrometeorol. 2010, 11, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Qin, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, S. Evaluation of global satellite mapping of precipitation project daily precipitation estimates over the Chinese mainland. Adv. Meteorol. 2016, 2016, 9365294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, S.; Song, F.; Udmale, P.; Jin, J.; Thapa, B.R.; Ishidaira, H. Error analysis and evaluation of the latest GSMaP and IMERG precipitation products over Eastern China. Adv. Meteorol. 2017, 2017, 1803492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Yong, B. A preliminary assessment of the gauge-adjusted near-real-time GSMaP precipitation estimate over Mainland China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Guo, B.; Xing, W.; Zhou, J.; Xu, F.; Xu, Y. Comprehensive evaluation of latest GPM era IMERG and GSMaP precipitation products over mainland China. Atmos. Res. 2020, 246, 105132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, Z.W.; Kuleshov, Y.; Watkins, A. Evaluation of satellite precipitation estimates over Australia. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiyoko, A.; Osawa, T.; Nuarsa, I.W. Evaluation of GSMaP precipitation estimates over Indonesia. Int. J. Environ. Geosci. 2019, 3, 26–43. [Google Scholar]
- Kuleshov, Y.; Kurino, T.; Kubota, T.; Tashima, T.; Xie, P. WMO Space-Based Weather and Climate Extremes Monitoring Demonstration Project (SEMDP): First Outcomes of Regional Cooperation on Drought and Heavy Precipitation Monitoring for Australia and South-East Asia. Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/books/rainfall-extremes-distribution-and-properties/wmo-space-based-weather-and-climate-extremes-monitoring-demonstration-project-semdp-first-outcomes-o (accessed on 15 October 2023).
- Zheng, D.; Yao, T.D. Research progress on formation and evolution of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and its environmental and resource effects. Chin. Basic Sci. 2004, 6, 15–21. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Chan, J.C.L. The East Asian summer monsoon: An overview. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2005, 89, 117–142. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.Y.; Shi, X.H. Climatological characteristics of summertime moisture budget over the southeast part of Tibetan Plateau with their impacts. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2008, 19, 41–46. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Wang, Z. A study of rainy seasons in China. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2008, 100, 121–138. [Google Scholar]
- Immerzeel, W.W.; Beek, L.P.V.; Bierkens, M.F. Climate change will affect the Asian water towers. Science 2010, 328, 1382–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Huang, W.; Jin, L.; Chen, J.; Chen, S.; Chen, F. A climatological northern boundary index for the East Asian summer monsoon and its interannual variability. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2018, 61, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.D.; Dong, L.L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.J. Effects of the Asian Water Tower over the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and the characteristics of atmospheric water circulation. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 2830–2841. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Huang, W.; Feng, S.; Zhang, Q.; Kuang, X.; Chen, J. The modulation of westerlies-monsoon interaction on climate over the monsoon boundary zone in East Asia. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 3049–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, R.L. Multiquadric equations of topography and other irregular surfaces. J. Geophys. Res. 1971, 76, 1905–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasshauer, G.E. Meshfree Approximation Methods with MATLAB; World Scientific Publishing Co., Inc.: Singapore, 2007; pp. 355–403. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, D.; Tang, J. Impacts of warming and water vapor content on the decrease in light rain days during the warm season over eastern China. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 45, 1841–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domroes, M.; Schaefer, D. Recent climate change affecting rainstorm occurrences: A case study in East China. Clim. Past 2008, 4, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, T.; Aonashi, K.; Ushio, T.; Shige, S.; Yamaji, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Hirose, H.; Takayabu, Y. A new version of Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation (GSMaP) product released in December 2021. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly 2022, Vienna, Austria, 23–27 May 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kubota, T.; Shige, S.; Hashizume, H.; Aonashi, K.; Takahashi, N.; Seto, S.; Hirose, M.; Takayabu, Y.N.; Ushio, T.; Nakagawa, K.; et al. Global Precipitation Map Using Satellite-Borne Microwave Radiometers by the GSMaP Project: Production and Validation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 2259–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tustison, B.; Harris, D.; Foufoula-Georgiou, E. Scale issues in verification of precipitation forecasts. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 11775–11784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Guo, H.; Tian, Y.; Meng, X.; Bao, A.; De Maeyer, P. Evaluation of GSMaP Version 8 Precipitation Products on an Hourly Timescale over Mainland China. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Yong, B.; Ke, L.; Wang, G.; Ren, L.; Chen, X. Tracing the error sources of global satellite mapping of precipitation for GPM (GPM-GSMaP) over the Tibetan Plateau, China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 2181–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wei, J.; Yin, J.; Qiao, Z.; Peng, W.; Peng, H. Multiscale comparative evaluation of the GPM and TRMM precipitation products against ground precipitation observations over Chinese Tibetan Plateau. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 14, 2295–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Yang, K.; Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Shen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, X. Atmospheric simulation-based precipitation datasets outperform satellite-based products in closing basin-wide water budget in the eastern Tibetan Plateau. Int. J. Climatol. 2022, 42, 7252–7268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Achberger, C.; Linderholm, H.W. Rain-season trends in precipitation and their effect in different climate regions of China during 1961–2008. Environ. Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 034025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Chen, C.; Lian, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, X. Long-term change of wet and dry climatic conditions in the southwest karst area of China. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2015, 127, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, H.; Xu, M.; Zhao, F.; Tijjani, S.B. Spatial and temporal variations in precipitation amount, frequency, intensity, and persistence in China, 1973–2016. J. Hydrometeorol. 2019, 20, 2215–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawky, M.; Moussa, A.; Hassan, Q.K.; El-Sheimy, N. Performance assessment of sub-daily and daily precipitation estimates derived from GPM and GSMaP products over an arid environment. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Yong, B. Evaluation and hydrological utility of the latest GPM IMERG V5 and GSMaP V7 precipitation products over the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen Liechti, T.; Matos, J.P.; Boillat, J.L.; Schleiss, A.J. Comparison and evaluation of satellite derived precipitation products for hydrological modeling of the Zambezi River Basin. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Clark, M.P.; Papalexiou, S.M.; Ma, Z.; Hong, Y. Have satellite precipitation products improved over last two decades? A comprehensive comparison of GPM IMERG with nine satellite and reanalysis datasets. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 240, 111697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, P.; Zhang, M.; Guo, H.; Xu, C.; Bing, J.; Jia, J. Error analysis and correction of the daily GSMaP products over Hanjiang River Basin of China. Atmos. Res. 2018, 214, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Wei, Y.; Wang, G.; Shi, R.; Chen, H.; Mo, C.; Rigo, T. Downscaling Correction and Hydrological Applicability of the Three Latest High-Resolution Satellite Precipitation Products (GPM, GSMAP, and MSWEP) in the Pingtang Catchment, China. Adv. Meteorol. 2022, 2022, 6507109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Li, Q. Towards Improved Satellite Data Utilization in China: Insights from an Integrated Evaluation of GSMaP-GNRT6 in Rainfall Patterns. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 755. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16050755
Wang Z, Li Q. Towards Improved Satellite Data Utilization in China: Insights from an Integrated Evaluation of GSMaP-GNRT6 in Rainfall Patterns. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(5):755. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16050755
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zunya, and Qingquan Li. 2024. "Towards Improved Satellite Data Utilization in China: Insights from an Integrated Evaluation of GSMaP-GNRT6 in Rainfall Patterns" Remote Sensing 16, no. 5: 755. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16050755
APA StyleWang, Z., & Li, Q. (2024). Towards Improved Satellite Data Utilization in China: Insights from an Integrated Evaluation of GSMaP-GNRT6 in Rainfall Patterns. Remote Sensing, 16(5), 755. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16050755