Machine-to-Machine Visual Dialoguing with ChatGPT for Enriched Textual Image Description
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Related Research Areas
1.1.1. RS Image Captioning (RSIC)
1.1.2. RS Visual Question Answering (RSVQA)
1.1.3. RS Visual Question Generation (RSVQG)
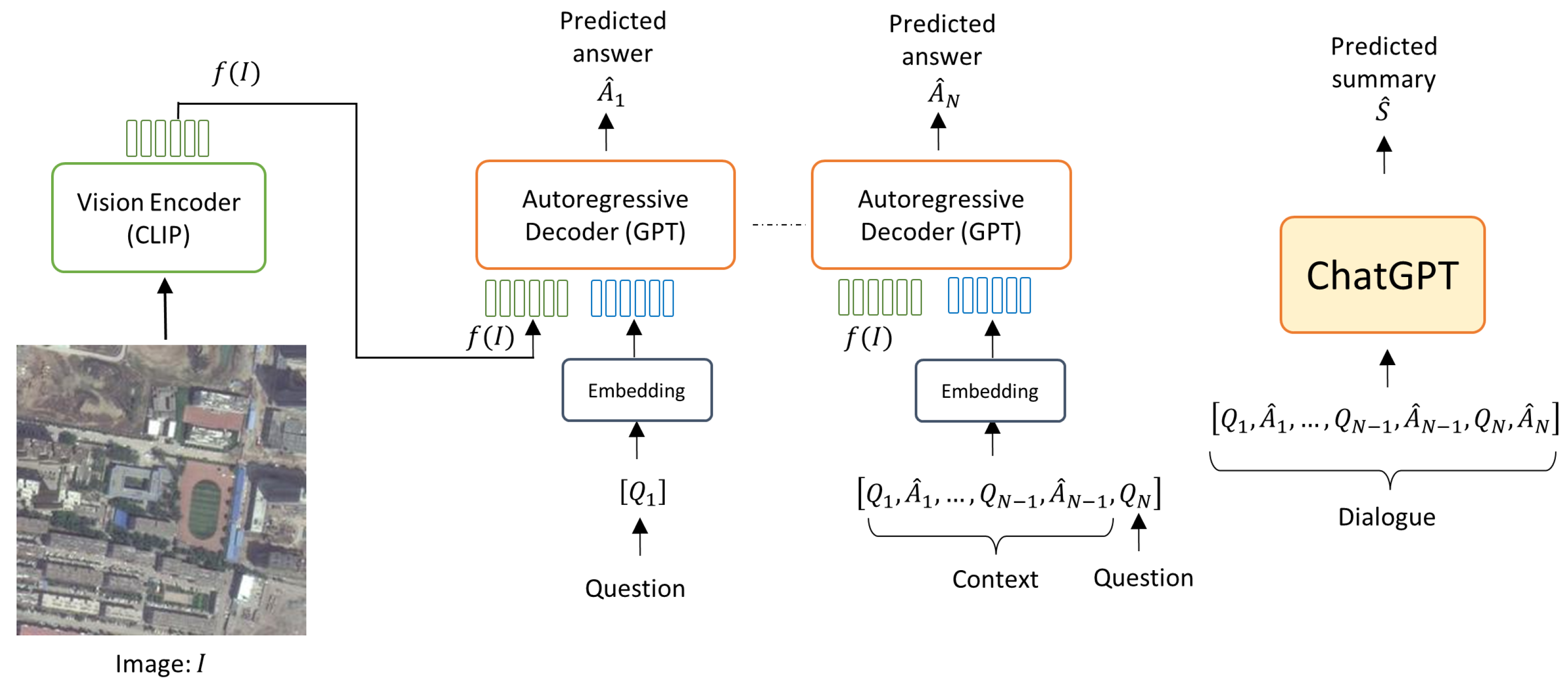
2. Materials and Methods
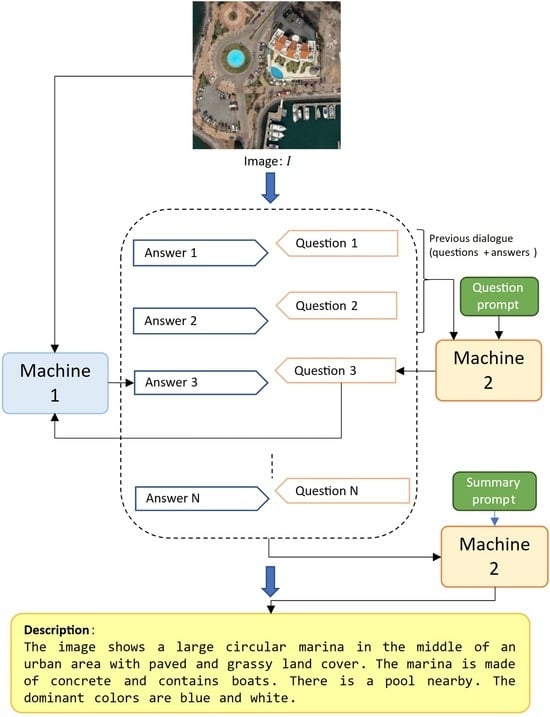
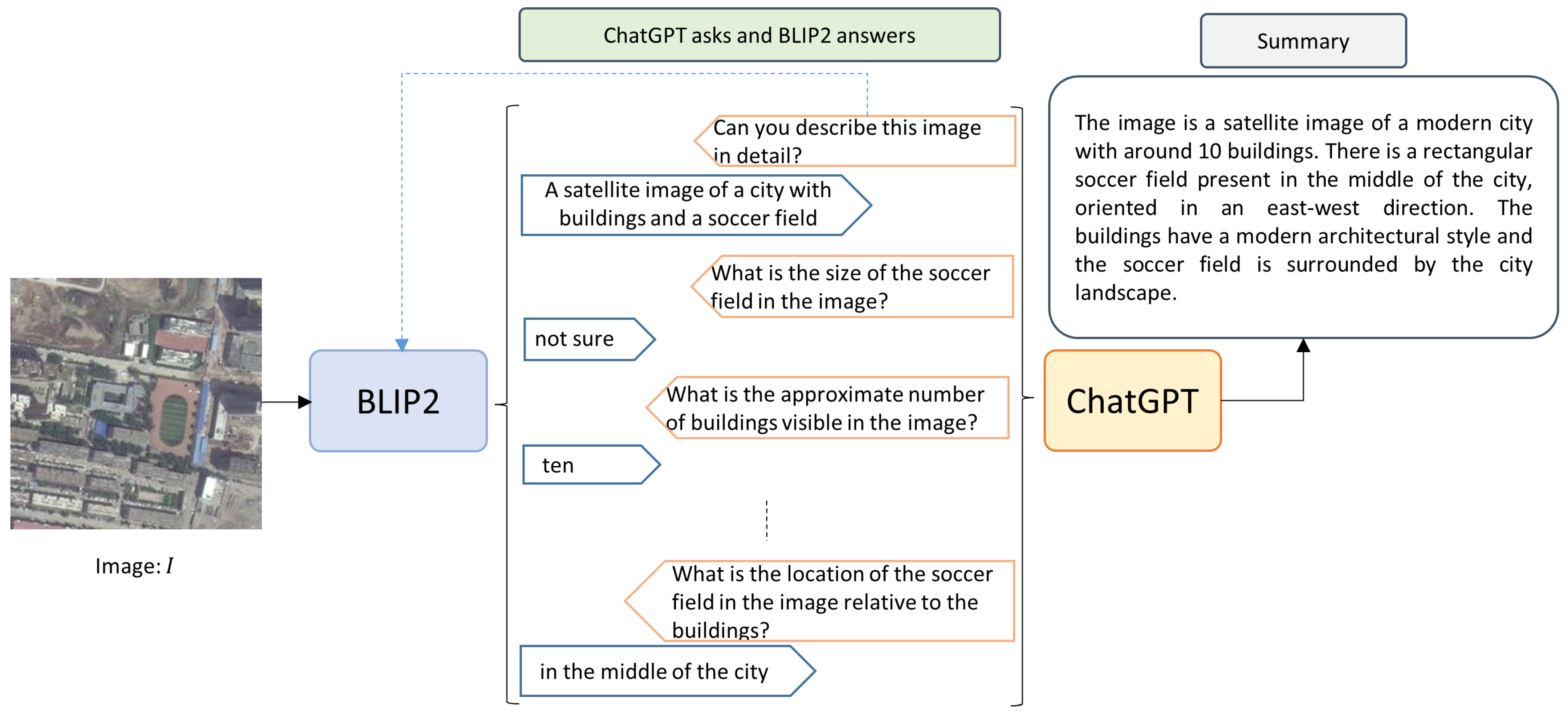
2.1. Open-Ended Dialogue
- A fixed prompt “Describe this image in detail” is used to spark the conversation.
- Blip-2 answers with a description of the image.
- ChatGPT generates a question based on the description.
- Blip-2 answers by looking at the image.
- ChatGPT, using the context of the first description and the dialoguing history, produces another question to further explore the image contents.
- Blip-2 answers by looking at the image.
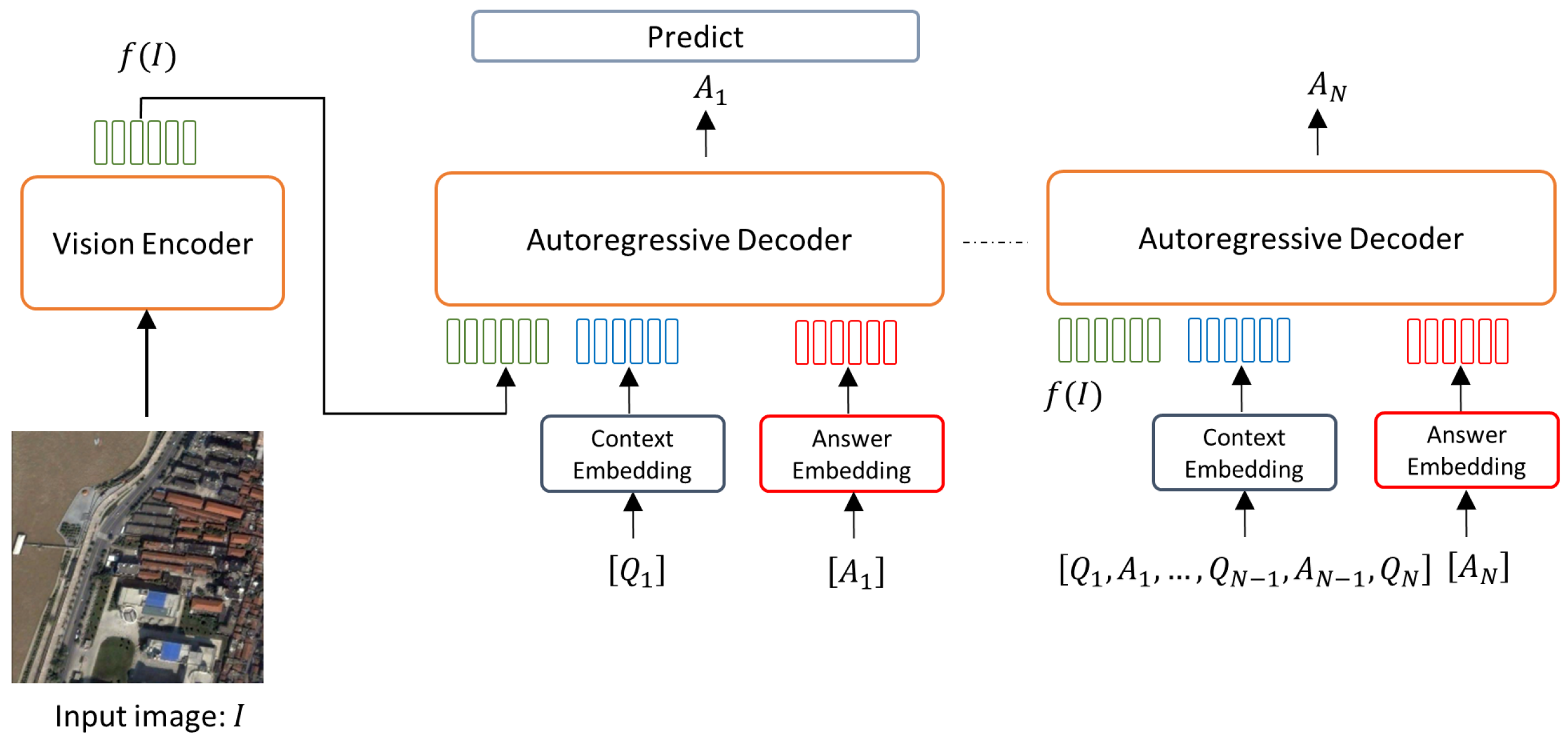
2.2. Closed-Form Dialogue
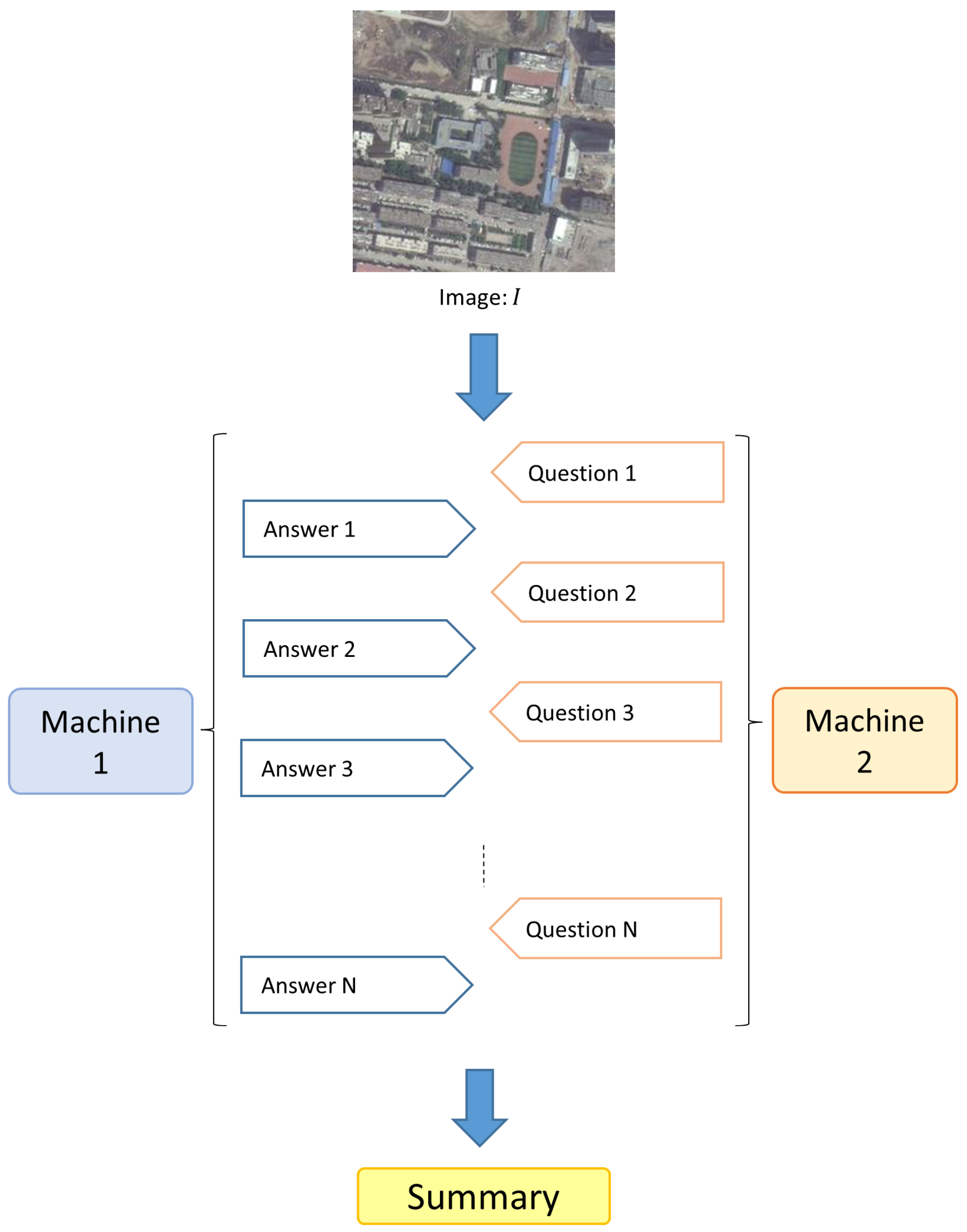
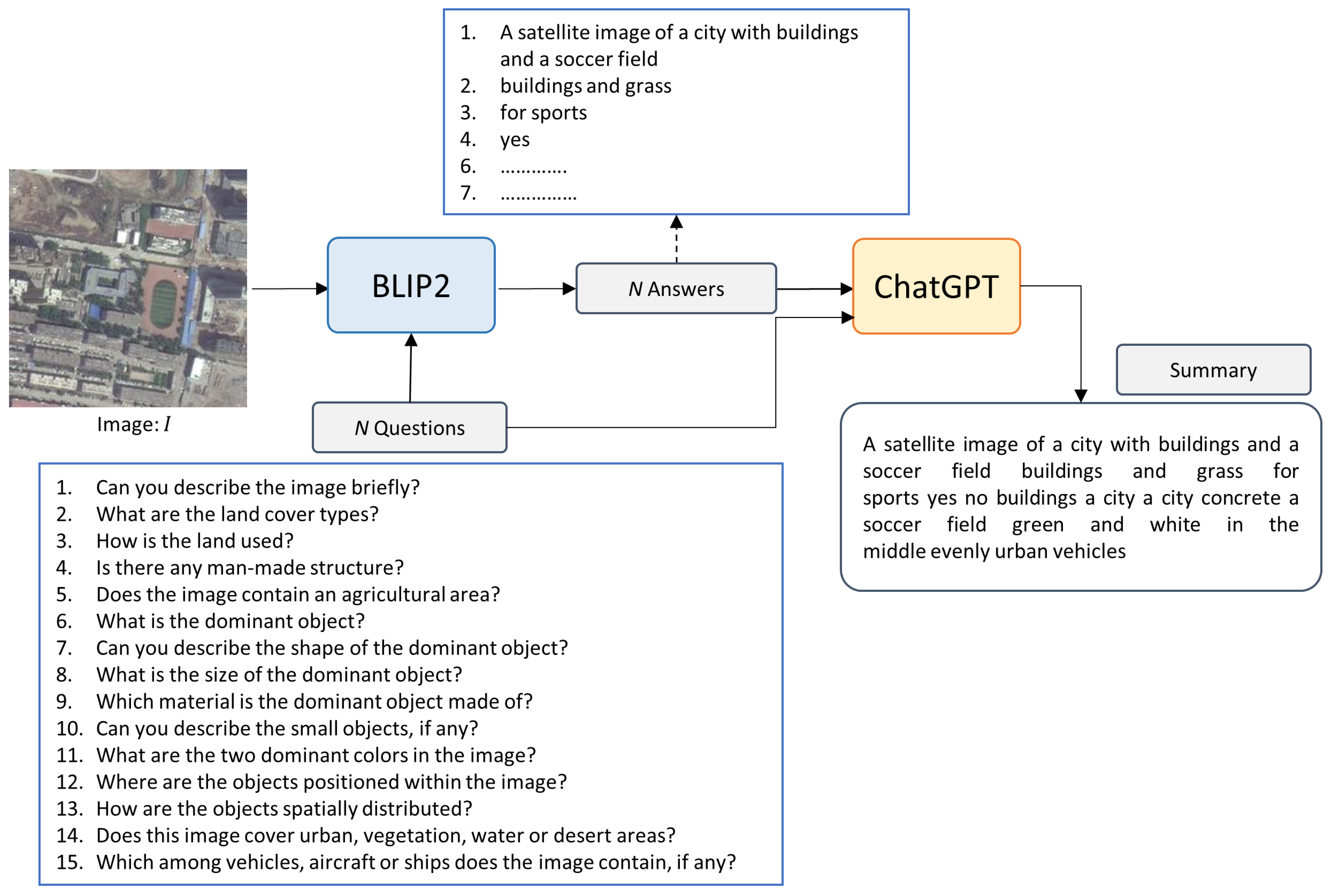
2.3. Closed-Form Dialogue with Context
2.4. Dataset and Metrics
2.5. Prompts
2.5.1. ChatGPT Prompts
- I have an image. Ask me questions about the content of this image. Carefully asking me informative questions to maximize your information about this image content. Each time ask one question only without giving an answer. Avoid asking yes/no questions. I’ll put my answer beginning with “Answer”:
- Next Question. Avoid asking yes/no questions. Question:
- Now summarize the information you get in a few sentences. Ignore the questions with answers no or not sure. Don’t add information. Don’t miss information. Summary:
2.5.2. Blip-2 Prompts
- Answer given questions. If you are not sure about the answer, say you don’t know honestly. Don’t imagine any contents that are not in the image.
- Answer:
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Input Image Integration
4.2. Adaptation of Answerer and Questioner to the RS Context
4.3. Removal of Uncertain Question–Answer Pairs
4.4. Better Predefined Questions for CFD Method
4.5. Evaluation Metrics and Generation of Targeted Datasets
4.6. Customizing the Dialogue and Multimodality
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| R@1-5-10 | Recall value considering the first match, the first five, and the first ten, respectively. |
| T2IC | Text-to-Image and Comparison |
| FID | Frechet Inception Distance |
| OED | Open-Ended Dialogue |
| CFD | Closed-Form Dialogue |
| CFD-C | Closed-Form Dialogue with Context |
References
- Wu, L.; Tan, X.; He, D.; Tian, F.; Qin, T.; Lai, J.; Liu, T.Y. Beyond Error Propagation in Neural Machine Translation: Characteristics of Language. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1809.00120. [Google Scholar]
- Hoxha, G.; Chouaf, S.; Melgani, F.; Smara, Y. Change Captioning: A New Paradigm for Multitemporal Remote Sensing Image Analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Zou, Z. Can a Machine Generate Humanlike Language Descriptions for a Remote Sensing Image? IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 3623–3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, B.; Li, X.; Tao, D.; Lu, X. Deep semantic understanding of high resolution remote sensing image. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Computer, Information and Telecommunication Systems (CITS), Kunming, China, 6–8 July 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1512.03385. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, K.; van Merrienboer, B.; Gulcehre, C.; Bahdanau, D.; Bougares, F.; Schwenk, H.; Bengio, Y. Learning Phrase Representations using RNN Encoder-Decoder for Statistical Machine Translation. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1406.1078. [Google Scholar]
- Hoxha, G.; Melgani, F. A Novel SVM-Based Decoder for Remote Sensing Image Captioning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Wang, B.; Zheng, X.; Li, X. Exploring Models and Data for Remote Sensing Image Caption Generation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 2183–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wang, Q.; Li, X. Denoising-Based Multiscale Feature Fusion for Remote Sensing Image Captioning. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 18, 436–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Tang, X.; Zhou, H.; Li, C. Description Generation for Remote Sensing Images Using Attribute Attention Mechanism. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Diao, W.; Zhang, W.; Yan, M.; Gao, X.; Sun, X. LAM: Remote Sensing Image Captioning with Label-Attention Mechanism. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Ma, A.; Zhong, Y. Capformer: Pure Transformer for Remote Sensing Image Caption. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2022 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 17–22 July 2022; pp. 7996–7999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Huang, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, Z. NWPU-Captions Dataset and MLCA-Net for Remote Sensing Image Captioning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antol, S.; Agrawal, A.; Lu, J.; Mitchell, M.; Batra, D.; Zitnick, C.L.; Parikh, D. VQA: Visual Question Answering. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lobry, S.; Marcos, D.; Murray, J.; Tuia, D. RSVQA: Visual Question Answering for Remote Sensing Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 8555–8566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Wang, B.; Du, X.; Lu, X. Mutual Attention Inception Network for Remote Sensing Visual Question Answering. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Mou, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, X.X. From Easy to Hard: Learning Language-Guided Curriculum for Visual Question Answering on Remote Sensing Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappuis, C.; Zermatten, V.; Lobry, S.; Le Saux, B.; Tuia, D. Prompt–RSVQA: Prompting visual context to a language model for Remote Sensing Visual Question Answering. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–20 June 2022; pp. 1371–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazi, Y.; Rahhal, M.M.A.; Mekhalfi, M.L.; Zuair, M.A.A.; Melgani, F. Bi-Modal Transformer-Based Approach for Visual Question Answering in Remote Sensing Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, C. Visual Question Generation: The State of the Art. ACM Comput. Surv. 2020, 53, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.; Kiros, R.; Zemel, R. Exploring Models and Data for Image Question Answering. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1505.020742. [Google Scholar]
- Geman, D.; Geman, S.; Hallonquist, N.; Younes, L. Visual Turing test for computer vision systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 3618–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Lu, J.; Lee, S.; Batra, D.; Parikh, D. Visual Curiosity: Learning to Ask Questions to Learn Visual Recognition. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.00912. [Google Scholar]
- Vedd, N.; Wang, Z.; Rei, M.; Miao, Y.; Specia, L. Guiding Visual Question Generation. arXiv 2012, arXiv:2110.08226. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, U.; Zhang, Z.; Schwing, A. Creativity: Generating Diverse Questions using Variational Autoencoders. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.03493. [Google Scholar]
- Bashmal, L.; Bazi, Y.; Melgani, F.; Ricci, R.; Al Rahhal, M.M.; Zuair, M. Visual Question Generation From Remote Sensing Images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 3279–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Chen, J.; Haydarov, K.; Shen, X.; Zhang, W.; Elhoseiny, M. ChatGPT Asks, BLIP-2 Answers: Automatic Questioning Towards Enriched Visual Descriptions. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.06594. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Li, D.; Savarese, S.; Hoi, S. BLIP-2: Bootstrapping Language-Image Pre-training with Frozen Image Encoders and Large Language Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.12597. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, T.B.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; et al. Language Models are Few-Shot Learners. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.14165. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, L.; Wu, J.; Jiang, X.; Almeida, D.; Wainwright, C.L.; Mishkin, P.; Zhang, C.; Agarwal, S.; Slama, K.; Ray, A.; et al. Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.02155. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; Ramesh, A.; Goh, G.; Agarwal, S.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Mishkin, P.; Clark, J.; et al. Learning Transferable Visual Models From Natural Language Supervision. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.00020. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Wu, J.; Child, R.; Luan, D.; Amodei, D.; Sutskever, I. Language Models are Unsupervised Multitask Learners. OpenAI Blog 2019, 1, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Huggingface: Distilgpt2. Available online: https://huggingface.co/distilgpt2 (accessed on 14 April 2022).
- Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Fermuller, C.; Aloimonos, Y. Neural Self Talk: Image Understanding via Continuous Questioning and Answering. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1512.03460. [Google Scholar]
- Hessel, J.; Holtzman, A.; Forbes, M.; Bras, R.L.; Choi, Y. CLIPScore: A Reference-free Evaluation Metric for Image Captioning. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2104.08718. [Google Scholar]
- Huggingface: CompVis/Stable-Diffusion-v1-4. Available online: https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4 (accessed on 14 April 2022).
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the Inception Architecture for Computer Vision. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1512.00567. [Google Scholar]




| Blip-2 | MLAT | Summary | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OED | CFD | CFD-C | ||||
| Clipscore | 65.2 | 69.0 | 66.1 | 72.7 | 67.8 | |
| ViT-L/14 | R@1 | 21.9 | 4.8 | 25.2 | 22.9 | 9.0 |
| R@5 | 59.5 | 20.0 | 61.0 | 59.5 | 36.2 | |
| R@10 | 83.8 | 37.1 | 84.8 | 81.4 | 63.3 | |
| T2IC | CosineSim | 0.59 | 0.59 | 0.60 | 0.59 | 0.58 |
| FID | 260.68 | 241.40 | 238.71 | 248.33 | 250.28 | |
| Blip-2 | MLAT | Summary | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OED | CFD | CFD-C | ||||
| Clipscore | 65.2 | 71.1 | 66.1 | 72.7 | 67.8 | |
| ViT-L/14 | R@1 | 9.2 | 2.56 | 11.0 | 6.7 | 3.9 |
| R@5 | 29.4 | 12.53 | 32.7 | 24.4 | 17.2 | |
| R@10 | 44.3 | 21.68 | 49.3 | 38.6 | 28.5 | |
| T2IC | CosineSim | 0.62 | 0.62 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.62 |
| FID | 140.02 | 151.23 | 122.03 | 122.89 | 128.65 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ricci, R.; Bazi, Y.; Melgani, F. Machine-to-Machine Visual Dialoguing with ChatGPT for Enriched Textual Image Description. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16030441
Ricci R, Bazi Y, Melgani F. Machine-to-Machine Visual Dialoguing with ChatGPT for Enriched Textual Image Description. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(3):441. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16030441
Chicago/Turabian StyleRicci, Riccardo, Yakoub Bazi, and Farid Melgani. 2024. "Machine-to-Machine Visual Dialoguing with ChatGPT for Enriched Textual Image Description" Remote Sensing 16, no. 3: 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16030441
APA StyleRicci, R., Bazi, Y., & Melgani, F. (2024). Machine-to-Machine Visual Dialoguing with ChatGPT for Enriched Textual Image Description. Remote Sensing, 16(3), 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16030441