Abstract
Faults, as unique geological structures, disrupt the mechanical connections between rock masses. During coal mining, faults in the overlying strata can disturb the original stress balance, leading to fault activation and altering the typical subsidence patterns. This can result in abnormal ground deformation and significant damage to surface structures, posing a serious geological hazard in mining areas. This study examines the influence of a known fault (F13 fault) on ground subsidence in the Wannian Mine of the Fengfeng Mining Area. We utilized 12 Sentinel-1A images and applied SBAS-InSAR, StaMPS-InSAR, and DS-InSAR time-series InSAR methods, alongside the D-InSAR method, to investigate surface deformations caused by the F13 fault. The monitoring accuracy of these methods was evaluated using leveling measurements from 28 surface movement observation stations. In addition, the density of effective monitoring points and the relative strengths and limitations of the three time-series methods were compared. The findings indicate that, in low deformation areas, DS-InSAR has a monitoring accuracy of 7.7 mm, StaMPS-InSAR has a monitoring accuracy of 16.4 mm, and SBAS-InSAR has an accuracy of 19.3 mm.
1. Introduction
China is one of the leading countries in coal mining and consumption. While the extensive extraction of coal resources has significantly contributed to rapid economic and social development, it has also led to various environmental problems [1,2,3]. These environmental issues can persist for a considerable time after coal extraction, posing ongoing threats to the local environment. Ground subsidence, a major geological hazard induced by human activities during coal mining, is one such issue. The goaf, or the void left after coal extraction, can create long-term geological hazards, significantly impacting land use in the mining areas [4]. China has a long history of coal mining, with coal reserves ranking third globally and annual mining output being the highest globally. Although the “carbon peak, carbon neutral” strategy aims to reduce coal mining output, coal will remain a dominant energy source in China for the foreseeable future [5,6]. Due to long-term, large-scale coal mining, shallow coal seams have been extensively depleted, prompting a shift toward deeper underground mining in more geologically complex areas. Faults, a common geological structure encountered in mining activities, are prevalent in coalfields. The presence of faults alters the typical patterns of mining subsidence, leading to abnormal surface deformation [7]. Moreover, mining-induced fault activation can trigger various mine disasters, such as water inrushes through faults, rock bursts, and coal and gas outbursts [8]. These events pose significant risks to the safety of underground miners. Consequently, research on faults primarily focuses on seismology, rock bursts, and the establishment of waterproof coal pillars in fault zones.
The influence of faults on mining subsidence is a crucial aspect of subsidence monitoring [9]. Traditionally, this monitoring has been conducted using leveling measurements or GPS-RTK, setting up a series of surface movement observation stations along the direction and inclination of the mining face to capture surface deformation characteristics [10]. Although these methods provide high accuracy, they are inefficient and costly and require workers to enter hazardous goaf areas, increasing safety risks. Furthermore, the limited number of observation points makes it challenging to comprehensively capture the spatial and temporal characteristics of fault-induced surface deformation, thereby complicating our understanding of fault disturbance patterns [11]. Numerical simulations and material analog models are also employed to study the impact of faults on mining subsidence, but these methods require detailed geological parameter data. By contrast, differential interferometry using spaceborne synthetic aperture radar and its derivative time-series InSAR techniques, such as SBAS-InSAR [12], PS-InSAR, StaMPS-InSAR [13], and DS-InSAR [14], offer high-precision measurements (at the millimeter level) of small surface deformations. These technologies are being increasingly applied in various fields, such as landslides [15,16,17,18,19], earthquakes [20,21], urban subsidence [22,23,24,25,26,27,28], infrastructure health monitoring [29,30], and mining subsidence [31,32,33,34,35,36]. At present, time-series InSAR technology is the mainstream technology for monitoring ground subsidence caused by coal mining, widely used for monitoring mining subsidence laws in various mining environments [37,38,39] and monitoring secondary disasters in closed mines [40]. Research using InSAR technology to investigate the effects of fault disturbances on surface deformation has primarily focused on large regional faults. For example, Yang et al. [41] conducted a detailed analysis using SBAS-InSAR technology to study fault impacts on surface deformation in the Datong Basin. Their findings indicate that ground fissures in Datong are influenced by groundwater extraction and regional fault activities, including seismic events and their interaction with ground subsidence. Similarly, Murgia et al. [23] utilized multi-frequency and multi-temporal InSAR techniques to monitor deformation in Ciudad Guzmán, Jalisco state, Mexico. Their research demonstrates that subsidence is largely driven by the exploitation of aquifers, with the spatial distribution of ground deformation controlled by the locations of underground faults.
The application of InSAR technology to monitor the abnormal distribution of mining subsidence caused by faults in mining areas is still relatively limited. For example, Diao et al. [42] employed SBAS-InSAR to study the abnormal surface deformation and building damage caused by the excavation of working face 162,601 in the Xinsan Mine of the Fengfeng Mining District. Using seven RadarSat-2 SAR images from October 2013 to March 2014, they found that the spatial distribution of surface deformation aligned with the strike of the F29 fault. This suggests that the abnormal damage to buildings in Shiqiao Village was closely related to the presence of this fault. Similarly, Qin et al. [43] employed Stacking InSAR combined with FDM-3D modeling to examine the surface deformation patterns influenced by the F0 fault during the mining activities in the Fanggezhuang coal mine.
Time-series InSAR technology is a crucial tool for monitoring abnormal deformation in mining areas. By utilizing the high-precision time-series monitoring of surface deformation through images captured at specific intervals, it is possible to analyze the spatiotemporal dynamics of abnormal deformation caused by faults. This study focuses on the Wannian Mine in the Fengfeng Mining Area and employs advanced time-series InSAR analysis techniques, such as SBAS-InSAR, StaMPS-InSAR, and DS-InSAR, to investigate the spatiotemporal process of surface deformation disturbances induced by the F13 fault. The underlying causes of “abnormal deformation” are explored through the mechanism of mining subsidence. The monitoring accuracy of these time-series methods and their effectiveness in detecting “abnormal deformation” in mining areas are assessed using on-site leveling data, providing valuable insights for “abnormal deformation” in mining environments.
2. Methods and Principles
The SBAS-InSAR method is a commonly used technique for monitoring deformation in mining areas. Although the subsidence caused by mining subsidence in mining areas does not satisfy the “linear deformation model” in a short period of time, this method can accurately acquire deformation information for areas with small subsidence levels and approximate linear deformation. StaMPS-InSAR technology is commonly used to monitor residual subsidence in mined-out areas or monitor the “activation” of old mined-out areas, fully demonstrating its strong monitoring capability for small deformations. The main role of the DS-InSAR method in monitoring deformation in mining areas is to increase the density of effective monitoring points. To better analyze the disturbance effect of faults on surface deformation caused by coal mining, three temporal InSAR techniques, namely SBAS-InSAR, StaMPS-InSAR, and DS-InSAR, were used to monitor surface deformation in the study area. Cross-validation was performed with leveling measurement results from the same period to obtain the spatiotemporal process of surface deformation caused by fault disturbances. The overall technical workflow is illustrated in Figure 1.
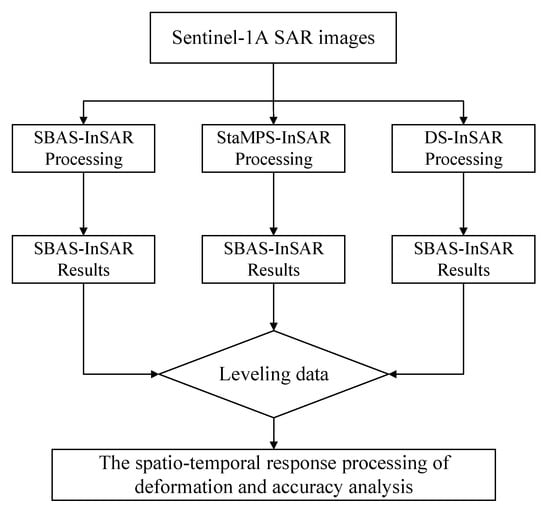
Figure 1.
Technical roadmap overview.
2.1. Principles of SBAS InSAR Technology
SBAS-InSAR technology synthesizes all available small baseline interferometric pairs simply and efficiently. It calculates the deformation rate and time-series deformation of coherent targets based on the minimum norm criterion of the deformation rate, using the SVD method. By utilizing all the acquired data within the differential small baseline set, SBAS-InSAR increases the temporal sampling rate while providing high spatial density for deformation measurements. This method is widely used in time-series InSAR analysis, particularly for urban deformation and mining applications, and has proven to deliver reliable results. The SBAS-InSAR technique was proposed by Berardino et al. [12] in 2002.
Assuming there are N + 1 (where N is an odd number) single-look complex SAR images with acquisition times t0,..., tN, the images are grouped based on a set vertical baseline threshold (for example, 300 m). Differential interferometric processing is then performed on the images within each group. The number of interferograms, K, that can be generated from these images satisfies the following condition:
For a point (x, r) on the j-th interferogram, its deformation phase is calculated by subtracting the remaining deformation phase from the two images acquired at times tA and tB, after removing the topographic phase. This can be expressed as:
In the equation above, and represent the surface deformations in the line-of-sight (LOS) direction relative to the reference time t0 at times tA and tB for the points (x, r), is the topographic residual phase, is the atmospheric phase, and represents other noise phases.
After removing the topographic residual phase and atmospheric phase from the differential interference phases, Equation (2) can be simplified as:
Assuming that the deformation rate within two adjacent time intervals is linear or approximately linear, the deformation value of the interference phase can be expressed as:
Thus, a new matrix equation can be obtained, as:
where represents the matrix of K × N. For the j-th row, the columns corresponding to the master and slave images are included, while all other columns are set to zero, . To obtain the average phase rate in the LOS direction in the sense of minimum norm, singular value decomposition must be performed on matrix B.
2.2. Principle of StaMPS-InSAR Technology
The core concept of StaMPS-InSAR technology is to identify certain targets on the ground, known as permanent scatterers, and separate the radar signals from the noise using specific spatiotemporal filtering methods [13]. This approach leverages the fact that different parts of the signal in the interferometric phase exhibit varying spatiotemporal characteristics. Consequently, StaMPS-InSAR does not require a predefined deformation model; instead, it derives surface deformation information through phase filtering and three-dimensional phase unwrapping.
The StaMPS-InSAR algorithm operates using a single reference image, with all other images registered to this reference to generate interferograms. The interferometric phase is then decomposed into four components: spatial correlation, vertical baseline correlation, temporal correlation, and noise phase:
where represents the differential interferometric phase of the target point P between the i-th and K-th images; denotes the spatially correlated phase, which includes the atmospheric phase, orbital error, spatially correlated DEM errors, and surface deformation phase; indicates the phase related to the vertical baseline, mainly due to different incident angles; signifies the time-dependent phase, which includes spatially uncorrelated surface deformation and seasonal atmospheric phase variations; and is the noise phase.
Hooper suggests that the spatial phase can be filtered out using a spatial domain low-pass filter. After removing the spatially correlated phase from the differential phase, the remaining components are minimal and primarily consist of phases related to the baseline and residual noise [13]. The non-spatially correlated parts include the deformation phase, atmospheric contribution phase, and orbit error phase, which are significantly reduced:
We defined a parameter based on the temporal coherence of pixels to assess whether a pixel qualifies as a PS point. This parameter is expressed as follows:
where γ represents the phase stability factor, N denotes the total number of differential interferograms, is the differential interferometric phase of the i-th differential interferogram, is the mean differential interferometric phase of the i-th interferogram at a given spatial scale, and represents the estimated residual phase of the terrain. By evaluating γ, it can be determined whether the point is a stable phase.
When the phase at a point is stable, the absolute deformation value must be recovered from the phase value through a process known as phase unwrapping. The StaMPS-InSAR technology utilizes a three-dimensional phase unwrapping algorithm to obtain the absolute interferometric phase [44]. After phase unwrapping, the atmospheric effect phase can be filtered out using a time high-pass filter, allowing for the extraction of the deformation phase.
2.3. Principles of DS-InSAR Technology
The core step of DS-InSAR technology involves homogeneous pixel filtering, which encompasses two main aspects: homogeneous point recognition and phase optimization. Homogeneous point recognition utilizes pixel statistical information to assess the similarity between central pixels and their neighboring pixels, selecting those that are homogeneous [45]. A commonly used method for identifying homogeneous points is hypothesis testing. The FaSHPS method applies hypothesis testing principles to convert the problem into confidence interval estimation [46]. By determining the confidence interval, the algorithm can assess the similarity between candidate points and reference points through logical operations. This approach significantly enhances the efficiency of homogeneous pixel selection while maintaining accuracy.
The principle is as follows: Given N time-series SAR images, for any DS point p to be estimated, the expected sample estimate can be expressed as . According to the central limit theorem, when N is sufficiently large, follows a Gaussian distribution, which can be expressed as:
In Formula (9), represents probability, denotes the quantile of the standard normal distribution, and indicates the true variance of point p. According to the statistical theory of SAR images, in homogeneous regions, the intensity of single-view SAR images follows a Rayleigh distribution, with a coefficient of variation, denoted as . Therefore, the equation can be simplified to an interval that only contains, expressed as:
When is known, Equation (10) yields a definite interval. In practical processing, for assumed reference pixels , the true value of is estimated as . Therefore, a point where the mean of all samples falls within this interval can be identified as a homogeneous point.
After selecting homogeneous pixels, phase optimization is crucial for accurately extracting deformation information. The distributed scatterer pixels, prior to optimization, often contain significant decoherence noise, which adversely affects the phase quality. Phase optimization relies on the principle of phase triangulation, which estimates the phase sequence of a single reference image using the interferometric phase from multiple images for each pixel. This method effectively removes coherent noise from distributed target pixels by estimating the phase related to the path length difference between the target and the sensor. A commonly used phase optimization method is maximum likelihood estimation. This approach maximizes the joint probability density of all SAR image amplitudes across multiple windows. The joint probability density function is computed from the probability density functions of all distributed target pixels within the homogeneous pixel set. The maximum likelihood estimation value serves as the optimized phase for the distributed target. The phase optimization function estimator based on the maximum likelihood estimation method is expressed by Equation (11):
where represents the sample coherence matrix estimated from all homogeneous pixel sets; denotes the interferometric phase value obtained by combining the mth and nth SAR images to form an interference; represents the interferogram between the main image and the m-th scene image; and denotes the interferogram between the main image and the nth scene image. Using Equation (11) and applying an unconstrained nonlinear optimization method, the maximum likelihood estimation value of the phase can be theoretically determined. The interferometric phase values in the sample coherence matrix represent the phase differences between each interferogram pair, reflecting the relative relationship between the unknown parameters . This estimation problem is underdetermined. In practical processing, the interference phase of the first interferogram can be set to zero (for example, by the conjugate multiplication of the main image with itself). Given the established constraints , this is equivalent to uniformly subtracting from the N-optimized phases . Consequently, the final optimized phase for distributed targets, obtained using the maximum likelihood estimation method, can be expressed as:
The optimized phase can be determined using the iterative quasi-Newton method. Once the optimized phase is acquired, the deformation rate and total deformation in the study area can be derived by constructing a triangular network and applying 3D phase unwrapping techniques.
3. Overview and Data of the Research Area
3.1. Overview of the Research Area
The Wannian Mine is situated in the Fengfeng Mining Area of Handan City, Hebei Province. The mining area extends approximately 9 km from north to south and 1–4 km from east to west, covering a total area of 21.2 km2. This region is known for its high-quality smokeless coal. The average thickness of the coal seam currently being mined is around 4 m. The mine’s designed annual production capacity is 1.8 million tons, with mining operations conducted at elevations ranging from 325 to −750 m. The specific research area of interest is near Boyan Town in Handan City. Boyan Town features flat terrain that gently slopes from south to north. The highest elevation in the area is Gu Mountain, standing at 860 m, while the lowest point is 196 m above sea level. The town is situated on an open alluvial plain at the northern base of Gu Mountain and the southern bank of a river. It is a historically significant town located at the junction of the Taihang Mountains and the eastern plain, bordered by Taihang Mountain to the west and North China Plain to the east. This strategic location serves as a vital conduit linking Shanxi, Hebei, and Henan provinces and is noted as one of the earliest important commercial towns in Wu’an City. In 2013, the town was designated as a famous historical and cultural town in China. The research area encompasses four working faces: 132,610, 132,158, 132,619, and 132,615. The 132,610 working face was mined from 2014 to 2017. Due to its distance from the F13 fault, the fault did not cause any disturbance to the surface deformation resulting from mining on this working face. The 132,158 face was mined from August 2019 to July 2020; and the 132,619 face was active from January 2020 to October 2020. Details of mining-related parameters for these working faces are provided in Table 1. As illustrated in Figure 2, there is a structural fault to the east of the 132,158 working face, which is named the F13 fault, characterized by a 100-meter drop and a dip angle of 65°. The F13 fault runs roughly parallel to the mining direction of the face and has an average burial depth of 736 me. The average mining depth at the 132,158 working face is 675 m, with a main influence angle of 59°, and it is situated on the hanging wall of the fault.

Table 1.
Parameters of the working face.
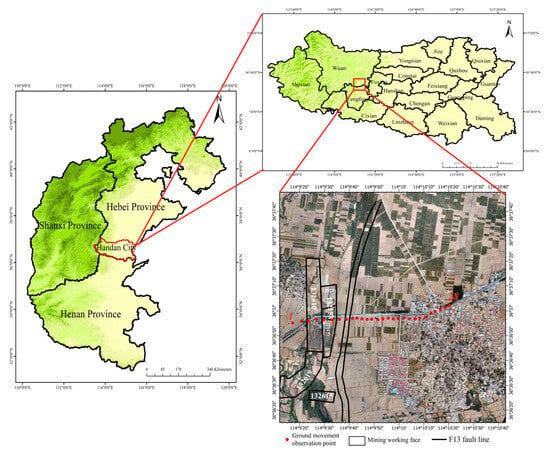
Figure 2.
Overview map of the research area.
3.2. Data Introduction
For the time-series InSAR technology processing, considering the comparison with leveling data, 12 Sentinel-1A images imaging in the two leveling measurement periods and 30-meter SRTM-DEM data were utilized. To monitor surface subsidence, 28 surface movement observation stations were established within the study area. Leveling measurements were conducted on 5 January 2020 and 3 May 2020 to obtain deformation results for these observation stations. The parameters of the Sentinel-1A images are detailed in Table 2.

Table 2.
Sentinel-1A parameters.
4. Monitoring Results and Analysis
4.1. Analysis of SBAS-InSAR Monitoring Results
SBAS-InSAR technology was employed to analyze 12 Sentinel-1a images covering the study area. To ensure a high coherence in the differential interferometry calculations, constraints were placed on the selection of a 36-day temporal baseline, and the spatial baseline was set to 5% of the critical baseline. This approach resulted in a total of 29 interferometric pairs used to calculate cumulative deformation and deformation rates. The spatiotemporal baseline configuration is depicted in Figure 3, where the longest spatial baseline is 97.8 m and the shortest is 2.35 m. The time-series deformation results derived from this process are shown in Figure 4.
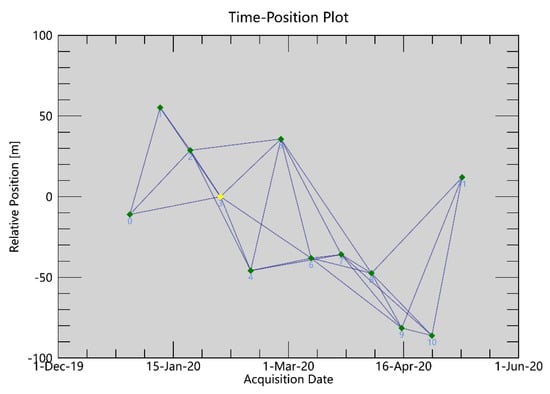
Figure 3.
Spatiotemporal baseline combination diagram. (The third image, acquired on 22 January 2020, is the super master image).
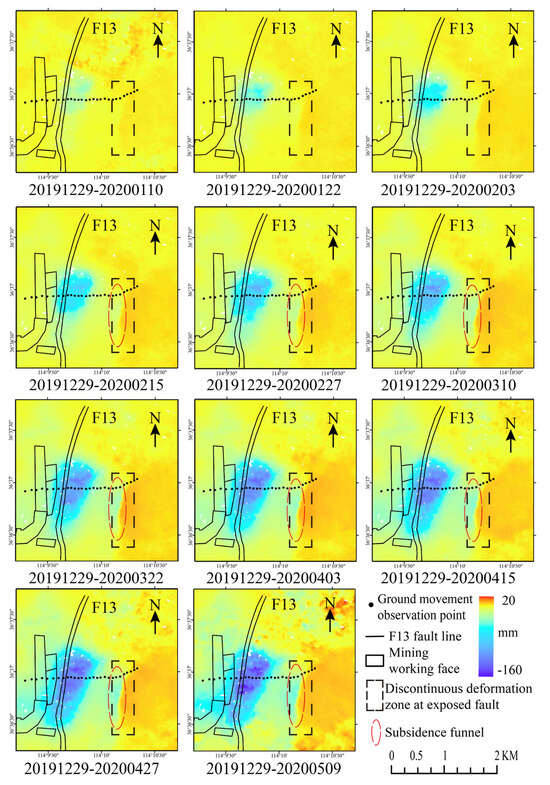
Figure 4.
SBAS−InSAR time−series deformation map.
The time-series deformation map generated by SBAS-InSAR technology reveals that, as the mining face advances, the surface deformation continually expands, clearly showing a “subsidence-uplift” boundary at the fault outcrop. In the deformation map from 29 December 2019 to 10 January 2020, the “subsidence-uplift” at the fault outcrop is noticeable. This phenomenon becomes even more pronounced in the subsequent cumulative deformation maps, indicating that the fault’s disturbance effect on the stress distribution of the overlying rock strata above the mining face was active during this period. The overlying rock strata above the mining face have not yet reached stress equilibrium, leading to ongoing surface deformation. From 19 December 2019 to 15 February 2020, a “subsidence funnel” phenomenon is observed on the west side of the fault outcrop. As the mining face continues to progress, both the deformation and its range above the mining face expand, and the “subsidence funnel” on the west side of the fault outcrop also grows. This pattern is highly consistent with the surface deformation response mechanism of mining activities on the hanging wall of a fault. Due to the significant mining depth and fault displacement of this mining face, the fault’s disturbance effects on the mining operations are prolonged.
The SBAS InSAR method is based on the principle of least squares to obtain deformation variables, while also obtaining deformation rates that reflect deformation trends. As shown in Figure 5, setting a certain transparency of the deformation rate and overlaying it with the drone image map can intuitively obtain the deformation trend of the surface rupture zone. Due to the linear model used by SBAS-INSAR in solving rates, it can achieve a high monitoring accuracy in small-scale deformation areas (approximately linear deformation) and reflect the trend of deformation in large-scale deformation areas that do not meet the linear model requirements. However, it is difficult to obtain accurate deformation variables.
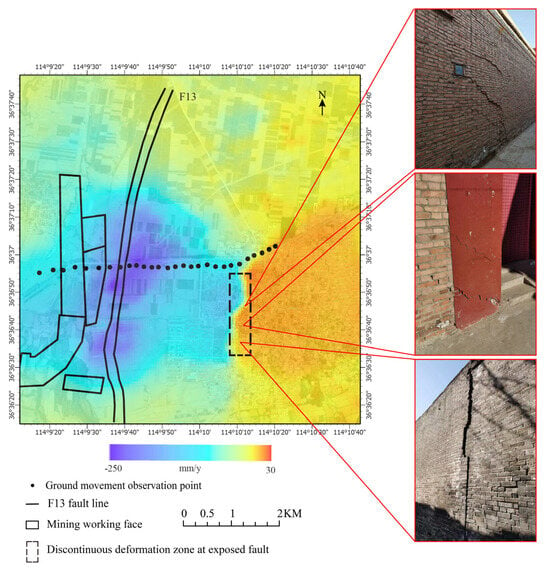
Figure 5.
SBAS−InSAR deformation rate map.
4.2. StaMPS-InSAR Results
Using the 10 March 2020 image as the reference, 12 Sentinel-1A images were processed following the StaMPS-InSAR data processing method to generate a deformation rate map of the study area, as illustrated in Figure 6.
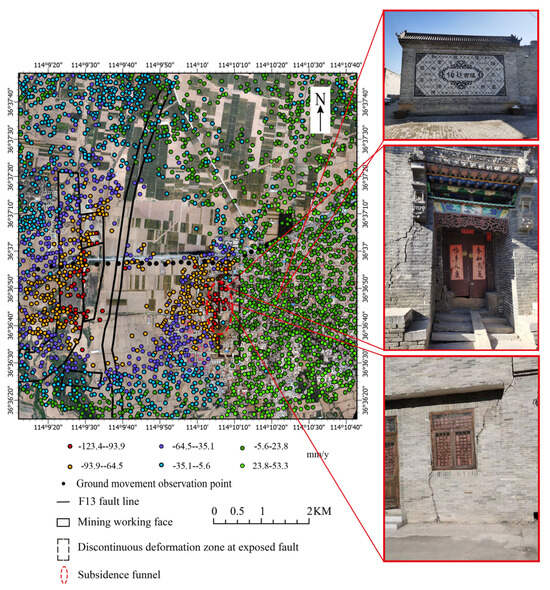
Figure 6.
Deformation rate map of the study area was obtained using the StaMPS−InSAR method.
As illustrated in Figure 6, the StaMPS-InSAR method provides a relatively sparse distribution of effective monitoring points in this area, yet it delineates the “subsidence-uplift” boundary at the fault’s surface exposure. In addition, the deformation rate distribution derived from the StaMPS-InSAR method effectively captures the “subsidence funnel” on the west side of the fault surface, which is associated with the creation of detachment space. The eastern side, directly above the mining face, is located in the farmland area. Due to significant crop coverage and considerable deformation, as indicated by SBAS-InSAR, this area experiences severe temporal and spatial-phase mismatches, resulting in a poor temporal-phase stability. Consequently, the StaMPS-InSAR method is unable to provide effective monitoring for this area, leading to a lack of deformation data. Photographs taken on-site reveal that, in the fault’s surface rupture zone, the stress redistribution induced by fault disturbance causes a “subsidence-uplift” on the surface, leading to varying degrees of damage to surface structures, including the destruction of ancient buildings in Boyan Ancient Town.
4.3. DS-InSAR Results
Using the 10 March 2020 image as the primary reference, 12 Sentinel-1A images were processed through the DS-InSAR method to generate the deformation rate map for the study area, as depicted in Figure 7.
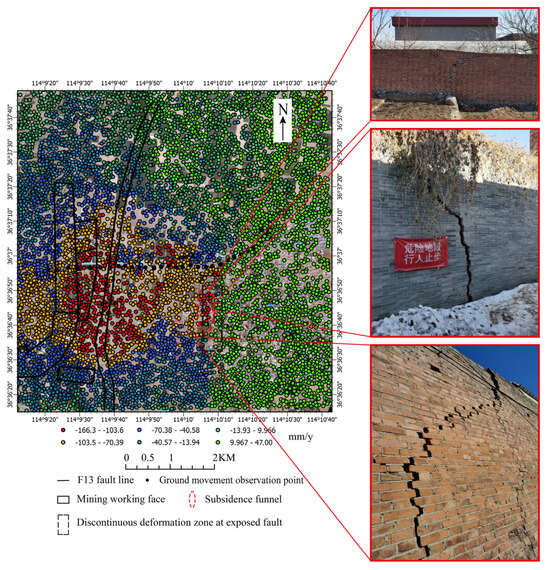
Figure 7.
The deformation rate map of the study area was obtained using the DS−InSAR method.
As depicted in Figure 7, the DS-InSAR method significantly increases the density of effective monitoring points. In addition, the DS-InSAR method effectively identifies the “subsidence-uplift” phenomenon at the exposed fault surface. The deformation rate determined by the DS-InSAR method can detect the “subsidence funnel” created by the detachment space on the west side of the fault surface outcrop. On-site photographs reveal that, in the surface rupture zone, the redistribution of geological stress due to fault disturbance has severely damaged surface structures, leading to the destruction of many houses.
4.4. Verification of Monitoring Accuracy
To verify the reliability of time-series InSAR in capturing surface deformation information, 28 surface movement observation stations were established along the dip direction. To ensure the verification effect, in the absence of time-series InSAR monitoring results at the surface movement observation station, the nearest point is searched for with a radius of 20 m from the center of the point. If no nearest point is found, the time-series InSAR monitoring results of the observation station are null. Two phases of leveling measurements were carried out to obtain surface subsidence data. For the convenience and safety of conducting leveling measurements, these observation stations were positioned along the highway. To ensure consistent comparison results, the LOS deformation measurements obtained from time-series InSAR were converted into vertical downward deformation. This conversion was based on the SAR imaging geometry relationship, taking into account the local incident angle. The conversion formula is presented in Equation (13):
In Formula (13), represents vertical deformation, represents LOS deformation, and represents the local incident angle. Figure 8 shows the analysis of leveling observation data, SBAS-InSAR monitoring data, StaMPS-InSAR monitoring data, and DS-InSAR data from the surface movement observation stations.
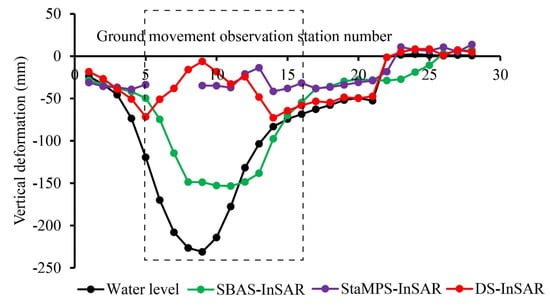
Figure 8.
Comparison of monitoring data from 28 surface movement observation stations.
In Figure 8, it is evident that the SBAS-InSAR, StaMPS-InSAR, and DS-InSAR methods all show less satisfactory monitoring results in areas with significant deformation levels (indicated by the black dashed box in Figure 8) compared to the leveling measurements. Although the SBAS-InSAR method is capable of monitoring large deformation levels, it still tends to underestimate the actual deformation. The StaMPS-InSAR method significantly underestimates deformation in areas with substantial deformation, while the DS-InSAR method, despite phase optimization, also results in a considerable underestimation of deformation. This discrepancy arises because the region experiences high levels of deformation and low image coherence, leading to phase unwrapping errors and underestimation of the deformation. The monitoring accuracy of the three methods was assessed using the leveling data from 28 surface movement observation stations. The SBAS-InSAR method has a root mean square error (RMSE) of 41.3 mm and a maximum absolute deviation (MAD) of 95.4 mm, occurring at point 6. The StaMPS-InSAR method has an RMSE of 71.2 mm and a MAD of 196.3 mm, occurring at point 9. The DS-InSAR method shows an RMSE of 87.7 mm and a MAD of 224.9 mm, also at point 9. When excluding the monitoring data from the areas of significant deformation (points 5–16), the RMSE and MAD of the three methods were evaluated. The SBAS-InSAR method exhibited an RMSE of 19.3 mm, with the maximum absolute deviation being 31.7 mm, observed at point 4. The StaMPS-InSAR method has an RMSE of 16.4 mm and a maximum absolute deviation of 34.3 mm, also occurring at point 4. The DS-InSAR method demonstrated the highest accuracy, with an RMSE of 7.7 mm and a maximum absolute deviation of 23.0 mm at point 4. A detailed comparison of the accuracy metrics for these methods is presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Comparison of monitoring accuracy of three time-series InSAR methods (in mm).
5. Discussion
5.1. Mechanism of the Influence of Faults on Surface Deformation
According to the theory of mining subsidence, extracting coal seams alters the original stress distribution near the mining face. This disturbance leads to rock movement as the system seeks a new stress equilibrium, manifesting on the surface as ground subsidence [47]. When faults are present in the rock layers near the mining face, they disrupt the original stress distribution, resulting in abnormal deformation [48]. Figure 9 illustrates the mechanism of surface deformation during mining on the hanging wall of a fault. This simulation, constructed with ideal parameters, does not account for the effects of coal seam inclination and loose layer thickness on deformation transfer. Figure 9 primarily aims to demonstrate the fault disturbance. In real scenarios, the geological parameters are more complex, and the presence of inclined coal seams and loose layers further influences deformation transfer. Consequently, the spatiotemporal dynamics of surface deformation captured by Sentinel-1A images reflect this complexity.
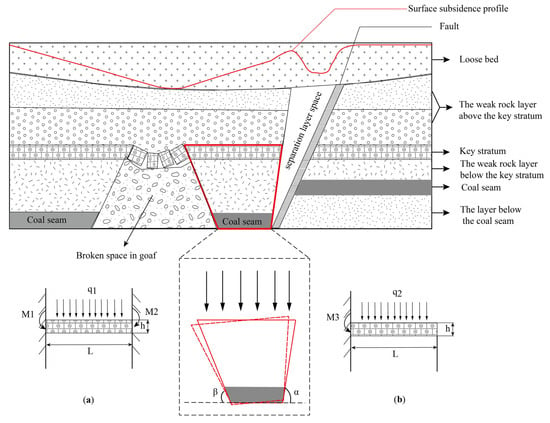
Figure 9.
Mechanism diagram of surface deformation induced by fault disturbance. (a) Mechanical model of key layer before initial fracture without fault; (b) Mechanical model of key layers before initial fracture with faults.
After coal seam mining, the overlying rock layers are categorized based on their strength into four distinct parts: the key layer, the weak rock layer beneath the key layer, the weak rock layer above the key layer, and the loose layer [49]. As the mining progresses, the extraction of coal results in pressure release through top caving. This causes the overlying rock strata to fracture and collapse behind the mining face, creating a fractured space above the goaf and establishing a roof collapse angle β. This angle is the inclination between the fracture surface and the roof layer directed toward the goaf. The roof collapse angle influences surface subsidence by shifting the inflection point of the subsidence curve toward the goaf direction, which is a significant factor in surface subsidence. When the collapse angle of the roof is less than the dip angle, α, of the fault, the weak rock layer below the key layer tends to tilt toward the goaf due to gravity and the load of the upper rock layers. The compressibility of the collapsed rock in the goaf causes the weak rock layer below the key layer to generate a detachment space on the fault plane. According to masonry beam theory, in the presence of a fault in the overlying rock layer, before the key layer fractures initially, the key layer acts as a “fixed support” at one end. The separation space created by the key layer and the lower weak rock layer triggers movement in the upper weak rock layer, leading to further separation at the fault junction [50]. This detachment space causes a change in the stress of the upper loose layer, equivalent to a goaf, resulting in the formation of a “subsidence funnel” above the detachment space. From a mechanical perspective, when the working face does not affect the fault area and the cover layer remains undamaged, the rock structure behaves as a cemented beam, as depicted in Figure 9a. Here, the rock beam bends and fractures above the goaf, with both ends providing horizontal and vertical stress constraints and transmitting bending moments. As the working face advances and the stress changes in the cover layer impact the fault plane, the mechanical strength of the weak fault plane is considerably lower than that of the cover layer. Consequently, the endpoint of the cover layer near the fault gradually transforms into a simply supported beam structure, as shown in Figure 9b. This structure is characterized by vertical displacement constraints and the ability of the beam end to rotate freely.
5.2. Analysis of Fault-Induced Disturbances on Surface Deformation
To assess the effects of mining activities on faults, a time-series differential interferogram sequence was obtained, as shown in Figure 10. Surface subsidence occurred between 29 December 2019 and 10 January 2020, due to underground mining at the 132,158 working face. During this period, the average coherence of the differential interferogram, created from two images, was 0.38 in the study area. High levels of noise in the interferogram resulted in blurred deformation boundaries, making it difficult to determine whether the fault had an impact on the deformation. From 10 January to 22 January 2020, the surface continued to subside, and the average coherence coefficient increased to 0.42. Although the noise level remained high, phase discontinuities (highlighted in the black box) were observed when the deformation reached the fault outcrop, indicating that the fault began to influence the distribution of surface deformation during this period.
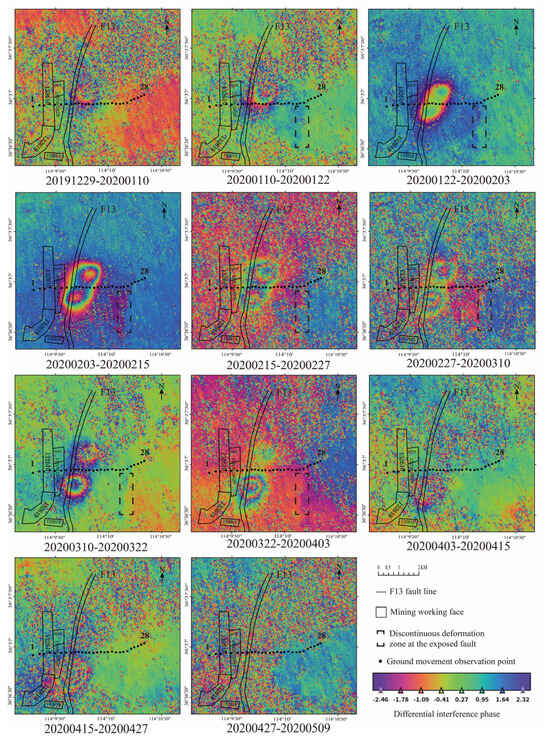
Figure 10.
Time−series differential interferometry phase map.
Between 22 January and 3 February 2020, significant surface subsidence was observed, with clear subsidence boundaries and an average coherence coefficient of 0.59. The noise level in the differential interferogram was lower, revealing distinct discontinuities in deformation at the fault outcrop. From 3 February to 15 February 2020, there was continued and significant subsidence, with the average coherence coefficient increasing to 0.63 and a low noise level. Deformation was discontinuous and intensified at the fault outcrop, forming a subsidence funnel near the fault, suggesting that a detachment space may have formed due to fault activation. From 15 February to 27 February 2020, subsidence persisted, and deformation discontinuities were evident at the exposed fault surface. The average coherence coefficient decreased to 0.39, with a noise level that made it challenging to confirm whether the fault continued to affect surface deformation.
From 27 February to 10 March 2020, the surface continued to sink, with an average coherence coefficient of 0.37 and high noise levels, yet it was still inferred that the fault influenced the distribution of surface deformation. From 10 March to 22 March 2020, substantial subsidence occurred, with an average coherence coefficient of 0.5 and moderate noise levels. Significant deformation discontinuities were observed at the exposed fault, indicating ongoing fault interference with surface deformation distribution. Between 22 March and 3 April 2020, the surface continued subsiding, with an average coherence coefficient of 0.45 and high noise levels, showing a weakening of deformation discontinuities at the fault exposure.
From 3 April to 15 April 2020, deformation continued with an average coherence coefficient of 0.42 with high noise levels in the interferogram, with no visible discontinuous signals at the fault exposure. From 15 April to 27 April 2020, subsidence continued, with an average coherence coefficient of 0.41 and high noise levels, showing no phase change signals at the fault exposure, suggesting that the disturbance effect of the fault on surface deformation had mostly ceased. From 27 April to 9 May 2020, the average coherence coefficient further decreased to 0.34, and the high noise level made it difficult to distinguish deformation phases from noise phases. The cumulative temporal deformation map obtained using the SBAS-InSAR method (Figure 4) shows continued surface deformation during this period. The three-dimensional cumulative deformation map (Figure 11) highlights a small “sinking funnel” near the surface “uplift” at the fault outcrop. This observation aligns with the theory of secondary subsidence caused by “separation space” formulation on the fault hanging wall during mining, confirming that fault disturbances during coal mining can lead to significant geological hazards and increased damage to surface structures.
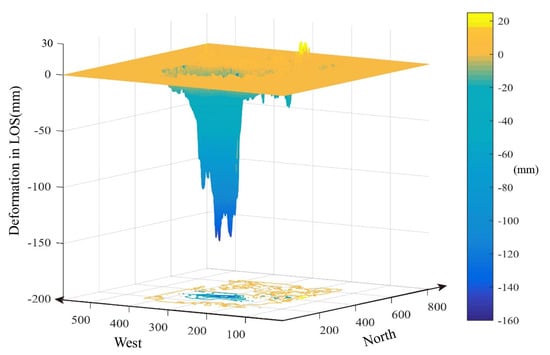
Figure 11.
Three−dimensional deformation map generated by SBAS−InSAR.
5.3. Comparison of Three Time-Series InSAR Methods
The mainstream temporal InSAR technologies, SBAS-InSAR, StaMPS-InSAR, and DS-InSAR, were used to monitor surface deformation patterns caused by mining subsidence in areas affected by fault disturbances. This analysis focused on two key aspects: monitoring accuracy and effective point density.
Measurement accuracy has been a significant concern in time-series InSAR data processing. Various approaches have been proposed to extract deformation information from differential interferometric phases. For instance, SBAS-InSAR employs SVD to address the rank efficiency in observation equations, enabling the optimal calculation of deformation rates. StaMPS-InSAR derives deformation information by applying spatiotemporal filtering to stable point phases, whereas DS-InSAR optimizes the phase of numerous distributed scatterer targets through 3D phase unwrapping to obtain deformation data.
In this study, all three methods were applied to gather surface deformation information, with the accuracy of monitoring assessed against leveling measurements from surface movement observation stations (refer to Figure 8 and Table 3). According to Figure 8, SBAS-InSAR shows the closest alignment with the leveling data. However, within the black dashed box, SBAS-InSAR tends to underestimate deformation at the center of the subsidence basin, a known issue for this method in mining subsidence monitoring. This underestimation is due to several factors: (1) high deformation gradients in extensive deformation zones exceed the unwrapping threshold of D-InSAR, leading to an underestimation of deformation; (2) low coherence in these regions results in phase unwrapping errors and phase underestimation; and (3) inherent issues with the SVD method, which sets the incremental phase delay between different baseline subsets to zero, potentially cause inaccuracies and deformation underestimation [51].
The StaMPS-InSAR method shows less agreement with leveling data in high deformation areas (indicated by the black dashed box), mainly because of large deformation gradients and severe phase decoherence, leading to errors in 3D phase unwrapping. DS-InSAR demonstrates the poorest fit in this large deformation trend opposite to the leveling measurements. This discrepancy arises from the large deformation gradient, which violates the “phase triangulation” requirement during phase optimization, leading to phase optimization errors [52]. In addition, severe decoherence significantly contributes to these errors. In areas of minor deformation, the monitoring accuracy of the three methods was validated using data from 16 surface movement monitoring stations. The DS-InSAR method achieved the highest accuracy of 7.7 mm, followed by StaMPS-InSAR at 16.4 mm, and SBAS-InSAR at 19.3 mm. The differences in accuracy can be attributed to the distinct strategies each InSAR method employs to extract deformation signals from differential interferometric phases. In areas of small-scale deformation, where phases meet the “triakis” condition, DS-InSAR can accurately optimize the phases of distributed targets, enhancing phase stability, coherence, and phase unwrapping quality, leading to precise monitoring results [53]. The StaMPS-InSAR method uses spatiotemporal filtering to differentiate between signals and noise. However, due to significant vegetation coverage and seasonal changes affecting vegetation growth, this method struggles with temporal incoherence, resulting in residual noise signals that compromise the accuracy of deformation data extraction. Finally, the SBAS-InSAR method, which combines temporal and spatial baselines, introduces more temporal decorrelation noise as the temporal baseline extends, particularly due to seasonal vegetation growth, which reduces the accuracy of deformation data extraction during the combination of an interference pair.
A higher effective monitoring point density reveals the disturbance process of faults on mining-induced subsidence. However, in practice, this density can vary significantly due to factors such as surface deformation gradients, temporal constraints, and the data processing strategies used. In this study, a coherence parameter threshold of 0.2 was chosen for SBAS-InSAR data processing, allowing the phase unwrapping of points with coherence greater than 0.2. As a result, the SBAS-InSAR method produced very few null points, and the effective monitoring point density was nearly equivalent to that of area observations. By contrast, the StaMPS-InSAR method showed a sparse effective monitoring point density in this region, particularly in areas with large deformations, where almost no effective monitoring points are available. This resulted in missing data from surface movement observation stations 6, 7, and 8 during accuracy verification. The sparse density in the StaMPS-InSAR method is mainly due to its point selection strategy.
The StaMPS-InSAR method initially employs an amplitude deviation index to preliminarily select monitoring points, followed by an iterative analysis of the temporal phase stability of these points. Only those points with stable phases over the time series are retained as effective monitoring points. In areas with significant deformation, the effective monitoring points are extremely sparse due to the combined effects of deformation gradients and temporal decoherence. By contrast, the DS-InSAR method achieved a high point monitoring density in this study because the area contained a large number of distributed scattering targets, which are also affected by deformation gradients and temporal decoherence. However, after phase optimization, the temporal phase stability of these scatterer targets was enhanced, leading to improved coherence and facilitating the acquisition of high-precision deformation data. As depicted in Figure 12, following phase optimization (Figure 12b), there is a noticeable improvement in the overall coherence, with the average coherence of the entire scene increasing from 0.45 to 0.65. Figure 12c further illustrates that, while phase optimization enhances the coherence at the ground movement observation station, the improvement is minimal in regions with significant deformation (indicated by the black box in Figure 12c). Even with the increased coherence, it remains relatively low across the entire scene.
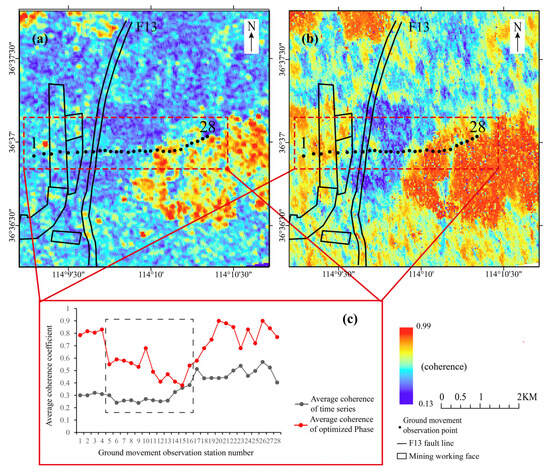
Figure 12.
Comparison of average correlation coefficients before and after phase optimization ((a) average correlation coefficient from time−series D−InSAR; (b) average correlation coefficient after phase optimization; (c) comparison of correlation coefficients before and after phase optimization for the surface movement observation stations).
The deformation rates of effective monitoring points within the sinking basin range were selected for Pearson correlation coefficient analysis, as illustrated in Figure 13. Figure 13a shows the correlation map of deformation rates obtained by the DS-InSAR and StaMPS-InSAR methods within the sinking basin. A significant number of deformation points are concentrated between −80 and 20 mm/year, with a Pearson correlation coefficient of 0.94. This high correlation indicates a strong consistency in the deformation rates derived from both StaMPS-InSAR and DS-InSAR methods, likely due to both methods employing 3D phase unwrapping technology to determine deformation.
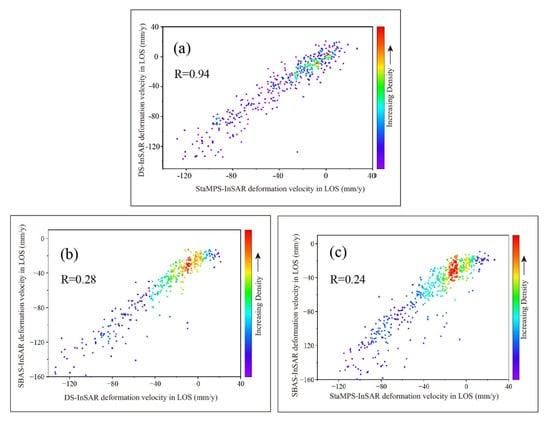
Figure 13.
Pearson correlation coefficient analysis of monitoring results in the deformation zone. ((a) Pearson correlation coefficient between DS−InSAR and StaMPS−InSAR; (b) Pearson correlation coefficient between SBAS−InSAR and DS−InSAR; (c) Pearson correlation coefficient between SBAS−InSAR and StaMPS−InSAR).
By contrast, the Pearson correlation coefficient between SBAS-InSAR and DS-InSAR is 0.28, suggesting that these two monitoring methods do not exhibit a linear relationship and that there is a substantial deviation between their results. The deformation rates determined by SBAS-InSAR are considerably higher than those from DS-InSAR, with many effective monitoring points concentrated within the −80 to 20 mm/year range. Similarly, the Pearson correlation coefficient between the SBAS-InSAR and StaMPS-InSAR deformation rates is 0.24, indicating that their monitoring results also lack a linear relationship. The deformation rates from SBAS-InSAR are notably higher than those from StaMPS-InSAR, with a large concentration of points between −80 and 20 mm/year. In the center of the subsidence basin, the deformation rate obtained by SBAS-InSAR is greater (but still an underestimation of the actual deformation), resulting in a lower Pearson correlation coefficient between SBAS-InSAR and StaMPS-InSAR as well as DS-InSAR. This further demonstrates the consistency of monitoring accuracy between StaMPS-InSAR and DS-InSAR.
6. Conclusions
The spaceborne SAR differential interferometry technology along with advanced temporal InSAR techniques such as SBAS-InSAR, StaMPS-InSAR, and DS-InSAR are widely utilized for monitoring surface subsidence in mining areas. To effectively capture the surface deformation patterns of mining subsidence under fault disturbances, combining D-InSAR with time-series InSAR technologies allows for a more comprehensive analysis. For examining surface deformation caused by the Boyan Town fault, methods including D-InSAR, SBAS-InSAR, StaMPS-InSAR, DS-InSAR, and other time-series InSAR techniques were employed. Cross-validation with leveling data from surface movement observation stations led to several key findings: (1) SBAS-InSAR technology provides a comprehensive view of surface deformation but tends to underestimate large-scale deformations at the center of subsidence basins. Its accuracy in detecting small-scale deformations is lower compared to DS-InSAR and StaMPS-InSAR. However, its primary advantage is the ability to offer a LOS deformation field that closely approximates the area; (2) The StaMPS-InSAR method effectively captures small-scale deformation with high accuracy and moderate point density; however, StaMPS-InSAR significantly underestimates large-scale deformation. Its monitoring point density is also inadequate in areas with low coherence, limiting its ability to accurately reflect subsidence basin deformation characteristics. However, it is sensitive in detecting anomalous deformation information related to surface subsidence uplift; (3) The DS-InSAR method increases the density of monitoring points significantly. However, in areas with substantial deformation, such as those in mining regions, the lack of “phase triangulation” over time can lead to incorrect deformation data post-phase optimization. Despite this, DS-InSAR is highly precise and sensitive in capturing surface deformation information, particularly in small-scale zones at the edges of subsidence basins. It has a monitoring accuracy of 7.7 mm for these areas, compared with 16.4 mm for StaMPS-InSAR and 19.3 mm for SBAS-InSAR, as verified by simultaneous leveling observations. Despite the varying levels of accuracy, all three methods effectively identify abnormal deformation areas characterized by “subsidence-uplift” at the surface exposure of faults due to fault disturbances.
Understanding the patterns of abnormal surface deformation due to mining subsidence under fault disturbances is crucial for preventing geological disasters induced by coal mining and ensuring safe production in mining areas. Given the hidden nature of small-scale faults and limited SAR satellite observation data, research in this field using time-series InSAR technology remains relatively sparse. However, recent advancements in spaceborne SAR sensors and high-quality Earth observation data have alleviated data constraints. As different temporal InSAR techniques extract deformation signals using varying strategies, it is recommended to employ multiple temporal InSAR methods to capture more detailed deformation patterns under fault disturbances. In addition, with the anticipated launch of more SAR sensors, multi-platform SAR observations will become crucial for obtaining three-dimensional deformation characteristics of the surface affected by fault disturbances.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.H. and Y.Z.; methodology, K.H. and Y.Z.; software, J.H.; validation, K.H., Z.H. and J.H.; formal analysis, Z.H.; investigation, Z.H. and J.H.; resources, K.H.; data curation, K.H.; writing—original draft preparation, K.H.; writing—review and editing, K.H. and Y.Z.; visualization, J.H.; supervision, Z.H.; project administration, Y.Z.; funding acquisition, J.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Henan Province Science and Technology Research Project, grant number 242102321173.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the European Space Agency for providing the SENTINEL-1A dataset. We also thank Hooper’s open-source software StaMPS and Jiangmi’s DSIpro for providing data processing support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Yunjia, W. Research progress and prospect on ecological disturbance monitoring in mining area. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2017, 46, 1705. [Google Scholar]
- Escayo, J.; Marzan, I.; Martí, D.; Tornos, F.; Farci, A.; Schimmel, M.; Carbonell, R.; Fernández, J. Radar Interferometry as a Monitoring Tool for an Active Mining Area Using Sentinel-1 C-Band Data, Case Study of Riotinto Mine. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Deng, K.; Fan, H.; Yan, S. An improved pixel-tracking method for monitoring mining subsidence. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 7, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Wang, E.Y.; Ma, Y.K.; Liu, Y.B.; Li, X.L. Research progress of coal and rock dynamic disasters and scientific and technological problems in China. J. China Coal Soc. 2023, 48, 1825–1845. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, H.; Ren, S.; Xie, Y.; Jiao, X. Development opportunities of the coal industry towards the goal of carbon neutrality. J. China Coal Soc. 2021, 46, 2197–2211. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Yu, H.; Bian, Z.; Yin, D. How to handle the crisis of coal industry in China under the vision of carbon neutrality. J. China Coal Soc. 2021, 46, 1808–1820. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Q. Mechanism of abnormal subsidence induced by fault slipping instability during mining on hanging-wall and foot-wall. J. Min. Saf. Eng. 2021, 38, 41–50. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Deng, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G. Different fault activation models in mining subsidence. J. China Coal Soc. 2019, 44, 2777–2786. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J.; Guo, Q.; Chen, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y. Experimental simulation study on abnormal response of surface subsidence caused by mining in footwall of reverse fault. Prog. Geophys. 2022, 37, 1280–1291. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Yang, Z.; Li, Z. Recent progress in retrieving and predicting mining-induced 3Ddisplace-ments using InSAR. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2019, 48, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, K.Z.; Chen, C.X.; Wang, T.L.; Yang, K.Y.; Zhang, C.Q. Investigation of Mining-Induced Fault Reactivation Associated with Sublevel Caving in Metal Mines. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2022, 55, 5953–5982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A.; Segall, P.; Zebker, H. Persistent scatterer interferometric synthetic aperture radar for crustal deformation analysis, with application to Volcán Alcedo, Galápagos. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2007, 112, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, N.; Lee, H.; Jung, H.C. Mathematical Framework for Phase-Triangulation Algorithms in Distributed-Scatterer Interferometry. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 1838–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Confuorto, P.; Casagli, N.; Casu, F.; De Luca, C.; Del Soldato, M.; Festa, D.; Lanari, R.; Manzo, M.; Onorato, G.; Raspini, F. Sentinel-1 P-SBAS data for the update of the state of activity of national landslide inventory maps. Landslides 2023, 20, 1083–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Dai, K.; Deng, J.; Ge, D.; Liang, R.; Li, W.; Xu, Q. Identifying potential landslides by stacking-InSAR in southwestern China and its performance comparison with SBAS-InSAR. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosi, A.; Tofani, V.; Tanteri, L.; Tacconi Stefanelli, C.; Agostini, A.; Catani, F.; Casagli, N. The new landslide inventory of Tuscany (Italy) updated with PS-InSAR: Geomorphological features and landslide distribution. Landslides 2018, 15, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frattini, P.; Crosta, G.B.; Rossini, M.; Allievi, J. Activity and kinematic behaviour of deep-seated landslides from PS-InSAR displacement rate measurements. Landslides 2018, 15, 1053–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Li, Y.; Zuo, X.; Bu, J.; Yang, F.; Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, C.; Shi, C. Image compression–based DS-InSAR method for landslide identification and monitoring of alpine canyon region: A case study of Ahai Reservoir area in Jinsha River Basin. Landslides 2024, 21, 2501–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Geng, D. Exploring the relationship between InSAR coseismic deformation and earthquake-damaged buildings. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 262, 112508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Elliott, J.R.; Craig, T.J.; Hooper, A.; Wright, T.J. Improving the resolving power of InSAR for earthquakes using time series: A case study in Iran. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL093043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.C.; Wei, M.; D Hondt, S. Subsidence in coastal cities throughout the world observed by InSAR. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL098477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murgia, F.; Bignami, C.; Brunori, C.A.; Tolomei, C.; Pizzimenti, L. Ground deformations controlled by hidden faults: Multi-frequency and multitemporal insar techniques for urban hazard monitoring. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Torres, E.A.; Cabral-Cano, E.; Novelo-Casanova, D.A.; Solano-Rojas, D.; Havazli, E.; Salazar-Tlaczani, L. Risk assessment of land subsidence and associated faulting in Mexico City using InSAR. Nat. Hazards 2022, 112, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yu, J.; Chen, B.; Wang, Y. Urban subsidence monitoring by SBAS-InSAR technique with multi-platform SAR images: A case study of Beijing Plain, China. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 53, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Doin, M.-P.; Lopez-Quiroz, P.; Tupin, F.; Fruneau, B.; Pinel, V.; Trouvé, E. Mexico City subsidence measured by InSAR time series: Joint analysis using PS and SBAS approaches. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2012, 5, 1312–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stramondo, S.; Bozzano, F.; Marra, F.; Wegmuller, U.; Cinti, F.R.; Moro, M.; Saroli, M. Subsidence induced by urbanisation in the city of Rome detected by advanced InSAR technique and geotechnical investigations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3160–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perissin, D.; Wang, T. Time-series InSAR applications over urban areas in China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2010, 4, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, G.; Hooper, A.; Wright, T.J.; Selvakumaran, S. Blind source separation for MT-InSAR analysis with structural health monitoring applications. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 7605–7618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Lin, H.; Wang, W.; Yu, H.; Chen, F.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, G.; Wang, J. Toward Fine Surveillance: A review of multitemporal interferometric synthetic aperture radar for infrastructure health monitoring. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2021, 10, 207–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modeste, G.; Doubre, C.; Masson, F. Time evolution of mining-related residual subsidence monitored over a 24-year period using InSAR in southern Alsace, France. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 102, 102392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawluszek-Filipiak, K.; Borkowski, A. Monitoring mining-induced subsidence by integrating differential radar interferometry and persistent scatterer techniques. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 54, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Q.; Wang, F.; Guo, Z.; Hu, L.; Yang, C.; Liu, T. Accuracy verification and evaluation of small baseline subset (SBAS) interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) for monitoring mining subsidence. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 54, 642–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przyłucka, M.; Kowalski, Z.; Perski, Z. Twenty years of coal mining-induced subsidence in the Upper Silesia in Poland identified using InSAR. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2022, 9, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kang, Y.; Wei, J.; Lu, Z.; Yan, W.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Lv, X.; Zhou, M.; Li, K. SAR interferometry on full scatterers: Mapping ground deformation with ultra-high density from space. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 302, 113965. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Zhu, C.; Yu, C.; Song, C.; Liu, N.; Liu, Z. A novel knowledge-learning coupling method for InSAR phase unwrapping of large surface displacements in coal mining areas. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 99, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Yang, J.; Li, Z.; Yu, C.; Yu, Y.; Qin, L.; Yang, Y.; Yu, H. A new sequential homogeneous pixel selection algorithm for distributed scatterer InSAR. GIScience Remote Sens. 2023, 60, 2218261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, B.; Li, Z.; Yu, C.; Song, C.; Guo, F. A novel phase unwrapping method for low coherence interferograms in coal mining areas based on a fully convolutional neural network. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 17, 601–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Li, Z.; Yu, C.; Fairbairn, D.; Kang, J.; Hu, J.; Liang, L. Three-dimensional time-varying large surface displacements in coal exploiting areas revealed through integration of SAR pixel offset measurements and mining subsidence model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 240, 111663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Liu, H.; Li, Z.; Zheng, M.; Yu, Y.; Yu, H.; Qin, L.; Yang, J.; Yang, Y. Research progress and prospect of secondary subsidence monitoring, prediction and stability evaluation in closed underground mines. J. China Coal Soc. 2023, 48, 943–958. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.S.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, C.Y.; Wang, Q.L.; Ji, L.Y. Monitoring land subsidence and fault deformation using the small baseline subset InSAR technique: A case study in the Datong Basin, China. J. Geodyn. 2014, 75, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, X.; Wu, K.; Chen, R.; Yang, J. Identifying the cause of abnormal building damage in mining subsidence areas using InSAR technology. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 172296–172304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Agarwal, V.; Gee, D.; Marsh, S.; Grebby, S.; Chen, Y.; Meng, N. Study of ground movement in a mining area with geological faults using FDM analysis and a stacking InSAR method. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 787053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A. A statistical-cost approach to unwrapping the phase of InSAR time series. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on ERS SAR Interferometry, Frascati, Italy, 4 December 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, M.; Ding, X.; Hanssen, R.F.; Malhotra, R.; Chang, L. Fast statistically homogeneous pixel selection for covariance matrix estimation for multitemporal InSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 53, 1213–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Guarnieri, A.M. Distributed scatterer interferometry with the refinement of spatiotemporal coherence. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 3977–3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, L.J. A review of international cases of fault reactivation during mining subsidence and fluid abstraction. Q. J. Eng. Geol. Hydrogeol. 2009, 42, 73–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.Y. Mechanism of Abnormal Surface Subsidence Induced by Fault Instability. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2021, 39, 4781–4794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, X.P.; Sun, Q.S.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, K.; Yang, J.; Lu, X.; Wang, Q.W.; Wang, J. Spatiotemporal Evolution Law and the Mechanism of Abnormal Surface Deformation in Fault-Affected Mining Zones. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 119733–119747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Deng, W.; Zou, Y. Analysis of fault separation generation and its increasing effect on mining zone. J. China Coal Soc. 2018, 43, 3286–3292. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Xu, W.; Li, Z. Review of the SBAS InSAR Time-series algorithms, applications, and challenges. Geod. Geodyn. 2022, 13, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Bian, Z.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, N.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, Y. The adaptive phase optimization algorithm for DSInSAR driven by priori information. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2024, 53, 409–420. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.L.; Yan, S.Y.; Zhao, F.; Chen, D.; Zhang, H.L. DS-InSAR Based Long-Term Deformation Pattern Analysis in the Mining Region with an Improved Phase Optimization Algorithm. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 799946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).