Monitoring Spatial-Temporal Variability of Vegetation Coverage and Its Influencing Factors in the Yellow River Source Region from 2000 to 2020
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
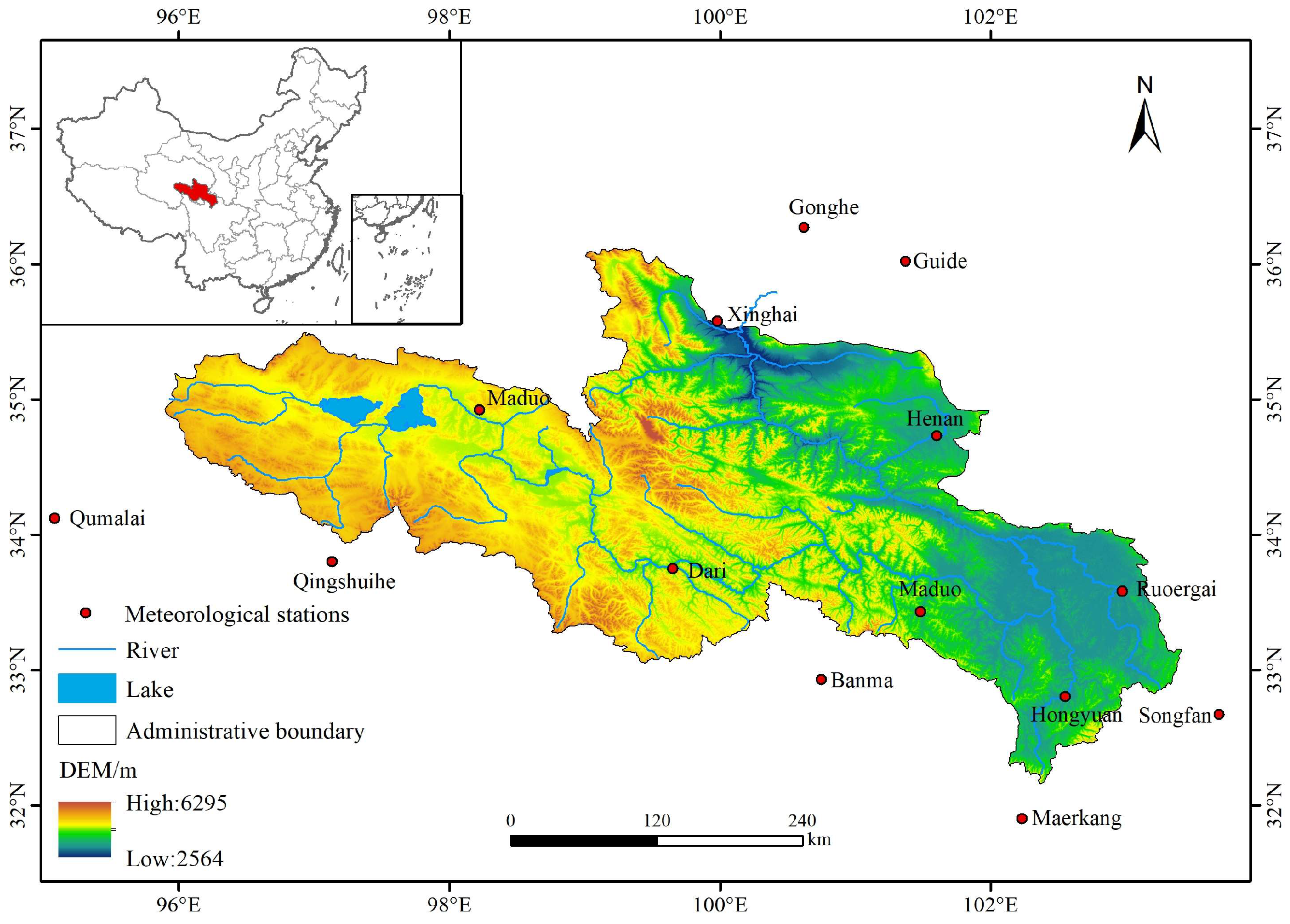
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources and Preprocessing
2.2.1. Remote Sensing Data
2.2.2. Influencing Factors Data
2.3. Data Analysis Method
2.3.1. Maximum Value Composite
2.3.2. Dimidiate Pixel Modeling
2.3.3. Theil–Sen Median Slope and Mann–Kendall Test
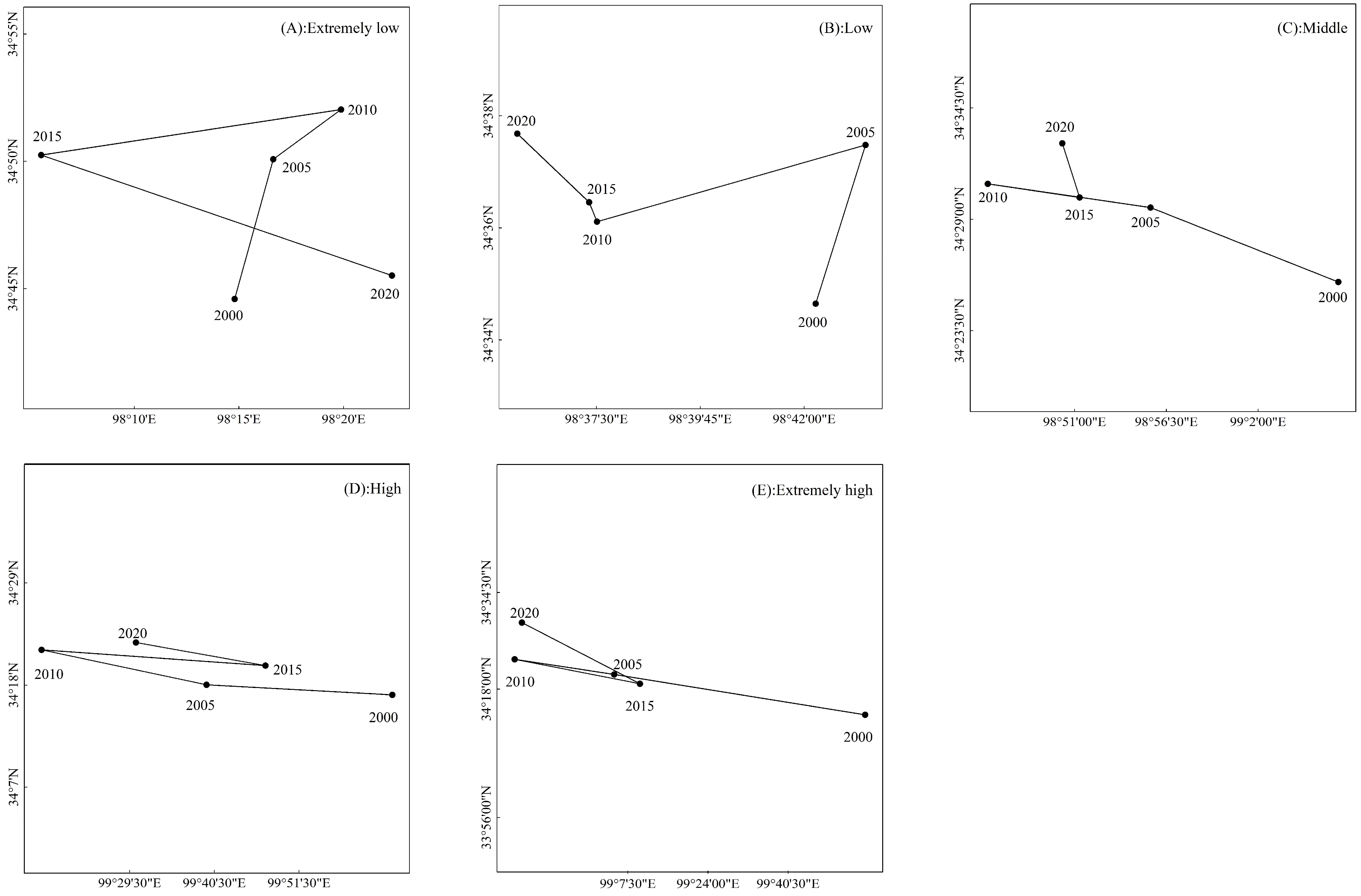
2.3.4. The Center of Gravity Migration Model
2.3.5. Geographic Detector
2.3.6. The Future Land Use Simulation Model (FLUS Model)
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Spatial-Temporal Changes of FVC in the YRSR
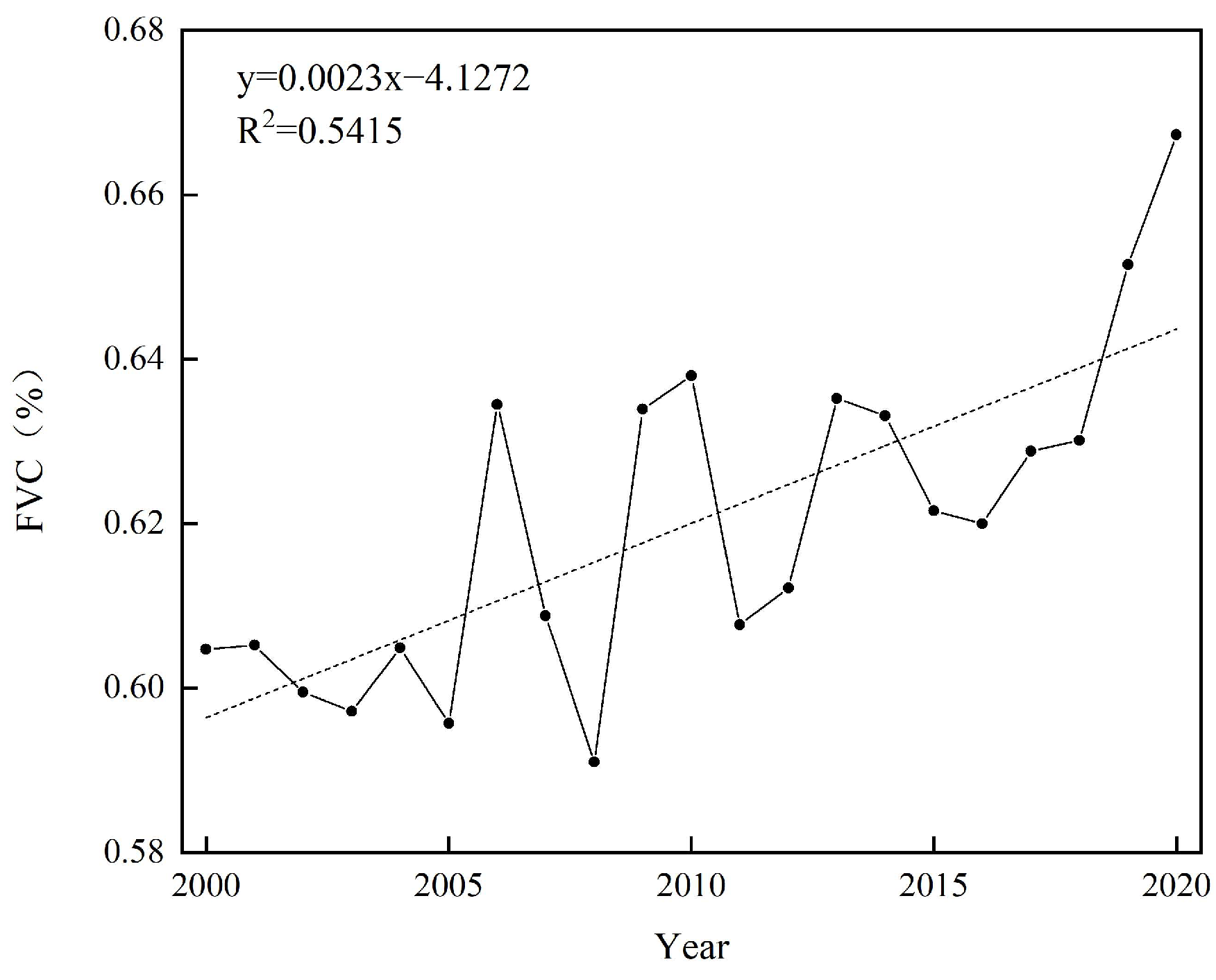
3.1.1. FVC Temporal Variation Characteristics
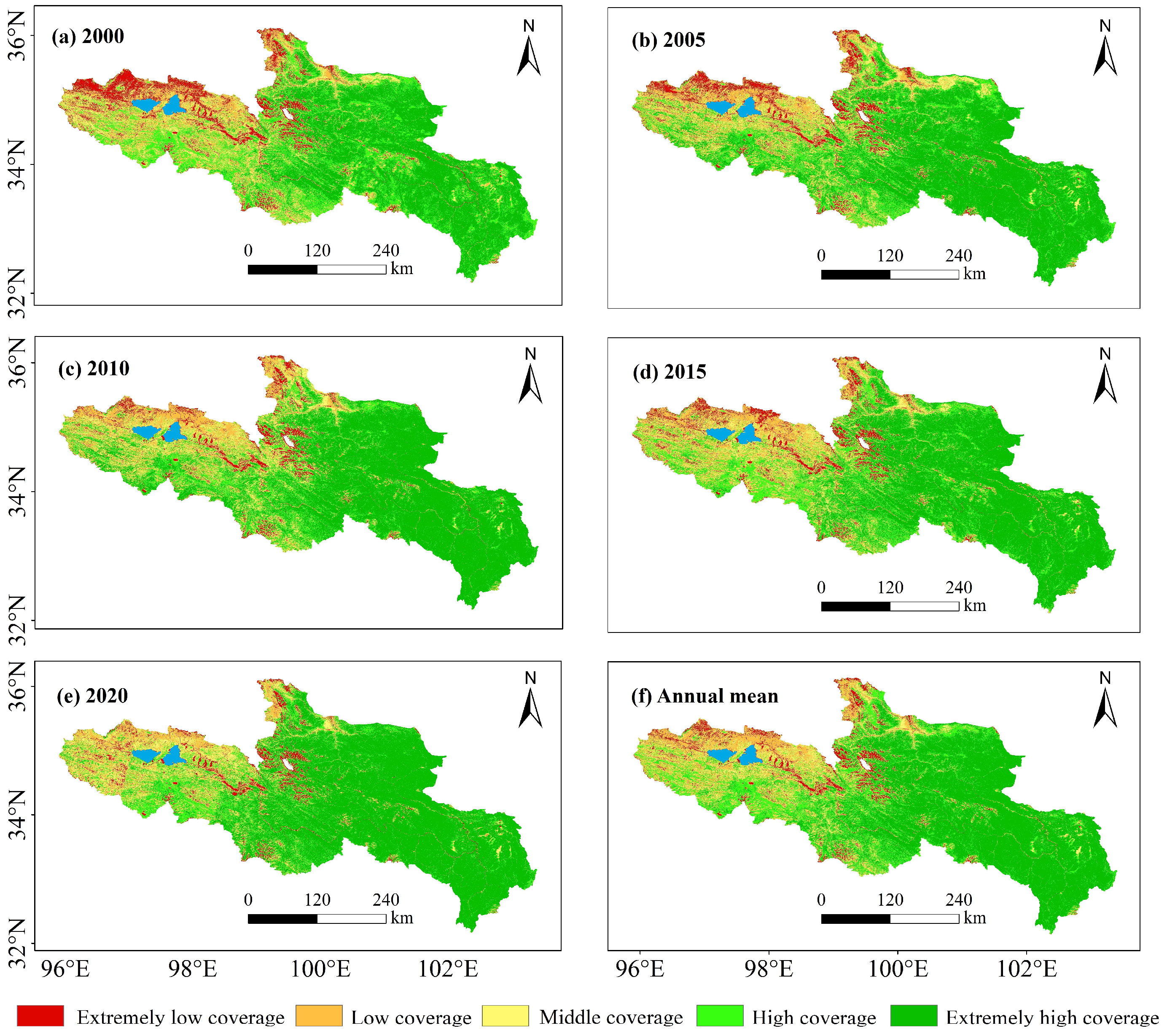
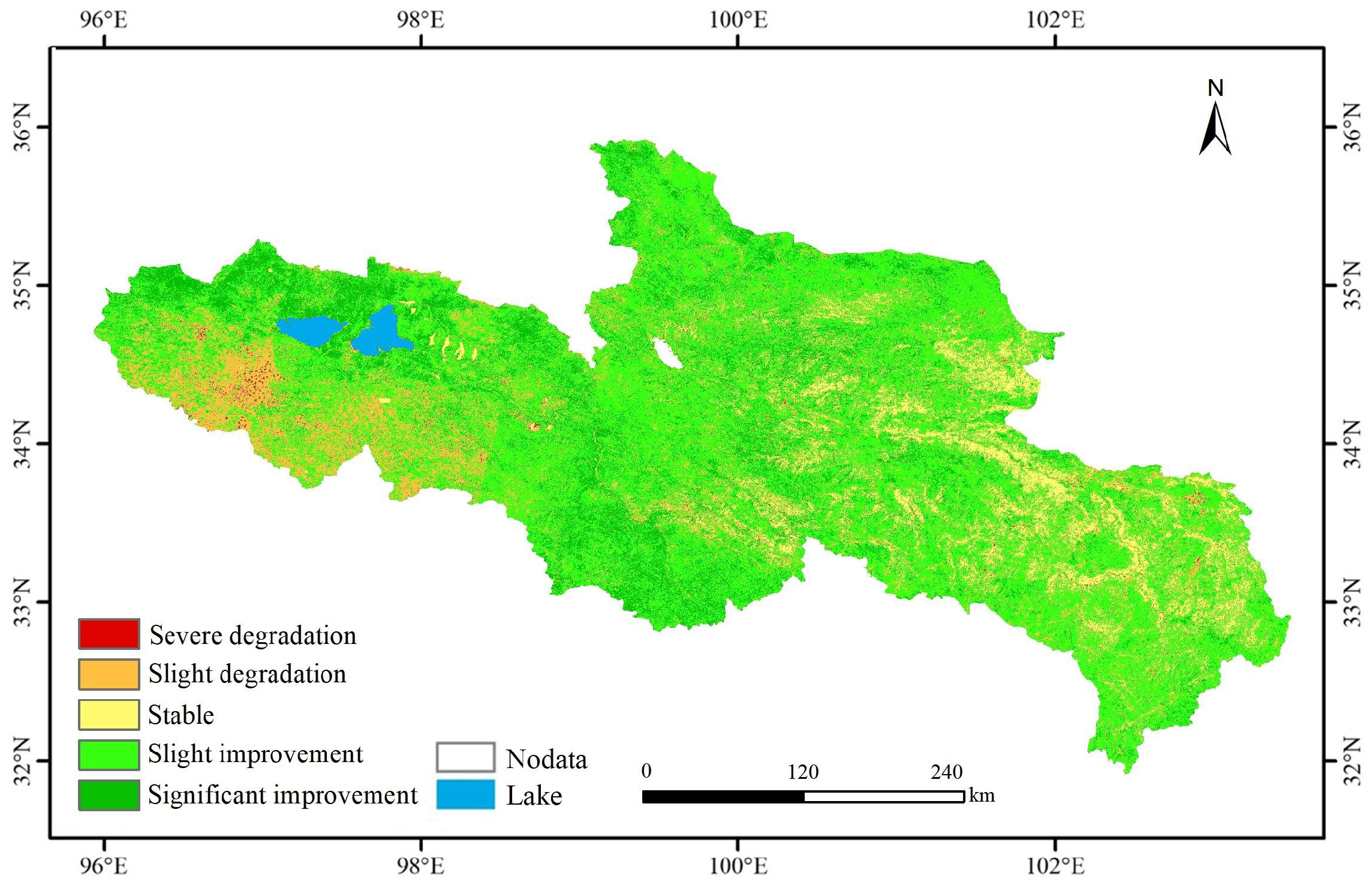
3.1.2. FVC Spatial Variation Characteristics
3.2. Driving Mechanisms of Vegetation Coverage Change in the YRSR
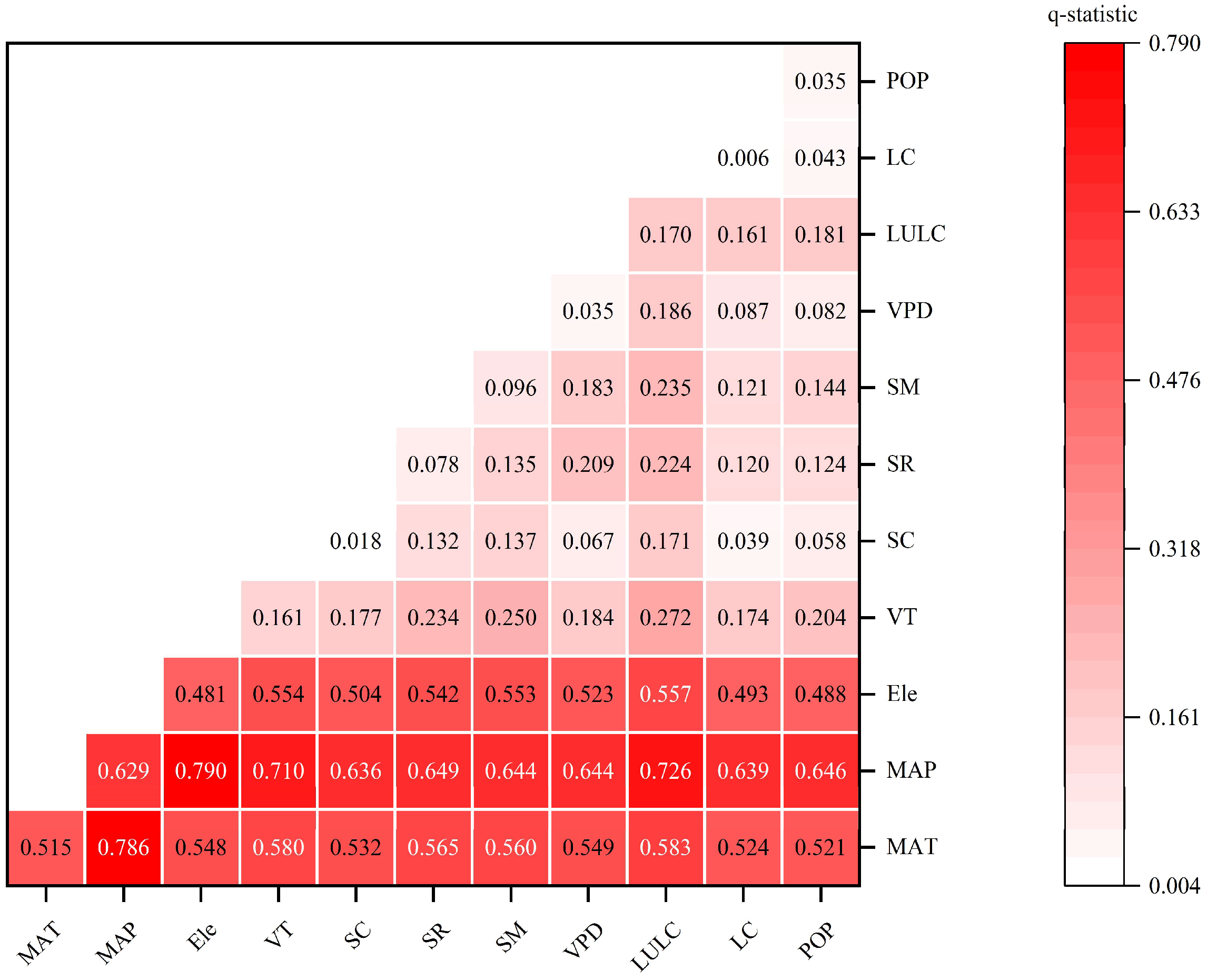
3.2.1. Influencing Factors Detection Analysis
3.2.2. Factors Interaction Detection Analysis
3.2.3. Suitable Types or Ranges of Climate Factors for Vegetation Growth
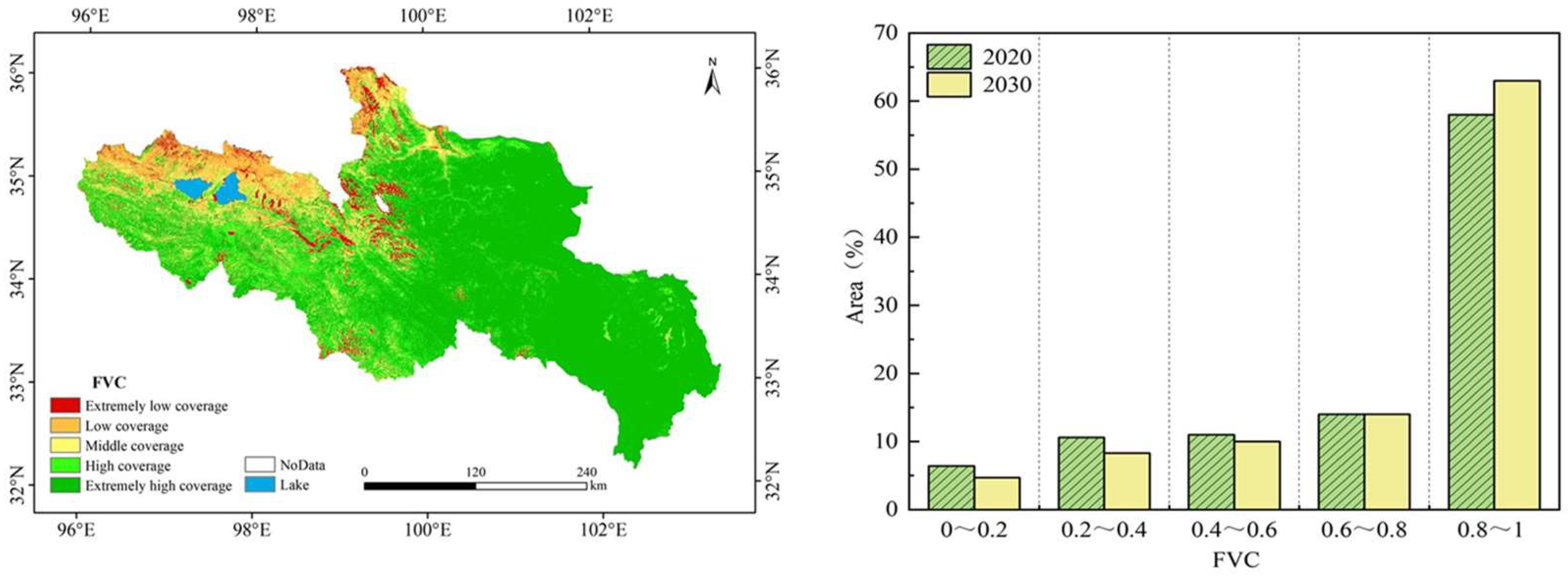
3.3. Future Trends Analysis in the YRSR
4. Discussion
4.1. Temporal and Spatial Changes in Vegetation Coverage
4.2. Impact of Influencing Factors on Vegetation Change
4.3. Future Trends of Vegetation Coverage Changes
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- In the last two decades, the average FVC in the YRSR has shown a fluctuating incline, with an annual growth rate of 0.23%. It is primarily dominated by high and extremely high vegetation coverage classes. Spatially, FVC exhibits characteristics of increased numbers in the southeast and decreased numbers in the northwest, with an overall improving trend from 2000 to 2020, particularly in the northern part of the YRSR, including Xinghai County and the southern part of Dari County.
- (2)
- This study, using the factor detector analysis, reveals that mean annual precipitation, mean annual temperature, and elevation are the key factors influencing FVC in the YRSR, with mean annual precipitation being the dominant factor. At the same time, the two-factor interactions were better at explaining the spatial distribution of FVC than the individual factors. This shows that annual rainfall plays a crucial role in changes in vegetation coverage.
- (3)
- The prediction results based on the FLUS model indicate that vegetation coverage in the YRSR will continue to increase by 2030, with the area of extremely high coverage rising by 5% compared to 2020. In contrast, the areas of extremely low, low, and medium coverage are expected to decrease. This trend suggests that the vegetation conditions in the YRSR will further improve over the next decade, particularly in the northern and northwestern areas, where the trend of vegetation recovery is notably pronounced.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, W.T.; Duveiller, G.; Wieneke, S.; Forkel, M.; Gentine, P.; Reichstein, M.; Niu, S.L.; Migliavacca, M.; Orth, R. Regulation of the global carbon and water cycles through vegetation structural and physiological dynamics. Environ. Res. Lett. 2024, 19, 073008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, J.F.; Stafford Smith, D.M.; Lambin, E.F.; Turner, B.L.; Mortimore, M.; Batterbury, S.P.J.; Downing, T.E.; Dowlatabadi, H.; Fernández, R.J.; Herrick, J.E.; et al. Global desertification: Building a science for dryland development. Science 2007, 316, 847–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Bai, J.; Feng, X.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X.; Yao, W.; Tu, Y.; Sun, Z.; Ma, J. Thresholds for ecosystem service response to changes of vegetation cover in the Qinba Mountain region. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 6811–6827. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Hao, L.; Xu, Q.; Li, J.; Chang, H. Spatio-temporal variations of vegetation coverage and its geographical factors analysis on the Loess Plateau from 2001 to 2019. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 2397–2407. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Z.; Feng, Q.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z.; Chang, Y.; Zhu, R. Vegetation coverage change and its influencing factors across the northwest region of China during 2000–2019. J. Desert Res. 2022, 42, 11–21. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, Y.; Chen, G.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Li, T. Analysis of vegetation coverage changes in Zhouqu County from 1998 to 2019 based on GEE platform. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2022, 30, 1534–1542. [Google Scholar]
- Song, M.; Chen, H.; Ding, H.; Cui, N.; Kang, G.; Wang, Y. Temporal and spatial variation characteristic and influencing factors of vegetation coverage in Tianjin during 1990–2020. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2023, 30, 154–163. [Google Scholar]
- De Keersmaecker, W.; Lhermitte, S.; Tits, L.; Honnay, O.; Somers, B.; Coppin, P. A model quantifying global vegetation resistance and resilience to short-term climate anomalies and their relationship with vegetation cover. Global Ecol. Biogeogr. 2015, 24, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulton, M.A.B.; Hesp, P.A.; da Silva, G.M.; Bouchez, C.; Lavy, M.; Fernandez, G.B. Changes in vegetation cover on the Younghusband Peninsula transgressive dunefields (Australia) 1949–2017. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2019, 44, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, R.; de Bruin, S.; de Wit, A.; Schaepman, M.E.; Dent, D.L. Analysis of monotonic greening and browning trends from global NDVI time-series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalisa, W.; Igbawua, T.; Henchiri, M.; Ali, S.; Zhang, S.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, J.H. Assessment of climate impact on vegetation dynamics over East Africa from 1982 to 2015. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y. Analysis of vegetation dynamics in the Qinling-Daba Mountains region from MODIS time series data. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 108029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Ma, J.; Li, C.; Peng, H.; Liang, J. Spatiotemporal changes of vegetation and their responses to temperature and precipitation in upper Shiyang river basin. Geogr. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2017, 60, 969–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Meng, J.; Zhu, L. Applying Geodetector to disentangle the contributions of natural and anthropogenic factors to NDVI variations in the middle reaches of the Heihe River Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Wang, X.M.; Fang, H.L.; Ye, J.S.; Han, L.K.; Gong, Y.; Cai, D.W. Vegetation coverage of desert ecosystems in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau is underestimated. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 137, 108780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Chen, L.; Lyu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Wang, F.; Song, J.; Cheng, L.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, J. Impact of vegetation change on evapotranspiration components in the Loess Plateau based on Google Earth Engine. Sci. Geogr. Sinica. 2023, 43, 1649–1658. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.X.; Zhang, X.D.; Wang, T.; Chen, G.Z.; Zhu, K.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J. Detection of vegetation coverage changes in the Yellow River Basin from 2003 to 2020. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 138, 108818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.H.; Guo, J.H.; Li, W.M.; Cai, Z.Y.; Cao, S.X. Regional differences in the factors that affect vegetation cover in China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 1961–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.D.; Zheng, C.; Liu, X.H.; Lu, Y.D.; Chen, Y.F.; Wei, Y.; Ma, Y.D. NDVI-based vegetation dynamics and their responses to climate change and human activities from 1982 to 2020: A case study in the Mu Us Sandy Land, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 137, 108745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.L.; Li, W.L.; Wang, W.Y.; Zhou, H.K.; Liang, T.G.; Hou, F.J.; Xu, J.; Xue, P.F. Quantitative spatial analysis of vegetation dynamics and potential driving factors in a typical alpine region on the north-eastern Tibetan Plateau using the Google Earth Engine. Catena 2021, 206, 105500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, H.; Dong, T.; Ma, L.; Zhu, X.; Huang, T. Variation characteristic of NDVI and its response to climate change in the Sichuan-Chongqing region. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 6743–6757. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Liu, Q.; Huang, C. Vegetation change and its response to climate extremes in the arid region of Northwest China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Zhao, D.X.; Zhang, B.E.; Zhu, Z.M.; Lu, H.Y.; Yang, C.C.; Zhao, M.W. Characteristics of spatial and temporal variations of multi-year vegetation cover in different climatic zones of China and their topographic effects. Environ. Sci. 2024, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Duan, Y.; Li, T.; Ting, T. The vegetation spatio-temporal evolution and their response to geographical environment of Qian-Gui region in 20 years. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2025, 32, 255–262. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Xie, Y.W.; Wang, X.Y.; Guo, K.M. Driving factors of recent vegetation changes in Hexi Region, Northwest China based on a new classification framework. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Dai, Q.Y.; Huang, W.T.; Pan, Y.C.; Zheng, Z.W.; Guo, Z.D. Spatio-temporal variation in vegetation cover and its driving mechanism exploration in Southwest China from 2000 to 2020. Environ. Sci. 2023, 44, 323–335. [Google Scholar]
- Piao, S.L.; Wang, X.H.; Park, T.; Chen, C.; Lian, X.; He, Y.; Bjerke, J.W.; Chen, A.P.; Ciais, P.; Tommervik, H.; et al. Characteristics, drivers and feedbacks of global greening. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.Y.; Yang, Q.K.; Yang, M.M. Spatio-temporal patterns and driving factors of vegetation change in the Pan-Third Pole region. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.X.; Li, J.; Shao, Y.; Hu, Z.Q.; Yang, Z.; Yin, S.Q.; Cui, I. Driving forces of grassland vegetation changes in Chen Barag Banner, Inner Mongolia. GIScience Remote Sens. 2020, 57, 753–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Xu, C.D. Geodetector: Principle and prospective. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.N.; Wu, Y.J.; Wang, H.Z.; Li, M.Y.; Wang, F.; Zhang, W.Y.; Ma, X.M.; Yu, X.Q. Spatial and temporal drivers of drought analysis using the geodetector in Ordos. Arid Land Res. Manag. 2024, 1–12. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/65.1095.X.20241115.1751.004 (accessed on 15 December 2024).
- Wang, D.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Tao, J.; Yang, Y.; Lin, J. Spatiotemporal evolution and attribution of vegetation coverage in the peak-cluster depression basins. China Environ. Sci. 2022, 42, 4274–4284. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, P.H.; Tian, J.; Zhang, N.; Gao, Y.S.; Feng, X.J.; Yang, C.C.; Peng, D.L. Characteristics of Spatial-Temporal Changes and Future Trends Forecast of Vegetation Cover in the Yellow River Basin from 1990 to 2022. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2024, 44, 8542–8553. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Li, C.Y.; Liu, J.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Duan, L.M. Decreased Streamflow in the Yellow River Basin, China: Climate Change or Human-Induced? Water 2017, 9, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Dong, Z.; Lu, J.; Yan, C. Spatial and Temporal Changes of Desertification Land and Its Influence Factors in the Source Region of the Yellow River from 1975 to 2005. J. Desert Res. 2011, 31, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.; Sheng, Y.; Cao, W.; Wu, J.; Hu, X.; Wang, S. Numerical Simulation of Spatial Distribution and Change of Permafrost in the Source Area of the Yellow River. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 1621–1633. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Q.; Fan, J.; Liu, J.; Huang, L.; Cao, W.; Liu, L. Target-Based Assessment on Effects of First-Stage Ecological Conservation and Restoration Project in Three-River Source Region, China and Policy Recommendations. Bull. Chinese Acad. Sci. 2017, 32, 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, J.; Fan, J. The Characteristics of Land Cover and Macroscopical Ecology Changes in the Source Region of Three Rivers on Qinghai-Tibet Plateau during the Last 30 Years. Geogr. Res. 2010, 29, 1439–1451. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Feng, J.H.; Rao, R.; He, T.; Chen, Y. Spatial-temporal changes of NDVI in Yellow River Basin and its dual response to climate change and human activities during 2000–2018. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 41, 276–286. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Q.T.; Chen, J.J.; Yang, Y.P.; Zhao, X.Y.; Zhou, G.Q.; You, H.T.; Han, X.W. Spatiotemporal variations of vegetation and its response to topography and climate in the source region of the Yellow River. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 41, 3832–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.Q.; Yang, T.B.; Dai, J.G.; Shi, L.; Lu, Z.Y. Vegetation cover changes and their relationship to climate variation in the source region of the Yellow River, China, 1990–2000. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 2085–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.P.; Gao, J.X.; Zhou, C.P.; Shi, P.L.; Zhao, L.; Shen, W.S.; Ouyang, H. Spatio-temporal changes of NDVI and its relation with climatic variables in the source regions of the Yangtze and Yellow rivers. J. Geogr. Sci. 2011, 21, 979–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Yuan, L.; Wang, W.; Cao, R.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, W. Spatio-temporal analysis of vegetation variation in the Yellow River Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 51, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Ahati, J.; Zhao, C.; Fang, S.; Liu, W.; Yin, J.; Yuan, X.; Xu, Y.; Shu, J.; He, P. Analysis of Vegetation Dynamics Using GIMMS NDVI3g in the Three-Rivers Headwater Region from 1982 to 2012. Acta Pratacult. Sin. 2016, 25, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Li, G.; Pan, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, F.; Shen, Y. Response of Vegetation Cover to Temperature and Precipitation in the Source Region of the Yellow River. Resour. Sci. 2015, 12, 512–521. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Bai, W.; Shen, Z.; Yan, J.; Ding, M.; Li, S.; Zheng, D. Grassland Degradation in the Source Region of the Yellow River. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2006, 61, 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, S.H.; Wan, L.; Li, Z.M.; Cao, W.B. Effects of Frozen Soil on Vegetation in the Source Region of the Yellow River. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2007, 29, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Si, J.H.; Li, J.M.; Yang, Y.; Qi, X.J.; Li, J.J.; Liu, Z.H.; Li, M.Y.; Lu, S.J.; Qi, Y.; Jin, C.; et al. Evaluation and Prediction of Groundwater Quality in the Source Region of the Yellow River. Water 2022, 14, 3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Song, Q.; Zhao, J.; Ding, Y. Changes in Ecological Land Patterns and Divergence Trends in the Yellow River Source Area from 2005 to 2020. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 42, 277–284. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, T.B.; Zhu, X.; Yi, G.H.; Li, J.J.; Bie, X.J.; Hu, J.; Liu, X. Quantitatively analyzing the driving factors of vegetation change in China: Climate change and human activities. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 82, 102667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Tan, S.; Li, Y.; Wu, H.; Wu, R. Quantitative analysis of fractional vegetation cover in southern Sichuan urban agglomeration using optimal parameter geographic detector model, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N. Characteristics of Maximum-Value Composite Images from Temporal AVHRR Data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1986, 7, 1417–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Zhang, J.; Shen, X.; Liu, B.; Lu, X.; Jiang, M. Impacts of climate change on fractional vegetation coverage of temperate grasslands in China from 1982 to 2015. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 350, 119694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Li, T.; Wang, K.; Sun, M.; Yu, C.; Yang, F.; Yang, L.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, K. Analysis of the Influence Mechanism of Spatial and Temporal Differences in Fraction Vegetation Coverage in the Guanyinyan Reservoir Area of the Jinsha River. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2024, 33, 997–1007. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, R.F.; Li, Q.B.; Ren, J. Study on the Characteristics of Changes in Vegetation Cover and Its Driving Forces in Typical Provinces in the Three-North Shelterbelt Program Regions: Taking Ningxia as Example. Arid Zone Res. 2024, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Ma, J.; Tang, Y.; Li, W. Spatio-temporal dynamics and attribution analysis of vegetation in Gansu Province. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2024, 33, 1163–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.R.; Guan, Q.Y.; Sun, Y.F.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L.Q.; Yang, E.Q.; Li, H.C.; Du, Q.Q. Three-dimensional dynamic characteristics of vegetation and its response to climatic factors in the Qilian Mountains. Catena 2022, 208, 105694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, P.; Geng, M.; Wang, M.; Lu, J. The Key Driving Factors of Land Use Spatio-Temporal Change and Its Influence Trend—A Case Study of Wuwei. China Environ. Sci. 2023, 43, 6583–6591. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, D.; Abdirahman, H.; Wang, D.; Tian, S. Spatio-Temporal Variations in Vegetation Cover in Hotan Oasis from 1994 to 2016. Acta Ecologica Sin. 2019, 39, 3710–3719. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Samat, A.; Abuduwaili, J. Geo-Detector Based Spatio-Temporal Variation Characteristics and Driving Factors Analysis of NDVI in Central Asia. Remote Sens. Land Res. 2019, 31, 32–40. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.F.; Haining, R.; Liu, T.J.; Li, L.F.; Jiang, C.S. Sandwich Estimation for Multi-Unit Reporting on a Stratified Heterogeneous Surface. Environ. Plan. A 2013, 45, 2515–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Li, Z.; Lin, J.; Wang, H.; Zheng, S.; Yang, S. Assessing current and future soil erosion under changing land use based on InVEST and FLUS models in the Yihe River Basin, North China. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2024, 12, 298–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congalton, R.G. A review of assessing the accuracy of classifications of remotely sensed data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1991, 37, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ma, B.; Li, D.; Chen, K.; Yao, H. Multi-Scenario Simulation and Prediction of Ecological Space in Hubei Province Based on FLUS Model. J. Nat. Resour. 2019, 35, 230–242. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Qin, T.L.; Yan, D.H.; Lv, X.Z.; Yuan, Z.; Wen, J.; Xu, S.; Yang, Y.H.; Feng, J.M.; Li, W. Response of Vegetation to Drought in the Source Region of the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers Based on Causal Analysis. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.G.; Tian, Z.H.; Wei, H.T.; Liu, Y.; Yu, Y.P. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Mechanisms of Vegetation in the Yellow River Basin, China during 2000–2020. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 138, 108832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.J.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, B.F.; Lyu, J.W.; Zheng, F.M.; Xu, W.; Gan, X.B. Variations of runoff and sediment and their response to human activities in the source region of the Yellow River, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jin, X. Vegetation dynamics and responses to climate change and anthropogenic activities in the Three-River Headwaters Region, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 131, 108223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Song, K.; Hu, L. China’s largest scale ecological migration in the three-river headwater region. Ambio 2010, 39, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, G.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z. Analysis of the spatiotemporal variation of critical vegetation coverage for soil and water conservation and windproof sand fixation functions in the Sanjiangyuan region. J. Mtn. Sci. 2024, 42, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Liang, X.; Yan, C.; Xing, X.; Jia, H.; Wei, X.; Feng, K. Vegetation dynamic changes and their response to ecological engineering in the Sanjiangyuan Region of China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Song, H.M.; An, Z.S.; Sun, C.F.; Trouet, V.; Cai, Q.F.; Liu, R.S.; Leavitt, S.W.; Song, Y.; Li, Q.; et al. Recent anthropogenic curtailing of Yellow River runoff and sediment load is unprecedented over the past 500 y. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 18251–18257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Ren, X.; Hu, H.; Liu, M.; Meng, Q. Vegetation Dynamics and Its Driving Force in Otindag Sandy Land Based on Geodetector. J. Desert Res. 2019, 41, 195–204. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.Q.; Wang, G.J.; Liang, S.H.; Du, H.; Peng, H.M. Extraction and Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Vegetation Coverage from 1996 to 2015 in the Source Region of the Yellow River. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2021, 43, 662–674. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, Y.H.; Hu, J.; Sun, F.X.; Zhang, L.W. Water Retention and Hydrological Regulation: Harmony but Not the Same in Terrestrial Hydrological Ecosystem Services. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 5191–5196. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Su, X.Q.; Li, L.; Yu, B.; Chen, X.; Luo, Z.B.; Chu, W.Y.; Zhang, W.T. Forecasting Future Vegetation Dynamics under SSP/RCP Pathways under Spatially Changing Climate and Human Activities Conditions. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.X.; Chang, J.; Xu, C.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, Y.H.; Chen, X.; Jiang, S.S.; Duan, Z. The Response of Lake Area and Vegetation Cover Variations to Climate Change over the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau during the Past 30 Years. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, D.L.; Zhang, Y.T.; Qin, D.H.; Li, S.C. Elevation-Dependent Decline in Vegetation Greening Rate Driven by Increasing Dryness Based on Three Satellite NDVI Datasets on the Tibetan Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 107, 105569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.J.; Cheng, L.R.; Ding, A.Z.; Yuan, Y.M.; Li, Z.Y.; Hou, Y.Z.; Ren, L.S.; Zhang, S.R. Geodetector model-based quantitative analysis of vegetation change characteristics and driving forces: A case study in the Yongding River basin in China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 132, 104027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ren, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Zhao, L.; He, H.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, M.; Zeng, N.; Gao, C. Spatio-Temporal Variation of Net Primary Productivity in Three-River-Source National Park Using a Multi-Model Integration Method. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 3084–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, K.; Gao, J.; Liu, Z. Precipitation drives the NDVI distribution on the Tibetan Plateau while high warming rates may intensify its ecological droughts. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Q.L.; Chen, X.Q.; He, X.H.; Tian, Z.H. Vegetation Dynamics and Its Response to Climate Change and Human Activities Based on Different Vegetation Types in China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 3557–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.C.; Fu, R.Y.; Guo, X.W.; Du, Y.G.; Zhang, F.W.; Cao, G.M. Soil moisture variations in response to precipitation across different vegetation types on the Northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 854152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, H.R.; Zhai, J.Q.; Ma, M.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ling, M.H.; Wang, Q.M. Temporal and Spatial Variation of Vegetation Coverage and Its Driving Forces During the Growing Season in Haihe River Basin. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2023, 30, 309–317. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X.Y.; Gao, X.; Li, S.Y.; Lei, J.Q. Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of Vegetation NDVI Changes and the Driving Forces in Mongolia During 1982–2015. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Ren, X.; Fan, L.; He, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Zeng, N.; Chen, X. Assessing the vegetation dynamics and its influencing factors in Central Asia from 2001 to 2020. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; He, B.; Wang, Y.-P.; Chen, H.W.; Chen, D.; Fu, Y.H.; Chen, Y.N.; Guo, L.; Deng, Y.; Huang, L.; et al. Disentangling the effects of vapor pressure deficit on northern terrestrial vegetation productivity. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadf3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Q.; Yang, K.; Li, H.H.; Ai, L.Y.; Wang, C.H.; Wu, T.H. Negative impacts of the withered grass stems on winter snow cover over the Tibetan Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2024, 352, 110053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.F.; Li, Y.H.; He, K.N.; Wen, Y.S. Temporal and Spatial Variation Characteristics of Vegetation Coverage and Quantitative Analysis of Its Potential Driving Forces in the Qilian Mountains, China, 2000–2020. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 143, 109429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Zhou, Z.F.; Wu, X.P.; Liu, R.P.; Zheng, J.J.; Wang, J.L.; Wan, J.X. Response of Vegetation Carbon Sequestration Potential to the Effectiveness of Vegetation Restoration in Karst Ecologically Fragile Areas in Guizhou, Southwest China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.-N.; Feng, Z.-D. Analysis of cause mechanism of desertification in headwater area of Yellow River. J. Nat. Disasters 2009, 18, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.H.; Cheng, L.; Li, M.C.; Zhao, R.F.; Duan, Y.W. Impacts of LUCC on soil properties in the riparian zones of desert oasis with remote sensing data: A case study of the middle Heihe River basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 506, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Gao, H.J.; Zeng, G. Landscape Pattern Change of Sandy Desertification Land in the Source Region of the Yellow River During the Past 45 Years. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2021, 35, 79–85. [Google Scholar]


| Influencing Factors | Abridge | Units |
|---|---|---|
| Mean annual temperature | MAT | °C |
| Mean annual precipitation | MAP | mm |
| Elevation | Ele | m |
| Vegetation type | VT | / |
| Snow cover | SC | % |
| Solar radiation | SR | MJ/m2 |
| Soil moisture | SM | cm·cm−3 |
| Vapor pressure deficit | VPD | kPa |
| Land use and land cover | LULC | / |
| Livestock capacity | LC | MU/km2 |
| Density of population | POP | person/km2 |
| Description | Interaction |
|---|---|
| q(X1∩X2) < Min(q(X1), q(X2)) | Weaken, nonlinear |
| Min(q(X1), q(X2)) < q(X1∩X2) < Max(q(X1), q(X2)) | Weaken, univariate |
| q(X1∩X2) > Max(q(X1), q(X2)) | Enhance, bivariate |
| q(X1∩X2) = q(X1) + q(X2) | Independent |
| q(X1∩X2) > q(X1) + q(X2) | Enhance, nonlinear |
| Level | Extremely Low Coverage | Low Coverage | Middle Coverage | High Coverage | Extremely High Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Domain Weight | 0.3 | 0.01 | 0.25 | 0.22 | 1 |
| Influencing Factors | MAT | MAP | Ele | VT | SC | SR | SM | VPD | LULC | LC | POP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| q-statistic | 0.515 | 0.629 | 0.481 | 0.161 | 0.018 | 0.078 | 0.096 | 0.035 | 0.170 | 0.006 | 0.035 |
| significance | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Two-Factor Interactions | Interaction Relationships | Two-Factor Interactions | Interaction Relationships |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAT ∩ MAP | B | VT ∩ SC | B |
| MAT ∩ Ele | B | VT ∩ SR | B |
| MAT ∩ VT | B | VT ∩ SM | B |
| MAT ∩ SC | B | VT ∩ VPD | B |
| MAT ∩ SR | B | VT ∩ LULC | B |
| MAT ∩ SM | B | VT ∩ LC | B |
| MAT ∩ VPD | B | VT ∩ POP | N |
| MAT ∩ LULC | B | SC ∩ SR | N |
| MAT ∩ LC | N | SC ∩ SM | N |
| MAT ∩ POP | B | SC ∩ VPD | N |
| MAP ∩ Ele | B | SC ∩ LULC | N |
| MAP ∩ VT | B | SC ∩ LC | N |
| MAP ∩ SC | B | SC ∩ POP | N |
| MAP ∩ SR | B | SR ∩ SM | B |
| MAP ∩ SM | B | SR ∩ VPD | N |
| MAP ∩ VPD | B | SR ∩ LULC | B |
| MAP ∩ LULC | B | SR ∩ LC | N |
| MAP ∩ LC | N | SR ∩ POP | N |
| MAP ∩ POP | B | SM ∩ VPD | N |
| Ele ∩ VT | B | SM ∩ LULC | N |
| Ele ∩ SC | N | SM ∩ LC | N |
| Ele ∩ SR | B | SM ∩ POP | N |
| Ele ∩ SM | B | VPD ∩ LULC | N |
| Ele ∩ VPD | N | VPD ∩ LC | N |
| Ele ∩ LULC | B | VPD ∩ POP | N |
| Ele ∩ LC | N | LULC ∩ LC | B |
| Ele ∩ POP | B | LULC ∩ POP | N |
| LC ∩ POP | N |
| Climate Indicators | Optimal Ranges | FVC | Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean annual temperature | 2.21–3.91 | 0.94 | °C |
| Mean annual precipitation | 836–964 | 0.95 | Mm |
| Snow cover | 25.42–32 | 0.80 | % |
| Solar radiation | 227–243 | 0.89 | MJ/m2 |
| Soil moisture | 0.25–0.30 | 0.90 | cm·cm−3 |
| Vapor pressure deficit | 0.12–0.15 | 0.81 | kPa |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, B.; Si, J.; Jia, B.; He, X.; Zhou, D.; Zhu, X.; Liu, Z.; Ndayambaza, B.; Bai, X. Monitoring Spatial-Temporal Variability of Vegetation Coverage and Its Influencing Factors in the Yellow River Source Region from 2000 to 2020. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4772. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16244772
Wang B, Si J, Jia B, He X, Zhou D, Zhu X, Liu Z, Ndayambaza B, Bai X. Monitoring Spatial-Temporal Variability of Vegetation Coverage and Its Influencing Factors in the Yellow River Source Region from 2000 to 2020. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(24):4772. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16244772
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Boyang, Jianhua Si, Bing Jia, Xiaohui He, Dongmeng Zhou, Xinglin Zhu, Zijin Liu, Boniface Ndayambaza, and Xue Bai. 2024. "Monitoring Spatial-Temporal Variability of Vegetation Coverage and Its Influencing Factors in the Yellow River Source Region from 2000 to 2020" Remote Sensing 16, no. 24: 4772. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16244772
APA StyleWang, B., Si, J., Jia, B., He, X., Zhou, D., Zhu, X., Liu, Z., Ndayambaza, B., & Bai, X. (2024). Monitoring Spatial-Temporal Variability of Vegetation Coverage and Its Influencing Factors in the Yellow River Source Region from 2000 to 2020. Remote Sensing, 16(24), 4772. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16244772







