Abstract
A novel Portable L-band radiometer (PoLRa), compatible with tower-, vehicle- and drone-based platforms, can provide gridded soil moisture estimations from a few meters to several hundred meters yet its retrieval accuracy has rarely been examined. This study aims to provide an initial assessment of the performance of PoLRa-derived soil moisture at a spatial resolution of approximately 0.7 m × 0.7 m at a set of sampling pixels in central Illinois, USA. This preliminary evaluation focuses on (1) the consistency of PoLRa-measured brightness temperatures from different viewing directions over the same area and (2) whether PoLRa-derived soil moisture retrievals are within an acceptable accuracy range. As PoLRa shares many aspects of the L-band radiometer onboard NASA’s Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) mission, two SMAP operational algorithms and the conventional dual-channel algorithm (DCA) were applied to calculate volumetric soil moisture from the measured brightness temperatures. The vertically polarized brightness temperatures from the PoLRa are typically more stable than their horizontally polarized counterparts across all four directions. In each test period, the standard deviations of observed dual-polarization brightness temperatures are generally less than 5 K. By comparing PoLRa-based soil moisture retrievals against the simultaneous moisture values obtained by a handheld capacitance probe, the unbiased root mean square error (ubRMSE) and the Pearson correlation coefficient (R) are mostly below 0.05 m3/m3 and above 0.7 for various algorithms adopted here. While SMAP models and the DCA algorithm can derive soil moisture from PoLRa observations, no single algorithm consistently outperforms the others. These findings highlight the significant potential of ground- or drone-based PoLRa measurements as a standalone reference for the calibration and validation of spaceborne L-band synthetic aperture radars and radiometers. The accuracy of PoLRa-yielded high-resolution soil moisture can be further improved via standardized operational procedures and appropriate tau-omega parameters.
1. Introduction
Accurate quantification and temporal monitoring of the varied soil water content of the land surface are important across multiple disciplines, including agricultural production, natural disaster predictions, plant responses to climate warming, land–atmosphere interactions, and weather forecasts [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]. Microwave remote sensing has emerged as an efficient and cost-effective means for estimating spatial soil moisture (SM) on a large scale [9,10,11]. Compared to optical and infrared sensors, microwave sensors are preferred for SM mapping partly due to their subsurface sensitivity and their resistance to cloud interference [12]. More importantly, the reflective and emissive properties of surfaces at microwave frequencies are closely correlated with the dielectric constant of the targeted medium, primarily being influenced by the water content within it [9,13].
In recent decades, both active and passive microwave sensors on various platforms have been extensively applied to monitor SM variations at different scales, particularly by spaceborne L-band microwave radiometers [14,15,16,17,18,19]. Compared to X-band (10 GHz) and C-band (6 GHz) radiometers, L-band frequencies can sense soil emissions originating from deeper in the soil (typically 5 cm) while experiencing less attenuation when passing through sparse to moderately dense vegetation [15]. In contrast, X- and C-band emissions primarily originate from the top 1 cm or less of the soil and are significantly attenuated even under low biomass conditions [15]. Within the L-band, radar-derived SM retrievals often exhibit relatively lower accuracy, as active sensors are more susceptible to surface roughness and vegetation scattering [15]. Hence, L-band radiometers are recognized as the optimal choice for SM observations, offering a balance between retrieval accuracy and vegetation effects. Numerous validation studies have further demonstrated the great performance of surface SM products from spaceborne missions relying on L-band radiometers, such as the Soil Moisture Ocean Salinity (SMOS) and Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) missions, across diverse surface and climatic conditions [20,21,22,23]. These data sets have been widely applied in research in multiple disciplines, enhancing our understanding of water and carbon cycles, drought dynamics and drivers, as well as climate change at the synoptic scale [24,25].
To maintain the high quality of SM retrievals from these operative missions and from emerging projects employing L-band radiometers, calibration and validation remain crucial [14,26,27]. Validation involves comparing thermal radiance measured by spaceborne sensors against simultaneous ground-based measurements [28] or ground-based soil moisture sensor references. The complicated interactions between radiative microwave signatures and surface features, typically characterized by various parameters in the retrieval algorithm, are primarily investigated through experimental studies [29]. With the ongoing need for suitable parameters that reflect diverse surface conditions and a more refined interpretation of the radiative transfer process between surface SM and L-band radiation, large-scale campaigns using tower-, truck-, and aircraft-mounted L-band radiometers continue to be vital [30,31,32]. However, these experiments are often limited to a few fixed areas, due in part to the scarcity of L-band radiometers and the high costs associated with their operation. Moreover, numerous disciplines such as agriculture and forestry require SM data at spatial resolutions in between kilometers and point scales and/or seek to understand the spatial variability of SM scalability from independent data sources [33,34].
The Portable L-band Radiometer (PoLRa), developed by TerraRad Tech, offers an effective alternative to address the above needs. PoLRa is a compact, lightweight, and dual-polarization L-band radiometer that can be easily installed on towers, vehicles, and unmanned aerial systems [35]. Depending on the measurement elevation, PoLRa can retrieve diverse environmental variables such as SM, sea surface salinity, and vegetation optical depth (VOD), with spatial resolutions ranging from a few meters to several hundred meters [35]. In comparison to traditional, larger ground-based microwave radiometers like the Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule L-Band Radiometer for soil moisture research (ELBARA) and Passive Active L-/S-band microwave aircraft instrument (PALS), PoLRa’s sensor weighs only 2.6 kg and has a volume of 0.0018 m3 [29,35,36]. Additionally, unlike other drone-mounted L-band radiometers such as the lobe differencing correlation radiometer (LDCR) and the airborne radiometer at L-band (ARIEL), which provide measurements from only one polarization, PoLRa offers off-nadir brightness temperatures at dual polarizations [37,38].
Although PoLRa has been applied for irrigation and canopy monitoring, the accuracy of its SM retrievals has not been examined. Therefore, the primary objective of this study is to conduct an initial evaluation of PoLRa-derived SM over bare soil and grassland within selected areas. Instead of drone- or vehicle-based observations, this study focuses on SM performance at four fixed pixels, with each pixel covering an area of approximately 0.7 m × 0.7 m, utilizing PoLRa mounted on a standing steel frame setup. Starting with fixed-location observations serves as a crucial first step in identifying the operational challenges of using PoLRa, thereby informing standardizing procedures for future drone-based applications. It is important to emphasize that this study is not intended to comprehensively evaluate PoLRa’s performance across all possible scenarios. Instead, it aims to provide an initial assessment of whether PoLRa can deliver stable brightness temperatures over time for a given area, as well as reasonable volumetric SM estimates in terms of magnitude and temporal variation. A more extensive evaluation of retrieval accuracy and the development of improved retrieval models is beyond the scope of this study.
Due to adopting the design of a constant incidence angle at 40° and many configurations akin to the SMAP radiometer, SM from PoLRa’s observations can be retrieved by directly implementing SMAP algorithms with minor adjustments. Prior to this study, the default model employed in PoLRa SM retrieval is the conventional dual-channel algorithm (DCA) but with all the parameters set at zero and a constant effective soil temperature of 292.15 K, considering the lack of reliable ancillary products at high resolutions. SMAP’s operational algorithms, namely the single-channel algorithm (SCA) and the regularized dual-channel algorithm (RDCA) with their corresponding parameters, have also been utilized and evaluated in the context of PoLRa [39,40]. In addition to soil effective temperature (), the roughness parameter () and vegetation single-scattering albedo () are crucial coefficients for the above algorithms [41]. The parameter accounts for the intensity of the integrated roughness effects and significantly influences the relationship between the observed emission intensity and SM [42]. is defined as the ratio of the scattering coefficient and the extinction coefficient, characterizing the scattering effects of the canopy layer on soil emissions [42]. Both coefficients vary across geographic features, land covers, and observation polarizations, etc. Hence, this study includes different algorithms with their paired parameter settings and analyzes the differences in SM retrieval accuracy to explore the optimal coefficient options other than the default configuration.
Though preliminary, this validation lays a solid foundation for PoLRa’s capabilities in tracking the spatiotemporal changes of SM and sets the stage for future advancements in algorithm refinements. Furthermore, these developments hold promise for integrating vehicle- and/or drone-based PoLRa measurements as a reliable reference for calibrating and validating satellite-based microwave sensors and bridging the resolution gap of SM information between airborne/spaceborne products and point-scale in situ sensors.
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Study Sites and Experimental Timeline
The experiment was structured into three phases, categorized by testing sites and experimental dates as depicted in Figure 1. Phase 1 (3–4 November 2023) and phase 2 (7–8 November 2023) involved field tests over two bare soil locations within a cornfield in central Illinois (Figure 1a,c) but were prematurely halted due to harvesting activities. The study area for phase 3 (11–25 November 2023) was then shifted to a bare soil location and a grassland plot on the campus of the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (Figure 1d). During phases 1 and 2, measurements were taken from four directions encircling the same elliptical area (Figure 1b). In phase 3, however, measurements were limited to one direction partly due to pedestrian and vehicular activity. Measurement times were consistently scheduled from 2 pm to 4 pm to minimize diurnal variations affecting the results.
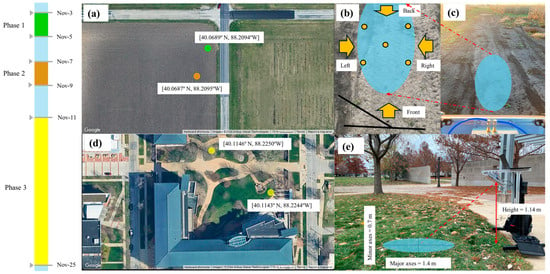
Figure 1.
Experimental sites, timeline, and instrument setup of ground-based PoLRa measurements: (a) geographical coordinates of experimental locations for phases 1 and 2; (b) microwave radiation measurements over the same area from four different directions (highlighted by the yellow arrows) and five measurement points for in situ sensor, i.e., TEROS12 capacitance probe; (c) the footprint area observed during phase 1; (d) geographical coordinates of experimental locations for phase 3; and (e) the setup and geometric view of ground-based PoLRa instruments.
2.2. Pre-Processing of Observed Brightness Temperatures
Given that the PoLRa’s sampling frequency across its four switch positions is approximately 69 milliseconds, thousands of dual-polarization brightness temperatures can be collected during each five to seven-minute measurement interval [35]. Initial data analysis revealed occasional outliers, likely due to improper operations and/or external interference. Thus, a series of pre-screening steps was employed before incorporating these brightness temperatures into SM retrieval algorithms (Figure 2). In accordance with the SMOS Level 1 manual, the maximum threshold was preset to 320 K for brightness temperature at both polarizations. Meanwhile, the minimum thresholds were computed using the forward tau-omega radiative transfer model by assuming a volumetric SM of 1 m3/m3 [39]. A constraint that the vertically polarized brightness temperature is larger than its coincident horizontal polarized brightness temperature was additionally applied. Although it is possible to generate a time series of SM from those filtered brightness temperatures, we only preserved one representative brightness temperature per measurement session for simplicity. We presumed that SM values averaged from the time series and derived from the representative brightness temperature have similar magnitudes. The use of the median as the representative brightness temperature was determined by an investigation that compared the 25th, 50th, and 75th percentiles and mean values of all the brightness temperatures from phase 3.
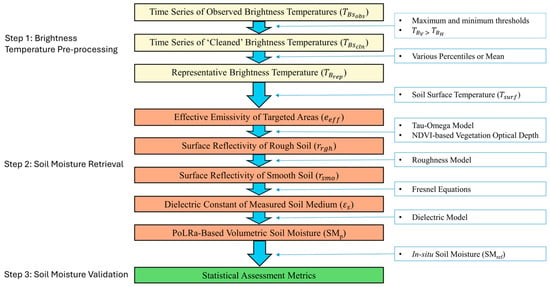
Figure 2.
Process flow chart that describes the conversion of PoLRa-derived brightness temperatures to areal soil moisture over the targeted locations with performance assessment.
2.3. Soil Moisture Retrieval Algorithms
Since PoLRa shares many aspects of the SMAP radiometer, the tau-omega microwave radiative transfer model designed for SMAP SM retrieval was employed here to estimate volumetric SM from PoLRa observations [39,43]. This model grouped the radiation intensity emitted from the land surface into three components: (1) upward soil emission attenuated by the overlying canopy, (2) upward vegetation emission, and (3) downward vegetation emission reflected by the soil surface and subsequently attenuated by the canopy, after excluding atmospheric, cosmic, and galaxy contributions (Equation (1)). The specific inversion process, illustrated in Figure 2, starts with calculating effective emissivity by normalizing the observed brightness temperature using a soil effective temperature () approximated by the weighted average of soil temperatures at the surface and 10 cm depth [39,44]. Here, is assumed to be numerically equal to the coincident soil temperature measured by in situ probe (i.e., METER TEROS 12 capacitance probe: https://metergroup.com/products/teros-12/teros-12-tech-specs (accessed on 2 December 2024) with a 5.5 cm tine. The effective soil emissivity is adjusted for vegetation contribution using the VOD and scattering coefficient () [39,43]. The roughness effect is often quantified through semi-empirical models to yield the soil emissivity from the smooth soil [45,46]. Using the Fresnel equations, the smooth soil emissivity is then converted into the complex dielectric permittivity of the bulk smooth soil–water–air system [39]. A dielectric mixing model, such as the Mironov model, can be subsequently used to transform the dielectric constant to volumetric (or gravimetric) SM [47,48,49,50]. Due to the complexity of inverting all these sub-models, in practice, SM retrievals usually rely on an optimization procedure that minimizes the differences between brightness temperatures observed by radiometers and simulated by the forward model.
where the subscript refers to the polarization, is the transmissivity of the overlying vegetation layer (as a function of vegetation optical depth and incidence angle), denotes the rough soil emissivity, represents the soil effective temperature, and is the effective vegetation scattering albedo.
Depending on the treatment of vegetation radiation, the operational SMAP algorithms are categorized into the single-channel algorithm (SCA) and the regularized dual-channel algorithm (RDCA). In the SCA approach, the annual climatology of vegetation opacity is quantified through the observed normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI), and then SM is estimated using the brightness temperature from a single polarization [39]. On the other hand, RDCA, which is derived from the modified dual-channel algorithm, utilizes the brightness temperatures from both polarizations to simultaneously estimate SM and VOD, with an additional regularized term in its cost function (Equation (4)) [40].
where represents the cost function for the soil moisture retrieval algorithm denoted by the subscript, refers to trail soil moisture used to forward simulation of brightness temperature, and is the vegetation opacity where is estimated using NDVI. is a regularized parameter equal to 20.
2.4. Ancillary Data
Besides the structural aspects of the algorithms, ancillary data associated with retrieval models such as and can also influence the accuracy of SM retrievals [42,45,51,52,53]. For SMAP, the and parameters remain temporally static and uniform within a given 1 km land cover class [39]. In the context of observations at hyper-resolutions finer than 1 km, however, these parameters are rarely available. This absence can be especially critical when attempting SM retrieval at meter-scale resolutions, particularly in areas with diverse land covers. To gauge the impact of insufficient ancillary information, the DCA where the parameters and temperature are arbitrarily assumed to be 0 and 292.15 K is included in the analysis. Table 1 details the configuration for each algorithm employed in PoLRa-observed SM retrieval, with the DCA further categorized as DCA0, DCA1, and DCA2 based on different parameters, temperatures, and dielectric model scenarios. However, it is worth noting that while directly using SMAP parameters from land cover look-up tables is not deemed optimal, it at least serves as a reasonable first guess for reference.

Table 1.
Soil moisture retrieval algorithms and configurations are considered in this study.
To estimate grassland SM during phase 3 using SCA, VOD values were estimated from NDVI. For this purpose, 30-m surface reflectance at the red (SR_B4) and near-infrared band (SR_B5) from the Landsat 9 Level 2 data set are used, specifically from November 2023 [54]. Observations affected by clouds were excluded using appropriate masking. NDVI images for four discrete dates—Nov 4th, 11th, 20th, and 27th—were calculated over the targeted spot. These images were then linearly interpolated to generate a daily time series of NDVI. These NDVI estimations were converted into VOD using the formulas outlined in [39]. Additionally, clay fraction, another vital input for the Mironov model, was obtained from the SoilWeb database, which is a web-based interface to the Soil Survey Geographic Database (SSURGO) and State Soil Geographic Database (STATSGO) [53]. Specifically, the clay fractions for the primary soil components at a depth of 5 cm at the testing sites were manually extracted from their graphic profile charts. Table 2 summarizes all the data sets and/or sources used in this study for SM retrievals and evaluation.

Table 2.
Summary of all the data sets used in this study for soil moisture retrieval and validation.
2.5. Validation Scheme
The setup of the measuring instrument, positioned 1.14 m above the ground, maintained a constant elliptical footprint with major and minor axes of 1.4 m and 0.7 m, respectively (Figure 3a). A squared area inscribed in this ellipse was selected and the SM average within this area was considered as benchmark. The geometric details of this square have been depicted in Figure 3a. In addition to the elliptical center, all the corner points of this square were also included as benchmark points (Figure 1b and Figure 3). Soil volumetric water content at these five points was measured by the TEROS12 probe immediately after the PoLRa measurements. Key measuring locations, including benchmark points and the two front wheels of the sensor stand, were marked with pins to ensure consistent testing areas (Figure 3b).
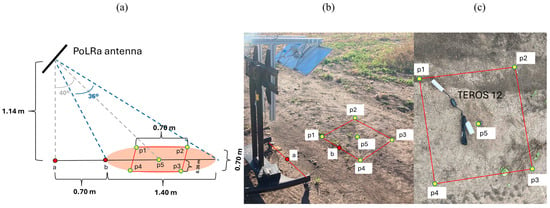
Figure 3.
(a) Conceptual geometric configuration of the footprint captured by PoLRa (mounted at a height of 1.14 m on the steel stand) and the centered square within the elliptical footprint used for initial validation of PoLRa-derived soil moisture retrievals. (b) Practical setup of PoLRa’s measurement position and the validation zone during the experiment. (c) Example of soil moisture benchmarking using the METER TEROS 12 capacitance probe at pre-selected points within the validation square.
The accuracy of SM retrievals is generally assessed by measuring the differences compared to in situ measurements. These discrepancies are usually described by four conventional metrics: bias, root mean square error (RMSE), unbiased root mean square error (ubRMSE), and Pearson correlation (R) [55]. These metrics could effectively reflect the discrepancies in terms of magnitudes as well as the temporal correlation between the referenced and testing SM products. Thus, PoLRa-derived () and in situ measured () SM vectors were then paired to compute these metrics using formulas shown in Equations (5)–(8).
where E […] represents the arithmetic mean; the subscript and denote SM retrievals from PoLRa observations and the spatially averaged in situ measurements; and refers to the standard deviation of the SM retrievals.
3. Results
3.1. Investigation of PoLRa-Observed Brightness Temperatures
For phases 1 and 2, the consistency of PoLRa observations was assessed by comparing brightness temperatures from four directions over the same area. Figure 4 describes boxplots of filtered brightness temperatures at both horizontal and vertical polarizations. Vertical polarizations show relative stability across directions compared to horizontal ones, where larger deviations in horizontally polarized brightness temperatures are partly attributed to their increased sensitivity to surface roughness. Within each box, fluctuations are generally minor, supported by their small standard deviations, mostly below 5 K. There are a few abnormal boxes, such as on Nov 8th (Figure 4d), likely because of improper operations. It was observed that keeping the laptop on and attaching the PoLRa to it via an ethernet cable during measurements could significantly increase the observed raw voltages, which will be subsequently converted into the brightness temperature and SM, with substantial noise (Figure A1).
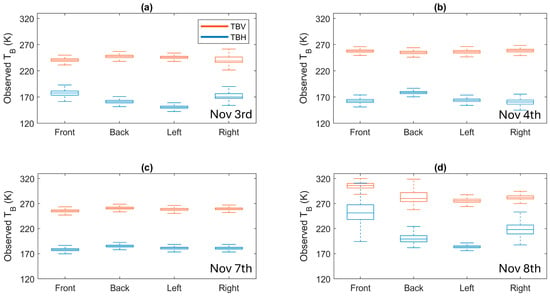
Figure 4.
Boxplots of polarized brightness temperatures over the testing sites from four different directions on four dates: (a) 3 November 2023; (b) 4 November 2023; (c) 7 November 2023; and (d) 8 November 2023.
The criteria for selecting representative brightness temperatures during phase 3 involved comparing the 25th, 50th, and 75th percentiles and mean values of brightness temperatures collected from two to three consecutive independent measurements (Figure 5). Again, brightness temperatures for the same pixel are typically clustered tightly. Variations in vertical polarizations are less pronounced than in horizontal. Over time, brightness temperatures at bare soil and grassland locations are consistent, though non-vegetated areas showed more pronounced fluctuations. Given the minor differences between the mean and median brightness temperatures, the median brightness temperature was chosen as the representative value for each test period over a given area.
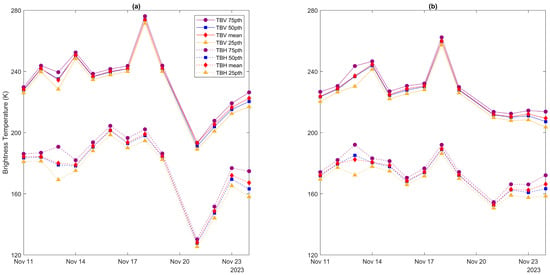
Figure 5.
Time series of different representative polarized brightness temperatures extracted from the daily sets of filtered brightness temperatures during phase three over (a) bare soil and (b) grassland.
3.2. Performance of PoLRa-Derived Soil Moisture
Statistical metrics that reflect the accuracy of PoLRa-derived SM for phase 3 are listed in Table 3. These metrics were computed utilizing Equations (5)–(8), with PoLRa-derived and in situ measurements separately representing and . The ubRMSE values are generally below 0.05 m3/m3. Correlation coefficients (i.e., R) mostly exceed 0.75, indicating strong temporal consistency between PoLRa-derived and in situ SM. The high R values for the continuous two-week observations confirm PoLRa’s adequacy to track SM trends at hyper-resolution. It should be noted that all the metrics for phases 1 and 2 were masked out due to the small number of samples. Additionally, the general positive bias indicates that PoLRa-derived SM retrievals tend to overestimate SM, especially after precipitation events, which might be caused by the use of raw in situ soil temperatures, improper polarization-independent values, and lagged sky calibration (Table 3 and Figure 6).

Table 3.
Statistical assessment metrics of PoLRa soil moisture retrievals for phase 3.
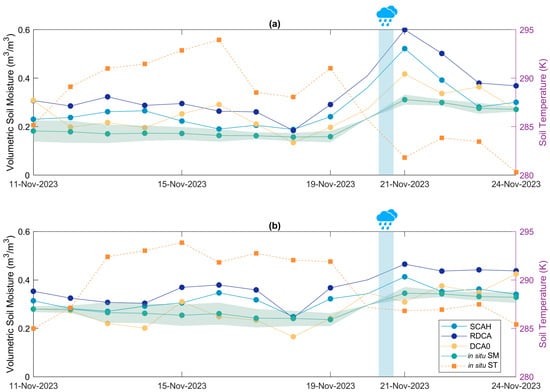
Figure 6.
Time series of soil moisture derived from PoLRa-derived brightness temperatures using three different algorithms (SCAH, RDCA, and DCA0) and measured by in situ probe during phase 3 over (a) bare soil and (b) grassland. The green shaded areas around the in situ soil moisture time series indicate the range of measured values within two standard deviations.
Comparing SM derived from three algorithms under six scenarios shows similar but complementary performances at different locations, highlighting the necessity of incorporating multiple algorithms retrieving high-resolution SM, especially in the absence of ancillary information. Given the available conditions and validation results for DCA0, DCA1, and DCA2, the use of an advanced dielectric model and soil temperature from the TEROS 12 capacitance probe did not yield significant improvements. The ubRMSE values for all the DCA-related algorithms are quite similar, with DCA0 and DCA1 even showing slightly better R values compared to DCA2 (Table 3). Similarly, incorporating land cover-based parameters and NDVI-derived VOD did also not yield significant advantages for SCAV, SCAH, and RDCA (Table 3), probably due to the relatively smooth soil surface and sparse vegetation in the selected pixels. Nonetheless, all metric values fall within reasonable ranges, demonstrating PoLRa’s capability to accurately measure volumetric SM and track its changes.
Notably, the performance of PoLRa-based sub-meter SM retrievals seems substantially contingent on testing sites. The ubRMSE values at the bare soil spot in the University of Illinois Urbana Champaign commonly exceed 0.045 m3/m3 whereas those in the phase 1 location are typically smaller than 0.01 m3/m3. This discrepancy may be due to the geographic compatibility of and used in the retrieval process or due to the relatively high magnitude of Radio Frequency Interference (RFI) present around the university campus. In terms of land cover, SM variations in bare areas align more closely with in situ measurements than those in grassland.
Time series of SM retrievals from different algorithms and in situ measurements for phase 3 are shown in Figure 6, where the light green patched areas surrounding in situ data represent the range of two standard deviations. No data were available on 20 November due to rainfall. The varying amplitudes of PoLRa-derived SM over the bare area are notably higher than those over grassland (Figure 6). However, such differences are not observed by in situ measurements. DCA0 SM occasionally exhibits the opposite trends relative to others (e.g., Figure 6a), likely due to ignoring temporal variations in . Nevertheless, this divergence cannot be simply regarded as an error, as variations in in situ SM at benchmark points do not always align perfectly (Figure A2).
4. Discussion
4.1. Parameter Challenges in High-Resolution Soil Moisture Retrievals
While SMAP algorithms effectively derive SM from PoLRa-observed brightness temperatures, the quality of these retrievals can be compromised by the lack of suitable parameters at the corresponding spatial resolution. Previous studies indicate that and could vary significantly across time and within the same land cover span of tens of kilometers, and more so at meter scales [41,46,56]. When mapping SM from drone-based PoLRa observations over large areas, using the correct parameters is crucial for accurately representing the spatial patterns of SM. High-resolution ancillary data for SM retrieval from ground- or drone-based microwave radiometry can be enhanced by integrating Lidar, optical, and near- and thermal-infrared sensors mounted on the unmanned aerial system alongside PoLRa detection [57]. Alternatively, SM data measured by handheld probes over small sections of targeted areas can be used to calibrate and in near real-time across land cover types. Assuming these parameters are constant in each land cover class within the targeted area, they can be applied to the remaining areas of their respective land cover.
Although most areas investigated in this study are either bare soil or sparsely vegetated, it is important to note that a significant challenge in accurately retrieving SM from PoLRa in areas with more vegetation is VOD quality. Here, the VOD was estimated by optical vegetation indices at 30 m through an empirical model introduced in [39]. However, in many cases, this method is prone to yielding inaccurate VOD estimations, which could introduce additional uncertainties into SM retrievals from the SCA algorithms [42,58]. For the RDCA algorithm, on the other hand, this priori information could drive the estimation of its VOD output (to be close to this prior value for reducing the objective loss), thereby indirectly affecting the quality and magnitude of retrieved SM [58,59]. More importantly, these retrievals cannot be considered fully independent of dynamics (or other key information) contained in the NDVI product. Recently, models developed for SMOS-IC and SMAP-IB products have implemented a self-calibration scheme to minimize the potential noises introduced by NDVI-derived VOD [58,59]. Instead of relying heavily on NDVI-derived VOD, these models use initial estimates for both VOD and SM based on the immediate previous estimations. Such a design can not only keep the outputs’ temporal consistency but also reduce the independence of their products from other ancillary data sets [58]. This self-calibration approach should be explored and integrated into PoLRa SM retrievals in future studies when more samples are collected.
4.2. Operational and Calibration Limitations of PoLRa Measurements
Moreover, the PoLRa-based brightness temperatures in this study may be impacted by imperfect operations, anthropogenic radio interference, and the absence of external calibration. For instance, during phases 1 and 2, the measurements were not taken continuously between different directions and not recorded under the same data file, potentially undermining the stability achieved through the initial warm-up procedures by frequently restarting. Additionally, the presence of an antenna tower near the phase three locations might have introduced signal interference. Future work is needed to understand and characterize the effects of electromagnetic interference on the performance of the instrument. The conversion of raw voltages from the PoLRa sensor to L-band brightness temperatures involves using two offsets typically determined by preliminary cold sky calibration [35]. During the experiment, however, these parameters were only calibrated once for phase 3, and offsets with the default setting at 0 were used for phases 1 and 2. Furthermore, the examination of the PoLRa-observed brightness temperature over the calm water surface would be another effective calibration means [29]. In the process of performing ground-based PoLRa field tests, the specific experimental steps have been gradually adjusted to pursue observations with better quality. However, some discrepancies from these changes may not be completely omitted.
4.3. Sampling Representativeness and Caveats
A limitation of this study is the small sample size used for statistical assessment. Although the experimental sites cover four distinct spots with two different land covers, there are only two samples separately available for phases 1 and 2, and thirteen samples for phase 3. While this number of samples may limit the statistical power of our results and affect the generalizability of our findings, it is important to emphasize that the primary goal of this study is to provide an initial assessment of PoLRa SM retrievals in a controlled scenario, rather than a comprehensive validation under diverse conditions. The objective is to demonstrate that PoLRa is capable of reliably collecting brightness temperatures, producing reasonable SM estimates, and capturing their changes over time. A more extensive demonstration of retrieval accuracy and exploration of improved retrieval models is beyond the scope of this study. Future work should focus on expanding data collection to include a larger number of samples across different conditions through the integrated use of drone-based PoLRa observations to provide a more in-depth assessment of retrieval accuracy and minimize representativeness concerns.
In terms of measurement areas, priority was given to finding pixels with smooth surfaces and low vegetation density, such as bare soil or short grassland, along with ensuring physical accessibility. These criteria help mitigate concerns about sampling representativeness following global-scale validation studies of SMAP SM products that have shown good and consistent performance over sparsely vegetated areas [20,60]. Additionally, the high spatial resolution achievable by PoLRa, determined by observation height, ensures relatively uniform land cover within each targeted pixel, reducing the impact of spatial heterogeneity within one pixel.
Furthermore, SM data from the TEROS 12 capacitance probe was used as the benchmark for the initial assessment. However, estimations from in situ probes may deviate from the “true” values typically obtained through the gravimetric method [61]. Without recalibrating the TEROS 12 probe against gravimetric SM measurements from the target sites, its accuracy is estimated to be ±0.03 m3/m3, which may affect the findings of this initial evaluation [61].
4.4. Other Potential Directions for PoLRa Application
Future investigations can expand drone-based PoLRa observations to areas with varied vegetation. Since the L-band radiometer detects the radiation intensity from an integrated soil–vegetation system, the improved accuracy of SM would also facilitate the precise retrieval of VOD. The microwave VOD has been widely used as a proxy of biomass content and vegetation water status as well as acting as a wildfire indicator for live fuel moisture [62,63]. Besides capturing diverse environmental parameters, another promising use of the PoLRa involves leveraging its aggregated dual-polarization brightness temperatures as an independent reference. This reference can be used for comparison and calibration with the upcoming L-band NASA-ISRO SAR (NISAR) and ESA ROSE-L missions, which aim to deliver high-resolution SM data at approximately 100 m resolution [27,64].
5. Conclusions
This study provides an initial assessment of SM retrievals from pole-fixed PoLRa across four pixels in central Illinois, each approximately 0.7 m 0.7 m. In the same pixel, the temporal stability of brightness temperatures recorded by PoLRa from different directions and/or over time was examined. In addition, the accuracy of PoLRa-based SM retrievals from various algorithms was evaluated by comparing them with benchmarked SM measurements obtained using a handheld capacitance probe. The key findings of this study are as follows:
- Vertically polarized brightness temperatures from PoLRa are generally more stable than their horizontally polarized counterpart.
- For any given pixel in our test, the standard deviation of brightness temperatures recorded by PoLRa from one direction is typically below 5 K.
- Under the experimental conditions adopted here, the average ubRMSE and R values for PoLRa-derived SM retrievals are generally less than 0.05 m3/m3 and greater than 0.7, respectively.
- While SMAP models and the DCA algorithm can derive SM from PoLRa observations, no single algorithm consistently outperforms the others.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.Z., D.H., A.W. and M.A.; methodology, R.Z. and D.H.; data curation, R.Z. and A.N.; data analysis, R.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, R.Z.; writing—review and editing, R.Z., D.H., A.W. and M.A.; supervision, E.S. and M.A.; funding acquisition, A.W., E.S. and M.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the United States Department of Agriculture Forest Service under grant 110789. The authors sincerely appreciate this support.
Data Availability Statement
The original data collected with the Portable L-band Radiometer (PoLRa) and in situ probes, along with additional details related to the experiments, are available upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A
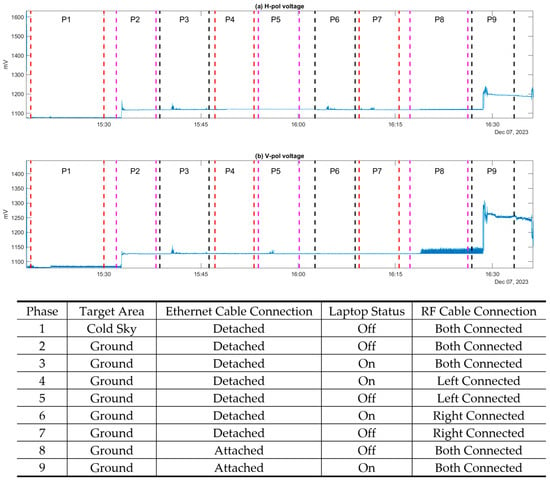
Figure A1.
Time series of raw voltages measured at (a) horizontal polarization and (b) vertical polarization by PoLRa’s antenna with different settings where the details are attached to the table below. The paired vertically lines reflect the beginning and end of each phase.
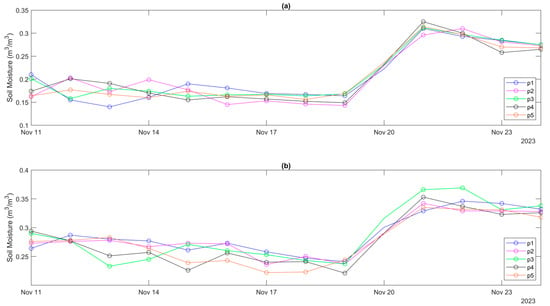
Figure A2.
Time series of volumetric soil moisture measured by in situ probes from five points within the same areas of (a) bare soil and (b) grassland during phase 3.

Table A1.
Record of soil moisture measured by the TEROS 12 capacitance probe from five points within the validation squares.
Table A1.
Record of soil moisture measured by the TEROS 12 capacitance probe from five points within the validation squares.
| Date (Phase) | Volumetric Soil Moisture Measurements Within Pixel 1 (m3/m3) | |||||
| p1 | p2 | p3 | p4 | p5 | Mean | |
| 3 November (1) | 0.248 | 0.236 | 0.244 | 0.249 | 0.236 | 0.243 |
| 4 November (1) | 0.225 | 0.224 | 0.240 | 0.237 | 0.238 | 0.233 |
| Volumetric Soil Moisture Measurements Within Pixel 2 (m3/m3) | ||||||
| p1 | p2 | p3 | p4 | p5 | Mean | |
| 7 November (2) | 0.225 | 0.250 | 0.246 | 0.255 | 0.204 | 0.236 |
| 8 November (2) | 0.236 | 0.248 | 0.196 | 0.226 | 0.240 | 0.229 |
| Volumetric Soil Moisture Measurements Within Pixel 3 (m3/m3) (Bare Soil) | ||||||
| p1 | p2 | p3 | p4 | p5 | Mean | |
| 10 November (3) | 0.188 | 0.199 | 0.191 | 0.189 | 0.201 | 0.194 |
| 11 November (3) | 0.210 | 0.162 | 0.201 | 0.174 | 0.164 | 0.182 |
| 12 November (3) | 0.155 | 0.203 | 0.158 | 0.201 | 0.177 | 0.179 |
| 13 November (3) | 0.140 | 0.173 | 0.180 | 0.191 | 0.167 | 0.170 |
| 14 November (3) | 0.161 | 0.199 | 0.174 | 0.170 | 0.160 | 0.173 |
| 15 November (3) | 0.190 | 0.177 | 0.163 | 0.155 | 0.174 | 0.172 |
| 16 November (3) | 0.181 | 0.145 | 0.166 | 0.162 | 0.163 | 0.163 |
| 17 November (3) | 0.169 | 0.153 | 0.167 | 0.157 | 0.166 | 0.162 |
| 18 November (3) | 0.167 | 0.146 | 0.164 | 0.152 | 0.156 | 0.157 |
| 19 November (3) | 0.164 | 0.143 | 0.168 | 0.149 | 0.169 | 0.159 |
| 21 November (3) | 0.310 | 0.296 | 0.312 | 0.325 | 0.314 | 0.311 |
| 22 November (3) | 0.293 | 0.310 | 0.297 | 0.300 | 0.297 | 0.299 |
| 23 November (3) | 0.284 | 0.281 | 0.285 | 0.258 | 0.270 | 0.276 |
| 24 November (3) | 0.275 | 0.273 | 0.275 | 0.265 | 0.268 | 0.271 |
| 25 November (3) | 0.266 | 0.255 | 0.257 | 0.221 | 0.237 | 0.247 |
| Volumetric Soil Moisture Measurements Within Pixel 4 (m3/m3) (Grassland) | ||||||
| p1 | p2 | p3 | p4 | p5 | Mean | |
| 11 November (3) | 0.264 | 0.273 | 0.290 | 0.294 | 0.276 | 0.279 |
| 12 November (3) | 0.287 | 0.276 | 0.277 | 0.277 | 0.278 | 0.279 |
| 13 November (3) | 0.280 | 0.278 | 0.233 | 0.251 | 0.283 | 0.265 |
| 14 November (3) | 0.277 | 0.267 | 0.245 | 0.257 | 0.264 | 0.262 |
| 15 November (3) | 0.261 | 0.273 | 0.271 | 0.226 | 0.239 | 0.254 |
| 16 November (3) | 0.273 | 0.272 | 0.260 | 0.256 | 0.243 | 0.261 |
| 17 November (3) | 0.258 | 0.236 | 0.253 | 0.240 | 0.222 | 0.242 |
| 18 November (3) | 0.247 | 0.250 | 0.243 | 0.241 | 0.223 | 0.241 |
| 19 November (3) | 0.241 | 0.237 | 0.237 | 0.221 | 0.244 | 0.236 |
| 21 November (3) | 0.329 | 0.342 | 0.366 | 0.353 | 0.335 | 0.345 |
| 22 November (3) | 0.346 | 0.329 | 0.369 | 0.337 | 0.332 | 0.343 |
| 23 November (3) | 0.342 | 0.329 | 0.331 | 0.323 | 0.331 | 0.331 |
| 24 November (3) | 0.332 | 0.328 | 0.338 | 0.326 | 0.318 | 0.328 |
References
- Koster, R.D.; Dirmeyer, P.A.; Guo, Z.; Bonan, G.; Chan, E.; Cox, P.; Gordon, C.T.; Kanae, S.; Kowalczyk, E.; Lawrence, D.; et al. Regions of strong coupling between soil moisture and precipitation. Science 2004, 305, 1138–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seneviratne, S.I.; Corti, T.; Davin, E.L.; Hirschi, M.; Jaeger, E.B.; Lehner, I.; Orlowsky, B.; Teuling, A.J. Investigating soil moisture–climate interactions in a changing climate: A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2010, 99, 125–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Thomasson, J.A.; Sui, R. Remote sensing of soil properties in precision agriculture: A review. Front. Earth Sci. 2011, 5, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petropoulos, G. Remote Sensing of Energy Fluxes and Soil Moisture Content; CRC press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Miralles, D.G.; Teuling, A.J.; Van Heerwaarden, C.C.; Vilà-Guerau de Arellano, J. Mega-heatwave temperatures due to combined soil desiccation and atmospheric heat accumulation. Nat. Geosci. 2014, 7, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, A.F.; Short Gianotti, D.J.; Trigo, I.F.; Salvucci, G.D.; Entekhabi, D. Satellite-based assessment of land surface energy partitioning–soil moisture relationships and effects of confounding variables. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 10657–10677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, A.; Trenberth, K.E.; Qian, T. A global dataset of Palmer Drought Severity Index for 1870–2002: Relationship with soil moisture and effects of surface warming. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 1117–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, A.F.; Short Gianotti, D.J.; Dong, J.; Akbar, R.; Crow, W.T.; McColl, K.A.; Konings, A.G.; Nippert, J.B.; Tumber-Dávila, S.J.; Holbrook, N.M.; et al. Remotely sensed soil moisture can capture dynamics relevant to plant water uptake. Water Resour. Res. 2023, 59, e2022WR033814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmugge, T.; Choudhury, B. A comparison of radiative transfer models for predicting the microwave emission from soils. Radio Sci. 1981, 16, 927–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmugge, T. Remote sensing of surface soil moisture. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1978, 17, 1549–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulaby, F.T.; Bradley, G.A.; Dobson, M.C. Microwave backscatter dependence on surface roughness, soil moisture, and soil texture: Part II-vegetation-covered soil. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Electron. 1979, 17, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulaby, F.T.; Moore, R.K.; Fung, A.K. Microwave Remote Sensing: Active and Passive. Volume 3-From Theory to Applications; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Njoku, E.G.; Entekhabi, D. Passive microwave remote sensing of soil moisture. J. Hydrol. 1996, 184, 101–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, Y.H.; Waldteufel, P.; Wigneron, J.-P.; Martinuzzi, J.; Font, J.; Berger, M. Soil moisture retrieval from space: The Soil Moisture and Ocean Salinity (SMOS) mission. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 1729–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entekhabi, D.; Njoku, E.G.; O’Neill, P.E.; Kellogg, K.H.; Crow, W.T.; Edelstein, W.N.; Entin, J.K.; Goodman, S.D.; Jackson, T.J.; Johnson, J.; et al. The soil moisture active passive (SMAP) mission. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njoku, E.G.; Jackson, T.J.; Lakshmi, V.; Chan, T.K.; Nghiem, S.V. Soil moisture retrieval from AMSR-E. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, W.; Hahn, S.; Kidd, R.; Melzer, T.; Bartalis, Z.; Hasenauer, S.; Figa-Saldaña, J.; De Rosnay, P.; Jann, A.; Schneider, S.; et al. The ASCAT soil moisture product: A review of its specifications, validation results, and emerging applications. Meteorol. Z. 2013, 22, 5–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imaoka, K.; Kachi, M.; Kasahara, M.; Ito, N.; Nakagawa, K.; Oki, T. Instrument performance and calibration of AMSR-E and AMSR2. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2010, 38, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, R.; Snoeij, P.; Geudtner, D.; Bibby, D.; Davidson, M.; Attema, E.; Potin, P.; Rommen, B.; Floury, N.; Brown, M.; et al. GMES Sentinel-1 mission. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Kim, S.; Sharma, A. A comprehensive validation of the SMAP Enhanced Level-3 Soil Moisture product using ground measurements over varied climates and landscapes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 223, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Kim, S.; Sharma, A.; Lakshmi, V. Identifying relative strengths of SMAP, SMOS-IC, and ASCAT to capture temporal variability. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 252, 112126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Wigneron, J.-P.; Kumar, S.; Dong, J.; Wagner, W.; Cosh, M.H.; Bosch, D.D.; Collins, C.H.; Starks, P.J.; Seyfried, M.; et al. Global scale error assessments of soil moisture estimates from microwave-based active and passive satellites and land surface models over forest and mixed irrigated/dryland agriculture regions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 251, 112052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Zeng, J.; Chen, N.; Zhang, X.; Cosh, M.H.; Wang, W. Satellite surface soil moisture from SMAP, SMOS, AMSR2 and ESA CCI: A comprehensive assessment using global ground-based observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McColl, K.A.; Alemohammad, S.H.; Akbar, R.; Konings, A.G.; Yueh, S.; Entekhabi, D. The global distribution and dynamics of surface soil moisture. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Ciais, P.; Wigneron, J.-P.; Gentine, P.; Feldman, A.F.; Makowski, D.; Viovy, N.; Kemanian, A.R.; Goll, D.S.; Stoy, P.C.; et al. Global critical soil moisture thresholds of plant water stress. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindlish, R.; Long, D.; Piepmeier, J.; Bailey, M. Global L-band Observatory for water cycle studies (GLOWS): Soil moisture continuity mission. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS, Brussels, Belgium, 11–16 July 2021; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2024; Volume PC13146. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, M.W.; Furnell, R. ROSE-L: Copernicus l-band SAR mission. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS, Brussels, Belgium, 11–16 July 2021; pp. 872–873. [Google Scholar]
- Schwank, M.; Wiesmann, A.; Werner, C.; Mätzler, C.; Weber, D.; Murk, A.; Völksch, I.; Wegmüller, U. ELBARA II, an L-band radiometer system for soil moisture research. Sensors 2009, 10, 584–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, W.J.; Yueh, S.H.; Dinardo, S.J.; Chazanoff, S.L.; Kitiyakara, A.; Li, F.K.; Rahmat-Samii, Y. Passive active L-and S-band (PALS) microwave sensor for ocean salinity and soil moisture measurements. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.M.; Walker, J.P.; Ye, N.; Kodikara, J. Toward an Improved Surface Roughness Parameterization Model for Soil Moisture Retrieval in Road Construction. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtzman, N.M.; Anderegg, L.D.L.; Kraatz, S.; Mavrovic, A.; Sonnentag, O.; Pappas, C.; Cosh, M.H.; Langlois, A.; Lakhankar, T.; Tesser, D.; et al. L-band vegetation optical depth as an indicator of plant water potential in a temperate deciduous forest stand. Biogeosciences 2021, 18, 739–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.; Negrón-Juárez, R.; Colliander, A.; Cosio, E.G.; Salinas, N.; Araujo, A.d.; Chambers, J.Q.; Wang, J. Calibration of the SMAP Soil Moisture Retrieval Algorithm to Reduce Bias Over the Amazon Rainforest. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 8724–8736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocca, L.; Ciabatta, L.; Massari, C.; Camici, S.; Tarpanelli, A. Soil moisture for hydrological applications: Open questions and new opportunities. Water 2017, 9, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Albergel, C.; Balenzano, A.; Brocca, L.; Cartus, O.; Cosh, M.H.; Crow, W.T.; Dabrowska-Zielinska, K.; Dadson, S.; Davidson, M.W.; et al. A roadmap for high-resolution satellite soil moisture applications–confronting product characteristics with user requirements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 252, 112162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houtz, D.; Naderpour, R.; Schwank, M. Portable l-band radiometer (polra): Design and characterization. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzler, C.; Weber, D.; Wuthrich, M.; Schneeberger, K.; Stamm, C.; Wydler, H.; Fluhler, H. ELBARA, the ETH L-band radiometer for soil-moisture research. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2003. 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Proceedings (IEEE Cat. No.03CH37477), Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003; Volume 3055, pp. 3058–3060. [Google Scholar]
- Acevo-Herrera, R.; Aguasca, A.; Bosch-Lluis, X.; Camps, A.; Martínez-Fernández, J.; Sánchez-Martín, N.; Pérez-Gutiérrez, C. Design and first results of an UAV-borne L-band radiometer for multiple monitoring purposes. Remote Sens. 2010, 2, 1662–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, E.M.; Gasiewski, A.J. An ultra-lightweight L-band digital Lobe-Differencing Correlation Radiometer (LDCR) for airborne UAV SSS mapping. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Barcelona, Spain, 23–28 July 2007; pp. 1095–1097. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neill, P.; Bindlish, R.; Chan, S.; Chaubell, J.; Colliander, A.; Njoku, E.; Jackson, T. Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document Level 2 & 3 Soil Moisture (Passive) Data Products; Revision G. 12 October 2021. SMAP Project. JPL D-66480; Jet Propulsion Laboratory: Pasadena, CA, USA. Available online: https://nsidc.org/sites/nsidc.org/files/technical-references/L2_SM_P_ATBD_rev_G_final_Oct2021.pdf (accessed on 18 March 2024).
- Chaubell, J.; Yueh, S.; Dunbar, R.S.; Colliander, A.; Entekhabi, D.; Chan, S.K.; Chen, F.; Xu, X.; Bindlish, R.; O’Neill, P.; et al. Regularized dual-channel algorithm for the retrieval of soil moisture and vegetation optical depth from SMAP measurements. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 15, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Watts, A.C.; Alipour, M. Inverse Dynamic Parameter Identification for Remote Sensing of Soil Moisture from SMAP Satellite Observations. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 16592–16607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigneron, J.-P.; Jackson, T.J.; O’neill, P.; De Lannoy, G.; de Rosnay, P.; Walker, J.P.; Ferrazzoli, P.; Mironov, V.; Bircher, S.; Grant, J.P.; et al. Modelling the passive microwave signature from land surfaces: A review of recent results and application to the L-band SMOS & SMAP soil moisture retrieval algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 192, 238–262. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, T.; Choudhury, B.; Schmugge, T.; Wang, J.R.; Jackson, T. A model for microwave emission from vegetation-covered fields. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1982, 87, 11229–11237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, B.; Schmugge, T.; Mo, T. A parameterization of effective soil temperature for microwave emission. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1982, 87, 1301–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, B.; Schmugge, T.J.; Chang, A.; Newton, R. Effect of surface roughness on the microwave emission from soils. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1979, 84, 5699–5706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, V.A.; Wallace, V.; Yildirim, E.; Eichinger, W.E.; Cosh, M.H.; Hornbuckle, B.K. From field observations to temporally dynamic soil surface roughness retrievals in the U.S. Corn Belt. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 287, 113458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.R.; Schmugge, T.J. An empirical model for the complex dielectric permittivity of soils as a function of water content. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1980, GE-18, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, M.C.; Ulaby, F.T.; Hallikainen, M.T.; El-Rayes, M.A. Microwave dielectric behavior of wet soil-Part II: Dielectric mixing models. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1985, GE-23, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironov, V.L.; Kosolapova, L.G.; Fomin, S.V. Physically and mineralogically based spectroscopic dielectric model for moist soils. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 2059–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.-H.; Berg, A.; Cosh, M.H.; Colliander, A.; Behrendt, A.; Manns, H.; Hong, J.; Lee, J.; Zhang, R.; Wulfmeyer, V. An inverse dielectric mixing model at 50 MHz that considers soil organic carbon. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 6407–6420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, T.; Schmugge, T. Vegetation effects on the microwave emission of soils. Remote Sens. Environ. 1991, 36, 203–212. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Wigneron, J.-P.; Jiang, L.-M.; Parrens, M.; Yu, X.-Y.; Al-Yaari, A.; Ye, Q.-Y.; Fernandez-Moran, R.; Ji, W.; Kerr, Y. Global-scale evaluation of roughness effects on C-band AMSR-E observations. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 5734–5757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Der Schalie, R.; Kerr, Y.H.; Wigneron, J.-P.; Rodríguez-Fernández, N.J.; Al-Yaari, A.; de Jeu, R.A. Global SMOS soil moisture retrievals from the land parameter retrieval model. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 45, 125–134. [Google Scholar]
- Masek, J.G.; Wulder, M.A.; Markham, B.; McCorkel, J.; Crawford, C.J.; Storey, J.; Jenstrom, D.T. Landsat 9: Empowering open science and applications through continuity. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 248, 111968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entekhabi, D.; Reichle, R.H.; Koster, R.D.; Crow, W.T. Performance metrics for soil moisture retrievals and application requirements. J. Hydrometeorol. 2010, 11, 832–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konings, A.G.; Piles, M.; Das, N.; Entekhabi, D. L-band vegetation optical depth and effective scattering albedo estimation from SMAP. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 198, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.Y.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, R.; Fang, B.; Cosh, M.H.; Russ, A.L.; Dai, E.; Elston, J.; Stachura, M.; Gasiewski, A.J.; et al. Precision Soil Moisture Monitoring with Passive Microwave L-band UAS Mapping. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 7684–7694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wigneron, J.-P.; Fan, L.; Frappart, F.; Yueh, S.H.; Colliander, A.; Ebtehaj, A.; Gao, L.; Fernandez-Moran, R.; Liu, X.; et al. A new SMAP soil moisture and vegetation optical depth product (SMAP-IB): Algorithm, assessment and inter-comparison. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 271, 112921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigneron, J.-P.; Li, X.; Frappart, F.; Fan, L.; Al-Yaari, A.; De Lannoy, G.; Liu, X.; Wang, M.; Le Masson, E.; Moisy, C. SMOS-IC data record of soil moisture and L-VOD: Historical development, applications and perspectives. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 254, 112238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colliander, A.; Reichle, R.H.; Crow, W.T.; Cosh, M.H.; Chen, F.; Chan, S.; Das, N.N.; Bindlish, R.; Chaubell, J.; Kim, S.; et al. Validation of Soil Moisture Data Products From the NASA SMAP Mission. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 364–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mane, S.; Das, N.; Singh, G.; Cosh, M.; Dong, Y. Advancements in dielectric soil moisture sensor Calibration: A comprehensive review of methods and techniques. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 218, 108686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Sadeghi, M.; Ebtehaj, A. Microwave retrievals of soil moisture and vegetation optical depth with improved resolution using a combined constrained inversion algorithm: Application for SMAP satellite. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 239, 111662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.; Williams, A.P.; Flefil, J.F.; Konings, A.G. SAR-enhanced mapping of live fuel moisture content. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 245, 111797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, P.; Singh, G.; Das, N.N.; Entekhabi, D.; Lohman, R.; Colliander, A.; Pandey, D.K.; Setia, R. A multi-scale algorithm for the NISAR mission high-resolution soil moisture product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 295, 113667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).