An Extended Omega-K Algorithm for Automotive SAR with Curved Path
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Near-field images. The range of automotive MMW radars’ environmental understanding is usually less than 200 m. Thus, the targets detected and ranged are in the short-range. However, most existing focusing methods are based on the assumption of far-field detection, because of the long detection distances of aircraft and satellites. As a result, the range space variance cannot be neglected.
- Complex imaging environment. The complex road environment and application scenarios, such as auxiliary parking, lead to flexible trajectories and variable motion speeds. Generally, curved paths are inevitable during automotive data collection scenarios, which lead to cross-coupling and spatial variation, which have a significant impact on the imaging results. The traditional imaging algorithms should be improved, which are based on uniform linear motion assumption. Meanwhile, motion errors are inevitable, which would affect the instantaneous slant range and degrade focusing performances [21]. As a result, motion compensation is an important problem to deal with in automotive SAR imaging.
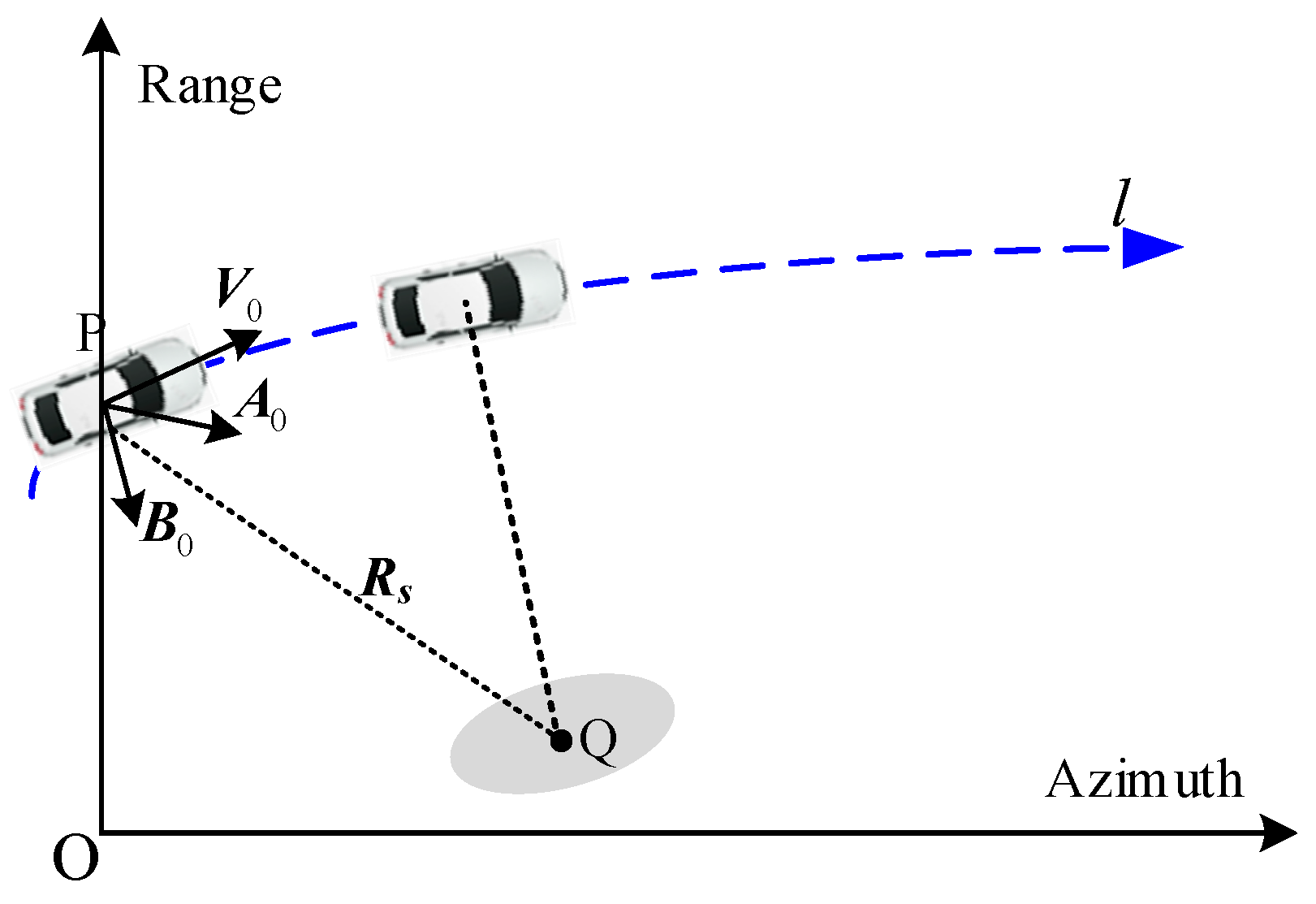
2. Signal Model
3. Imaging Algorithm
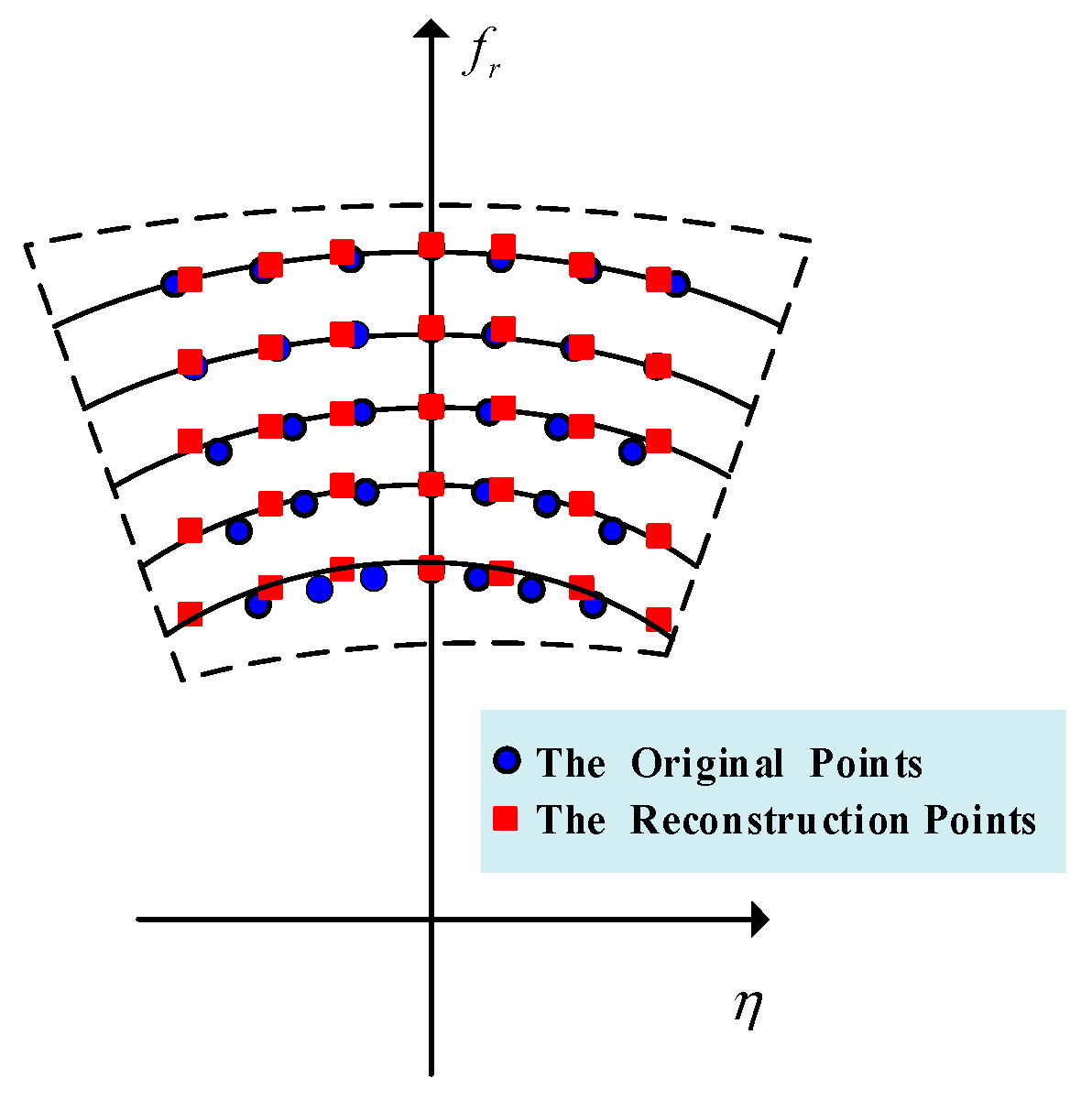
3.1. Range History Reconstruction
3.2. Extended Omega-K Algorithm
4. Experiment and Discussion
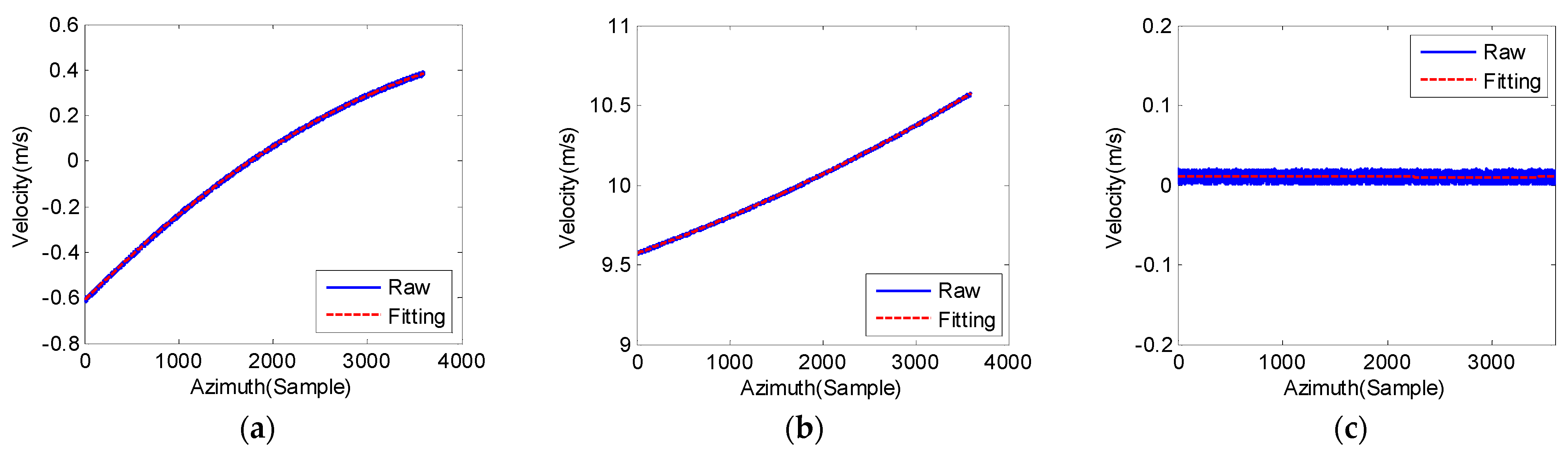
4.1. Simulation Analysis
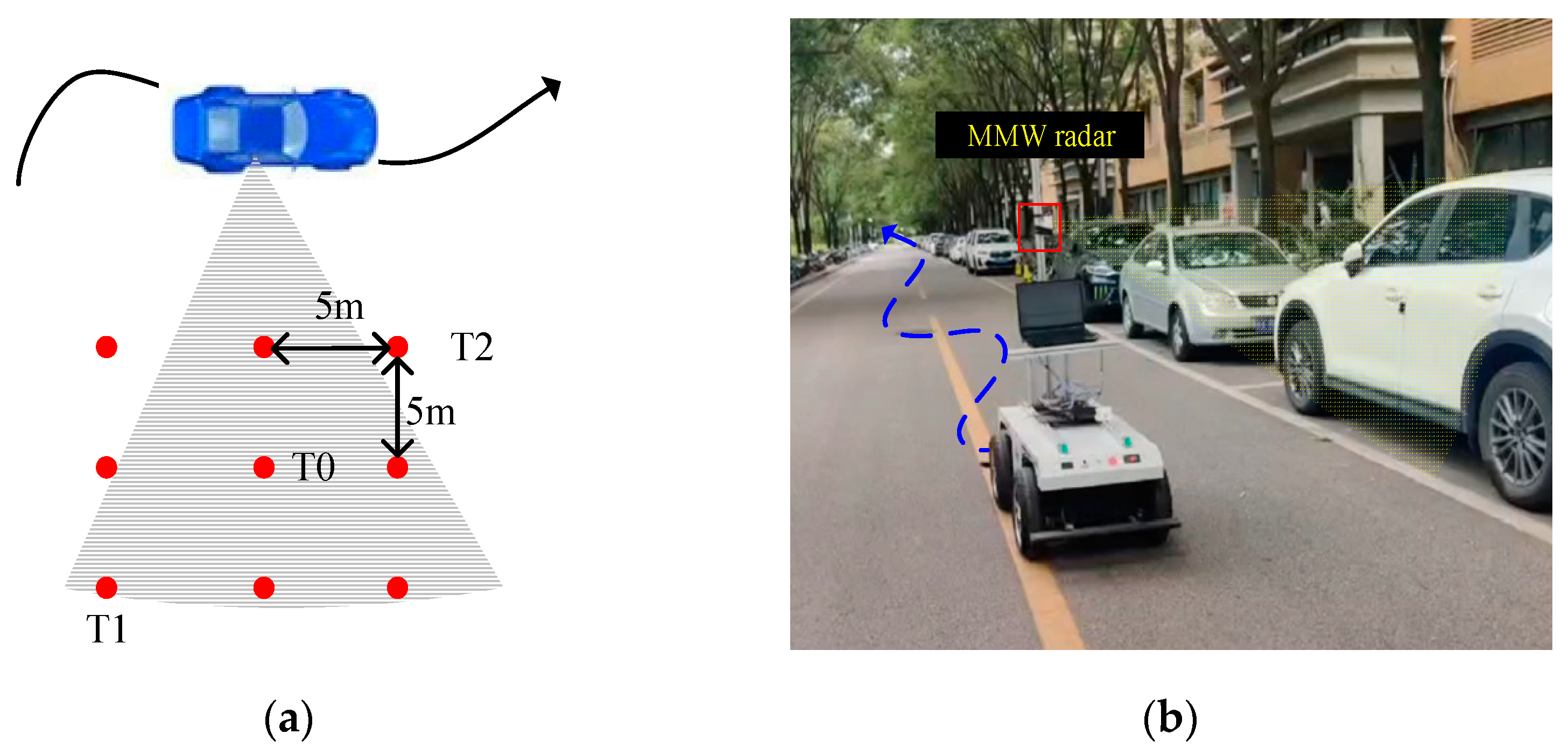
4.2. Real Data Experiments
4.3. Computational Complexity
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shopovska, I.; Stojkovic, A.; Aelterman, J.; Hamme, D.V.; Philips, W. High-Dynamic-Range Tone Mapping in Intelligent Automotive Systems. Sensors 2023, 23, 5767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patole, S.M.; Torlak, M.; Wang, D.; Ali, M. Automotive radars: A review of signal processing techniques. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2017, 34, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engels, F.; Heidenreich, P.; Wintermantel, M.; Stäcker, L. Automotive Radar Signal Processing: Research Directions and Practical Challenges. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2021, 15, 865–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Lei, C.; Shen, Y.; Du, Y.; Chen, Q. Improving Autonomous Vehicle Visual Perception by Fusing Human Gaze and Machine Vision. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 12716–12725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Bamminger, N.; Magosi, Z.F.; Feichtinger, C.; Zhao, Y.; Mihalj, T.; Orucevic, F.; Eichberger, A. The Effect of Rainfall and Illumination on Automotive Sensors Detection Performance. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilik, I.; Longman, O.; Villeval, S.; Tabrikian, J. The Rise of Radar for Autonomous Vehicles: Signal Processing Solutions and Future Research Directions. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2019, 36, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadoriya, A.S.; Vegamoor, V.; Rathinam, S. Vehicle Detection and Tracking Using Thermal Cameras in Adverse Visibility Conditions. Sensors 2022, 22, 4567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekigawa, Y.; Kidera, S. Doppler Velocity Decomposed Radar Imaging Method for 79 GHz Band Millimeter Wave Radar. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (ISAP), Sydney, Australia, 31 October–3 November 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Reina, G.; Johnson, D.; Underwood, J. Radar sensing for intel-ligent vehicles in urban environments. Sensors 2015, 15, 14661–14678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, P.; He, N.; He, Z. Super resolution DOA based on relative motion for FMCW automotive radar. IEEE Trans. 2020, 69, 8698–8709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, H.; Löffler, A.; Mejdoub, M.N.; Gruson, F. Realistic SAR implementation for automotive applications. In Proceedings of the 2020 17th European Radar Conference (EuRAD), Utrecht, The Netherlands, 10–15 January 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, H.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Chowdhary, G.; Norris, W. 3D Detection and Tracking for On-road Vehicles with a Monovision Camera and Dual Low-cost 4D mmWave Radars. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC), Indianapolis, IN, USA, 19–22 September 2021; pp. 2931–2937. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, B.; Ma, Z.; Zhu, X.; Li, S.; Zheng, L.; Chen, S.; Huang, L.; Bai, J. 3-D Object Detection for Multiframe 4-D Automotive Millimeter-Wave Radar Point Cloud. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 11125–11138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Zheng, L.; Ma, Z.; Bai, J.; Zhu, X.; Huang, L. Learning-based 4D Millimeter Wave Automotive Radar Sensor Model Simulation for Autonomous Driving Scenarios. In Proceedings of the 2023 7th International Conference on Machine Vision and Information Technology (CMVIT), Xiamen, China, 24–26 March 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.; Zhang, Y.D. 4D Automotive Radar Sensing for Autonomous Vehicles: A Sparsity-Oriented Approach. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2021, 15, 879–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisto, M.A.; Dell’Aversano, A.; Brancaccio, A.; Russo, I.; Solimene, R. A Computationally Light MUSIC Based Algorithm for Automotive RADARs. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2024, 10, 446–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Wu, F.; Tang, S.; Jiang, C.; Liu, C. Implementation Method of Automotive Video SAR (ViSAR) Based on Sub-Aperture Spectrum Fusion. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laribi, A.; Hahn, M.; Dickmann, J.; Waldschmidt, C. Performance Investigation of Automotive SAR Imaging. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE MTT-S International Conference on Microwaves for Intelligent Mobility (ICMIM), Munich, Germany, 15–17 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Walter, G.; Ron, S.; Ronald, M. Spotlight Synthetic Aperture Radar: Signal Processing Algorithms. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1995, 59, 597–598. [Google Scholar]
- Franceschetti, G.; Lanari, R. Synthetic Aperture Radar Processing; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Tang, S.; Chen, Z.; Ren, Y.; Lian, Z.; Guo, P.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; So, H.C. Precise Motion Compensation Approach for High-Resolution Multirotor UAV SAR in the Presence of Multiple Errors. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 15148–15165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebaldini, S.; Rizzi, M.; Manzoni, M.; Guarnieri, A.; Prati, C.; Tagliaferri, D.; Nicoli, M.; Spagnolini, U.; Russo, I.; Mazzucco, C. SAR imaging in automotive scenarios. In Proceedings of the 2022 Microwave Mediterranean Symposium (MMS), Pizzo Calabro, Italy, 9–13 May 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Feger, R.; Haderer, A.; Stelzer, A. Experimental verification of a 77-GHz synthetic aperture radar system for automotive applications. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE MTT-S International Conference on Microwaves for Intelligent Mobility (ICMIM), Nagoya, Japan, 19–21 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Feil, P.; Kraus, T.; Menzel, W. Short Range mm-Wave SAR for Surveillance and Security Applications. In Proceedings of the 8th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Aachen, Germany, 7–10 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Tagliaferri, D.; Rizzi, M.; Tebaldini, S.; Nicoli, M.; Russo, I.; Mazzucco, C.; Monti-Guarnieri, A.; Prati, C.; Spagnolini, U. Cooperative Synthetic Aperture Radar in an Urban Connected Car Scenario. In Proceedings of the 2021 1st IEEE International Online Symposium on Joint Communications & Sensing (JC&S), Dresden, Germany, 23–24 February 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.; Tang, S.; Zhang, L.; Sun, J. Real Data Imaging Approach Design for Automotive SAR Experiments. In Proceedings of the 2021 CIE International Conference on Radar (Radar), Haikou, China, 15–19 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, J.; Wang, Y. An Improved Omega-K Algorithm for Squinted SAR with Curved Trajectory. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 21, 4000905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Zhou, J.; Jiang, G.; Fu, Q. Range Migration Algorithm for Near-Field MIMO-SAR Imaging. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 14, 2280–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Guo, X.; Liang, X.; Lin, Z. Implementation of Real-time Automotive SAR Imaging. In Proceedings of the IEEE 11th Sensor Array and Multichannel Signal Processing Workshop (SAM), Hangzhou, China, 8–11 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, B.; Wu, Y. RMA-Based Azimuth-Range Decouple Method for Automotive SAR Sparse Imaging. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2023, 59, 3480–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zwirello, L.; Li, X.; Reichardt, L.; Zwick, T. Motion compensation with one-axis gyroscope and two-axis accelerometer for automotive SAR. In Proceedings of the 2011 German Microwave Conference, Darmstadt, Germany, 14–16 March 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Farhadi, M.; Feger, R.; Fink, J.; Wagner, T.; Gonser, M.; Hasch, J.; Stelzer, A. Space-variant Phase Error Estimation and Correction for Automotive SAR. In Proceedings of the 2020 17th European Radar Conference (EuRAD), Utrecht, The Netherlands, 10–15 January 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Manzoni, M.; Rizzi, M.; Tebaldini, S.; Monti-Guarnieri, A.; Prati, C.; Tagliaferri, D.; Nicoli, M.; Russo, L.; Mazzucco, C.; Duque, S.; et al. Residual Motion Compensation in Automotive MIMO SAR Imaging. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf22), New York, NY, USA, 21–25 March 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Zhu, Z. A novel autofocus algorithm based on minimum entropy criteria for SAR images. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2003, 25, 867–869. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.; Guo, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, W.; Truong, T. Full-Aperture Azimuth Spatial-Variant Autofocus Based on Contrast Maximization for Highly Squinted Synthetic Aperture Radar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 330–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Guo, P.; Wang, R.; Zhang, M.; Pan, Z. An improved range migration algorithm based on azimuth time resampling for automotive SAR with curved trajectory. IET Int. Radar Conf. 2024, 2023, 3489–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, A.; Yamada, H.; Muramatsu, S. Experimental Study on Automotive Millimeter Wave SAR in Curved Tracks. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (ISAP), Xi’an, China, 27–30 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Qiao, Z.; Xing, M.; Bao, Z. Integrating autofocus techniques with fast factorized back-projection for high resolution spotlight SAR imaging. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi, M.; Feger, R.; Fink, J.; Wagner, T.; Stelzer, A. Synthetic Aperture Radar Imaging of Moving Targets for Automotive Applications. In Proceedings of the 2021 18th European Radar Conference (EuRAD), London, United Kingdom, 5–7 April 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Tagliaferri, D. Navigation-aided automotive SAR for high-resolution imaging of driving environments. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 35599–35615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Bao, Y.; Mao, X. Automotive Millimeter Wave SAR Imaging in Curved Trajectory. In Proceedings of the 2022 14th International Conference on Signal Processing Systems (ICSPS), Jiangsu, China, 18–20 November 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, H.; Deng, J.; Xiao, Z.; Cheng, C.; Li, X.; Cui, G. Joint Implementation Method for Clutter Suppression and Coherent Maneuvering Target Detection Based on Sub-Aperture Processing with Airborne Bistatic Radar. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.; Ma, Y.; Li, B.; Hou, X.; Shi, Y.; Li, W. A Sub-Aperture Overlapping Imaging Method for Circular Synthetic Aperture Radar Carried by a Small Rotor Unmanned Aerial Vehicle. Sensors 2023, 23, 7849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Tao, M.; Shi, T.; Wang, J.; Mao, X. Sub-Aperture Polar Format Algorithm for Curved Trajectory Millimeter Wave Radar Imaging. IEEE Trans. Radar Syst. 2024, 2, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoni, M.; Tebaldini, S.; Monti-Guarnieri, A.V.; Prati, C.M.; Russo, I. A comparison of processing schemes for automo-tive MIMO SAR imaging. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Tang, S.; Guo, P.; Zhang, L.; So, H.C. 2-D Spatially Variant Motion Error Compensation for High-Resolution Airborne SAR Based on Range-Doppler Expansion Approach. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5201413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liang, Y.; Xing, M.; Huai, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zeng, L.; Bao, Z. An Improved Range Model and Omega-K-Based Imaging Algorithm for High-Squint SAR With Curved Trajectory and Constant Acceleration. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
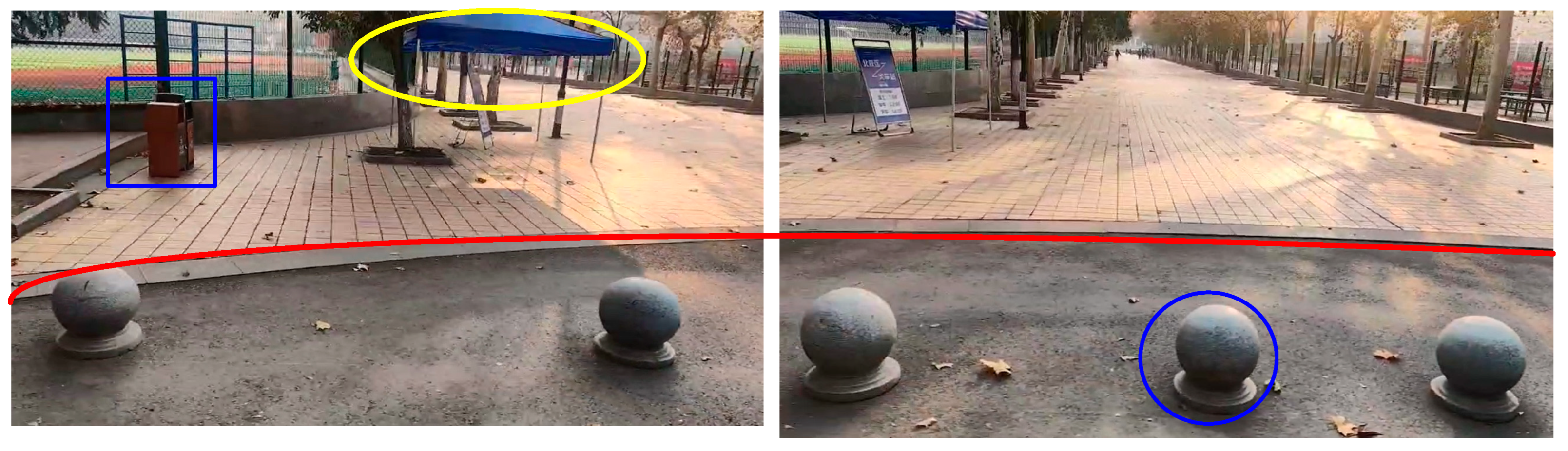


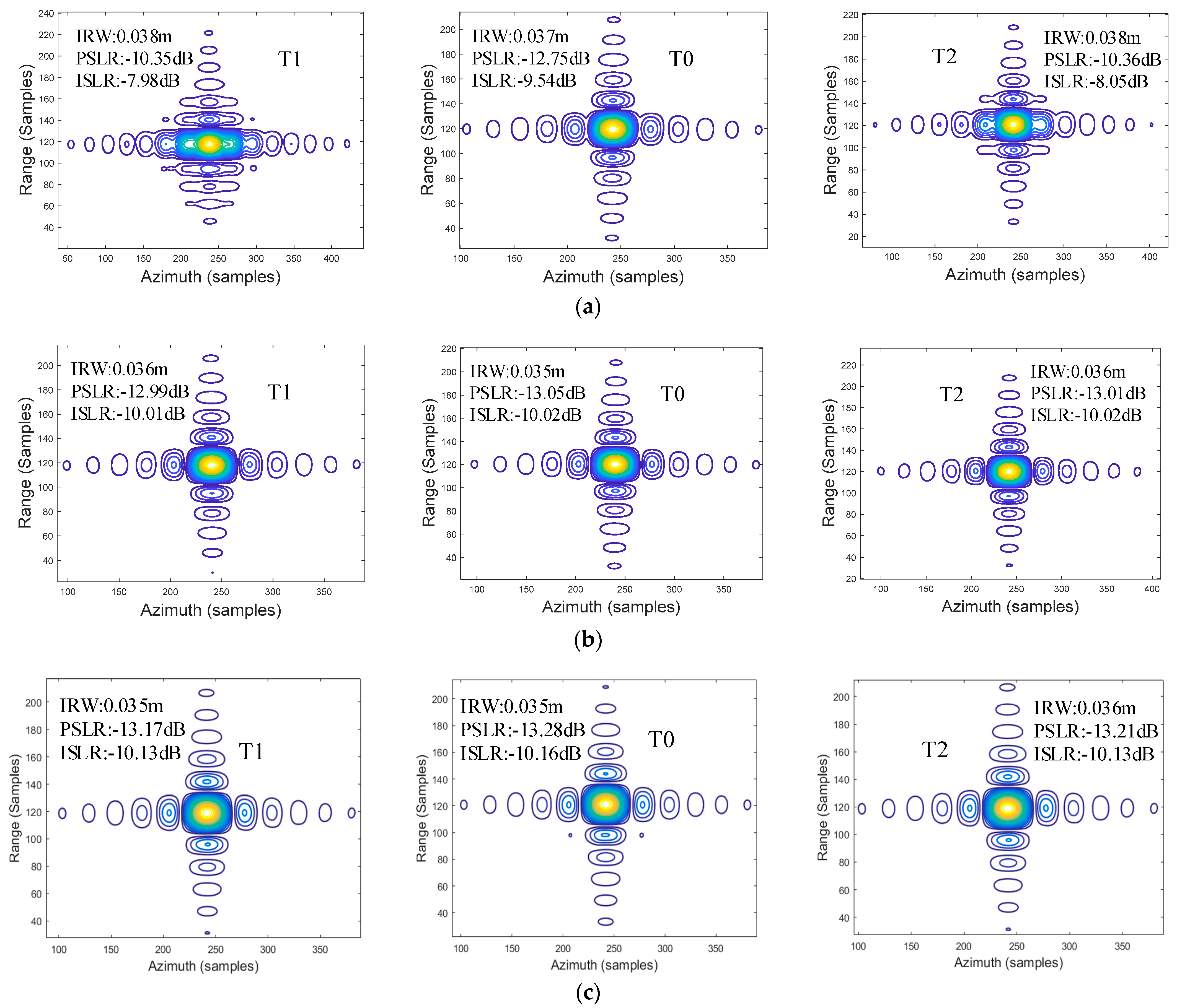

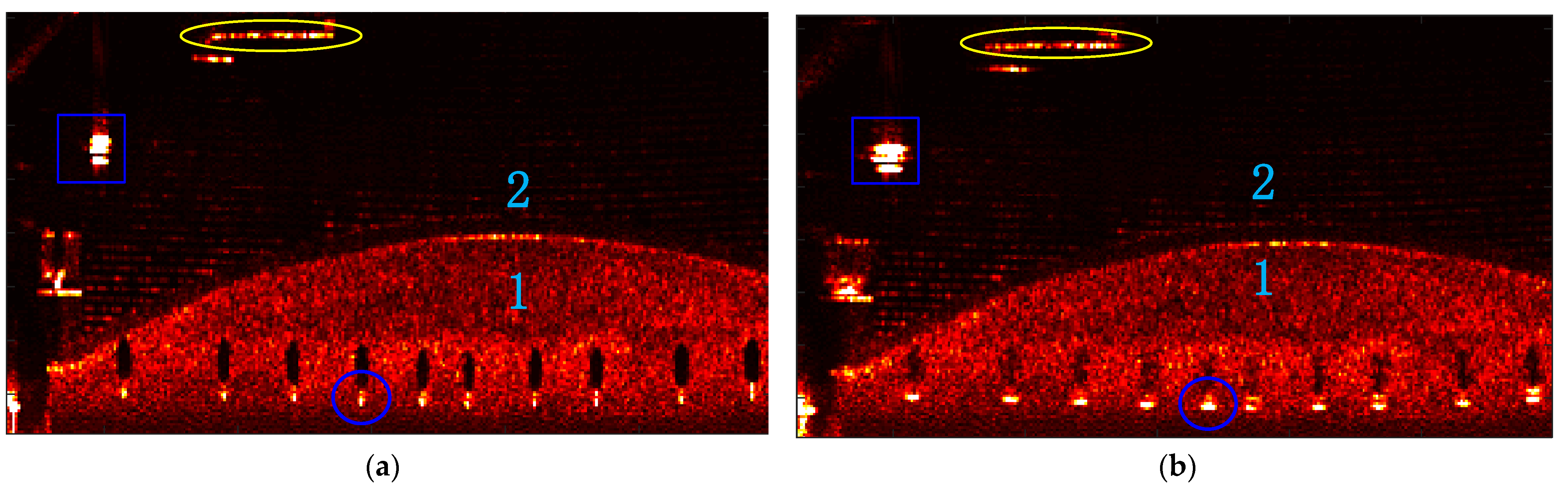

| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Carrier frequency | 77 GHz |
| Bandwidth | 3000 MHz |
| Frequency Sweep Period | 51.2 μs |
| Reference slant range | 30 m |
| Height | 1.5 m |
| Velocity vector | (12, 0, 0) m/s |
| Acceleration vector | (1, 1, 0) m/s2 |
| Method | Scene | Processing Time |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional OKA | Obstacle | 15 s |
| Parking lot | 9 s | |
| Open road | 8 s | |
| Proposed | Obstacle | 20 s |
| Parking lot | 11 s | |
| Open road | 10 s | |
| FFBPA | Obstacle | 110 s |
| Parking lot | 68 s | |
| Open road | 55 s |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, P.; Li, C.; Li, H.; Luan, Y.; Wang, A.; Wang, R.; Tang, S. An Extended Omega-K Algorithm for Automotive SAR with Curved Path. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4508. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16234508
Guo P, Li C, Li H, Luan Y, Wang A, Wang R, Tang S. An Extended Omega-K Algorithm for Automotive SAR with Curved Path. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(23):4508. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16234508
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Ping, Chao Li, Haolan Li, Yuchen Luan, Anyi Wang, Rongshu Wang, and Shiyang Tang. 2024. "An Extended Omega-K Algorithm for Automotive SAR with Curved Path" Remote Sensing 16, no. 23: 4508. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16234508
APA StyleGuo, P., Li, C., Li, H., Luan, Y., Wang, A., Wang, R., & Tang, S. (2024). An Extended Omega-K Algorithm for Automotive SAR with Curved Path. Remote Sensing, 16(23), 4508. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16234508






