Improving the ERA5-Land Temperature Product through a Deep Spatiotemporal Model That Uses Fused Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Source
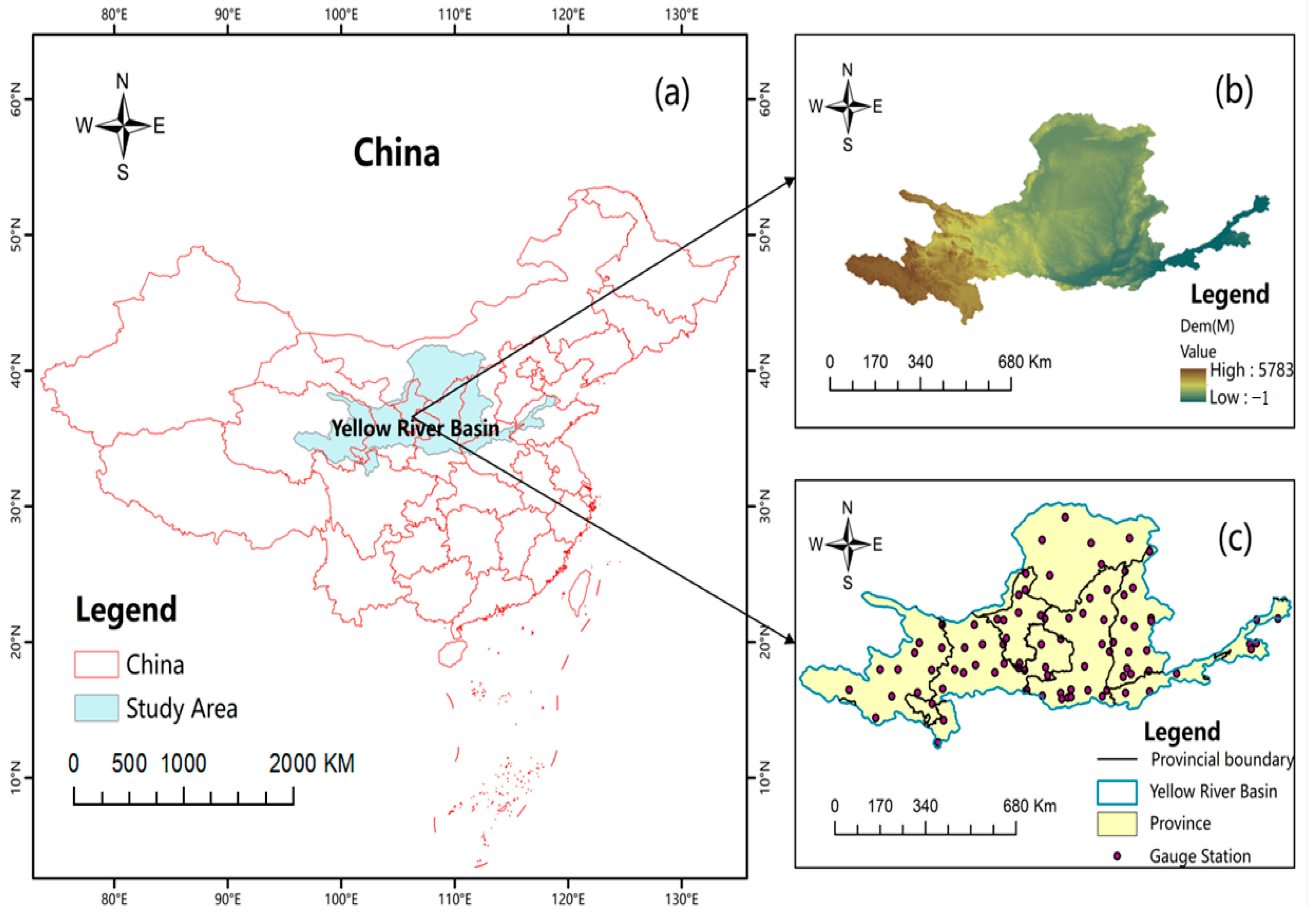
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Source
3. Research Method
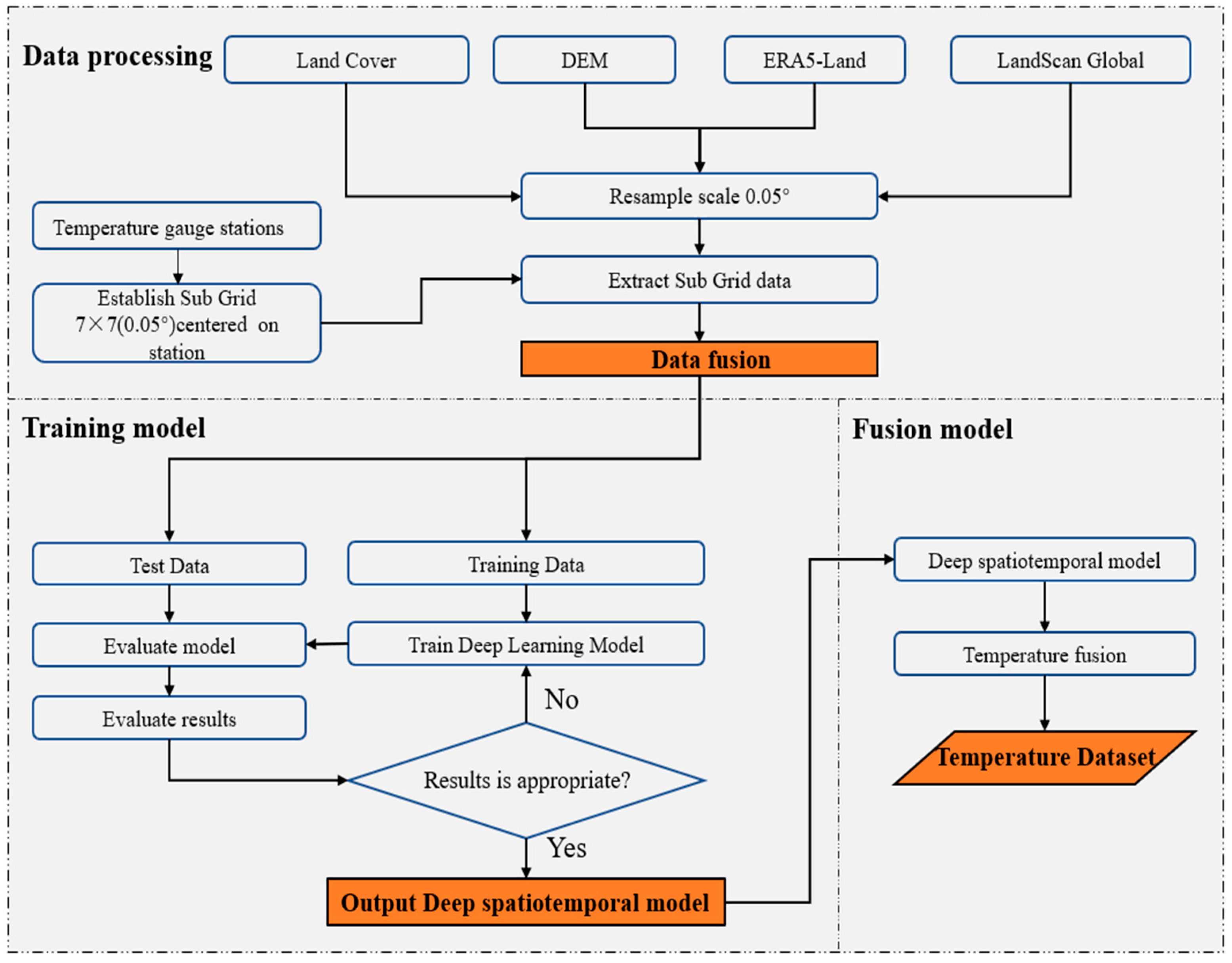
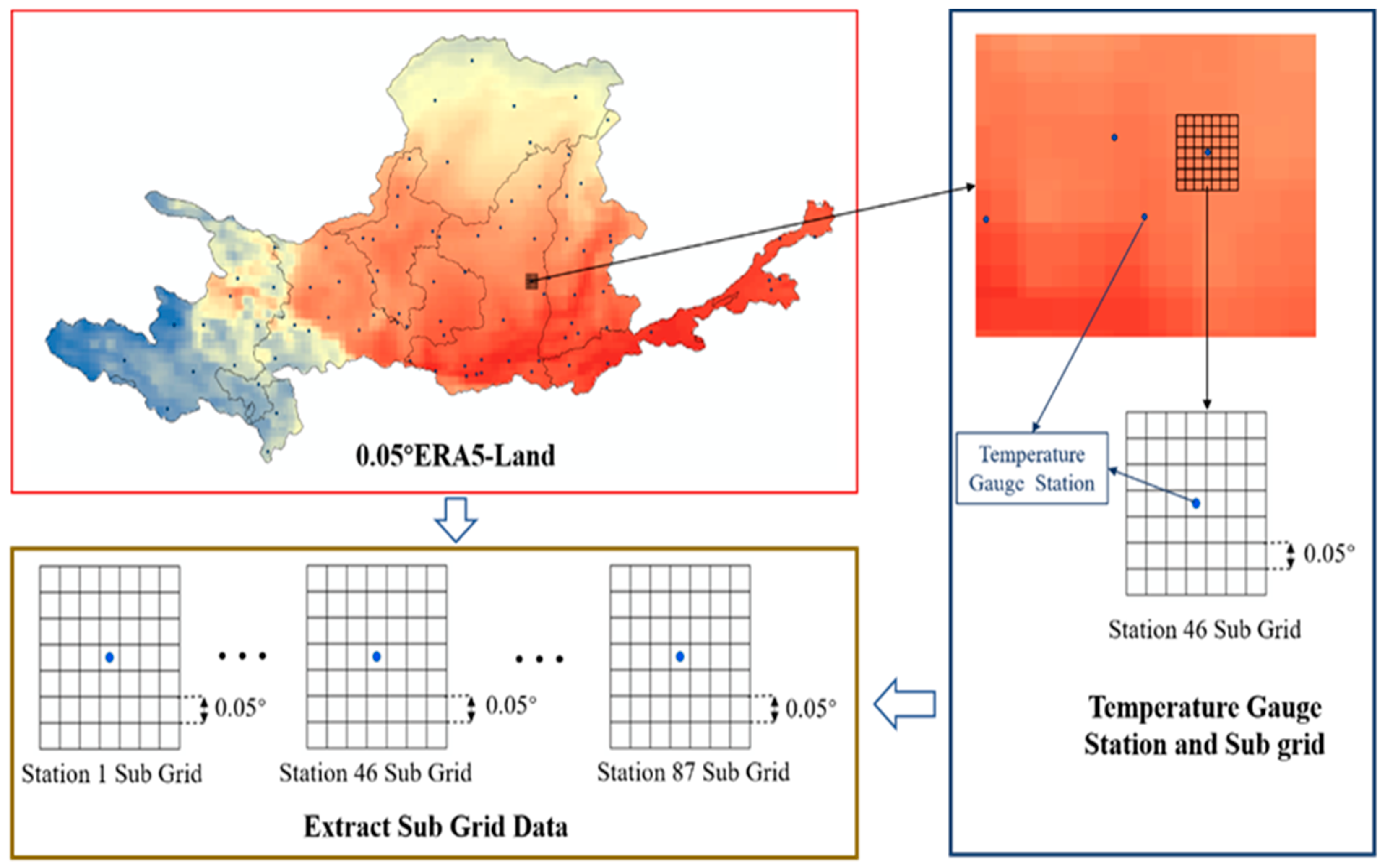
3.1. Data Processing
3.2. Neural Network
3.3. Deep Spatiotemporal Model
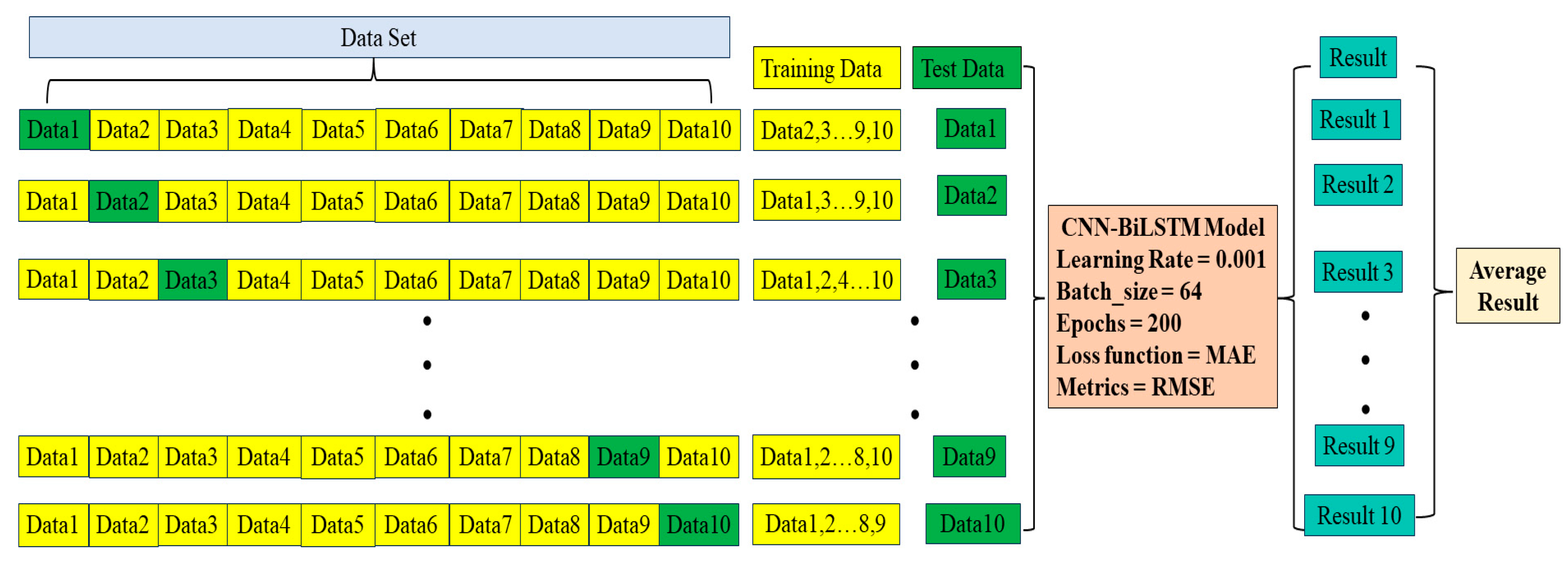
3.4. Model Training
4. Results and Analysis
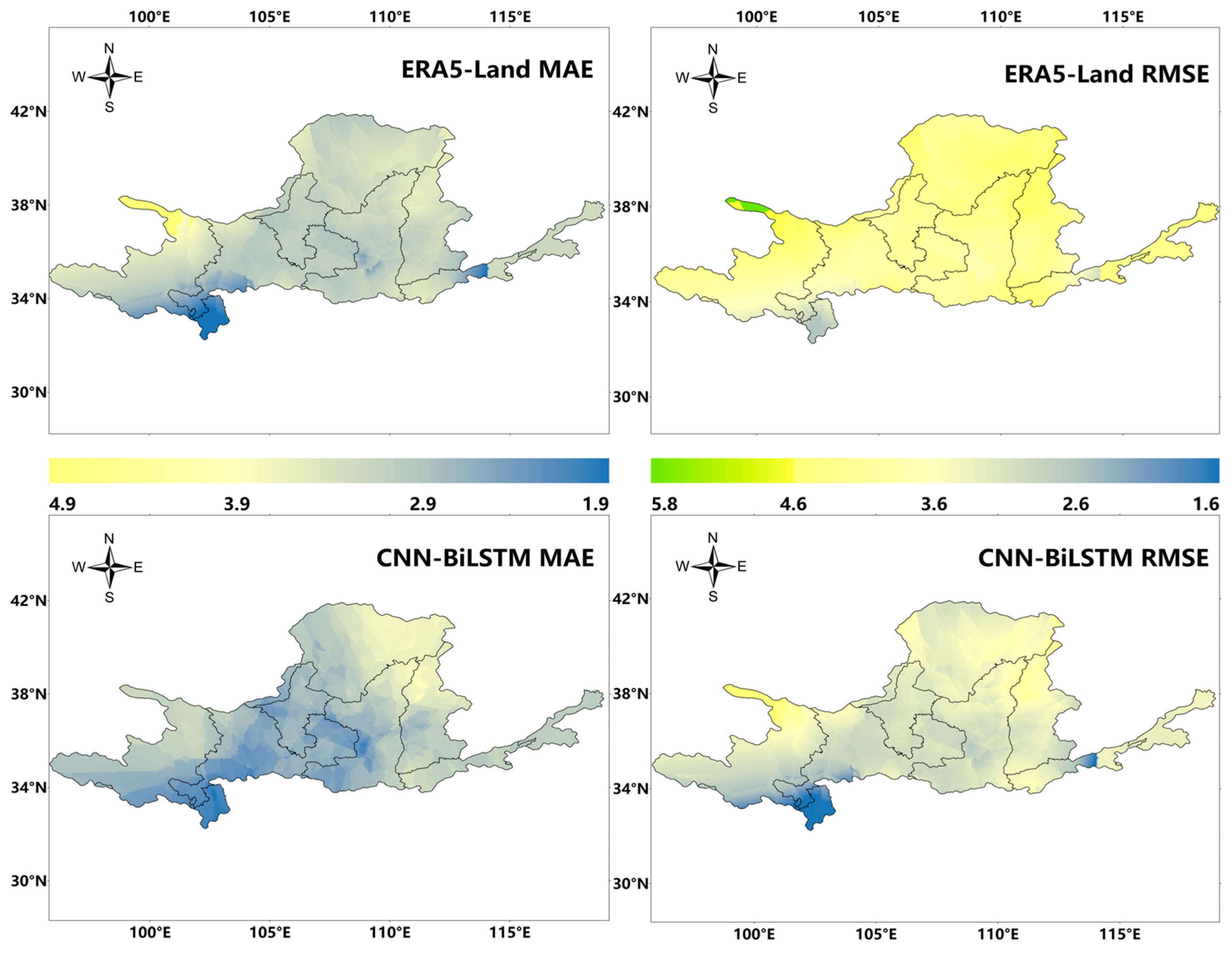
4.1. Temperature Deep Spatiotemporal Model Accuracy
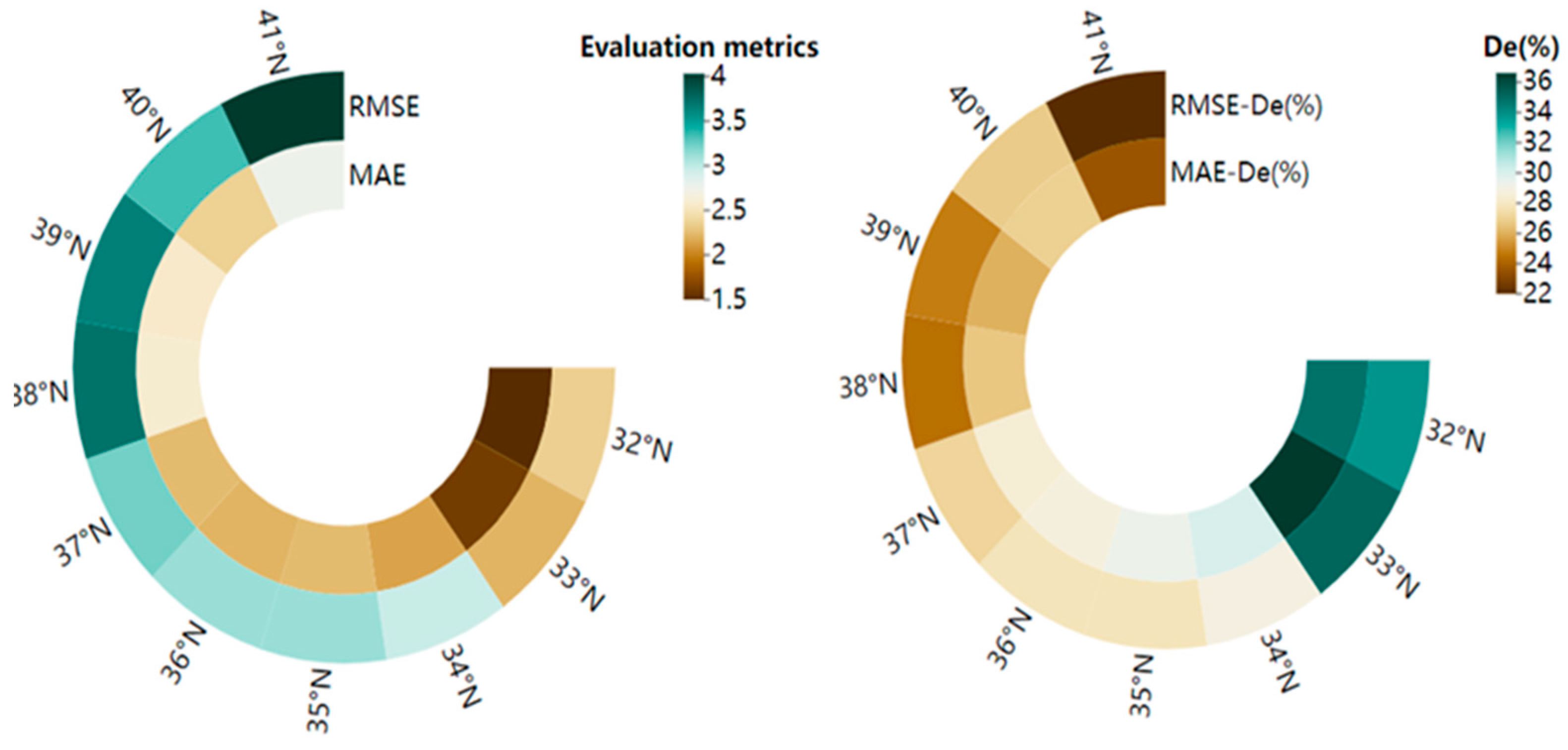
4.2. Temperature Deep Spatiotemporal Model Accuracy in Different Latitude
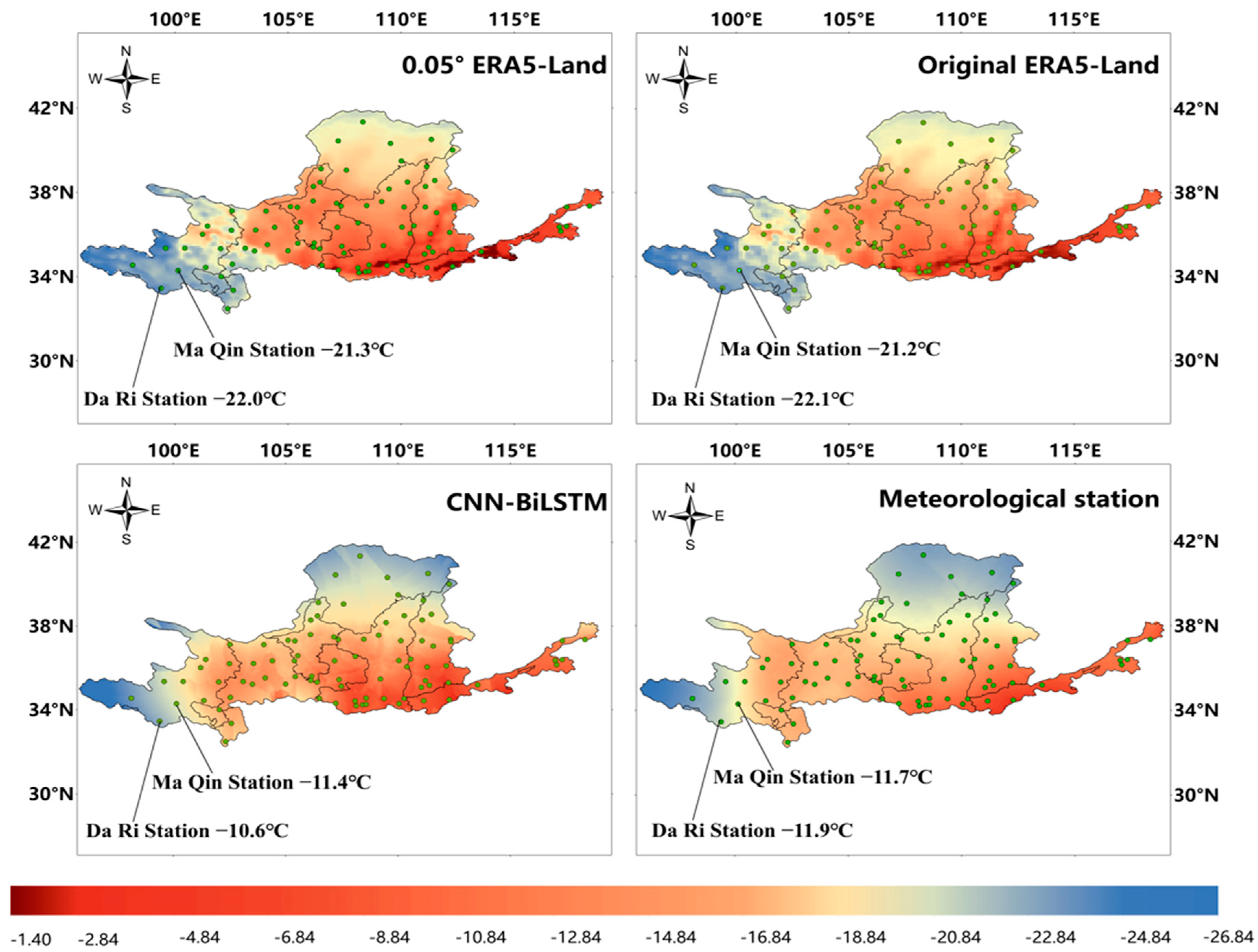
4.3. Temperature Spatial Distribution
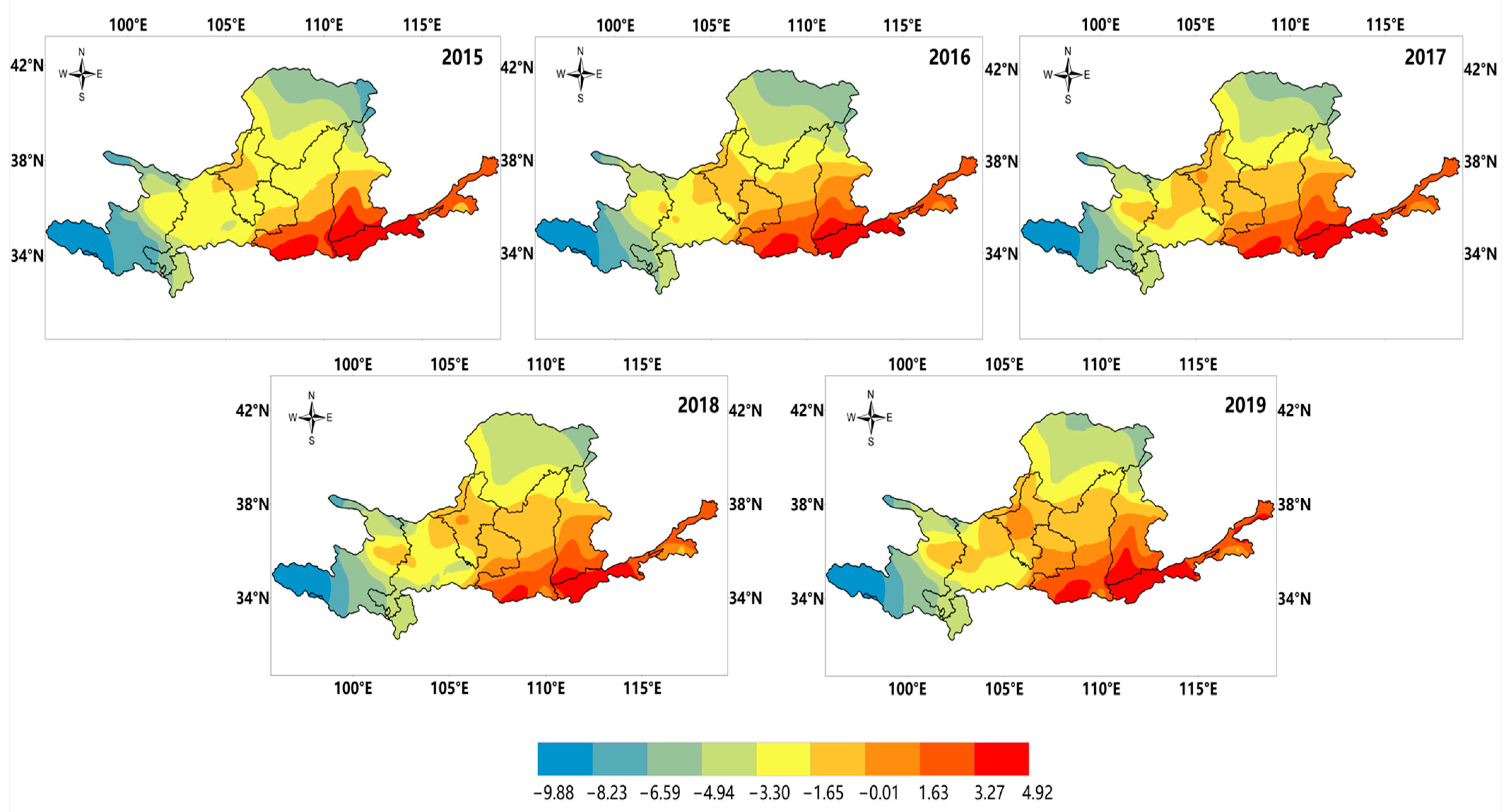
4.4. Change Trend of Annual Cold Months Average Temperature in the Yellow River Basin
4.5. Compare with Existing Research Result
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hsiang, S.M.; Burke, M.; Miguel, E. Quantifying the influence of climate on human conflict. Science 2013, 341, 1235367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regan, J.M.; Young, S.K. Climate change in the Horn of Africa: Causations for violent extremism. Behav. Sci. Terror. Political Aggress. 2024, 16, 185–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muruganandam, M.; Rajamanickam, S.; Sivarethinamohan, S.; Reddy, M.K.; Velusamy, P.; Gomathi, R.; Ravindiran, G.; Gurugubelli, T.R.; Munisamy, S.K. Impact of climate change and anthropogenic activities on aquatic ecosystem—A review. Environ. Res. 2023, 238, 117233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Li, T.; Przybysz, A.; Liu, H.; Zhang, B.; An, W.; Zhu, C. Effects of urban lakes and neighbouring green spaces on air temperature and humidity and seasonal variabilities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 91, 104438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Wu, W.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, J.; Hu, T.; Wang, P. Correlation analysis of land surface temperature and topographic elements in Hangzhou, China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, E.J.; Ghent, D.J.; Bulgin, C.E.; Remedios, J.J. A spatiotemporal analysis of the relationship between near-surface air temperature and satellite land surface temperatures using 17 years of data from the ATSR series. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 9185–9210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.X.; Pla, F.; Latorre-Carmona, P.; Myint, S.W.; Caetano, M.; Kieu, H.V. Characterizing the relationship between land use land cover change and land surface temperature. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 124, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, S.; Deng, X. Estimation of Summer Air Temperature over China Using Himawari-8 AHI and Numerical Weather Prediction Data. Adv. Meteorol. 2019, 2019, 2385310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Jiang, L.; Shi, C.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, Z.; Liao, J.; Yao, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, M.; Wang, H. CRA-40/atmosphere—The first-generation Chinese atmospheric reanalysis (1979–2018): System description and performance evaluation. J. Meteorol. Res. 2023, 37, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnay, E.; Kanamitsu, M.; Kistler, R.; Collins, W.; Deaven, D.; Gandin, L.; Iredell, M.; Saha, S.; White, G.; Woollen, J. The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. In Renewable Energy; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2018; pp. Vol1_146–Vol1_194. [Google Scholar]
- Gelaro, R.; McCarty, W.; Suárez, M.J.; Todling, R.; Molod, A.; Takacs, L.; Randles, C.A.; Darmenov, A.; Bosilovich, M.G.; Reichle, R. The modern-era retrospective analysis for research and applications, version 2 (MERRA-2). J. Clim. 2017, 30, 5419–5454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Ota, Y.; Harada, Y.; Ebita, A.; Moriya, M.; Onoda, H.; Onogi, K.; Kamahori, H.; Kobayashi, C.; Endo, H. The JRA-55 reanalysis: General specifications and basic characteristics. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. Ser. II 2015, 93, 5–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Shi, C.; Zhou, Z.; Jiang, L.; Liang, X.; Zhang, T.; Liao, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, M.; Yao, S. CMA global reanalysis (CRA-40): Status and plans. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Reanalysis, Rome, Italy, 13–17 November 2017; pp. 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Zhu, X.; Guo, R.; Xu, K.; Zhang, S. Applicability of ERA5 reanalysis of precipitation data in China. Arid. Land Geogr. 2022, 45, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, J.; Liang, S.; Wang, D. A practical reanalysis data and thermal infrared remote sensing data merging (RTM) method for reconstruction of a 1-km all-weather land surface temperature. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 260, 112437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Shen, H.; Wu, P.; Wu, J.; Gao, M.; Meng, C. Generating gapless land surface temperature with a high spatio-temporal resolution by fusing multi-source satellite-observed and model-simulated data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 278, 113083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Du, Q. Hourly mapping of surface air temperature by blending geostationary datasets from the two-satellite system of GOES-R series. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 183, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banzon, V.; Smith, T.M.; Chin, T.M.; Liu, C.; Hankins, W. A long-term record of blended satellite and in situ sea-surface temperature for climate monitoring, modeling and environmental studies. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2016, 8, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, R. Assessing scaling effect in downscaling land surface temperature in a heterogenous urban environment. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 96, 102256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, R.; Hang, R.; Ge, L.; Shi, C.; Liu, Q. Statistical downscaling of temperature distributions in southwest China by using terrain-guided attention network. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 1678–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Cao, R. Downscaling of surface air temperature over the Tibetan Plateau based on DEM. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 73, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsin, P.K.; Knudby, A.; Krayenhoff, E.S.; Brauer, M.; Henderson, S.B. Land use regression modeling of microscale urban air temperatures in greater Vancouver, Canada. Urban Clim. 2020, 32, 100636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Katzschner, L.; Ng, E. Modelling the fine-scale spatiotemporal pattern of urban heat island effect using land use regression approach in a megacity. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 891–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silver, D.; Schrittwieser, J.; Simonyan, K.; Antonoglou, I.; Huang, A.; Guez, A.; Hubert, T.; Baker, L.; Lai, M.; Bolton, A. Mastering the game of go without human knowledge. Nature 2017, 550, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willi, M.; Pitman, R.T.; Cardoso, A.W.; Locke, C.; Swanson, A.; Boyer, A.; Veldthuis, M.; Fortson, L. Identifying animal species in camera trap images using deep learning and citizen science. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2019, 10, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scher, S.; Messori, G. Predicting weather forecast uncertainty with machine learning. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 144, 2830–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malakouti, S.M. Utilizing time series data from 1961 to 2019 recorded around the world and machine learning to create a Global Temperature Change Prediction Model. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2023, 7, 100312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyn, J.A.; Durran, D.R.; Caruana, R. Improving data-driven global weather prediction using deep convolutional neural networks on a cubed sphere. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2020, 12, e2020MS002109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karevan, Z.; Suykens, J.A. Transductive LSTM for time-series prediction: An application to weather forecasting. Neural Netw. 2020, 125, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, A.G.; Heryadi, Y.; Abdurahman, E.; Suparta, W. Single layer & multi-layer long short-term memory (LSTM) model with intermediate variables for weather forecasting. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 135, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Chen, N.; Hu, C.; Wang, K.; Gong, J.; Chen, Z. Short and mid-term sea surface temperature prediction using time-series satellite data and LSTM-AdaBoost combination approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 233, 111358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zrira, N.; Kamal-Idrissi, A.; Farssi, R.; Khan, H.A. Time series prediction of sea surface temperature based on BiLSTM model with attention mechanism. J. Sea Res. 2024, 198, 102472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmaz, F.; Eyckerman, R.; Casteels, W.; Latré, S.; Hellinckx, P. CNN-LSTM architecture for predictive indoor temperature modeling. Build. Environ. 2021, 206, 108327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, G.; Wang, X.; Chen, D.; Yang, M.; Liu, L. Evaluation of a climate simulation over the Yellow River Basin based on a regional climate model (REMO) within the CORDEX. Atmos. Res. 2021, 254, 105522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Dutra, E.; Agustí-Panareda, A.; Albergel, C.; Arduini, G.; Balsamo, G.; Boussetta, S.; Choulga, M.; Harrigan, S.; Hersbach, H. ERA5-Land: A state-of-the-art global reanalysis dataset for land applications. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 4349–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Store, C.C.D. Land cover classification gridded maps from 1992 to present derived from satellite observations. Copernic. Clim. Change Serv. 2019, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, A.; McKee, J.; Sims, K.; Bright, E.; Reith, A.; Urban, M. LandScan Global 2019; LandScan Global, Oak Ridge National Laboratory: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siami-Namini, S.; Tavakoli, N.; Namin, A.S. The Performance of LSTM and BiLSTM in Forecasting Time Series. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), Los Angeles, CA, USA, 9–12 December 2019; pp. 3285–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tan, D.; Han, L.; Li, D. Review of climate change in the Yellow River Basin. J. Desert Res. 2021, 41, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, G.; Yu, H.; Wang, S.; Guan, X.; Ren, Y. Characteristics of climate change in the Yellow River basin during recent 40 years. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2020, 51, 1048–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Ji, Z.; Wen, X.; Lee, S.Y.; Wei, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Dong, W. Historical and projected climate change over three major river basins in China from Fifth and Sixth Coupled Model Intercomparison Project models. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 6455–6473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, N.; Xu, Y. A downscaling method for land surface air temperature of ERA5 reanalysis dataset under complex terrain conditions in mountainous areas. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2022, 24, 750–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebbar, B.E.; Khabba, S.; Merlin, O.; Simonneaux, V.; Hachimi, C.E.; Kharrou, M.H.; Chehbouni, A. Machine-Learning-Based Downscaling of Hourly ERA5-Land Air Temperature over Mountainous Regions. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Dataset | Time Frequency | Resolution | Data Resource |
|---|---|---|---|
| China daily surface climate dataset (V3.0) | Day | / | CMDC https://data.cma.cn, accessed on 15 April 2023 |
| ERA5-Land hourly data | Hourly | 0.1° | Ecmwf https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu, accessed on 15 April 2023 |
| Land cover classification gridded map | Year | 300 m | Ecmwf https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu, accessed on 18 April 2023 |
| SRTM 90M DEM | / | 90 m | Geospatial Data Cloud https://www.gscloud.cn, accessed on 20 April 2023 |
| Land Scan Global Population distribution | Year | 1 km | Oak Ridge National Laboratory https://landscan.ornl.gov, accessed on 21 April 2023 |
| MAE | Decreased | RMSE | Decreased | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERA5-Land | 3.14 | / | 4.37 | / |
| CNN-BiLSTM | 2.22 | 28.7% | 3.24 | 25.8% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, L.; Du, J.; Ren, J.; Hu, Q.; Qin, F.; Mu, W.; Hu, J. Improving the ERA5-Land Temperature Product through a Deep Spatiotemporal Model That Uses Fused Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3510. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16183510
Xu L, Du J, Ren J, Hu Q, Qin F, Mu W, Hu J. Improving the ERA5-Land Temperature Product through a Deep Spatiotemporal Model That Uses Fused Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(18):3510. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16183510
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Lei, Jinjin Du, Jiwei Ren, Qiannan Hu, Fen Qin, Weichen Mu, and Jiyuan Hu. 2024. "Improving the ERA5-Land Temperature Product through a Deep Spatiotemporal Model That Uses Fused Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data" Remote Sensing 16, no. 18: 3510. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16183510
APA StyleXu, L., Du, J., Ren, J., Hu, Q., Qin, F., Mu, W., & Hu, J. (2024). Improving the ERA5-Land Temperature Product through a Deep Spatiotemporal Model That Uses Fused Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sensing, 16(18), 3510. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16183510






