Semi-Automatic Detection of Ground Displacement from Multi-Temporal Sentinel-1 Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry Analysis and Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise in Xining City, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Datasets
2.1. Geological Setting of Xining City

2.2. Datasets
3. Methodology
3.1. SBAS InSAR Analysis
3.2. 2D Displacements Extraction
3.3. DBSCAN Cluster for Landslide Detection
4. Results
4.1. Mean LOS and 2D Displacement Rate Maps
4.2. Landslide and Subsidence Detection Results
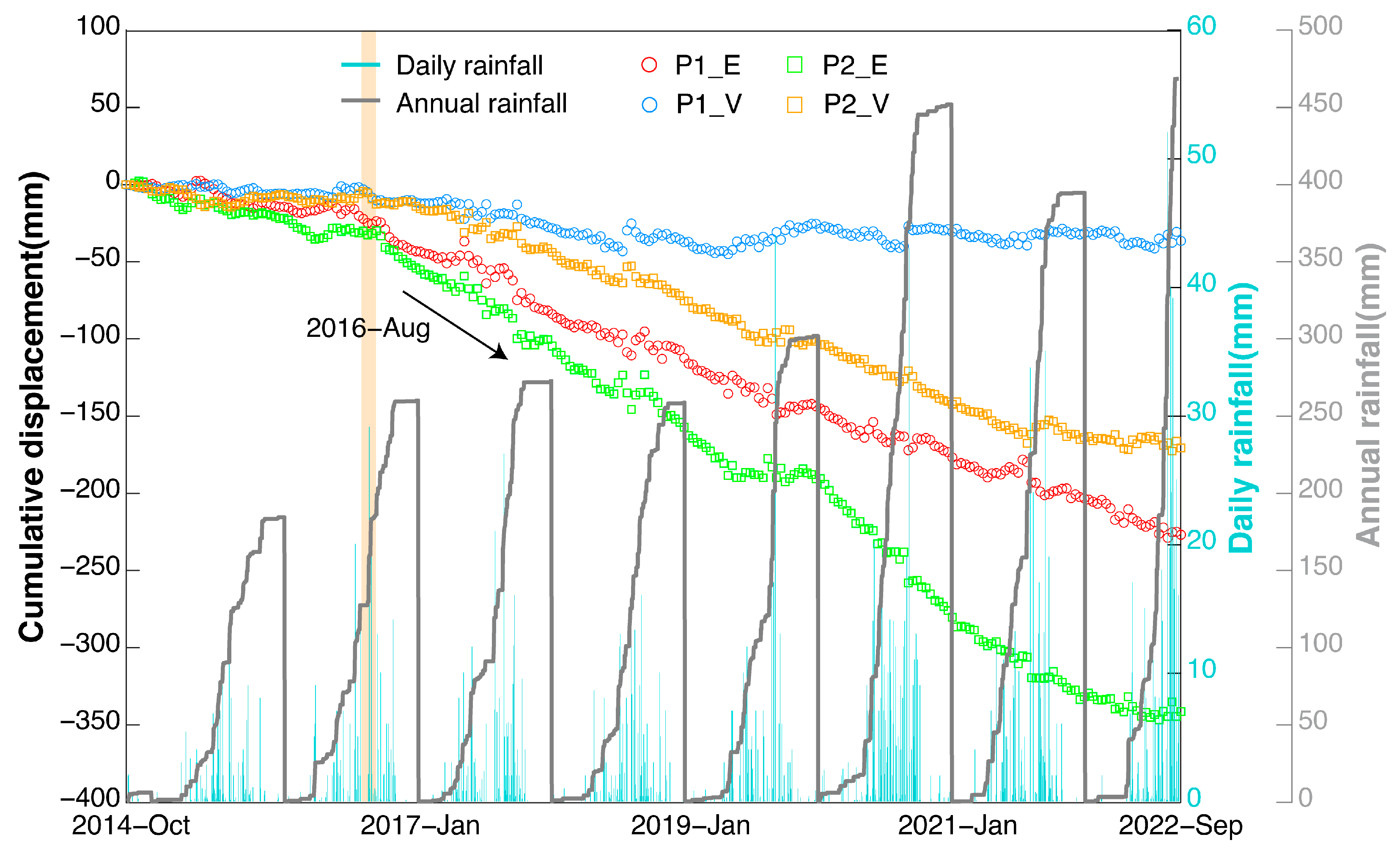
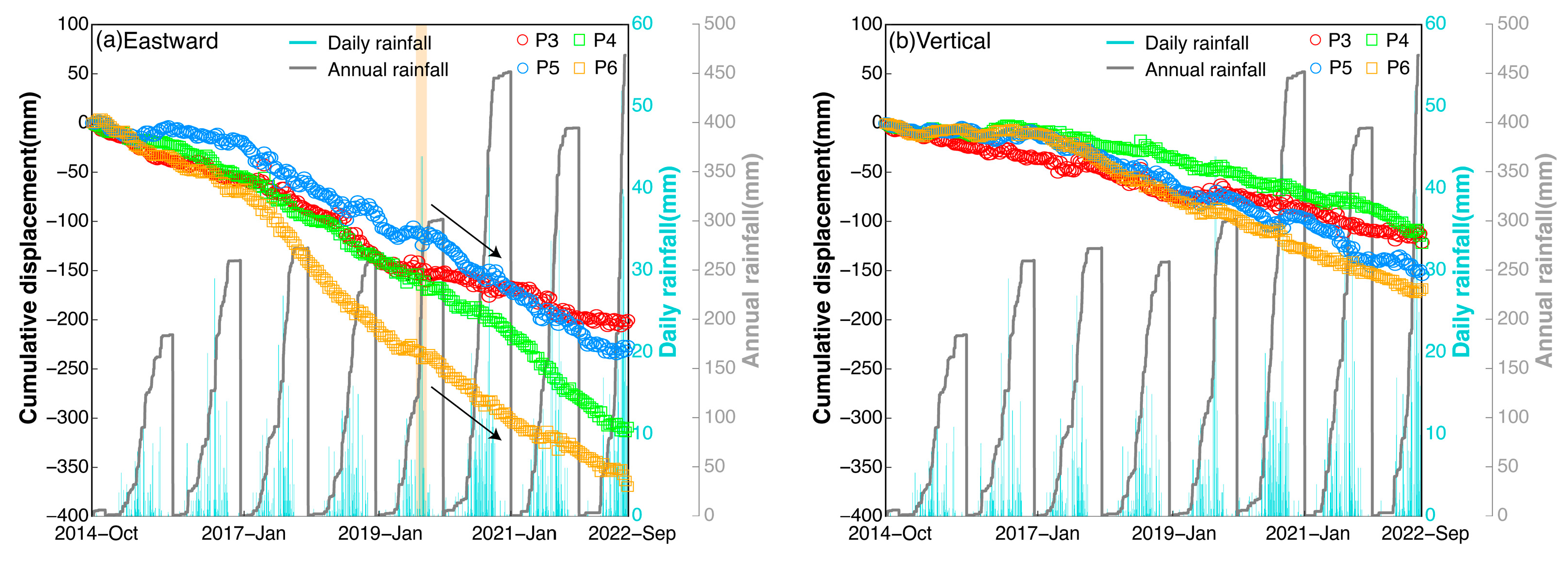
4.3. The Jiujiawan Landslide
4.4. Landslides along the LXHR
4.5. Anthropogenic Activity-Related Subsidence
5. Discussion
5.1. Loess Slope Stability Impact Factors
5.2. Limitations and Future Improvements
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cui, Y.; Xu, C.; Xu, S.; Chai, S.; Fu, G.; Bao, P. Small-scale catastrophic landslides in loess areas of China: An example of the March 15, 2019, Zaoling landslide in Shanxi Province. Landslides 2020, 17, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, G. Study of the 1920 Haiyuan earthquake-induced landslides in loess (China). Eng. Geol. 2007, 94, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.-q.; Peng, J.-b. A coupled slope cutting—A prolonged rainfall-induced loess landslide: A 17 October 2011 case study. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2014, 73, 997–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Xu, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Guo, M.; Cui, Z. Rainfall-triggered mass movements on steep loess slopes and their entrainment and distribution. CATENA 2019, 183, 104238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhu, C.; Zheng, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z. Landslide disaster in the loess area of China. J. For. Res. 2002, 13, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Tian, B.; Li, G.; Huang, D.; Zeng, T.; He, J.; Song, D. Landslide susceptibility mapping in the Loess Plateau of northwest China using three data-driven techniques-a case study from middle Yellow River catchment. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 10, 1033085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zheng, F.-l.; Liu, W.-z.; Flanagan, D.C. Spatial distribution and temporal trends of extreme temperature and precipitation events on the Loess Plateau of China during 1961–2007. Quat. Int. 2010, 226, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Peng, J.; Wang, G.; Javed, I.; Wang, Y.; Li, W. Distribution and characteristics of landslide in Loess Plateau: A case study in Shaanxi province. Eng. Geol. 2018, 236, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhuang, J.; Huang, W.; Zhu, X.; Leng, Y.; Ma, P. Distribution and genetic types of loess landslides in China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2019, 170, 329–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Wu, Y.; Liu, S.; Cheng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Wang, L.; Yu. Dokuchits, E.; Nkwazema, O.C. How 2022 extreme drought influences the spatiotemporal variations of terrestrial water storage in the Yangtze River Catchment: Insights from GRACE-based drought severity index and in-situ measurements. J. Hydrol. 2023, 626, 130245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Sun, P.; Li, R.; Wang, F.W. Preliminary investigation on a catastrophic loess landslide induced by heavy rainfall on 1 September 2022 in Qinghai, China. Landslides 2023, 20, 1553–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.; Ren, G.M.; Yang, X.L. Mechanism of a catastrophic landslide occurred on May 12, 2019, Qinghai Province, China. Landslides 2021, 18, 707–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Zhang, J.; Cao, X.; Wei, S.; Yan, H. Causes and influential factor analysis of landslides and rockfalls in north & south mountain areas of Xining City, Qinghai Province. Chin. J. Geol. Hazard Control 2021, 32, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Wu, X.T.; He, Z.W.; Xue, D.J.; Bai, W.Q.; Kang, G.C.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.X. Landslide Identification and Deformation Monitoring Analysis in Xining City Based on the Time Series InSAR of Sentinel-1A with Ascending and Descending Orbits. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2024, 83, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Cao, X.; Zhang, J.; Ying, Z.; Yan, H.; Wei, S. Temporal and spatial characteristics of landslide, rockfall and debris flow disasters in Qinghai Province during the period. Chin. J. Geol. Hazard Control 2021, 32, 134–142. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.W.; Chen, Y.; Yan, K.M. A destructive mudstone landslide hit a high-speed railway on 15 September 2022 in Xining city, Qinghai province, China. Landslides 2023, 20, 871–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, J. Controlling factors of loess landslides in western China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 59, 1671–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.J.; Ma, P.H.; Peng, J.B. Characteristics of loess landslides triggered by different factors in the Chinese Loess Plateau. J. Mt. Sci. 2021, 18, 3218–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Xue, L.; Yu, Y.T.; Guo, S.F.; Cui, Y.F.; Li, Y.; Qi, S.W. Remote Sensing Characterization of Mountain Excavation and City Construction in Loess Plateau. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL095230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.G.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, K.Y.; Dong, J.; Jiang, H.J.; Liao, M.S. Surface displacements of the Heifangtai terrace in Northwest China measured by X and C-band InSAR observations. Eng. Geol. 2019, 259, 105181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.G.; Wang, J.N.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, S.C.; Wu, Y.L.; Zhong, Y.L. Extreme rainfall-related accelerations in landslides in Danba County, Sichuan Province, as detected by InSAR. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 115, 103109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lin, H.; Wang, M.; Liu, X.; Chen, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H. A Review of Satellite Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry Applications in Permafrost Regions: Current status, challenges, and trends. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2022, 10, 93–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zuo, B.; Le, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, J. Penetrating remote sensing: Next-generation remote sensing for transparent earth. Innov. 2023, 4, 100519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Fumagalli, A.; Novali, F.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F.; Rucci, A. A New Algorithm for Processing Interferometric Data-Stacks: SqueeSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3460–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.Y.; Zhang, Q.; He, Y.; Peng, J.B.; Yang, C.S.; Kang, Y. Small-scale loess landslide monitoring with small baseline subsets interferometric synthetic aperture radar technique-case study of Xingyuan landslide, Shaanxi, China. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2016, 10, 026030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhao, C.Y.; Yan, M.; Wang, B.H.; Liu, X.J. The Early Identification and Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of Loess Landslides with SENTINEL-1A Datasets: A Case of Dingbian County, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.R.; Qiu, H.J.; Yang, D.D.; Liu, Z.J.; Ma, S.Y.; Pei, Y.Q.; He, J.Y.; Du, C.; Sun, H.S. Pre- and post-failure spatiotemporal evolution of loess landslides: A case study of the Jiangou landslide in Ledu, China. Landslides 2021, 18, 3475–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, A.J.; Ma, K.Q.; Zhang, M.S.; Meng, X.M.; Zhu, K.; Qiao, D.D.; Liu, T.M.; Li, Y.X.; Liu, W.C. Geomorphic understanding of loess landslides activity on the loess tableland:A case study in the Bailu Tableland, China. Catena 2024, 234, 107641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Gong, Y.F.; Huang, W.; Wang, X.; Ke, Z.Y.; Liu, Y.R.; Huo, A.D.; Adnan, A.; Abuarab, M.E. Identification of Potential Landslide Hazards Using Time-Series InSAR in Xiji County, Ningxia. Water 2023, 15, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Yao, X.; Gu, Z.; Ren, K.; Zhou, Z. Analysis on the development law of active geological hazards in the Loess Plateau based on InSAR identification. J. Geomech. 2022, 28, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Yang, C.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, H.; Liao, M.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X. Mapping and characterizing displacements of active loess slopes along the upstream Yellow River with multi-temporal InSAR datasets. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 674, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, C.H.; Xu, Q.; Zhao, K.Y.; Chen, W.L.; Wang, X.C.; Li, H.J.; Liu, J.L.; Kou, P.L. Spatiotemporal evolution and surface response of land subsidence over a large-scale land creation area on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 111, 102835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.D.; Lan, H.X.; Burgmann, R.; Warner, T.A.; Clague, J.J.; Li, L.P.; Wu, Y.M.; Zhao, X.X.; Zhang, Y.X.; Yao, J.M. Application of an improved multi-temporal InSAR method and forward geophysical model to document subsidence and rebound of the Chinese Loess Plateau following land reclamation in the Yan’an New District. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 279, 113102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Ge, D.; Yu, J.; Zhang, L.; Ma, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wan, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L. Active Deformation Areas of Potential Landslide Mapping with a Generalized Convolutional Neural Network. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.R.; Feng, G.C.; Xiong, Z.Q.; Wang, H.Y.; Zhao, Y.G.; Li, K.F.; Deng, K.L.; Wang, Y.X. An Improved Method for Automatic Identification and Assessment of Potential Geohazards Based on MT-InSAR Measurements. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wang, W.H.; Zhang, L.F.; Chen, Y.D.; Chen, Y.; Chen, B.S.; He, X.; Zhao, Z.A. An identification method of potential landslide zones using InSAR data and landslide susceptibility. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2023, 14, 2185120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, W.; Cheng, Y.; Li, Z. Landslide Detection in the Linzhi–Ya’an Section along the Sichuan–Tibet Railway Based on InSAR and Hot Spot Analysis Methods. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, J.; Zhang, L.; Deng, S.H.; Zhang, G.K.; Liao, M.S.; Gong, J.Y. Automatic detection and update of landslide inventory before and after impoundments at the Lianghekou reservoir using Sentinel-1 InSAR. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 118, 103224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Yu, C.; Li, Z.; Utili, S.; Frattini, P.; Crosta, G.; Peng, J. Triggering and recovery of earthquake accelerated landslides in Central Italy revealed by satellite radar observations. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, T.; Li, W.; Xu, Q.; Ge, D. Detecting slow-moving landslides using InSAR phase-gradient stacking and deep-learning network. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 963322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Zhang, L.; Dong, J.; Guo, J.; Wang, Y.; Liao, M. Automatic identification of active landslides over wide areas from time-series InSAR measurements using Faster RCNN. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 124, 103516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.; Xu, Q.; Jin, S.; Li, W.; Dong, X.; Guo, Q. Automatic Object Detection of Loess Landslide Based on Deep Learning. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2020, 45, 1747–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Survey, C.G. Xining City Pushes forward the Management of Geologic Hazards in Beishan Mountain. Available online: https://www.cgs.gov.cn/gzdt/dzhy/201603/t20160309_302410.html (accessed on 16 May 2024).
- He, L.; Wu, X.T.; He, Z.W.; Xue, D.J.; Luo, F.; Bai, W.Q.; Kang, G.C.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.X. Susceptibility Assessment of Landslides in the Loess Plateau Based on Machine Learning Models: A Case Study of Xining City. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Y.; Kaixiong, Q.; Qingli, D. Study on the distribution law of hidden dangers of major geological disasters in Xining City. J. Qinghai Environ. 2015, 25, 113–116. [Google Scholar]
- Qinghai Provincial Bureau of Statistics. Qinghai Statistical Yearbooks. Available online: http://tjj.qinghai.gov.cn/tjData/qhtjnj/ (accessed on 20 May 2024).
- Li, C.; Wang, X.; He, C.; Wu, X.; Kong, Z.; Li, X. China National Digital Geological Map (Public Version at 1:200 000 Scale) Spatial Database. Geol. China 2019, 46, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Wegnüller, U.; Werner, C.; Strozzi, T.; Wiesmann, A.; Frey, O.; Santoro, M. Sentinel-1 Support in the GAMMA Software. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 100, 1305–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A.; Bekaert, D.; Spaans, K.; Arıkan, M. Recent advances in SAR interferometry time series analysis for measuring crustal deformation. Tectonophysics 2012, 514-517, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Chen, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, P.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, C.; Wang, L. Refined landslide inventory and susceptibility of Weining County, China, inferred from machine learning and Sentinel-1 InSAR analysis. Trans. GIS 2024, 00, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M. Sentinel-1 TOPS co-registration over low-coherence areas and its application to velocity estimation using the all pairs shortest path algorithm. J. Geod. 2020, 94, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.G.; Liao, M.S.; Li, M.H.; Zhang, L.; Cunningham, C. Wide-Area Landslide Deformation Mapping with Multi-Path ALOS PALSAR Data Stacks: A Case Study of Three Gorges Area, China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.G.; Zhang, L.; Balz, T.; Liao, M.S. Landslide deformation monitoring using point-like target offset tracking with multi-mode high-resolution TerraSAR-X data. Isprs J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 105, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsonov, S.; Dille, A.; Dewitte, O.; Kervyn, F.; d‘Oreye, N. Satellite interferometry for mapping surface deformation time series in one, two and three dimensions: A new method illustrated on a slow-moving landslide. Eng. Geol. 2020, 266, 105471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Xu, L.; Guo, F.; Lee, J.; Yan, B.P. A local-density based spatial clustering algorithm with noise. Inf. Syst. 2007, 32, 978–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahsler, M.; Piekenbrock, M.; Doran, D. Dbscan: Fast Density-Based Clustering with R. J. Stat. Softw. 2019, 91, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanagala, H.K.; Krishnaiah, V. A Comparative Study of K-Means, Dbscan and Optics. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Communication and Informatics (ICCCI), Coimbatore, India, 7–9 January 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, C.; Xu, X.D.; Liu, W.R.; Xiong, F.; Lin, Y.; Cao, C.; Liu, X. Softening Damage Analysis of Gypsum Rock with Water Immersion Time Based on Laboratory Experiment. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 125575–125585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.R.; Qiu, H.J.; Cui, P.; Liu, Z.J.; Ye, B.F.; Yang, D.D.; Kamp, U. Early detection of potential landslides along high-speed railway lines: A pressing issue. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2023, 48, 3302–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Wide Web. Precipitation in Xining City, Qinghai Breaks Several Historical Records, Urban Precipitation is 237% More than the Same Period in Previous Years. Available online: https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1742012962818694306&wfr=spider&for=pc (accessed on 20 May 2024).
- Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Han, B.; An, N.; Zhang, H.; Ma, Y. Identification and hazard analysis of landslides triggered by earthquakes and rainfall. Earthq. Res. Adv. 2023, 4, 100272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Lu, P.; Thiebes, B. Comparing characteristics of rainfall- and earthquake-triggered landslides in the Upper Minjiang catchment, China. Eng. Geol. 2020, 268, 105518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, T. Triggering Factors and Forming Mechanism of Loess Landslides. J. Eng. Geol. 2011, 19, 530–540. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Zhang, S.; Yu, P. Analysis on the cause of landslide in Beishan Temple, Xining City. Manag. Strategy Qinghai Land Resour. 2006, 30–32. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Lin, G.; Liu, Q.; Su, X. Hydraulic property variations with depth in a loess mudstone landslide. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.; Wang, T. Water-temperature controlled deformation patterns in Heifangtai loess terraces revealed by wavelet analysis of InSAR time series and hydrological parameters. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 957339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Peng, J.; Xu, C.; Li, Z.; Densmore, A.; Milledge, D.; Iqbal, J.; Cui, Y. Distribution and characteristics of loess landslides triggered by the 1920 Haiyuan Earthquake, Northwest of China. Geomorphology 2018, 314, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Scaringi, G.; Xu, Q.; Huang, R. Internal erosion controls failure and runout of loose granular deposits: Evidence from flume tests and implications for postseismic slope healing. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 5518–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.W.; Liu, S.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Liu, C.C. Impacts of the Chi-Chi earthquake on subsequent rainfall-induced landslides in central Taiwan. Eng. Geol. 2006, 86, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Du, W.; Tian, H. Demonstration of monitoring and early warning of mega landslides in Xining City. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2021, 21, 7806–7813. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, C.N.; Peng, L.; Y., S. Genetic mechanisms and a stability evaluation of large landslides in Zhangjiawan, Qinghai Province. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2021, 21, 927–934. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Wu, H.; Yang, M.; Huang, C.; Tang, B. Trend Classification of InSAR Displacement Time Series Using SAE–CNN. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Li, M.; Huang, C.; Zhang, R.; Liu, R. Exploring the InSAR Deformation Series Using Unsupervised Learning in a Built Environment. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
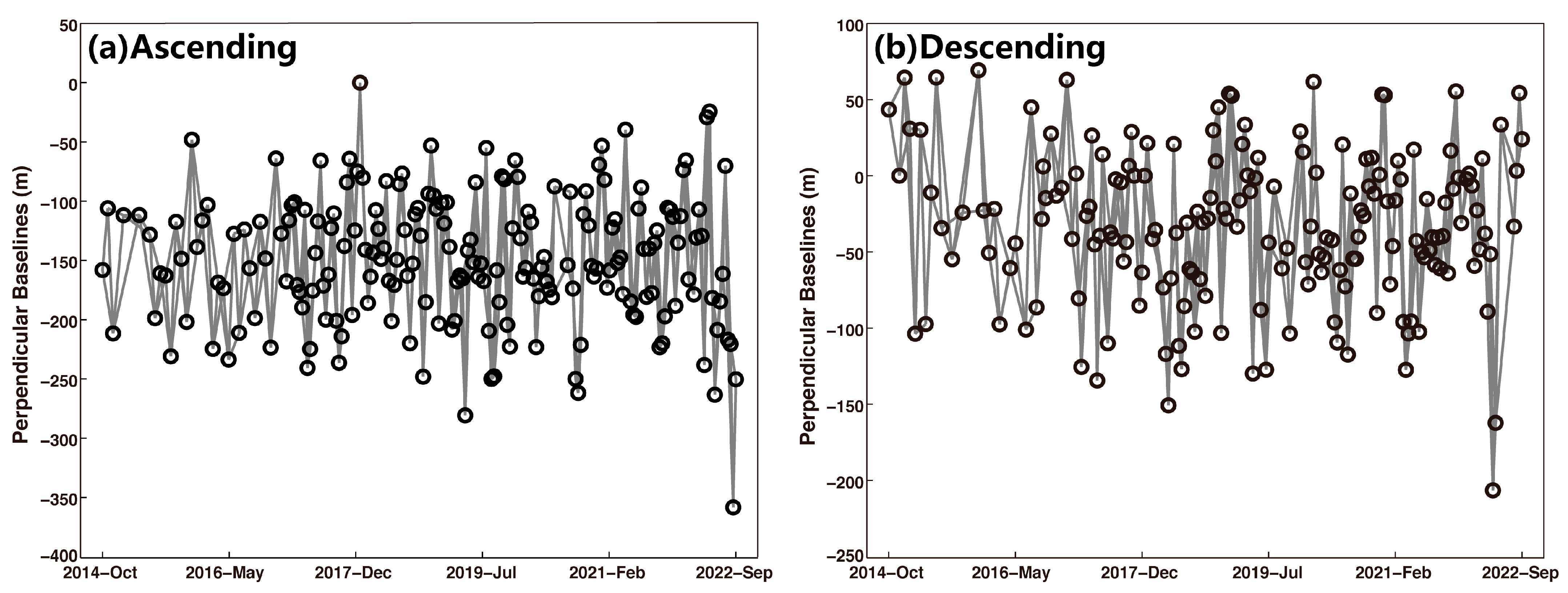








| Sensor | Sentinel-1A/B | |
|---|---|---|
| Path number | 128 | 135 |
| Orbit direction | Ascending | Descending |
| Heading angle (°) | −13.19 | 193.18 |
| Look angle (°) | 36.83 | 43.86 |
| Period | October 2014–September 2022 | October 2014–September 202 |
| Reference image | 2 January 2018 | 2 January 2018 |
| Number of scenes | 197 | 177 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, D.; Wu, Q.; Sun, Z.; Shi, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y. Semi-Automatic Detection of Ground Displacement from Multi-Temporal Sentinel-1 Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry Analysis and Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise in Xining City, China. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3066. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16163066
Chen D, Wu Q, Sun Z, Shi X, Zhang S, Zhang Y, Wu Y. Semi-Automatic Detection of Ground Displacement from Multi-Temporal Sentinel-1 Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry Analysis and Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise in Xining City, China. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(16):3066. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16163066
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Dianqiang, Qichen Wu, Zhongjin Sun, Xuguo Shi, Shaocheng Zhang, Yi Zhang, and Yunlong Wu. 2024. "Semi-Automatic Detection of Ground Displacement from Multi-Temporal Sentinel-1 Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry Analysis and Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise in Xining City, China" Remote Sensing 16, no. 16: 3066. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16163066
APA StyleChen, D., Wu, Q., Sun, Z., Shi, X., Zhang, S., Zhang, Y., & Wu, Y. (2024). Semi-Automatic Detection of Ground Displacement from Multi-Temporal Sentinel-1 Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry Analysis and Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise in Xining City, China. Remote Sensing, 16(16), 3066. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16163066







