A Contrastive Learning Based Multiview Scene Matching Method for UAV View Geo-Localization
Abstract
1. Introduction
- To better capture global information and reduce model complexity, we proposed the MSM-Transformer architecture, which reduces model complexity by leveraging a weight-sharing strategy and employs a self-attention mechanism to fuse features, thereby capturing global information. This framework, while maintaining low model complexity, significantly enhances inference speed and the ability to capture global contextual information.
- To address the issue of sample imbalance between drone and satellite images, we proposed a symmetric DCL loss function that decouples positive and negative samples, thereby eliminating their coupling effect and addressing the challenge of the small proportion of positive samples in training. In comparison with existing loss functions, our approach is capable of overcoming the difficulty of low positive sample ratios in the training process, thus enhancing the overall performance and robustness of the model.
- We validated the effectiveness of our method on the University-1652 benchmark dataset, achieving the highest accuracy with the least number of parameters.
2. Related Works
2.1. UAV to Satellite Cross-View Geo-Localization
2.2. Transformer in Vision
2.3. Image Retrieval Methods for Contrastive Learning
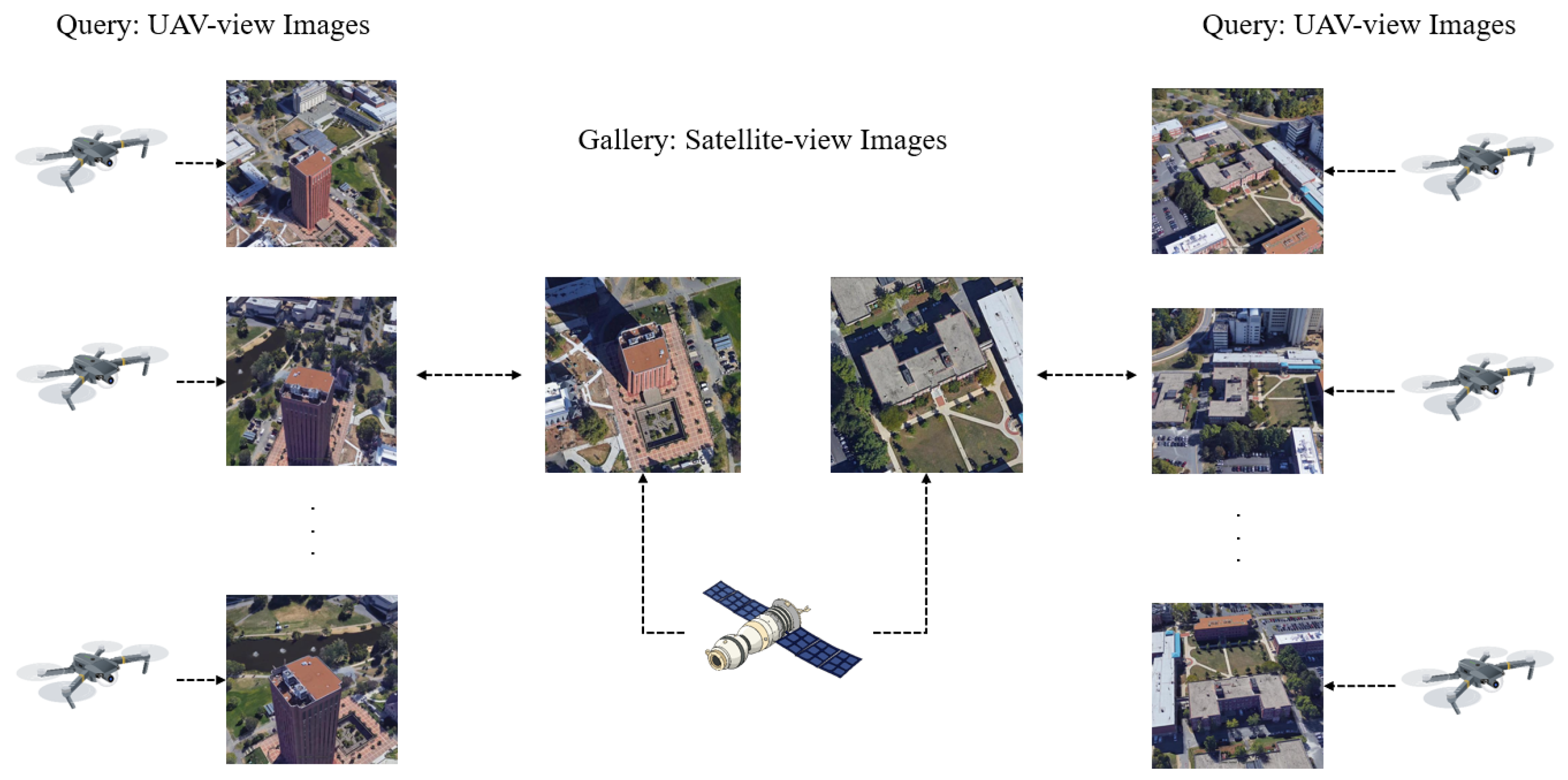
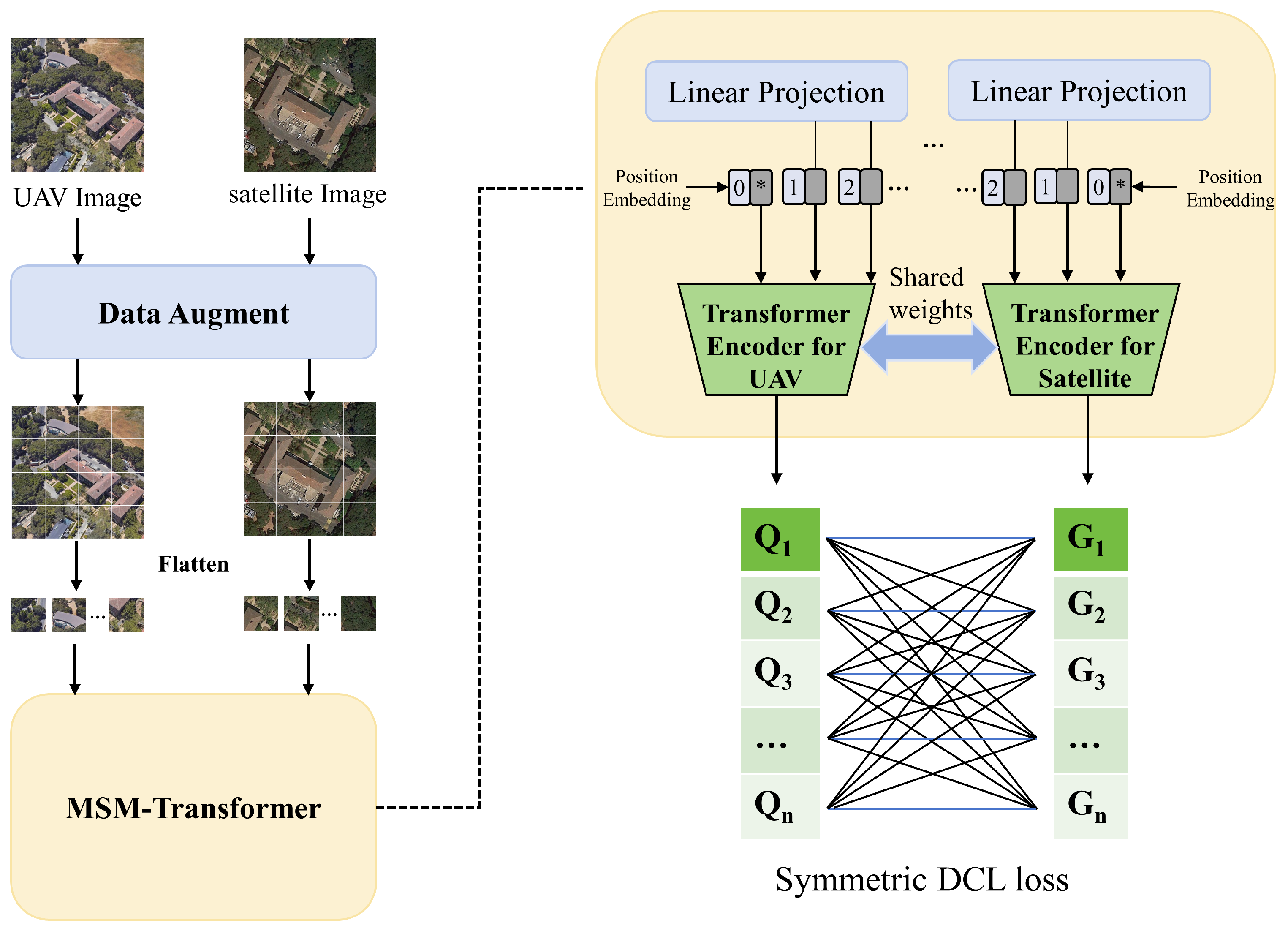
3. Proposed Method
3.1. Overview
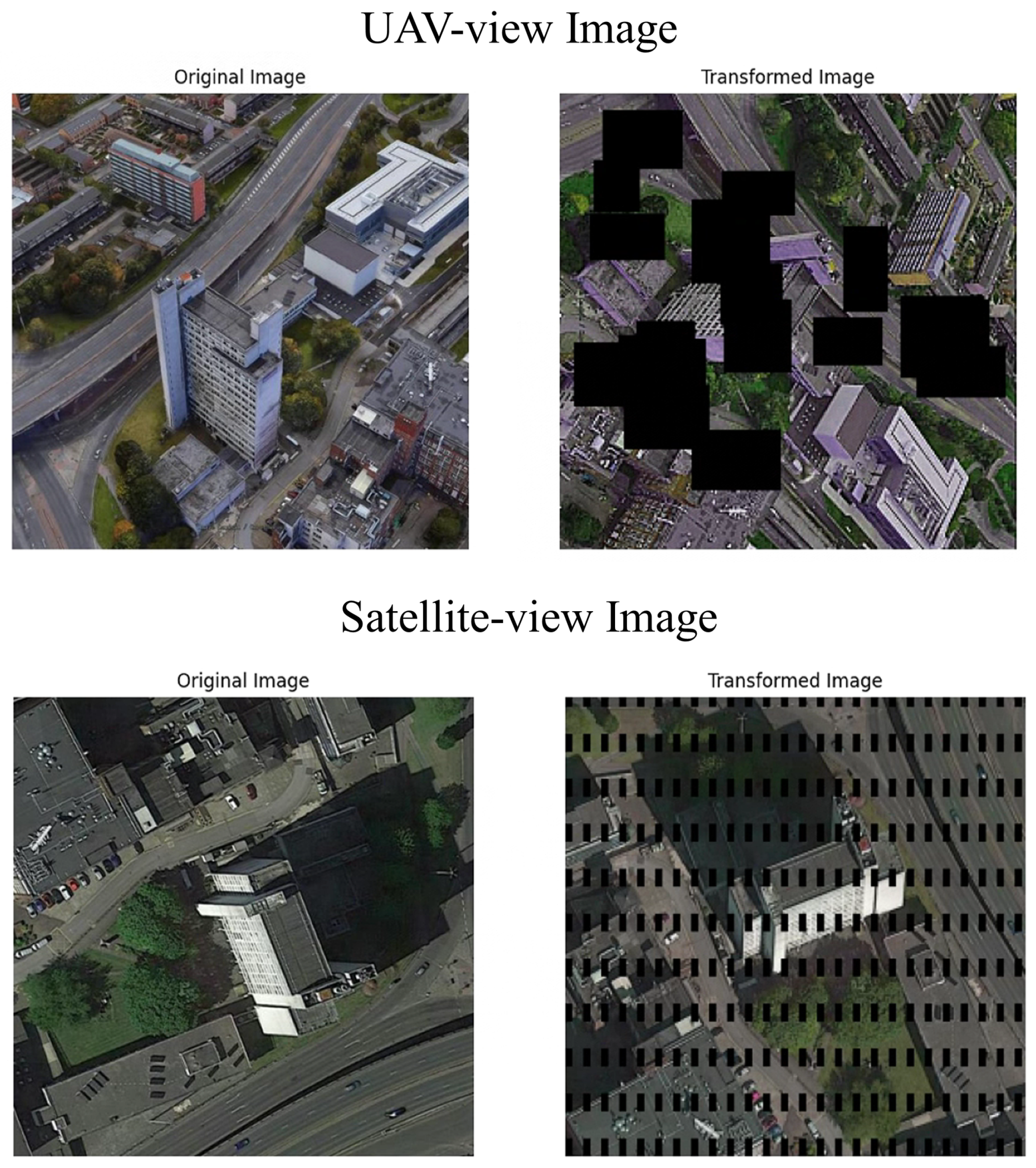
3.2. Data Augmentation
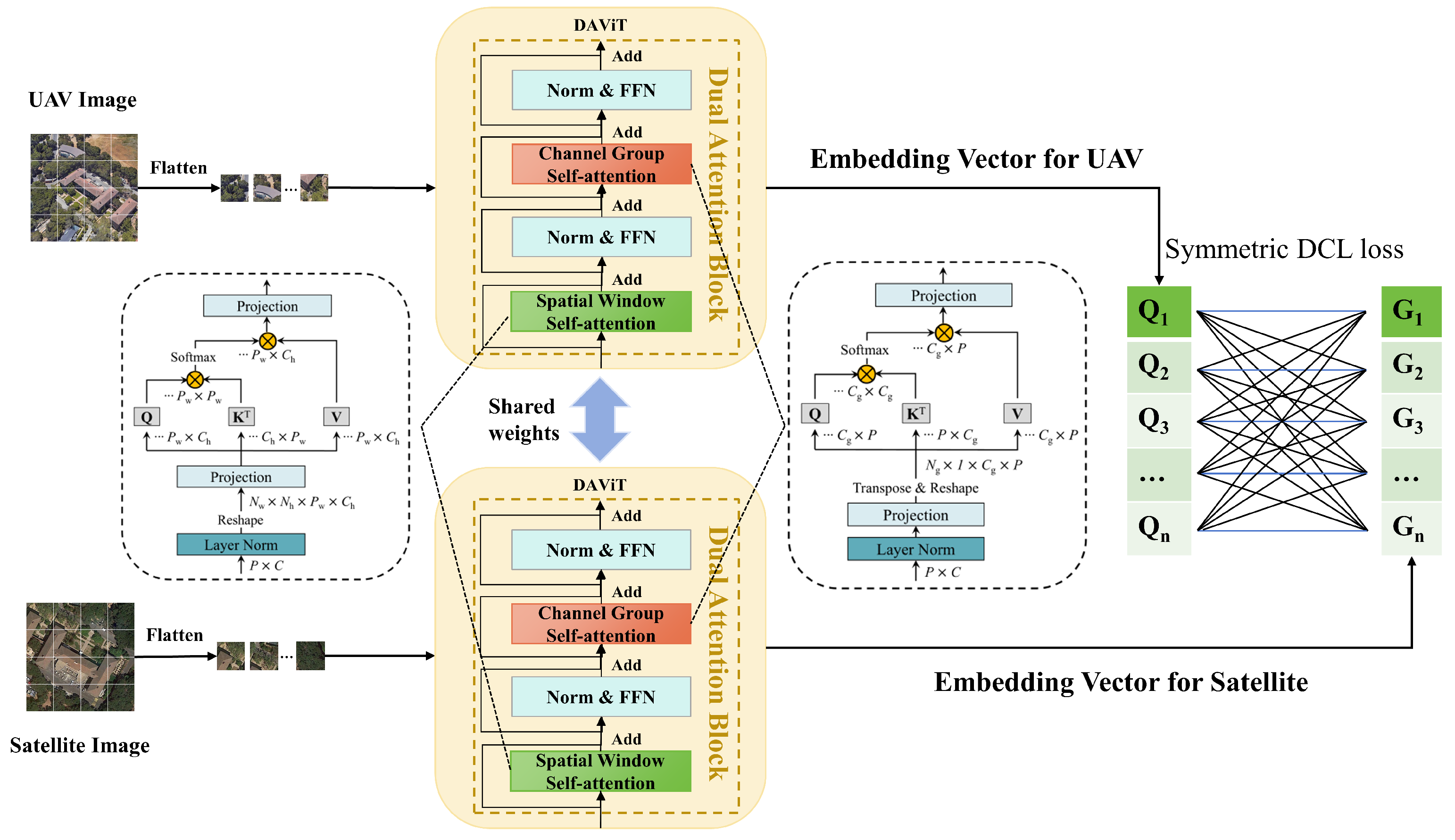
3.3. MSM-Transformer
3.4. Symmetric DCL Loss
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Evaluation Metric
4.3. Implementation Details
4.4. Ablation Study
4.5. Comparison with Other State-of-the-Art Methods
- (1)
- ResNet-50 + contrastive loss [54]: A Siamese network with VGG-16 as the backbone and contrastive loss as the loss function.
- (2)
- ResNet-50 + triplet loss [55]: A Siamese network with ResNet-50 as the backbone and triplet loss as the loss function.
- (3)
- TResNet-50 + instance loss [56]: A Siamese network with ResNet-50 as the backbone and instance loss as the loss function.
- (4)
- LCM [57]: As a solution to the multi-view problem, LCM uses a multi-query strategy to supplement missing features in single-view images during the query process, enhancing the algorithm’s robustness.
- (5)
- LPN [58]: In similarity measurement, LPN adopts a square ring feature segmentation strategy, focusing on the distance from the image center. It simplifies block matching, enabling block representation learning and similarity measurement.
- (6)
- F3-Net [59]: After multi-view feature learning, F3-Net uses a Feature Alignment and Unification (FAU) module with EM distance to compute the similarity of misaligned features.
- (7)
- PCL [60]: To address the geometric spatial relationship between UAV and satellite views, PCL proposes an end-to-end cross-view matching method that integrates a cross-view synthesis module and a geo-location module, fully considering the spatial correspondence and surrounding area information of UAV-satellite views.
- (8)
- FSRA [13]: To tackle the sample imbalance problem, FSRA proposes a multi-sampling strategy to overcome the differences in the number of satellite images and images from other sources.
- (9)
- TransFG [8]: In response to the cross-view image matching problem, TransFG introduces a transformer pipeline that integrates Feature Aggregation (FA) and Gradient Guidance (GG) modules to effectively balance feature representation and alignment.
- (10)
- GeoFormer [61]: To significantly enhance the accuracy and efficiency of drone cross-view geo-localization, GeoFormer introduces a Transformer-based Siamese network that achieves a balance between matching accuracy and efficiency through efficient Transformer feature extraction, multi-scale feature aggregation, and a semantic-guided region segmentation module.
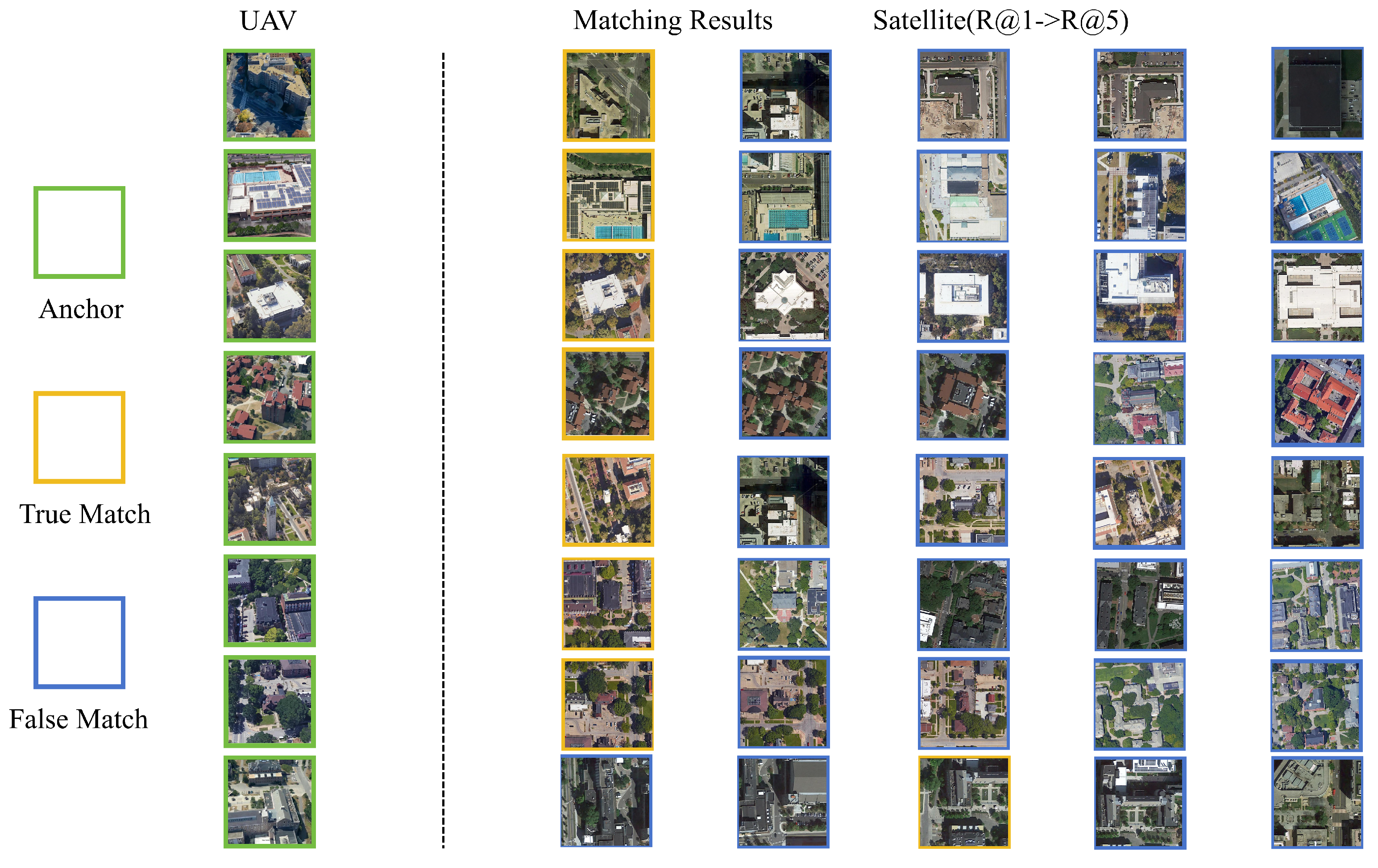
4.6. Retrieval Results
4.7. Algorithm Efficiency Test
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Radoglou–Grammatikis, P.; Sarigiannidis, P.; Lagkas, T.; Moscholios, I. A compilation of uav applications for precision agriculture. Comput. Netw. 2020, 172, 107148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ružić, I.; Benac, Č.; Jovančević, S.D.; Radišić, M. The application of uav for the analysis of geological hazard in krk island, croatia, mediterranean sea. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yao, Z.; Li, T.; Ying, Z.; Wu, X.; Hao, S.; Liu, M.; Wang, Z.; Gu, T. Enhanced open biomass burning detection: The brantnet approach using uav aerial imagery and deep learning for environmental protection and health preservation. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, Z.; Ullah, F.; Munawar, H.S.; Al-Turjman, F. Addressing disasters in smart cities through uavs path planning and 5g communications: A systematic review. Comput. Commun. 2021, 168, 114–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Dong, W.; Liu, S.; Song, L.; Zhou, J.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Xu, T.; He, X.; Sun, J. Mapping super high resolution evapotranspiration in oasis-desert areas using uav multi-sensor data. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 287, 108466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Zhou, P.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y. A novel geo-localization method for uav and satellite images using cross-view consistent attention. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Wei, S.; Lu, M. Fully convolutional networks for multisource building extraction from an open aerial and satellite imagery data set. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 57, 574–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Ren, K.; Yue, T.; Zhang, C.; Yuan, S. Transfg: A cross-view geo-localization of satellite and uavs imagery pipeline using transformer-based feature aggregation and gradient guidance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 4700912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Bruzzone, L.; Shan, J.; Bovolo, F.; Zhu, Q. Fast and robust matching for multimodal remote sensing image registration. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 9059–9070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, C.; Qi, B.; Zhu, M.; Wu, N. 4scig: A four-branch framework to reduce the interference of sky area in cross-view image geo-localization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 4703818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Sun, B.; Lu, X.; Jia, S. Geographic semantic network for cross-view image geo-localization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 4704315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, M.; Hu, J.; Zhuang, J.; Zheng, E. A transformer-based feature segmentation and region alignment method for uav-view geo-localization. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2021, 32, 4376–4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpi, R.; Namkoong, H.; Sener, O.; Duchi, J.C.; Murino, V.; Savarese, S. Generalizing to unseen domains via adversarial data augmentation. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 31: 31st Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Montréal, QC, Canada, 3–8 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, Q.; Huang, R.; Cheng, H.; Zhan, H.; Li, J.; Liu, Z. Learning quintuplet loss for large-scale visual geolocalization. IEEE MultiMedia 2020, 27, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-Y.; Manmatha, R.; Smola, A.J.; Krahenbuhl, P. Sampling matters in deep embedding learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2840–2848. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, M.; Xiao, B.; Codella, N.; Luo, P.; Wang, J.; Yuan, L. Davit: Dual attention vision transformers. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 74–92. [Google Scholar]
- Bansal, M.; Daniilidis, K.; Sawhney, H. Ultrawide baseline facade matching for geo-localization. In Large-Scale Visual Geo-Localization; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 77–98. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, M.; Bessinger, Z.; Workman, S.; Jacobs, N. Predicting ground-level scene layout from aerial imagery. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 867–875. [Google Scholar]
- Vo, N.N.; Hays, J. Localizing and orienting street views using overhead imagery. In Proceedings of the ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Proceedings, Part I 14. Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 494–509. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, J.; Jiang, L. Style alignment-based dynamic observation method for uav-view geo-localization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 3000914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regmi, K.; Shah, M. Bridging the domain gap for ground-to-aerial image matching. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 470–479. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, S.; Guo, Y.; Khan, S.; Hu, J.; Wen, G. Ground-to-aerial image geo-localization with a hard exemplar reweighting triplet loss. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 8391–8400. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.; Shah, M.; Chen, C. Transgeo: Transformer is all you need for cross-view image geo-localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 1162–1171. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30: Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2017, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Touvron, H.; Cord, M.; Douze, M.; Massa, F.; Sablayrolles, A.; Jégou, H. Training data-efficient image transformers & distillation through attention. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 10347–10357. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Miao, D.; Zhao, X. Hyneter: Hybrid network transformer for multiple computer vision tasks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2024, 20, 8773–8785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lu, X.; Zhu, Y. Cross-view geo-localization with layer-to-layer transformer. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 29009–29020. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Kornblith, S.; Norouzi, M.; Hinton, G. A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 13–18 July 2020; pp. 1597–1607. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Fan, H.; Wu, Y.; Xie, S.; Girshick, R. Momentum contrast for unsupervised visual representation learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 9729–9738. [Google Scholar]
- Khosla, P.; Teterwak, P.; Wang, C.; Sarna, A.; Tian, Y.; Isola, P.; Maschinot, A.; Liu, C.; Krishnan, D. Supervised contrastive learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 18661–18673. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Krishnan, D.; Isola, P. Contrastive multiview coding. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Proceedings, Part XI 16. Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 776–794. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Yu, S.X.; Lin, D. Unsupervised feature learning via non-parametric instance discrimination. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 3733–3742. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, H.; Huang, L.; Nie, J.; Wei, Z. Unsupervised deep hashing with fine-grained similarity-preserving contrastive learning for image retrieval. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 34, 4095–4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Dong, L.; Dong, W.; Shi, G. Supervised contrastive learning based on fusion of global and local features for remote sensing image retrieval. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5208513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.H.; Hong, C.Y.; Hsu, Y.C.; Liu, T.L.; Chen, Y.; LeCun, Y. Decoupled contrastive learning. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 668–684. [Google Scholar]
- Shorten, C.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M. A survey on image data augmentation for deep learning. J. Big Data 2019, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yang, F.; Satoh, S. Geo-localization via ground-to-satellite cross-view image retrieval. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2022, 25, 2176–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xiang, Y.; Li, S. Combining convolutional and vision transformer structures for sheep face recognition. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 205, 107651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroff, F.; Kalenichenko, D.; Philbin, J. Facenet: A unified embedding for face recognition and clustering. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 815–823. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.; Feng, M.; Nguyen, R.M.H.; Lee, G.H. Cvm-net: Cross-view matching network for image-based ground-to-aerial geo-localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7258–7267. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; Ramesh, A.; Goh, G.; Agarwal, S.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Mishkin, P.; Clark, J.; et al. Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 8748–8763. [Google Scholar]
- Güldenring, R.; Nalpantidis, L. Self-supervised contrastive learning on agricultural images. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 191, 106510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, A.; Babu, A.R.; Zadeh, M.Z.; Banerjee, D.; Makedon, F. A survey on contrastive self-supervised learning. Technologies 2020, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shubodh, S.; Omama, M.; Zaidi, H.; Parihar, U.S.; Krishna, M. Lip-loc: Lidar image pretraining for cross-modal localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2024; pp. 948–957. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Wei, Y.; Yang, Y. University-1652: A multi-view multi-source benchmark for drone-based geo-localization. In Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Seattle WA USA, 12–16 October 2020; pp. 1395–1403. [Google Scholar]
- Workman, S.; Souvenir, R.; Jacobs, N. Wide-area image geolocalization with aerial reference imagery. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 3961–3969. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Li, H. Lending orientation to neural networks for cross-view geo-localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 5624–5633. [Google Scholar]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; et al. Pytorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 32: Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2019, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J. A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Loshchilov, I.; Hutter, F. Fixing weight decay regularization in adam. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR 2018), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Loshchilov, I.; Hutter, F. Sgdr: Stochastic gradient descent with warm restarts. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1608.03983. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, W.; Zheng, L.; Ye, Q.; Kang, G.; Yang, Y.; Jiao, J. Image-image domain adaptation with preserved self-similarity and domain-dissimilarity for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 994–1003. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Feng, J.; Qi, M.; Jiang, J.; Yan, S. End-to-end comparative attention networks for person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 3492–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Zheng, L.; Garrett, M.; Yang, Y.; Xu, M.; Shen, Y.-D. Dual-path convolutional image-text embeddings with instance loss. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl. 2020, 16, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Zhou, J.; Meng, L.; Long, Z. A practical cross-view image matching method between uav and satellite for uav-based geo-localization. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zheng, Z.; Yan, C.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, B.; Yang, Y. Each part matters: Local patterns facilitate cross-view geo-localization. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2021, 32, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Liu, G.; Yuan, Y. F3-net: Multi-view scene matching for drone-based geo-localization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5610611. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, X.; Shao, J.; Ouyang, D.; Shen, H.T. Uav-satellite view synthesis for cross-view geo-localization. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2021, 32, 4804–4815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yang, X.; Fan, J.; Lu, R.; Tang, B.; Wang, S.; Su, S. Geoformer: An effective transformer-based siamese network for uav geo-localization. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 9470–9491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Configuration |
|---|---|
| CPU | Intel Core i7-12700KF |
| GPU | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090 (24 GB) |
| CUDA version | CUDA 11.7 |
| Python version | Python 3.9.13 |
| Deep learning framework | Pytorch 2.0.0 |
| Operating system | Ubuntu 22.04.2 LTS |
| Method | DaViT-Tiny | Share Weight | Symmetric DCL Loss | Params/M | R@1 | R@5 | R@10 | AP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| baseline | 51.2 (25.6 × 2) | 58.19 | 79.00 | 85.21 | 62.90 | |||
| Method (1) | ✓ | 56.8 (28.4 × 2) | 72.79 | 87.97 | 92.02 | 76.24 | ||
| Method (2) | ✓ | ✓ | 28.4 | 81.96 | 93.74 | 95.68 | 84.58 | |
| Method (2) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 28.4 | 89.22 | 97.29 | 98.18 | 91.04 |
| Method | Backbone | Params/M | R@1 | R@5 | R@10 | AP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contrastive loss (224 × 224) | VGG-16 | 276.8 (138.4 × 2) | 41.70 | 63.61 | 73.98 | 46.93 |
| triplet loss (224 × 224) | ResNet-50 | 51.2 (25.6 × 2) | 58.19 | 79.00 | 85.21 | 62.90 |
| instance loss (224 × 224) | ResNet-50 | 51.2 (25.6 × 2) | 58.49 | 79.40 | 85.31 | 63.31 |
| LCM (224 × 224) | ResNet-50 | 51.2 (25.6 × 2) | 66.65 | 84.93 | 90.02 | 70.82 |
| LPN (512 × 512) | ResNet-50 | 51.2 (25.6 × 2) | 77.71 | / | / | 80.80 |
| F3-Net (384 × 384) | SF | / | 78.64 | 91.71 | 94.57 | 81.60 |
| PCL (512 × 512) | ResNet-50 | 51.2 (25.6 × 2) | 83.27 | 90.32 | 95.56 | 87.32 |
| FSRA (256 × 256) | ViT-small | 44.2 (22.1 × 2) | 82.25 | / | / | 84.82 |
| FSRA (512 × 512) | ViT-small | 44.2 (22.1 × 2) | 85.50 | / | / | 87.53 |
| TransFG (512 × 512) | ViT-small | 44.2 (22.1 × 2) | 87.92 | / | / | 89.90 |
| GeoFormer (224 × 224) | E-Swin-large | 157.0 | 89.08 | 96.83 | 98.09 | 90.83 |
| Ours (224 × 224) | DaViT-tiny | 28.4 | 89.22 | 97.29 | 98.18 | 91.04 |
| Ours (224 × 224) | DaViT-small | 49.7 | 91.81 | 98.83 | 99.27 | 92.23 |
| Method | Backbone | Params/M | Flops/G | Time-Consuming |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contrastive loss | VGG-16 | 276.8 | 31.00 | 6 min 30 s |
| triplet loss | ResNet-50 | 51.2 | 8.24 | 4 min 14 s |
| LPN | ResNet-50 | 51.2 | 8.24 | 4 min 23 s |
| FSRA | ViT-small | 44.2 | 9.20 | 5 min 11 s |
| Ours | DaViT-tiny | 28.4 | 4.54 | 1 min 13 s |
| Ours | DaViT-small | 49.7 | 8.80 | 1 min 52 s |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, Q.; Xu, A.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, Z.; Zhou, W.; Xi, R.; Lin, Q. A Contrastive Learning Based Multiview Scene Matching Method for UAV View Geo-Localization. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3039. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16163039
He Q, Xu A, Zhang Y, Ye Z, Zhou W, Xi R, Lin Q. A Contrastive Learning Based Multiview Scene Matching Method for UAV View Geo-Localization. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(16):3039. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16163039
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Qiyi, Ao Xu, Yifan Zhang, Zhiwei Ye, Wen Zhou, Ruijie Xi, and Qiao Lin. 2024. "A Contrastive Learning Based Multiview Scene Matching Method for UAV View Geo-Localization" Remote Sensing 16, no. 16: 3039. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16163039
APA StyleHe, Q., Xu, A., Zhang, Y., Ye, Z., Zhou, W., Xi, R., & Lin, Q. (2024). A Contrastive Learning Based Multiview Scene Matching Method for UAV View Geo-Localization. Remote Sensing, 16(16), 3039. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16163039






