Calibration of Receiver-Dependent Pseudorange Bias and Its Impact on BDS Augmentation Positioning Accuracy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Pseudorange Bias Definition
2.2. Pseudorange Bias Calibration
2.3. Pseudorange Bias Analysis for the BDS-3 High-Precision Service
2.3.1. Dual-Frequency Pseudorange Augmentation Service
2.3.2. PPP Service
3. Data and Strategies
4. Results
4.1. Pseudorange Bias Spatial and Temporal Variation Characteristics
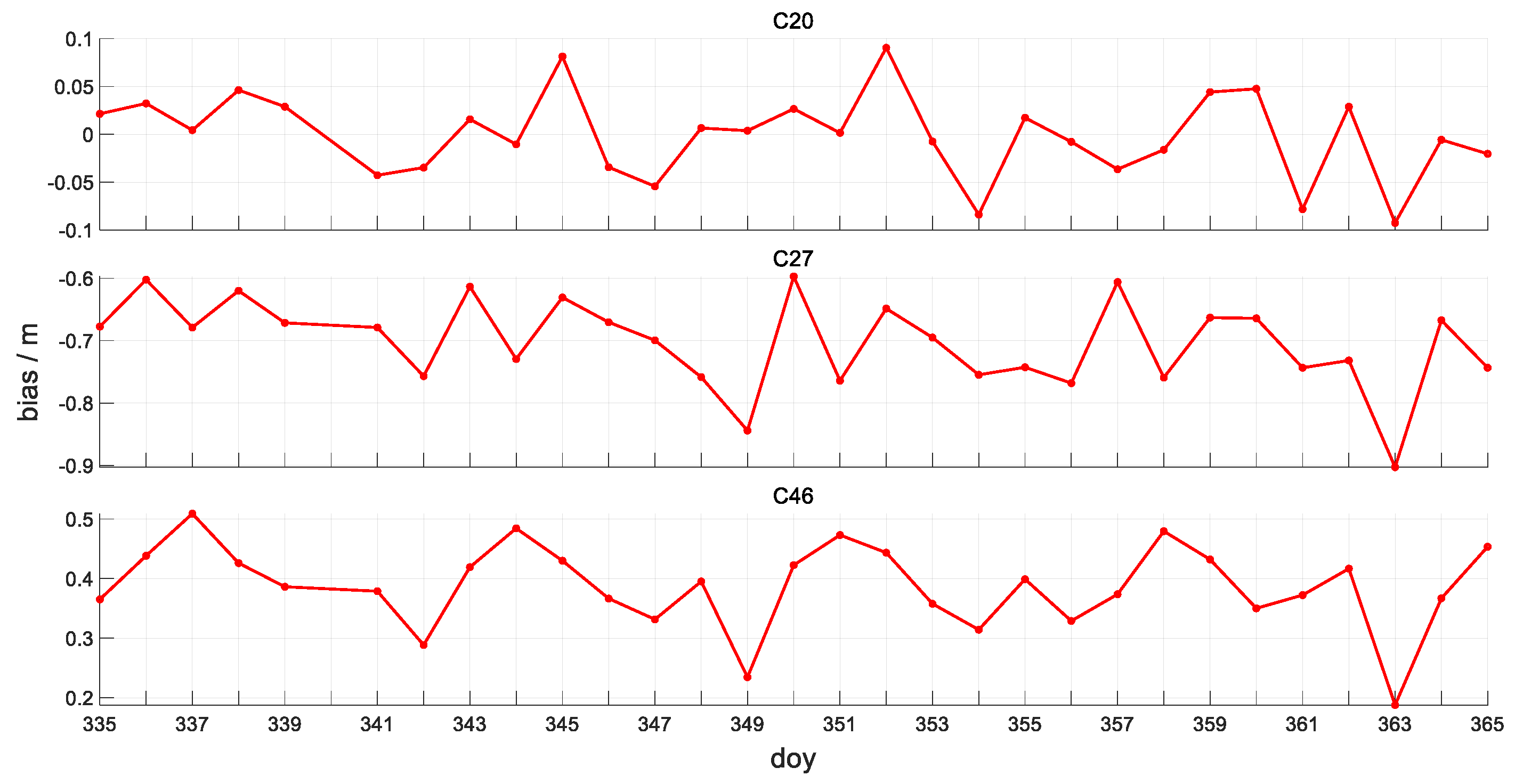
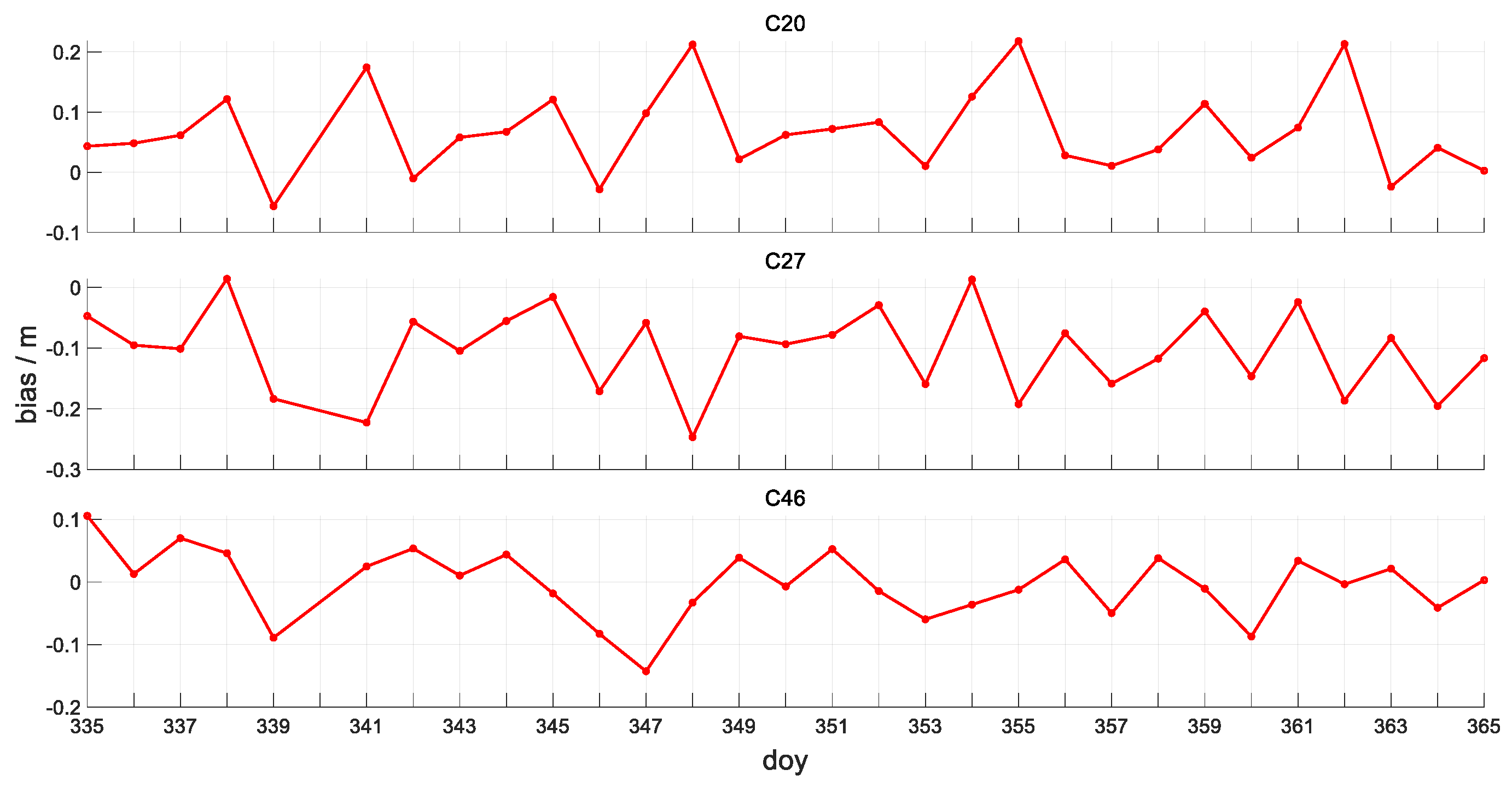
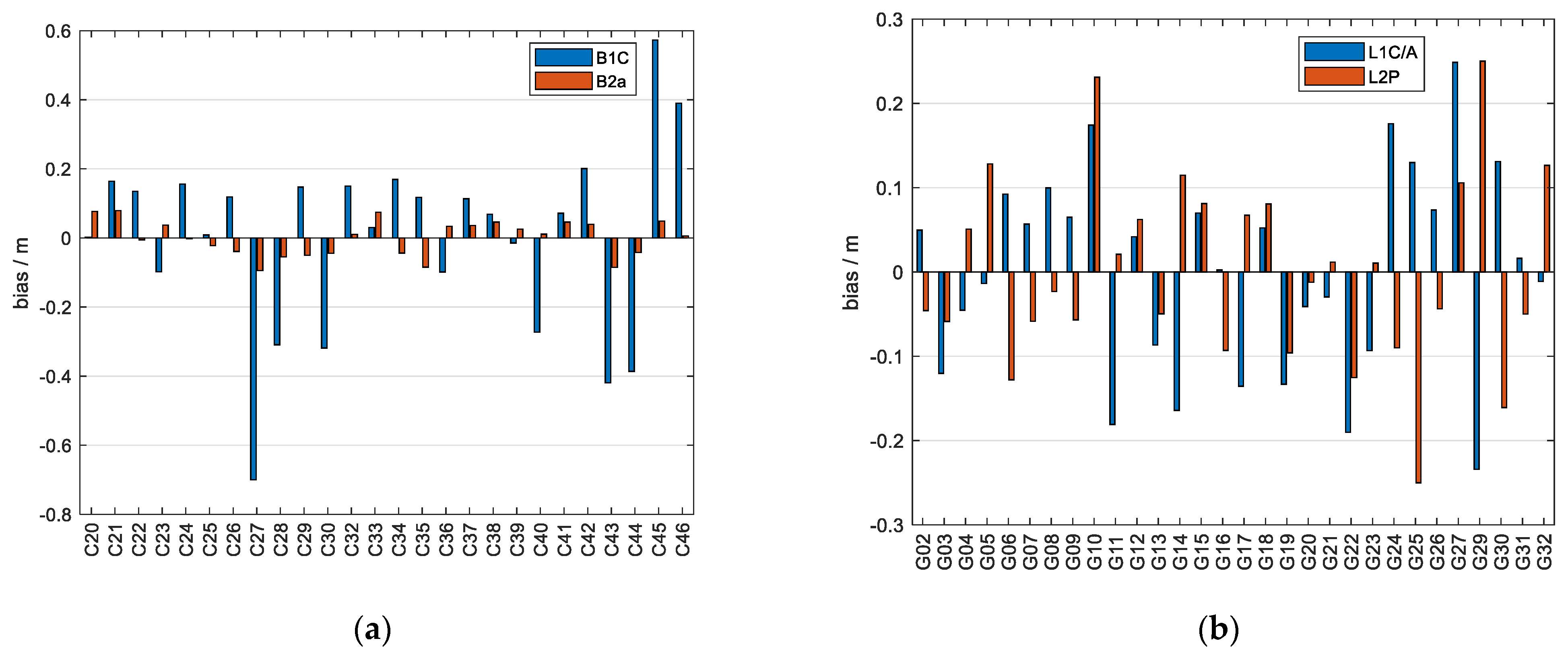
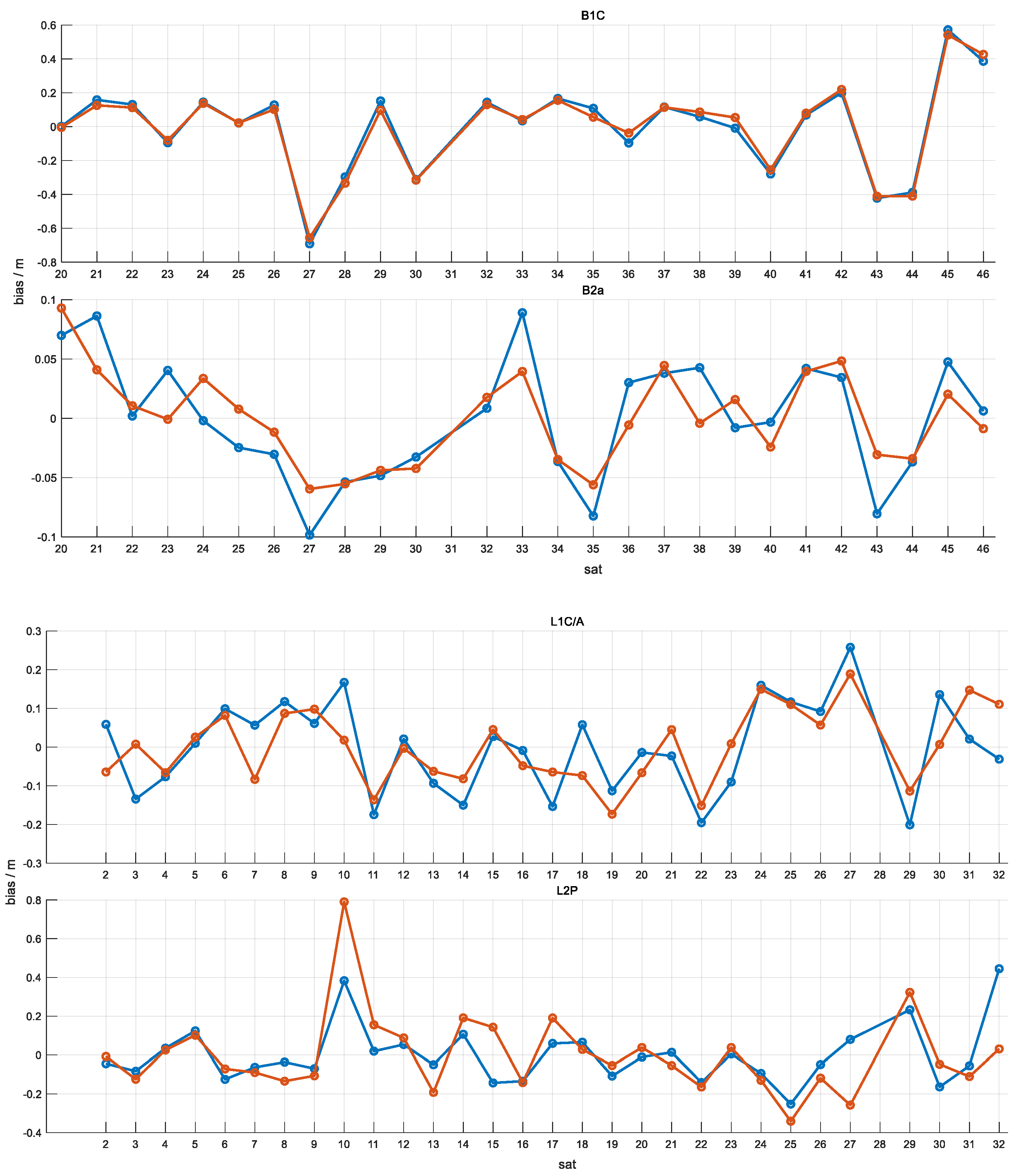
4.1.1. Temporal Variation Characteristics
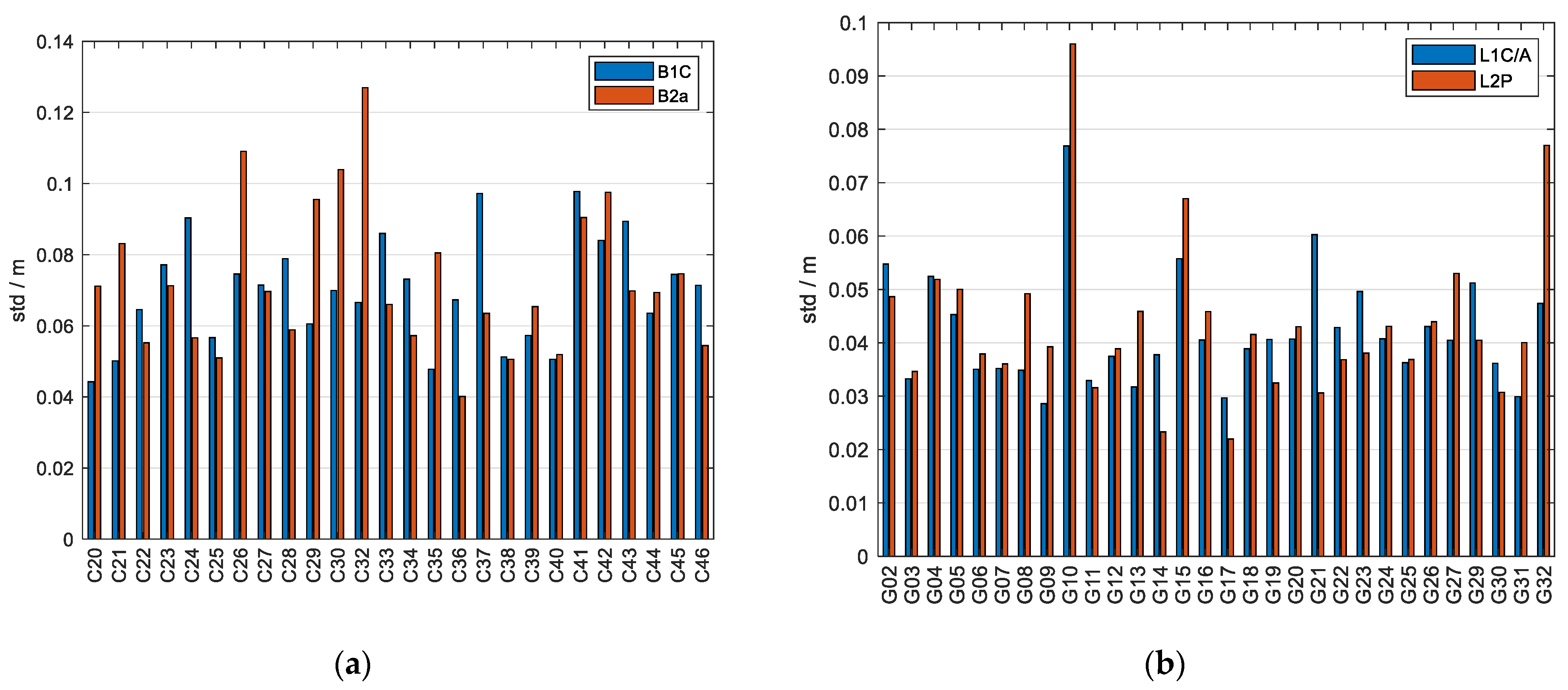
4.1.2. Spatial Variation Characteristics
4.2. Dual-Frequency Pseudorange Augmentation Positioning Service
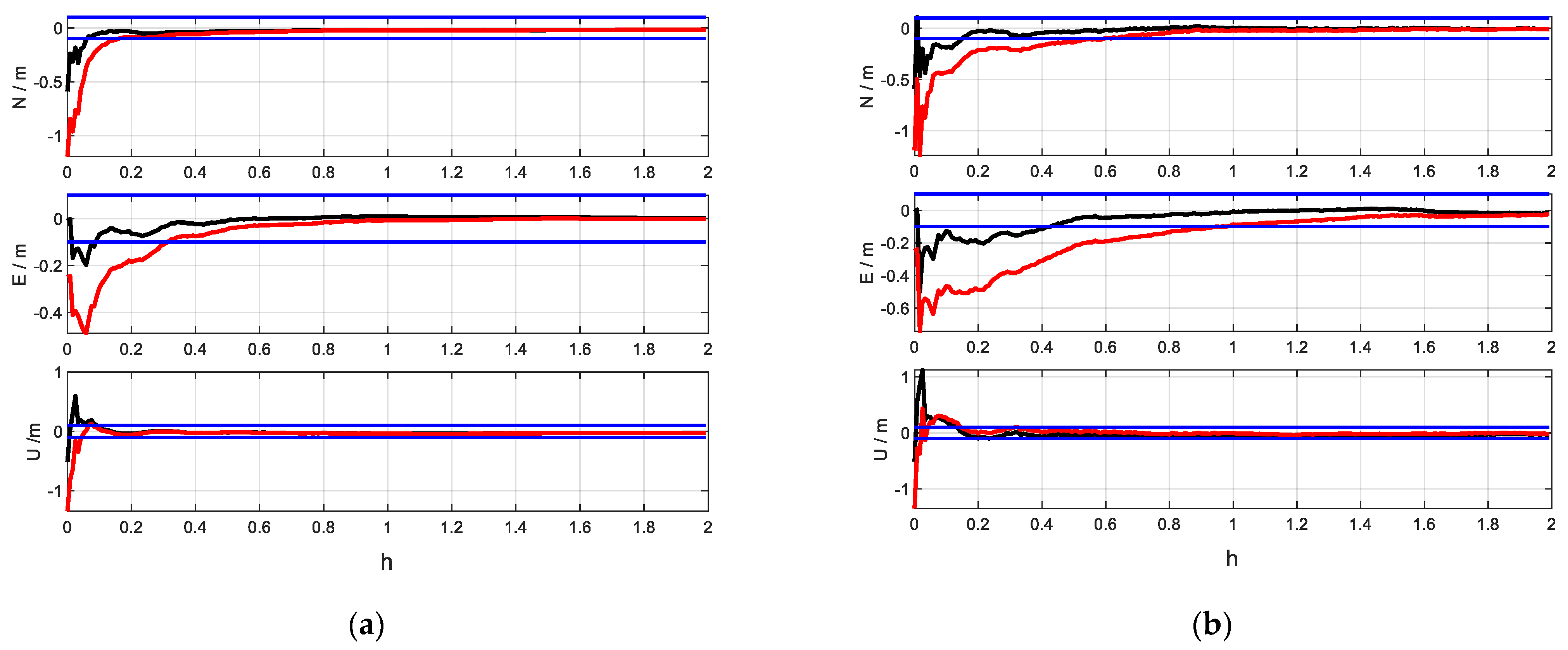
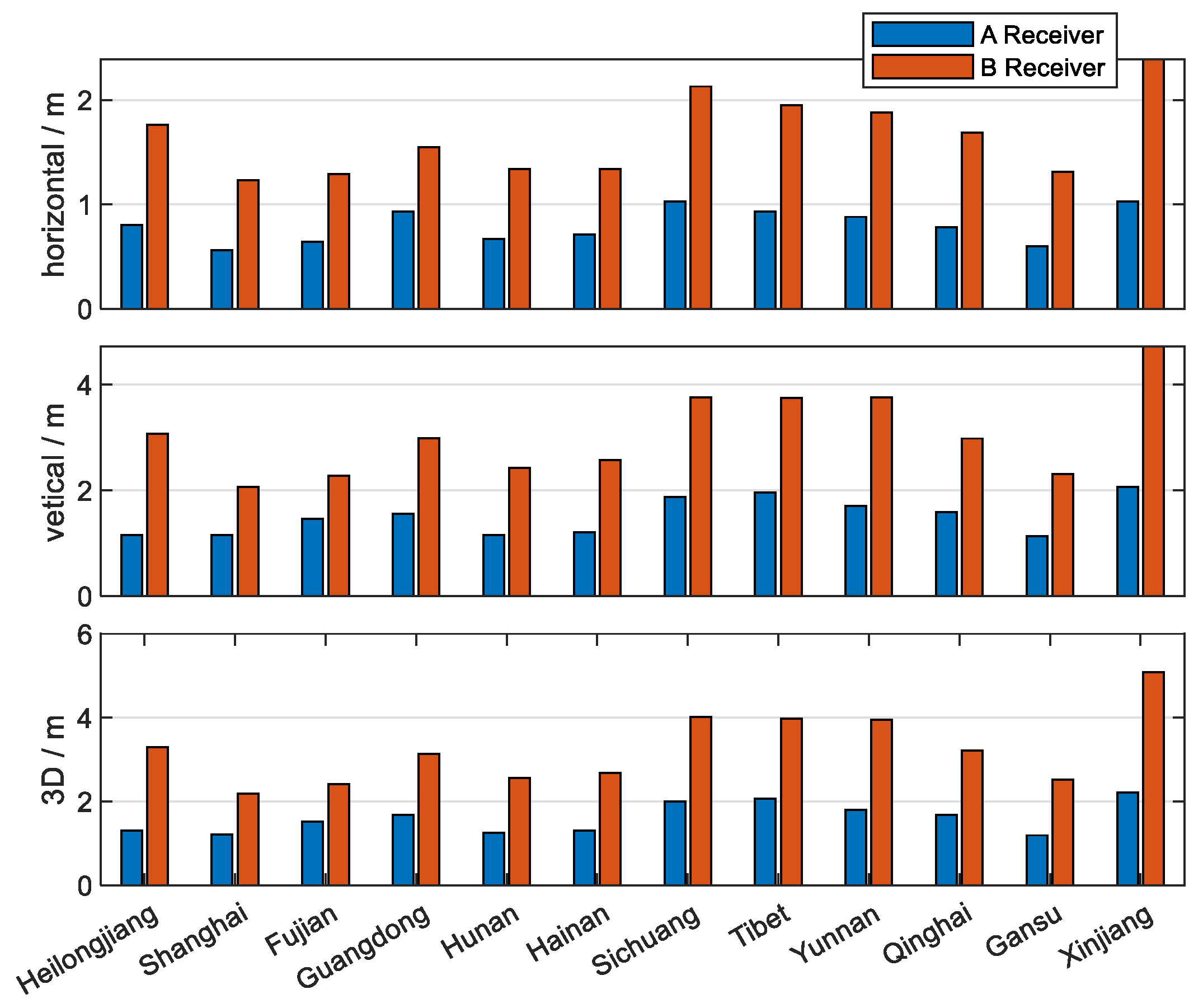
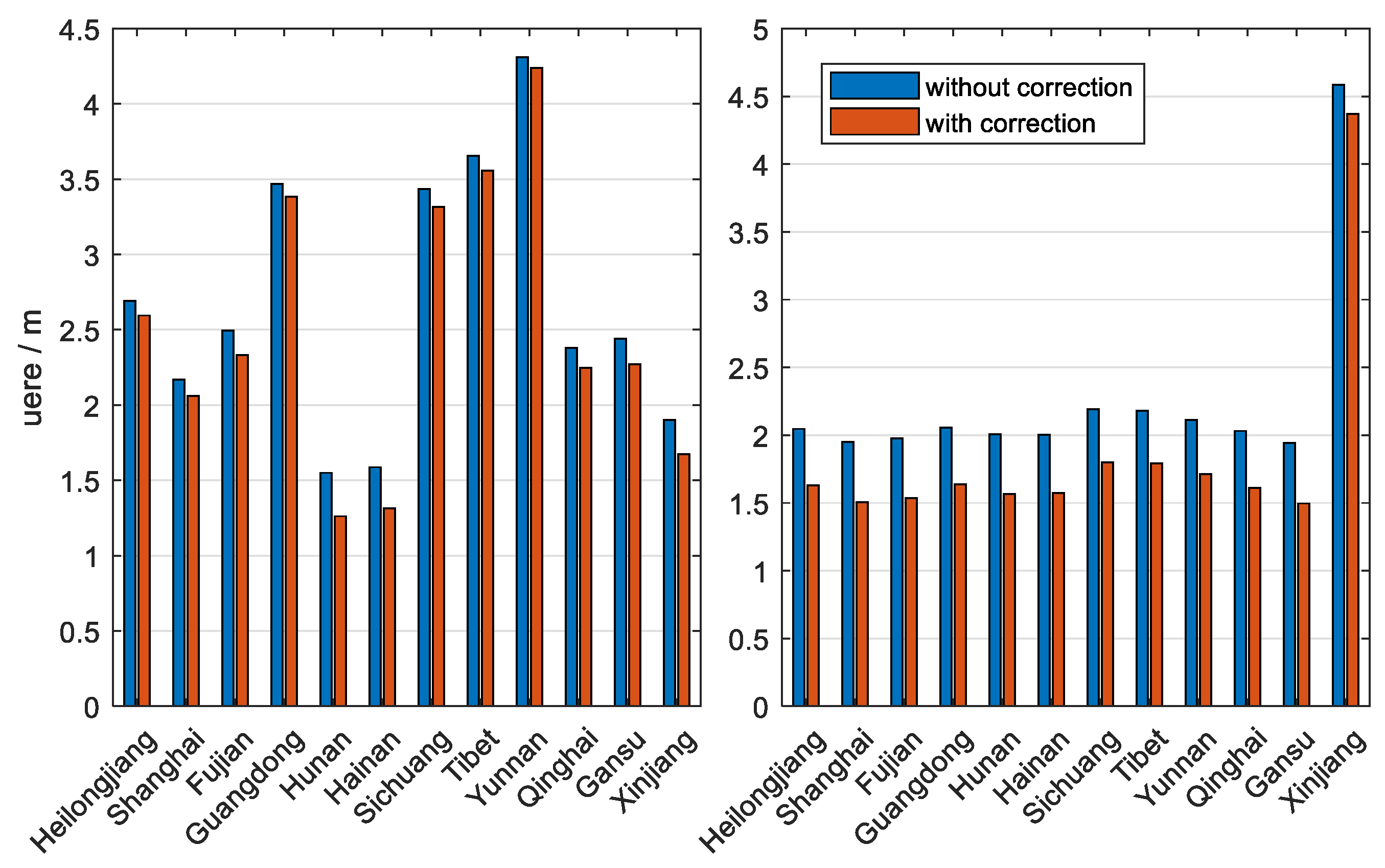
4.2.1. The Impact of Pseudorange Bias on Dual-Frequency Pseudorange Augmentation Positioning
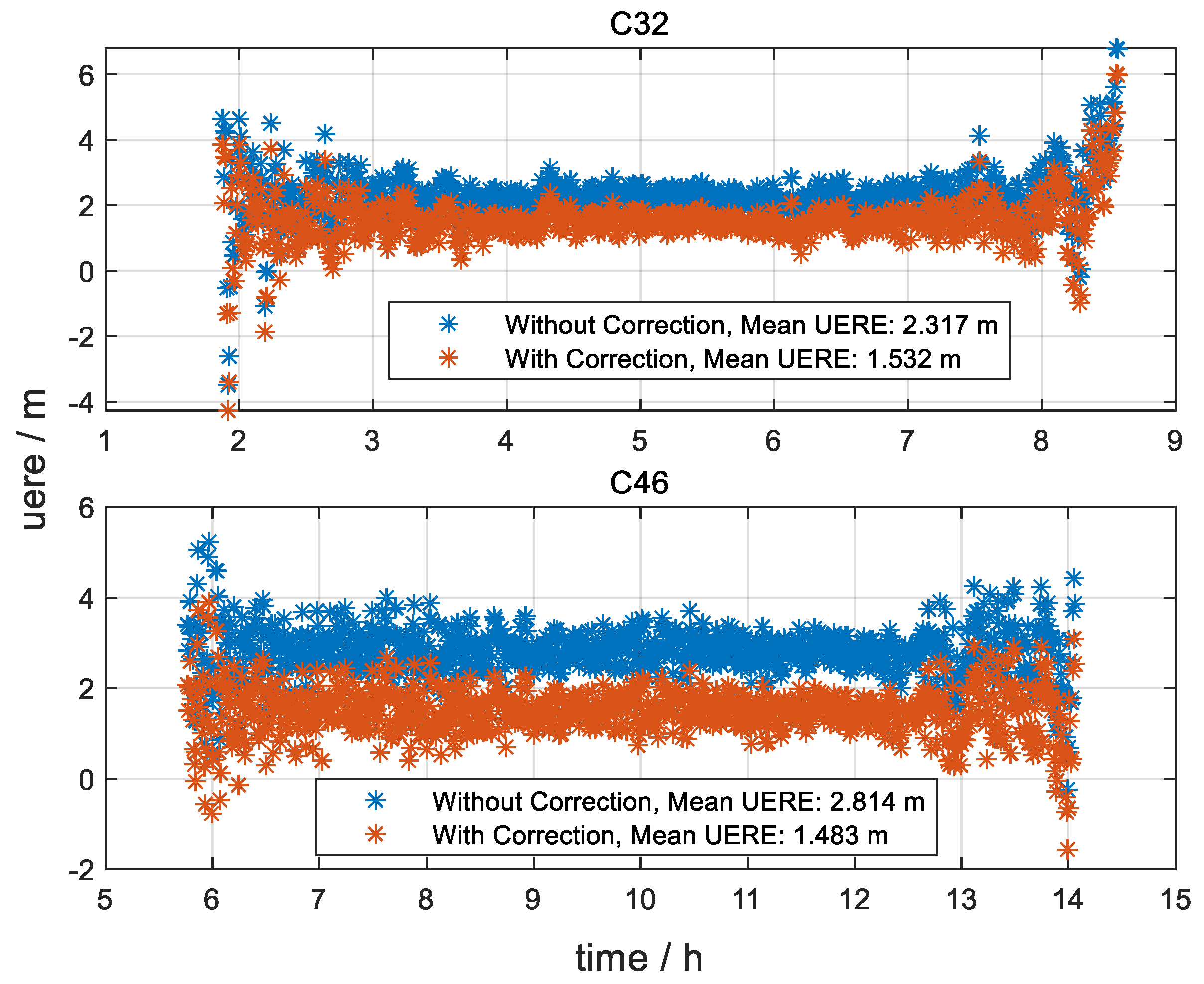
4.2.2. User-Side Pseudorange Bias Correction
4.3. PPP Service
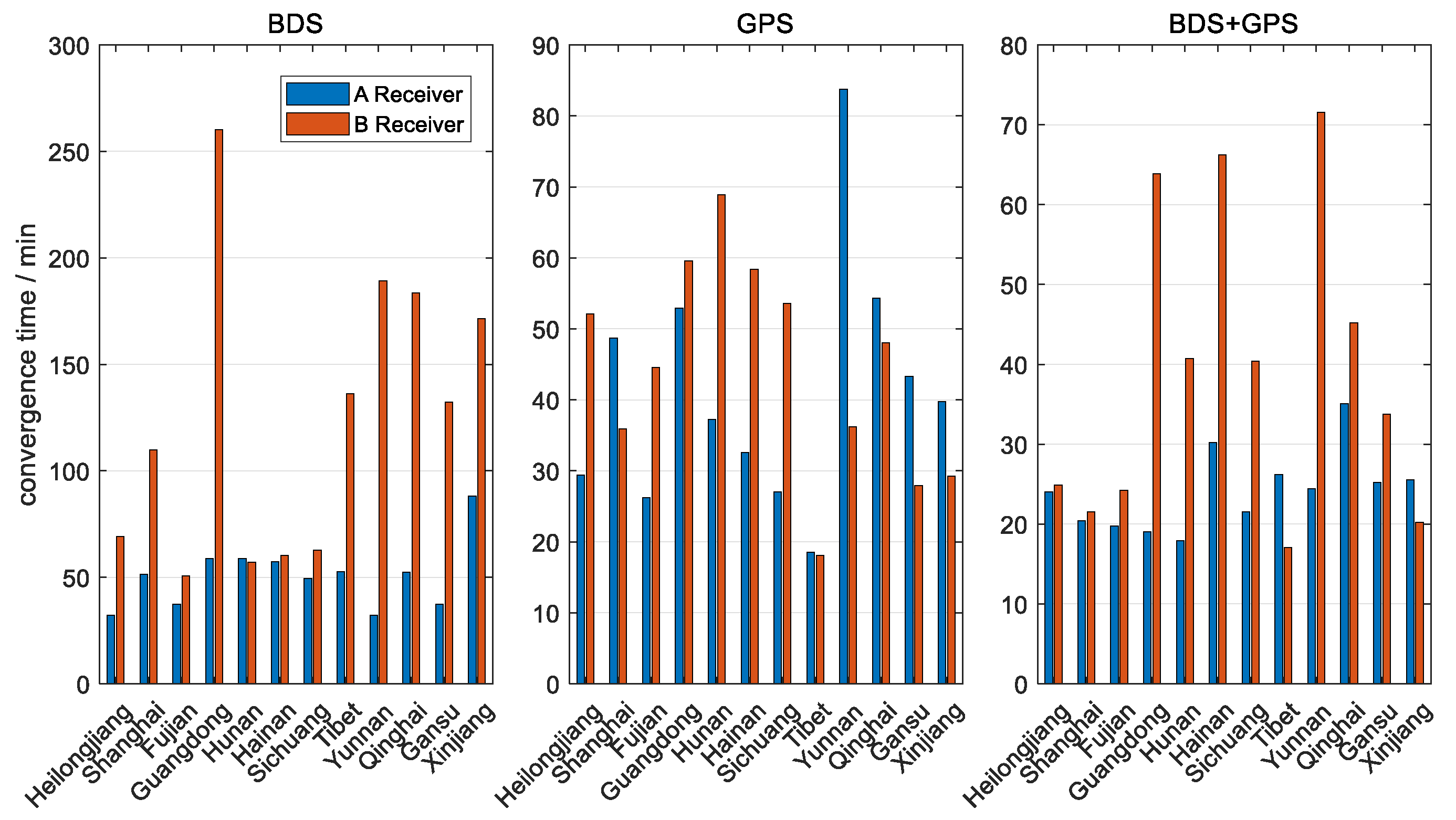
4.3.1. The Impact of Pseudorange Bias on PPP
4.3.2. User-Side Pseudorange Bias Correction
5. Conclusions and Discussions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hauschild, A.; Montenbruck, O. A study on the dependency of GNSS pseudorange biases on correlator spacing. GPS Solut. 2016, 20, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, C.; Czopek, F.; Barker, B. A co-operative anomaly resolution on PRN-19. In Proceedings of the 12th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation, Nashville, NT, USA, 14–17 September 1999; pp. 2268–2269. [Google Scholar]
- Mitelman, A.M.; Phelts, R.E.; Akos, D.M.; Pullen, S.P.; Enge, P.K. Signal deformations on nominally healthy GPS satellites. In Proceedings of the 2004 National Technical Meeting of the Institute of Navigation, San Diego, CA, USA, 26–28 January 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Pini, M.; Akos, D.M.; Esterhuizen, S.; Mitelman, A. Analysis of GNSS signals as observed via a high gain parabolic antenna. In Proceedings of the 18th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation, Long Beach, CA, USA, 13–16 September 2005; pp. 1686–1695. [Google Scholar]
- Phelts, R.E.; Akos, D.M. Effects of signal deformations on modernized GNSS signals. Positioning 2006, 5, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, G.; Chen, Y.H.; Phelts, R.E.; Walter, T.; Enge, P. Measuring code-phase differences due to inter-satellite hardware differences. In Proceedings of the 25th International Technical Meeting of The Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation, Nashville, TN, USA, 17–21 September 2012; pp. 2150–2158. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, G.; Chen, Y.H.; Phelts, R.E.; Walter, T.; Enge, P. Mitigation of nominal signal deformations on dual-frequency WAAS position errors. In Proceedings of the 27th International Technical Meeting of The Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation, Tampa, FL, USA, 8–12 September 2014; pp. 3129–3147. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, C.; Tian, Y.; Zheng, F.; Hu, Y. Accounting for Signal Distortion Biases for Wide-Lane and Narrow-Lane Phase Bias Estimation with Inhomogeneous Networks. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Lv, Y.; Geng, T. GNSS receiver-related pseudorange biases: Characteristics and effects on wide-lane ambiguity resolution. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Q.; Zhang, B.; Yuan, Y.; Xu, T.; Chen, Y.; Tan, B. Evaluation and mitigation of the influence of pseudorange biases on GNSS satellite clock offset estimation. Measurement 2022, 193, 111015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Li, Z.; Wang, N.; Tang, C.; Ma, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wu, J. Considering inter-receiver pseudorange biases for BDS-2 precise orbit determination. Measurement 2021, 177, 109251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Su, C.; Hu, X.; Gao, W.; Liu, L.; Lu, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, W.; Zhou, S. Characterization of pesudorange bias and its effect on positioning for BDS satellites. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2020, 49, 1131–1138. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Gong, X.; Zheng, F.; Gu, S.; Shi, C. Estimating GPS satellite and receiver differential code bias based on signal distortion bias calibration. GPS Solut. 2023, 27, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Yuan, Y.; Li, Z.; Montenbruck, O.; Tan, B. Determination of diferential code biases with multi-GNSS observations. J. Geod. 2016, 90, 209–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauschild, A.; Steigenberger, P.; Montenbruck, O. Inter-receiver GNSS pseudorange biases and their effect on clock and DCB estimation. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation, Miami, FL, USA, 16–20 September 2019; pp. 3675–3685. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, X.; Zheng, F.; Gu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Lou, Y. The long-term characteristics of GNSS signal distortion biases and their empirical corrections. GPS Solut. 2022, 26, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Hu, X.; Chen, J.; Liu, L.; Zhou, S.; Guo, R.; Li, X.; He, F.; Liu, J.; Yang, J. Orbit determination, clock estimation and performance evaluation of BDS-3 PPP-B2b service. J. Geod. 2022, 96, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Hu, X.; Tang, C.; Cao, Y.; Zhou, S.; Yang, Y.; Liu, L.; Guo, R. Generation of DFMC SBAS corrections for BDS-3 satellites and improved positioning performances. Adv. Space Res. 2020, 66, 702–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Tang, C.; Chen, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, S.; Hu, X.; Tian, Q.; Yang, Y. Pseudorange Bias Analysis and Preliminary Service Performance Evaluation of BDSBAS. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.H.; Tang, C.P.; Song, Y.Z.; Hu, X.; Zhou, S.; Chang, Z. Analysis of signal-in-space ranging error of GNSS navigation message. Sci. Sin. Phys. Mech. Astron. 2020, 51, 019508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Shao, B.; Tang, C.; Zhou, S.; Hu, X.; Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Li, P. Research on performance improvement method of BDSBAS multi-GNSS service with DFMC protocol. Adv. Space Res. 2023, 72, 2283–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IRNSSICD. 2016. Available online: http://irnss.isro.gov.in/ (accessed on 14 May 2019).
- Ishijima, Y.; Inaba, N.; Matsumoto, A.; Terada, K.; Yonechi, H.; Ebisutani, H.; Ukawa, S.; Okamoto, T. Design and development of the first Quasi-Zenith Satellite attitude and orbit control system. In Proceedings of the IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 7–14 March 2009; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Rebischung, P.; Schmid, R. IGS14/igs14.atx: A New Framework for the IGS Products; AGU Fall Meeting: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Petit, G.; Luzum, B. IERS Conventions (2010); IERS technical note No.36; Verlag des Bundesamts für Kartographie und Geodäsie: Frankfurt, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Saastamoinen, J. Contributions to the theory of atmospheric refraction. Bull. Géodésique 1972, 105, 279–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, J.; Niell, A.; Tregoning, P.; Schuh, H. Global mapping function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L07304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RTCA DO-229D; Minimum Operational Performance Standards for Global Positioning System/Wide Area Augmentation System Airborne Equipment. RTCA, Inc.: Washington, DC, USA, 2016.
- ED-259; Minimum Operational Performance Standard for Galileo Global Positioning System/Satellite-based Augmentation System Airborne Equipment. EUROCAE: Saint-Denis, France, 2019.





| BDS-3 (B1C/B2a) | GPS (L1/L2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fundamental Service | Pseudorange Augmentation Service | Fundamental Service | Pseudorange Augmentation Service | |
| SISRE | 0.35 m | 0.13 m | 0.49 m | 0.13 m |
| Error of tropospheric delay model | <0.10 m | <0.10 m | <0.10 m | <0.10 m |
| Multipath errors | 0.70 m | 0.70 m | 0.70 m | 0.70 m |
| UERE without pseudorange biases | 0.79 m | 0.72 m | 0.86 m | 0.72 m |
| Pseudorange biases | 0.50 m | 0.50 m | 0.30 m | 0.30 m |
| UERE with pseudorange biases | 0.93 m | 0.87 m | 0.91 m | 0.78 m |
| The proportion of pseudorange bias in UERE | 15.10% | 17.20% | 5.50% | 7.70% |
| PPP | Convergence Time | |
|---|---|---|
| Without Pseudorange Biases | With Pseudorange Biases | |
| Static PPP | 6 | 19 |
| Kinematic PPP | 26 | 58 |
| Strategy | |
|---|---|
| Frequency | BDS-3: B1C/B2a GPS: L1/L2 |
| Observations | Dual-frequency IF combinations of pseudorange and carrier-phase observation. |
| Elevation angle | Cut-off: 7°. |
| Orbits | Fix with precise satellite orbits of IGS MGEX. |
| Satellite/Receiver PCO and PCV | BDS-3: Provided by manufacturers; GPS: igs14.atx [24]. |
| Station displacement | Correcting solid Earth tide, ocean tide, pole tide [25]. |
| Relativity | Corrected [25]. |
| Troposphere delay | Saastamoinen model [26] for wet and dry hydrostatic delay with the GMF [27] without the gradient model; residual tropospheric delay as a random-walk process. |
| Ionosphere delay | The first-order ionosphere delay is eliminated by the dual-frequency combinations. |
| Receiver clock | Estimating as white noise per epoch. |
| Satellite clock | Estimating as white noise. |
| Carrier-phase ambiguities | Estimating as floats and constant parameters. |
| Estimation method | Kalman filter. |
| Strategy | |
|---|---|
| Frequency | BDS-3: B1C/B2a GPS: L1/L2 |
| Observations | Dual-frequency IF combinations of pseudorange observation. |
| Elevation angle | Cut-off: 7°. |
| Satellite orbits | BDS-3: Orbit in CNAV broadcasted navigation message + orbit correction messages. GPS: Orbit in LNAV broadcasted navigation message + orbit correction messages. |
| Satellite clock | BDS-3: Clock in CNAV broadcasted navigation message + clock correction messages. GPS: Clock in LNAV broadcasted navigation message + clock correction messages. |
| Relativity | Corrected [25]. |
| Troposphere delay | Correcting with empirical model recommended in RTCA DO-229F [28] and ED-259 [29]. |
| Ionosphere delay | Eliminating through the dual-frequency IF combinations. |
| Receiver clock | Estimating as white noise per epoch, the dual-system needs to estimate ISB. |
| Receiver coordinate | Estimating as white noise per epoch. |
| Estimation method | Least squares estimation. |
| Strategy | |
|---|---|
| Frequency | BDS-3: B1C/B2a GPS: L1/L2 |
| Observations | Dual-frequency IF combinations of pseudorange and carrier-phase observation. |
| Elevation angle | Cut-off: 7°. |
| Satellite orbits | BDS-3: Orbit in CNAV broadcasted navigation message + orbit correction messages. GPS: Orbit in LNAV broadcasted navigation message + orbit correction messages. |
| Satellite clock | BDS-3: Clock in CNAV broadcasted navigation message + clock correction messages. GPS: Clock in LNAV broadcasted navigation message + clock correction messages. |
| Relativity | Corrected [25]. |
| Station displacement | Correcting solid Earth tide, ocean tide, pole tide [25]. |
| Troposphere delay | Saastamoinen model [26] for wet and dry hydrostatic delay with the GMF [27] without the gradient model; residual tropospheric delay as a random-walk process. |
| Ionosphere delay | The first-order ionosphere delay is eliminated by the dual-frequency combinations. |
| Receiver clock | Estimating as white noise per epoch, the dual-system needs to estimate ISB. |
| Receiver coordinate | Estimating as constant parameters for Static PPP and as white noise for Kinematic PPP. |
| Carrier-phase ambiguities | Estimating as constant parameters. |
| Estimation method | Kalman filter. |
| Without Correction | With Correction | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Station | Horizontal | Vertical | 3D | Horizontal | Vertical | 3D |
| Heilongjiang | 2.68 | 5.90 | 6.14 | 2.66 | 5.68 | 5.93 |
| Shanghai | 1.20 | 2.95 | 3.08 | 1.16 | 2.91 | 3.04 |
| Fujian | 1.25 | 2.70 | 2.83 | 1.23 | 2.59 | 2.73 |
| Guangdong | 1.73 | 4.29 | 4.48 | 1.73 | 4.07 | 4.28 |
| Hunan | 1.31 | 2.92 | 3.05 | 1.27 | 2.74 | 2.89 |
| Hainan | 1.34 | 3.04 | 3.18 | 1.36 | 3.09 | 3.21 |
| Sichuang | 2.43 | 4.94 | 5.17 | 2.40 | 4.87 | 5.11 |
| Tibet | 2.04 | 3.87 | 4.13 | 1.99 | 3.77 | 4.00 |
| Yunnan | 1.93 | 4.05 | 4.24 | 1.93 | 4.07 | 4.27 |
| Qinghai | 1.64 | 3.38 | 3.54 | 1.60 | 3.11 | 3.29 |
| Gansu | 1.26 | 2.57 | 2.70 | 1.20 | 2.29 | 2.42 |
| Xinjiang | 2.45 | 4.55 | 4.84 | 1.64 | 2.93 | 3.12 |
| Mean | 1.77 | 3.76 | 3.94 | 1.68 | 3.51 | 3.69 |
| Without Correction | With Correction | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Station | Horizontal | Vertical | 3D | Horizontal | Vertical | 3D |
| Heilongjiang | 1.76 | 3.07 | 3.30 | 1.46 | 2.33 | 2.54 |
| Shanghai | 1.23 | 2.06 | 2.19 | 0.76 | 1.39 | 1.46 |
| Fujian | 1.29 | 2.28 | 2.41 | 0.88 | 1.61 | 1.70 |
| Guangdong | 1.55 | 2.99 | 3.14 | 1.26 | 2.41 | 2.56 |
| Hunan | 1.34 | 2.42 | 2.56 | 0.96 | 1.78 | 1.89 |
| Hainan | 1.34 | 2.57 | 2.68 | 0.98 | 1.86 | 1.97 |
| Sichuang | 2.13 | 3.76 | 4.02 | 1.90 | 3.36 | 3.65 |
| Tibet | 1.95 | 3.75 | 3.97 | 1.69 | 3.34 | 3.52 |
| Yunnan | 1.88 | 3.76 | 3.95 | 1.64 | 3.24 | 3.46 |
| Qinghai | 1.69 | 2.98 | 3.22 | 1.36 | 2.55 | 2.71 |
| Gansu | 1.31 | 2.31 | 2.52 | 0.83 | 1.60 | 1.70 |
| Xinjiang | 2.39 | 4.72 | 5.09 | 2.06 | 4.37 | 4.64 |
| Mean | 1.65 | 3.05 | 3.25 | 1.31 | 2.48 | 2.65 |
| Without Correction | With Correction | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Station | Horizontal | Vertical | 3D | Horizontal | Vertical | 3D |
| Heilongjiang | 1.32 | 3.23 | 3.35 | 1.22 | 2.55 | 2.67 |
| Shanghai | 0.80 | 1.85 | 1.92 | 0.65 | 1.27 | 1.34 |
| Fujian | 0.85 | 1.85 | 1.94 | 0.72 | 1.4 | 1.48 |
| Guangdong | 1.09 | 2.42 | 2.53 | 1.01 | 2.07 | 2.17 |
| Hunan | 0.93 | 1.89 | 1.98 | 0.79 | 1.51 | 1.60 |
| Hainan | 0.93 | 2.12 | 2.19 | 0.83 | 1.86 | 1.92 |
| Sichuang | 1.53 | 2.88 | 3.05 | 1.48 | 2.66 | 2.85 |
| Tibet | 1.36 | 2.59 | 2.74 | 1.27 | 2.52 | 2.67 |
| Yunnan | 1.31 | 2.67 | 2.80 | 1.22 | 2.46 | 2.59 |
| Qinghai | 1.15 | 2.16 | 2.30 | 1.05 | 1.96 | 2.07 |
| Gansu | 0.86 | 1.86 | 1.95 | 0.76 | 1.42 | 1.50 |
| Xinjiang | 1.62 | 3.01 | 3.19 | 1.57 | 2.89 | 3.07 |
| Mean | 1.14 | 2.37 | 2.49 | 1.04 | 2.04 | 2.16 |
| BDS | GPS | BDS + GPS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Station | Without Correction | With Correction | Without Correction | With Correction | Without Correction | With Correction |
| Heilongjiang | 39.07 | 27.74 | 27.90 | 28.74 | 28.90 | 35.57 |
| Shanghai | 59.06 | 41.23 | 23.73 | 19.90 | 30.06 | 22.90 |
| Fujian | 42.56 | 27.73 | 24.39 | 22.56 | 21.23 | 15.40 |
| Guangdong | 39.56 | 37.73 | 27.73 | 24.40 | 14.39 | 17.06 |
| Hunan | 64.39 | 64.90 | 28.89 | 19.56 | 20.56 | 20.90 |
| Hainan | 44.23 | 40.23 | 35.73 | 14.06 | 28.39 | 18.40 |
| Sichuang | 33.06 | 34.73 | 16.73 | 19.73 | 16.06 | 19.56 |
| Tibet | 29.57 | 25.74 | 15.57 | 17.40 | 16.73 | 18.40 |
| Yunnan | 51.56 | 46.90 | 20.89 | 14.06 | 17.06 | 15.73 |
| Qinghai | 55.56 | 52.40 | 29.23 | 31.23 | 20.06 | 22.90 |
| Gansu | 72.56 | 37.40 | 18.39 | 21.40 | 19.23 | 19.06 |
| Xinjiang | 54.73 | 25.73 | 19.23 | 20.40 | 14.56 | 17.06 |
| Mean | 48.83 | 38.54 | 24.03 | 21.12 | 20.60 | 20.25 |
| BDS | GPS | BDS + GPS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Station | Without Correction | With Correction | Without Correction | With Correction | Without Correction | With Correction |
| Heilongjiang | 69.07 | 41.40 | 52.07 | 51.90 | 24.90 | 28.40 |
| Shanghai | 109.73 | 57.56 | 35.90 | 34.56 | 21.56 | 15.23 |
| Fujian | 54.98 | 41.23 | 44.56 | 41.56 | 24.23 | 16.06 |
| Guangdong | 260.23 | 88.06 | 62.73 | 56.73 | 63.90 | 17.40 |
| Hunan | 57.06 | 58.73 | 68.90 | 42.90 | 40.73 | 18.90 |
| Hainan | 60.23 | 51.40 | 58.40 | 31.40 | 66.23 | 33.06 |
| Sichuang | 62.73 | 50.90 | 53.56 | 39.56 | 40.40 | 25.06 |
| Tibet | 80.24 | 61.99 | 23.74 | 35.49 | 17.07 | 22.74 |
| Yunnan | 189.23 | 50.56 | 36.23 | 41.73 | 71.56 | 23.56 |
| Qinghai | 67.23 | 64.23 | 48.06 | 37.06 | 45.23 | 32.06 |
| Gansu | 132.23 | 27.23 | 27.90 | 32.06 | 33.73 | 18.56 |
| Xinjiang | 171.40 | 162.56 | 29.23 | 45.06 | 20.23 | 24.23 |
| Mean | 109.53 | 62.99 | 45.10 | 40.83 | 39.15 | 22.94 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liao, M.; Tang, C.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, S.; Hu, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, K.; Gui, Y. Calibration of Receiver-Dependent Pseudorange Bias and Its Impact on BDS Augmentation Positioning Accuracy. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3022. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16163022
Liao M, Tang C, Zhao L, Zhou S, Hu X, Chen Y, Li K, Gui Y. Calibration of Receiver-Dependent Pseudorange Bias and Its Impact on BDS Augmentation Positioning Accuracy. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(16):3022. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16163022
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiao, Min, Chengpan Tang, Liqian Zhao, Shanshi Zhou, Xiaogong Hu, Yilun Chen, Kai Li, and Yubo Gui. 2024. "Calibration of Receiver-Dependent Pseudorange Bias and Its Impact on BDS Augmentation Positioning Accuracy" Remote Sensing 16, no. 16: 3022. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16163022
APA StyleLiao, M., Tang, C., Zhao, L., Zhou, S., Hu, X., Chen, Y., Li, K., & Gui, Y. (2024). Calibration of Receiver-Dependent Pseudorange Bias and Its Impact on BDS Augmentation Positioning Accuracy. Remote Sensing, 16(16), 3022. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16163022





