Finding Oasis Cold Island Footprints Based on a Logistic Model—A Case Study in the Ejina Oasis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Case Study
2.1. Methods
2.1.1. Logistic Model
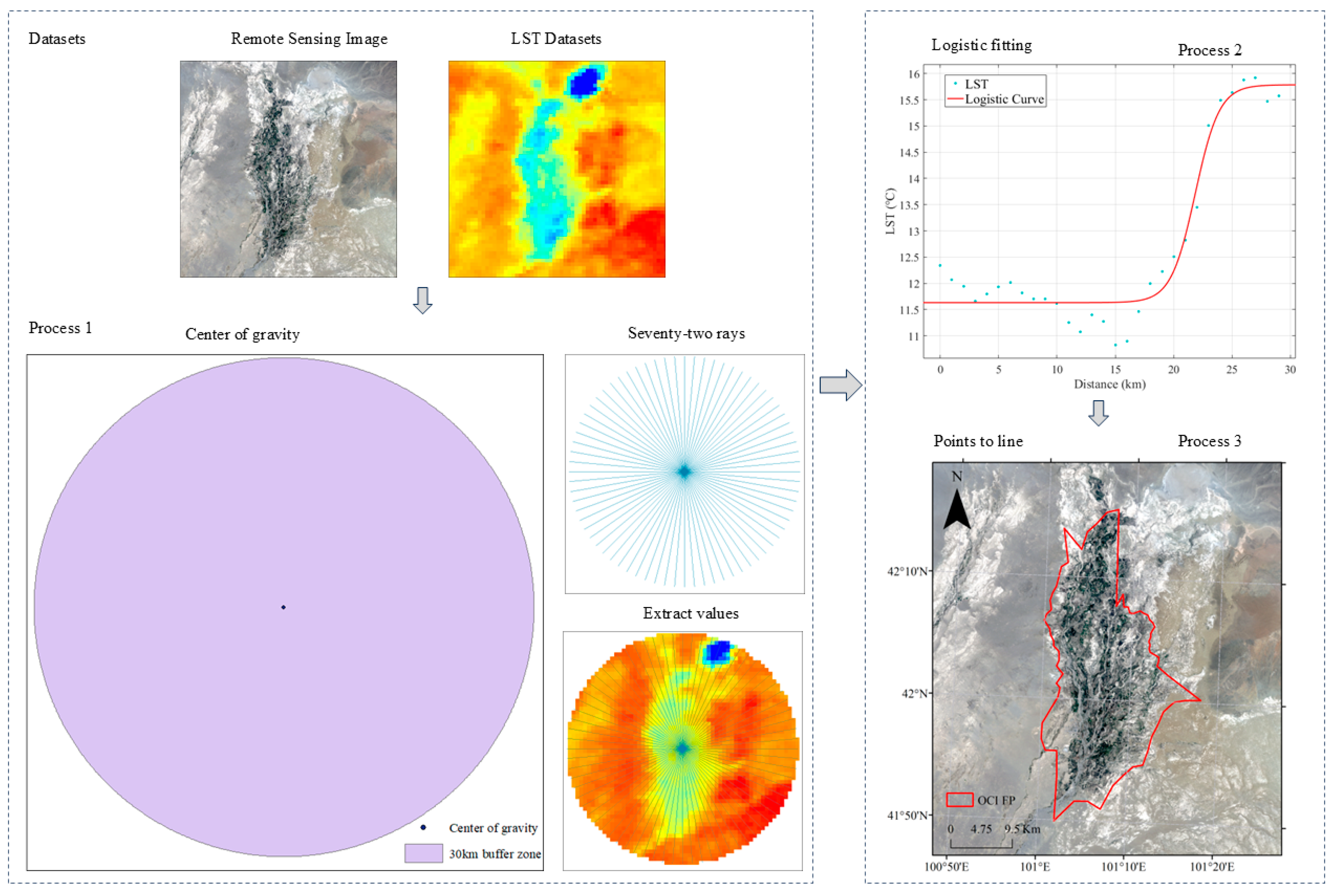
2.1.2. Oasis Cold Island Footprint
2.1.3. Spatiotemporal Evolution Analysis of SUHI FPs
2.1.4. Oasis Cold Island Effect Intensity
2.2. Case Study
2.2.1. Data Source
2.2.2. Experimental Designs
3. Results
3.1. Assessment of Results
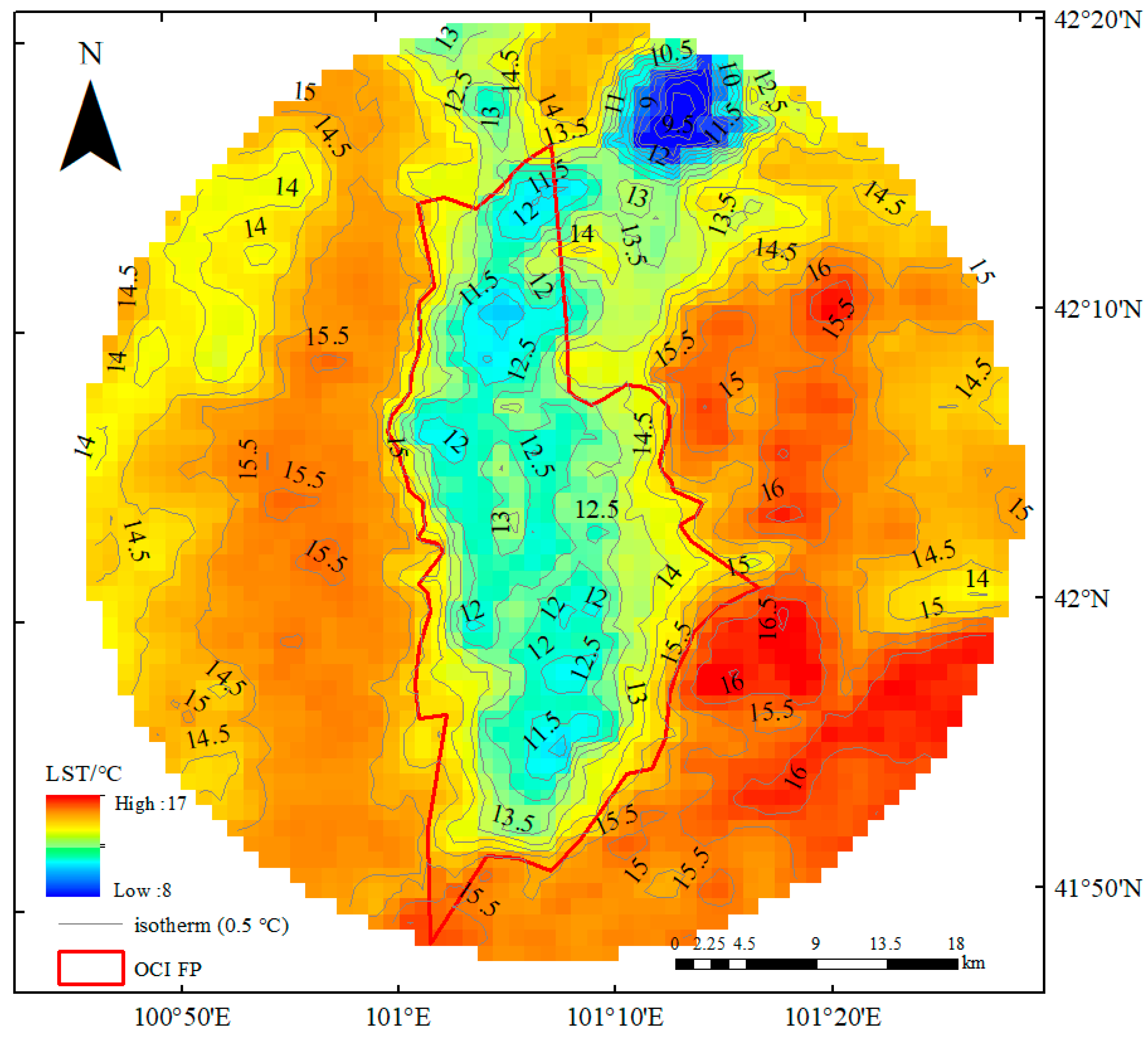
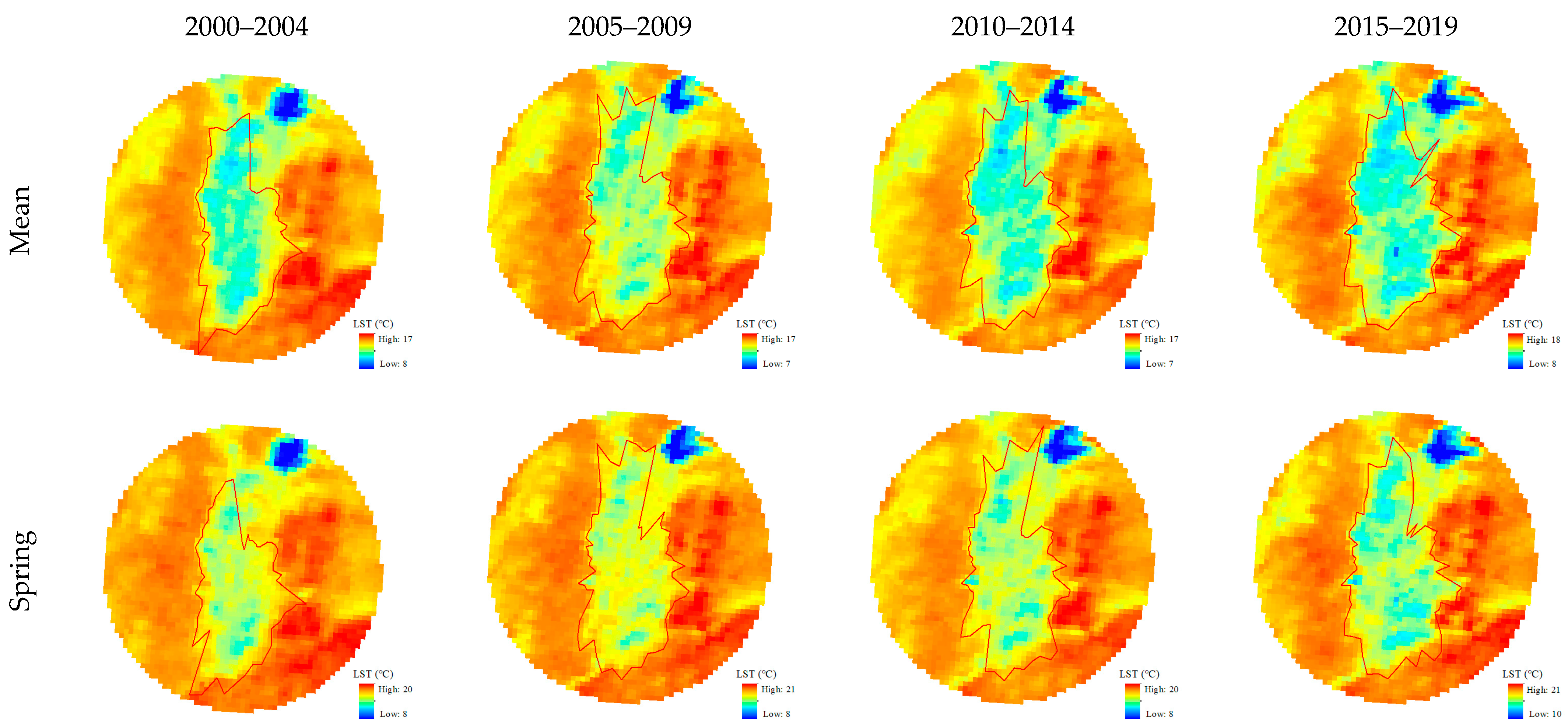
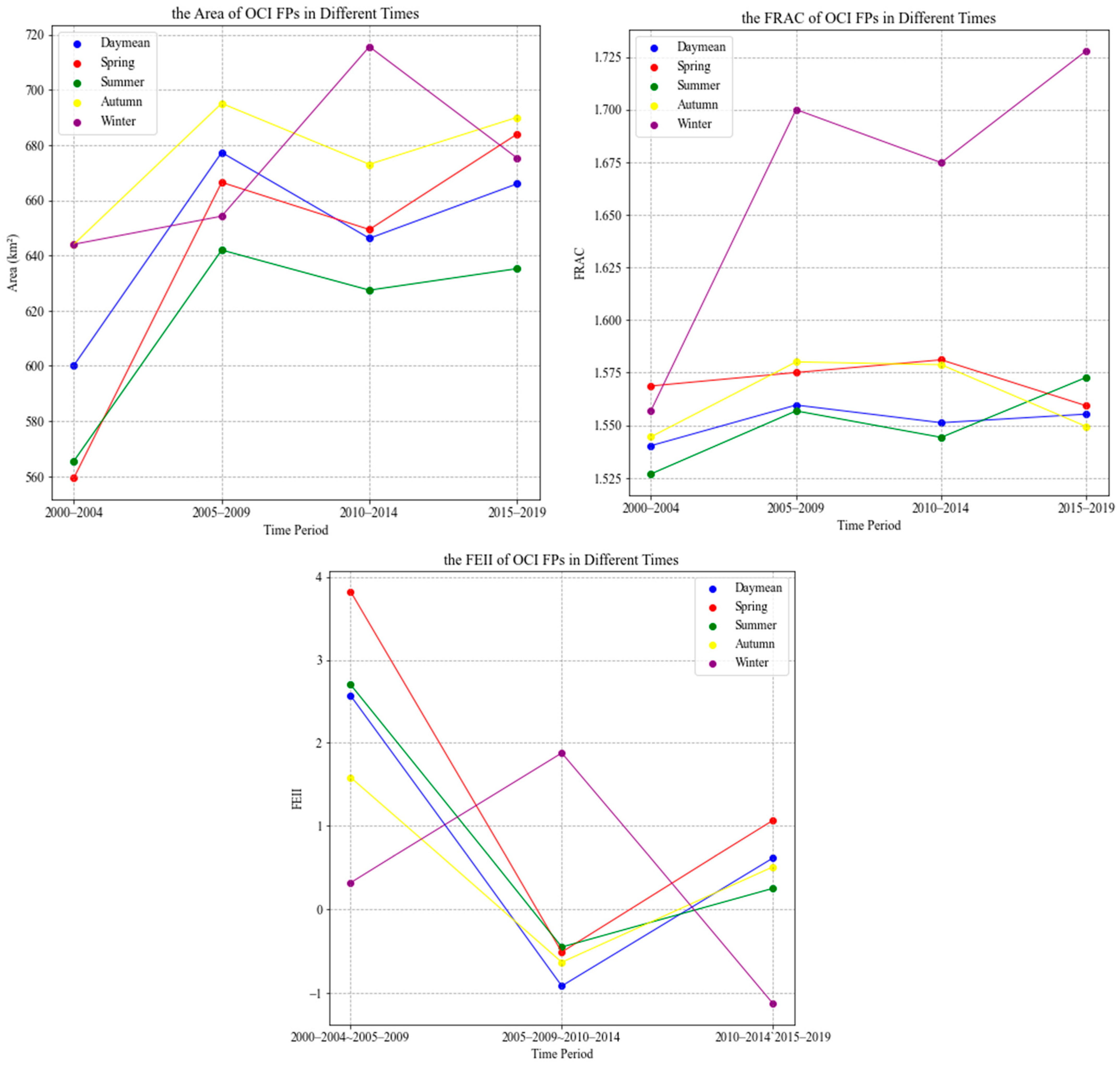
3.2. The Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of OCI FPs in the Ejina Oasis
3.3. Intensity of Oasis Cold Island Effect
4. Discussion
4.1. Elimination of Artificial Bias in Background Temperatures
4.2. Factors Influencing OCI FPs
4.3. Limitations and Outlook
4.3.1. Poor Fitting in Some Directions
4.3.2. Comparative Analysis between Multiple Oases
4.3.3. OCI FPs Influencing Factors
4.3.4. The Effect of Internal Heterogeneity in Oases on OCI FPs
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, J.P.; Yu, H.P.; Guan, X.D.; Wang, G.Y.; Guo, R.X. Accelerated dryland expansion under climate change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016, 6, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.J.; Jiang, F.Q.; Wang, Y.J. Correct understanding of the stability of oases in China’s arid zones. Arid Zone Res. 2010, 3, 319–323. [Google Scholar]
- Han, D.L. The progress of research on oasis in China. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 1999, 19, 313–319. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T. Review and Prospect of research on oasification and desertification in Arid Regions. J. Desert Res. 2009, 29, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Yang, K.; Zhou, Y. Progress in the study of oasis-desert interactions. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2016, 130, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivoni, E.R.; Kindler, M.; Wang, Z.C.; Pérez-Ruiz, E.R. Abiotic mechanisms drive enhanced evaporative losses under urban oasis conditions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL090123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, T.T. Desert Meteorology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Hu, Y.Q. Oasis effect in arid zones. Chin. J. Nat. 2001, 4, 234–236. [Google Scholar]
- Kai, k.; Matsuda, M.; Sato, R. Oasis effect observed at Zhangye Oasis in the Hexi Corridor, China. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 1997, 75, 1171–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.X. About the history of arid climate research at our institute. Plateau Meteorol. 1989, 2, 103–106. [Google Scholar]
- Su, C.X.; Hu, Y.Q.; Zhang, Y.F.; Wei, G.A. Microclimate characterization and cold island effect in oases of the Hexi region. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 1987, 4, 390–396. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.L.; Shi, Y.J.; Yao, Y.M.; Tian, F.P.; Hu, Y. Spatial and temporal variation of oasis cold island effect in Ganzhou District, Zhangye City, China, based on Landsat TM/ETM+. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2014, 9, 139–144. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.P.; Pan, X.P.; Liu, J.; Xie, W.; Ma, M. Temporal and spatial patterns of surface temperature and cold island effect in Ejina Oasis based on Landsat images. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2019, 2, 116–121. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, X.; Li, W. Oasis cold island effect and its influence on air temperature: A case study of Tarim Basin, Northwest China. J. Arid Land 2016, 8, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.X.; Zhang, M.J.; Wang, S.J. Intensity of cold and wet island effects in typical oases in Xinjiang. Chin. J. Ecol. 2015, 6, 1523–1531. [Google Scholar]
- Potchter, O.; Goldman, D.; Kadish, D.; Iluz, D. The oasis effect in an extremely hot and arid climate: The case of southern Israel. J. Arid Environ. 2008, 72, 1721–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potchter, O.; Goldman, D.; Iluz, D.; Kadish, D. The climatic effect of a manmade oasis during winter season in a hyper arid zone: The case of Southern Israel. J. Arid Environ. 2012, 87, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domroes, M.; El-Tantawi, A. Recent temporal and spatial temperature changes in Egypt. Int. J. Climatol. 2005, 25, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunel, J.-P.; Ihab, J.; Droubi, A.M.; Samaan, S. Energy budget and actual evapotranspiration of an arid oasis ecosystem: Palmyra (Syria). Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 84, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebert, S.; Nagieb, M.; Buerkert, A. Climate and irrigation water use of a mountain oasis in northern Oman. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 89, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.H.; Zhang, W.Q. Remote sensing analysis of spatial and temporal pattern of cold island effect in Zhangye oasis. Arid Zone Res. 2010, 4, 481–486. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.G.; Teibai, T.; Ding, J.L.; Xu, C.B. Analysis of the “cold island” effect and its correlation with vegetation cover in the oasis at the southern edge of the Tarim- A case study in Yutian Oasis. Arid Land Geogr. 2007, 6, 865–870. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, P.X.; Yao, Y.L.; Yong, G.Z.; Wang, Y. Spatial-temporal characteristics and factor analysis of the cold island effect in the Shihezi oasis based on remote sensing images. J. Nat. Resour. 2015, 8, 1319–1331. [Google Scholar]
- Georgescu, M.; Moustaoui, M.; Mahalov, A.; Dudhia, J. An alternative explanation of the semiarid urban area “oasis effect”. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, D24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.H.; Chen, Y.C. Numerical simulation of the effect of oasis and desert subsurface states on atmospheric boundary layer characteristics. J. Desert Res. 1995, 2, 116–123. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, L.J.; Lv, S.H.; Meng, X.H.; Bao, Y. Numerical simulation study on the influence of ambient wind field on oasis cold island effect. J. Desert Res. 2006, 5, 754–758. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, D.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, L.; Sun, G.; Liu, Y. The footprint of urban heat island effect in China. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.C.; Li, C.L.; Hu, Y.M.; Wang, C.; Wen, D.; Li, Z.X.; Ping, X.Y.; Wang, Q.Y.; Li, Q. Spatiotemporal evolution and influencing factors of surface urban heat island footprint across different-sized cities. Urban Clim. 2024, 54, 101852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Z.; Wu, C.; Zhao, D.Q.; Xu, X.L.; Yang, J.L.; Feng, L.; Sun, Z.L.; Liu, L. Determining the boundary and probability of surface urban heat island footprint based on a logistic model. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.B.; Li, K.M.; Huang, Z. Characteristics of spatial and temporal changes of oasis effect in Hexi region in the last 20 a and attribution analysis. Arid Zone Res. 2023, 12, 2031–2042. [Google Scholar]
- Pearl, R.; Reed, L.J. On the rate of growth of the population of the United States since 1790 and its mathematical representation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1920, 6, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Zelenay, P. Kinetic models for the degradation mechanisms of PGM-free ORR catalysts. ECS Trans. 2018, 85, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bie, Q.; Xie, Y.W.; Wang, X.Y.; Wei, B.C.; He, L.; Duan, H.M.; Wang, J. Understanding the attributes of the dual oasis effect in an arid region using remote sensing and observational data. Ecosyst. Health Sustain. 2020, 6, 681–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.; Tang, W.; Ding, L.; Ma, J.; Zhang, X. Daily 1-km All-Weather Land Surface Temperature Dataset for Western China (TRIMS LST-TP; 2000–2022) V2; National Tibetan Plateau Data Center: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, J.; Liang, S.; Wang, D. A practical reanalysis data and thermal infrared remote sensing data merging (RTM) method for reconstruction of a 1-km all-weather land surface temperature. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 260, 112437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, J.; Göttsche, F.; Zhan, W.; Liu, S.; Cao, R. A Method Based on Temporal Component Decomposition for Estimating 1-km All-Weather Land Surface Temperature by Merging Satellite Thermal Infrared and Passive Microwave Observations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 4670–4691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhan, W.; Göttsche, F.-M.; Liu, S.; Olesen, F.-S.; Hu, W.; Dai, F. A thermal sampling depth correction method for land surface temperature estimation from satellite passive microwave observation over barren land. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 4743–4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Zhou, J.; Ma, J.; Wang, Z.; Ding, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X. TRIMS LST: A daily 1 km all-weather land surface temperature dataset for China’s landmass and surrounding areas (2000–2022). Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2024, 16, 387–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.X.; Hu, Y.Q. Cold Island Effect in oases and lakes. Chin. Sci. Bull. 1987, 10, 756–758. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, B.C.; Gui, D.W.; Liu, Q.; Abd-Elmabod, S.K.; Liu, Y.F.; Lu, B.B. Distribution and growth drivers of oases at a global scale. Earth’s Future 2024, 12, e2023EF004086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Chen, Y.H.; Li, J.; Weng, Q.H.; Yi, W.B. A volume model for urban heat island based on remote sensing imagery and its application: A case study in Beijing. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 5, 734–742. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, Z.; Tian, G.J. Dynamic monitoring of the footprint and capacity for urban heat island in Beijing between 2001 and 2012 based on MODIS. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 3, 476–484. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.H.; Chen, Y.C.; Lv, S.H. Numerical simulation of the critical scale of oasis maintenance and development in the arid regions of Northwest China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2004, 21, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.H.; Lv, S.H.; Zhang, T.T.; Ao, Y.H.; Li, S.; Bao, Y.; Wen, L.J.; Luo, S. Impacts of inhomogeneous landscapes in oasis interior on the oasis self-maintenance mechanism by integrating numerical model with satellite data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 3729–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kueppers, L.M.; Snyder, M.A.; Sloan, L.C. Irrigation cooling effect: Regional climate forcing by land-use change. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L03703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacks, W.J.; Cook, B.I.; Buenning, N.; Levis, S.; Helkowski, J.H. Effects of global irrigation on the near-surface climate. Clim. Dyn. 2009, 33, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.F.; Liang, S.L.; Pan, Y.Z. Observational evidence of the cooling effect of agricultural irrigation in Jilin, China. Clim. Chang. 2012, 114, 799–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.J.; Yang, Z.Y. Cooling effect of agricultural irrigation over Xinjiang, Northwest China from 1959 to 2006. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 24–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.J.; Wang, G.X.; Yao, R.; Wang, L.C.; Yu, D.Q.; Gui, X. Investigating Surface Urban Heat Islands in South America Based on MODIS Data from 2003–2016. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haashemi, S.; Weng, Q.H.; Darvishi, A.; Alavipanah, S.K. Seasonal Variations of the Surface Urban Heat Island in a Semi-Arid City. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzarini, M.; Marpu, P.R.; Ghedira, H. Temperature-land cover interactions: The inversion of urban heat island phenomenon in desert city areas. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 130, 136–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


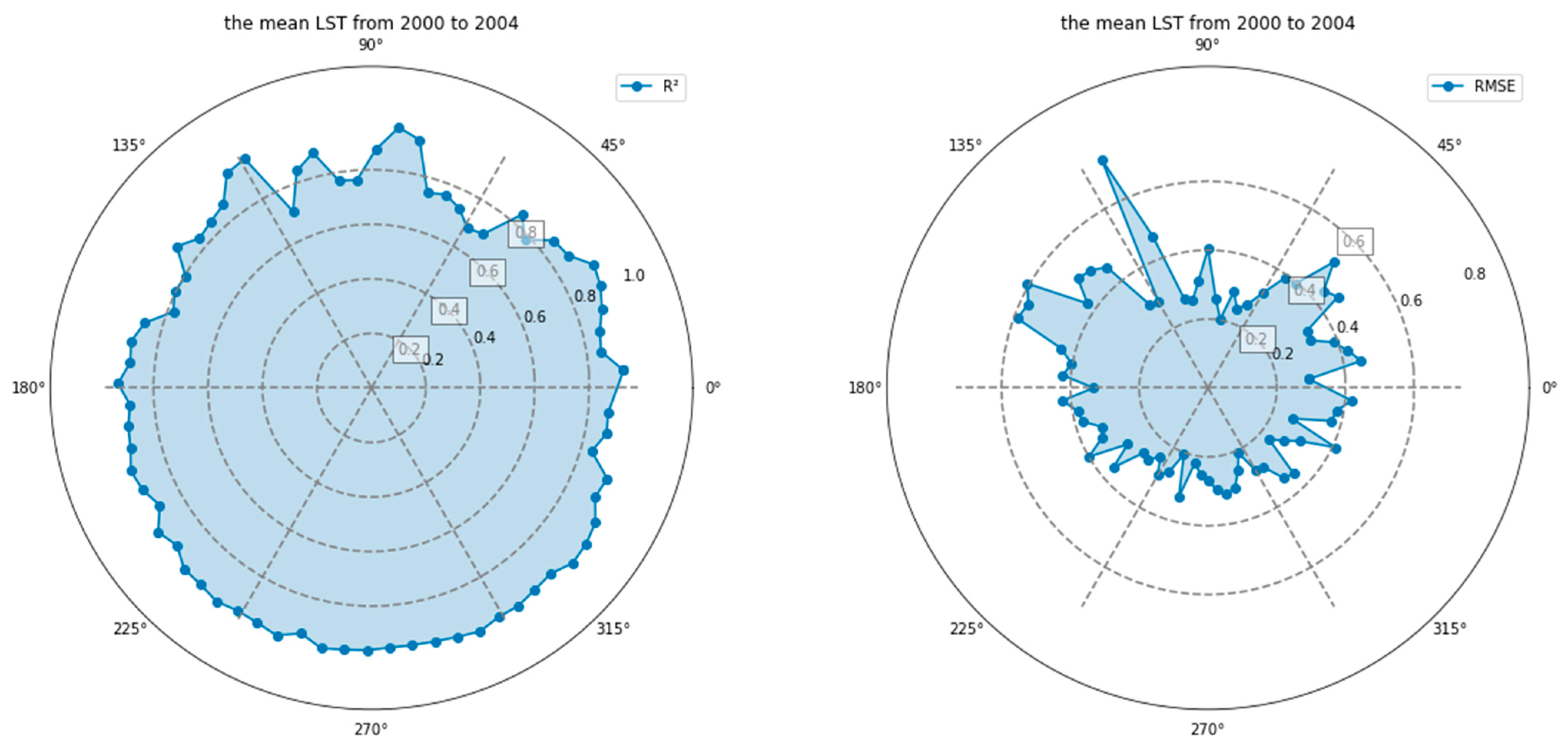


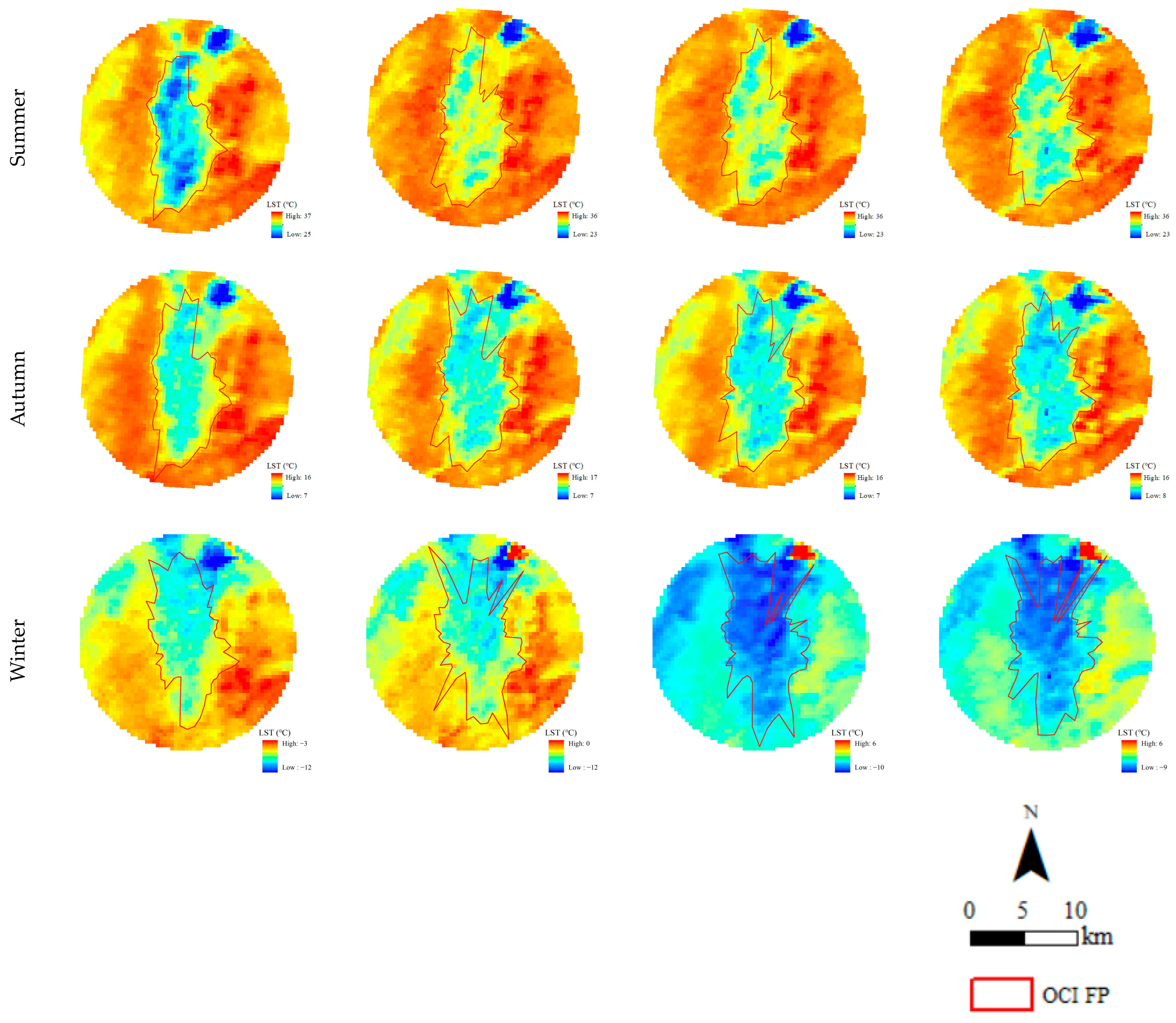


| Times | Mean | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000–2004 | the mean of R2 | 0.89 | 0.83 | 0.88 | 0.90 | 0.85 |
| the mean of RMSE | 0.35 | 0.39 | 0.56 | 0.36 | 0.25 | |
| 2005–2009 | the mean of R2 | 0.82 | 0.81 | 0.82 | 0.85 | 0.82 |
| the mean of RMSE | 0.44 | 0.47 | 0.60 | 0.45 | 0.31 | |
| 2010–2014 | the mean of R2 | 0.84 | 0.81 | 0.83 | 0.86 | 0.82 |
| the mean of RMSE | 0.42 | 0.48 | 0.60 | 0.41 | 0.35 | |
| 2014–2019 | the mean of R2 | 0.86 | 0.82 | 0.84 | 0.86 | 0.82 |
| the mean of RMSE | 0.44 | 0.56 | 0.64 | 0.45 | 0.35 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, W.; Chen, R. Finding Oasis Cold Island Footprints Based on a Logistic Model—A Case Study in the Ejina Oasis. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2895. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16162895
Wu W, Chen R. Finding Oasis Cold Island Footprints Based on a Logistic Model—A Case Study in the Ejina Oasis. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(16):2895. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16162895
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Wentong, and Rensheng Chen. 2024. "Finding Oasis Cold Island Footprints Based on a Logistic Model—A Case Study in the Ejina Oasis" Remote Sensing 16, no. 16: 2895. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16162895
APA StyleWu, W., & Chen, R. (2024). Finding Oasis Cold Island Footprints Based on a Logistic Model—A Case Study in the Ejina Oasis. Remote Sensing, 16(16), 2895. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16162895





