Modelling and Mitigating Wind Turbine Clutter in Space–Air Bistatic Radar
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The study developed an accurate space–time clutter model for the SABR configuration. The model considered the impact of several factors, including the launch satellite orbit inclination, Earth’s curved surface, and Earth’s rotation. The study derived the bistatic equal distance, rings’ spatial frequencies, and Doppler frequency expressions;
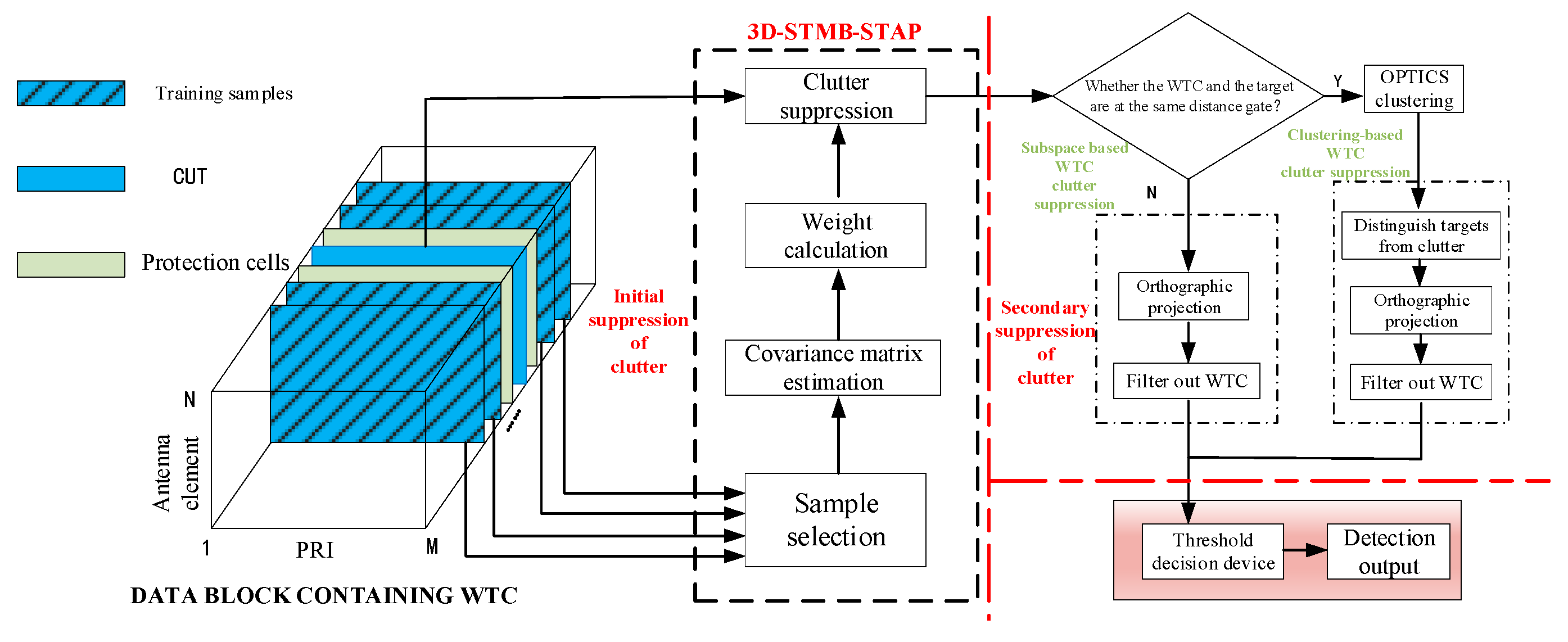
- Based on the above work, we explore the influence of wind turbines on radar clutter suppression. We established a clutter geometric model and a corresponding space–time echo model considering the influence of wind turbines under the SABR configuration. A three-dimensional STMB strategy incorporating the OPTICS clustering algorithm is introduced. This algorithm comprises two main phases: Initially, the 3D-STMB method is utilized for the initial clutter reduction. Subsequently, we leverage the distinct distribution characteristics of targets versus WTC using OPTICS clustering. This approach not only differentiates targets from clutter but also facilitates enhanced secondary clutter suppression, thereby improving the performance of the SABR system in a downward-looking configuration.
2. Geometric Configuration and Space–Time Clutter Model for SABR
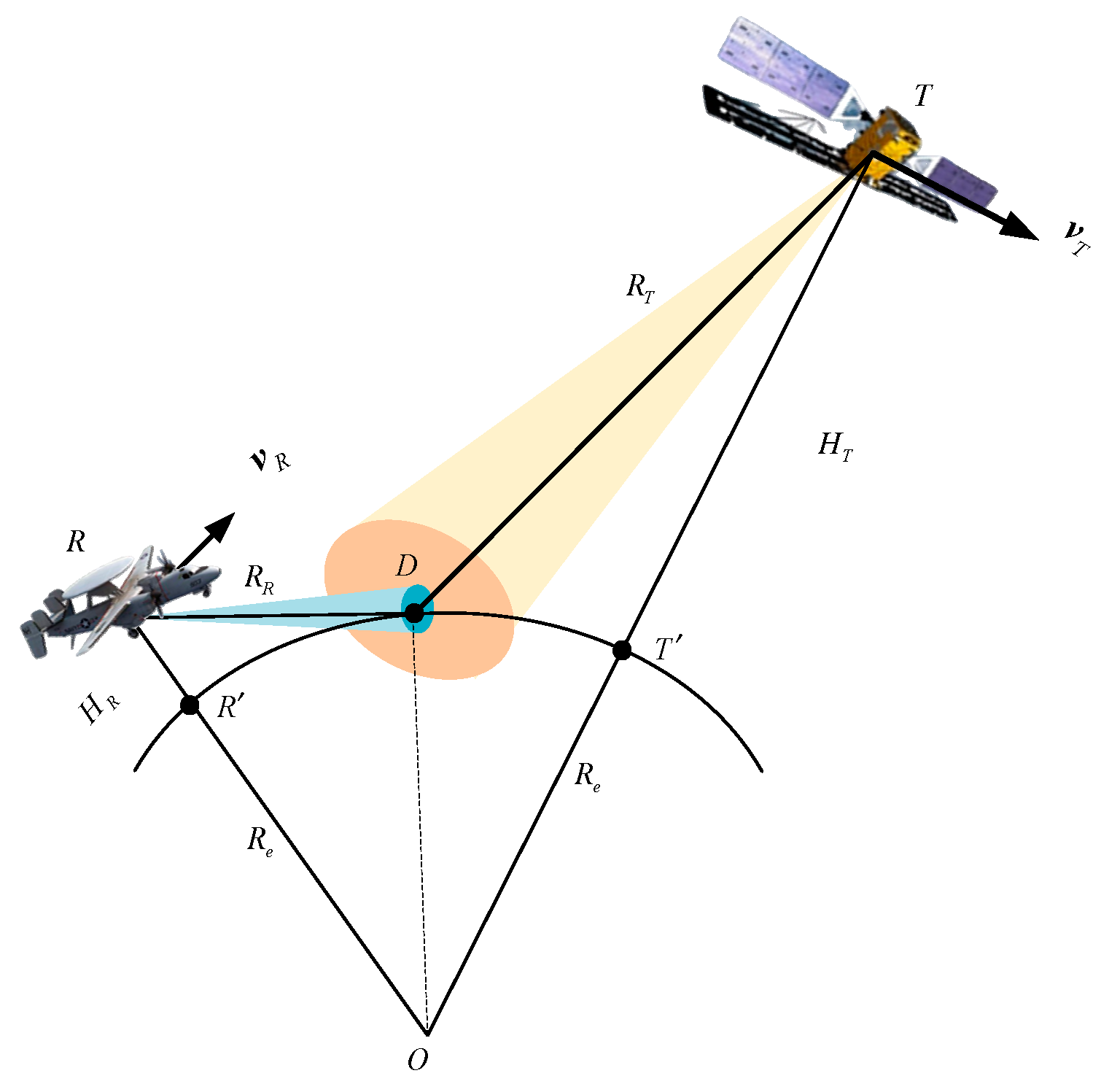
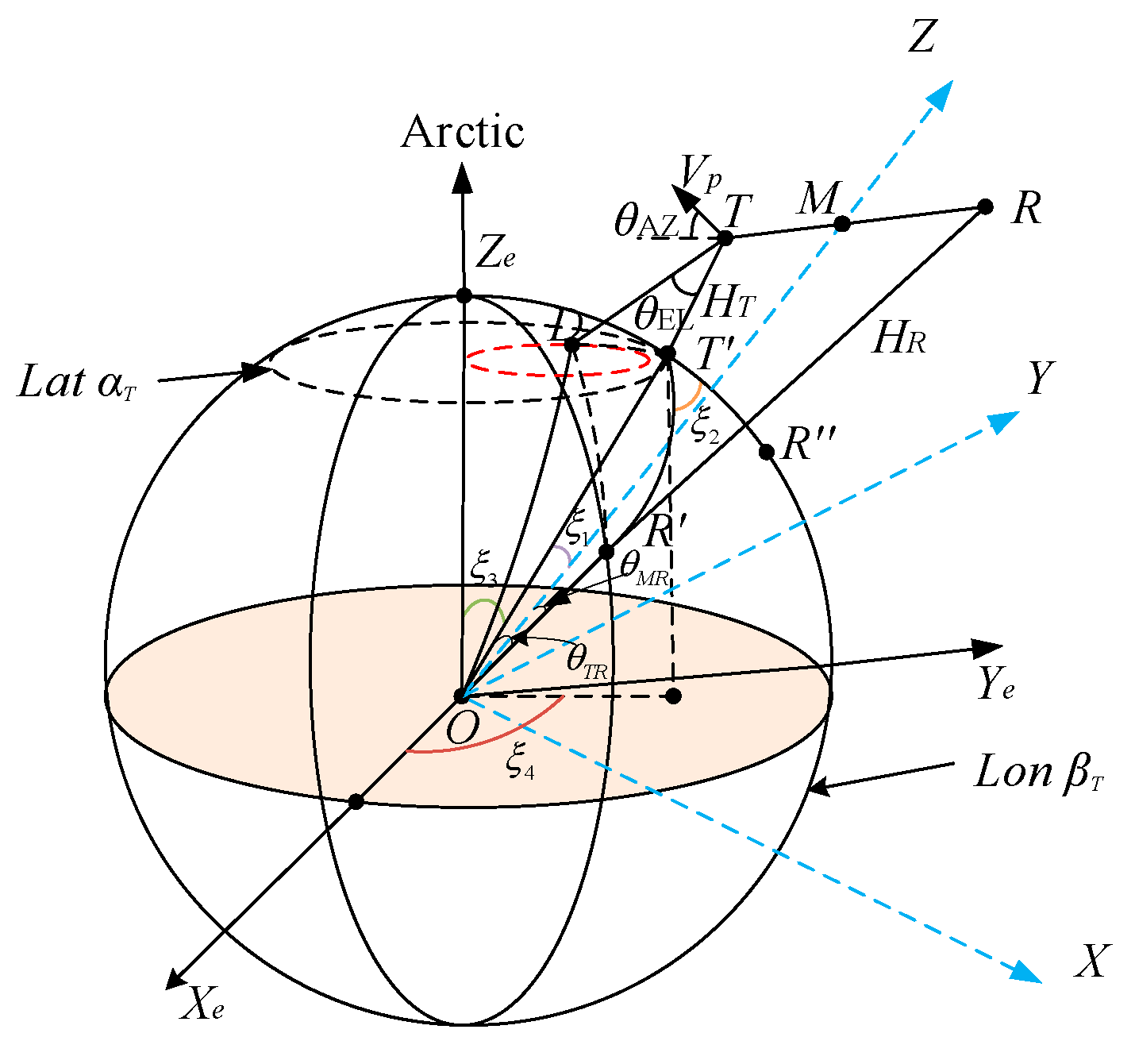
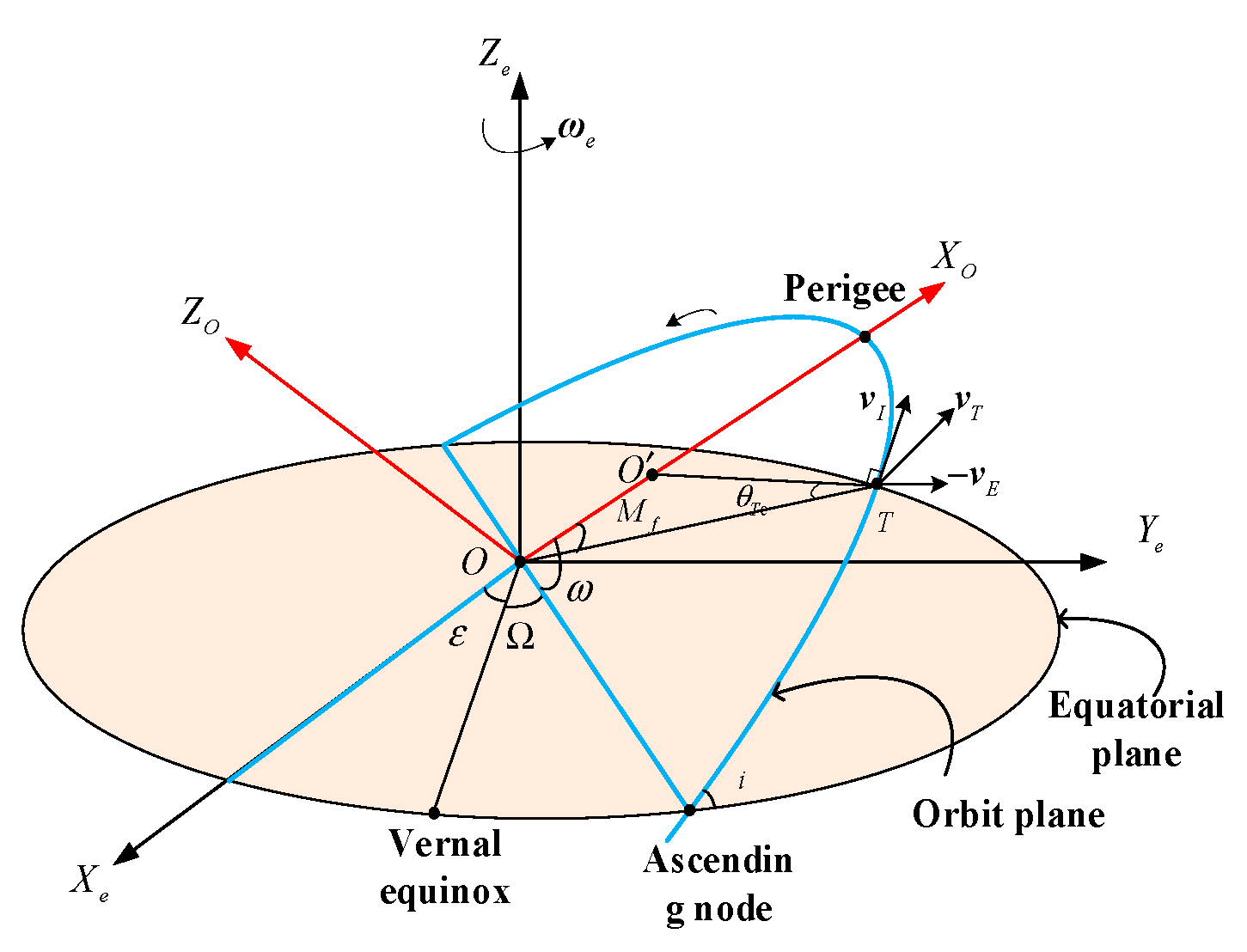
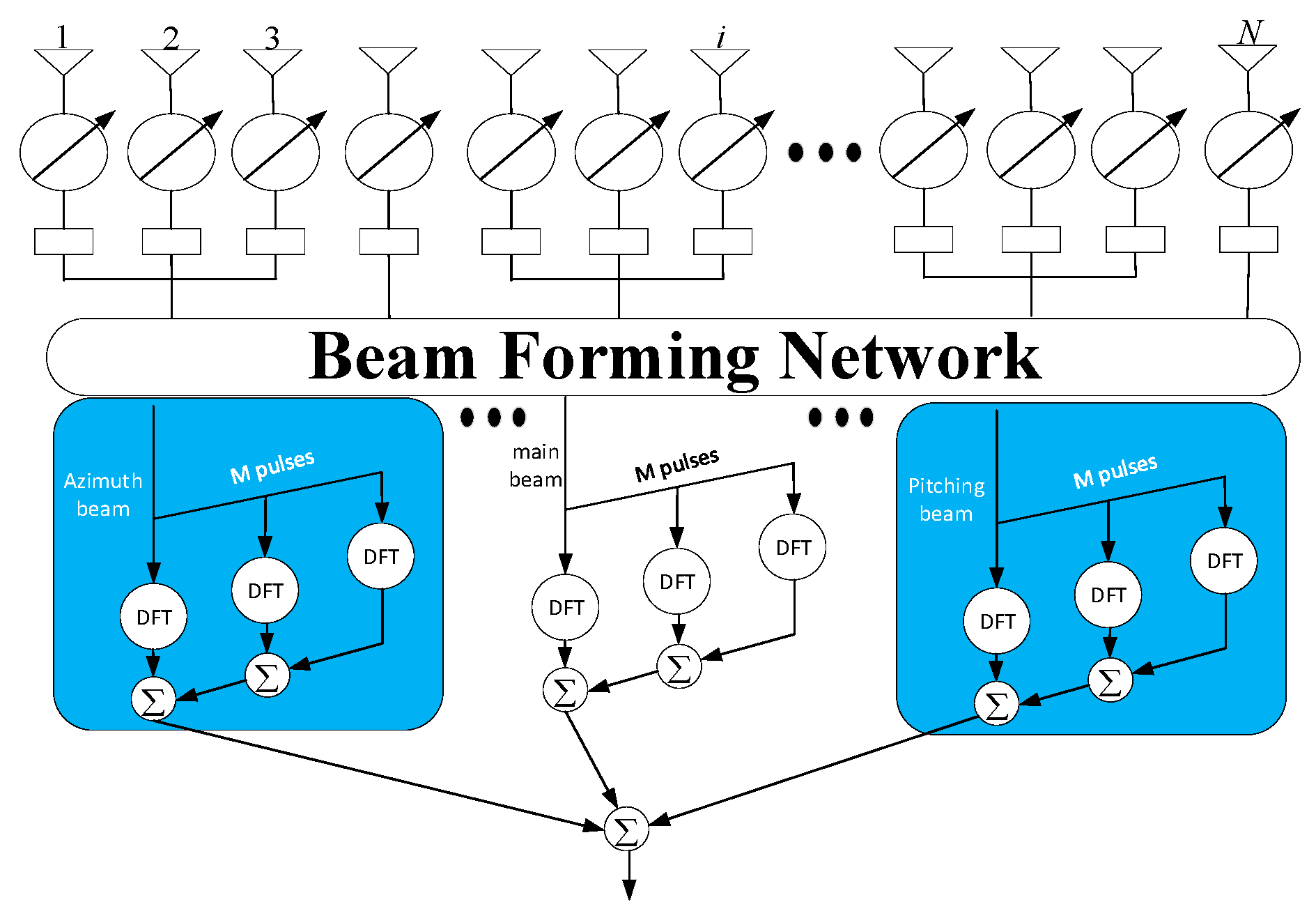
2.1. Geometric Configuration of SABR
2.2. Doppler Frequency and Spatial Frequency
2.3. Clutter Signal Model
3. Modelling and Suppression for WTC
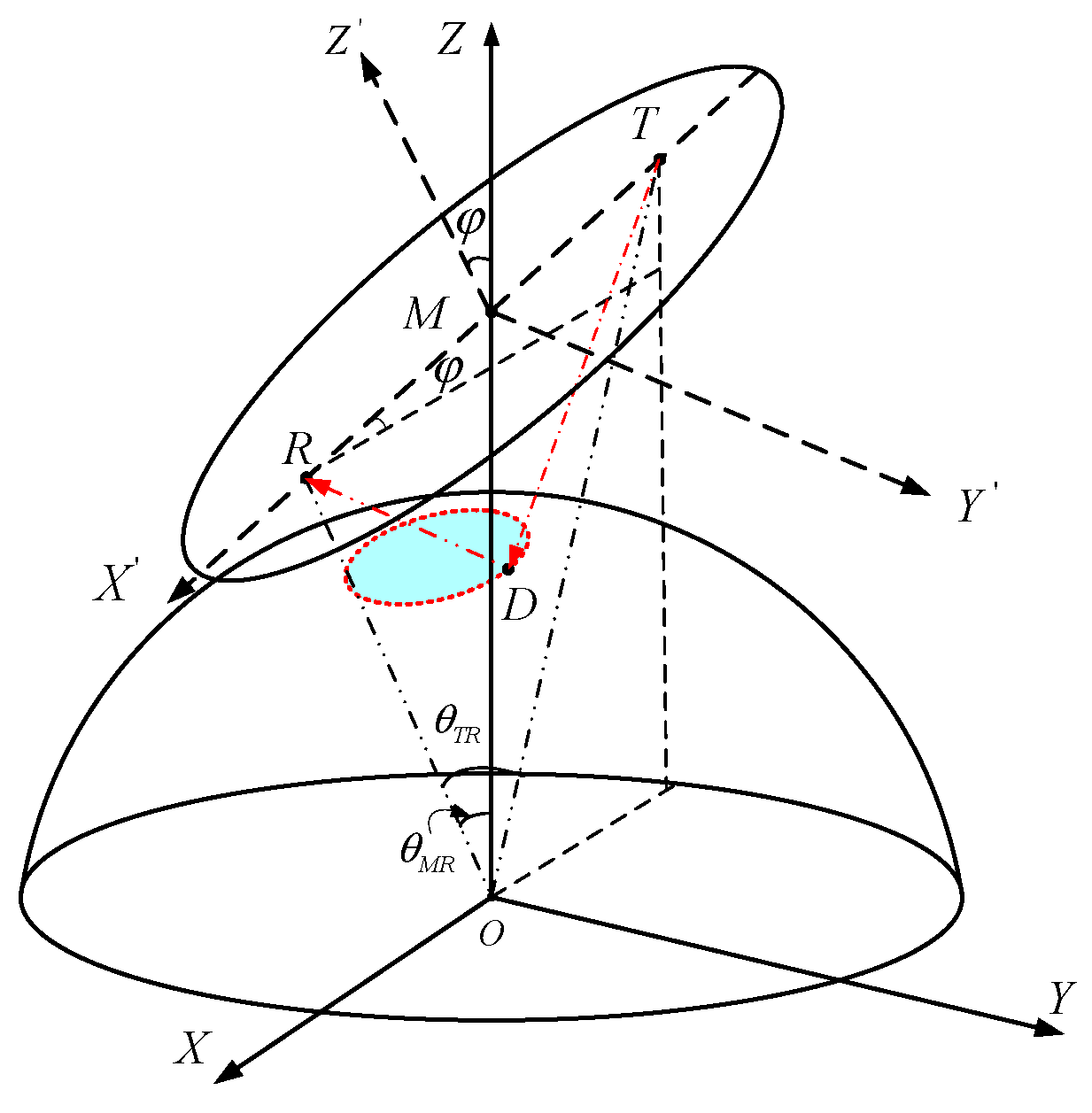
3.1. Geometric Model and Space–Time Signal Model of WTC
3.1.1. Geometric Model
3.1.2. Space–Time Signal Model of Windmill Motion Clutter
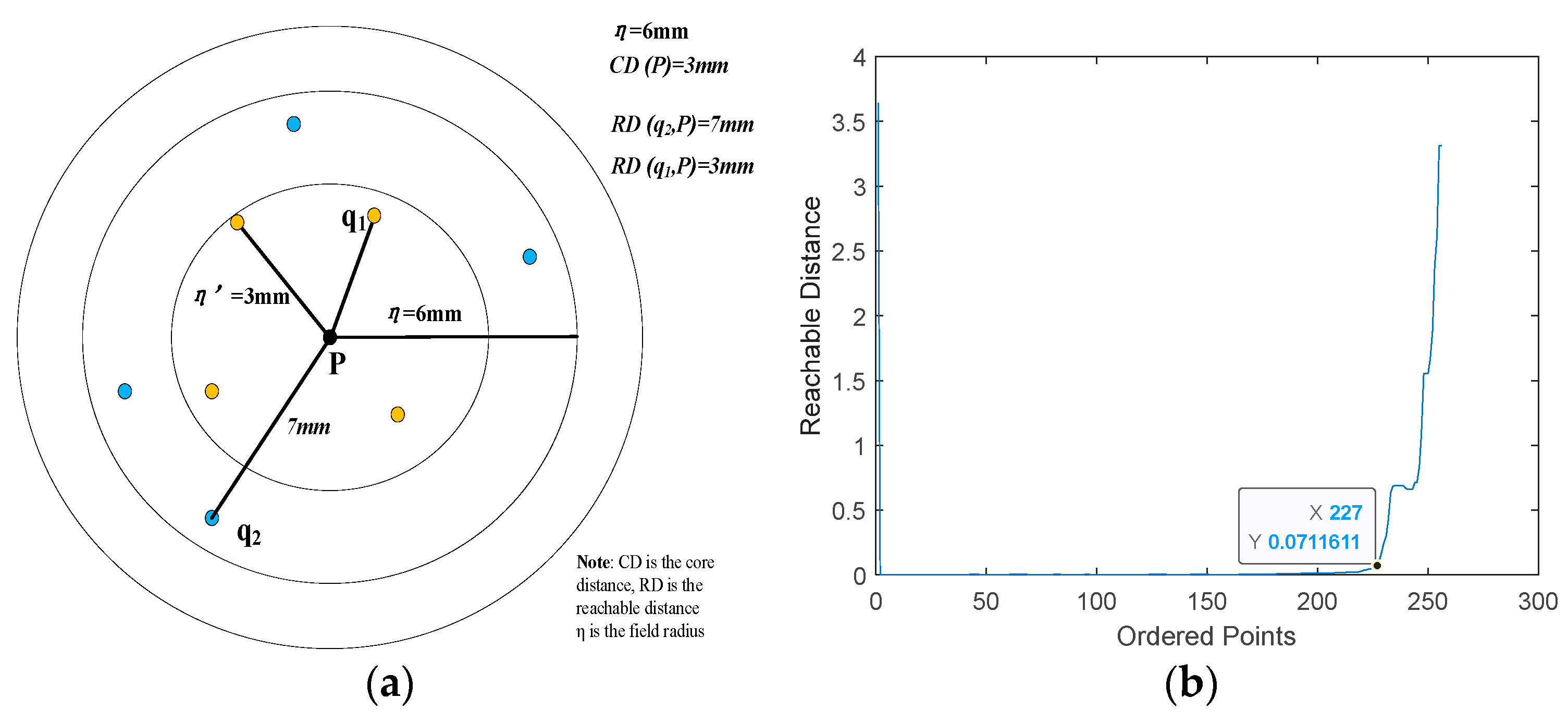
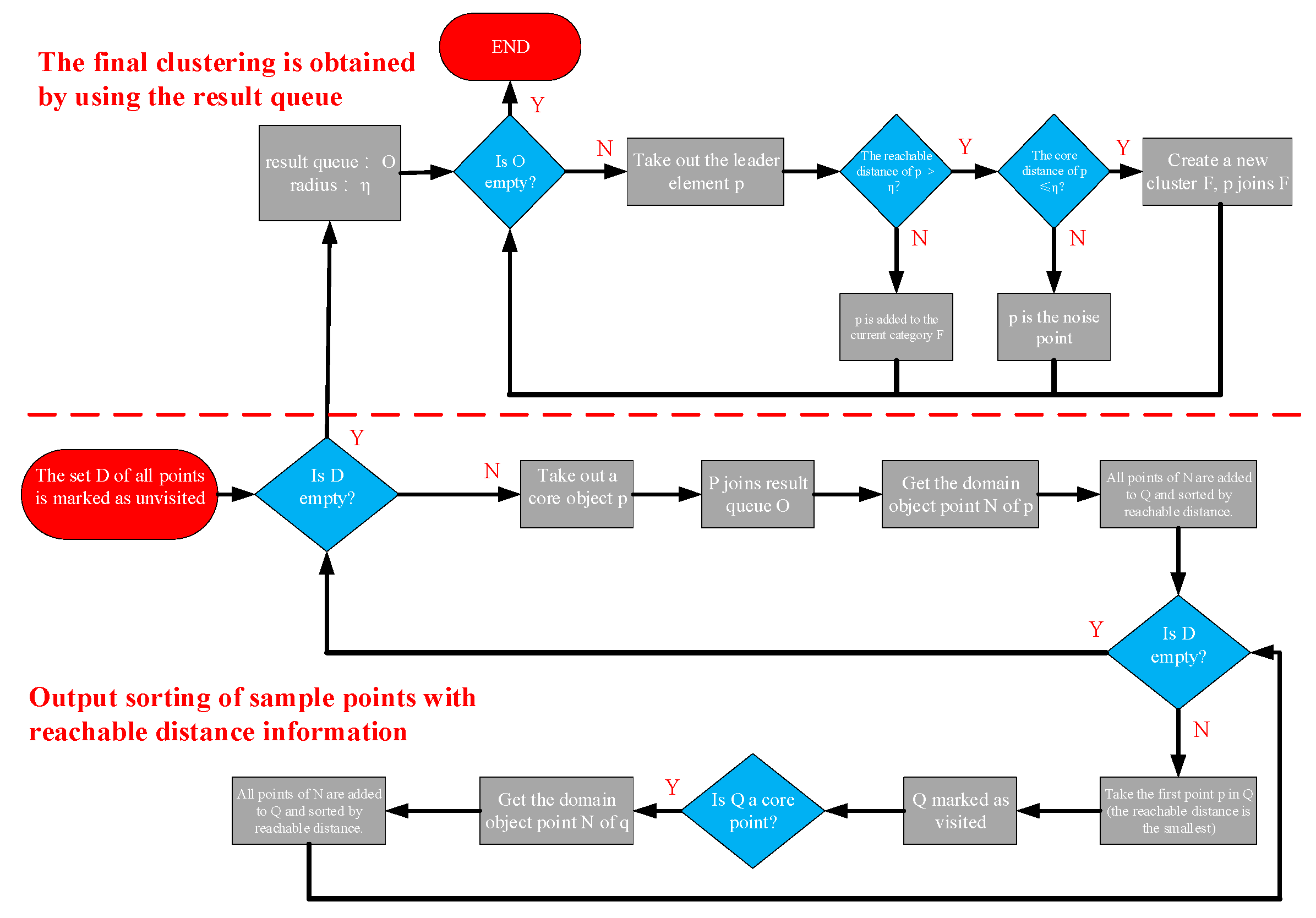
3.2. Clutter Suppression Based on STMB Combined with OPTICS Clustering
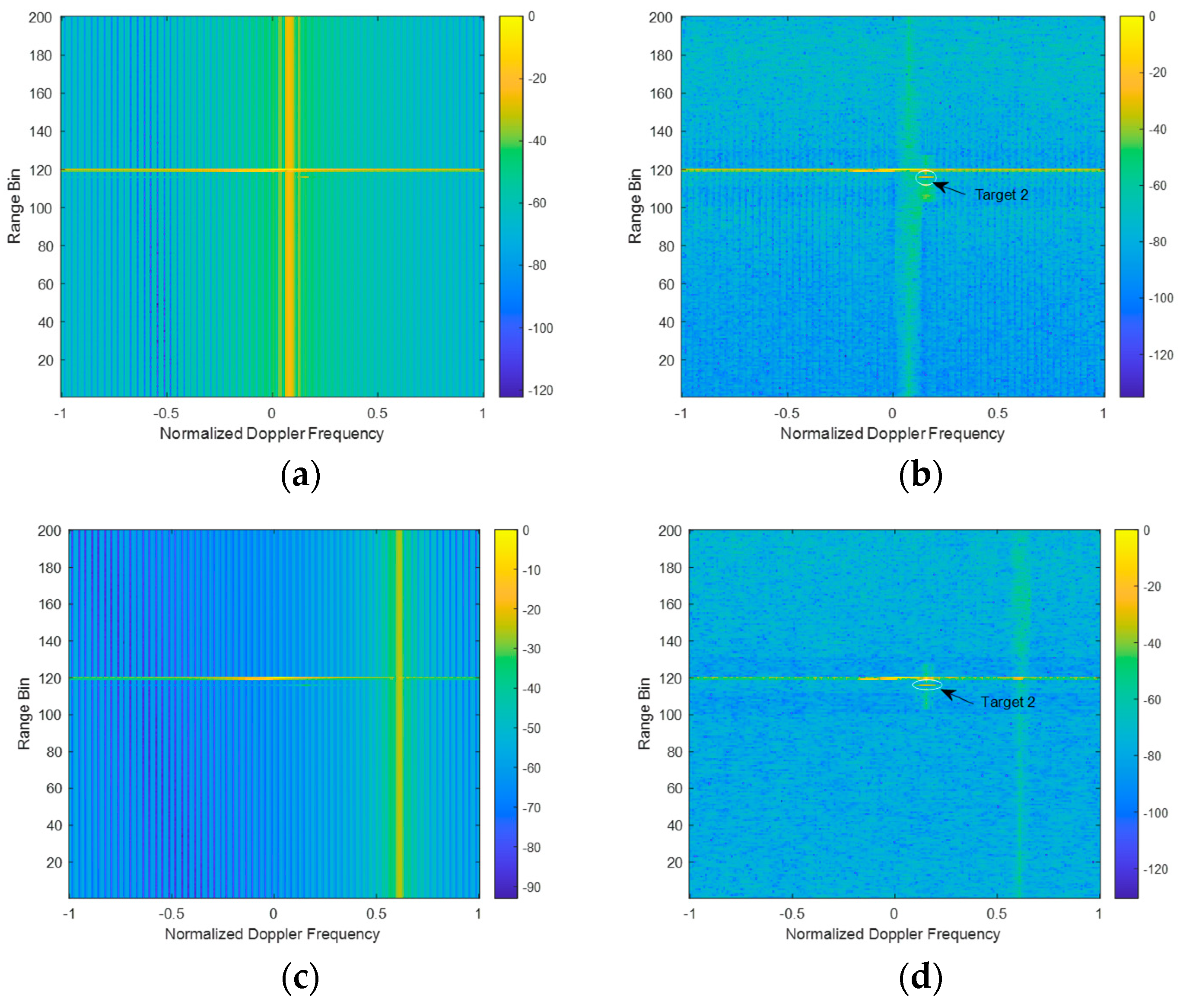
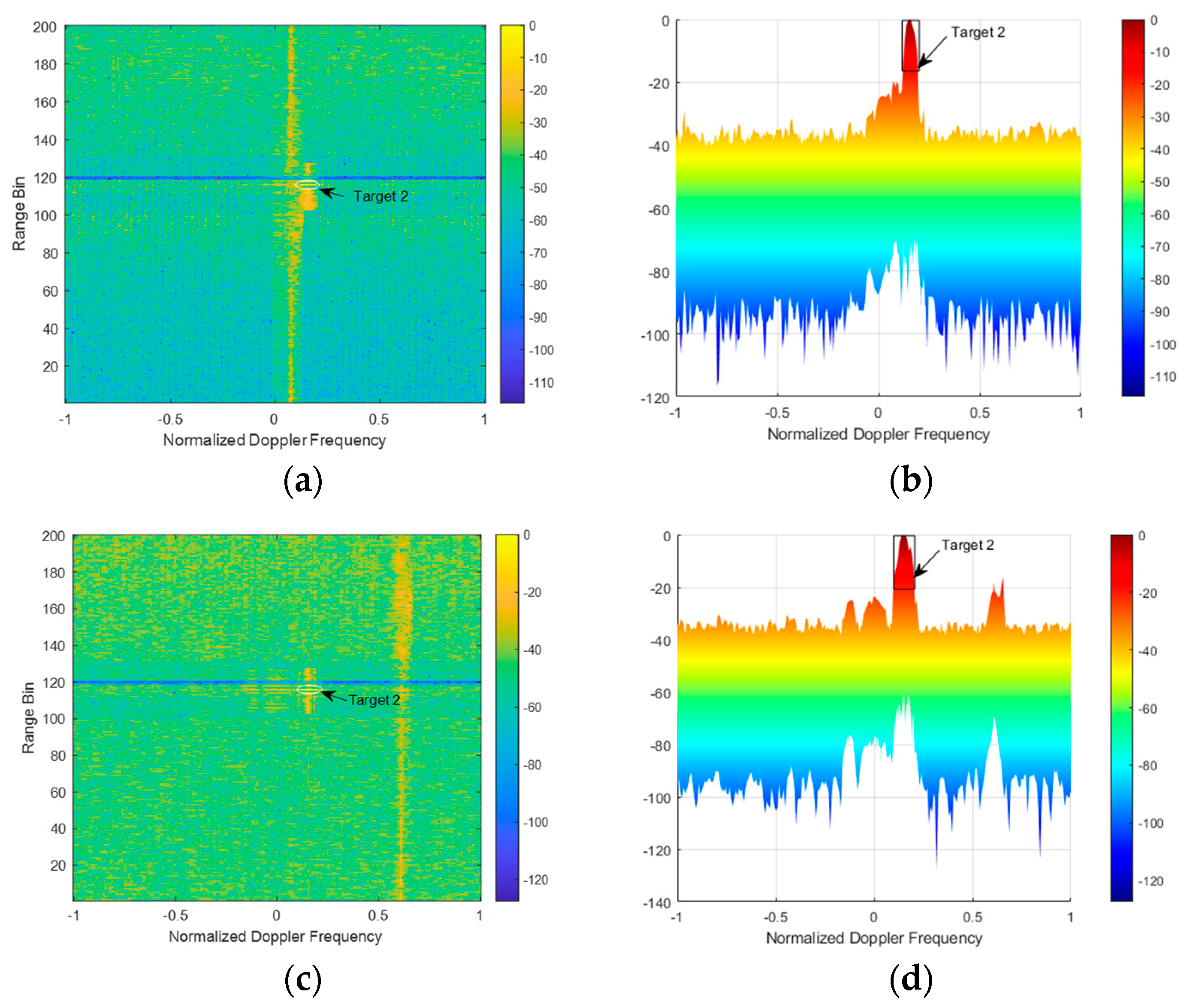
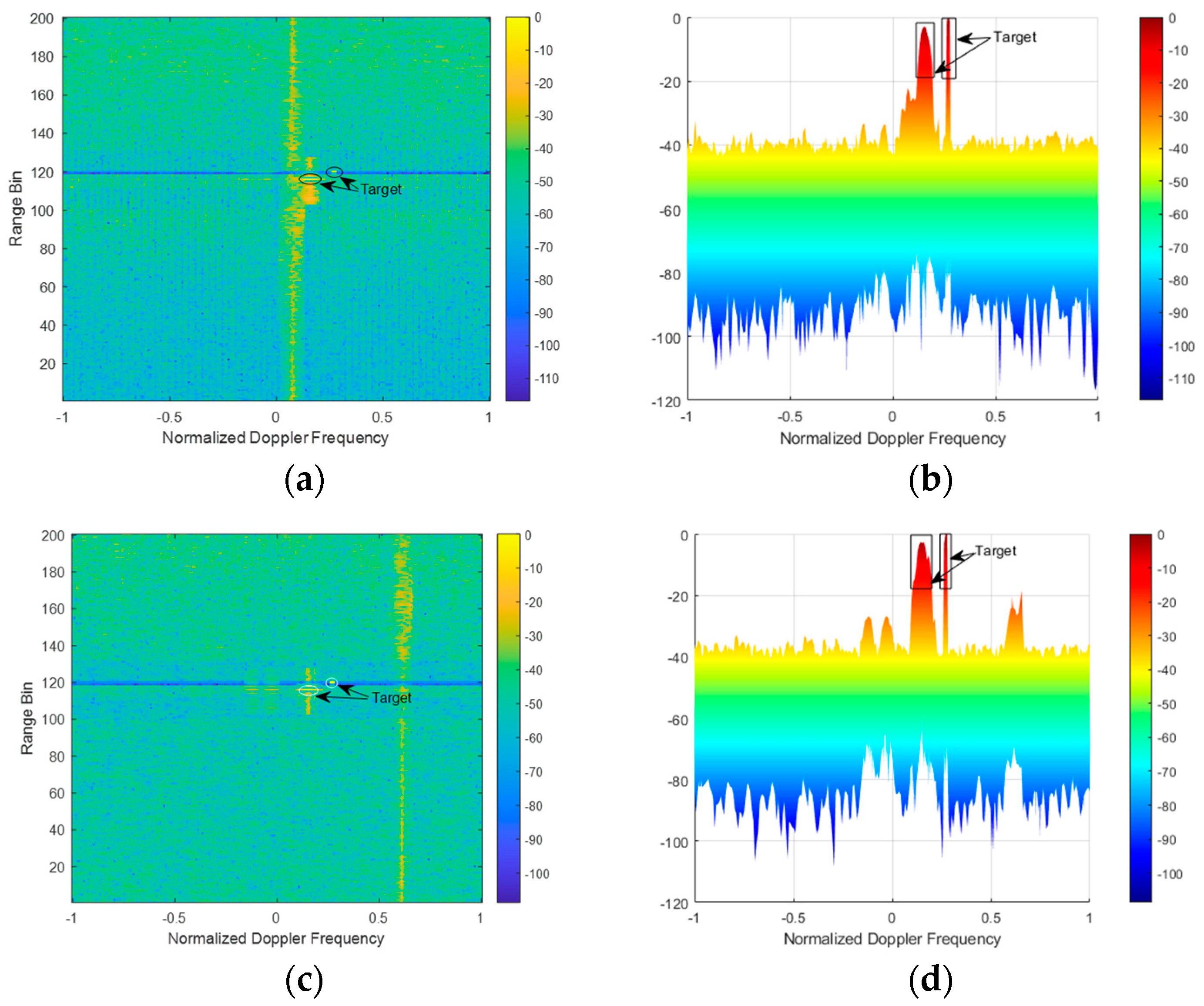
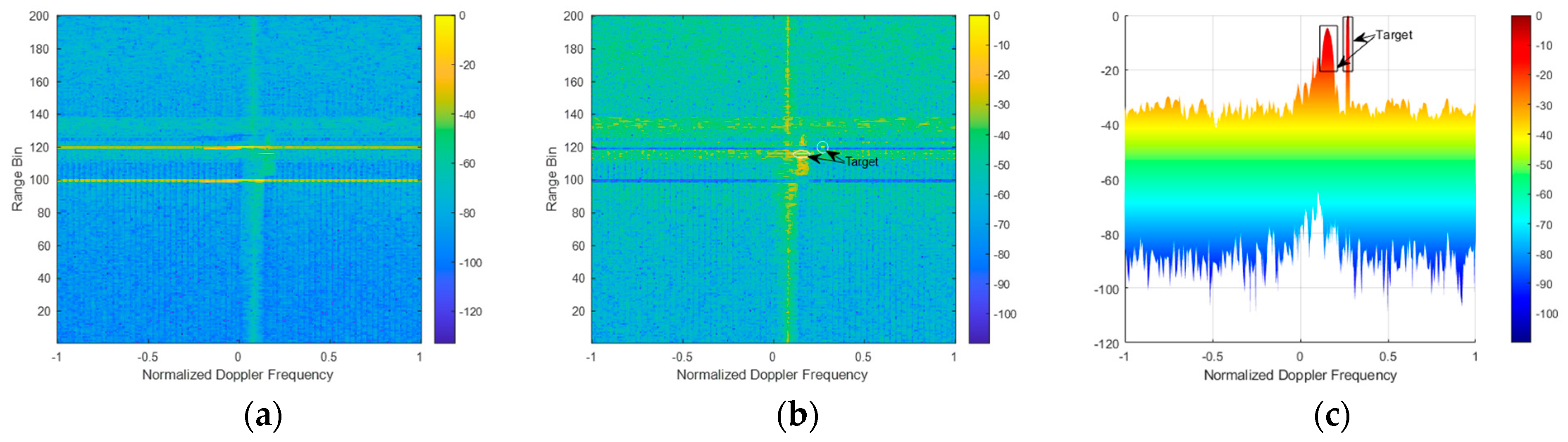
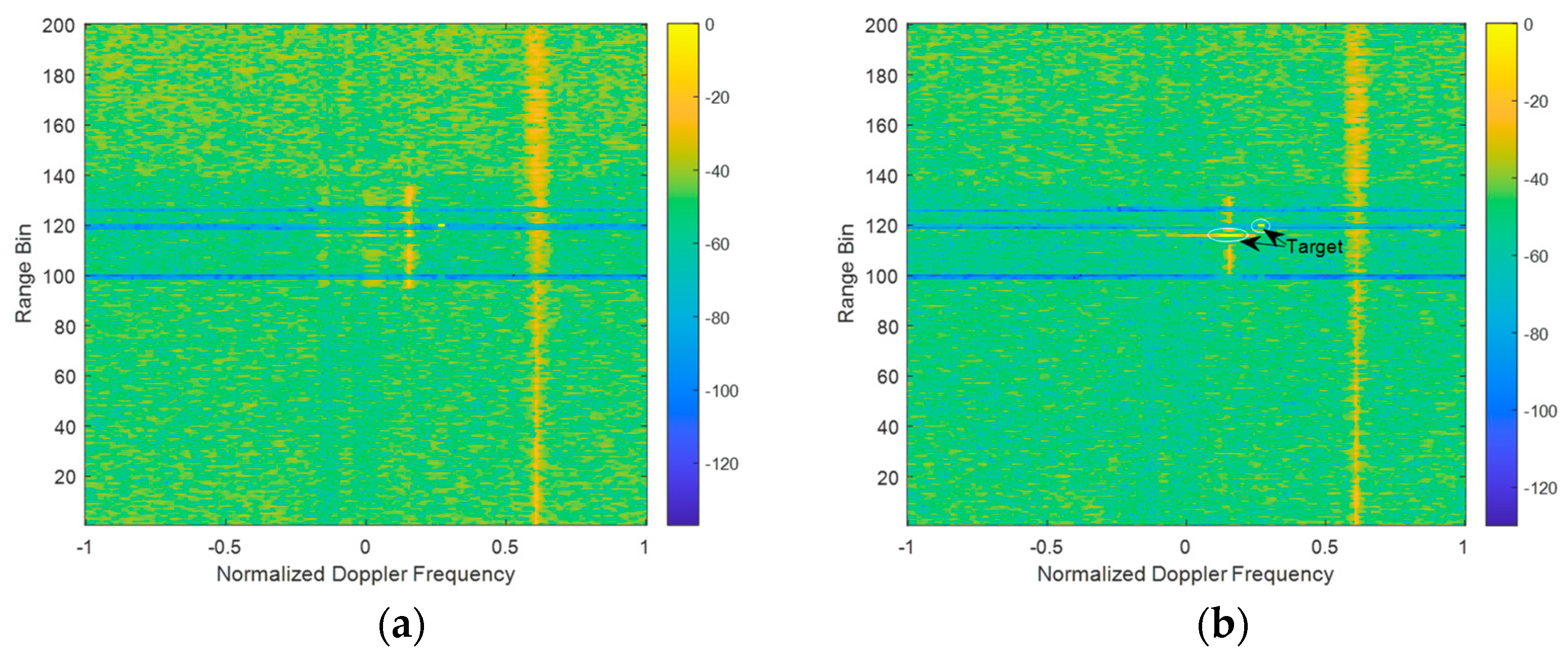
4. Simulation
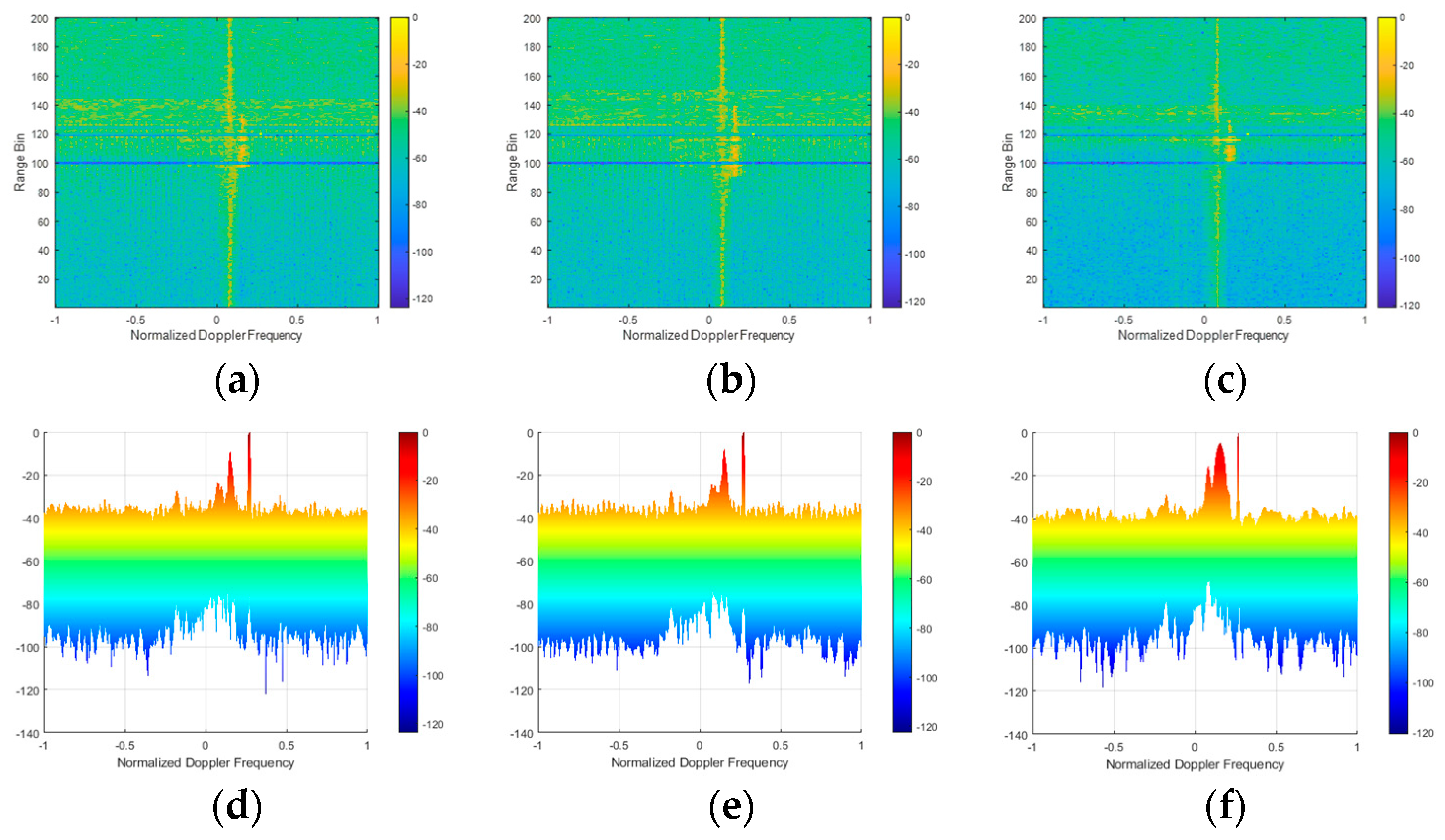
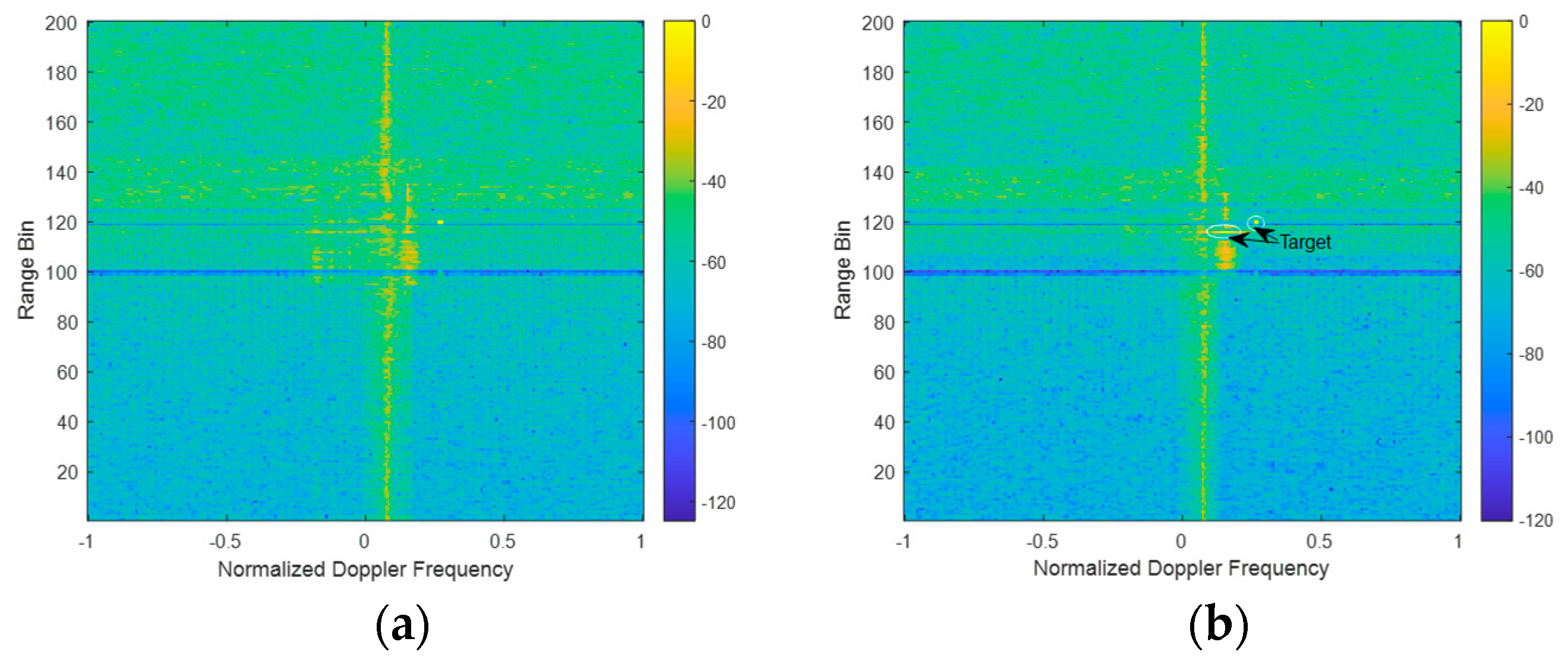
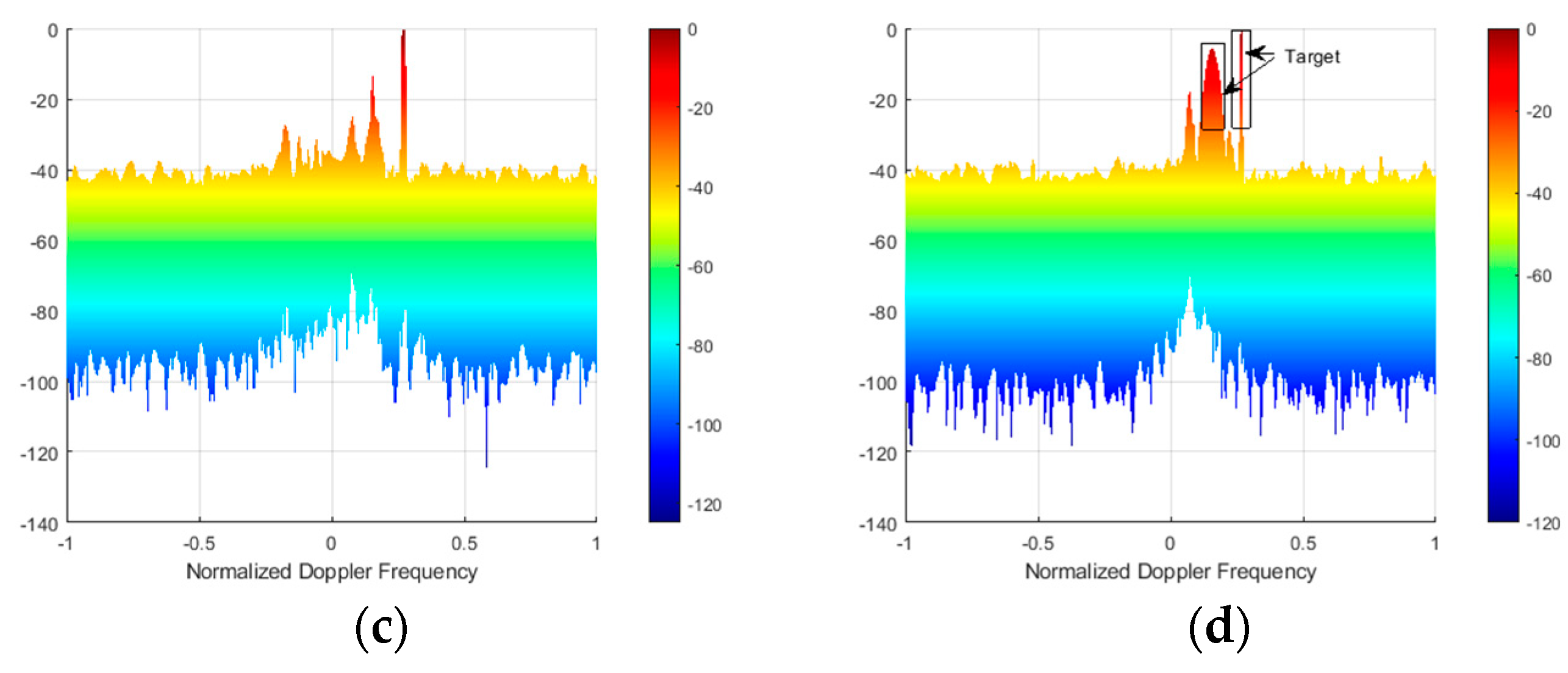
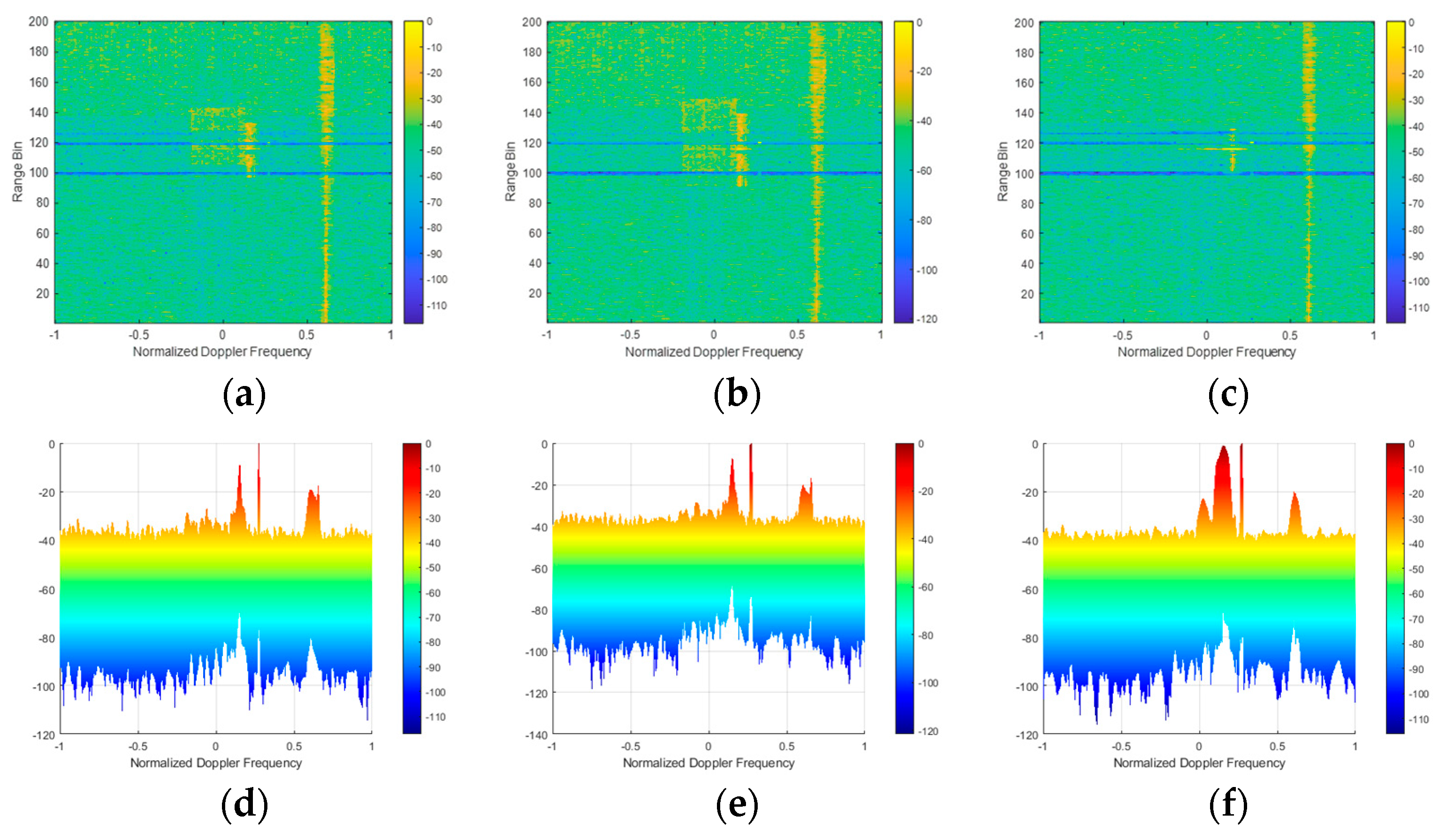
4.1. Single Wind Turbine
4.2. Multiple Wind Turbines
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nohara, T.J. Design of a Space-Based Radar Signal Processor. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1998, 34, 366–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.E.; Himed, B.; Zasada, D. Design of Large Space Based Radar for Multimode Surveillance. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE Radar Conference (Cat. No. 03CH37474), Huntsville, AL, USA, 8 May 2003; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hartnett, M.P.; Davis, M.E. Bistatic Surveillance Concept of Operations. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE Radar Conference (Cat. No. 01CH37200), Atlanta, GA, USA, 7 May 2001; pp. 75–80. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Yu, J.; Liang, G.; Sun, S.; Jiang, X.; Huang, P. Maneuvering Target Coherent Integration and Detection in PRI-Staggered Radar Systems. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 3105904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Xia, X.-G.; Wang, L.; Xu, H.; Liu, X.; Liao, G.; Jiang, X. Imaging and Relocation for Extended Ground Moving Targets in Multichannel SAR-GMTI Systems. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 3106906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, H.D. From a Different Perspective: Principles, Practice and Potential of Bistatic Radar. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Radar (IEEE Cat. No. 03EX695), Adelaide, SA, Australia, 3–5 September 2003; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, Y.; He, Z. GEO-UAV Bistatic Circular Synthetic Aperture Radar: Concepts and Technologies. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 4195–4198. [Google Scholar]
- Guttrich, G.L.; Sievers, W.E.; Tomljanovich, N.M. Wide Area Surveillance Concepts Based on Geosynchronous Illumination and Bistatic Unmanned Airborne Vehicles or Satellite Reception. In Proceedings of the 1997 IEEE National Radar Conference, Syracuse, NY, USA, 13–15 May 1997; pp. 126–131. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, F.; Zhang, Y.; Palmer, R. Wind Turbine Clutter Mitigation for Weather Radar by Adaptive Spectrum Processing. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Radar Conference, Atlanta, GA, USA, 7–11 May 2012; pp. 471–474. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, H.; Long, T. Signal-to-Noise Ratio Analysis in Satellite-Airship Bistatic Space Based Radar. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Conference on Radar, Adelaide, Australia, 2–5 September 2008; pp. 434–439. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Wu, J.; Pei, J.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y.; Yang, J. Inclined Geosynchronous Spaceborne–Airborne Bistatic SAR: Performance Analysis and Mission Design. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Cassola, M.; Baumgartner, S.V.; Krieger, G.; Moreira, A. Bistatic TerraSAR-X/F-SAR Spaceborne–Airborne SAR Experiment: Description, Data Processing, and Results. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 781–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espeter, T.; Walterscheid, I.; Klare, J.; Ender, J.H.G. Synchronization Techniques for the Bistatic Spaceborne/Airborne SAR Experiment with TerraSAR-X and PAMIR. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Barcelona, Spain, 23–28 July 2007; pp. 2160–2163. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, C.; Dong, X.; Hu, C. Performance Analysis and Configuration Design of Geosynchronous Spaceborne-Airborne Bistatic Moving Target Indication System. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2020—2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 26 September–2 October 2020; pp. 6559–6562. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, T.; Zhang, J.; Tang, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y. A Novel Iterative Inner-Pulse Integration Target Detection Method for Bistatic Radar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 3186012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ding, T.; Zhang, L. Longtime Coherent Integration Algorithm for High-Speed Maneuvering Target Detection Using Space-Based Bistatic Radar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 3038199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xing, M.; Sun, G.-C.; Zhang, S.; Xiang, J. A Novel Two-Step Scheme Based on Joint GO-DPCA and Local STAP in Image Domain for Multichannel SAR-GMTI. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 8259–8272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Sun, Z.; Huang, Y.; Yang, J.; Lv, Y.; Wang, Z. Geosynchronous Spaceborne-Airborne Bistatic SAR: Potentials and Prospects. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarCon), Arlington, VA, USA, 10–15 May 2015; pp. 1172–1176. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, T.; Hu, C.; Wu, L.; Liu, F.; Tian, W.; Zhu, M.; Long, T. Extended NLCS Algorithm of BiSAR Systems with a Squinted Transmitter and a Fixed Receiver: Theory and Experimental Confirmation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 5019–5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, Q.H. Omega-K Imaging Algorithm for One-Stationary Bistatic SAR. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2014, 50, 33–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Zou, Z.; Xia, X.-G.; Liu, X.; Liao, G.; Xin, Z. Multichannel Sea Clutter Modeling for Spaceborne Early Warning Radar and Clutter Suppression Performance Analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 8349–8366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Zou, Z.; Xia, X.-G.; Liu, X.; Liao, G. A Novel Dimension-Reduced Space–Time Adaptive Processing Algorithm for Spaceborne Multichannel Surveillance Radar Systems Based on Spatial–Temporal 2-D Sliding Window. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 3144668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ye, H.; Liu, Z.; Sun, Z.; An, H.; Wu, J.; Yang, J. Bistatic SAR Clutter-Ridge Matched STAP Method for Nonstationary Clutter Suppression. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 3125043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Duan, K. Clutter Modeling and Analysis for Bistatic Space-Based Early Warning Radar with GEO Transmitter and LEO Receiver. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Radar Conference, Sydney, Australia, 6–10 November 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, P.; Yang, H.; Xia, X.-G.; Zou, Z.; Liu, X.; Liao, G. A Novel Sea Clutter Rejection Algorithm for Spaceborne Multichannel Radar Systems. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 3204324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Yang, H.; Zou, Z.; Xia, X.-G.; Liao, G.; Zhang, Y. Range-Ambiguous Sea Clutter Suppression for Multichannel Spaceborne Radar Applications Via Alternating APC Processing. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2023, 59, 6954–6970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Tang, J.; Peng, Y. Effects of Geometry on Clutter Characteristics of Hybrid Bistatic Space Based Radar. In Proceedings of the 2006 CIE International Conference on Radar, Shanghai, China, 16–19 October 2006; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Tang, J.; Peng, Y. Clutter Modeling and Characteristics Analysis for Bistatic SBR. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Radar Conference, Waltham, MA, USA, 17–20 April 2007; pp. 513–517. [Google Scholar]
- Kan, Q.; Xu, J.; Liao, G.; Wang, K.; Xu, Y. Clutter Compensation for Space-Air Bistatic Radar Based on Unitary Subspace Transformation. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Radar Conference (RADAR), Sydney, Australia, 6–10 November 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Kan, Q.; Xu, J.; Liao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, W. Clutter Characteristics Analysis and Range-Dependence Compensation for Space-Air Bistatic Radar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 62, 5101615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Dong, X.; Chen, Z.; Hu, C.; Tian, W. A Long-Time Coherent Integration STAP for GEO Spaceborne-Airborne Bistatic SAR. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Shen, Y.; Li, W. The Seamless Model for Three-Dimensional Datum Transformation. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2012, 55, 2099–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Xue, B.; Hu, X.; Wu, G.; Zhao, W. Robust Space–Time Joint Sparse Processing Method with Airborne Active Array for Severely Inhomogeneous Clutter Suppression. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemm, R. Comparison between Monostatic and Bistatic Antenna Configurations for STAP. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2000, 36, 596–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, T.; Liu, C.; Ren, B. A Fast IAA–Based SR–STAP Method for Airborne Radar. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, I.S.; Mallett, J.D.; Brennan, L.E. Rapid Convergence Rate in Adaptive Arrays. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1974, AES-10, 853–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liao, G.; Zeng, C.; Tao, H.; Xu, J.; Zhu, S.; Juwono, F.H. Reweighted Extreme Learning Machine-Based Clutter Suppression and Range Compensation Algorithm for Non-Side-Looking Airborne Radar. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, N.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, S.; Du, Q.; Wang, Y. A Novel Non-Stationary Clutter Suppression Approach for Space-Based Early Warning Radar Using an Interpulse Multi-Frequency Mode. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, W.; Zhang, T.; Xing, M.; Wang, Y. Improved Dimension-Reduced Structures of 3D-STAP on Nonstationary Clutter Suppression for Space-Based Early Warning Radar. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, Z.; Xing, M.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y. Research on Multi-Domain Dimensionality Reduction Joint Adaptive Processing Method for Range Ambiguous Clutter of FDA-Phase-MIMO Space-Based Early Warning Radar. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Zhai, Q.; Wang, X.; Wu, R. Wind Turbine Clutter Detection and Mitigation in Scanning ATC Surveillance Radar. Acta Aeronaut. Et Astronaut. Sin. 2016, 37, 1316–1326. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Li, G.; Zhang, Y.D. Micro-Doppler Interference Removal via Histogram Analysis in Time-Frequency Domain. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2016, 52, 755–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, L.; Brown, A. Partial Treatment of Wind Turbine Blades with Radar Absorbing Materials (RAM) for RCS Reduction. In Proceedings of the Fourth European Conference on Antennas and Propagation, Barcelona, Spain, 12–16 April 2010; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Karabayir, O.; Unal, M.; Coskun, A.F.; Yucedag, S.M.; Saynak, U.; Bati, B.; Biyik, M.; Bati, O.; Serim, H.A.; Kent, S. CLEAN Based Wind Turbine Clutter Mitigation Approach for Pulse-Doppler Radars. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarCon), Arlington, VA, USA, 10–15 May 2015; pp. 1541–1544. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, R.B.; Mao, J.; Wang, X.L.; Jia, Q.Q. Target Detection of Primary Surveillance Radar in Wind Farm Clutter. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2013, 35, 754–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal, F.; Pillai, U.; Selesnick, I.; Himed, B. Signal Decomposition for Wind Turbine Clutter Mitigation. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Radar Conference, Cincinnati, OH, USA, 19–23 May 2014; pp. 0060–0063. [Google Scholar]
- Naqvi, A.; Ling, H. Signal Filtering Technique to Remove Doppler Clutter Caused by Wind Turbines. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2012, 54, 1455–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Tan, X.; Qu, Z.; Luo, Y.; Chi, P. Wind Turbine Clutter Suppression Method Based on Dynamic Reconstruction. Acta Aeronaut. Et Astronaut. Sin. 2020, 41, 323269. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.; Rao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, F. Wind Turbine Clutter Suppression Method Based on Reference Signal Correction for Passive Radar. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2023, 45, 2446–2454. [Google Scholar]
- Zulch, P.; Davis, M.; Adzima, L.; Hancock, R.; Theis, S. The Earth Rotation Effect on a LEO L-Band GMTI SBR and Mitigation Strategies. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE Radar Conference (IEEE Cat. No. 04CH37509), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 29 April 2004; pp. 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Pillai, S.U.; Li, K.Y.; Himed, B. Space Based Radar: Theory & Applications; McGraw-Hill Professional Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 77–137. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, J. Robust STAP Approach in Nonhomogeneous Clutter Environments. In Proceedings of the 2001 CIE International Conference on Radar Proceedings (Cat No. 01TH8559), Beijing, China, 15–18 October 2001; pp. 753–757. [Google Scholar]
- Ankerst, M.; Breunig, M.M.; Kriegel, H.-P.; Sander, J. OPTICS: Ordering Points to Identify the Clustering Structure. SIGMOD Rec. 1999, 28, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
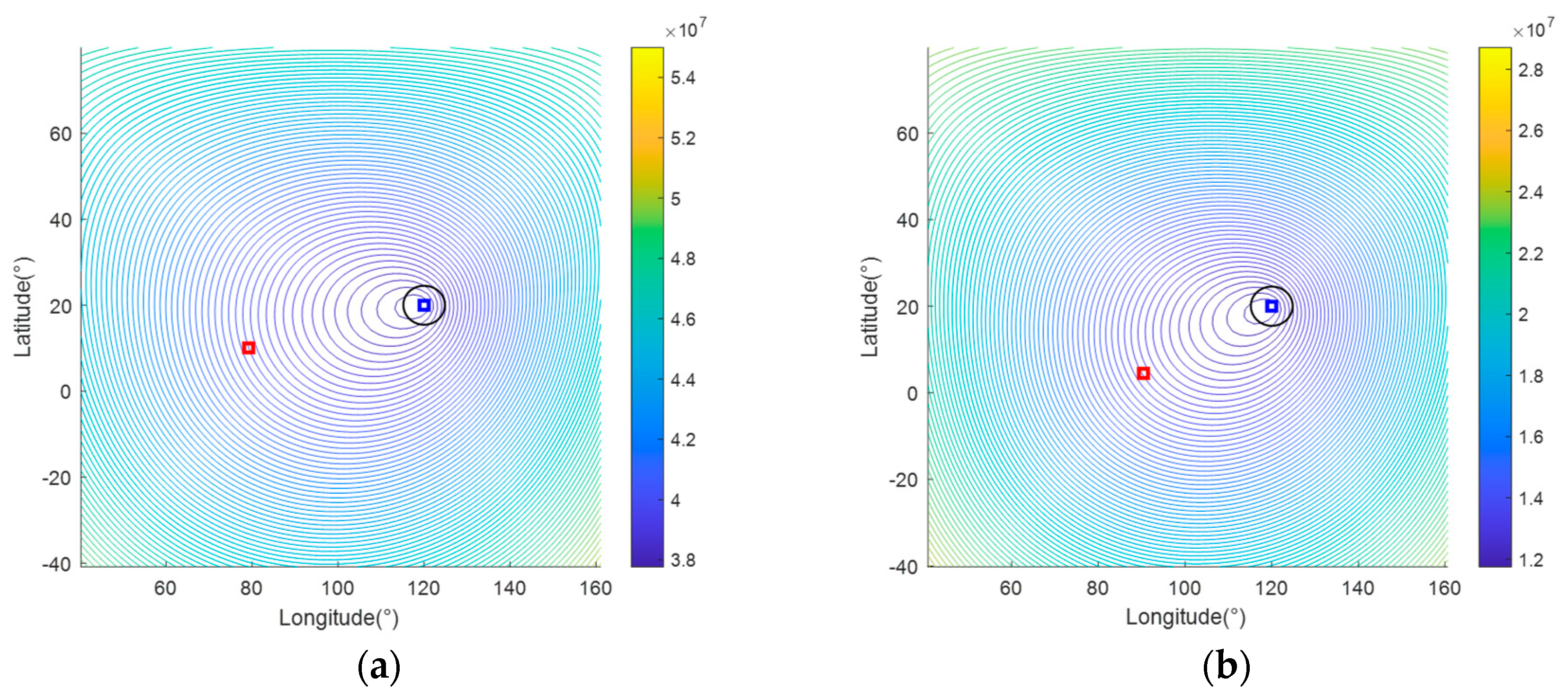
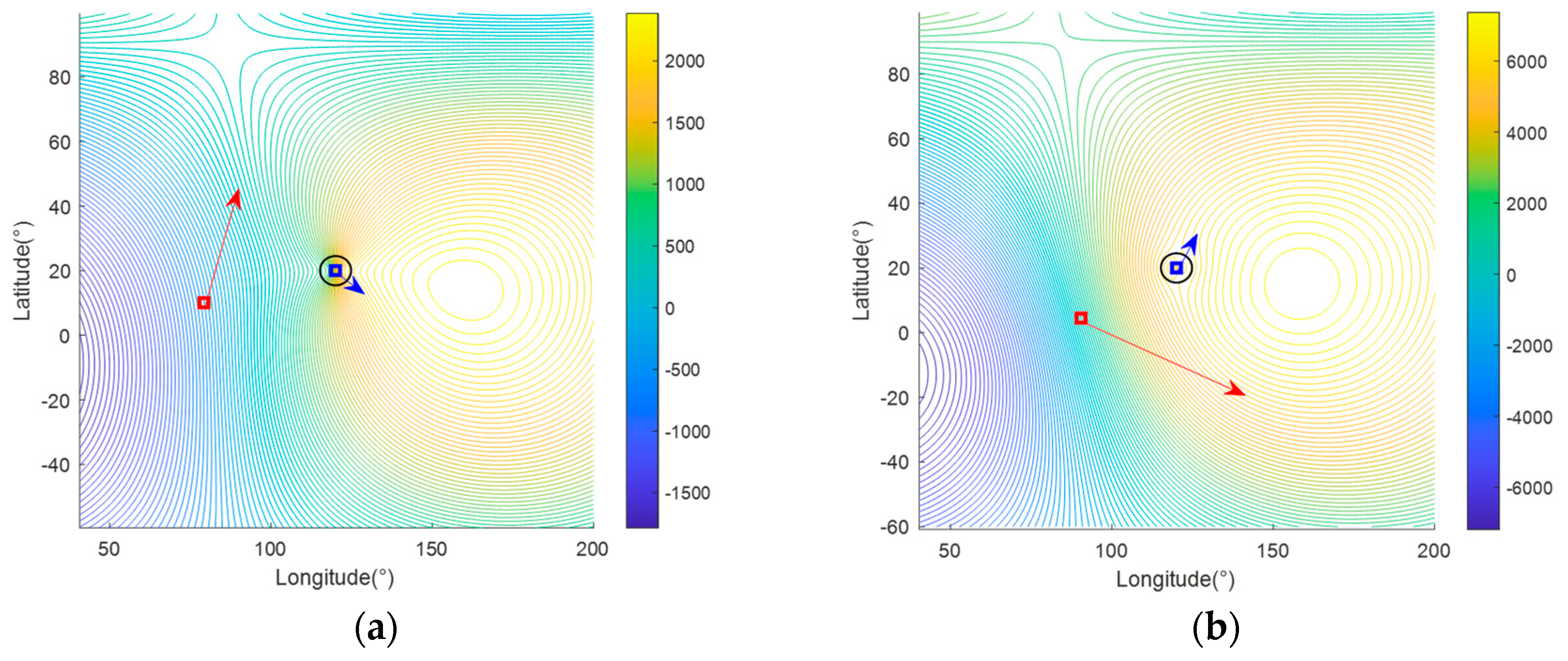
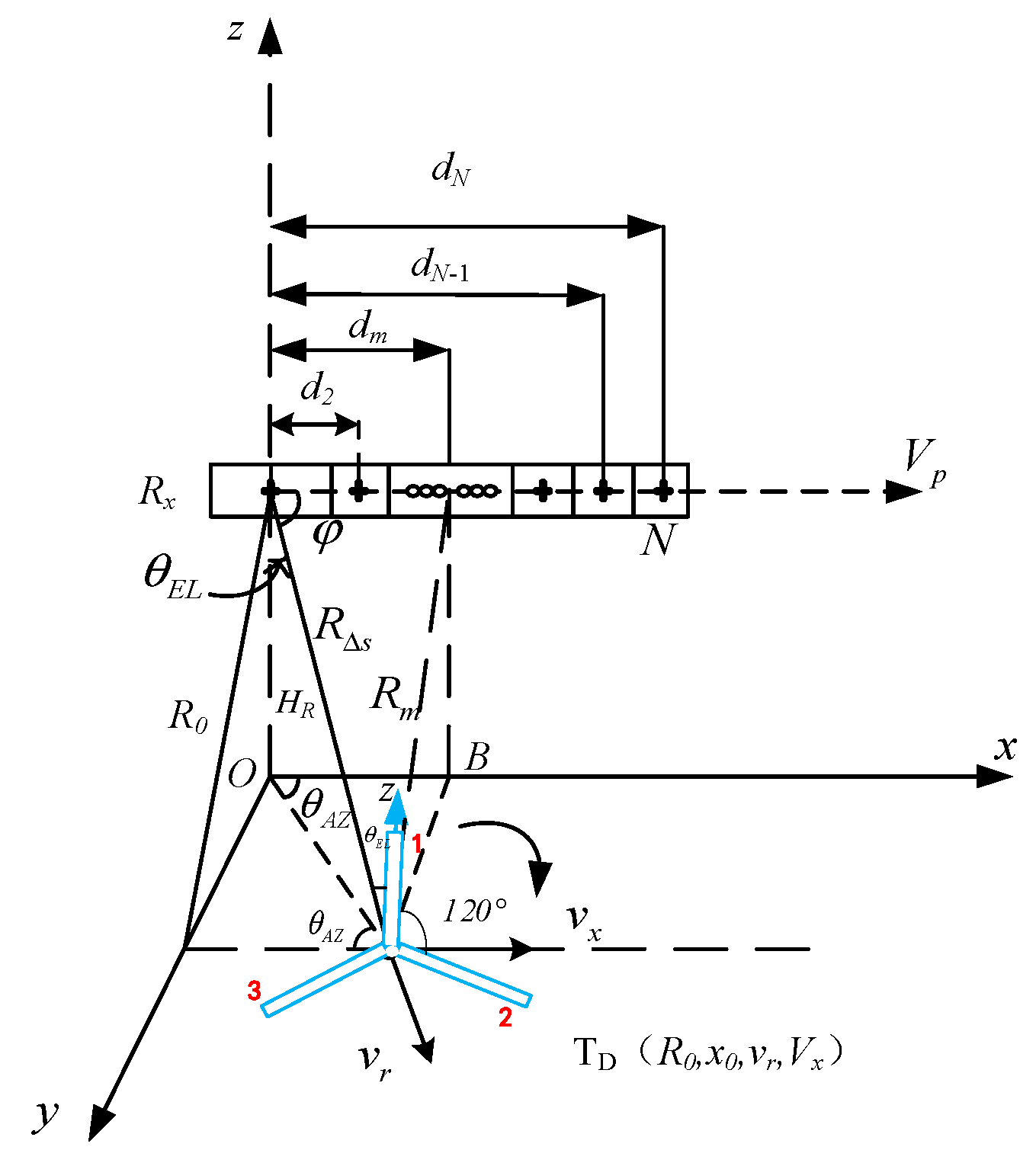
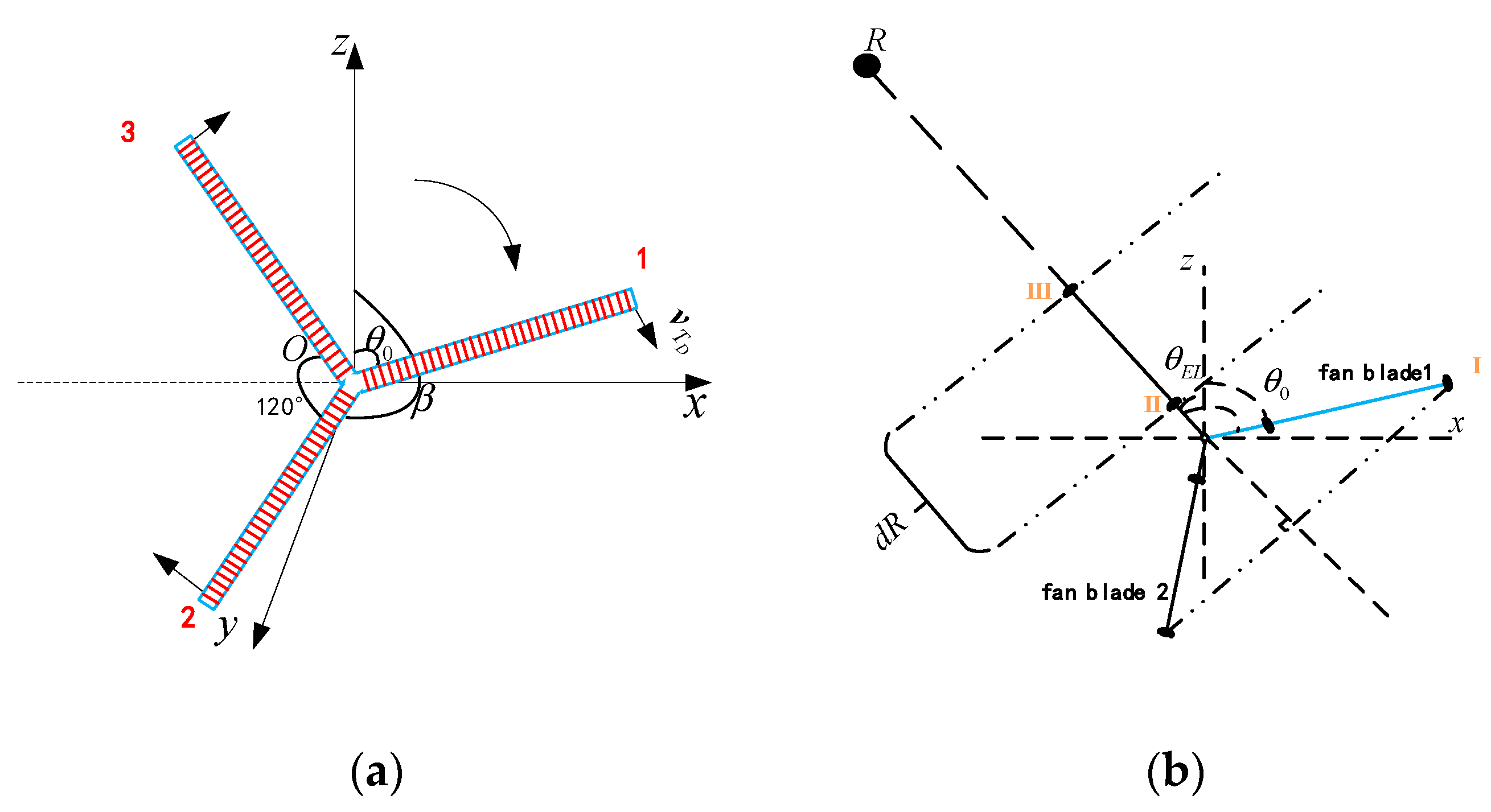




| Type | Parameters | Values and Units | |
|---|---|---|---|
| GEO satellite | MEO satellite | ||
| Transmitter | Altitude | 35,784 km | 10,000 km |
| Velocity | 3.07 km/s | 4.93 km/s | |
| Longitude and latitude | (79.21°E,10.08°N) | (90.4°E, 4.47°N) | |
| Orbit inclination | 15.31° | ||
| Receiver | Altitude | 20 km | |
| Velocity | 125 m/s | ||
| Longitude and latitude | (120°E, 20°N) | ||
| Parameters | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Number of column channels | N | 16 (subarray synthesis) |
| Number of row channels | M | 14 |
| Carrier frequency | fc | 1.25 GHz |
| Channel spacing | d | 0.24 m |
| Pulse repetition frequency | fr | 2 kHz |
| Number of pulses in a CPI | K | 64 |
| Range ring width | dR | 60 m |
| Clutter-to-noise ratio | CNR | 45 dB |
| Doppler Dimension and Azimuth Dimension Channels | Select Method |
|---|---|
| 3-3 | 1 |
| 3-5 | 2 |
| 3-7 | 3 |
| 5-3 | 4 |
| 5-5 | 5 |
| 7-3 | 6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Zhang, S.; Qiao, N.; Wang, Y.; Du, Q. Modelling and Mitigating Wind Turbine Clutter in Space–Air Bistatic Radar. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2674. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16142674
Zhang S, Zhang S, Qiao N, Wang Y, Du Q. Modelling and Mitigating Wind Turbine Clutter in Space–Air Bistatic Radar. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(14):2674. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16142674
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shuo, Shuangxi Zhang, Ning Qiao, Yongliang Wang, and Qinglei Du. 2024. "Modelling and Mitigating Wind Turbine Clutter in Space–Air Bistatic Radar" Remote Sensing 16, no. 14: 2674. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16142674
APA StyleZhang, S., Zhang, S., Qiao, N., Wang, Y., & Du, Q. (2024). Modelling and Mitigating Wind Turbine Clutter in Space–Air Bistatic Radar. Remote Sensing, 16(14), 2674. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16142674






