Lake and Atmospheric Heatwaves Caused by Extreme Dust Intrusion in Freshwater Lake Kinneret in the Eastern Mediterranean
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
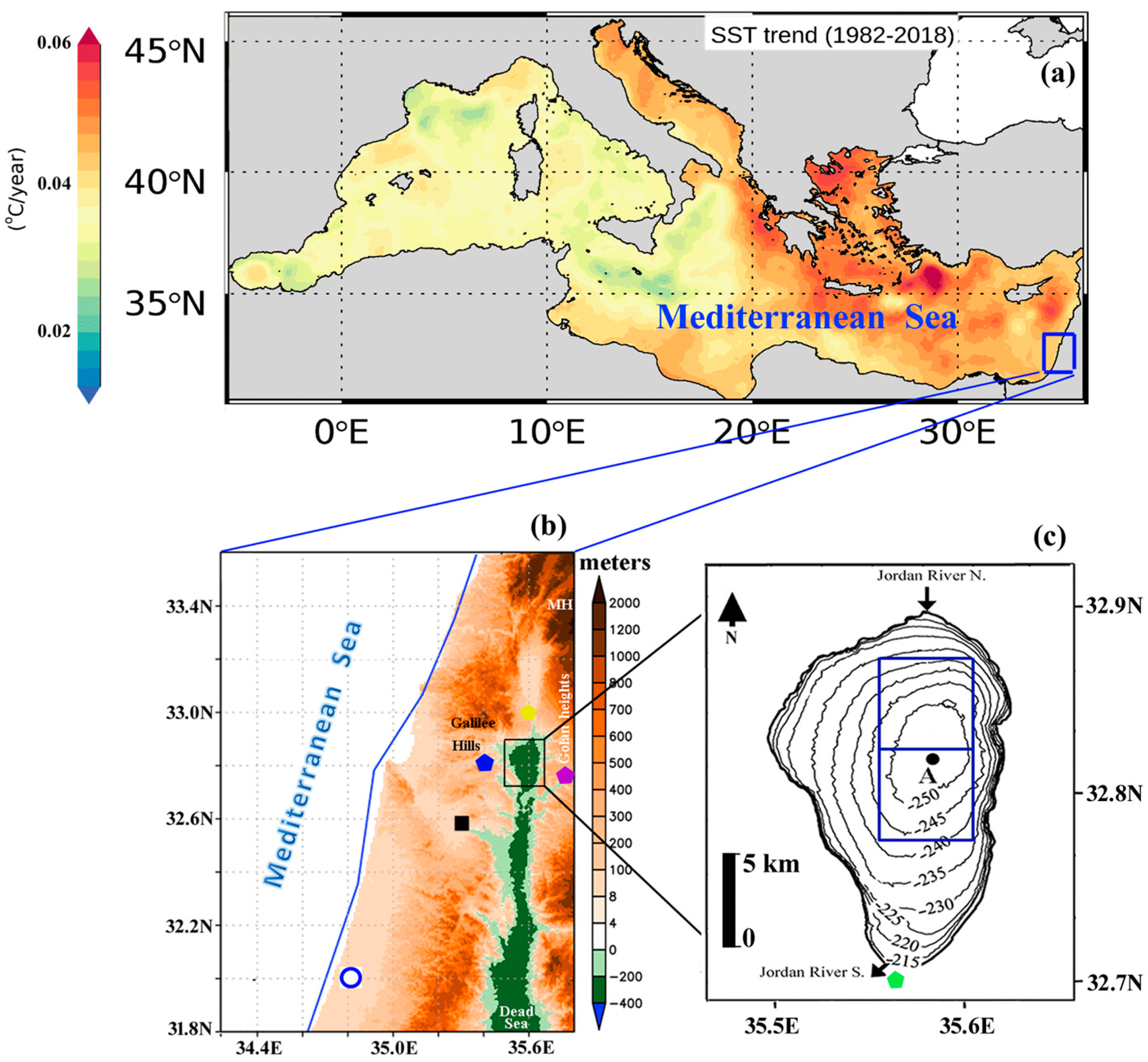
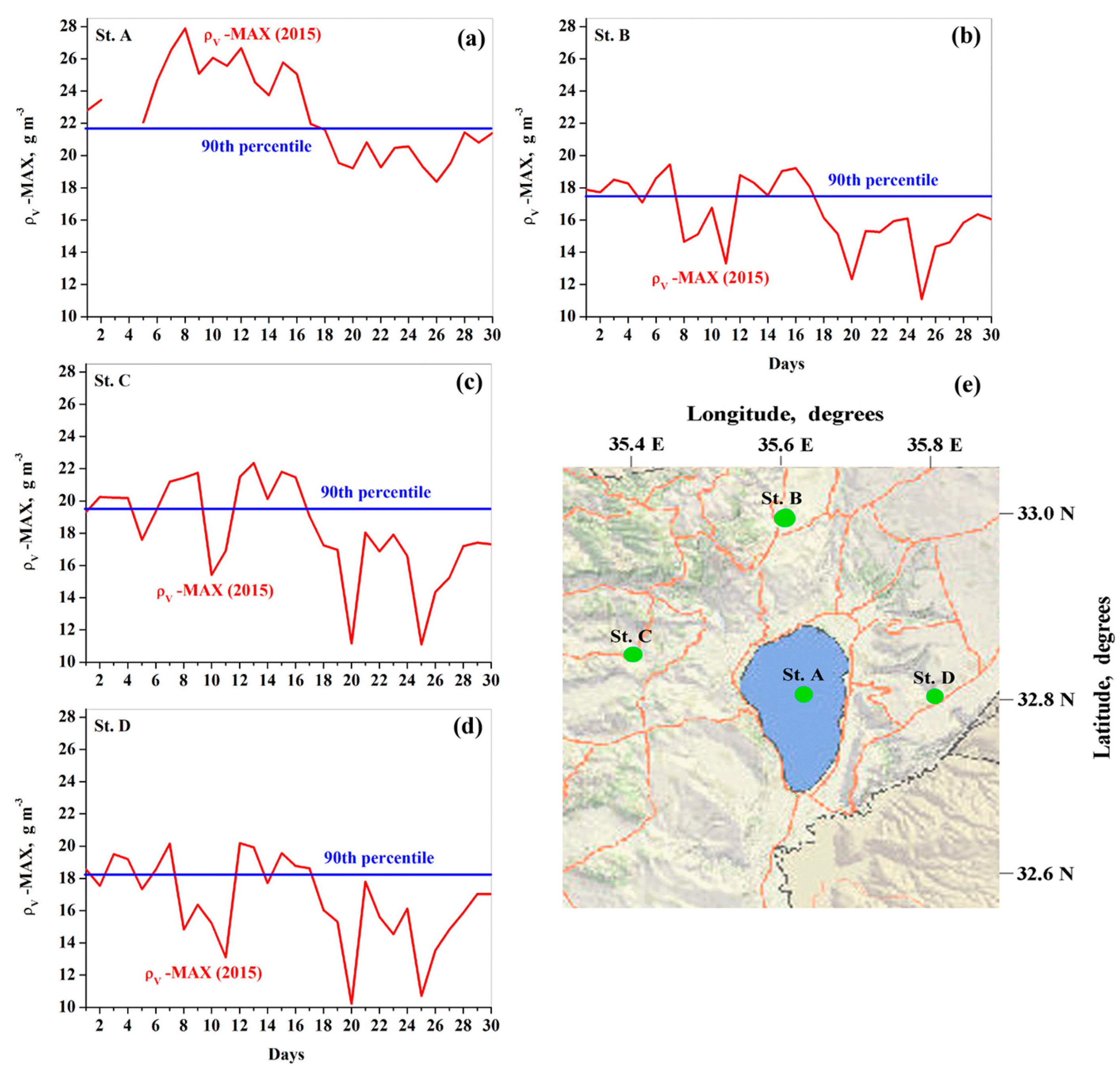
2.1. Study Area
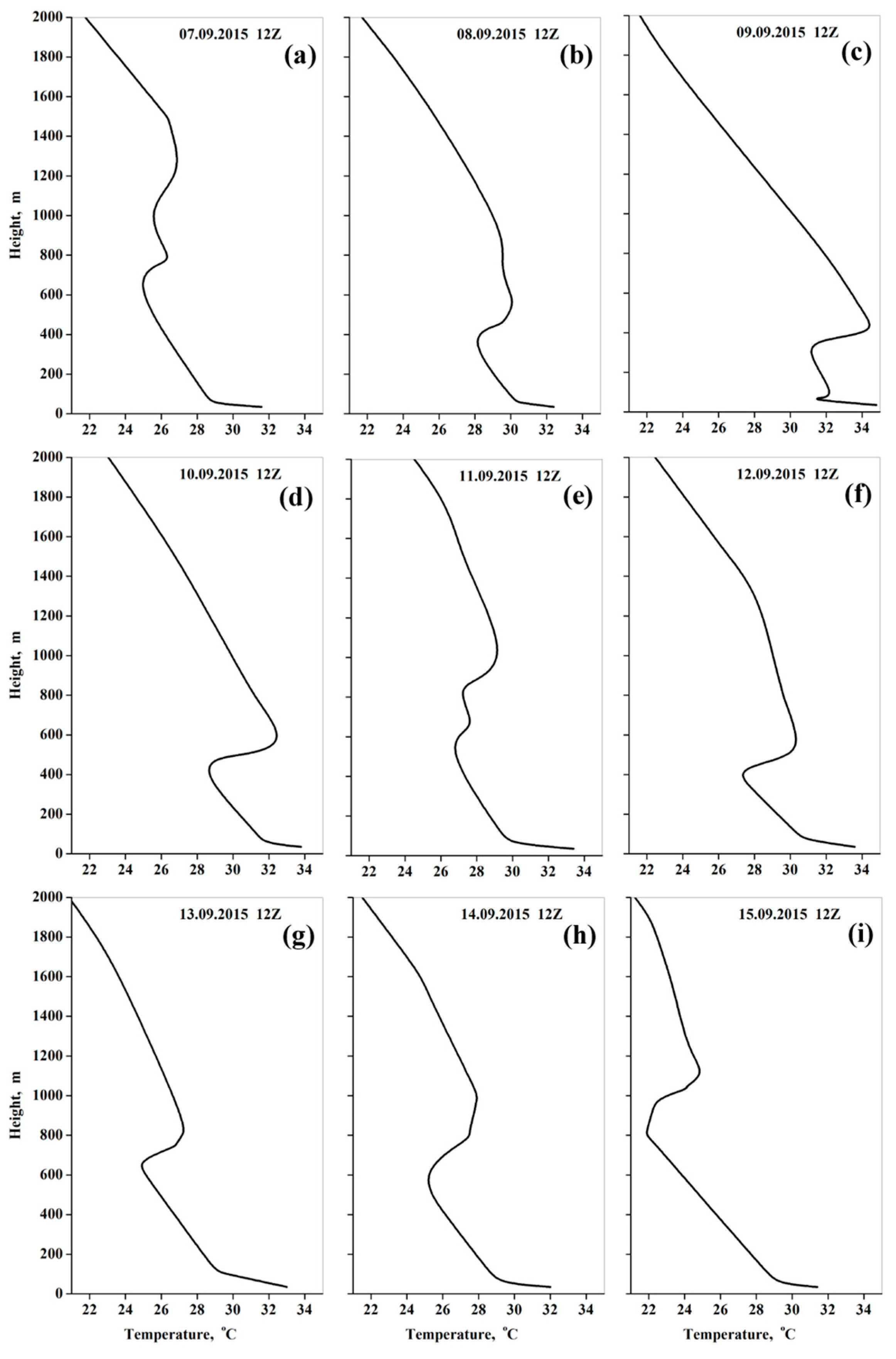
2.2. September 2015 Extreme Dust Event in the Study Area
2.3. Method
2.4. Data
3. Results
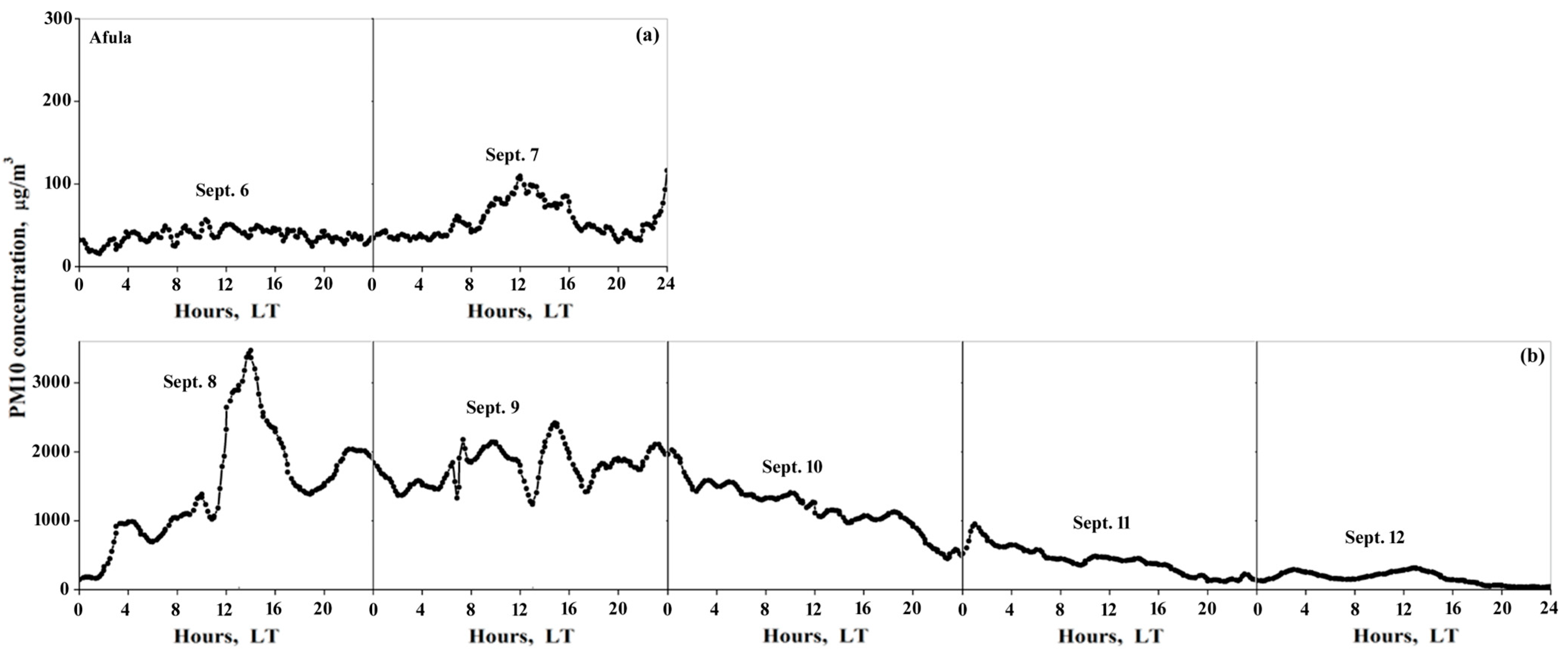
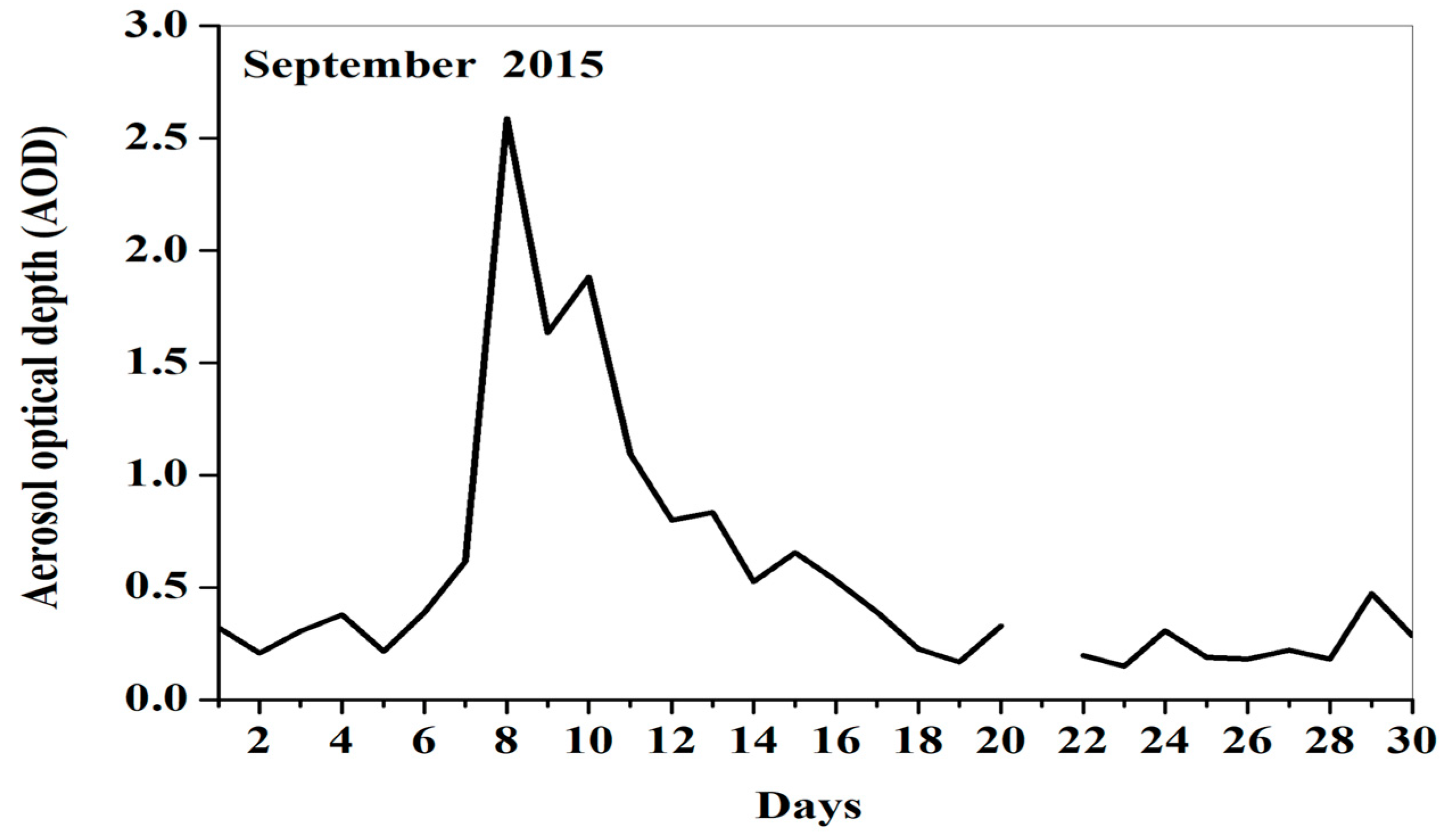
3.1. PM10 and AOD Day-to-Day Variations
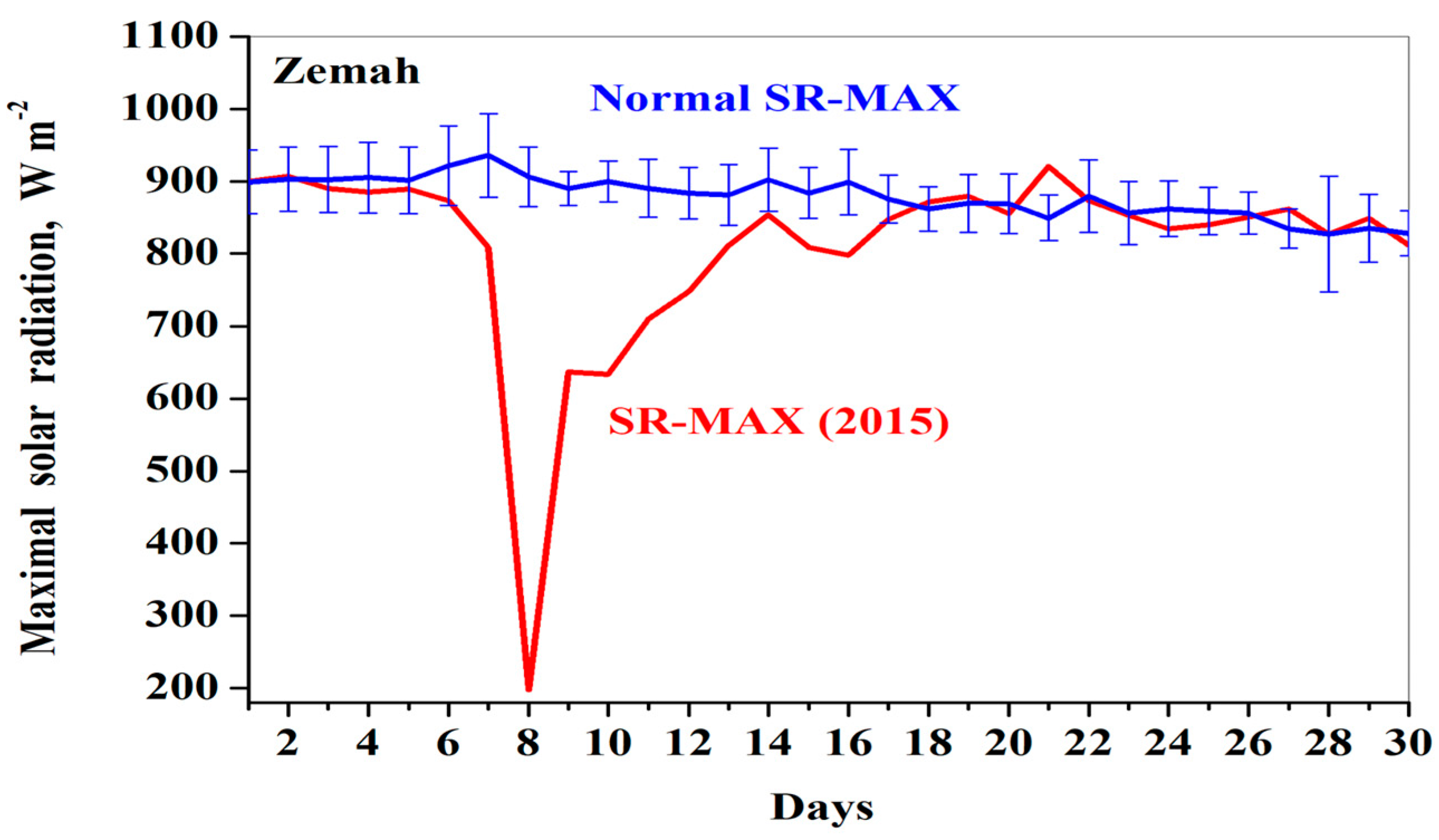
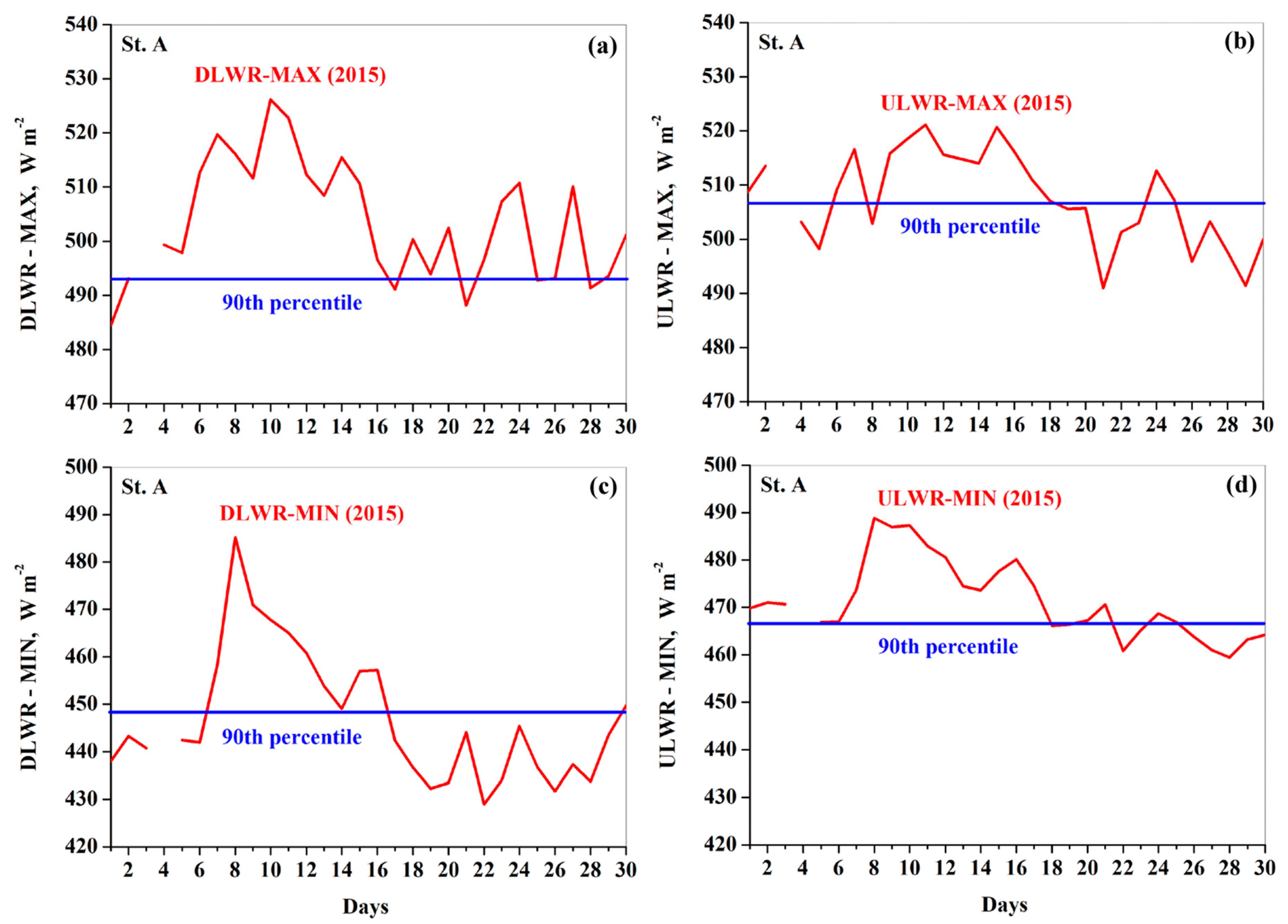
3.2. Day-to-Day Variations in Solar and Thermal Radiation
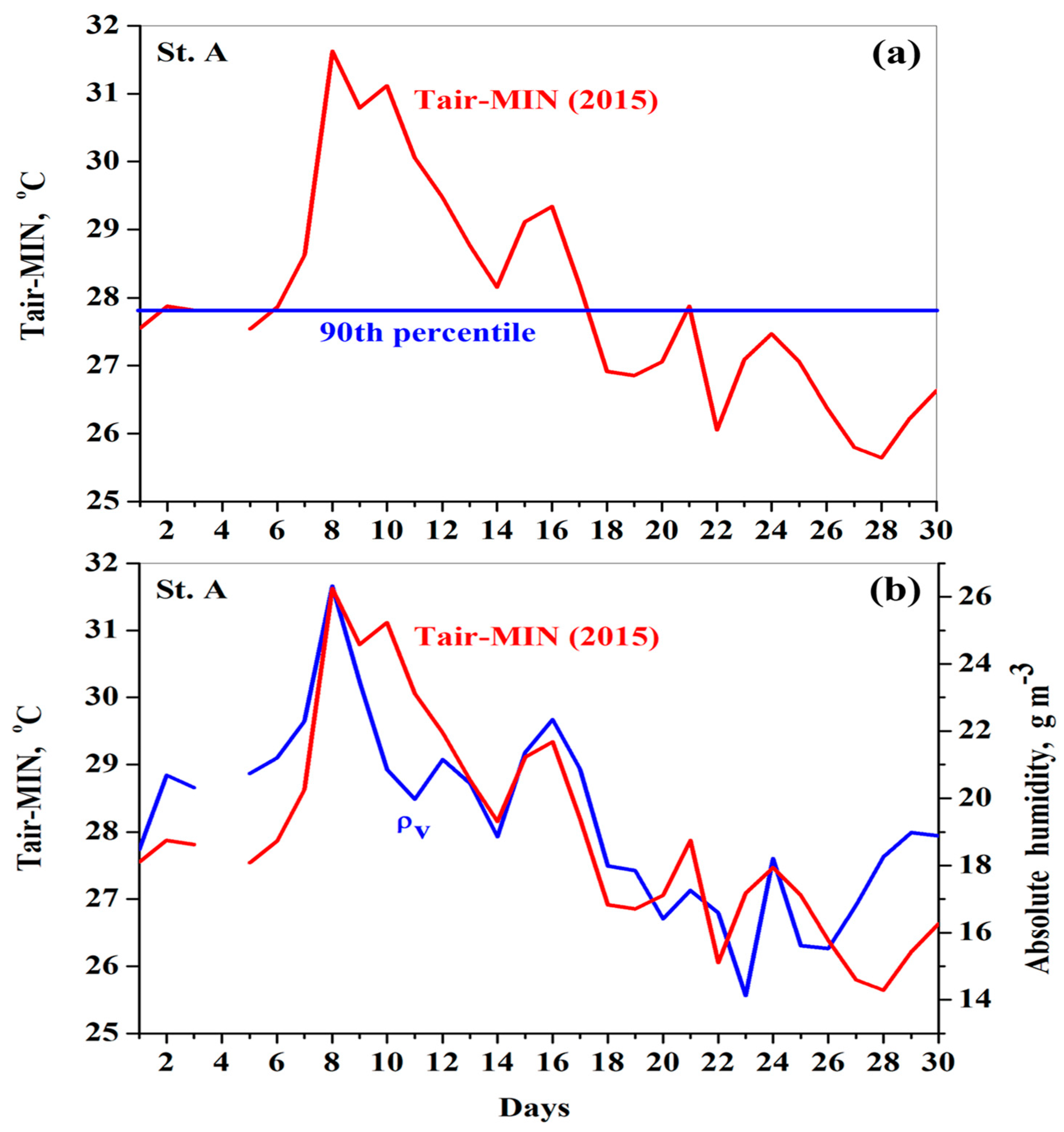
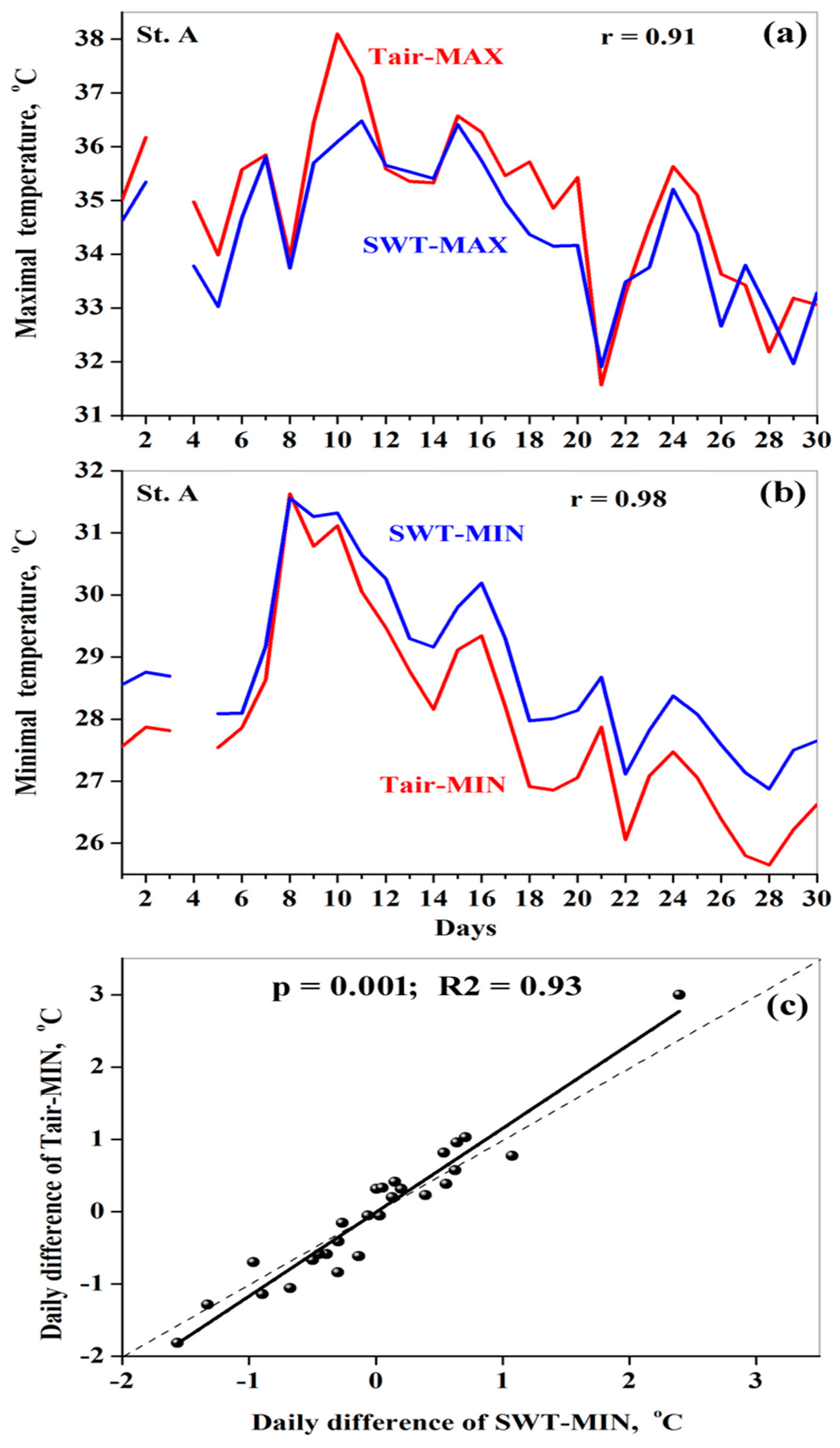
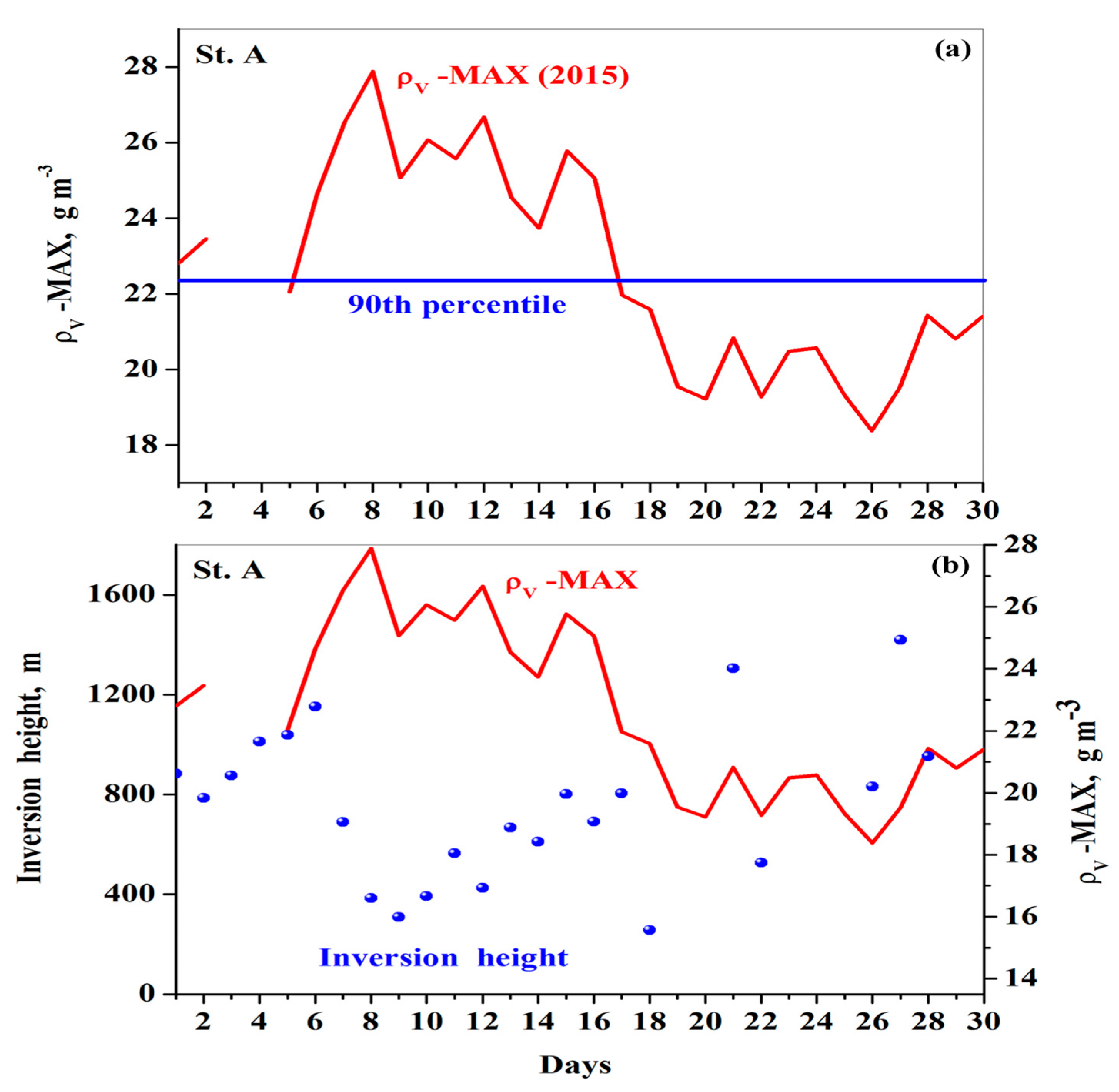
3.3. Atmospheric Heatwave
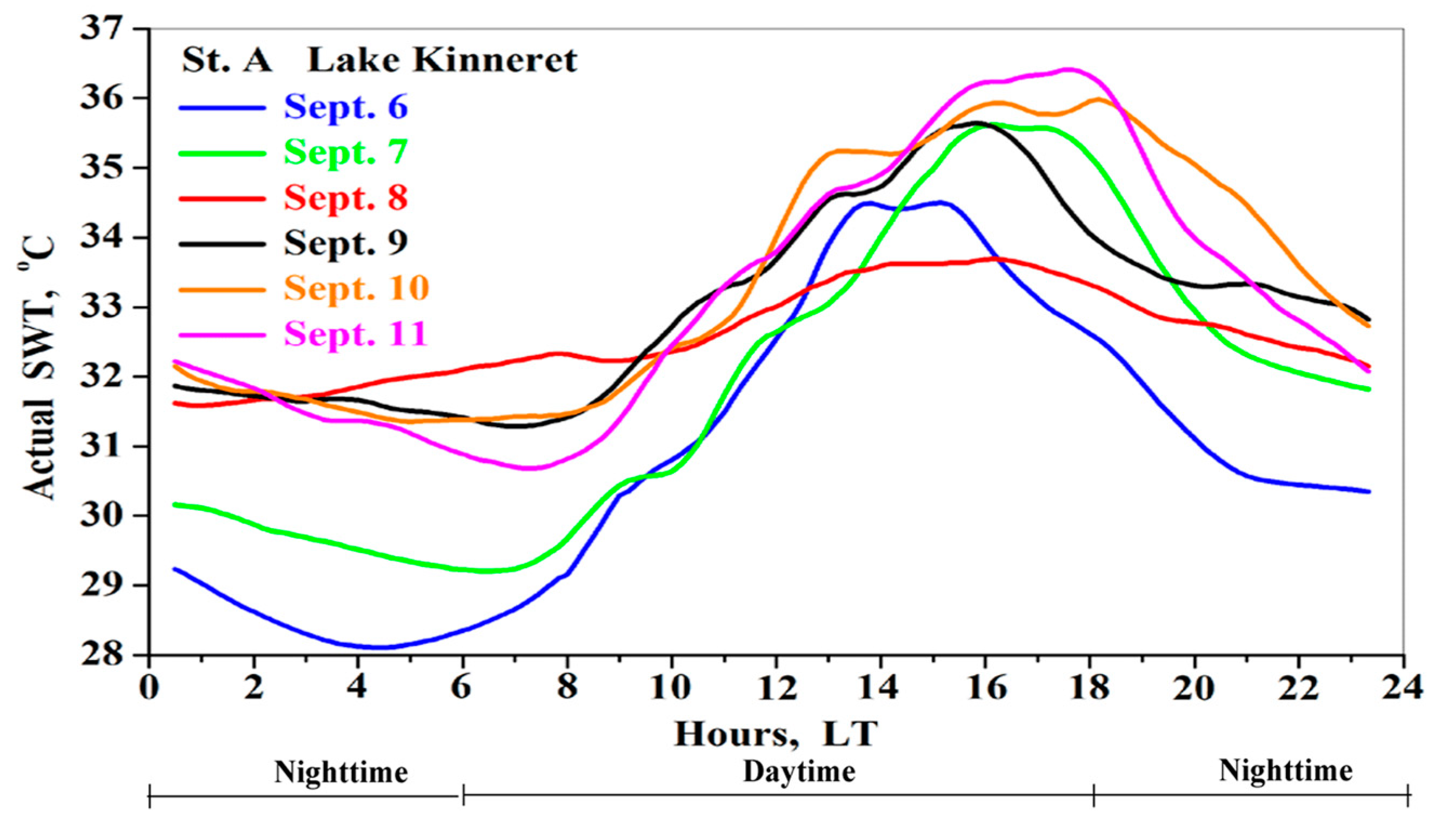
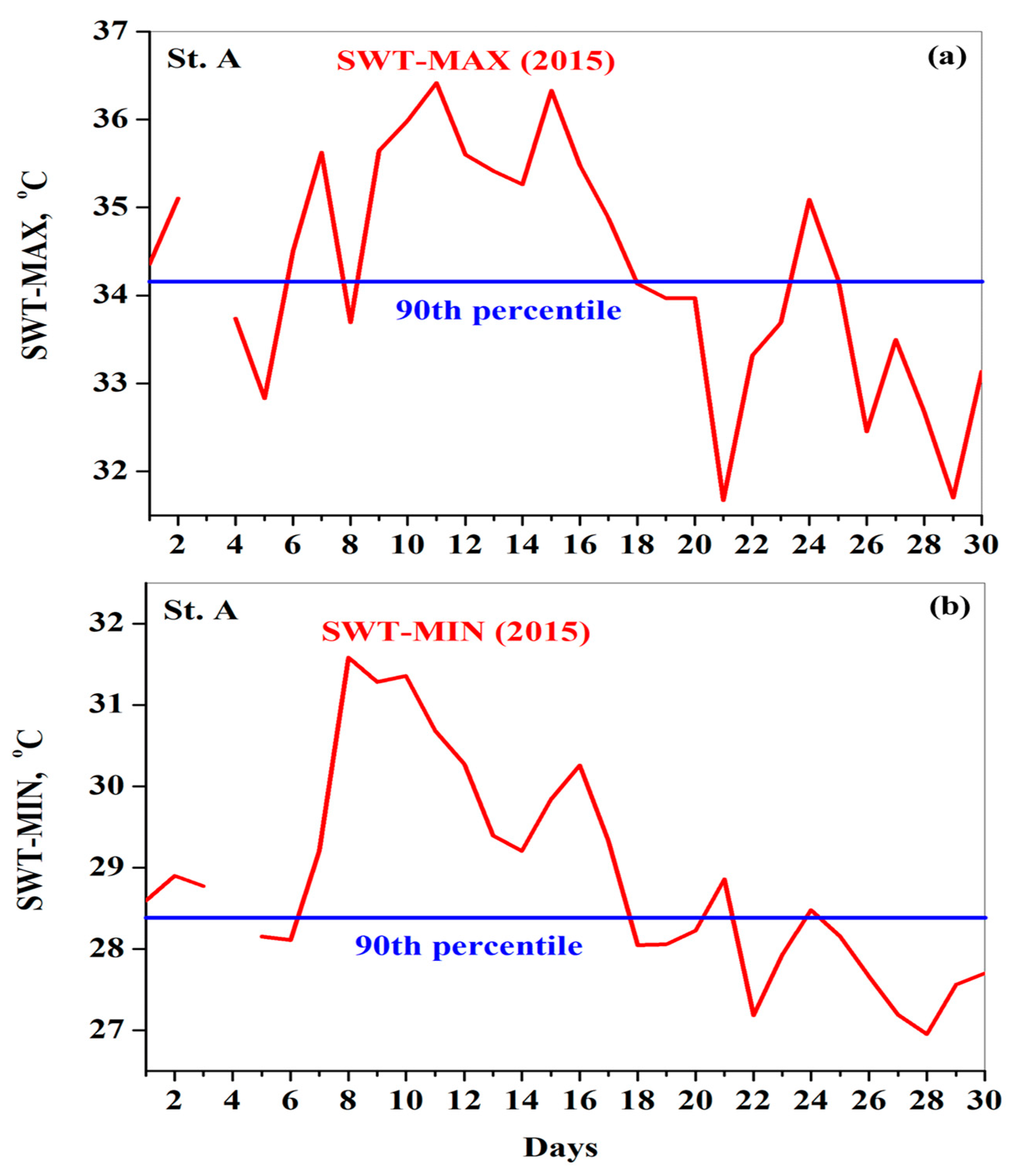
3.4. Lake Heatwave
3.4.1. In Situ SWT
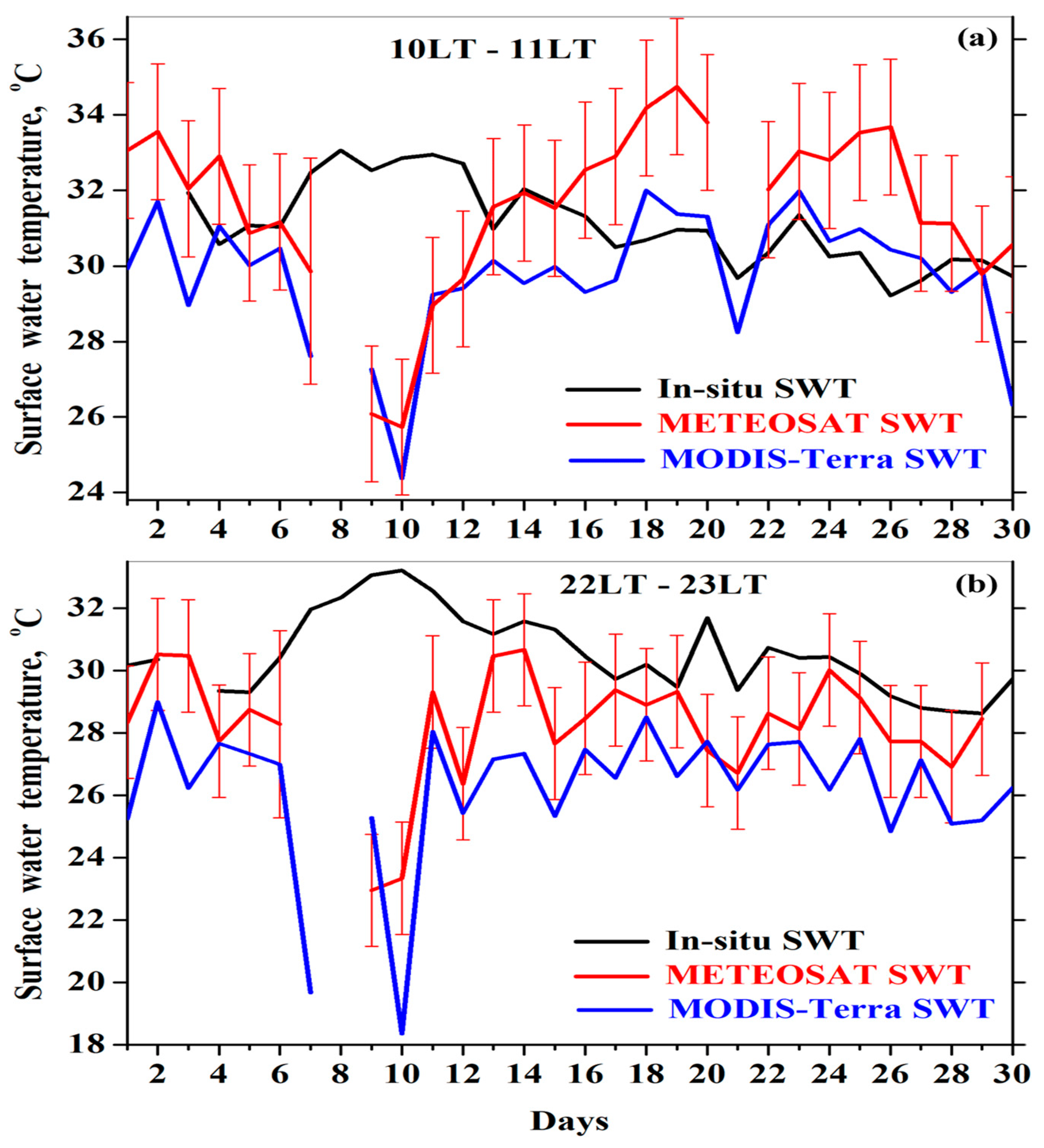
3.4.2. Satellite-Based SWT
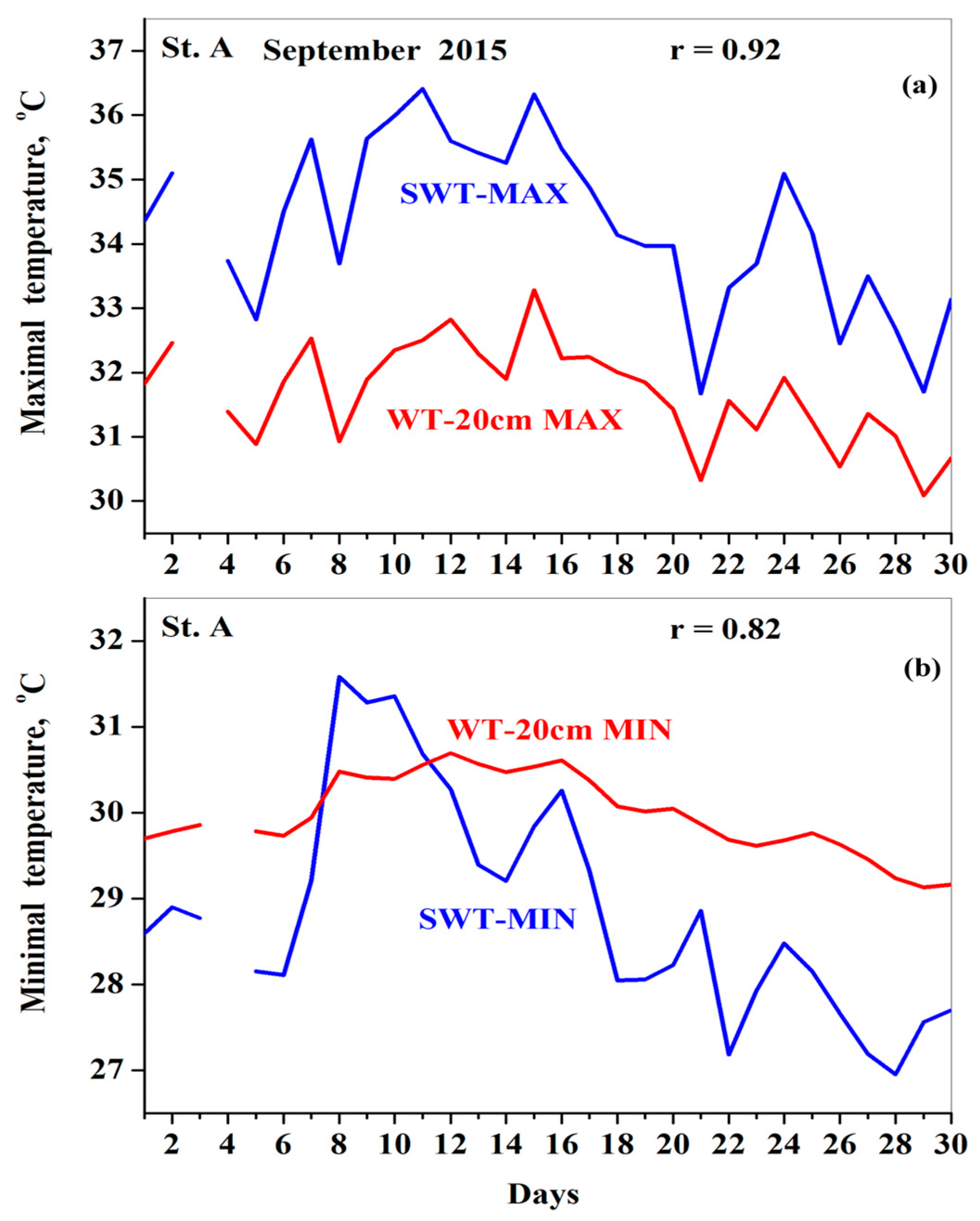
3.5. Subsurface LHW
3.6. Day-to-Day Variations in Absolute Humidity
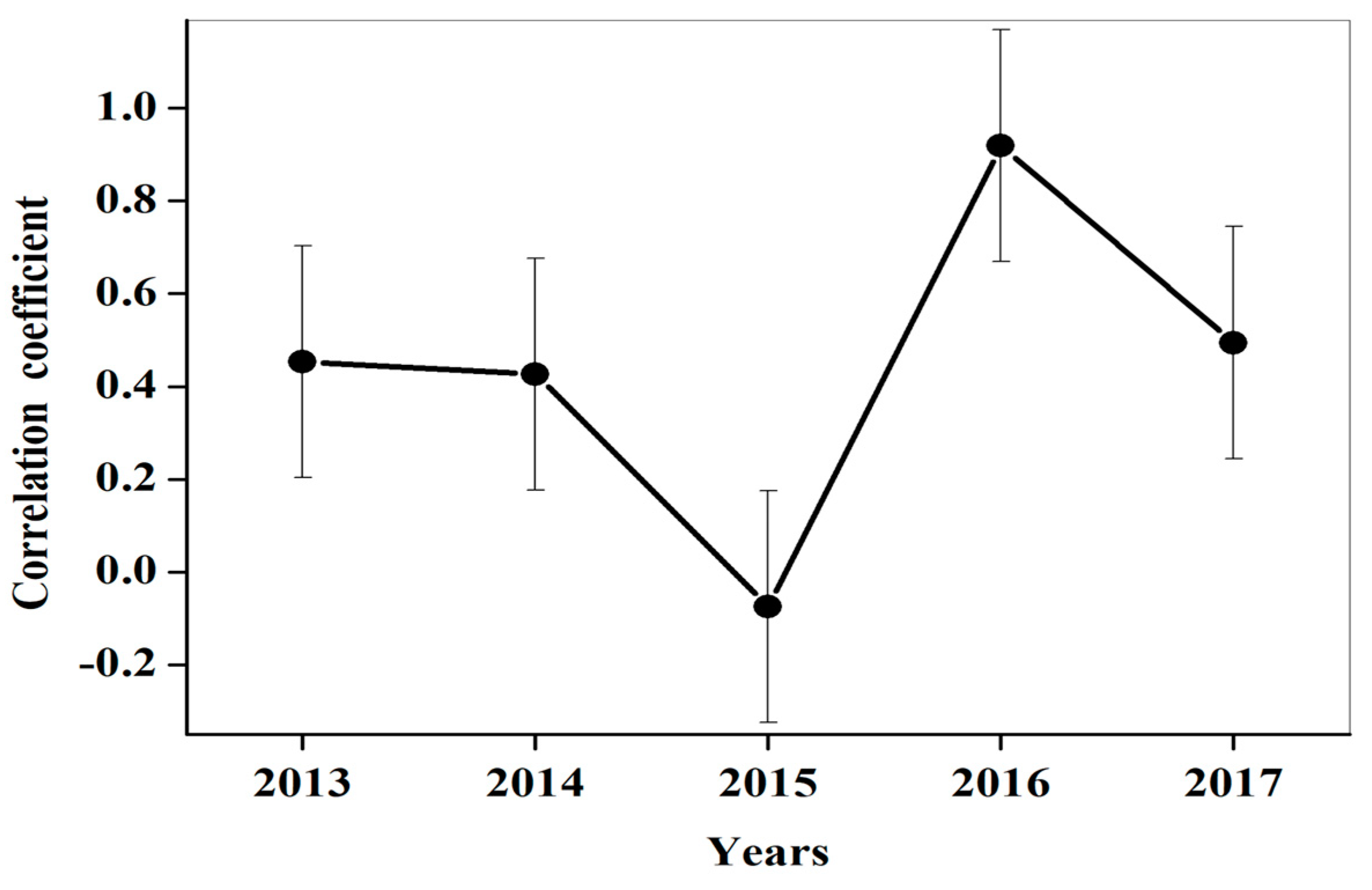
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A


References
- Zittis, G.; Almazroui, M.; Alpert, P.; Ciais, P.; Cramer, W.; Dahdal, Y.; Fnais, M.; Francis, D.; Hadjinicolaou, P.; Howari, F.; et al. Climate change and weather extremes in the Eastern Mediterranean and Middle East. Rev. Geophys. 2022, 60, e2021RG000762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochman, A.; Marra, F.; Messori, G.; Pinto, J.G.; Raveh-Rubin, S.; Yosef, Y.; Zittis, G. Extreme weather and societal impacts in the eastern Mediterranean. Earth Syst. Dyn. 2022, 13, 749–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsikerdekis, A.; Zanis, P.; Georgoulias, A.K.; Alexandri, G.; Katragkou, E.; Karacostas, T.; Solmon, F. Direct and semi-direct radiative effect of North African dust in present and future regional climate simulations. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 53, 4311–4336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, A.; Wu, R.; Lelieveld, J.; Yousefi, R.; Aldabash, M. Winter AOD trend changes over the Eastern Mediterranean and Middle East region. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 5516–5535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Kalashnikova, O.V.; Garay, M.J.; Lee, H.; Notaro, M. Identification and characterization of dust source regions across North Africa and the Middle East using MISR satellite observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 6690–6701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelieveld, J.; Hadjinicolaou, P.; Kostopoulou, E.; Chenoweth, J.; El Maayar, M.; Giannakopoulos, C.; Hannides, C.; Lange, M.A.; Tanarhte, M.; Tyrlis, E.; et al. Climate change and impacts in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Middle East. Clim. Chang. 2012, 114, 667–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuels, R.; Hochman, A.; Baharad, A.; Givati, A.; Levi, Y.; Yosef, Y.; Saaroni, H.; Ziv, B.; Harpaz, H.; Alpert, P. Evaluation and projection of extreme precipitation indices in the eastern Mediterranean based on CMIP5 multi-model ensemble. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 2280–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisano, A.; Marullo, S.; Artale, V.; Falcini, F.; Yang, C.; Leonelli, F.E.; Santoleri, R.; Buongiorno Nardelli, B. New Evidence of Mediterranean Climate Change and Variability from Sea Surface Temperature Observations. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmaraki, S.; Somot, S.; Sevault, F.; Nabat, P. Past variability of Mediterranean Sea marine heatwaves. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 9813–9823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayan, H.; McAdam, R.; Juza, M.; Masina, S.; Speich, S. Marine heat waves in the Mediterranean Sea: An assessment from the surface to the subsurface to meet national needs. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1045138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobday, A.J.; Alexander, L.V.; Perkins, S.E.; Smale, D.A.; Straub, S.C.; Oliver, E.C.J.; Benthuysen, J.A.; Burrows, M.T.; Donat, M.G.; Peng, M.; et al. A hierarchical approach to defining marine heatwaves. Prog. Oceanogr. 2016, 141, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holbrook, N.J.; Sen Gupta, A.; Oliver, E.; Hobday, A.; Benthuysen, J.; Scannell, H.; Smal, D.; Wernberg, T. Keeping pace with marine heatwaves. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 482–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marullo, S.; Serva, F.; Iacono, R.; Napolitano, E.; di Sarra, A.; Meloni, D.; Monteleone, F.; Sferlazzo, D.; De Silvestri, L.; de Toma, V.; et al. Record-breaking persistence of the 2022/23 marine heatwave in the Mediterranean Sea. Environ. Res. Lett. 2023, 18, 114041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolway, I.; Jennings, E.; Shatwell, T.; Golub, M.; Pierson, D.C.; Maberly, S.C. Lake heatwaves under climate change. Nature 2021, 589, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolway, I.; Anderson, E.; Albergel, C. Rapidly expanding lake heatwaves under climate change. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 094013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shi, K.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Woolway, R.I.; Piao, S.; Jeppesen, E. Zhang Climate change drives rapid warming and increasing heatwaves of lakes. Sci. Bull. 2023, 68, 1574–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolway, I.; Eleanor Jennings, E.; Carrea, L. Impact of the 2018 European heatwave on lake surface water temperature. Inland Waters 2020, 10, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, K.; Qian, H.; Yang, H.; Niu, Y.; Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Woolway, R.I.; et al. The unprecedented 2022 extreme summer heatwaves increased harmful cyanobacteria blooms. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 896, 165312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Z.; Gao, W.; Cheng, G.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, X. Warming surface and Lake heatwaves as key drivers to harmful algal Blooms: A case study of Lake Dianchi, China. J. Hydrol. 2024, 632, 130971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimmer, A.; Givati, A.; Samuels, R.; Alpert, P. Using ensemble of climate models to evaluate future water and solutes budgets in Lake Kinneret, Israel. J. Hydrol. 2011, 410, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Fuente, S.; Jennings, E.; Gal, G.; Kirillin, G.; Shatwell, T.; Ladwig, R.; Moore, T.; Couture, R.-M.; Côté, M.; Love Råman Vinnå, C.; et al. Multi-model projections of future evaporation in a sub-tropical lake. J. Hydrol. 2022, 615, 128729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishcha, P.; Lechinsky, Y.; Starobinets, B. Impact of a Severe Dust Event on Diurnal Behavior of Surface Water Temperature in Subtropical Lake Kinneret. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziv, B.; Shilo, E.; Lechinsky, Y.; Rimmer, A. Meteorology. In Lake Kinneret—Ecology and Management; Zohary, T., Sukenik, A., Berman, T., Nishri, A., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 81–96. [Google Scholar]
- Kishcha, P.; Lechinsky, Y.; Starobinets, B. Cooling by Cyprus Lows of Surface and Epilimnion Water in Subtropical Lake Kinneret in Rainy Seasons. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishcha, P.; Starobinets, B.; Lechinsky, Y.; Alpert, P. Absence of surface water temperature trends in Lake Kinneret despite present atmospheric warming: Comparisons with Dead Sea trends. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishcha, P.; Volpov, E.; Starobinets, B.; Alpert, P.; Nickovic, S. Dust Dry Deposition over Israel. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzan, L.; Egert, S.; Alpert, P. Ceilometer evaluation of the eastern Mediterranean summer boundary layer height—First study of two Israeli sites. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 4387–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzan, L.; Egert, S.; Alpert, P. New insights into the vertical structure of the September 2015 dust storm employing eight ceilometers and auxiliary measurements over Israel. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 3203–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasch, P.; Rieger, D.; Walter, C.; Khain, P.; Levi, Y.; Knippertz, P.; Vogel, B. Revealing the meteorological drivers of the September 2015 severe dust event in the Eastern Mediterranean. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 13573–13604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platnick, S.; Hubanks, P.; Meyer, K.; King, M.D. MODIS Atmosphere L3 Monthly Product; NASA MODIS Adaptive Processing System, Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2015; Available online: https://doi.org/10.5067/MODIS/MOD08_M3.006 (accessed on 2 April 2024).
- Schmid, M.; Read, J. Heat budget of lakes. In Encyclopedia of Inland Waters 2022, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Volume 1, pp. 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okwen, R.; Pu, R.; Cunningham, J. Remote sensing of temperature variations around major power plants as point sources of heat. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 3791–3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, N.; Alpert, P.; Messer, H. Technical note: Novel method for water vapor monitoring using wireless communication networks measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 2413–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton, D. The computation of equivalent potential temperature. Mon. Weather Rev. 1980, 108, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duguay-Tetzlaff, A.; Bento, V.A.; Göttsche, F.-M.; Stöckli, R.; Martins, J.P.A.; Trigo, I.; Olesen, F.-S.; Bojanowski, J.S.; Dacamara, C.C.; Kunz, H. Meteosat Land Surface Temperature Climate Data Record: Achievable Accuracy and Potential Uncertainties. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 13139–13156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Product User Manual (PUM) Meteosat Land Surface Temperature. 2017. Available online: https://www.cmsaf.eu/SharedDocs/Literatur/document/2017/saf_cm_meteoswiss_pum_met_lst_1_1_pdf.pdf?__blob=publicationFile (accessed on 2 February 2024).
- LP DAAC Land Processes Distributed Active Archive Center: MOD11A1.006 MODIS/Terra Land Surface Temperature/Emissivity Daily L3 Global 1 km V006. Available online: https://e4ftl01.cr.usgs.gov/MOLT/MOD11A1.061/ (accessed on 26 May 2024).
- Emery, W.J.; Castro, S.; Wick, G.A.; Schluessel, P.; Donlon, C. Estimating sea surface temperature from infrared satellite and in situ temperature data. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2001, 82, 2773–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishcha, P.; Da Silva, A.; Starobinets, B.; Long, C.; Kalashnikova, O.; Alpert, P. Saharan dust as a causal factor of hemispheric asymmetry in aerosols and cloud cover over the tropical Atlantic Ocean. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 3423–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hondzo, M.; You, J.; Taylor, J.; Bartlet, G.; Voller, V.R. Measurement and scaling of lake surface skin temperatures. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2021GL093226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kishcha, P.; Lechinsky, Y.; Starobinets, B. Lake and Atmospheric Heatwaves Caused by Extreme Dust Intrusion in Freshwater Lake Kinneret in the Eastern Mediterranean. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2314. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16132314
Kishcha P, Lechinsky Y, Starobinets B. Lake and Atmospheric Heatwaves Caused by Extreme Dust Intrusion in Freshwater Lake Kinneret in the Eastern Mediterranean. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(13):2314. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16132314
Chicago/Turabian StyleKishcha, Pavel, Yury Lechinsky, and Boris Starobinets. 2024. "Lake and Atmospheric Heatwaves Caused by Extreme Dust Intrusion in Freshwater Lake Kinneret in the Eastern Mediterranean" Remote Sensing 16, no. 13: 2314. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16132314
APA StyleKishcha, P., Lechinsky, Y., & Starobinets, B. (2024). Lake and Atmospheric Heatwaves Caused by Extreme Dust Intrusion in Freshwater Lake Kinneret in the Eastern Mediterranean. Remote Sensing, 16(13), 2314. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16132314






