Reconstruction of Hourly FY-4A AGRI Land Surface Temperature under Cloud-Covered Conditions Using a Hybrid Method Combining Spatial and Temporal Information
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. FY-4A AGRI L2 LST
2.2.2. Predictor Variables of LST
- ERA5-Land Reanalysis Data
- MODIS Data
- ASTER GDEM Data
2.2.3. LST Measurements of Meteorological Stations
2.3. Methods
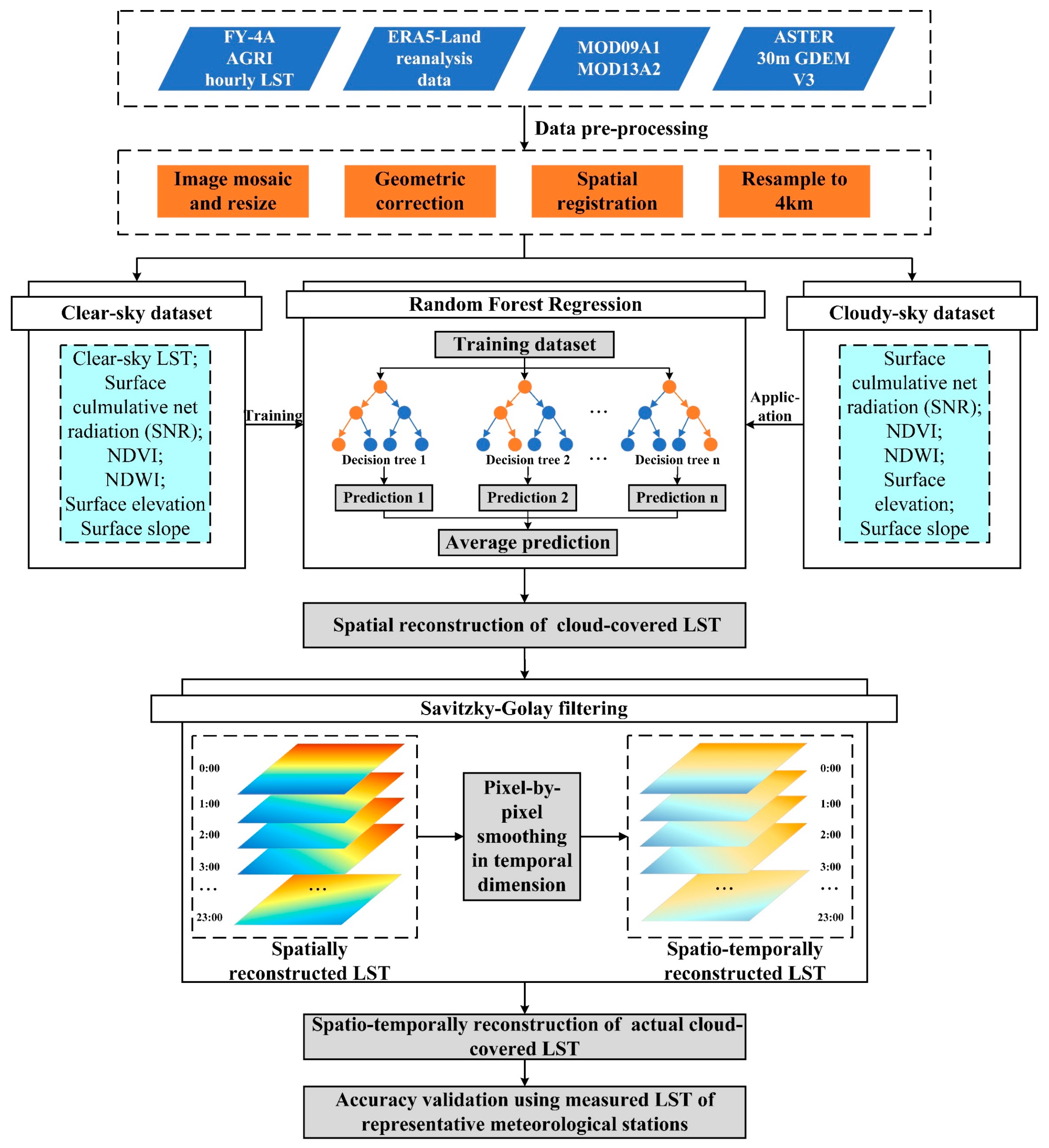
2.3.1. Flowchart Description
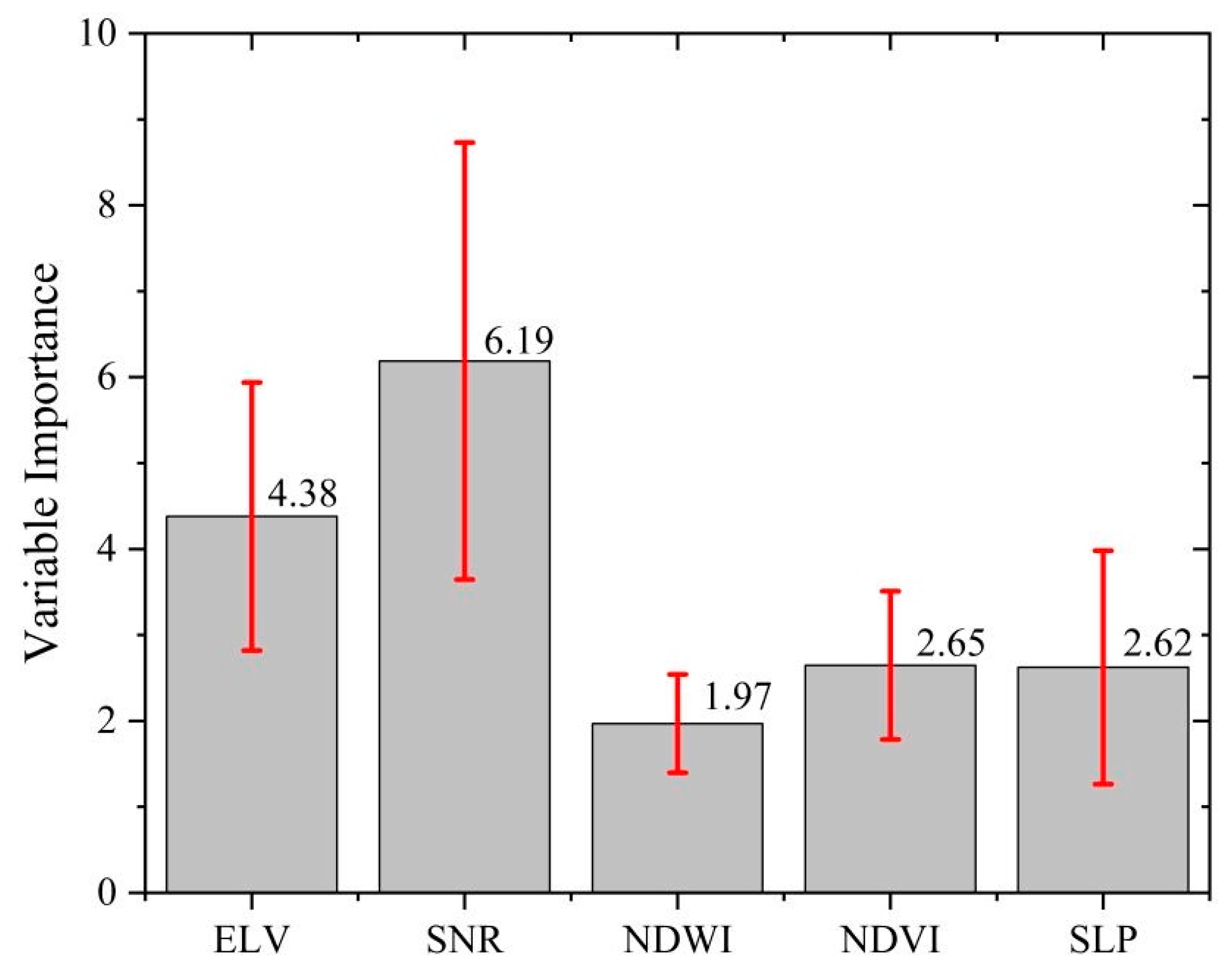
2.3.2. LST Correlation Model Based on Random Forest Regression
2.3.3. Temporally Smoothing Based on S–G Filtering Method
2.3.4. Selection of Representative Meteorological Stations and Scale Conversion of Measured LST
- Selection of Representative Meteorological Stations
- 2.
- Scale Conversion of Measured LST
2.4. Accuracy Variation Method
3. Results
3.1. Results of Selecting Representative Meteorological Stations and Scale Conversion of Measured LST
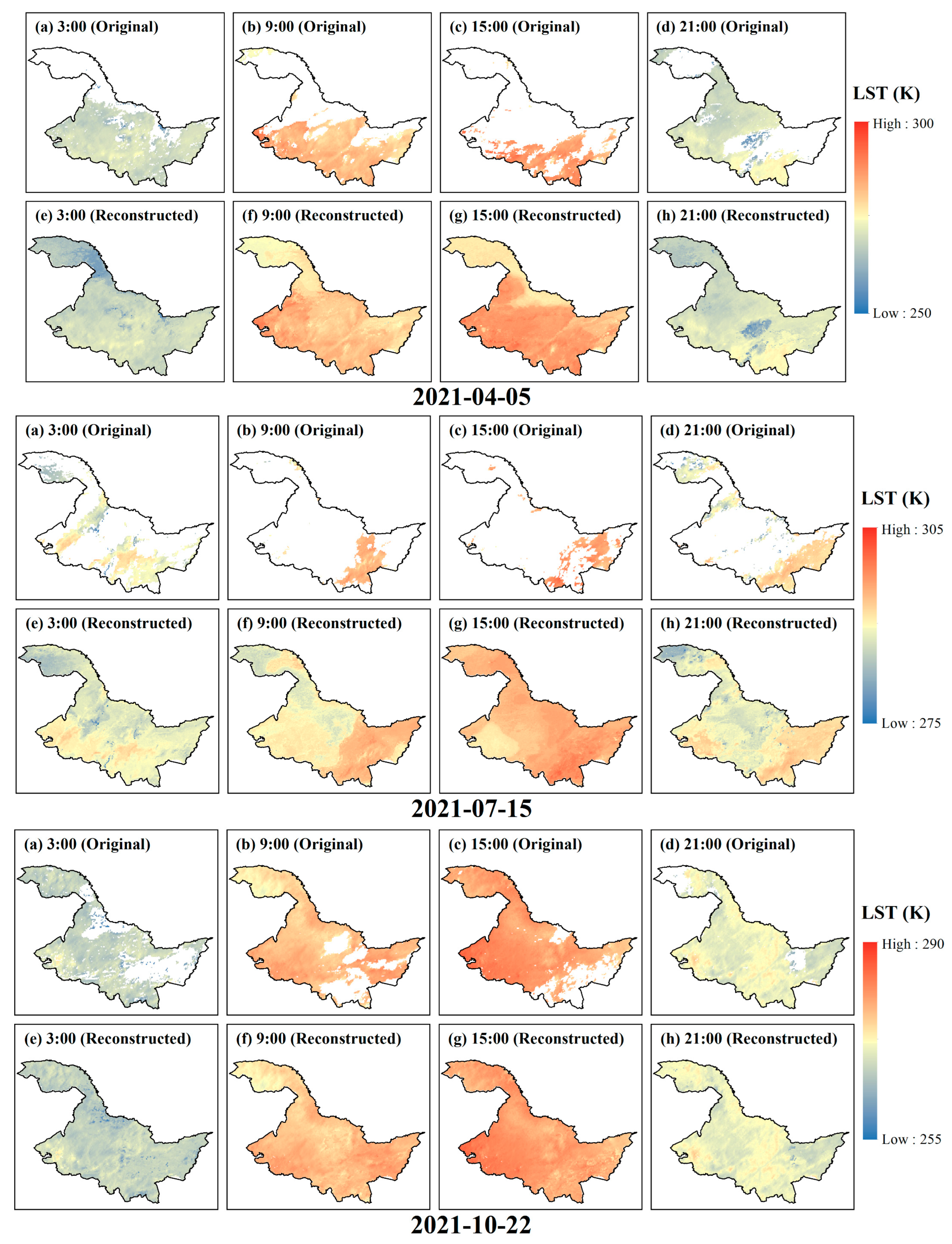
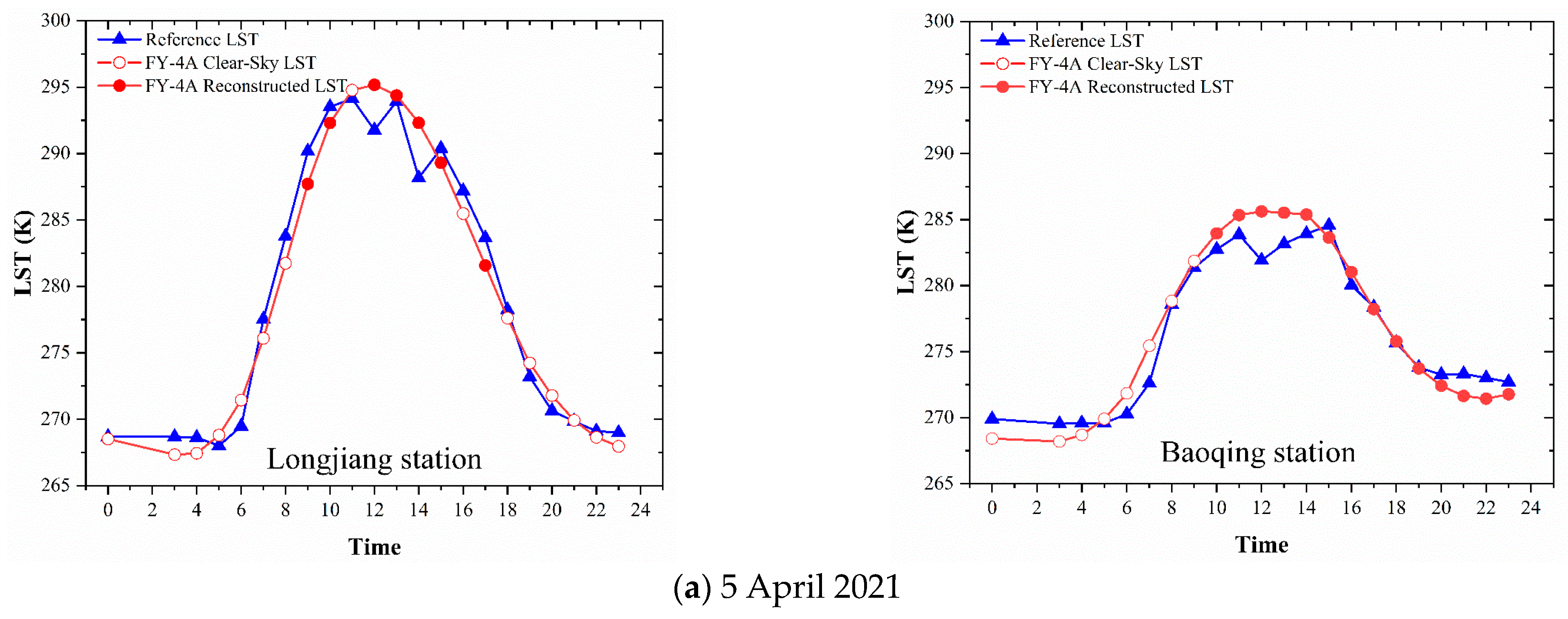
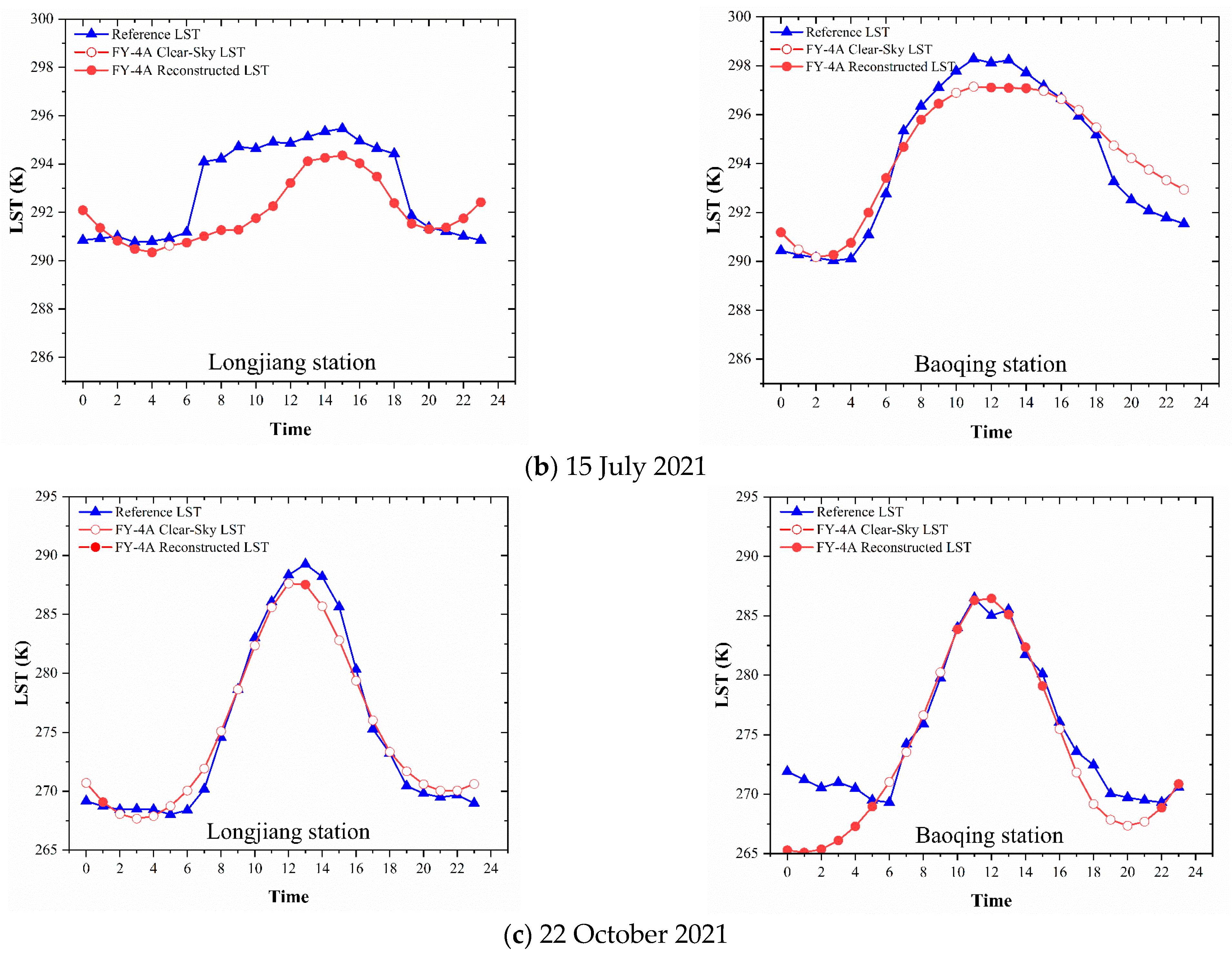
3.2. Reconstruction of Hourly FY-4A AGRI Cloudy-Sky LST
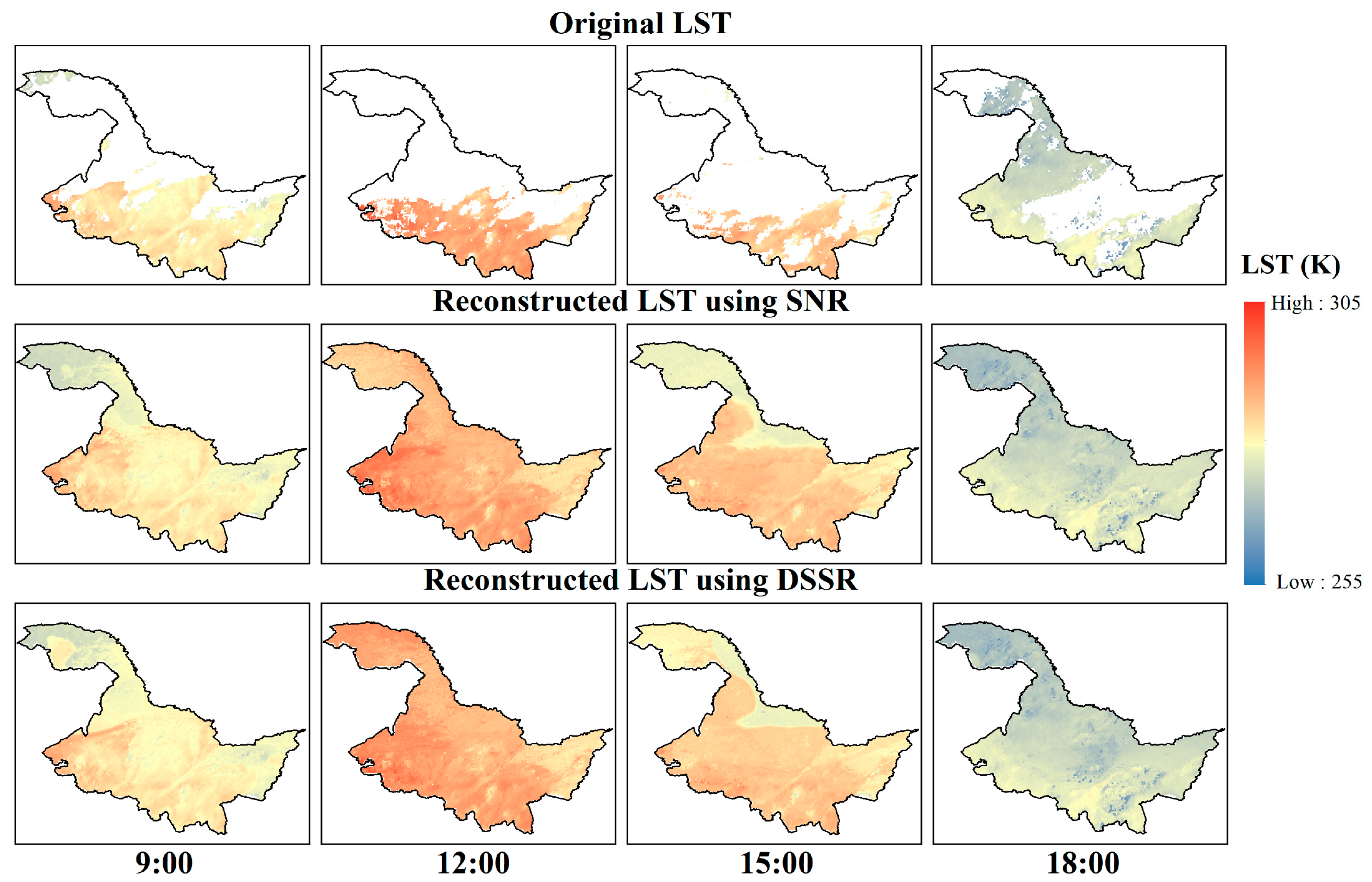
3.3. Methods Comparison
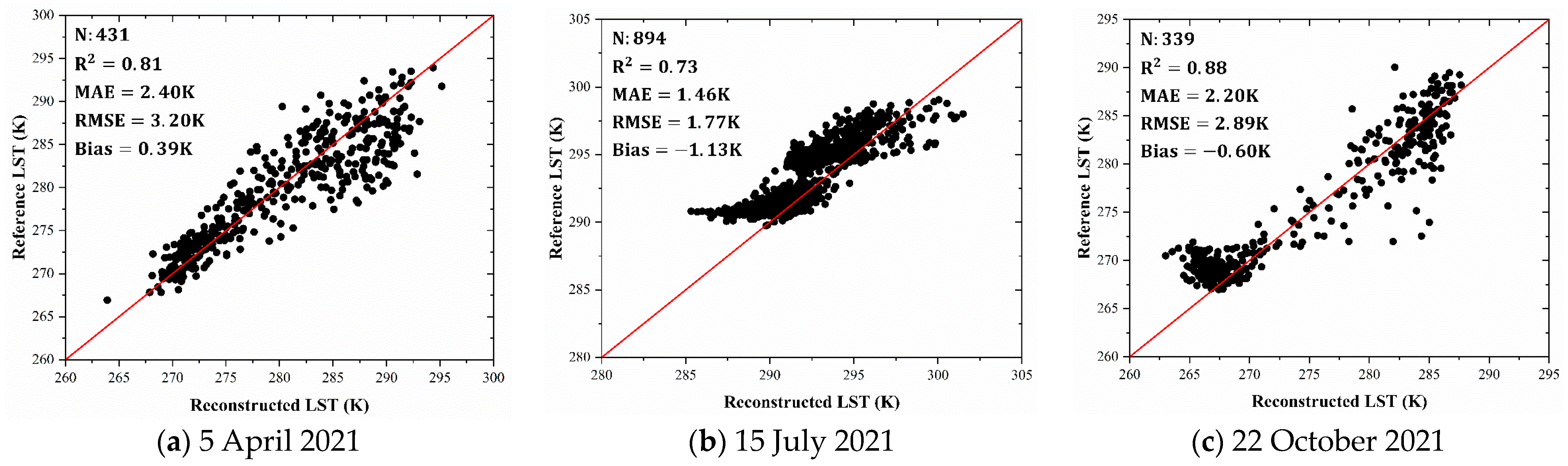
3.4. Accuracy Verification and Error Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Advantages
4.2. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xian, G.; Shi, H.; Zhou, Q.; Auch, R.; Gallo, K.; Wu, Z.; Kolian, M. Monitoring and Characterizing Multi-Decadal Variations of Urban Thermal Condition Using Time-Series Thermal Remote Sensing and Dynamic Land Cover Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 269, 112803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coolbaugh, M.F.; Kratt, C.; Fallacaro, A.; Calvin, W.M.; Taranik, J.V. Detection of Geothermal Anomalies Using Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) Thermal Infrared Images at Bradys Hot Springs, Nevada, USA. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 106, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, W.; Oliva, P.; Giglio, L.; Csiszar, I.A. The New VIIRS 375 m Active Fire Detection Data Product: Algorithm Description and Initial Assessment. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 143, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crow, W.T.; Kustas, W.P.; Prueger, J.H. Monitoring Root-Zone Soil Moisture through the Assimilation of a Thermal Remote Sensing-Based Soil Moisture Proxy into a Water Balance Model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 1268–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.M.; Liu, J. Evolution of Evapotranspiration Models Using Thermal and Shortwave Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Tan, J.; Ma, M.; Li, X.; She, X.; Song, Z. An Effective Similar-Pixel Reconstruction of the High-Frequency Cloud-Covered Areas of Southwest China. Remote Sen. 2019, 11, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.-B.; Li, Z.-L.; Leng, P. A Framework for the Retrieval of All-Weather Land Surface Temperature at a High Spatial Resolution from Polar-Orbiting Thermal Infrared and Passive Microwave Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 195, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, J.; Göttsche, F.-M.; Zhan, W.; Liu, S.; Cao, R. A Method Based on Temporal Component Decomposition for Estimating 1-Km All-Weather Land Surface Temperature by Merging Satellite Thermal Infrared and Passive Microwave Observations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 4670–4691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Yin, Z.; Yang, H.; Wu, Y.; Ma, X. Reconstructing Geostationary Satellite Land Surface Temperature Imagery Based on a Multiscale Feature Connected Convolutional Neural Network. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neteler, M. Estimating Daily Land Surface Temperatures in Mountainous Environments by Reconstructed MODIS LST Data. Remote Sens. 2010, 2, 333–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, L.; Ding, X.; Song, C. Reconstruction of Time-Series MODIS LST in Central Qinghai-Tibet Plateau Using Geostatistical Approach. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 1602–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, A.; Ma, H.; Liang, S.; Wang, D. Cloudy-Sky Land Surface Temperature from VIIRS and MODIS Satellite Data Using a Surface Energy Balance-Based Method. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 263, 112566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Dickinson, R.E. A Generalized Algorithm for Retrieving Cloudy Sky Skin Temperature from Satellite Thermal Infrared Radiances. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2000, 105, 27037–27047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.; Ghosh, S.K. A Deep-Learning-Based Forecasting Ensemble to Predict Missing Data for Remote Sensing Analysis. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 5228–5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yuan, Q.; Zeng, C.; Li, X.; Wei, Y. Missing Data Reconstruction in Remote Sensing Image With a Unified Spatial–Temporal–Spectral Deep Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 4274–4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Duan, S.-B. Reconstruction of Daytime Land Surface Temperatures under Cloud-Covered Conditions Using Integrated MODIS/Terra Land Products and MSG Geostationary Satellite Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 111931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parton, W.J.; Logan, J.A. A Model for Diurnal Variation in Soil and Air Temperature. Agric. Meteorol. 1981, 23, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Dickinson, R.E. Interpolation of Surface Radiative Temperature Measured from Polar Orbiting Satellites to a Diurnal Cycle: 1. Without Clouds. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 2105–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M. Interpolation of Surface Radiative Temperature Measured from Polar Orbiting Satellites to a Diurnal Cycle: 2. Cloudy-Pixel Treatment. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2000, 105, 4061–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, P.; Weng, Q. Consistent Land Surface Temperature Data Generation from Irregularly Spaced Landsat Imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 184, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Zhan, W.; Duan, S.-B.; Ju, W.; Quan, J. A Generic Framework for Modeling Diurnal Land Surface Temperatures with Remotely Sensed Thermal Observations under Clear Sky. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 150, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Yang, Y.; Pan, X.; Hu, J. Land Surface Temperature Reconstruction Model of FY-4A Cloudy Pixels Considering Spatial and Temporal Characteristics. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2021, 46, 852–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Zhou, J.; Li, Z.-L.; Ma, J.; Shi, C.; Sun, S.; Wang, Z. Reconstruction of Hourly All-Weather Land Surface Temperature by Integrating Reanalysis Data and Thermal Infrared Data From Geostationary Satellites (RTG). IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5003917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m Annual Land Cover Dataset and Its Dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Dickinson, R.E. Land Surface Skin Temperature Climatology: Benefitting from the Strengths of Satellite Observations. Environ. Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 044004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhao, W.; Li, A.; Wen, F.; Yu, D. The Impact of the Terrain Effect on Land Surface Temperature Variation Based on Landsat-8 Observations in Mountainous Areas. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 1808–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, A.; Liang, S.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, G. Comprehensive Assessment of Global Surface Net Radiation Products and Uncertainty Analysis. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 1970–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S). C.C.C. C3S ERA5-Land Reanalysis. Copernic. Clim. Chang. Serv. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Duan, S.-B.; Li, A.; Yin, G. A Practical Method for Reducing Terrain Effect on Land Surface Temperature Using Random Forest Regression. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 221, 635–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăguţ, L. Random Forest in Remote Sensing: A Review of Applications and Future Directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savitzky, A.; Golay, M.J.E. Smoothing and Differentiation of Data by Simplified Least Squares Procedures. Anal. Chem. 1964, 36, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Data | Spatial Resolution | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| FY-4A AGRI L2 LST | 4 km | As the target of this study |
| ERA5-Land reanalysis data (SNSR, SNLR, DSSR) | 0.1° | As the radiation factor of LST |
| MOD09A1 8-day synthetic reflectance data | 500 m | As the spectral factor of LST |
| MOD13A2 16-day synthetic NDVI data | 1 km | |
| ASTER GDEM V3 surface elevation data | 30 m | As the topographic factor of LST |
| Measured LST of meteorological stations | / | As the reference LST for accuracy validation |
| Land cover data | 30 m | As the reference data to select representative meteorological stations |
| Date | Samples | Gains (a) | Offsets (b) | R2 | RMSE (K) before Correction | RMSE (K) after Correction | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 April 2021 | Daytime | 313 | 0.69 | 82.17 | 0.74 | 7.59 | 3.19 |
| Nighttime | 356 | 0.61 | 103.90 | 0.63 | 3.27 | 1.51 | |
| 15 July 2021 | Daytime | 133 | 0.13 | 254.70 | 0.35 | 21.22 | 1.64 |
| Nighttime | 173 | 0.41 | 169.60 | 0.30 | 7.72 | 1.93 | |
| 22 October 2021 | Daytime | 409 | 0.71 | 77.89 | 0.85 | 5.03 | 2.19 |
| Nighttime | 452 | 0.46 | 145.50 | 0.22 | 2.97 | 1.90 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, G.; Xu, W.; Jiang, W.; Xu, Y. Reconstruction of Hourly FY-4A AGRI Land Surface Temperature under Cloud-Covered Conditions Using a Hybrid Method Combining Spatial and Temporal Information. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1777. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16101777
Li Y, Zhu S, Zhang G, Xu W, Jiang W, Xu Y. Reconstruction of Hourly FY-4A AGRI Land Surface Temperature under Cloud-Covered Conditions Using a Hybrid Method Combining Spatial and Temporal Information. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(10):1777. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16101777
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yuxin, Shanyou Zhu, Guixin Zhang, Wenjie Xu, Wenhao Jiang, and Yongming Xu. 2024. "Reconstruction of Hourly FY-4A AGRI Land Surface Temperature under Cloud-Covered Conditions Using a Hybrid Method Combining Spatial and Temporal Information" Remote Sensing 16, no. 10: 1777. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16101777
APA StyleLi, Y., Zhu, S., Zhang, G., Xu, W., Jiang, W., & Xu, Y. (2024). Reconstruction of Hourly FY-4A AGRI Land Surface Temperature under Cloud-Covered Conditions Using a Hybrid Method Combining Spatial and Temporal Information. Remote Sensing, 16(10), 1777. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16101777







