Abstract
The 6 February 2023 earthquakes that hit south-eastern Turkey were amongst the deadliest in the past century. Here, we report the ability to map and quantify areas impacted by these earthquakes using changes in nighttime lights, as mapped by NASA’s VIIRS/DNB sensor. We show the correspondence between the 7.8 magnitude earthquake and impacted areas, located in cities and towns, mostly along the fault line, in areas where macroseismic intensity values were higher than 7. We verified the darkening of night lights as recorded by VIIRS using the new SDGSAT-1 Glimmer multispectral nighttime sensor, as well as by comparing changes in nighttime lights with reports on damaged buildings. The ability to rapidly map impacted areas from space using nighttime lights is of key importance for prioritizing and directing emergency and rescue services globally.
1. Introduction
Two major earthquakes of magnitudes 7.8 and 7.5 hit south-eastern Turkey on 6 February 2023, resulting in more than 52,000 deaths and widespread damage, making these earthquakes the deadliest since the 2010 Haiti earthquake [1,2]. Earthquakes represent one of the deadliest and least predictable natural disasters that human societies face. While areas of high earthquake risk are well known, forecasting earthquakes is not possible [3] (although it has been suggested that there may be periods of increased geodynamic activity regionally [4]), and earthquake early alarm systems offer just seconds to one minute [5]. Given the vast amount of damage inflicted by earthquakes, rescue and recovery operations require timely information on areas affected and the amount of damage. While intensity maps are now produced routinely, e.g., using the Modified Mercalli Intensity (MMI) scale, estimating the potential impact on people, objects and buildings [6], they do not provide mapping of the actual effects of an earthquake. Remote sensing is now commonly used for mapping the impact of disasters, either naturally occurring ones [7,8] or anthropogenic ones such as armed conflicts [9,10]. Remote sensing of the impact to earthquakes can be used to map seismic displacements using interferometric synthetic aperture radar (SAR) [11] or subpixel deformation from optical imagery [12]. In addition, high-spatial-resolution satellite imagery is used to identify buildings that were either destroyed or damaged by earthquakes, in products delivered by the International Charter Space and Major Disasters [13] and by the Copernicus Emergency Management Service (CEMS) [14]. Out of 805 activations globally on the International Charter, 95 activations were related to earthquake events (https://cgt.disasterscharter.org/en accessed on 28 February 2023), and out of 652 rapid CEMS activations, 32 activations were for earthquake events (https://emergency.copernicus.eu/mapping accessed on 28 February 2023).
Remote sensing of artificial night lights provides an indicator of human activity, and nighttime lights (NTL) are correlated with population density and with economic activity [15]. Human and natural disasters can lead to interruptions and damage to electricity networks, and thus to the darkening of areas which were impacted. Whereas in the past, global products of satellite-derived night lights were only available on an annual or monthly basis, NASA’s Black Marble product now provides nightly products of night lights from the VIIRS/DNB sensor [16], allowing for continuous monitoring of changes in nighttime lights [17] and to assess acute disasters [18]. This product has been previously used to assess electricity restoration following hurricane Maria in Puerto Rico [19], and to identify areas affected by the 2022 floods in Brisbane, Australia [20]. Considerable effort is required to analyze dozens or hundreds of high-spatial-resolution images to identify buildings that were impacted in earthquakes, hence the motivation for using changes in night-time lights as observed from space.
Following the major earthquakes that took place in southern Turkey on 6 February 2023 [21], also affecting parts of Syria, and the need for rapid assessment of areas impacted by earthquakes, in this paper we demonstrate the feasibility of quantifying impacts of the earthquake using nightly images of night lights.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Earthquake Data
We used the USGS earthquake website (https://earthquake.usgs.gov/ accessed on 6 March 2023) to download the locations and magnitudes of recent earthquake events in Turkey, and to download the shakemaps [6], which included modeled macroseismic intensity. We downloaded the products for the 7.8 and 7.5 magnitude earthquake events of 6 February 2023, and the 6.3 magnitude event of 20 February 2023. We used the Modified Mercalli Intensity (MMI) product as a proxy of macroseismic intensity, which is provided at a spatial resolution of about 0.03 degrees (~3 km).
2.2. Night Lights Satellite Data
To examine the impact of earthquake events on artificial nighttime lights, we used the nightly VIIRS Black Marble product of VNP46A1 [16]. This product provides nightly at-sensor top-of-atmosphere radiance (in units of nW cm−2 sr−1) at a spatial resolution of 15 arc seconds (~450 m at the equator; https://ladsweb.modaps.eosdis.nasa.gov/missions-and-measurements/products/VNP46A1/ accessed on 6 March 2023). We downloaded all nightly products of granule h21v05 between calendar days 1 and 61 (1 January 2023 and 2 March 2023, 61 days). For our analysis, we only included cloud-free pixels from each of the nights (based on the VNP46A1 cloud mask status). We extracted all lit grid cells (grid cells where the brightness value in 2021 was greater than 3 nW cm−2 sr−1, and where the combined Modified Mercalli Intensity values of both of the 6 February earthquake events exceeded 11; n = 42,528) within this granule, and divided the time frame into two periods: (1) pre-earthquake (1 January–5 February 2023, 36 days); (2) post-earthquake (7 February–20 February 2023, 14 days). We ran t-tests to examine whether brightness levels differed between periods 1 and 2 (areas impacted by earthquake may record a decrease in nighttime brightness levels). Given that we analyzed more than 10,000 grid cells, we considered only grid cells where the p value of the t-test was less than 0.01 as statistically significant. We also calculated the difference and ratio between the brightness levels of these two periods. To test the robustness of our approach, we also ran t-tests for shorter time periods for the post-earthquake period. To examine the impact of the earthquakes on changes in NTL, we calculated the following ratio:
We then examined the distribution of NTL ratio changes as a function of MMI values, expecting to find higher values of NTL ratio changes in areas impacted by the earthquakes. We quantified the recovery of night lights by computing trends in NTL using Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient for two time periods: 7–19 February 2023 and 7 February–2 March 2023. In addition, we used monthly time series of VIIRS (available online at https://lighttrends.lightpollutionmap.info/ accessed on 6 March 2023), to examine changes in NTL for selected cities since 2012. We used Sustainable Development Goals Satellite 1 (SDGSAT-1) Glimmer multispectral nighttime imagery, offering a higher spatial resolution of 40 m (available from http://www.sdgsat.ac.cn/ accessed on 16 April 2023 [22]), to examine changes in nighttime lights between a pre-earthquake image (22 August 2022) and a post-earthquake image (12 February 2023). We calibrated the DN values of SDGSAT-1 to apparent radiance using the sensor’s calibration coefficients of gain and bias, provided in [23]. To quantitatively compare the correlation between change in VIIRS NTL values and SDGSAT-1 NTL values, we ran an 11-pixel moving window low-pass filter on the three bands of the SDGSAT-1 (to match the spatial resolutions between the two night-time sensors) and summed their values to obtain the total amount of apparent radiance measured by the SDGSAT-1.
2.3. Additional Datasets
We used the GEM Global Active Faults Database available from (https://github.com/GEMScienceTools/gem-global-active-faults accessed on 6 March 2023; [24]) to show the locations of major fault lines on our maps. We present the distribution of built areas on some of the maps based on the Global Human Settlements Layer (GHSL, https://ghsl.jrc.ec.europa.eu/index.php; [25]); accessed on 6 March 2023). To examine the correspondence of NTL changes with actual damages, we used reports on damaged buildings in Turkey at the province level [26]). To present an overview map of damaged buildings, we used data published by the Humanitarian OpenStreetMap Team, available at https://data.humdata.org/dataset/hotosm_tur_destroyed_buildings? accessed on 1 March 2023).
3. Results
The 7.8 magnitude earthquake hit south-eastern Turkey near the town of Gaziantep at 4:17 am of 6 February 2023, and the 7.5 magnitude earthquake hit about ~100 km to the north at 13:24 pm of the same day (Figure 1). These earthquakes followed different fault lines, with the 7.8 earthquake following a SW–NE fault line, with macroseismic intensity values >7 covering an area of ~20,680 km2 (Figure 1a), with many towns and cities located along this fault line (with an approx. built area of 347 km2). The 7.5 earthquake followed a W–E fault line, with macroseismic intensity values >7 covering a smaller area of ~8350 km2, which is less populated (with an approx. built area of just 41 km2) (Figure 1b).
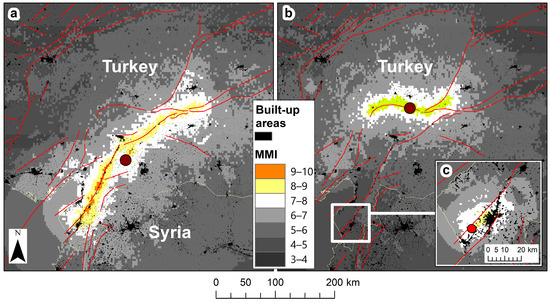
Figure 1.
Shake maps of macroseismic intensity (we will hereafter refer to macroseismic intensity as “MMI” for Modified Mercalli Intensity) of three major earthquakes: (a) 7.8 magnitude earthquake, 6 February 2023; (b) 7.5 magnitude earthquake, 6 February 2023; (c) 6.3 magnitude earthquake, 20 February 2023. All maps show the location of their respective epicenter, and are overlaid by major fault lines and built areas from the global human settlements layer.
Examining changes in nighttime lights in VIIRS/DNB lit grid cells (>3 nW cm−2 sr −1) where the combined MMI values of the both earthquakes were >11, 6.6% of the analyzed grid cells experienced a statistically significant decrease in nighttime lights (NTL) comparing the average NTL value in the period before the earthquakes (1 January–5 February, 36 days) and the average NTL value in the period after the earthquakes (7–20 February, 14 days). Statistically significant changes in NTL were well aligned with the fault line of the 7.8 earthquake, and corresponded well with the spatial patterns of destroyed buildings of Turkey provided by the Humanitarian OpenStreetMap Team (3415 buildings, as of 1 March 2023). Note, however, that the actual number of buildings that were heavily or moderately damaged was nearly 230,000; [26]) (Figure 2). Statistically significant decreases in NTL were mostly found in areas where MMI values following the 7.8 magnitude earthquake were higher than 7 (Figure 3). In areas with MMI values > 7.5 following the 7.8 magnitude earthquake, 27% of the lit grid cells experienced a statistically significant decrease of at least 30% in their NTL values following the earthquakes. Decreases in NTL did not correspond with high MMI values from the 7.5 magnitude earthquake (Figure 4). We ran a sensitivity analysis, examining NTL change maps based on other temporal periods (e.g., 3, 7 and 14 days after the earthquake), and we found that these changes and their spatial patterns were very similar between the different temporal periods, indicating the robustness of this approach (Figure 5).
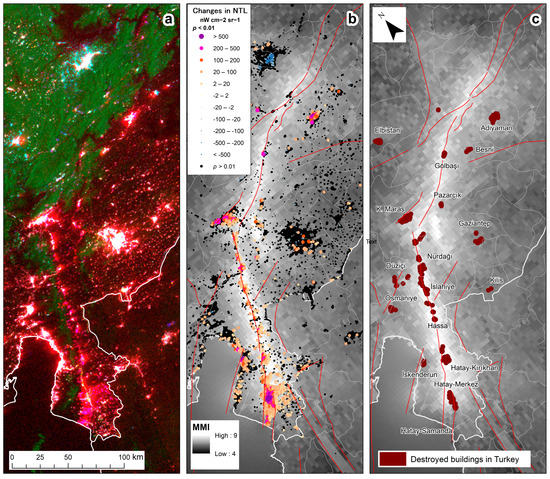
Figure 2.
(a) False-color composite of VIIRS nighttime lights (NTL) in the cloud-free nights of 26 January (before the earthquake, in red), 9 February (in green) and 12 February (in blue). Areas that experienced a decrease in night lights appear in red hues, lit areas that did not experience changes appear in white, green hues represent unlit areas with increased nighttime brightness due to snow cover, and lit areas that were covered with snow appear in cyan. (b) Statistically significant changes in NTL (p < 0.01), comparing the 36 days before the 6 February earthquakes and the 14 days after the 6 February earthquakes. Positive values of NTL changes signify a decrease in NTL. Very few areas with statistically significant changes in NTL were found outside of the area shown on the map. Black dots represent VIIRS lit grid cells, where no statistically significant changes in NTL were found. (c) Destroyed buildings in Turkey, as mapped by the Humanitarian OpenStreetMap Team. Both maps (b,c) are overlaid by the USGS shakemap of the 7.8 magnitude earthquake (in units of MMI) and by major fault lines.
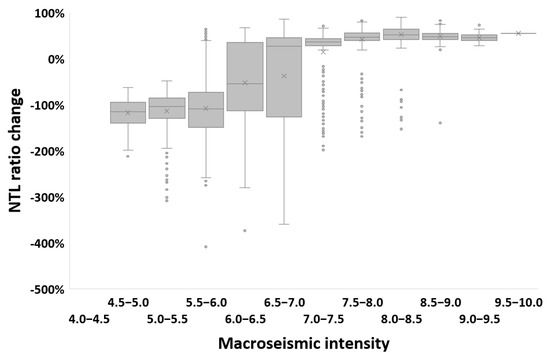
Figure 3.
Statistically significant (p < 0.01) NTL changes between the median of the period before the earthquakes (1 January–5 February, 36 days) and the median of the period after the earthquakes (7–20 February, 14 days), expressed as the ratio between the difference and pre-earthquake NTL values. NTL ratio changes > 0% indicate a decrease in NTL, whereas negative ratios indicate an increase in NTL. Boxplots of NTL ratio changes for VIIRS lit grid cells in the study area are shown as a function of MMI values based on the shakemap of the 7.8 magnitude earthquake.
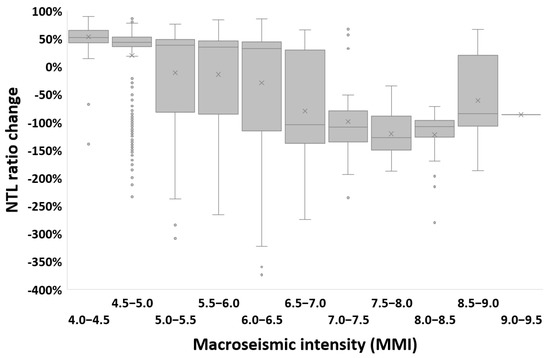
Figure 4.
Statistically significant (p < 0.01) NTL changes between the median of the period before the earthquakes (1 January–5 February, 36 days) and the median of the period after the earthquakes (7–20 February, 14 days), expressed as the ratio between the difference and pre-earthquake NTL values. NTL ratio changes > 0% indicate a decrease in NTL, whereas negative ratios indicate an increase in NTL. Boxplots of NTL ratio changes for VIIRS lit grid cells in the study area are shown as a function of MMI values based on the shakemap of the 7.5 magnitude earthquake.
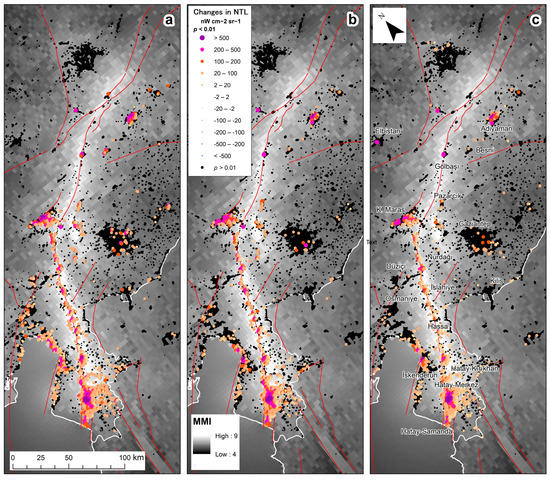
Figure 5.
Statistically significant changes in NTL (p < 0.01), comparing the 36 days before the 6 February earthquakes, and selected periods after the 6 February earthquakes: (a) 3 days, (b) 7 days, (c) 14 days. Positive values of NTL changes signify a decrease in NTL. Very few areas with statistically significant changes in NTL were found outside of the area shown on the map. Black dots represent VIIRS lit grid cells, where no statistically significant changes in NTL were found. All maps are overlaid by the USGS shakemap of the 7.8 magnitude earthquake (in units of MMI) and by major fault lines.
The three administrative areas that were most impacted in terms of the number of VIIRS lit grid cells with statistically significant decreases in NTL were Antakya (Hatay-Merkez) (n = 1323), Hatay-Kirkhan (n = 223) and K. Maras (n = 163). The three administrative areas that were most impacted in terms of the percentage of VIIRS lit grid cells with statistically significant decreases in NTL were Antakya (Hatay-Merkez) (63% of all lit grid cells), Hatay-Samanda (43%) and Hatay-Kirkhan (29%). Decreases in NTL detected by VIIRS matched well with areas in which NTL decreases were mapped using the higher-spatial-resolution images of SDGSAT-1 (Figure 6), and were significantly correlated (r = 0.70, n = 1228 for the VIIRS lit grid cells of Antakya; Figure 7).
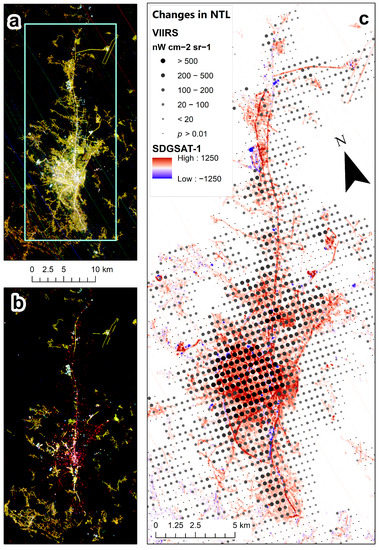
Figure 6.
(a) SDGSAT-1 nighttime image acquired on 22 August 2022; (b) SDGSAT-1 nighttime image acquired on 12 February 2023; (c) statistically significant changes in VIIRS NTL (p < 0.01), comparing the 36 days before the 6 February earthquakes and the 14 days after the 6 February earthquakes. Positive values of NTL changes signify a decrease in NTL. Very few areas with statistically significant changes in NTL were found outside of the area shown on the map. Small black dots represent VIIRS lit grid cells, where no statistically significant changes in NTL were found.
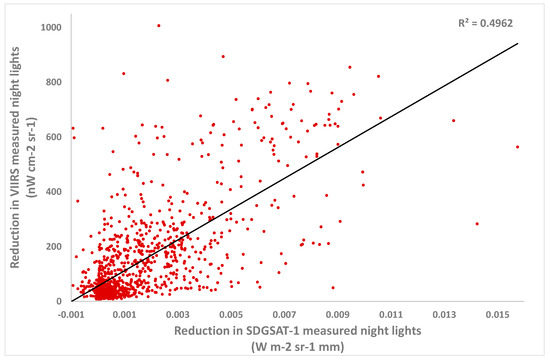
Figure 7.
The correlation between lit VIIRS grid cells with statistically significant changes in VIIRS NTL (p < 0.01) (comparing the 36 days before the 6 February earthquakes, and the 14 days after the 6 February earthquakes), and changes in SDGSAT-1 NTL values between 22 August 2022 and 12 February 2023. The lit grid cells analyzed here are those presented in Figure 4, for city of Antakya, Turkey (n = 1228).
The decrease in NTL values was clearly evident when examining time series of these three cities with some recovery in NTL starting in the second week after the major earthquakes (Figure 8). However, in the cities of Antakya (Hatay-Merkez) and Hatay-Samanda, an additional decrease in NTL was observed on 20 February 2023, following a 6.3 magnitude earthquake that hit on that day with its epicenter located between these two cities (Figure 1c). Decreases in NTL were significantly correlated with heavily damaged buildings as well as for the total number of damaged buildings, for which data were available in Turkey at the province level (Figure 9). Time series of VIIRS NTL also allowed us to monitor the recovery of NTL in the affected areas. In the first 13 days after the earthquake (7–19 February 2023), statistically significant increases in NTL were found in 37.8% of the grid cells in which NTL decreases were recorded following the earthquakes (Figure 10a). Over a longer period of 24 days after the earthquake (7 February–2 March 2023) statistically significant increases in NTL were found in 50.4% of the grid cells in which NTL decreases were recorded following the earthquakes (Figure 10b). The NTL recovery trends over the longer time period of 24 days were weaker in the cities of Antakya and Samanda in the south, in the vicinity of where the 20 February 2023 earthquake took place.
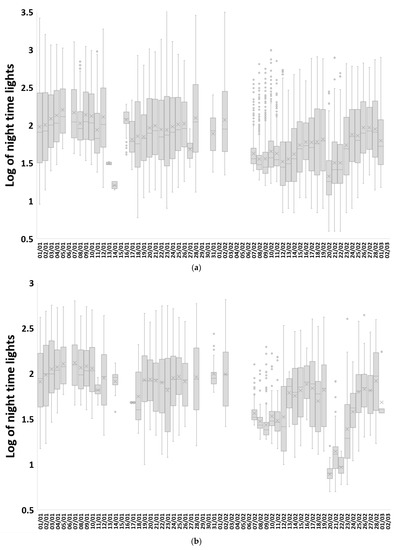
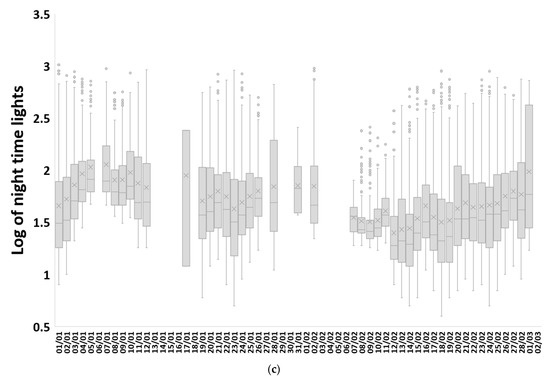
Figure 8.
Time series of box plots of nighttime lights for lit grid cells within three regions that experienced a statistically significant decrease in NTL values between the period before the earthquakes (1 January–5 February, 36 days) and the period after the earthquakes (7–14 February, 14 days): (a) Antakya (Hatay-Merkez), (b) Hatay-Samanda, (c) Hathay-Kirkhan. Dates with no boxplots had no cloud-free pixels.
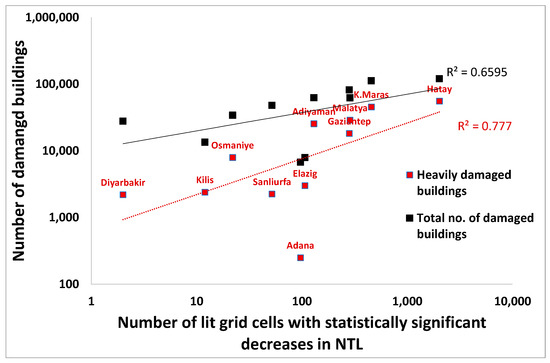
Figure 9.
The correspondence between VIIRS lit grid cells that experienced statistically significant decreases in NTL before and after the 7.8 magnitude earthquake and damaged buildings at the province level in Turkey, as of 27 February 2023 (source: [26]).
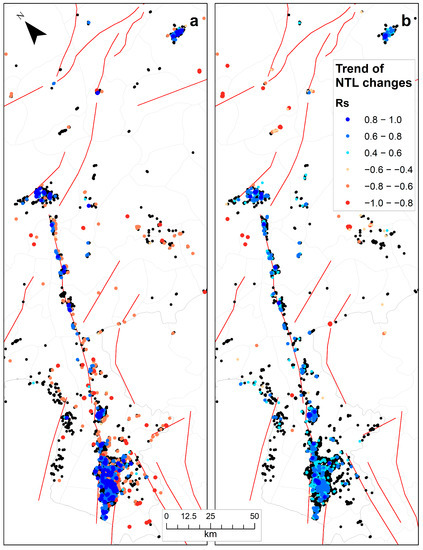
Figure 10.
Recovery of NTL in lit VIIRS grid cells (colored dots) based on time series of VIIRS data, as computed using Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient for two time periods following the earthquakes: (a) 7–19 February 2023; (b) 7 February–2 March 2023. Black dots represent VIIRS lit grid cells in which there were statistically significant decreases in NTL following the earthquakes but no recovery was detected over the time period shown.
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Extreme events and natural disasters impacting human livelihoods, infrastructure and properties require rapid assessment of both damage and the monitoring of recovery, giving space agencies and Earth observation platforms an important role. While high-spatial-resolution satellite images enable space agencies, NGOs and citizen science to map damaged buildings [27], they often require manual and visual interpretation of dozens (if not more) of satellite images, and hence the resulting damage assessment will be impacted by the efforts devoted to mapping and the capability of the interpreters [28]. Analyzing changes in night lights can therefore provide a rapid and large-area assessment of damage, as has been previously shown for other types of human crises [10,19]. Previous studies that used the monthly product of VIIRS/DNB to assess the impact of earthquakes on NTL (e.g., the 2015 Nepal earthquake) were less successful in mapping these NTL changes [29,30,31], which may be due to the temporal averaging and smoothing of nightly data into a single monthly product, and the fact that the recovery of electricity may happen within a week or two, as we found in this case. Studies using nightly VIIRS/DNB to detect the impact of earthquakes on NTL may better identify such changes; however, nightly images are more prone to be affected by cloud cover [32]. To overcome cloud cover problems, we examined changes in NTL between pre-earthquake and post-earthquake periods, enabling us to also test for statistically significant changes in NTL. The areas identified as those with significant decreases in NTL were much more extensive than those mapped by humanitarian OSM as having damaged buildings (Figure 2). This is probably mostly an artefact of the mapping effort invested or of visual interpretation errors, but may also show the value of assessing changes in NTL; areas may be cut out of electricity because of damages to infrastructure in other areas, even if buildings were not damaged directly. The robustness of this approach can also be appreciated by the similarity of NTL change maps that were based on different time periods, showing that statistically significant changes in NTL were already rapidly detected three days after the earthquakes had hit the region (Figure 5).
Through our analysis, we were able to attribute the NTL changes to specific earthquake events, using the USGS shakemaps as a proxy for macroseismic intensity. While two major earthquakes hit south-eastern Turkey on 6 February 2023 [2,21], it was the first earthquake, of 7.8 magnitude, that inflicted most of the damage. This may be explained by the greater human vulnerability to earthquake risk [28] in the case of the 7.8 earthquake, which coincided with a fault line located in an area that is densely populated. Recurring acute disasters pose great risk to human populations [18], and two cases can be noted here. The first example of a recurring acute disaster was the 6.3 magnitude earthquake that hit the region of Hatay, Turkey, on February 20th, inflicting additional damages to the same area that had already been hit two weeks earlier. A second case of a recurring disaster refers to the ability of assessing earthquake damages in Syria. The war in Syria, which started in 2010, led to depopulation and widespread damages, with one of the main areas to be affected being that of the District of Aleppo, in northern Syria [10,16]. The war led to cities, towns and villages in Syria becoming much darker than in Turkey (Figure 11); hence, the ability to use NTL changes to detect the impact of the earthquake in northern Syria was not high, given that about of 26% of Syria’s urban areas and about 49% of its rural settlements are unlit (compared with 0% and 4%, respectively, in Turkey; [33]).
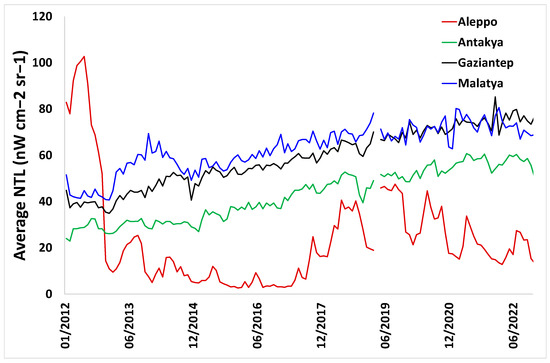
Figure 11.
Average monthly nighttime lights (derived from BRDF corrected VIIRS monthly data) for the city centers of Aleppo, Syria and three cities in Turkey: Antakya (Hatay Merkez), Gaziantep and Malatya.
China’s SDGSAT-1 is the first multispectral satellite to freely offer nighttime light images of the Earth at a moderate spatial resolution, as already advocated in 2007 [34]. We call for the launch of additional operational Earth observation missions, such as the recent SDGSAT-1, with sensors for monitoring nighttime lights at higher spatial resolutions, to allow finer mapping of the impacts of extreme events. We found that changes in NTL due to the earthquake were well correlated between the two sensors of VIIRS and SDGSAT-1, in spite of the differences in their spatial resolution, their spectral bands and radiometric sensitivity, and especially the different times for which data were available for each of these satellites. While higher-spatial-resolution images of night lights allow for mapping in greater detail, SDGSAT-1 does not acquire nighttime images in an operational manner with a fixed revisit time, and the availability of its nighttime images varies between regions. For the study area of the earthquake, a pre-earthquake SDGSAT-1 night-time image was only available for 22 August 2022. Given the seasonality of nighttime lights, especially in areas with snow in winter [35], having a pre-earthquake image that is acquired within days or weeks of the earthquake is better for detecting changes in NTL. Following the earthquake, in order to assist in assessing the damages of the earthquake [36], several SDGSAT-1 night-time images were acquired: 12 February 2023, 27 February 2023 and several images in March 2023 (available from https://data.sdgsat.ac.cn/dataQuery accessed on 13 April 2023). However, the nighttime images of SDGSAT-1 are often acquired only using the Glimmer sensor, without its Thermal Infrared Spectrometer (TIS), so the detection of cloud cover hampering the mapping of night lights within the nighttime imagery is not always possible. Coarse-spatial-resolution images as provided by VIIRS offer better temporal resolution (nightly revisit time) and include quality data information on cloud cover, and thus the two types of nighttime imagery are complementary, enabling rapid detection of the impact of natural disasters such as these earthquakes on nighttime lights [36,37,38]. Emergency and rescue agencies are thus urged to use satellite-derived nighttime light products to quickly identify areas impacted by natural disasters, to prioritize and direct their actions in near-real time.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
All data used in the analysis is freely available online.
Acknowledgments
We thank NASA for providing access to the VNP46A1 product of VIIRS, and we thank the International Research Center of Big Data for Sustainable Development Goals (CBAS) for providing access to SDGSAT-1 imagery.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Bilham, R. Lessons from the Haiti Earthquake. Nature 2010, 463, 878–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dal Zilio, L.; Ampuero, J.-P. Earthquake Doublet in Turkey and Syria. Commun. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geller, R.J.; Jackson, D.D.; Kagan, Y.Y.; Mulargia, F. Earthquakes Cannot Be Predicted. Science 1997, 275, 1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stemberk, J.; Košťák, B.; Cacoń, S. A Tectonic Pressure Pulse and Increased Geodynamic Activity Recorded from the Long-Term Monitoring of Faults in Europe. Tectonophysics 2010, 487, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.M.; Stogaitis, M. Global Growth of Earthquake Early Warning. Science 2022, 375, 717–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worden, C.B. ShakeMap Manual 2016; U. S. Geological Survey: Reston, Virginia, 2016.
- Joyce, K.E.; Belliss, S.E.; Samsonov, S.V.; McNeill, S.J.; Glassey, P.J. A Review of the Status of Satellite Remote Sensing and Image Processing Techniques for Mapping Natural Hazards and Disasters. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2009, 33, 183–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tralli, D.M.; Blom, R.G.; Zlotnicki, V.; Donnellan, A.; Evans, D.L. Satellite Remote Sensing of Earthquake, Volcano, Flood, Landslide and Coastal Inundation Hazards. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2005, 59, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witmer, F.D.W. Remote Sensing of Violent Conflict: Eyes from Above. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 2326–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, N.; Ali, S.; Crandall, D. Utilizing Remote Sensing and Big Data to Quantify Conflict Intensity: The Arab Spring as a Case Study. Appl. Geogr. 2018, 94, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, J. Shifting Ground. Science 2021, 371, 876–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provost, F.; Michéa, D.; Malet, J.-P.; Boissier, E.; Pointal, E.; Stumpf, A.; Pacini, F.; Doin, M.-P.; Lacroix, P.; Proy, C.; et al. Terrain Deformation Measurements from Optical Satellite Imagery: The MPIC-OPT Processing Services for Geohazards Monitoring. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 274, 112949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stryker, T.; Jones, B. Disaster Response and the International Charter Program. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2009, 2009, 1342–1344. [Google Scholar]
- Directorate Space, Security and Migration, European Commission Joint Research Centre (EC JRC). Copernicus Emergency Management Service; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxemburg, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Levin, N.; Kyba, C.C.M.; Zhang, Q.; Sánchez de Miguel, A.; Román, M.O.; Li, X.; Portnov, B.A.; Molthan, A.L.; Jechow, A.; Miller, S.D.; et al. Remote Sensing of Night Lights: A Review and an Outlook for the Future. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, M.O.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Q.; Kalb, V.; Miller, S.D.; Molthan, A.; Schultz, L.; Bell, J.; Stokes, E.C.; Pandey, B.; et al. NASA’s Black Marble Nighttime Lights Product Suite. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 210, 113–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Román, M.O.; Kalb, V.L.; Zhao, Y. Continuous Monitoring of Nighttime Light Changes Based on Daily NASA’s Black Marble Product Suite. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 282, 113269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machlis, G.E.; Román, M.O.; Pickett, S.T.A. A Framework for Research on Recurrent Acute Disasters. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabk2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, M.O.; Stokes, E.C.; Shrestha, R.; Wang, Z.; Schultz, L.; Carlo, E.A.S.; Sun, Q.; Bell, J.; Molthan, A.; Kalb, V.; et al. Satellite-Based Assessment of Electricity Restoration Efforts in Puerto Rico after Hurricane Maria. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, N.; Phinn, S. Assessing the 2022 Flood Impacts in Queensland Combining Daytime and Nighttime Optical and Imaging Radar Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naddaf, M. Turkey–Syria Earthquake: What Scientists Know. Nature 2023, 614, 398–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Hu, Y.; Li, X.M.; Kang, C.; Yan, L. AOD Derivation from SDGSAT-1/GLI Dataset in Mega-City Area. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Dou, C.; Li, X.; Liu, J. SDGSAT-1 Data Users Handbook (Draft); International Research Center of Big Data for Sustainable Development Goals: Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Styron, R.; Pagani, M. The GEM Global Active Faults Database. Earthq. Spectra 2020, 36, 160–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchiorri, M.; Pesaresi, M.; Florczyk, A.; Corbane, C.; Kemper, T. Principles and Applications of the Global Human Settlement Layer as Baseline for the Land Use Efficiency Indicator—SDG 11.3.1. IJGI 2019, 8, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DEEP Türkiye Earthquake February 2023, Bi-Weekly Highlights—03/03/2023 2023. Data Frinedly Space. Available online: https://reliefweb.int/report/turkiye/turkiye-earthquake-february-2023-bi-weekly-highlights-03032023 (accessed on 14 April 2023).
- Herfort, B.; Lautenbach, S.; Porto de Albuquerque, J.; Anderson, J.; Zipf, A. The Evolution of Humanitarian Mapping within the OpenStreetMap Community. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiß, C.; Taubenböck, H. Remote Sensing Contributing to Assess Earthquake Risk: From a Literature Review towards a Roadmap. Nat. Hazards 2013, 68, 7–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yu, B.; Liu, Y.; Yao, S.; Lian, T.; Chen, L.; Yang, C.; Chen, Z.; Wu, J. NPP-VIIRS DNB Daily Data in Natural Disaster Assessment: Evidence from Selected Case Studies. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Chen, Y.; Liang, L.; Gong, A. Post-Earthquake Night-Time Light Piecewise (PNLP) Pattern Based on NPP/VIIRS Night-Time Light Data: A Case Study of the 2015 Nepal Earthquake. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tveit, T.; Skoufias, E.; Strobl, E. Using VIIRS Nightlights to Estimate the Impact of the 2015 Nepal Earthquakes. Geoenviron. Disasters 2022, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Nie, G.; Deng, Y.; An, J.; Zhou, J.; Li, H. Rapid Detection of Earthquake Damage Areas Using VIIRS Nearly Constant Contrast Night-Time Light Data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 2386–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCallum, I.; Kyba, C.C.M.; Bayas, J.C.L.; Moltchanova, E.; Cooper, M.; Cuaresma, J.C.; Pachauri, S.; See, L.; Danylo, O.; Moorthy, I.; et al. Estimating Global Economic Well-Being with Unlit Settlements. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Cinzano, P.; Pettit, D.R.; Arvesen, J.; Sutton, P.; Small, C.; Nemani, R.; Longcore, T.; Rich, C.; Safran, J.; et al. The Nightsat Mission Concept. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 2645–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, N. The Impact of Seasonal Changes on Observed Nighttime Brightness from 2014 to 2015 Monthly VIIRS DNB Composites. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 193, 150–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNOSAT. Light Loss Assessment Following the Marash/Antep Earthquake (6 February 2022, Mw 7.8) Using Night-Time Light Imagery; UNOSAT, United Nations Institute for Training and Research (UNITAR): Geneva, Switzerland, 2023; Available online: https://unosat.org/products/3495 (accessed on 14 April 2023).
- Ghosh, T.; Elvidge, C.; Zhizhin, M. VIIRS Day/Night Band Power Outage Analysis for the 6 February 2023 Earthquake in Turkey and Syria; Colorado School of Mines Repository: Golden, CO, USA, 2023; p. 9. Available online: https://repository.mines.edu/handle/11124/16505 (accessed on 14 April 2023).
- Yu, B.; Chen, F.; Wang, N.; Wang, L.; Guo, H. Assessing Changes in Nighttime Lighting in the Aftermath of the Turkey-Syria Earthquake Using SDGSAT-1 Satellite Data. Innovation 2023, 4, 100419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).