Prediction of Soil Properties in a Field in Typical Black Soil Areas Using in situ MIR Spectra and Its Comparison with vis-NIR Spectra
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
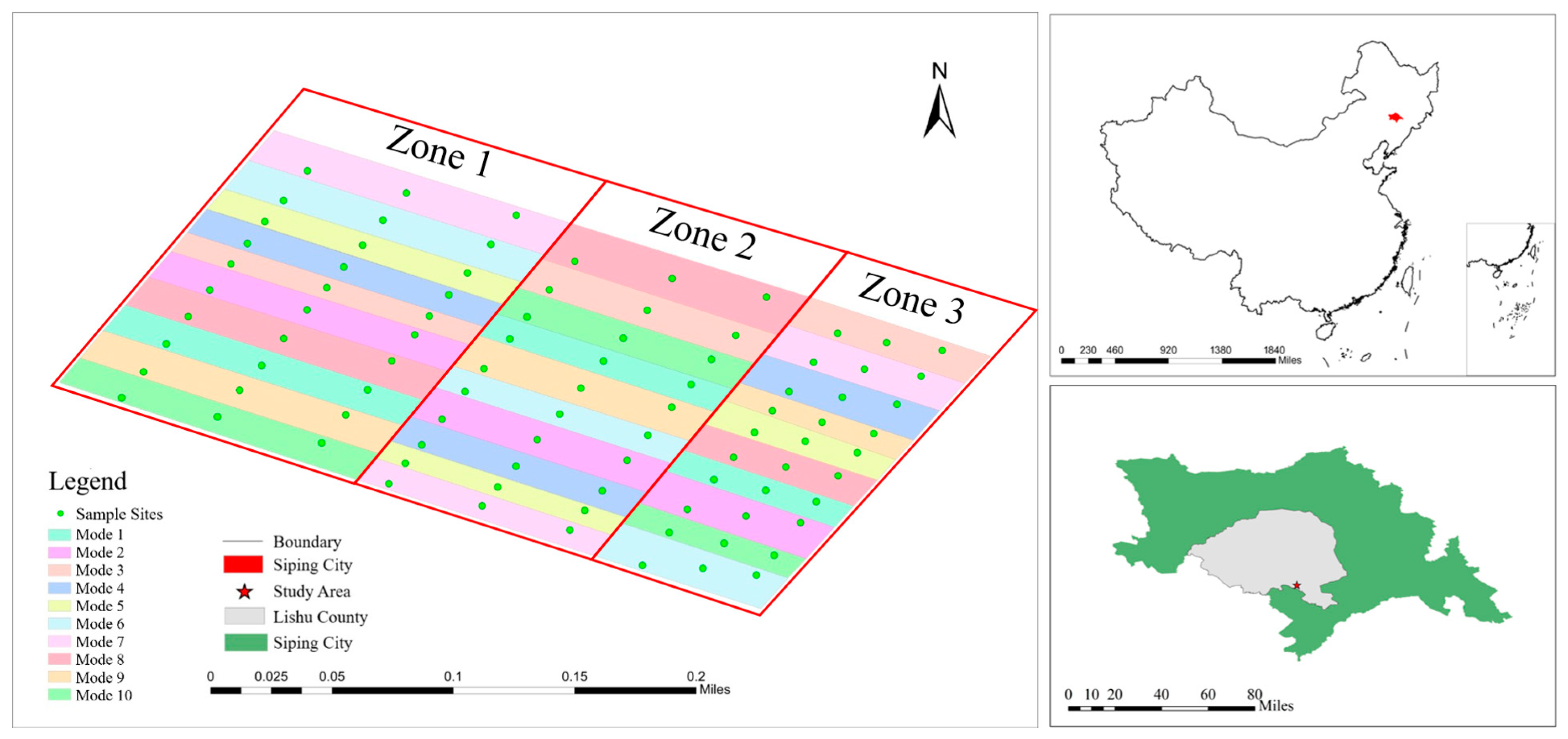
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Soil Samples Collection
| Mode | Tillage Method | Row Spacing | Straw Returning |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mode 1 | Ridge Tillage | 60 cm | No |
| Mode 2 | Ridge Tillage | 60 cm | Yes (cover) |
| Mode 3 | Shallow Rotary Tillage | 40:80 cm | Yes (crushing) |
| Mode 4 | Deep Rotary Tillage | 40:80 cm | Yes (crushing) |
| Mode 5 | Rotary Plowing | 40:80 cm | Yes (crushing) |
| Mode 6 | No Tillage | 40:80 cm | Yes (cover) |
| Mode 7 | No Tillage | 40:100 cm | Yes (cover) |
| Mode 8 | No Tillage | 40:140 cm | Yes (cover) |
| Mode 9 | Strip Tillage | 40:90 cm | Yes (cover) |
| Mode 10 | Strip Tillage | 70 cm | Yes (cover) |
2.3. Soil Spectral Measurement and Chemical Analysis
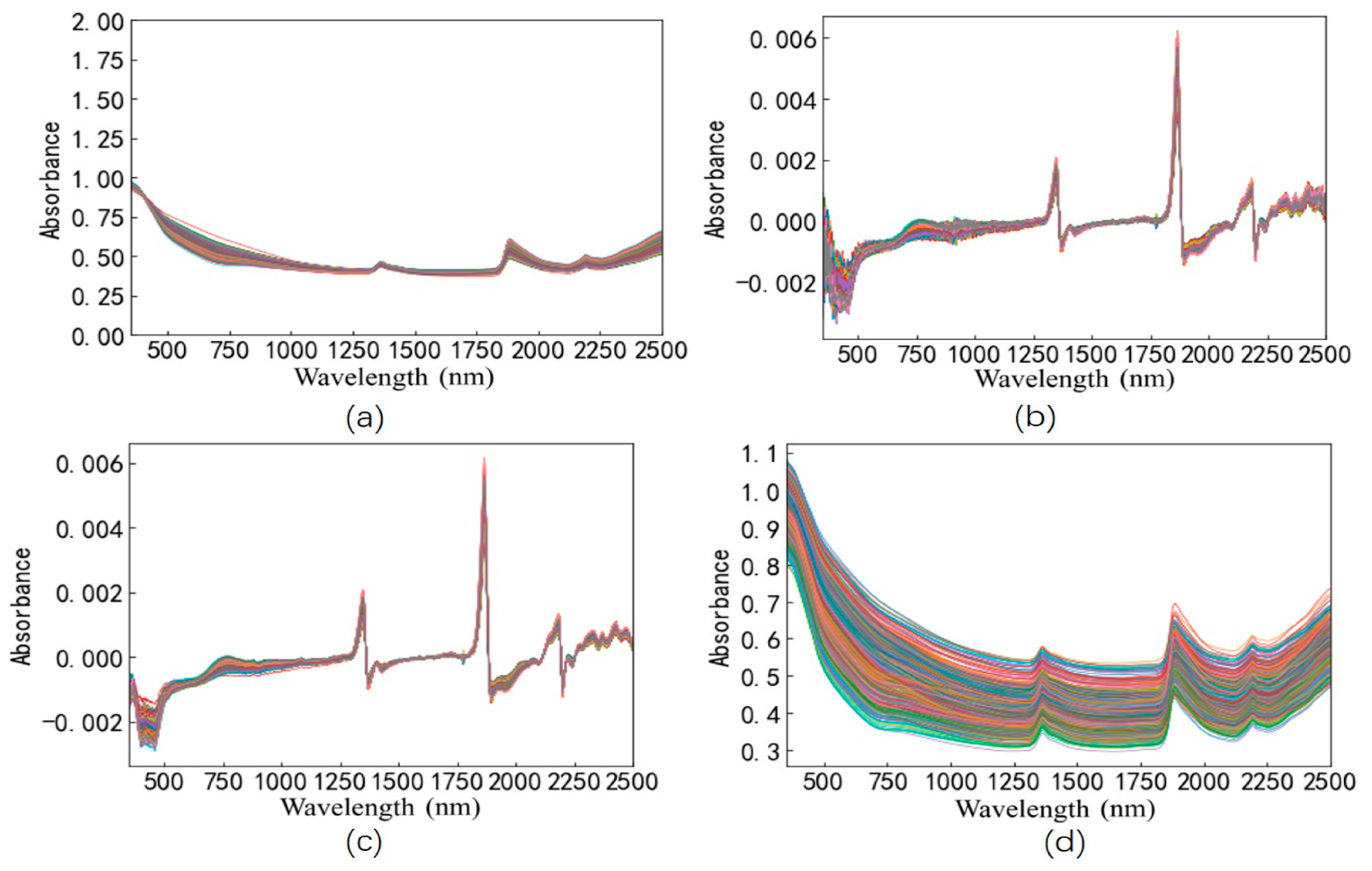
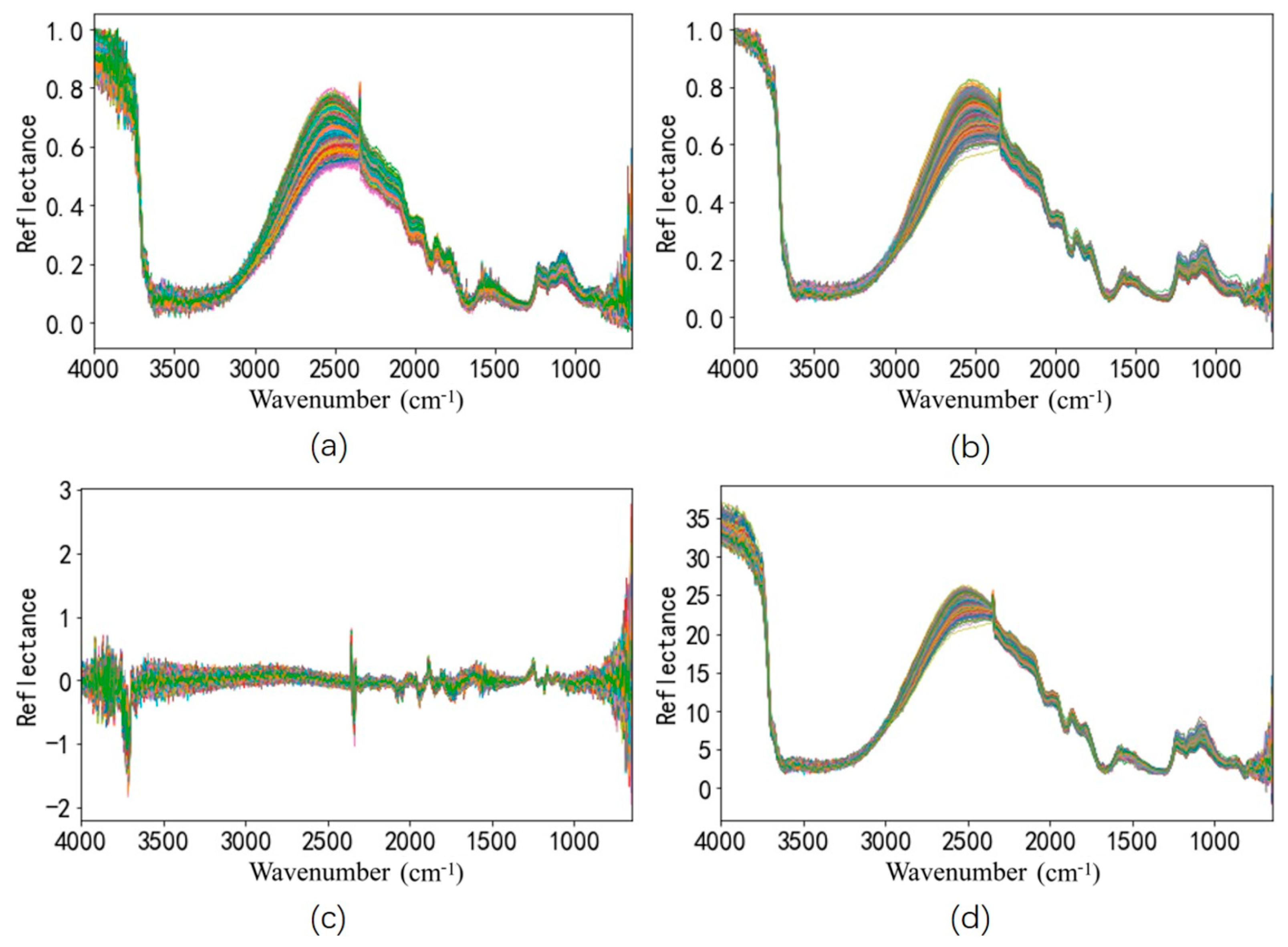
2.3.1. Soil Spectral Measurement
2.3.2. Chemical Analysis
2.4. Pre-Processing of Spectra
2.5. Soil Spectral Predictive Algorithms
2.5.1. Partial Least Squares Regression
2.5.2. Multivariate Adaptive Regression Splines
2.5.3. Random Forest
2.5.4. Data Splitting
2.6. Model Assessment
3. Results
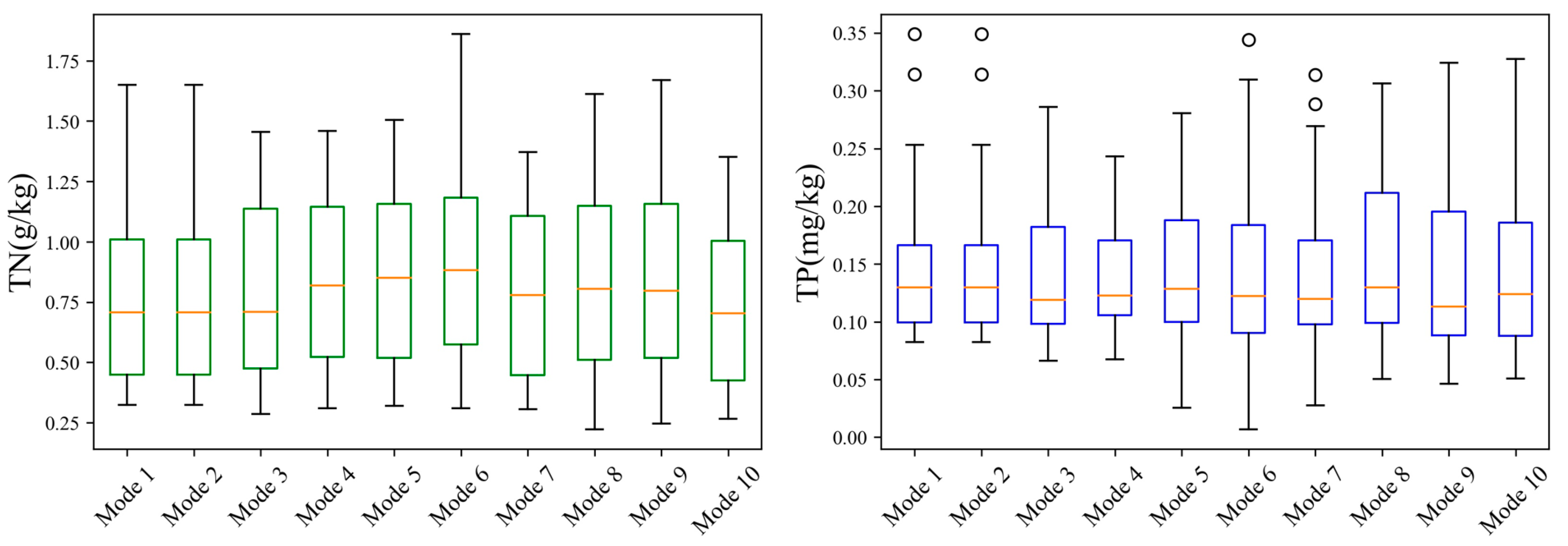
3.1. Soil Properties Distribution
| Soil Properties | Whole Dataset (450) | Training Set (300) | Validation Set (150) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min. | Mean | Max. | SD | Min. | Mean | Max. | SD | Min. | Mean | Max. | SD | |
| TN (g/kg) | 0.22 | 0.82 | 1.86 | 0.37 | 0.22 | 0.84 | 1.86 | 0.36 | 0.28 | 0.79 | 1.65 | 0.35 |
| TP (mg/kg) | 7.00 | 145.26 | 591.96 | 71.13 | 7.00 | 156.03 | 591.96 | 70.25 | 25.70 | 124.28 | 323.79 | 65.49 |
3.2. Comparison of Spectra Pre-Processing Combinations
| Soil Properties | Spectral Preprocessing Combinations | R2 | RMSE | RPD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| vis-NIR | ||||
| TN (g/kg) | ABS+FD | 0.79 | 0.16 | 2.23 |
| ABS+SG | 0.81 | 0.15 | 2.31 | |
| ABS+SG+FD | 0.78 | 0.16 | 2.12 | |
| ABS+MSC+SG | 0.80 | 0.16 | 2.24 | |
| TP (mg/kg) | ABS+FD | 0.26 | 56.09 | 1.17 |
| ABS+SG | 0.48 | 46.93 | 1.40 | |
| ABS+SG+FD | 0.39 | 50.89 | 1.29 | |
| ABS+MSC+SG | 0.25 | 56.71 | 1.16 | |
| MIR | ||||
| TN (g/kg) | MSC+MAN | 0.88 | 0.11 | 3.00 |
| SG+MAN | 0.90 | 0.11 | 3.11 | |
| SG+FD | 0.79 | 0.16 | 2.21 | |
| MSC+SG | 0.81 | 0.15 | 2.31 | |
| TP (mg/kg) | MSC+MAN | 0.21 | 57.26 | 1.13 |
| SG+MAN | 0.33 | 52.60 | 1.23 | |
| SG+FD | 0.25 | 55.69 | 1.16 | |
| MSC+SG | 0.21 | 57.21 | 1.11 | |
3.3. Prediction of Soil Properties Based on in situ Spectra
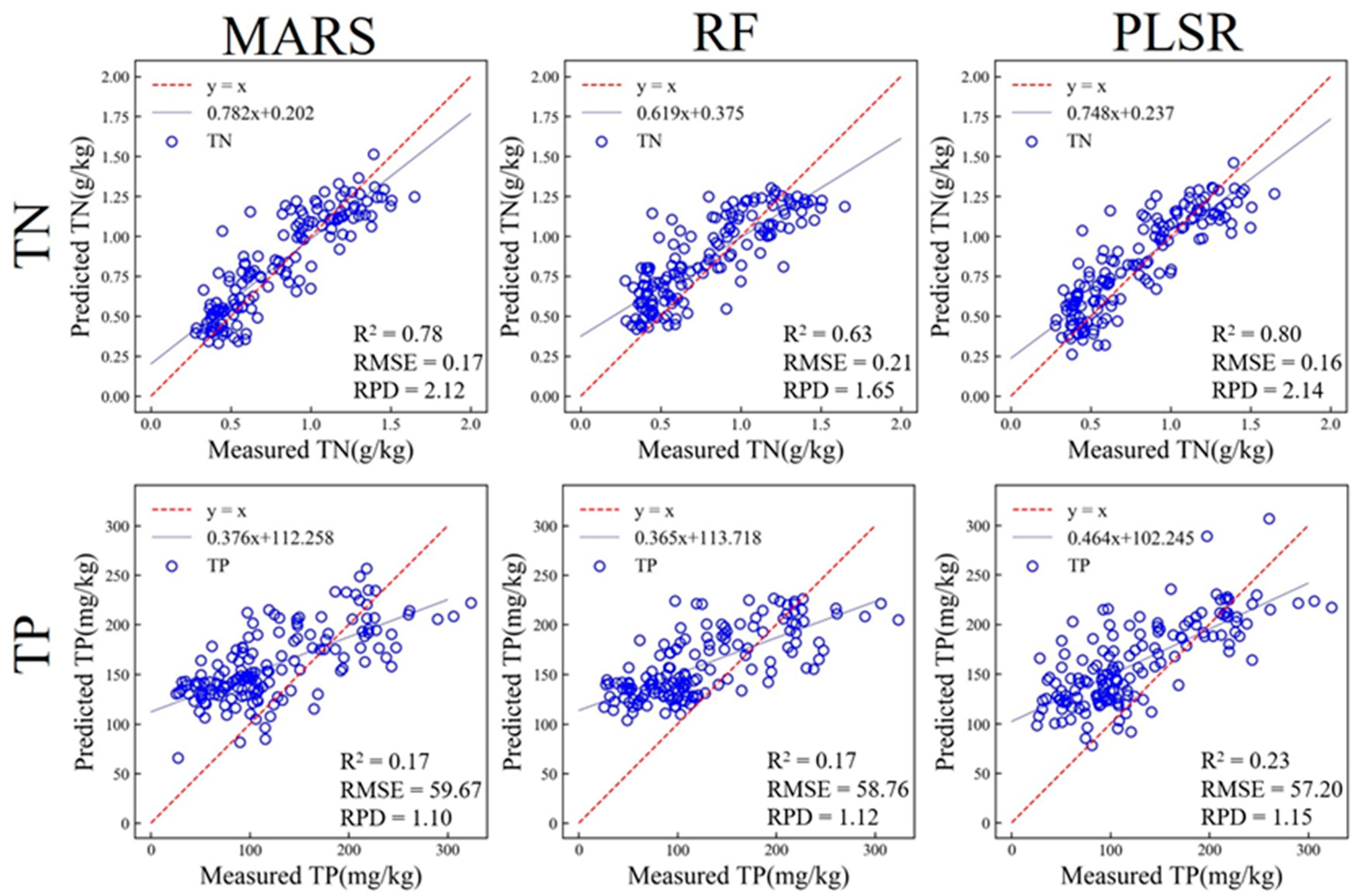
3.3.1. Prediction of Soil Properties Based on in situ vis-NIR
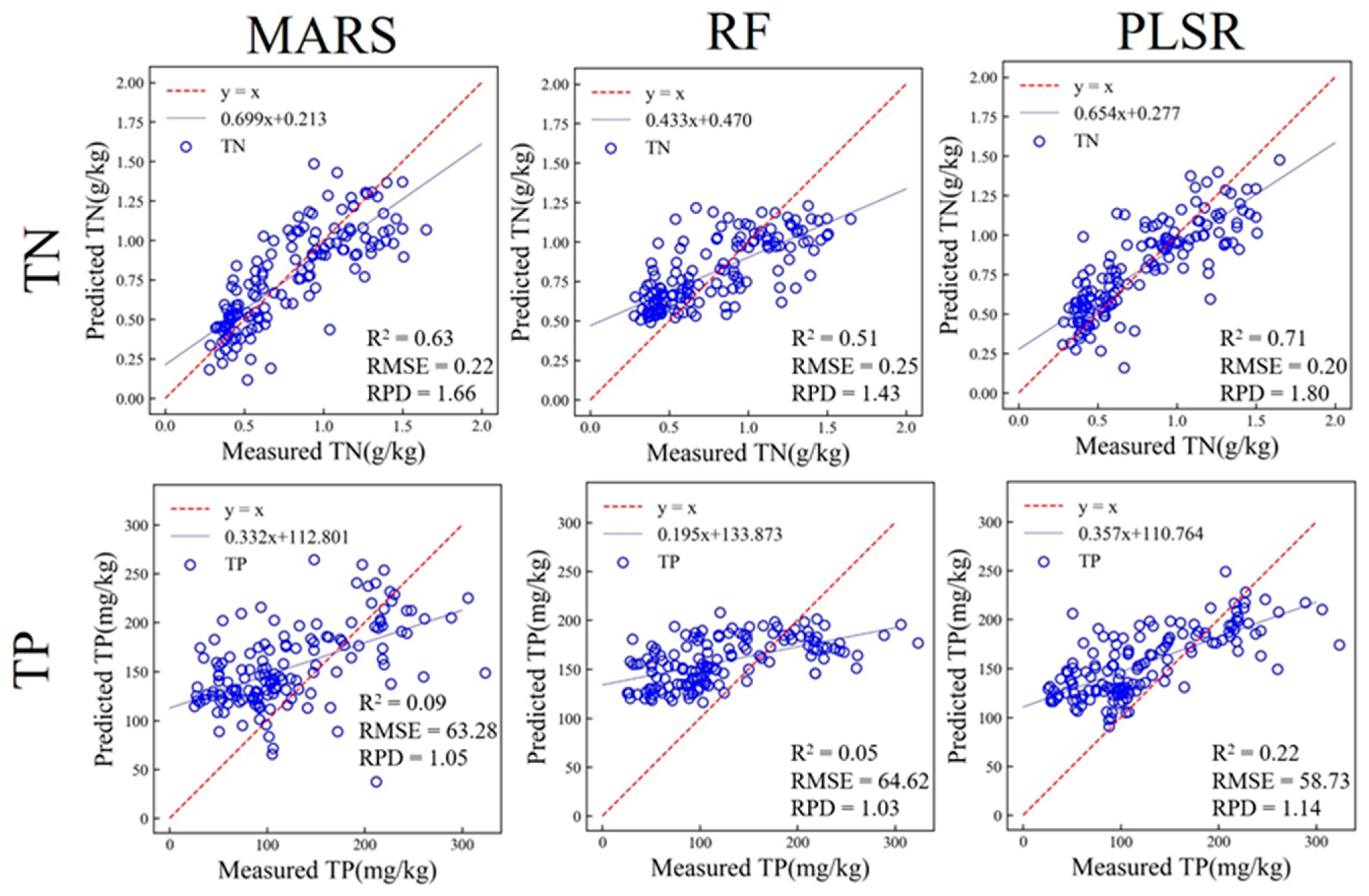
3.3.2. Prediction of Soil Properties Based on in situ MIR
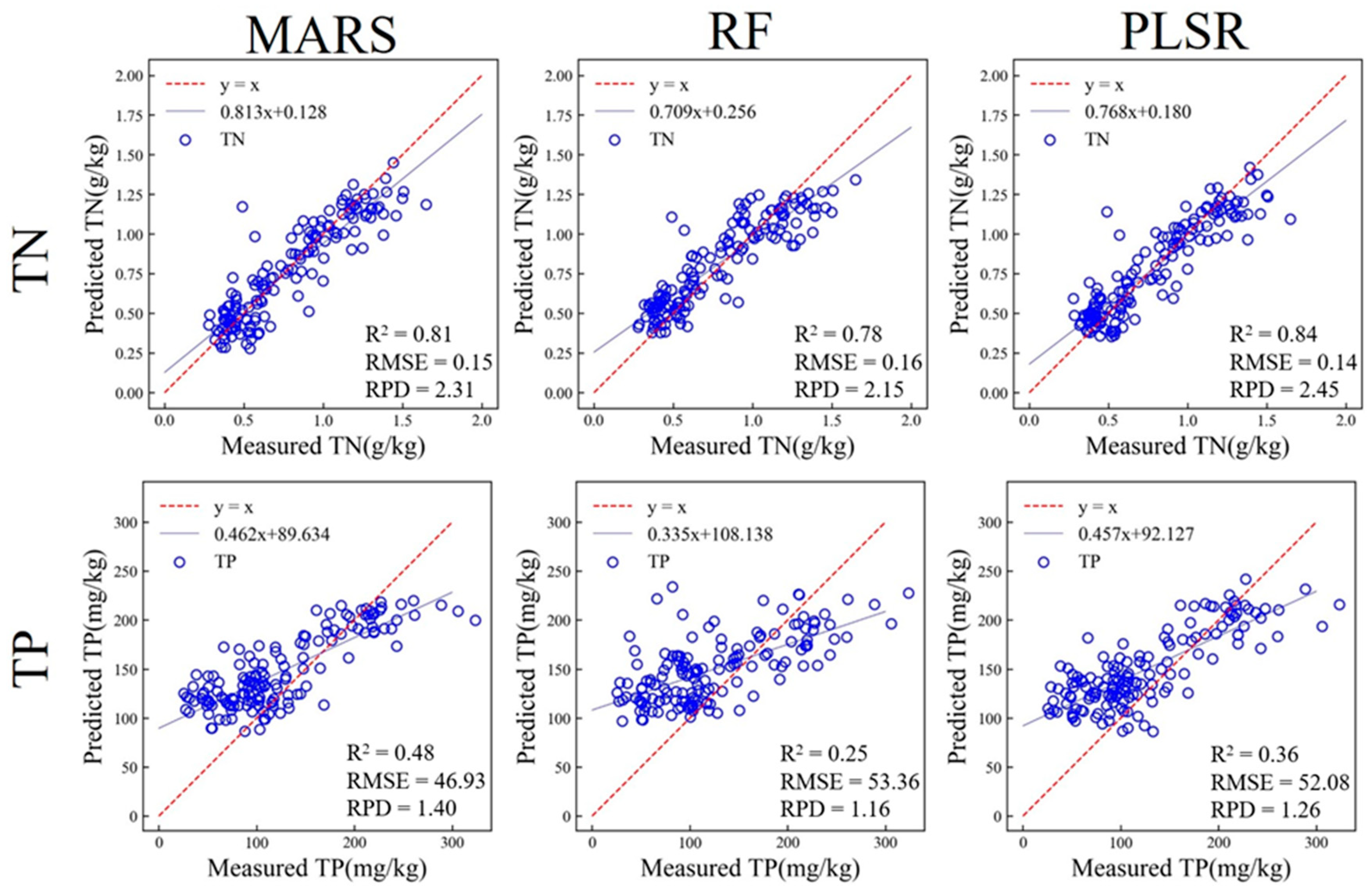
3.4. Prediction of Soil Properties Based on Laboratory Spectra
3.4.1. Prediction of Soil Properties Based on Laboratory vis-NIR
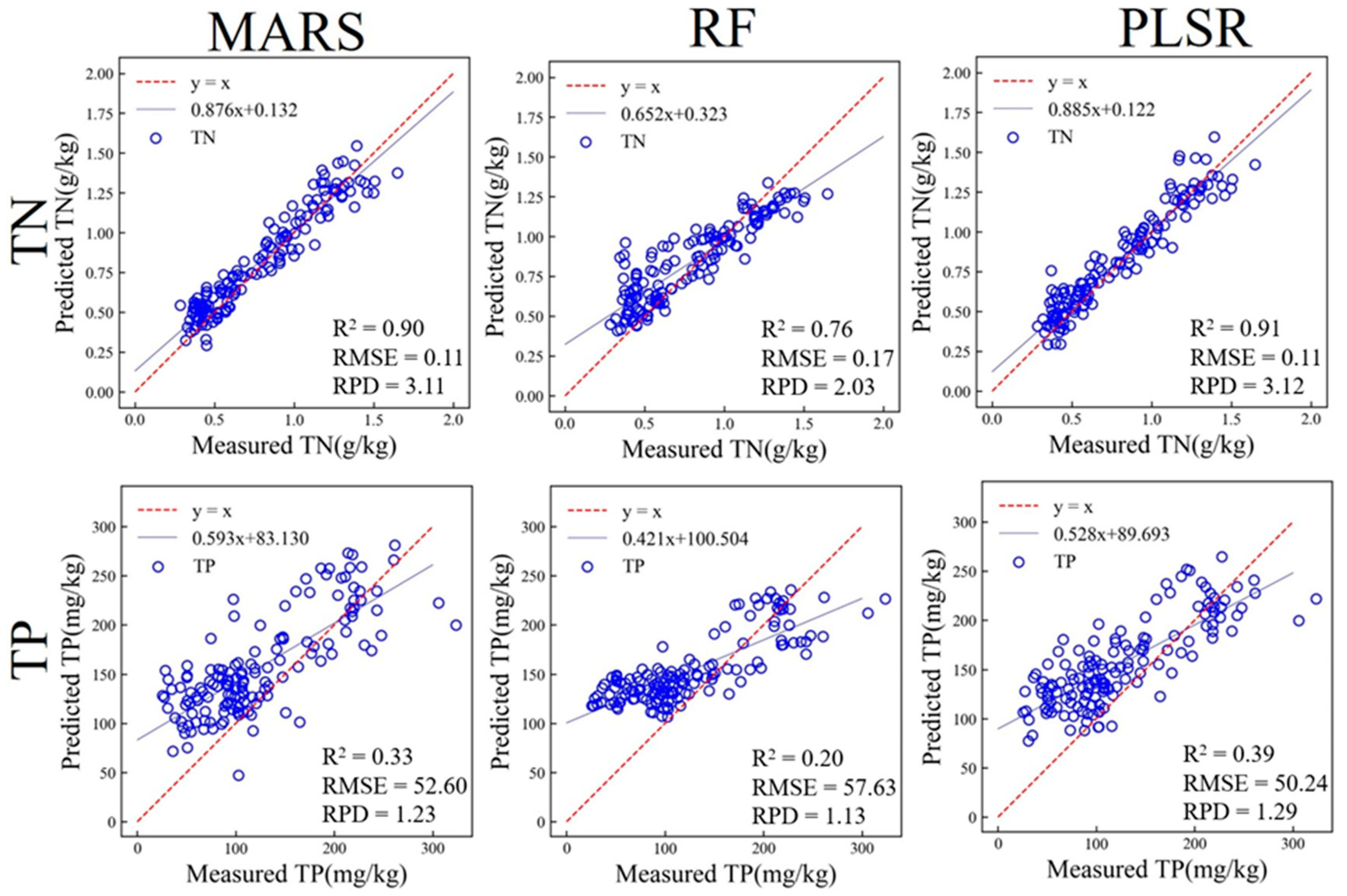
3.4.2. Prediction of Soil Properties Based on Laboratory MIR
| Soil Properties | Modeling Algorithms | Training Set | Validation Set | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | RPD | ||
| in situ vis-NIR | ||||||
| TN (g/kg) | MARS | 0.79 | 0.17 | 0.78 | 0.17 | 2.12 |
| RF | 0.77 | 0.17 | 0.63 | 0.21 | 1.65 | |
| PLSR | 0.77 | 0.17 | 0.80 | 0.16 | 2.14 | |
| TP (mg/kg) | MARS | 0.24 | 61.05 | 0.17 | 59.67 | 1.10 |
| RF | 0.36 | 56.01 | 0.17 | 58.76 | 1.12 | |
| PLSR | 0.33 | 57.34 | 0.23 | 57.20 | 1.15 | |
| in situ MIR | ||||||
| TN (g/kg) | MARS | 0.76 | 0.18 | 0.63 | 0.22 | 1.66 |
| RF | 0.68 | 0.21 | 0.51 | 0.25 | 1.43 | |
| PLSR | 0.73 | 0.19 | 0.71 | 0.20 | 1.80 | |
| TP (mg/kg) | MARS | 0.13 | 66.29 | 0.09 | 63.28 | 1.05 |
| RF | 0.25 | 61.63 | 0.05 | 64.62 | 1.03 | |
| PLSR | 0.22 | 62.85 | 0.22 | 58.73 | 1.14 | |
| Laboratory vis-NIR | ||||||
| TN (g/kg) | MARS | 0.78 | 0.17 | 0.81 | 0.15 | 2.31 |
| RF | 0.87 | 0.13 | 0.78 | 0.16 | 2.15 | |
| PLSR | 0.75 | 0.18 | 0.84 | 0.14 | 2.45 | |
| TP (mg/kg) | MARS | 0.26 | 60.37 | 0.48 | 46.93 | 1.40 |
| RF | 0.63 | 42.27 | 0.25 | 53.36 | 1.16 | |
| PLSR | 0.37 | 55.78 | 0.36 | 52.08 | 1.26 | |
| Laboratory MIR | ||||||
| TN (g/kg) | MARS | 0.87 | 0.13 | 0.90 | 0.11 | 3.11 |
| RF | 0.95 | 0.08 | 0.76 | 0.17 | 2.03 | |
| PLSR | 0.88 | 0.12 | 0.91 | 0.11 | 3.12 | |
| TP (mg/kg) | MARS | 0.45 | 52.67 | 0.33 | 52.60 | 1.23 |
| RF | 0.83 | 29.49 | 0.20 | 57.63 | 1.13 | |
| PLSR | 0.31 | 59.01 | 0.39 | 50.24 | 1.29 | |
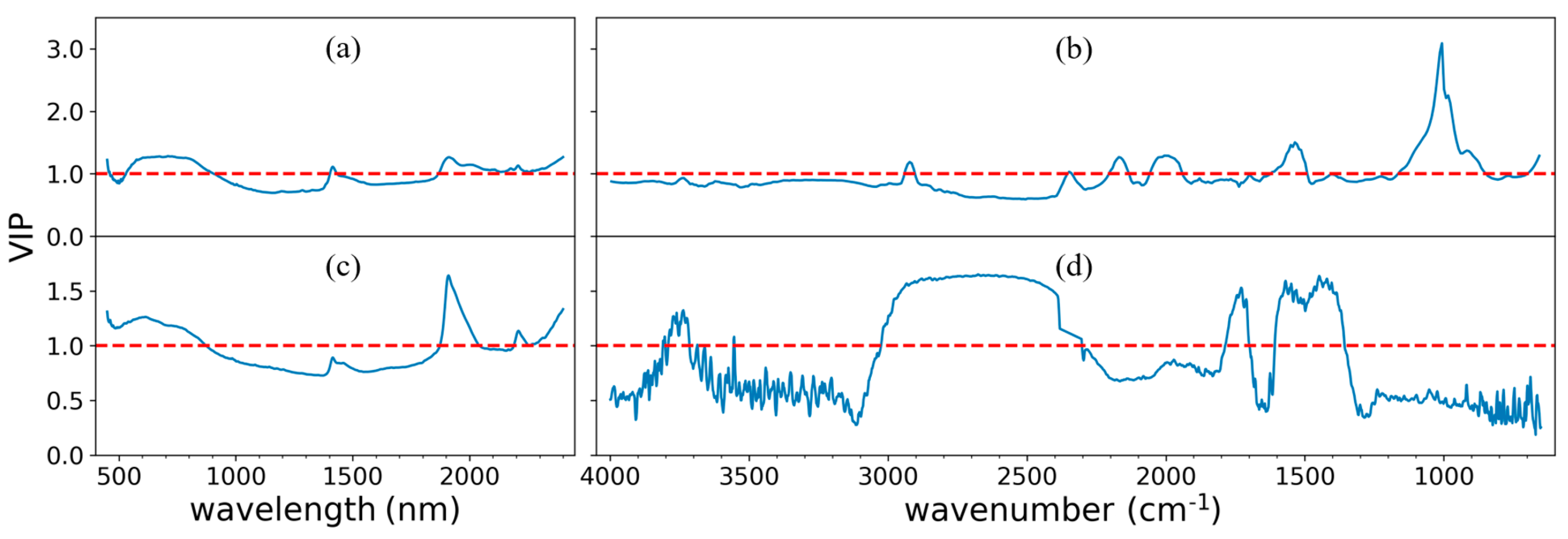
3.5. The Scores of Variable Importance in Projection (VIP)
4. Discussion
4.1. Prediction Performance of Soil Properties Using in situ vs. Laboratory Spectra
4.2. The Feature Bands of TN Prediction with the Four Kinds of Spectra
4.3. Feasibility Analysis for Rapid Prediction of Soil Properties Based on in situ MIR
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Yang, X.M.; Zhang, X.P.; Deng, W.; Fang, H.J. Black Soil Degradation by Rainfall Erosion in Jilin, China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2003, 14, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Liu, W.; Zheng, J.; Luo, Y.; Li, R.; Wang, H.; Qi, H. Effect of Long-Term Tillage on Soil Aggregates and Aggregate-Associated Carbon in Black Soil of Northeast China. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.Z.; Xu, Y.; Chen, S.C.; Xu, S.G.; Zhang, H.W. Soil Loss and Conservation in the Black Soil Region of Northeast China: A Retrospective Study. Environ. Sci. Policy 2010, 13, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Hou, R.; Li, T.; Fu, Q.; Zhang, S.; Su, A.; Xue, P.; Yang, X. Study of Soil Nitrogen Cycling Processes Based on the 15N Isotope Tracking Technique in the Black Soil Areas. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 375, 134173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossel, R.V.; Walvoort, D.J.J.; McBratney, A.B.; Janik, L.J.; Skjemstad, J.O. Visible, near Infrared, Mid Infrared or Combined Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy for Simultaneous Assessment of Various Soil Properties. Geoderma 2006, 131, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Behrens, T.; Ben-Dor, E.; Brown, D.J.; Demattê, J.A.M.; Shepherd, K.D.; Shi, Z.; Stenberg, B.; Stevens, A.; Adamchuk, V.; et al. A Global Spectral Library to Characterize the World’s Soil. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 155, 198–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Xu, H.; Xu, D.; Ji, W.; Li, S.; Yang, M.; Hu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, N.; Arrouays, D.; et al. Evaluating Validation Strategies on the Performance of Soil Property Prediction from Regional to Continental Spectral Data. Geoderma 2021, 400, 115159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossel, R.V.; McBratney, A.B. Soil Chemical Analytical Accuracy and Costs: Implications from Precision Agriculture. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 1998, 38, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janik, L.J.; Merry, R.H.; Skjemstad, J.O. Can Mid Infrared Diffuse Reflectance Analysis Replace Soil Extractions? Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 1998, 38, 681–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocita, M.; Stevens, A.; van Wesemael, B.; Aitkenhead, M.; Bachmann, M.; Barthès, B.; Dor, E.B.; Brown, D.J.; Clairotte, M.; Csorba, A. Soil Spectroscopy: An Alternative to Wet Chemistry for Soil Monitoring. Adv. Agron. 2015, 132, 139–159. [Google Scholar]
- Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Behrens, T.; Ben-Dor, E.; Chabrillat, S.; Demattê, J.A.M.; Ge, Y.; Gomez, C.; Guerrero, C.; Peng, Y.; Ramirez-Lopez, L.; et al. Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy for Estimating Soil Properties: A Technology for the 21st Century. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2022, 73, e13271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBratney, A.; de Gruijter, J.; Bryce, A. Pedometrics Timeline. Geoderma 2019, 338, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poppiel, R.R.; da Silveira Paiva, A.F.; Demattê, J.A.M. Bridging the Gap between Soil Spectroscopy and Traditional Laboratory: Insights for Routine Implementation. Geoderma 2022, 425, 116029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Wang, J.; Zhao, X.; Triantafilis, J. Clay Content Mapping and Uncertainty Estimation Using Weighted Model Averaging. Catena 2022, 209, 105791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Arshad, M.; Li, N.; Triantafilis, J. Predicting Soil Physical and Chemical Properties Using Vis-NIR in Australian Cotton Areas. Catena 2021, 196, 104938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Arshad, M.; Wang, J.; Triantafilis, J. Soil Exchangeable Cations Estimation Using Vis-NIR Spectroscopy in Different Depths: Effects of Multiple Calibration Models and Spiking. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 182, 105990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.; Norris, K. Near-Infrared Technology in the Agricultural and Food Industries; American Association of Cereal Chemists, Inc.: St. Paul, MN, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Janik, L.J.; Skjemstad, J.O.; Raven, M.D. Characterization and Analysis of Soils Using Mid-Infrared Partial Least-Squares. 1. Correlations with XRF-Determined Major-Element Composition. Soil Res. 1995, 33, 621–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossel, R.V.; Walvoort, D.J.J.; MacBratney, A.B. Proximal Sensing of Soil PH and Lime Requirement by Mid Infrared Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy. In Proceedings of the Third European Conference on Precision Agriculture (3 ECPA), Montpellier, France, 18–20 June 2001; pp. 497–502. [Google Scholar]
- Soriano-Disla, J.M.; Janik, L.J.; Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Macdonald, L.M.; McLaughlin, M.J. The performance of visible, near-, and mid-infrared reflectance spectroscopy for prediction of soil physical, chemical, and biological properties. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2014, 49, 139–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarty, G.W.; Reeves, J.B. Comparison of near Infrared and Mid Infrared Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy for Field-Scale Measurement of Soil Fertility Parameters. Soil Sci. 2006, 171, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terra, F.S.; Demattê, J.A.; Rossel, R.A.V. Spectral Libraries for Quantitative Analyses of Tropical Brazilian Soils: Comparing Vis–NIR and Mid-IR Reflectance Data. Geoderma 2015, 255, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenberg, B. Effects of Soil Sample Pretreatments and Standardised Rewetting as Interacted with Sand Classes on Vis-NIR Predictions of Clay and Soil Organic Carbon. Geoderma 2010, 158, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Adamchuk, V.I.; Biswas, A.; Dhawale, N.M.; Sudarsan, B.; Zhang, Y.; Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Shi, Z. Assessment of Soil Properties in Situ Using a Prototype Portable MIR Spectrometer in Two Agricultural Fields. Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 152, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutengs, C.; Seidel, M.; Oertel, F.; Ludwig, B.; Vohland, M. In Situ and Laboratory Soil Spectroscopy with Portable Visible-to-near-Infrared and Mid-Infrared Instruments for the Assessment of Organic Carbon in Soils. Geoderma 2019, 355, 113900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-España, R.; Bueno-Crespo, A.; Soto, J.; Janik, L.J.; Soriano-Disla, J.M. Developing an Intelligent System for the Prediction of Soil Properties with a Portable Mid-Infrared Instrument. Biosyst. Eng. 2019, 177, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources. International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps, 4th ed.; International Union of Soil Sciences (IUSS): Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Geladi, P.; MacDougall, D.; Martens, H. Linearization and Scatter-Correction for near-Infrared Reflectance Spectra of Meat. Appl. Spectrosc. 1985, 39, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinnan, Å.; Van Den Berg, F.; Engelsen, S.B. Review of the Most Common Pre-Processing Techniques for near-Infrared Spectra. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2009, 28, 1201–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellon-Maurel, V.; McBratney, A. Near-Infrared (NIR) and Mid-Infrared (MIR) Spectroscopic Techniques for Assessing the Amount of Carbon Stock in Soils–Critical Review and Research Perspectives. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1398–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wold, S.; Martens, H.; Wold, H. The Multivariate Calibration Problem in Chemistry Solved by the PLS Method. In Matrix Pencils; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1983; pp. 286–293. [Google Scholar]
- Wold, S.; Johansson, E.; Cocchi, M. PLS: Partial Least Squares Projections to Latent Structures. In 3D QSAR in Drug Design: Theory, Methods and Applications; Kluwer ESCOM Science Publisher: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1993; pp. 523–550. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, S.; Shen, R.; Hu, B.; Peng, J.; Wang, N.; Guo, L.; Zhuo, Z.; Yang, Y. Data Mining of Urban Soil Spectral Library for Estimating Organic Carbon. Geoderma 2022, 426, 116102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosselin, R.; Rodrigue, D.; Duchesne, C. A Bootstrap-VIP Approach for Selecting Wavelength Intervals in Spectral Imaging Applications. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2010, 100, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, T.; Sæbø, S.; Liland, K.H. Comparison of Variable Selection Methods in Partial Least Squares Regression. J. Chemom. 2020, 34, e3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, T.; Liland, K.H.; Snipen, L.; Sæbø, S. A Review of Variable Selection Methods in Partial Least Squares Regression. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2012, 118, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihaka, R.; Gentleman, R. R: A Language for Data Analysis and Graphics. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 1996, 5, 299–314. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, J.H. Multivariate Adaptive Regression Splines. Ann. Stat. 1991, 19, 1–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, J.; Chen, Z. Survey of Boosting and Bagging. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2000, 36, 31–32. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.-W.; Laird, D.A.; Mausbach, M.J.; Hurburgh, C.R. Near-Infrared Reflectance Spectroscopy–Principal Components Regression Analyses of Soil Properties. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2001, 65, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Wang, X.; Han, B.; Ouyang, Z.; Duan, X.; Zheng, H.; Miao, H. Soil Carbon Sequestrations by Nitrogen Fertilizer Application, Straw Return and No-Tillage in China’s Cropland. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2009, 15, 281–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittelkow, C.M.; Liang, X.; Linquist, B.A.; Van Groenigen, K.J.; Lee, J.; Lundy, M.E.; Van Gestel, N.; Six, J.; Venterea, R.T.; Van Kessel, C. Productivity Limits and Potentials of the Principles of Conservation Agriculture. Nature 2015, 517, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Ji, W.; Li, B.; Wang, G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, C.; Mouazen, A.M. Effects of Long-Term Straw Return and Environmental Factors on the Spatiotemporal Variability of Soil Organic Matter in the Black Soil Region: A Case Study. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzluebbers, A.J. Soil Organic Matter Stratification Ratio as an Indicator of Soil Quality. Soil Tillage Res. 2002, 66, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, I.; Seidel, M.; Vohland, M.; Koch, H.-J.; Ludwig, B. Performance of in Situ vs Laboratory Mid-Infrared Soil Spectroscopy Using Local and Regional Calibration Strategies. Geoderma 2022, 409, 115614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weindorf, D.C.; Chakraborty, S.; Herrero, J.; Li, B.; Castañeda, C.; Choudhury, A. Simultaneous Assessment of Key Properties of Arid Soil by Combined PXRF and V Is–NIR Data. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2016, 67, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, S.; Hu, B.; Ji, W.; Li, S.; Hong, Y.; Xu, H.; Wang, N.; Xue, J.; Zhang, X.; et al. Global Soil Salinity Prediction by Open Soil Vis-NIR Spectral Library. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.T.; Yang, X.M.; Drury, C.F.; Yang, J.Y.; Zhang, X.D. Predicting Soil Organic Carbon and Total Nitrogen Using Mid- and near-Infrared Spectra for Brookston Clay Loam Soil in Southwestern Ontario, Canada. Can. J. Soil. Sci. 2011, 91, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, J.B., III; Follett, R.F.; McCarty, G.W.; Kimble, J.M. Can near or Mid-Infrared Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy Be Used to Determine Soil Carbon Pools? Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2006, 37, 2307–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, I.; Linsler, D.; Vohland, M.; Ludwig, B. Robustness of Visible Near-Infrared and Mid-Infrared Spectroscopic Models to Changes in the Quantity and Quality of Crop Residues in Soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2020, 84, 963–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vohland, M.; Ludwig, M.; Thiele-Bruhn, S.; Ludwig, B. Determination of Soil Properties with Visible to Near-and Mid-Infrared Spectroscopy: Effects of Spectral Variable Selection. Geoderma 2014, 223, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zhao, R.; Li, S.; Chen, S.; Jiang, Q.; Zhou, L.; Shi, Z. Multi-Sensor Fusion for the Determination of Several Soil Properties in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2019, 70, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, X.; Drury, C.; Chantigny, M.; Gregorich, E.; Miller, J.; Bittman, S.; Reynolds, D.; Yang, J. Infrared Spectroscopy Prediction of Organic Carbon and Total Nitrogen in Soil and Particulate Organic Matter from Diverse Canadian Agricultural Regions. Can. J. Soil. Sci. 2017, 98, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutengs, C.; Eisenhauer, N.; Schaedler, M.; Lochner, A.; Seidel, M.; Vohland, M. VNIR and MIR Spectroscopy of PLFA-Derived Soil Microbial Properties and Associated Soil Physicochemical Characteristics in an Experimental Plant Diversity Gradient. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 160, 108319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; McBratney, A.B. Laboratory Evaluation of a Proximal Sensing Technique for Simultaneous Measurement of Soil Clay and Water Content. Geoderma 1998, 85, 19–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madari, B.E.; Reeves, J.B., III; Machado, P.L.; Guimarães, C.M.; Torres, E.; McCarty, G.W. Mid-and near-Infrared Spectroscopic Assessment of Soil Compositional Parameters and Structural Indices in Two Ferralsols. Geoderma 2006, 136, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.N.; Rencz, A.N. Spectroscopy of Rocks and Minerals, and Principles of Spectroscopy. Man. Remote Sens. 1999, 3, 3–58. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Dor, E. Quantitative Remote Sensing of Soil Properties. Adv. Agron. 2002, 75, 173–243. [Google Scholar]
- Cobo, J.G.; Dercon, G.; Yekeye, T.; Chapungu, L.; Kadzere, C.; Murwira, A.; Delve, R.; Cadisch, G. Integration of Mid-Infrared Spectroscopy and Geostatistics in the Assessment of Soil Spatial Variability at Landscape Level. Geoderma 2010, 158, 398–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelago, A.; Bibiso, M. Performance of Mid Infrared Spectroscopy to Predict Nutrients for Agricultural Soils in Selected Areas of Ethiopia. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijewardane, N.K.; Ge, Y.; Wills, S.; Libohova, Z. Predicting Physical and Chemical Properties of US Soils with a Mid-Infrared Reflectance Spectral Library. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2018, 82, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salisbury, J.W.; D’Aria, D.M. Infrared (8–14 μm) Remote Sensing of Soil Particle Size. Remote Sens. Environ. 1992, 42, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutengs, C.; Ludwig, B.; Jung, A.; Eisele, A.; Vohland, M. Comparison of Portable and Bench-Top Spectrometers for Mid-Infrared Diffuse Reflectance Measurements of Soils. Sensors 2018, 18, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Lin, Q.; Huang, X.; Shen, Y.; Wang, L. Experimental Study on Total Nitrogen Concentration in Soil by VNIR Reflectance Spectrum. Geogr. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2005, 21, 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Bai, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Yang, L. Determination for total nitrogen content in black soil using hyperspectral data. Trans. CSAE 2010, 26, 256–261. [Google Scholar]
- Breure, T.S.; Prout, J.M.; Haefele, S.M.; Milne, A.E.; Hannam, J.A.; Moreno-Rojas, S.; Corstanje, R. Comparing the Effect of Different Sample Conditions and Spectral Libraries on the Prediction Accuracy of Soil Properties from Near- and Mid-Infrared Spectra at the Field-Scale. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 215, 105196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- England, J.R.; Viscarra Rossel, R.A. Proximal Sensing for Soil Carbon Accounting. Soil 2018, 4, 101–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, A.; De Neve, S.; Mouazen, A.M. Current Sensor Technologies for in Situ and On-Line Measurement of Soil Nitrogen for Variable Rate Fertilization: A Review. Adv. Agron. 2021, 168, 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Seidel, M.; Vohland, M.; Greenberg, I.; Ludwig, B.; Ortner, M.; Thiele-Bruhn, S.; Hutengs, C. Soil Moisture Effects on Predictive VNIR and MIR Modeling of Soil Organic Carbon and Clay Content. Geoderma 2022, 427, 116103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, J.; Shi, Z.; Li, B.; Sun, F.; Miao, T.; Shi, Z.; Chen, S.; Yang, M.; Ji, W. Prediction of Soil Properties in a Field in Typical Black Soil Areas Using in situ MIR Spectra and Its Comparison with vis-NIR Spectra. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2053. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15082053
Yin J, Shi Z, Li B, Sun F, Miao T, Shi Z, Chen S, Yang M, Ji W. Prediction of Soil Properties in a Field in Typical Black Soil Areas Using in situ MIR Spectra and Its Comparison with vis-NIR Spectra. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(8):2053. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15082053
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Jianxin, Zhan Shi, Baoguo Li, Fujun Sun, Tianyu Miao, Zhou Shi, Songchao Chen, Meihua Yang, and Wenjun Ji. 2023. "Prediction of Soil Properties in a Field in Typical Black Soil Areas Using in situ MIR Spectra and Its Comparison with vis-NIR Spectra" Remote Sensing 15, no. 8: 2053. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15082053
APA StyleYin, J., Shi, Z., Li, B., Sun, F., Miao, T., Shi, Z., Chen, S., Yang, M., & Ji, W. (2023). Prediction of Soil Properties in a Field in Typical Black Soil Areas Using in situ MIR Spectra and Its Comparison with vis-NIR Spectra. Remote Sensing, 15(8), 2053. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15082053








