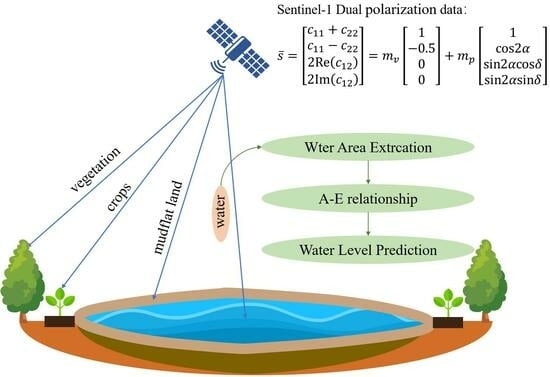
Water Area Extraction and Water Level Prediction of Dongting Lake Based on Sentinel-1 Dual-Polarization Data Decomposition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
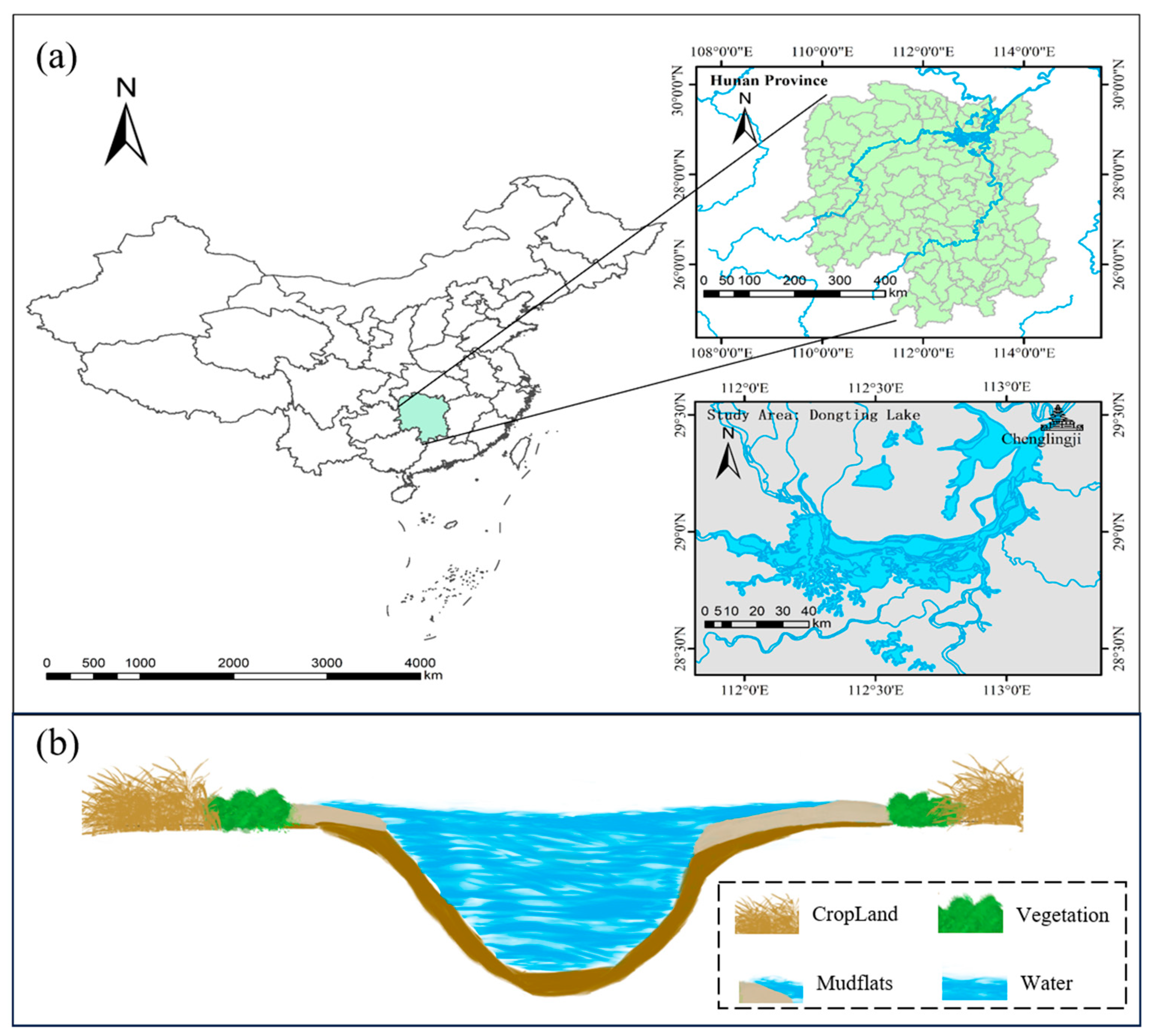
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. SAR Data
2.2.2. Optical Image Data
2.2.3. Water Level Data
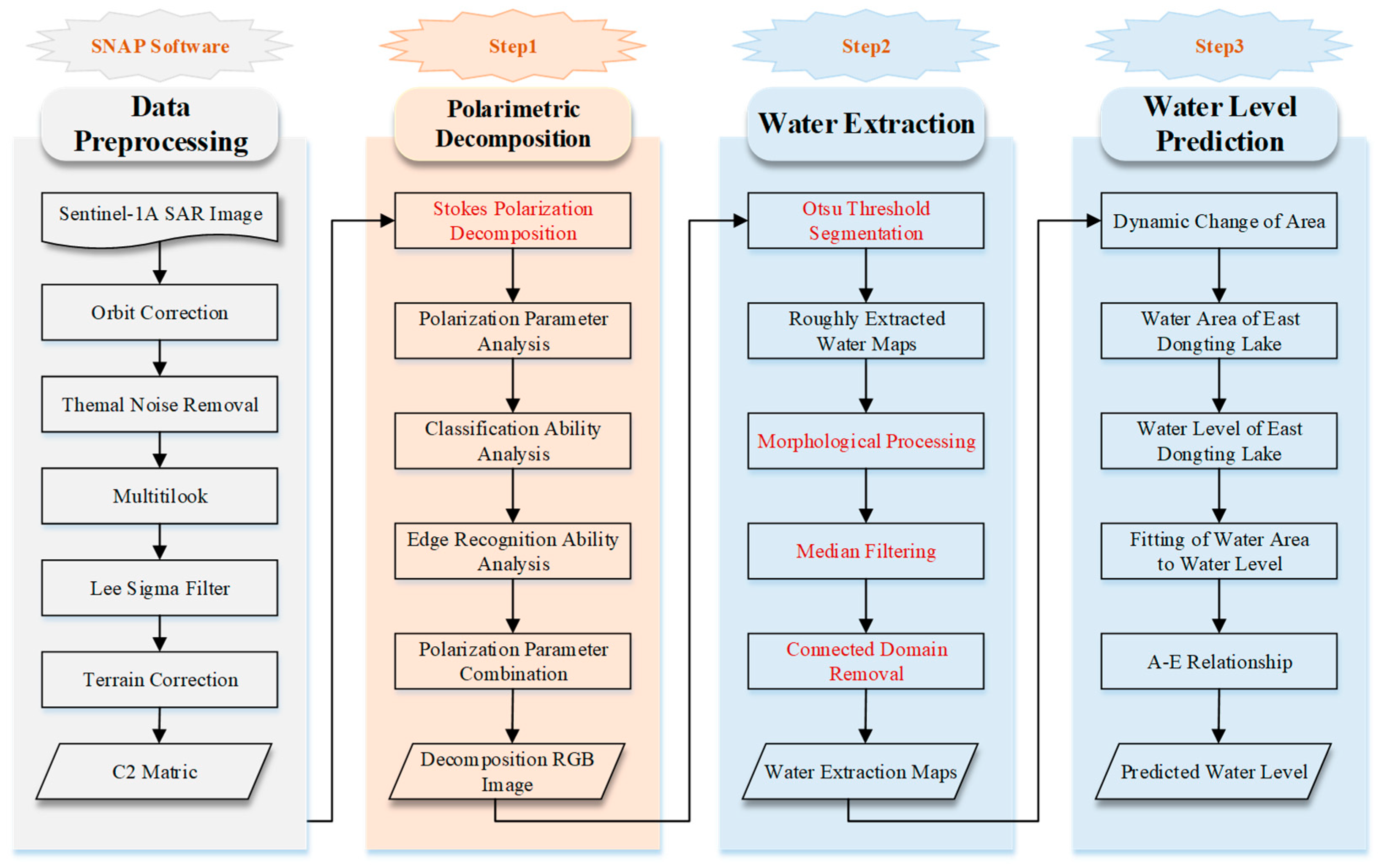
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Data Preprocessing
2.3.2. Stokes Decomposition
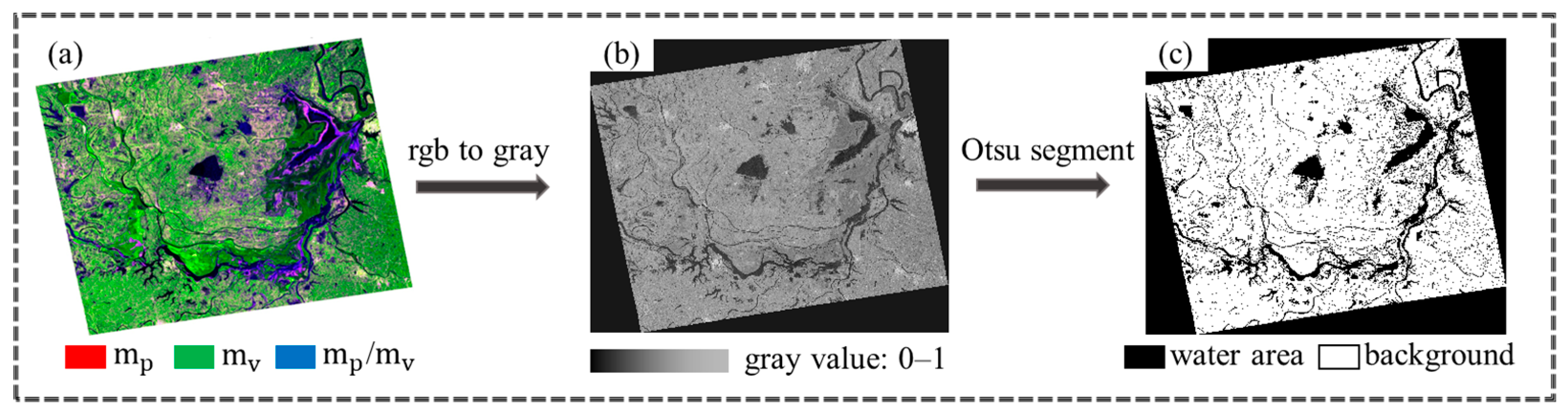
2.3.3. Otsu Threshold Segmentation Algorithm
2.3.4. Morphological Operation and Filtering
3. Results and Discussion
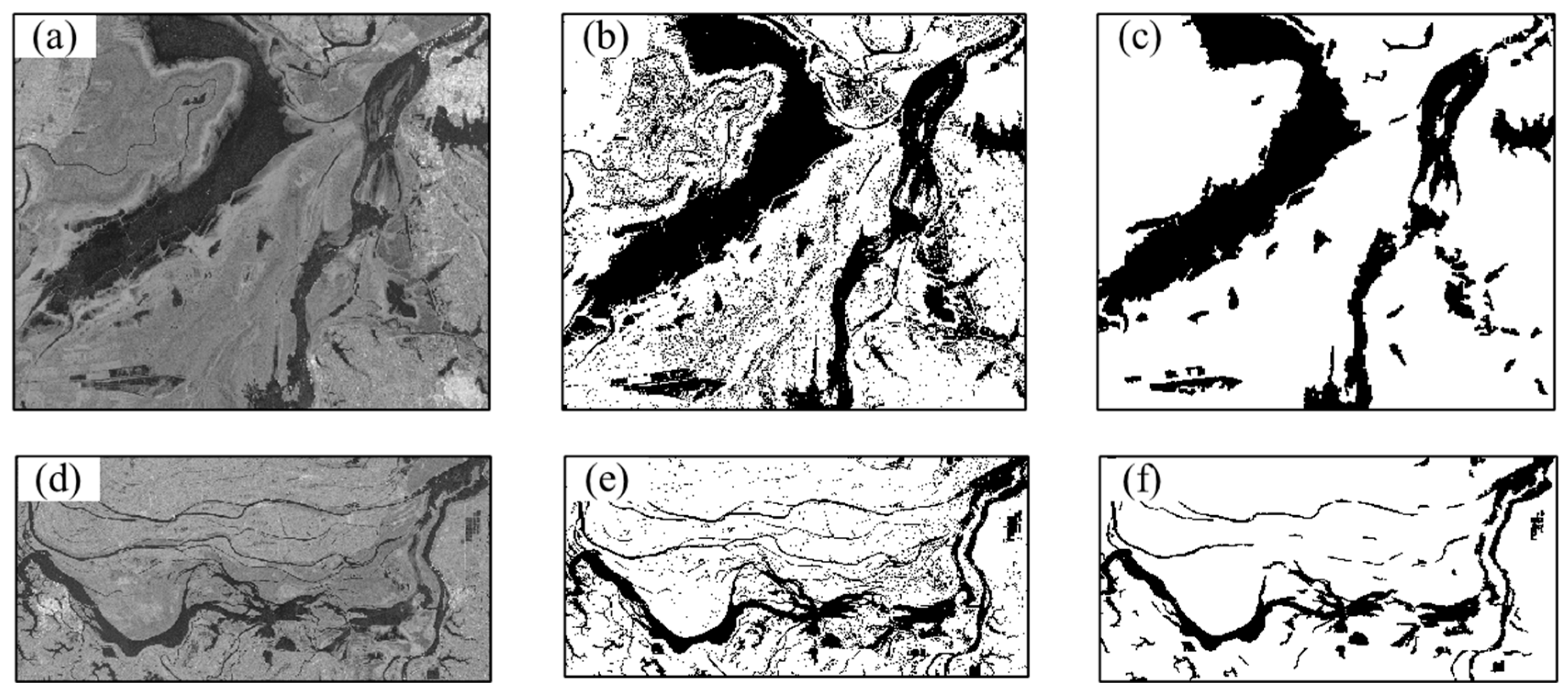
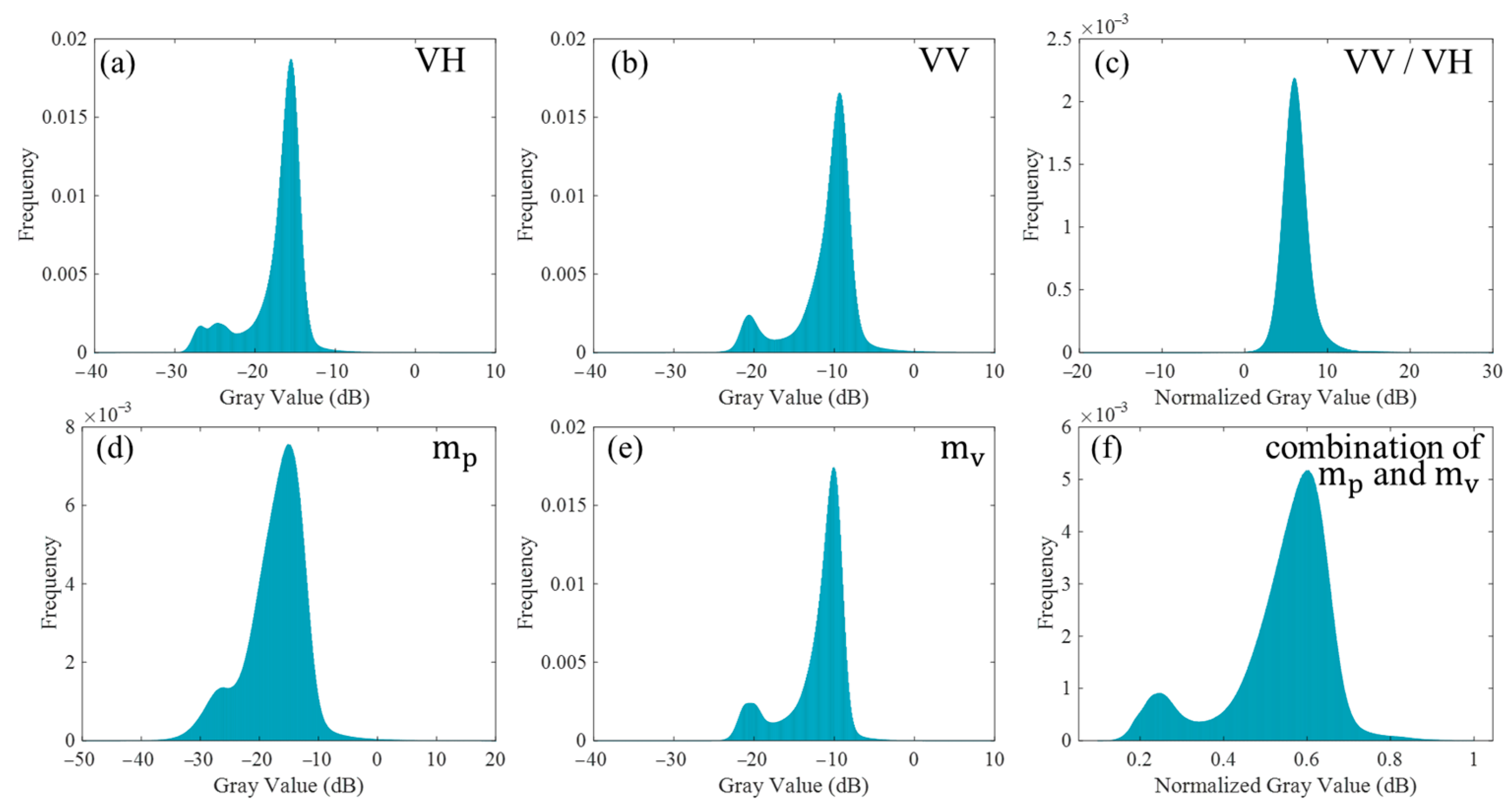
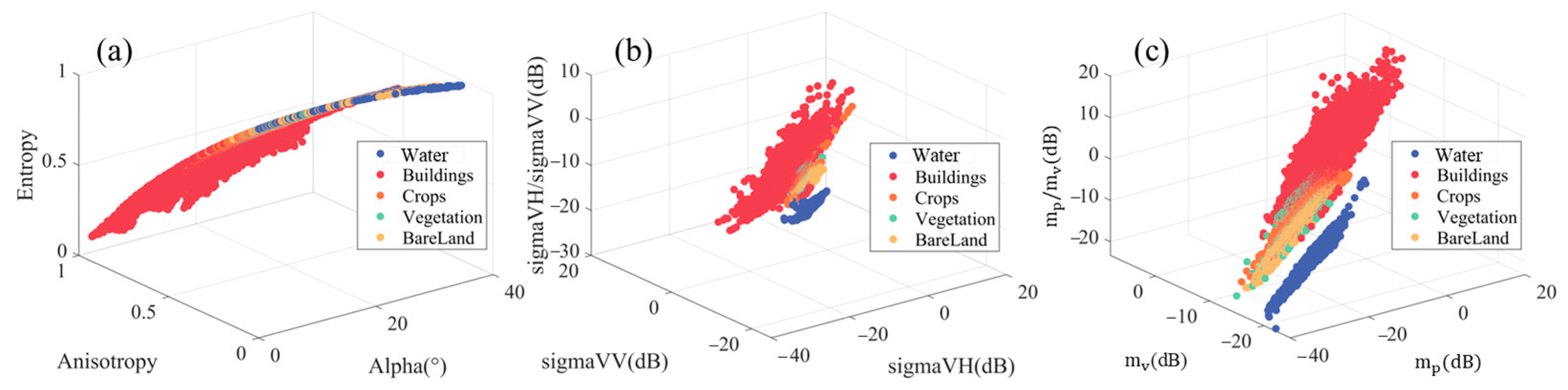
3.1. Polarization Decomposition of Dongting Lake
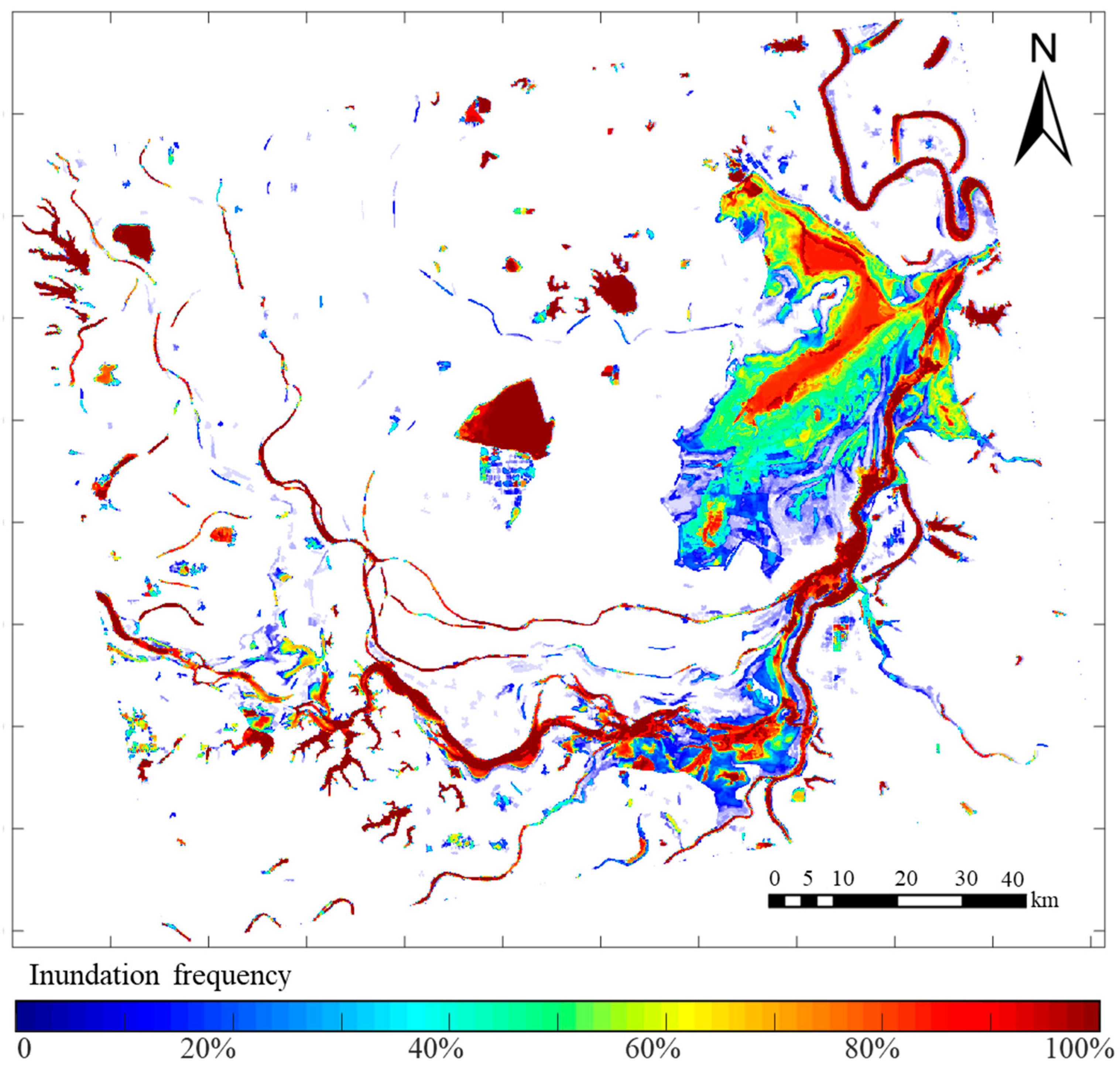
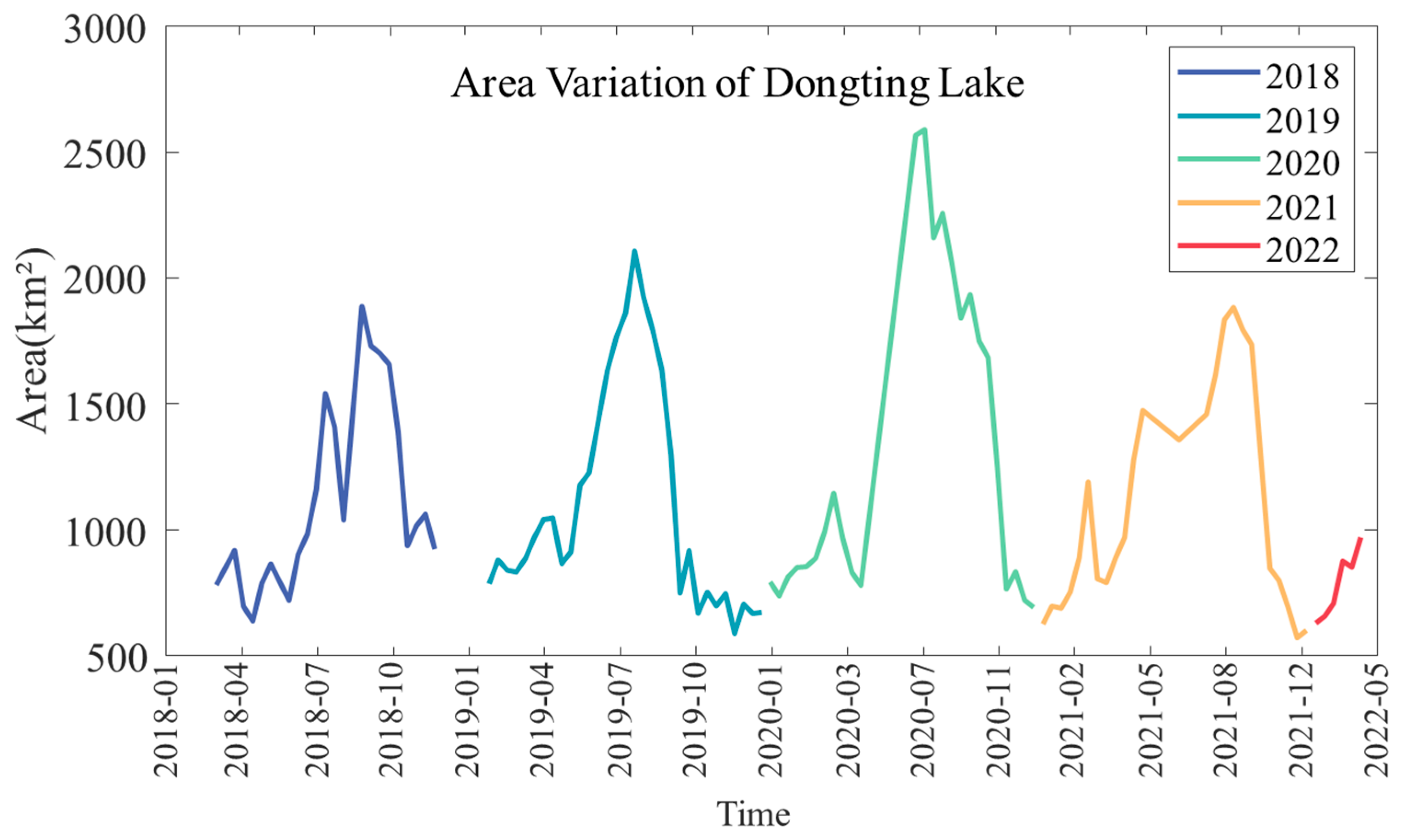
3.2. Dongting Lake Water Area Extraction
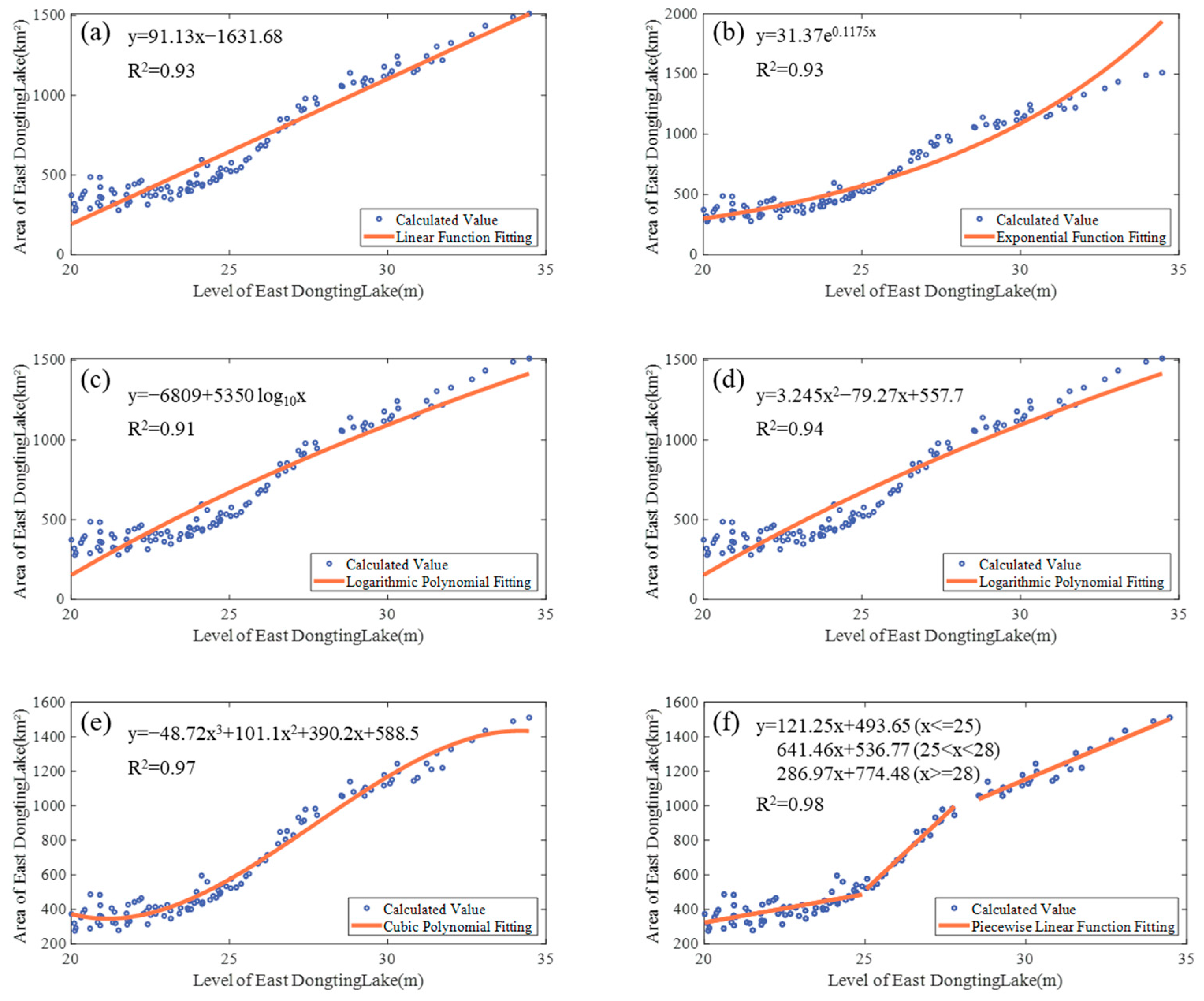
3.3. Relation between Area and Water Level of East Dongting Lake
3.4. The Predicted Water Area and Water Level
3.5. Method Performance Analysis
3.5.1. Water Body Segmentation Algorithm
3.5.2. Water Area Extraction
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- As for the Stokes polarization decomposition method, this paper proves that it has a certain classification ability in the Dongting Lake wetland and can distinguish water from other types of ground objects. At the edge of Dongting Lake, this method makes full use of Sentinel-1 SAR data polarization information and can clearly distinguish between dry mudflats and lake water, which is of great significance for the accurate extraction of water areas.
- (2)
- For the extraction of the water area of Dongting Lake, this paper combines Otsu threshold segmentation, morphological processing, and connected domain removal methods to obtain accurate and reliable water extraction results and realize the long-term dynamic monitoring of the Dongting Lake area. The Otsu threshold segmentation algorithm has a good effect on the segmentation of the Stokes polarization decomposition parameters and can obtain a binary segmentation map of water quickly and easily. The interference of other small water areas can be eliminated through morphological filtering and connected domain removal. For areas with more clouds and rain, SAR data can make up for the shortage of optical images and obtain accurate water areas, to realize the dynamic monitoring of lake areas.
- (3)
- For the relationship between the water area and water level of East Dongting Lake, this paper uses several different functional models to describe the relationship between them and finds that the piecewise linear function model can better fit the water area and water level of East Dongting Lake (R2 = 0.98). At the same time, we use the measured water level data to verify the obtained function model. It is found that the RMSE of the water level predicted by the model is 0.4857 m, and the R2 is 0.9930, which further confirms the reliability of the A–E relationship constructed using the method in this paper and provides a good idea for the water level monitoring of lakes lacking hydrological observation stations.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allen, M.R.; Ingram, W. Constraints on future changes in climate and the hydrologic cycle. Nature 2002, 419, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehner, B.; Döll, P. Development and validation of a global database of lakes, reservoirs and wetlands. J. Hydrol. 2004, 296, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Li, X. Monitoring of the water-area variations of Lake Dongting in China with ENVISAT ASAR images. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2011, 13, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.C.; Sheng, Y.; MacDonald, G.M.; Hinzman, L.D. Disappearing Arctic Lakes. Science 2005, 308, 1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; Green, P.; Salisbury, J.; Lammers, R.B. Global Water Resources: Vulnerability from Climate Change and Population Growth. Science 2000, 289, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolway, R.; Kraemer, B.; Lenters, J.; Merchant, C.; Oreilly, C.; Sharma, S. Global lake responses to climate change. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 388–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilby, R.; Battarbee, R.; Kernan, M.; Wade, A. A Review of the Potential Impacts of Climate Change on Surface Water Quality. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2009, 54, 101–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.Q.; Xie, H.J.; Kang, S.C.; Yi, D.H.; Ackley, S.F. Monitoring lake level changes on the Tibetan Plateau using ICESat altimetry data (2003–2009). Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.L. Satellite remote sensing of large lakes and reservoirs: From elevation and area to storage. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2015, 2, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, S.C.J.; Kutser, T.; Hunter, P.D. Remote sensing of inland waters: Challenges, progress and future directions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 157, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, K.; Li, Y. Changes in Lake Area in Response to Climatic Forcing in the Endorheic Hongjian Lake Basin, China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, R.W.; Shu, H.; Yaseen, A.; Sajjad, A.; Abidin, S.Z.U. Identification of time-varying wetlands neglected in Pakistan through remote sensing techniques. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 74031–74044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop-Taylor, R.; Sagar, S.; Lymburner, L.; Alam, I.; Sixsmith, J. Sub-Pixel Waterline Extraction: Characterising Accuracy and Sensitivity to Indices and Spectra. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Liu, T. The Impact of Artificial Wetland Expansion on Local Temperature in the Growing Season—The Case Study of the Sanjiang Plain, China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, P.S.; Page, K.J. Water body detection and delineation with Landsat TM data. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2000, 66, 1461–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthon, J.F.; Zibordi, G. Optically black waters in the northern Baltic Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L09605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, A.; Flood, N.; Danaher, T. Comparing Landsat water index methods for automated water classification in eastern Australia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 175, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFeeters, S.K. The use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. Modification of normalised difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y. A Study on Information Extraction of Water System in Semi-arid Regions with the Enhanced Water Index (EWI) and GIS Based Noise Remove Techniques. Remote Sens. Inf. 2007, 6, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyisa, G.L.; Meilby, H.; Fensholt, R.; Proud, S. Automated Water Extraction Index: A New Technique for Surface Water Mapping Using Landsat Imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markert, K.N.; Chishtie, F.A.; Anderson, E.R.; Saah, D.S.; Griffin, R.E. On the merging of optical and SAR satellite imagery for surface water mapping applications. Results Phys. 2018, 9, 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisco, B.; Touzi, R.; van der Sanden, J.J.; Charbonneau, F.; Pultz, T.J.; D’Iorio, M. Water resource applications with RADARSAT-2-a preview. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2008, 1, 130–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.Z.; Guo, H.D.; Liao, J.J. Object oriented method for detection of inundation extent using multi-polarized synthetic aperture radar image. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2008, 2, 23512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsyganskaya, V.; Martinis, S.; Marzahn, P. Flood Monitoring in Vegetated Areas Using Multitemporal Sentinel-1 Data: Impact of Time Series Features. Water 2019, 11, 1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerhoff, R.S.; Kleuskens, M.P.H.; Winsemius, H.C.; Huizinga, H.J.; Brakenridge, G.R.; Bishop, C. Automated global water mapping based on wide-swath orbital synthetic-aperture radar. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twele, A.; Cao, W.; Plank, S.; Martinis, S. Sentinel-1-based flood mapping: A fully automated processing chain. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 2990–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, G.X.; Zhang, R.; Fu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Cai, J.L.; Wang, X.W.; Li, Z.L. Monitoring Dynamic Evolution of the Glacial Lakes by Using Time Series of Sentinel-1A SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.R.; Xie, F.; Ling, F.; Du, Y. Monitoring Surface Water Inundation of Poyang Lake and Dongting Lake in China Using Sentinel-1 SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binh, P.D.; Prigent, C.; Aires, F. Surface Water Monitoring within Cambodia and the Vietnamese Mekong Delta over a Year, with Sentinel-1 SAR Observations. Water 2017, 9, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amitrano, D.; Di Martino, G.; Iodice, A.; Riccio, D.; Ruello, G. Unsupervised Rapid Flood Mapping Using Sentinel-1 GRD SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 3290–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.Y.; Liu, D.S. A local thresholding approach to flood water delineation using Sentinel-1 SAR imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2020, 159, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.R.; Pottier, E. A review of target decomposition theorems in radar polarimetry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1996, 34, 498–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascolo, L.; Cloude, S.R.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.M. Model-Based Decomposition of Dual-Pol SAR Data: Application to Sentinel-1. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsu, N. A Threshold Selection Method from Gray-Level Histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, J.P.F. Image Analysis and Mathematical Morphology; International Biometric Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1983; Volume 39, pp. 536–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Xue, H.P.; Wu, S.J.; Ling, F.; Xiao, F.; Wei, X.H. Lake area changes in the middle Yangtze region of China over the 20th century. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 1248–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Q.; Xu, K.Q.; Yang, Y.H.; Qi, L.H.; Hayashi, S.; Watanabe, M. Measuring water storage fluctuations in Lake Dongting, China, by Topex/Poseidon satellite altimetry. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2006, 115, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zeng, G.; Liang, J.; Huang, L.; Hua, S.; Li, F.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, H.; Liu, J.; He, X.; et al. Variation of water level in Dongting Lake over a 50-year period: Implications for the impacts of anthropogenic and climatic factors. J. Hydrol. 2015, 525, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.Q.; Fang, J.Y. Impact of impoldering and lake restoration on land-cover changes in Dongting Lake area, Central Yangtze. AMBIO 2004, 33, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESA. Sentinel-1 Technical Guides. Available online: https://sentinel.esa.int/web/sentinel/technical-guides/sentinel-1-sar (accessed on 2 July 2022).
- Torres, R.; Snoeij, P.; Geudtner, D.; Bibby, D.; Davidson, M.; Attema, E.; Potin, P.; Rommen, B.; Floury, N.; Brown, M.; et al. GMES Sentinel-1 mission. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascolo, L.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.M.; Cloude, S.R. Thermal Noise Removal from Polarimetric Sentinel-1 Data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 4009105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajnsek, I.; Desnos, Y.-L. Polarimetric Synthetic Aperture Radar Principles and Application: Principles and Application; Springer: Cham, Swizerland, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, A.B.; Luque-Escamilla, P.L.; Martínez-Aroza, J.; Román-Roldán, R. Removing Noise and Preserving Details with Relaxed Median Filters. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 1999, 11, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.; Pottier, E. An entropy based classication scheme for land applications of polarimetric SAR. Geosci. Remote Sens. IEEE Trans. 1997, 35, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, C.; Long, Y.; Deng, B.; Jiang, J.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Z. Study on the Water Level–Discharge Relationship Changes in Dongting Lake Outlet Section over 70 Years and the Impact of Yangtze River Backwater Effect. Water 2023, 15, 2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.Z.; Xiong, L.H.; Guo, S.L.; Shu, N. Study of Dongting Lake area variation and its influence on water level using MODIS data. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2005, 50, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Bastiaanssen, W.G.M. Estimating water volume variations in lakes and reservoirs from four operational satellite altimetry databases and satellite imagery data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 134, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Peng, J.H.; Zhang, D.Z.; Zhao, H.; Li, B. Application of Robust Estimation Method in Study of Relationship Between Lake’s Water Area and Water Level. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2018, 46, 1595–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuraji, K.; Saito, H. Long-Term Changes in Relationship between Water Level and Precipitation in Lake Yamanaka. Water 2022, 14, 2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Xu, C.-Y.; Ye, X. Spatial-temporal variations of stage-area hysteretic relationships in large heterogeneous lake–floodplain systems. J. Hydrol. 2023, 620, 129507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Li, X.; Mei, J. Studying on the relation of the area, the volume and the water of Dongting lake and evaluating about the ability to modulate and store the flood water. Hunan Geol. 2000, 19, 267–270. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Q. Study on the relationship between area and water level of Dongting Lake based on MODIS remote sensing images. Water Sav. Irrig. 2011, 20, 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Du, T.; Xiong, L.; Yi, F.; Xiao, Y.; Song, Q. Relation of the water area of dongting lake to the water levels of hydrological stations based on modis images. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2012, 21, 756–765. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, W.; Chen, C.; Ji, H.; Chen, M.; Liu, Y. The rope relationship between the water surface area of Dongting Lake and the water level of Chenglingji. J. Lake Sci. 2017, 29, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Luo, J.; Chen, Z. Study on Relationship Between Water Level and Water Area Based on Google Earth Engine. Comput. Syst. Appl. 2021, 30, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

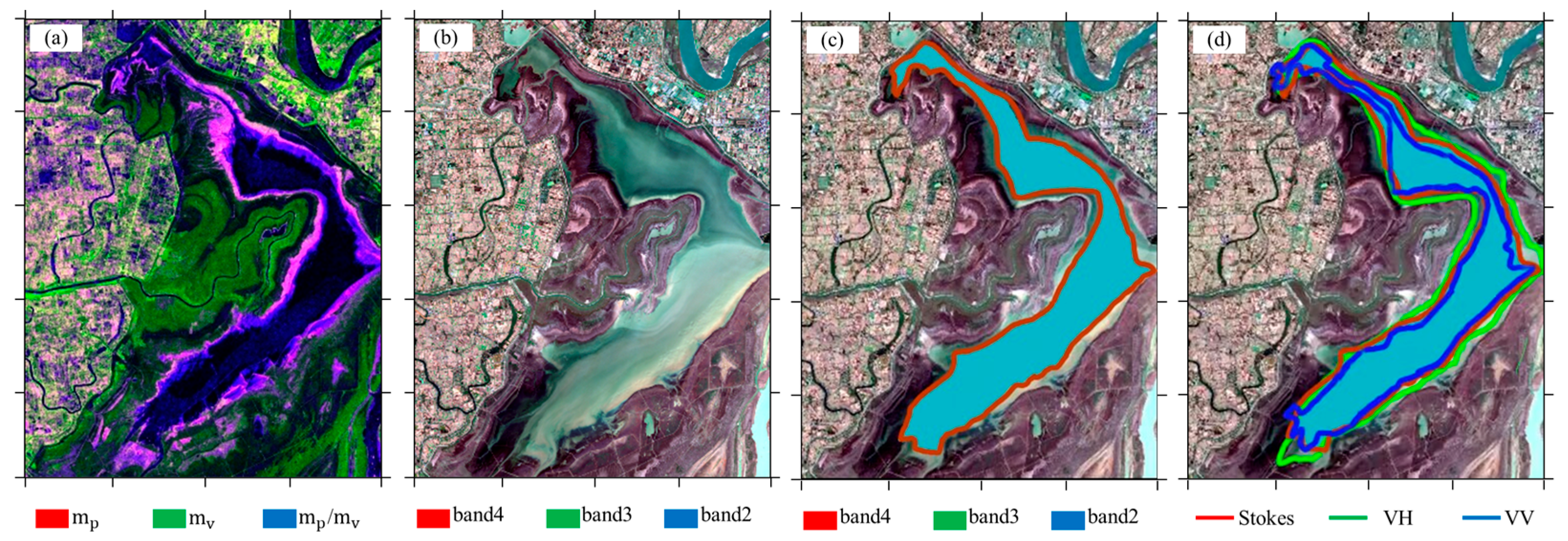



| Methods | ACC | PPV | TPR | TNR | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VV band | 0.9868 | 0.9834 | 0.9759 | 0.9921 | 0.9839 |
| VH band | 0.9680 | 0.9242 | 0.9817 | 0.9614 | 0.9715 |
| Stokes parameters | 0.9915 | 0.9920 | 0.9818 | 0.9962 | 0.9889 |
| Type of Function | Functional Relation Expression | R2 | RMSE (km2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear | 0.93 | 89.13 | |
| Exponential | 0.93 | 738.49 | |
| Logarithmic | 0.91 | 55.13 | |
| Quadratic polynomial | 0.94 | 77.32 | |
| Cubic polynomial | 0.97 | 55.92 | |
| Piecewise Linear | 0.98 | 45.72 |
| Time | Water Area (km2) | Predicted Water Level (m) | Measured Water Level (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 17 April 2017 | 574.9366 | 25.3588 | 25.49 |
| 4 June 2017 | 765.3197 | 26.4501 | 26.43 |
| 10 July 2017 | 1410.7703 | 33.2929 | 32.98 |
| 3 August 2017 | 953.4846 | 27.5287 | 27.85 |
| 8 September 2017 | 870.9352 | 27.0555 | 27.11 |
| 14 October 2017 | 1057.7628 | 28.7698 | 28.36 |
| 7 November 2017 | 630.2489 | 25.6758 | 24.92 |
| 13 December 2017 | 365.7828 | 21.2623 | 20.30 |
| Time | Water Area (km2) | Predicted Water Level (m) |
|---|---|---|
| 2 November 2018 | 432.3501 | 23.2810 |
| 14 November 2018 | 451.6224 | 23.8655 |
| 26 November 2018 | 474.2844 | 24.5527 |
| 8 December 2018 | 491.9597 | 25.0887 |
| 20 December 2018 | 383.6675 | 21.8047 |
| 10 March 2022 | 398.9127 | 22.2670 |
| 22 March 2022 | 406.7829 | 22.5057 |
| 3 April 2022 | 458.4635 | 24.0729 |
| 15 April 2022 | 497.8067 | 25.2661 |
| 9 May 2022 | 956.1027 | 27.5437 |
| 2 June 2022 | 1227.9767 | 29.1022 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Q.; Zhao, R.; Fu, H.; Zhu, J.; Li, Y. Water Area Extraction and Water Level Prediction of Dongting Lake Based on Sentinel-1 Dual-Polarization Data Decomposition. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4655. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194655
Song Q, Zhao R, Fu H, Zhu J, Li Y. Water Area Extraction and Water Level Prediction of Dongting Lake Based on Sentinel-1 Dual-Polarization Data Decomposition. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(19):4655. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194655
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Qing, Rong Zhao, Haiqiang Fu, Jianjun Zhu, and Yi Li. 2023. "Water Area Extraction and Water Level Prediction of Dongting Lake Based on Sentinel-1 Dual-Polarization Data Decomposition" Remote Sensing 15, no. 19: 4655. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194655
APA StyleSong, Q., Zhao, R., Fu, H., Zhu, J., & Li, Y. (2023). Water Area Extraction and Water Level Prediction of Dongting Lake Based on Sentinel-1 Dual-Polarization Data Decomposition. Remote Sensing, 15(19), 4655. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194655