Impacts of Climate Change and Human Activities on Plant Species α-Diversity across the Tibetan Grasslands
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
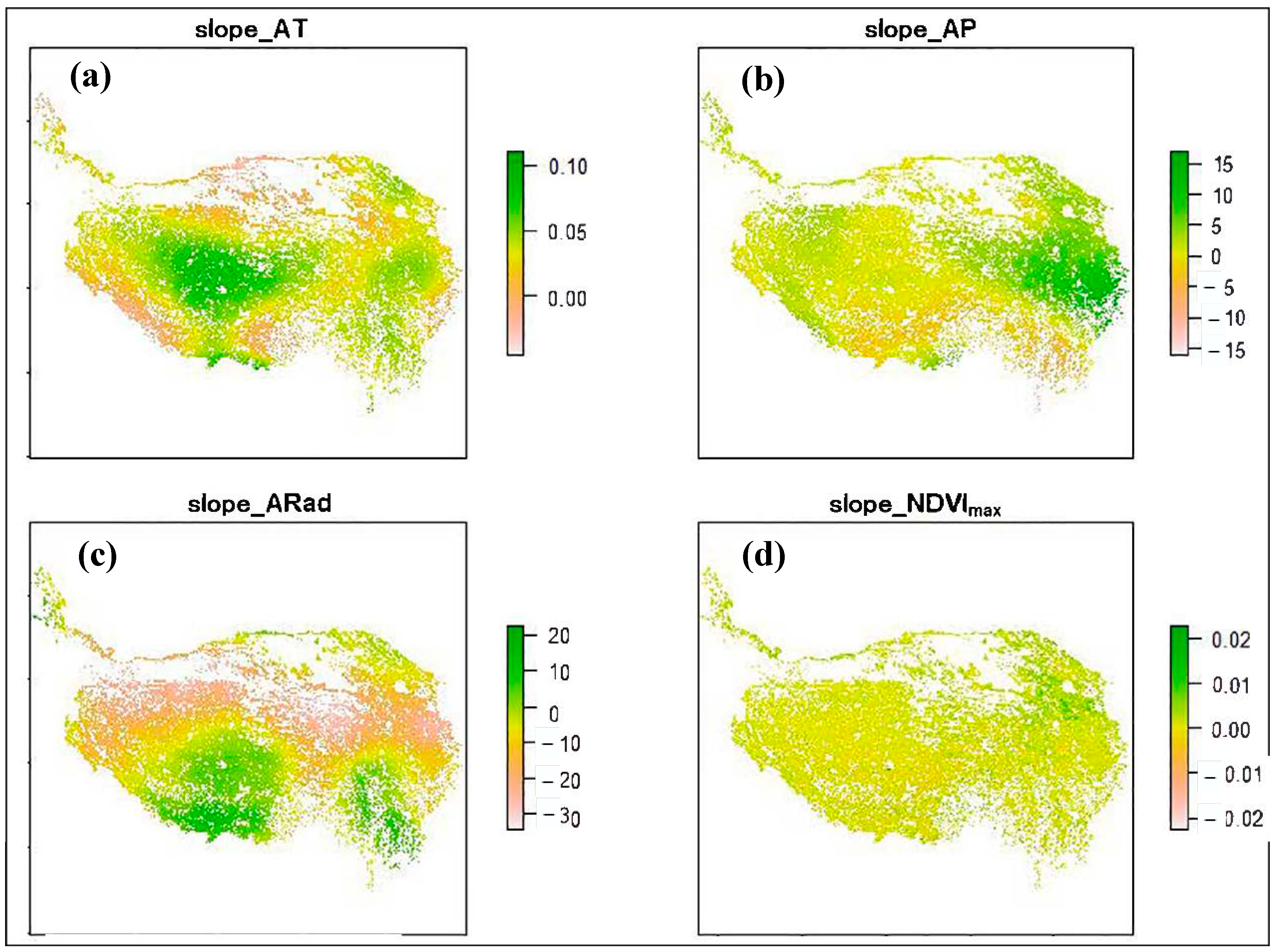
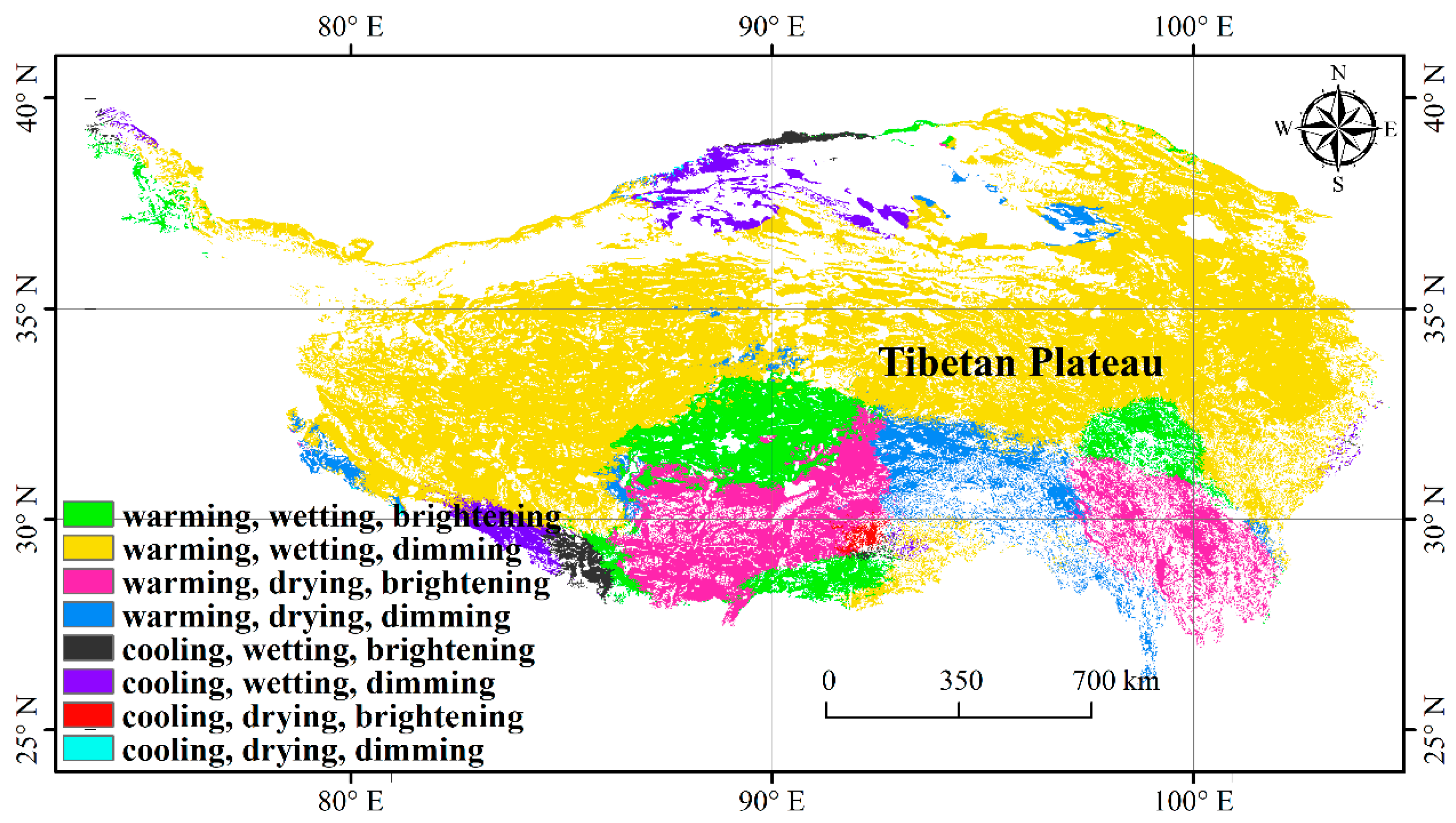
3.1. Climate Change and NDVImax Change
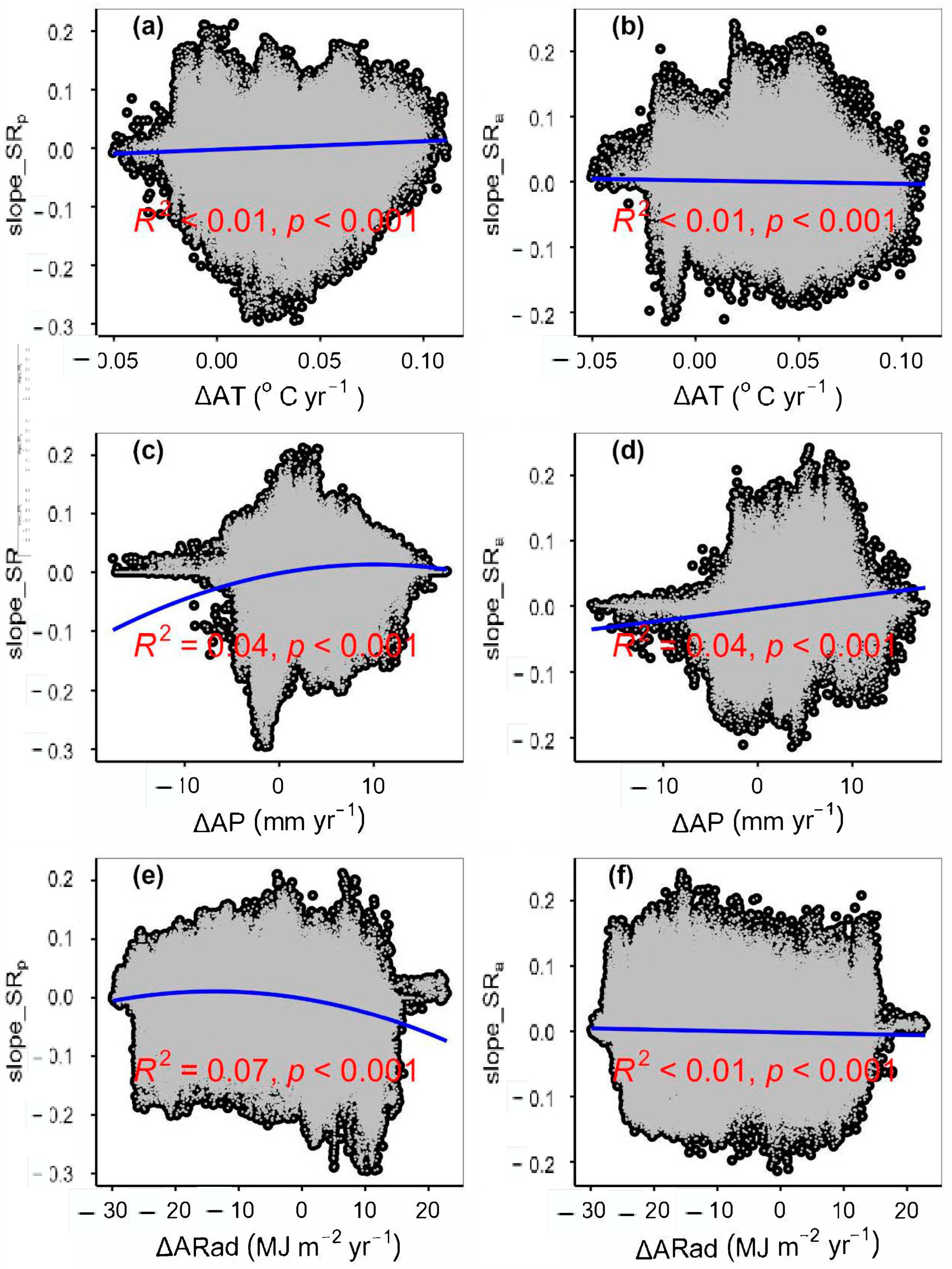
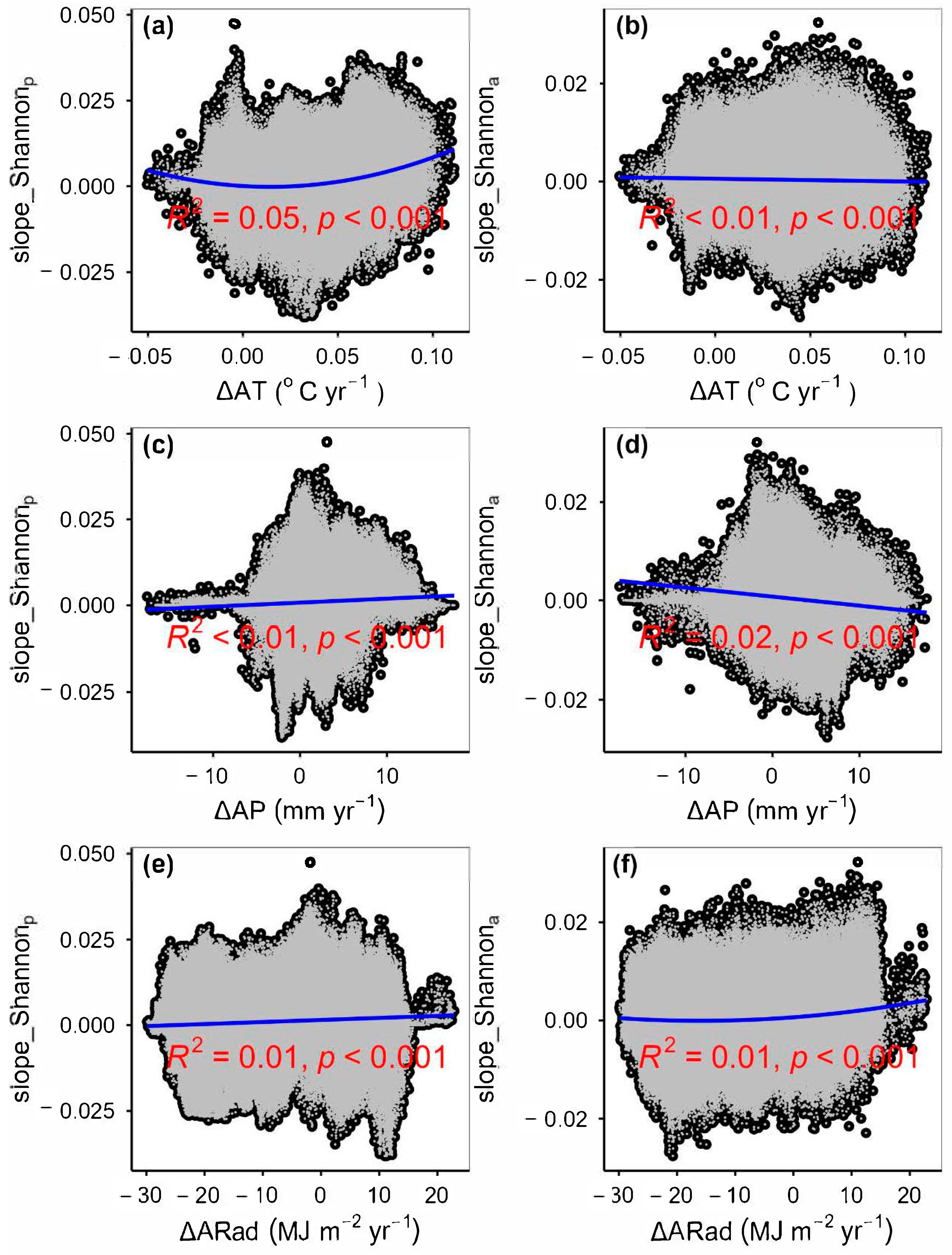
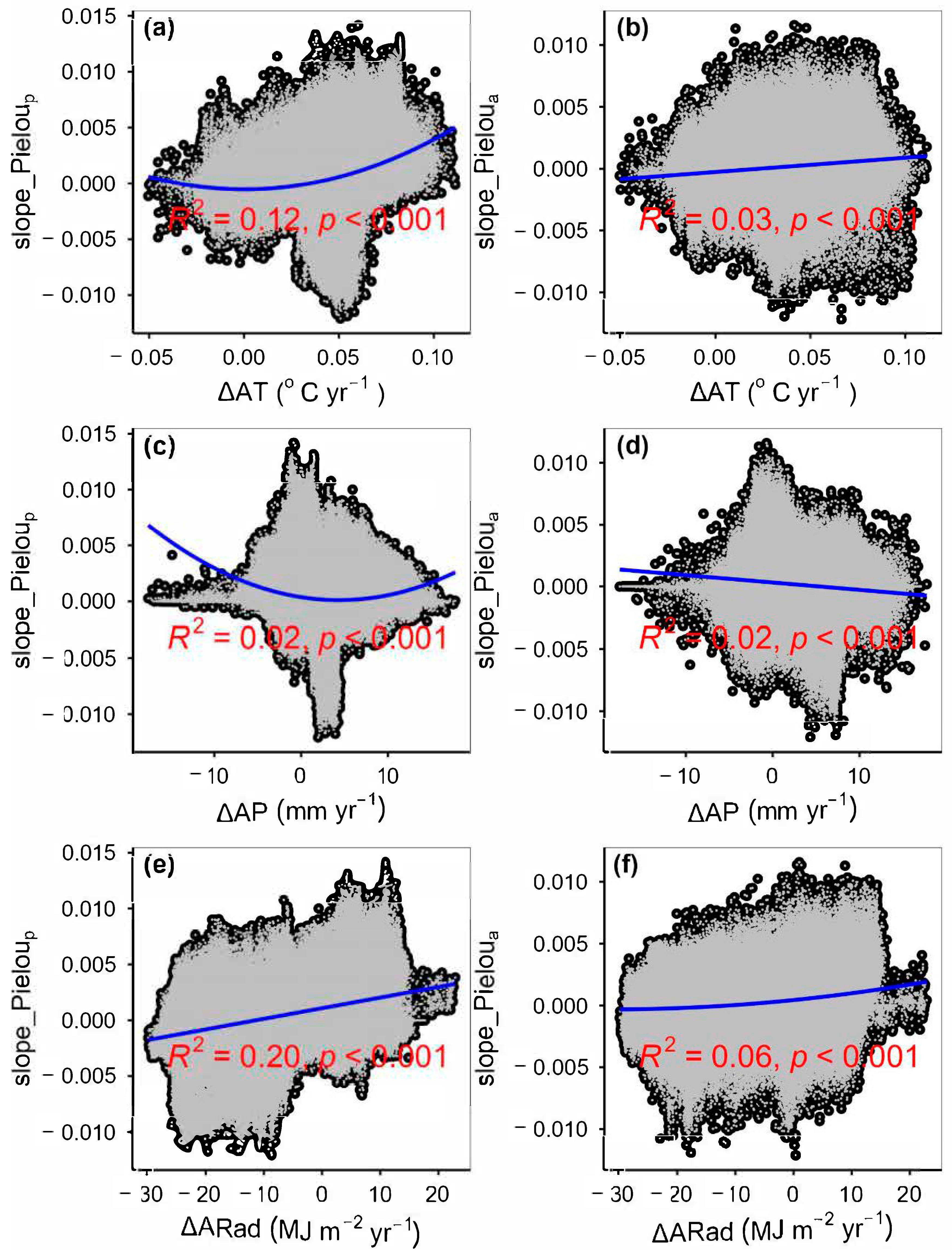
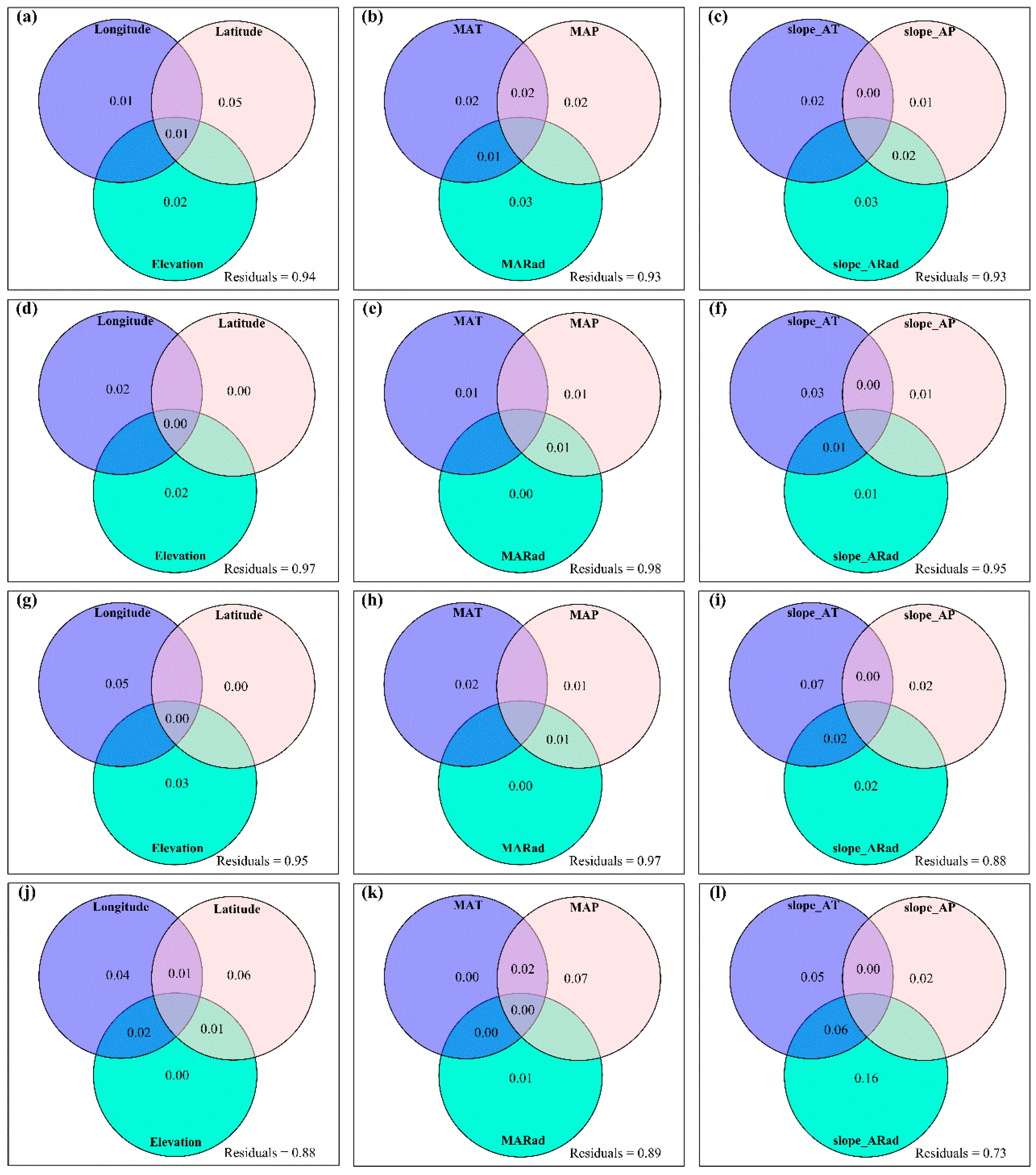
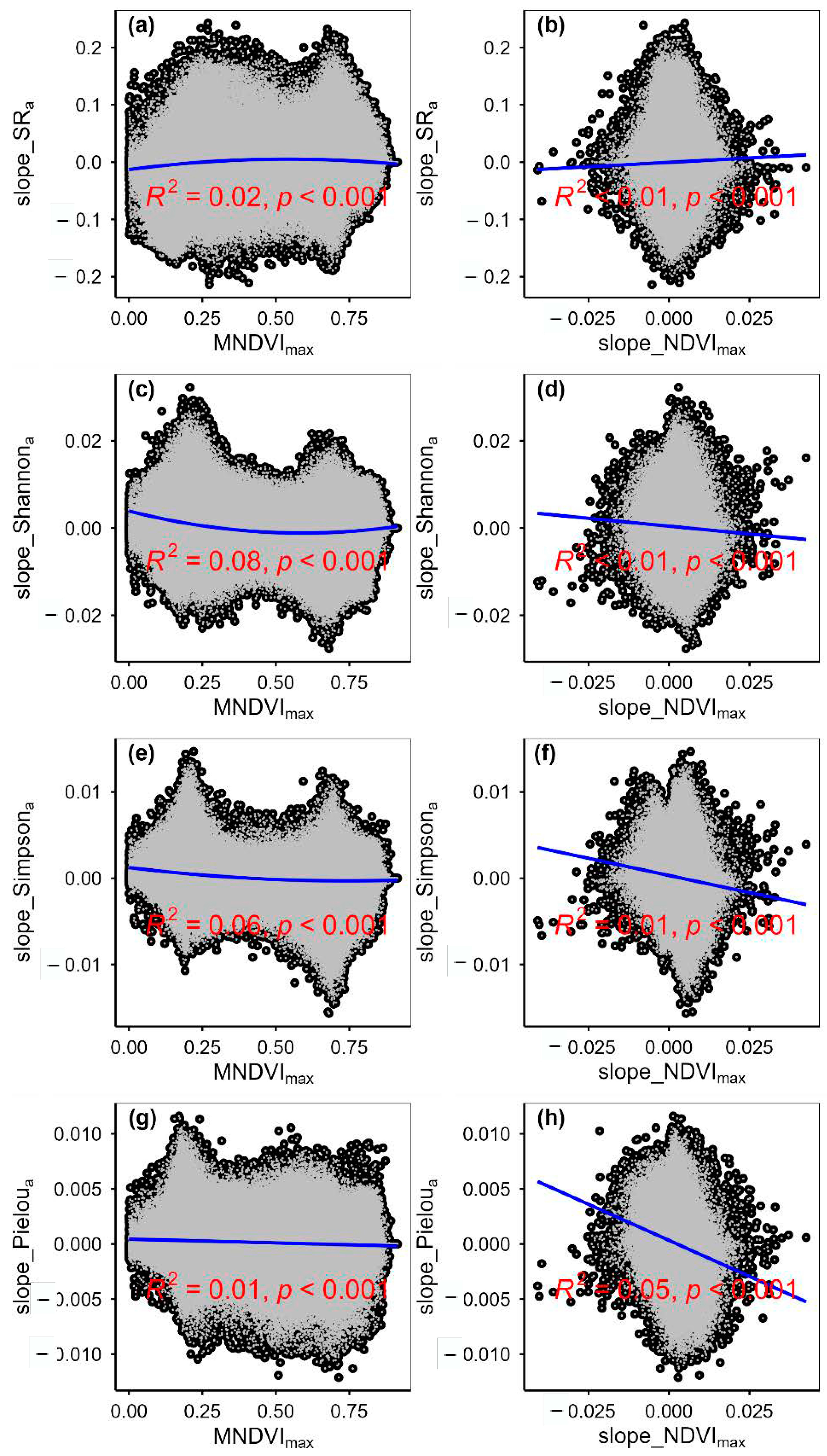
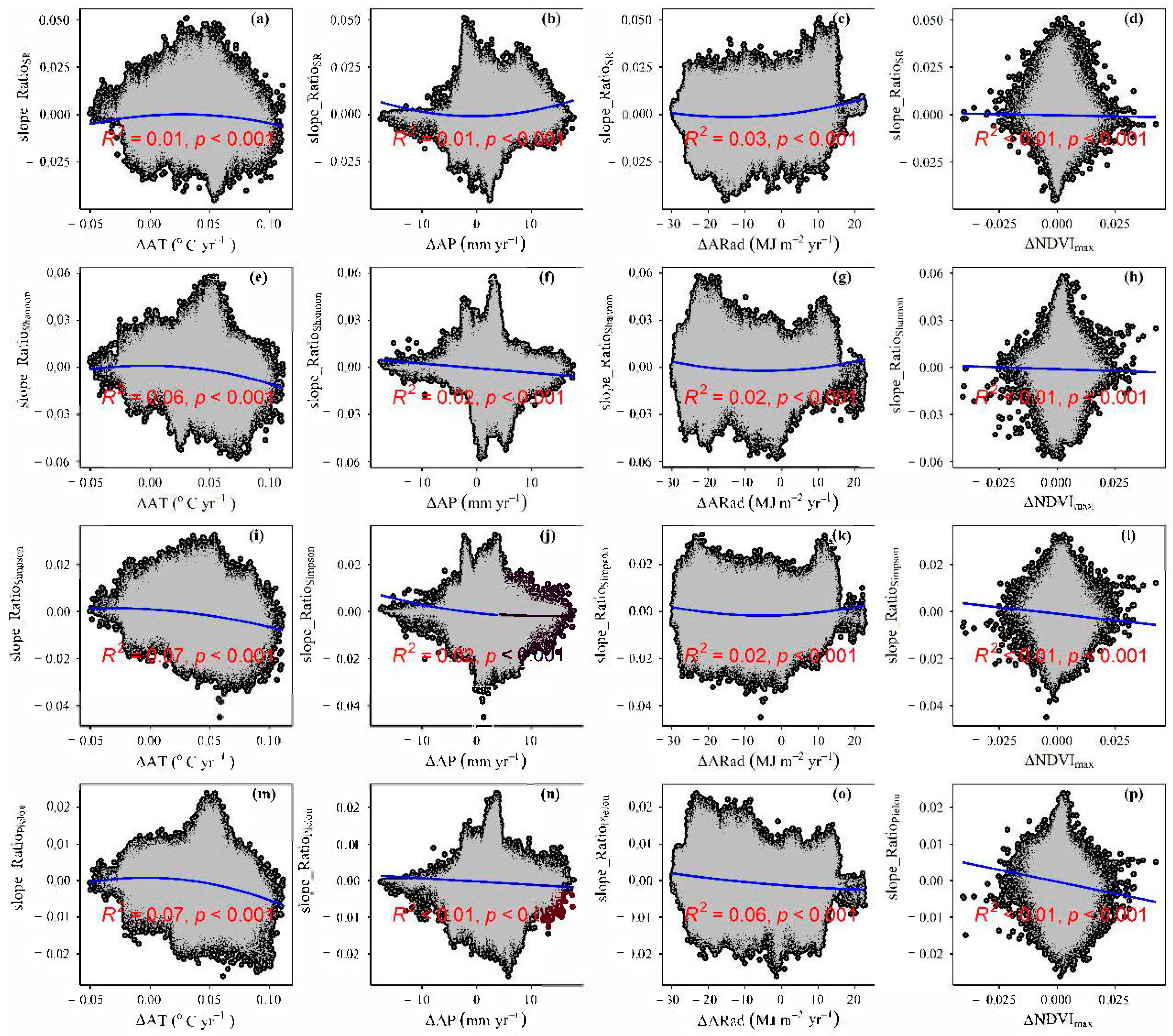
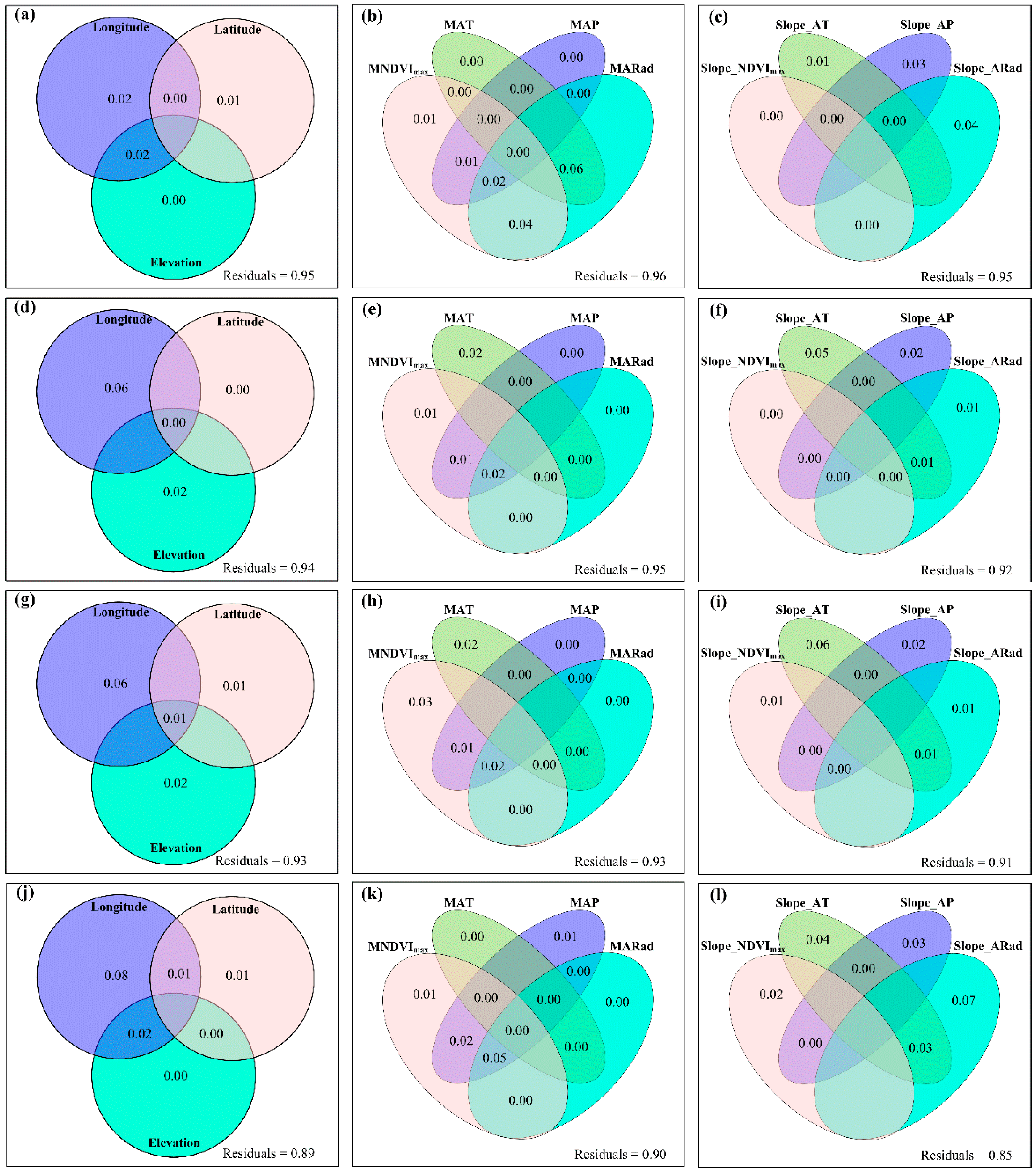
3.2. Change Rates of Plant α-Diversity and Their Correlations with Environmental Factors
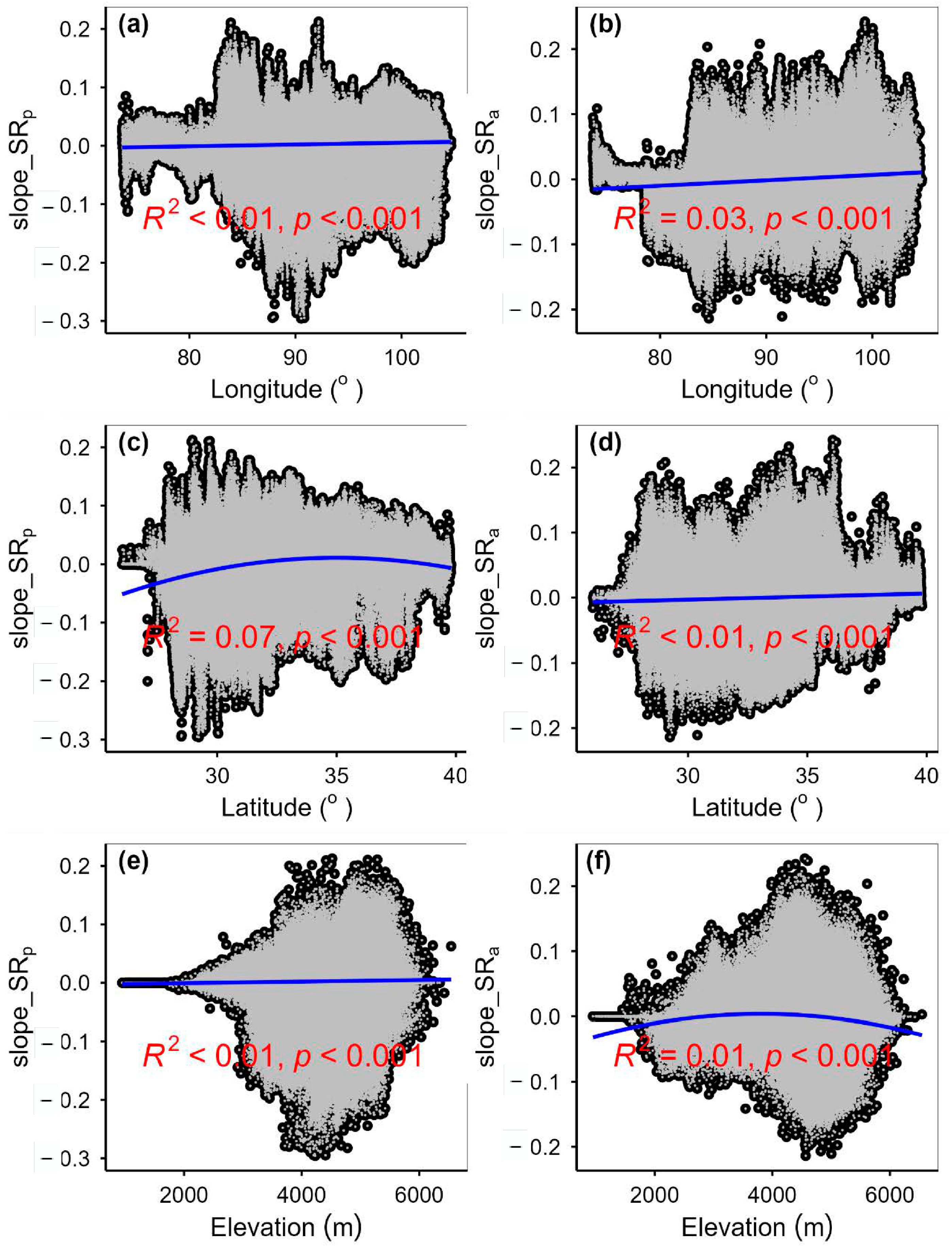
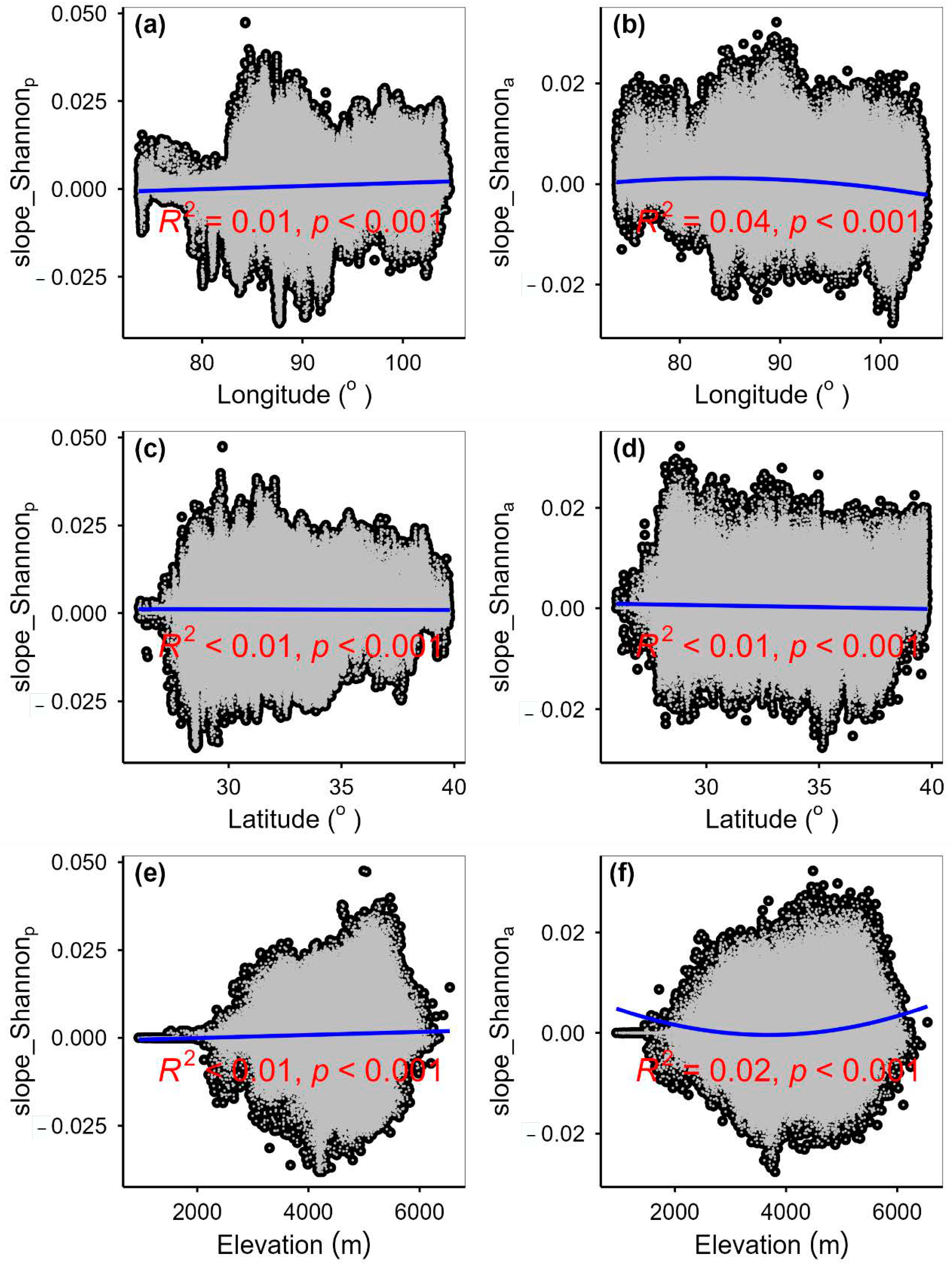
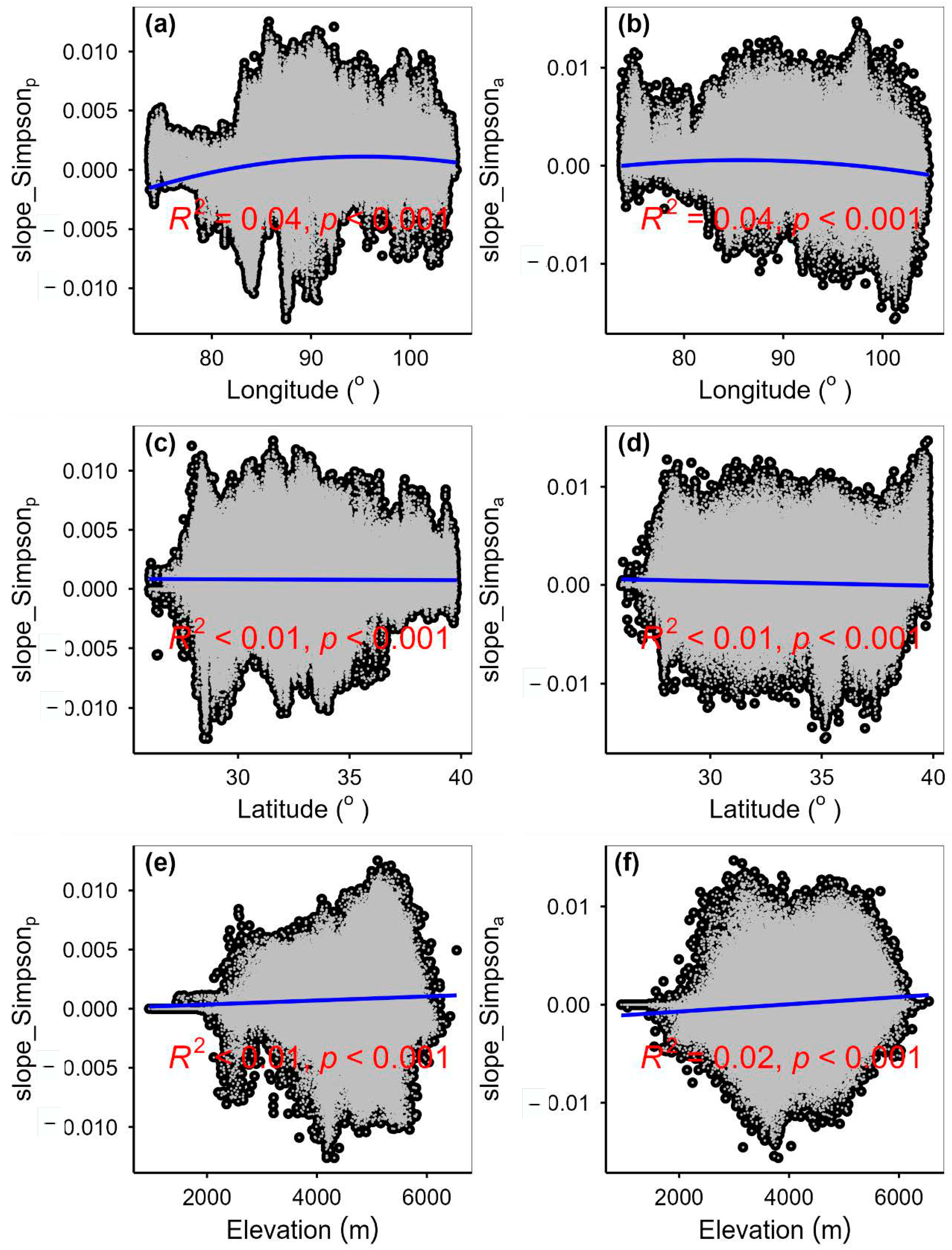
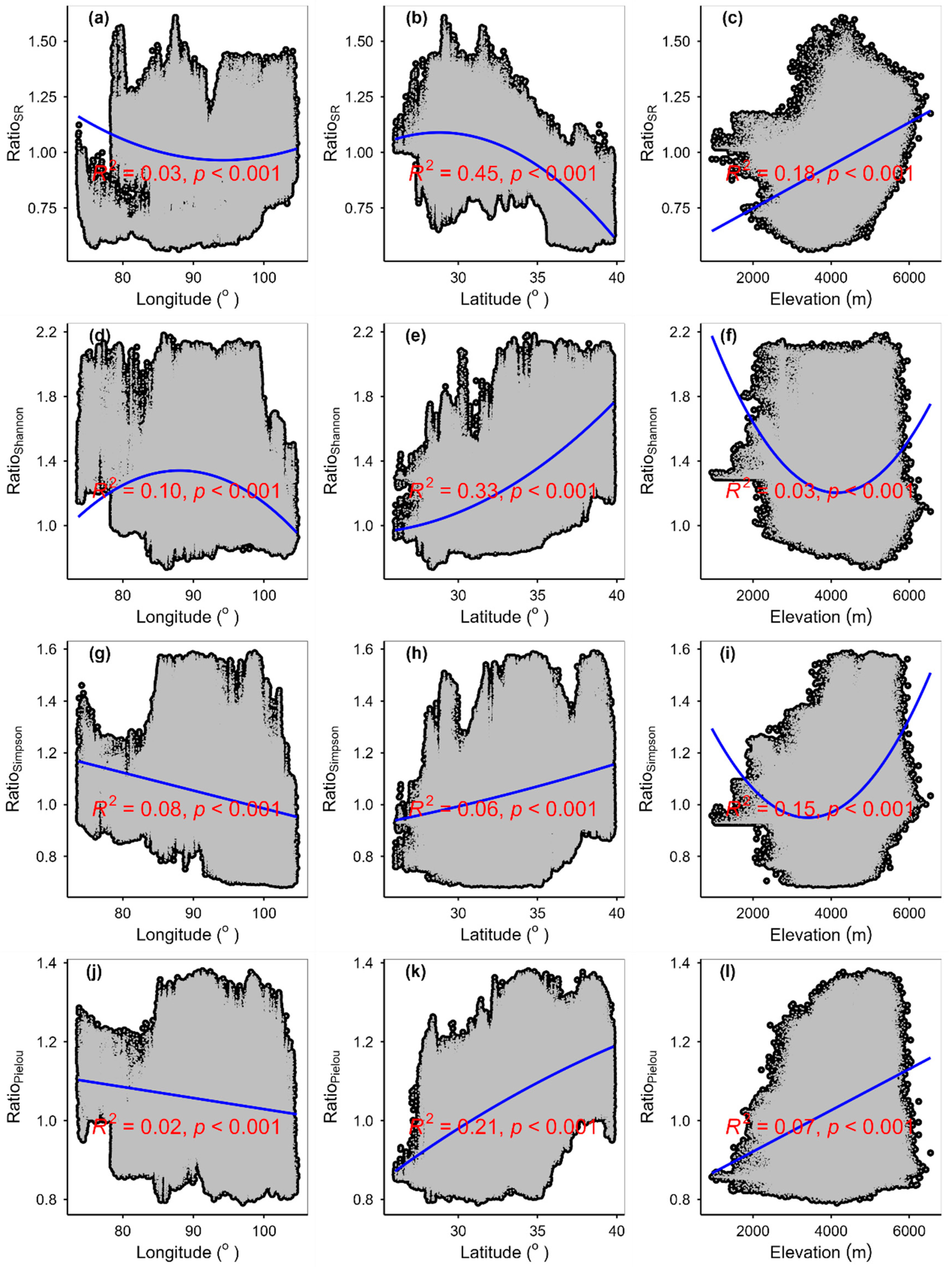
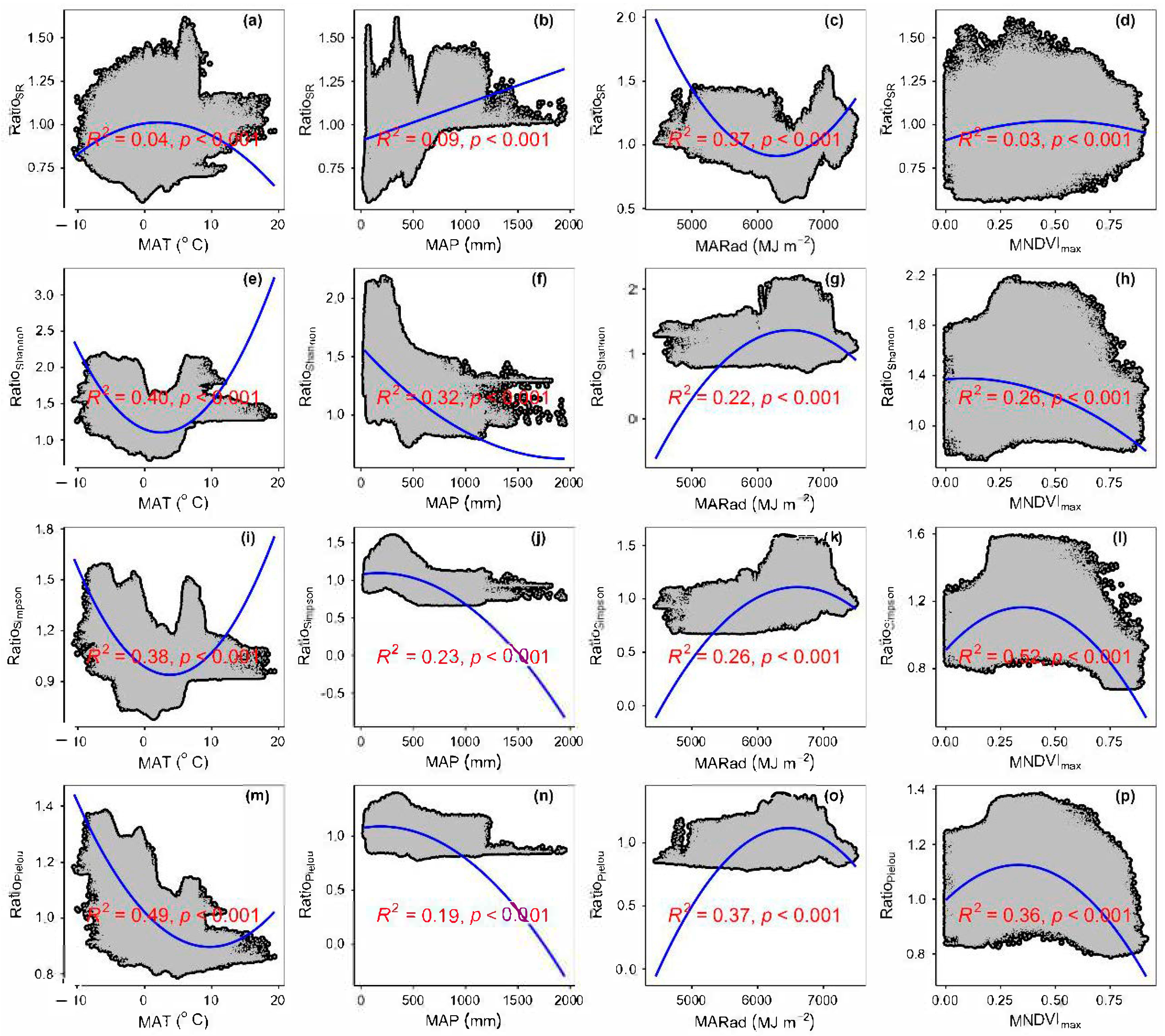
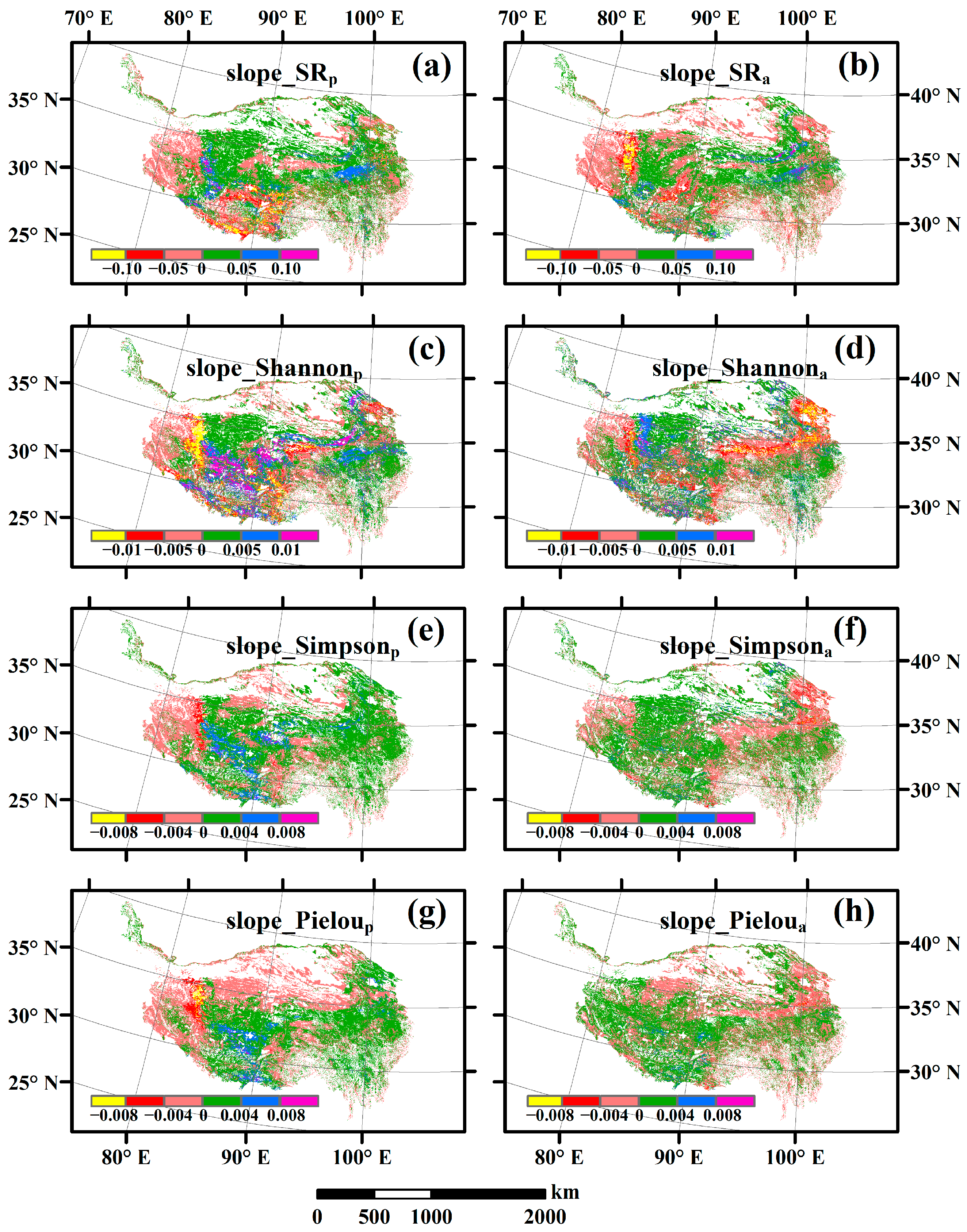
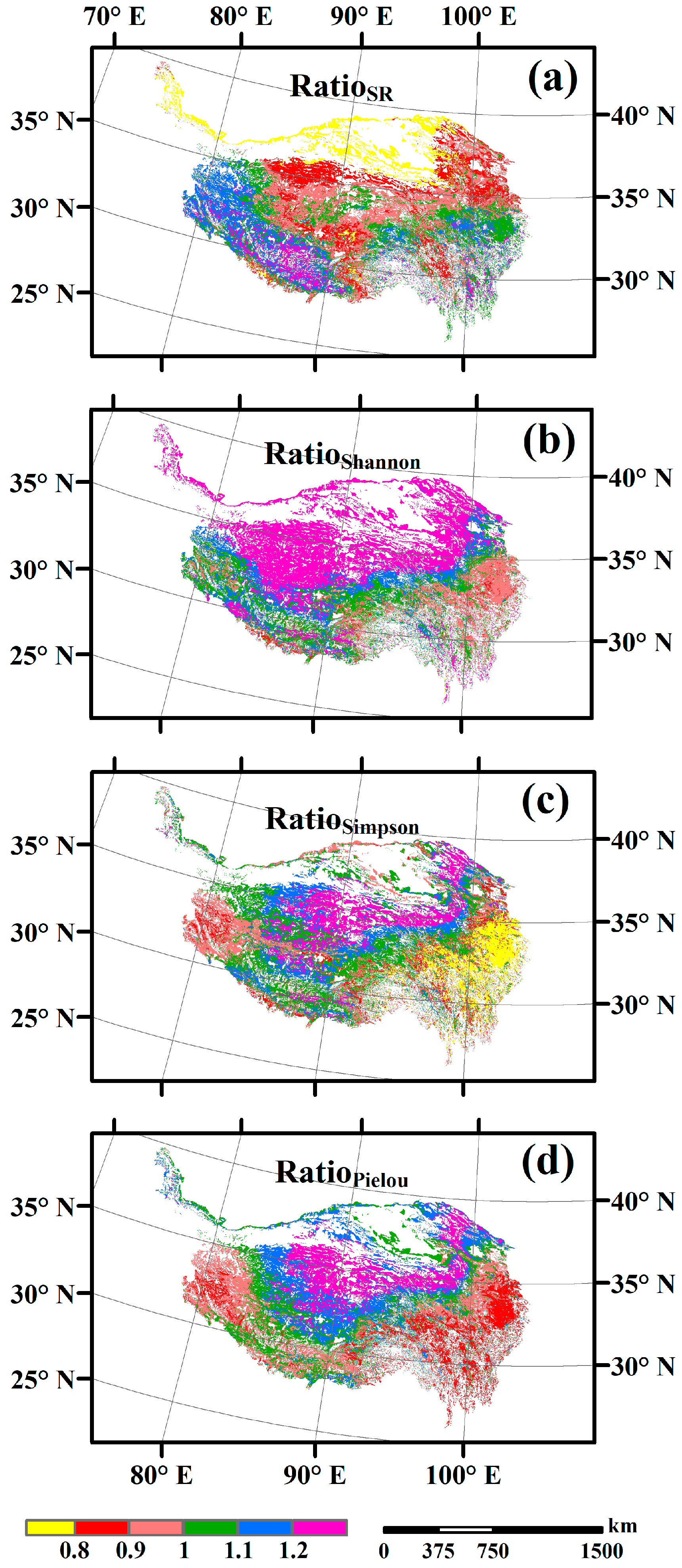
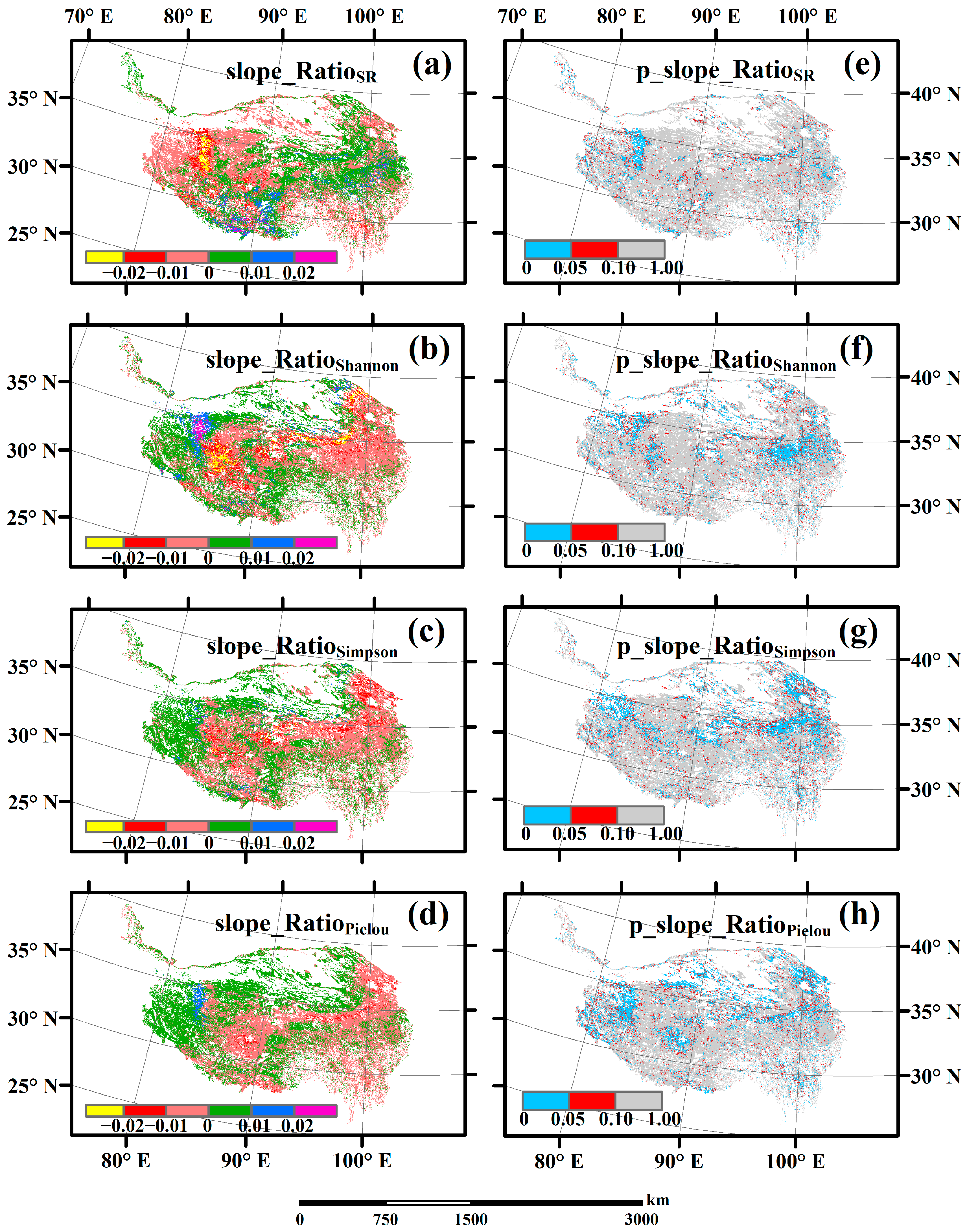
3.3. Spatial Variations of RSR, RShannon, RSimpson and RPielou, and Their Correlations with Environmental Factors
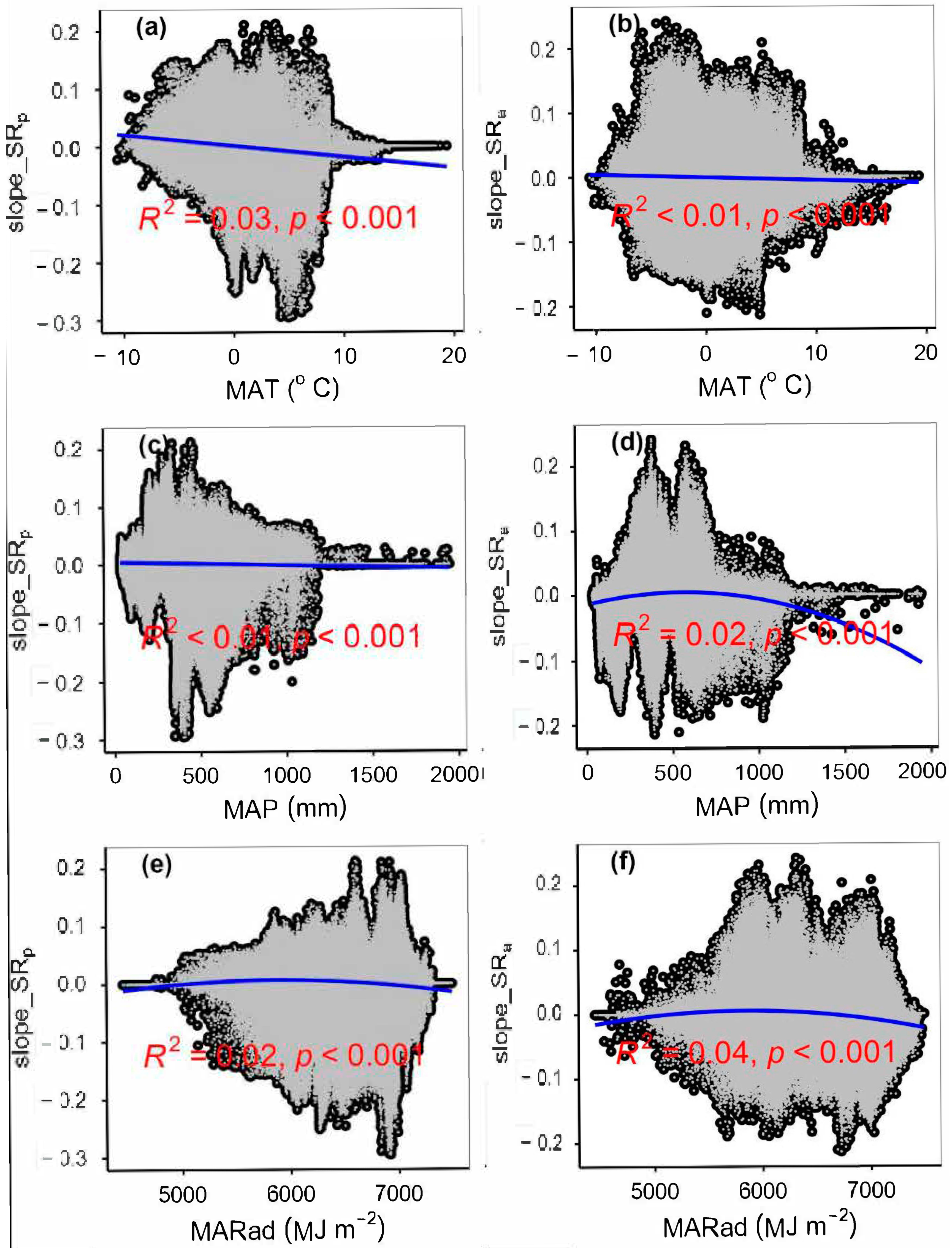
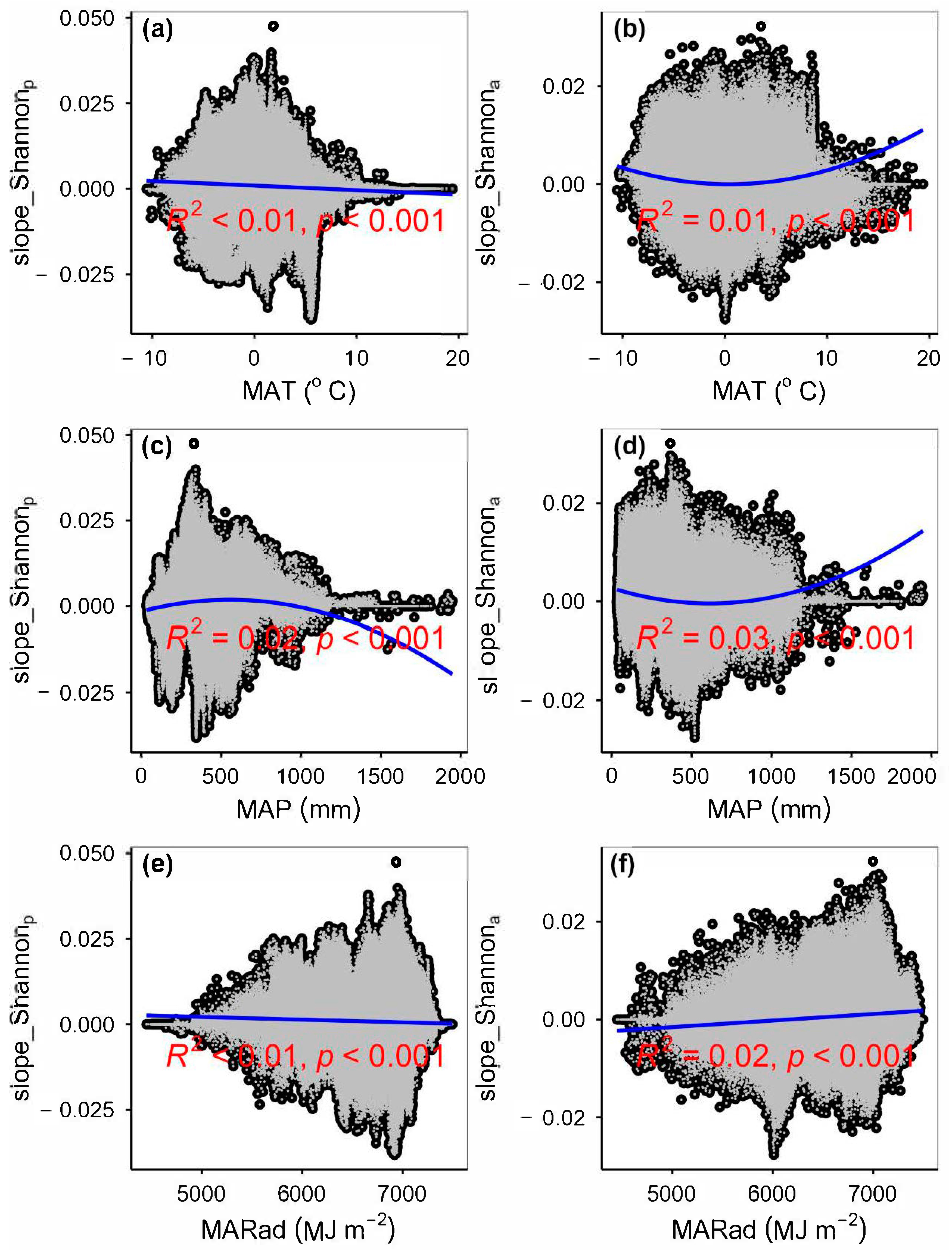
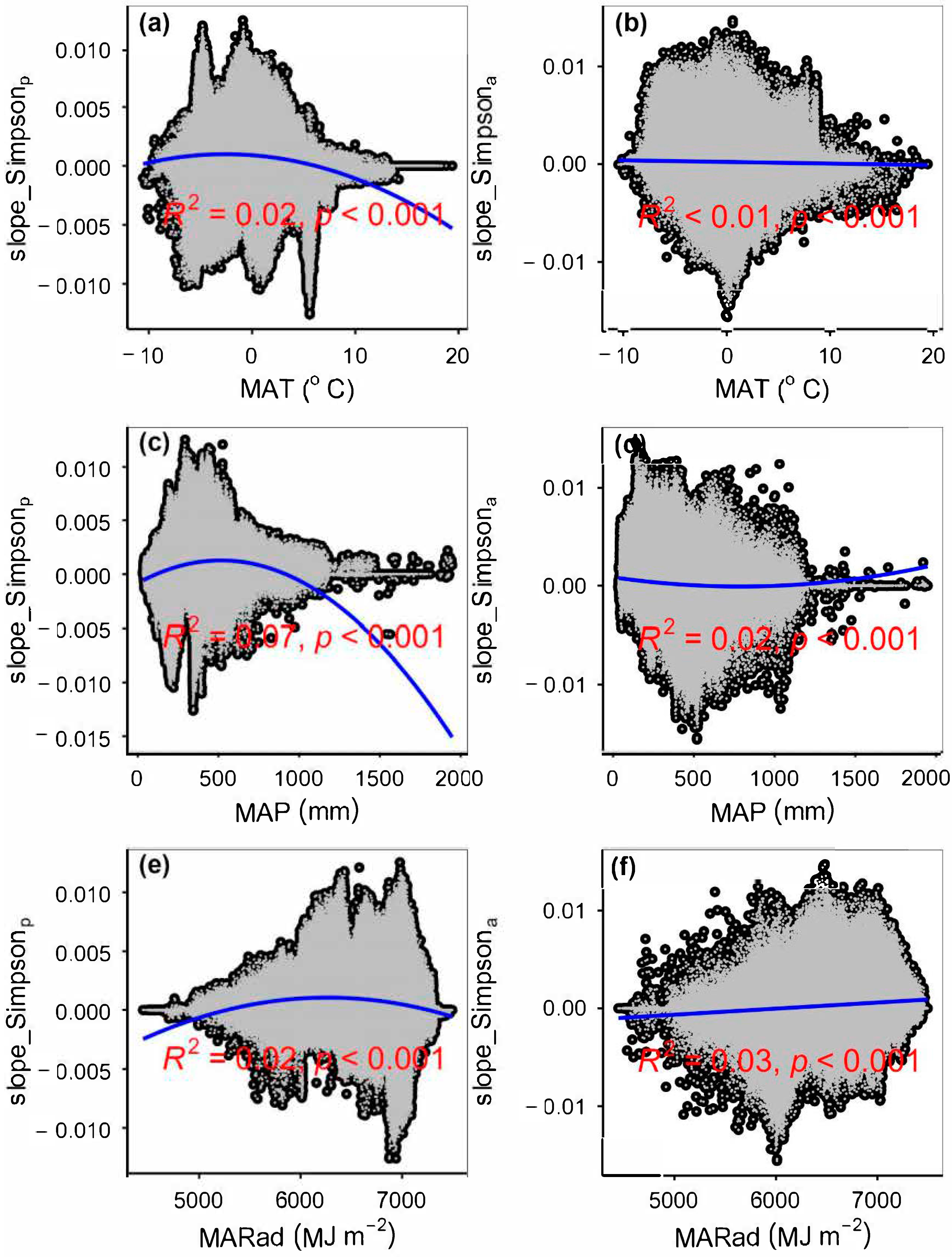
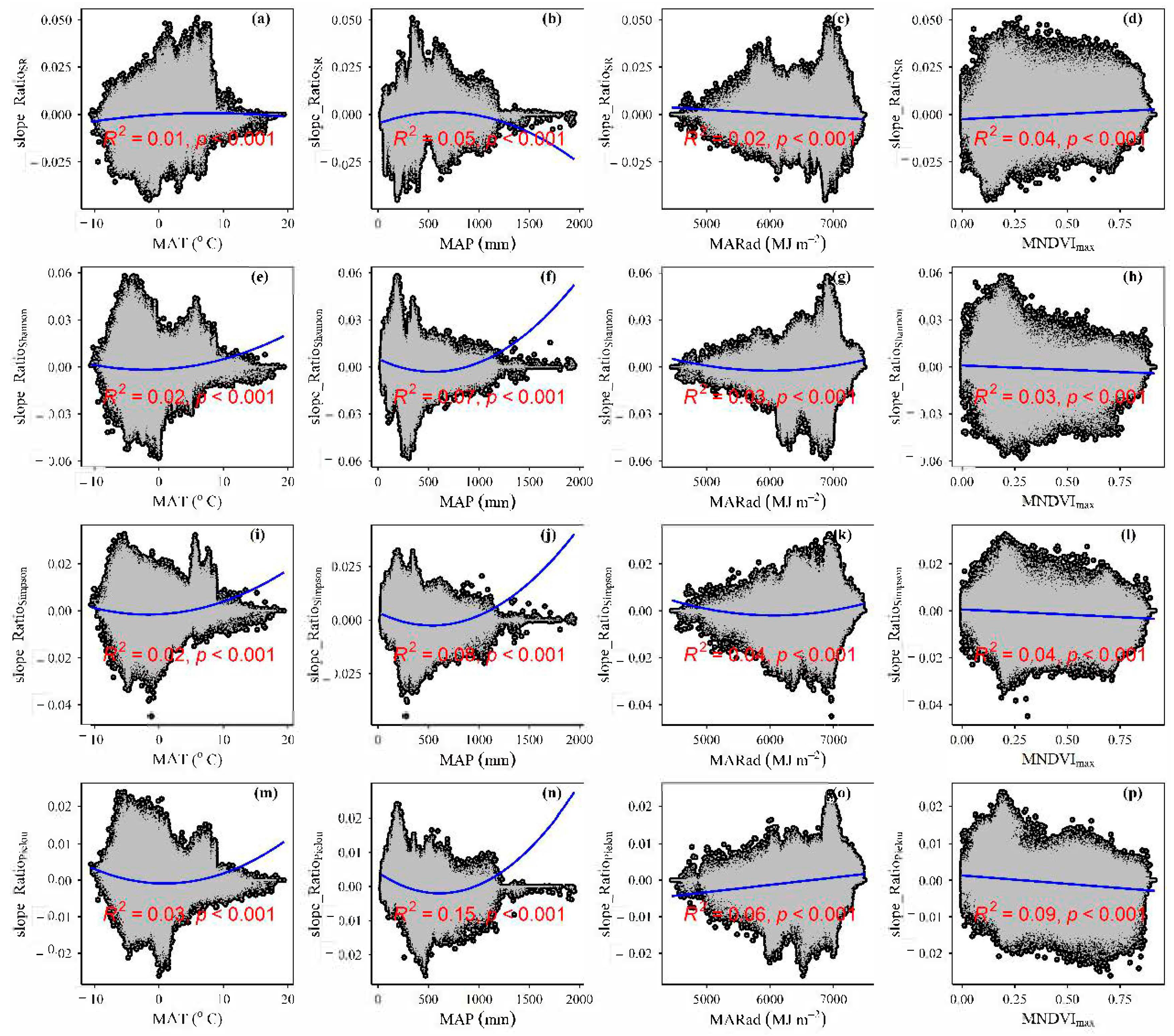
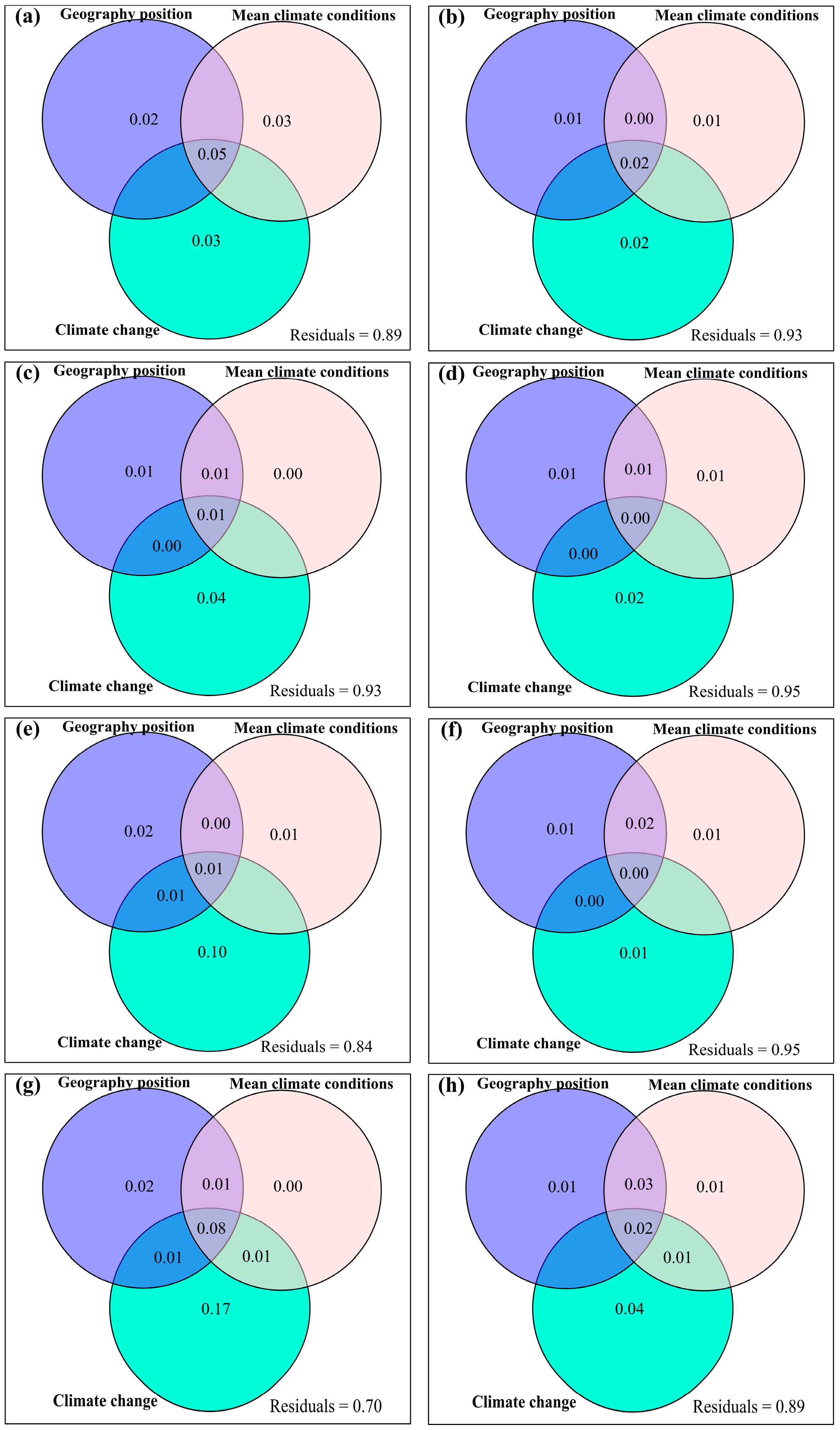
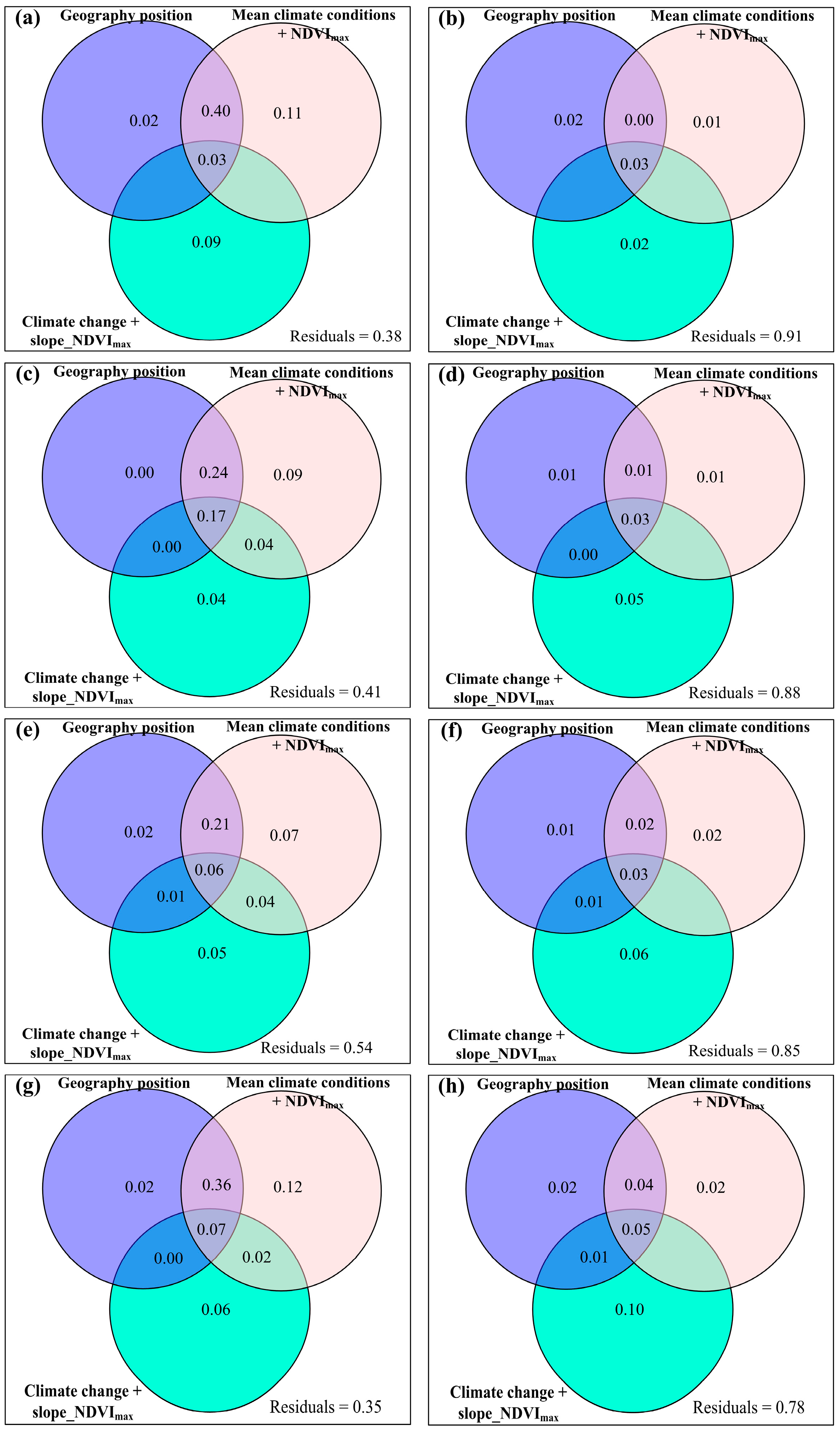
3.4. Temporal Changes in Human Activities Effects on Plant α-Diversity and Their Correlations with Environmental Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Impacts of Climate Change on Plant Species α-Diversity
4.2. Impacts of Human Activities on Plant Species α-Diversity
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A







| Index | Grassland Types | Change Rate of Potential α-Diversity | Change Rate of Actual α-Diversity | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Standard Deviation | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | Standard Deviation | Minimum | Maximum | ||
| Species richness | temperate meadow-steppe | 0.0018 | 0.0108 | −0.16 | 0.06 | −0.0065 | 0.0174 | −0.12 | 0.14 |
| temperate steppe | −0.0148 | 0.0515 | −0.29 | 0.20 | 0.0054 | 0.0310 | −0.17 | 0.21 | |
| temperate desert-steppe | 0.0000 | 0.0157 | −0.13 | 0.07 | 0.0007 | 0.0174 | −0.10 | 0.09 | |
| alpine meadow-steppe | −0.0042 | 0.0512 | −0.29 | 0.18 | −0.0021 | 0.0369 | −0.16 | 0.19 | |
| alpine steppe | 0.0060 | 0.0350 | −0.29 | 0.21 | −0.0015 | 0.0339 | −0.21 | 0.24 | |
| alpine desert-steppe | 0.0024 | 0.0191 | −0.22 | 0.13 | −0.0148 | 0.0323 | −0.17 | 0.09 | |
| temperate steppe-desert | −0.0020 | 0.0102 | −0.05 | 0.03 | −0.0038 | 0.0124 | −0.11 | 0.06 | |
| temperate desert | 0.0031 | 0.0114 | −0.06 | 0.08 | 0.0010 | 0.0076 | −0.13 | 0.11 | |
| alpine desert | 0.0040 | 0.0118 | −0.10 | 0.10 | −0.0056 | 0.0219 | −0.14 | 0.12 | |
| warm-temperate tussock | 0.0005 | 0.0039 | −0.01 | 0.04 | −0.0047 | 0.0123 | −0.07 | 0.07 | |
| warm-temperate shrub tussock | −0.0008 | 0.0045 | −0.06 | 0.06 | −0.0080 | 0.0160 | −0.14 | 0.07 | |
| tropical tussock | 0.0003 | 0.0034 | 0.00 | 0.06 | −0.0004 | 0.0037 | −0.05 | 0.01 | |
| tropical shrub tussock | −0.0001 | 0.0010 | −0.01 | 0.01 | −0.0025 | 0.0096 | −0.08 | 0.02 | |
| lowland meadow | 0.0012 | 0.0082 | −0.12 | 0.07 | −0.0007 | 0.0093 | −0.16 | 0.09 | |
| montane meadow | 0.0027 | 0.0190 | −0.18 | 0.17 | 0.0019 | 0.0185 | −0.17 | 0.18 | |
| alpine meadow | 0.0025 | 0.0409 | −0.30 | 0.21 | 0.0034 | 0.0319 | −0.21 | 0.23 | |
| swamp | 0.0020 | 0.0120 | −0.13 | 0.08 | 0.0018 | 0.0111 | −0.11 | 0.13 | |
| Shannon | temperate meadow-steppe | −0.0014 | 0.0032 | −0.02 | 0.01 | −0.0004 | 0.0024 | −0.01 | 0.01 |
| temperate steppe | −0.0011 | 0.0059 | −0.04 | 0.03 | 0.0009 | 0.0050 | −0.02 | 0.03 | |
| temperate desert-steppe | 0.0001 | 0.0020 | −0.02 | 0.01 | 0.0018 | 0.0045 | −0.01 | 0.02 | |
| alpine meadow-steppe | 0.0044 | 0.0089 | −0.03 | 0.04 | 0.0007 | 0.0047 | −0.02 | 0.03 | |
| alpine steppe | 0.0014 | 0.0067 | −0.04 | 0.05 | 0.0012 | 0.0047 | −0.02 | 0.03 | |
| alpine desert-steppe | −0.0019 | 0.0058 | −0.03 | 0.02 | 0.0011 | 0.0038 | −0.02 | 0.03 | |
| temperate steppe-desert | −0.0003 | 0.0011 | −0.01 | 0.01 | 0.0015 | 0.0039 | −0.01 | 0.02 | |
| temperate desert | 0.0000 | 0.0013 | −0.01 | 0.02 | 0.0014 | 0.0025 | −0.01 | 0.02 | |
| alpine desert | −0.0002 | 0.0033 | −0.02 | 0.02 | 0.0025 | 0.0036 | −0.01 | 0.02 | |
| warm-temperate tussock | −0.0002 | 0.0012 | −0.01 | 0.00 | −0.0005 | 0.0021 | −0.01 | 0.01 | |
| warm-temperate shrub tussock | −0.0003 | 0.0013 | −0.02 | 0.01 | −0.0009 | 0.0023 | −0.01 | 0.01 | |
| tropical tussock | 0.0000 | 0.0010 | −0.02 | 0.00 | 0.0000 | 0.0013 | −0.01 | 0.01 | |
| tropical shrub tussock | 0.0000 | 0.0003 | −0.01 | 0.00 | −0.0003 | 0.0018 | −0.01 | 0.01 | |
| lowland meadow | 0.0000 | 0.0010 | −0.01 | 0.01 | 0.0009 | 0.0035 | −0.02 | 0.02 | |
| montane meadow | 0.0012 | 0.0032 | −0.03 | 0.02 | 0.0005 | 0.0033 | −0.02 | 0.02 | |
| alpine meadow | 0.0013 | 0.0055 | −0.03 | 0.04 | −0.0007 | 0.0048 | −0.03 | 0.03 | |
| swamp | 0.0012 | 0.0019 | −0.01 | 0.02 | 0.0007 | 0.0023 | −0.01 | 0.02 | |
| Simpson | temperate meadow-steppe | −0.0003 | 0.0010 | −0.01 | 0.00 | −0.0002 | 0.0009 | −0.01 | 0.00 |
| temperate steppe | −0.0001 | 0.0020 | −0.01 | 0.01 | 0.0002 | 0.0023 | −0.01 | 0.01 | |
| temperate desert-steppe | 0.0002 | 0.0008 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.0005 | 0.0018 | −0.01 | 0.01 | |
| alpine meadow-steppe | 0.0021 | 0.0027 | −0.01 | 0.01 | 0.0008 | 0.0017 | −0.01 | 0.01 | |
| alpine steppe | 0.0010 | 0.0023 | −0.01 | 0.01 | 0.0006 | 0.0019 | −0.01 | 0.01 | |
| alpine desert-steppe | −0.0006 | 0.0018 | −0.01 | 0.01 | 0.0003 | 0.0012 | −0.01 | 0.01 | |
| temperate steppe-desert | −0.0002 | 0.0006 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.0005 | 0.0014 | 0.00 | 0.01 | |
| temperate desert | 0.0001 | 0.0008 | −0.01 | 0.01 | 0.0004 | 0.0012 | −0.01 | 0.01 | |
| alpine desert | 0.0000 | 0.0015 | −0.01 | 0.01 | 0.0006 | 0.0013 | −0.01 | 0.01 | |
| warm-temperate tussock | −0.0001 | 0.0005 | 0.00 | 0.00 | −0.0001 | 0.0007 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| warm-temperate shrub tussock | −0.0002 | 0.0005 | −0.01 | 0.00 | −0.0002 | 0.0007 | −0.01 | 0.00 | |
| tropical tussock | 0.0000 | 0.0004 | −0.01 | 0.00 | 0.0000 | 0.0006 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| tropical shrub tussock | 0.0000 | 0.0001 | 0.00 | 0.00 | −0.0001 | 0.0008 | −0.01 | 0.00 | |
| lowland meadow | 0.0001 | 0.0005 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.0002 | 0.0012 | −0.01 | 0.01 | |
| montane meadow | 0.0006 | 0.0010 | −0.01 | 0.01 | 0.0001 | 0.0015 | −0.01 | 0.01 | |
| alpine meadow | 0.0010 | 0.0018 | −0.01 | 0.01 | −0.0001 | 0.0019 | −0.02 | 0.01 | |
| swamp | 0.0007 | 0.0006 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.0002 | 0.0010 | −0.01 | 0.01 | |
| Pielou | temperate meadow-steppe | 0.0005 | 0.0008 | 0.00 | 0.00 | −0.0001 | 0.0010 | −0.01 | 0.00 |
| temperate steppe | 0.0001 | 0.0016 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.0004 | 0.0023 | −0.01 | 0.01 | |
| temperate desert-steppe | 0.0000 | 0.0007 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.0002 | 0.0012 | −0.01 | 0.01 | |
| alpine meadow-steppe | 0.0019 | 0.0020 | −0.01 | 0.01 | 0.0009 | 0.0017 | −0.01 | 0.01 | |
| alpine steppe | 0.0002 | 0.0024 | −0.01 | 0.01 | 0.0004 | 0.0015 | −0.01 | 0.01 | |
| alpine desert-steppe | −0.0019 | 0.0024 | −0.01 | 0.01 | 0.0000 | 0.0009 | −0.01 | 0.01 | |
| temperate steppe-desert | −0.0003 | 0.0007 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.0004 | 0.0009 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| temperate desert | −0.0003 | 0.0008 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.0001 | 0.0008 | −0.01 | 0.01 | |
| alpine desert | −0.0014 | 0.0017 | −0.01 | 0.00 | −0.0001 | 0.0008 | 0.00 | 0.01 | |
| warm-temperate tussock | 0.0000 | 0.0002 | 0.00 | 0.00 | −0.0002 | 0.0007 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| warm-temperate shrub tussock | 0.0002 | 0.0006 | 0.00 | 0.00 | −0.0003 | 0.0008 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| tropical tussock | 0.0000 | 0.0003 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.0000 | 0.0003 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| tropical shrub tussock | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.00 | 0.00 | −0.0001 | 0.0005 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| lowland meadow | −0.0003 | 0.0010 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.0001 | 0.0008 | −0.01 | 0.01 | |
| montane meadow | 0.0005 | 0.0012 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.0001 | 0.0013 | −0.01 | 0.01 | |
| alpine meadow | 0.0008 | 0.0017 | −0.01 | 0.01 | 0.0000 | 0.0017 | −0.01 | 0.01 | |
| swamp | 0.0002 | 0.0011 | −0.01 | 0.01 | 0.0001 | 0.0007 | −0.01 | 0.01 | |
| Index | Grassland Types | Mean | Standard Deviation | Minimum | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species richness | temperate meadow-steppe | 0.93 | 0.09 | 0.79 | 1.41 |
| temperate steppe | 0.93 | 0.17 | 0.07 | 1.59 | |
| temperate desert-steppe | 0.82 | 0.21 | 0.06 | 1.56 | |
| alpine meadow-steppe | 1.04 | 0.13 | 0.08 | 1.48 | |
| alpine steppe | 0.99 | 0.15 | 0.06 | 1.61 | |
| alpine desert-steppe | 0.97 | 0.17 | 0.07 | 1.47 | |
| temperate steppe-desert | 0.87 | 0.25 | 0.06 | 1.56 | |
| temperate desert | 0.74 | 0.11 | 0.06 | 1.21 | |
| alpine desert | 0.91 | 0.14 | 0.06 | 1.24 | |
| warm-temperate tussock | 1.01 | 0.07 | 0.75 | 1.27 | |
| warm-temperate shrub tussock | 1.00 | 0.07 | 0.84 | 1.43 | |
| tropical tussock | 1.03 | 0.04 | 0.91 | 1.20 | |
| tropical shrub tussock | 1.04 | 0.05 | 0.15 | 1.17 | |
| lowland meadow | 0.75 | 0.09 | 0.58 | 1.22 | |
| montane meadow | 1.00 | 0.11 | 0.05 | 1.46 | |
| alpine meadow | 1.02 | 0.13 | 0.05 | 1.60 | |
| swamp | 1.01 | 0.13 | 0.65 | 1.39 | |
| Shannon | temperate meadow-steppe | 1.32 | 0.20 | 0.84 | 1.58 |
| temperate steppe | 1.35 | 0.21 | 0.14 | 2.12 | |
| temperate desert-steppe | 1.40 | 0.24 | 0.09 | 2.13 | |
| alpine meadow-steppe | 1.22 | 0.23 | 0.09 | 2.12 | |
| alpine steppe | 1.36 | 0.29 | 0.09 | 2.17 | |
| alpine desert-steppe | 1.43 | 0.29 | 0.10 | 2.18 | |
| temperate steppe-desert | 1.33 | 0.31 | 0.12 | 2.11 | |
| temperate desert | 1.43 | 0.19 | 0.11 | 2.14 | |
| alpine desert | 1.55 | 0.23 | 0.11 | 2.15 | |
| warm-temperate tussock | 1.35 | 0.12 | 0.92 | 1.62 | |
| warm-temperate shrub tussock | 1.36 | 0.11 | 0.91 | 1.55 | |
| tropical tussock | 1.29 | 0.08 | 0.90 | 1.47 | |
| tropical shrub tussock | 1.33 | 0.07 | 0.18 | 1.50 | |
| lowland meadow | 1.59 | 0.25 | 0.84 | 2.13 | |
| montane meadow | 1.05 | 0.19 | 0.05 | 2.08 | |
| alpine meadow | 1.12 | 0.22 | 0.05 | 2.13 | |
| swamp | 1.07 | 0.30 | 0.85 | 1.95 | |
| Simpson | temperate meadow-steppe | 1.00 | 0.11 | 0.70 | 1.16 |
| temperate steppe | 1.10 | 0.14 | 0.10 | 1.55 | |
| temperate desert-steppe | 1.01 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 1.30 | |
| alpine meadow-steppe | 1.13 | 0.13 | 0.09 | 1.57 | |
| alpine steppe | 1.11 | 0.15 | 0.08 | 1.58 | |
| alpine desert-steppe | 1.08 | 0.14 | 0.09 | 1.58 | |
| temperate steppe-desert | 0.98 | 0.12 | 0.09 | 1.40 | |
| temperate desert | 0.98 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 1.34 | |
| alpine desert | 1.13 | 0.12 | 0.09 | 1.57 | |
| warm-temperate tussock | 0.99 | 0.08 | 0.77 | 1.12 | |
| warm-temperate shrub tussock | 1.00 | 0.08 | 0.72 | 1.15 | |
| tropical tussock | 0.93 | 0.05 | 0.74 | 1.09 | |
| tropical shrub tussock | 0.97 | 0.06 | 0.14 | 1.10 | |
| lowland meadow | 1.04 | 0.09 | 0.69 | 1.49 | |
| montane meadow | 0.84 | 0.14 | 0.04 | 1.57 | |
| alpine meadow | 1.00 | 0.17 | 0.04 | 1.59 | |
| swamp | 0.85 | 0.18 | 0.69 | 1.36 | |
| Pielou | temperate meadow-steppe | 0.89 | 0.05 | 0.79 | 1.16 |
| temperate steppe | 1.02 | 0.09 | 0.10 | 1.33 | |
| temperate desert-steppe | 1.04 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 1.26 | |
| alpine meadow-steppe | 1.11 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 1.36 | |
| alpine steppe | 1.10 | 0.12 | 0.08 | 1.38 | |
| alpine desert-steppe | 1.08 | 0.13 | 0.10 | 1.35 | |
| temperate steppe-desert | 1.01 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 1.25 | |
| temperate desert | 1.05 | 0.07 | 0.10 | 1.31 | |
| alpine desert | 1.14 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 1.38 | |
| warm-temperate tussock | 0.87 | 0.04 | 0.82 | 1.14 | |
| warm-temperate shrub tussock | 0.87 | 0.03 | 0.81 | 1.17 | |
| tropical tussock | 0.86 | 0.01 | 0.83 | 0.93 | |
| tropical shrub tussock | 0.86 | 0.03 | 0.12 | 0.95 | |
| lowland meadow | 1.03 | 0.05 | 0.82 | 1.33 | |
| montane meadow | 0.89 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 1.35 | |
| alpine meadow | 1.02 | 0.13 | 0.04 | 1.38 | |
| swamp | 0.92 | 0.12 | 0.82 | 1.28 |
| Index | Grassland Types | Mean | Standard Deviation | Minimum | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species richness | temperate meadow-steppe | −0.0016 | 0.0030 | −0.02 | 0.02 |
| temperate steppe | 0.0035 | 0.0092 | −0.03 | 0.05 | |
| temperate desert-steppe | −0.0006 | 0.0043 | −0.03 | 0.02 | |
| alpine meadow-steppe | 0.0007 | 0.0089 | −0.04 | 0.04 | |
| alpine steppe | −0.0014 | 0.0070 | −0.05 | 0.05 | |
| alpine desert-steppe | −0.0046 | 0.0066 | −0.04 | 0.03 | |
| temperate steppe-desert | −0.0006 | 0.0026 | −0.02 | 0.01 | |
| temperate desert | −0.0003 | 0.0022 | −0.03 | 0.01 | |
| alpine desert | −0.0029 | 0.0056 | −0.03 | 0.02 | |
| warm-temperate tussock | −0.0008 | 0.0021 | −0.01 | 0.01 | |
| warm-temperate shrub tussock | −0.0016 | 0.0029 | −0.02 | 0.01 | |
| tropical tussock | −0.0002 | 0.0011 | −0.02 | 0.00 | |
| tropical shrub tussock | −0.0005 | 0.0016 | −0.01 | 0.00 | |
| lowland meadow | −0.0005 | 0.0018 | −0.02 | 0.02 | |
| montane meadow | 0.0003 | 0.0037 | −0.03 | 0.03 | |
| alpine meadow | 0.0009 | 0.0063 | −0.04 | 0.05 | |
| swamp | 0.0008 | 0.0031 | −0.02 | 0.02 | |
| Shannon | temperate meadow-steppe | 0.0016 | 0.0035 | −0.01 | 0.02 |
| temperate steppe | 0.0014 | 0.0073 | −0.04 | 0.04 | |
| temperate desert-steppe | 0.0021 | 0.0052 | −0.03 | 0.03 | |
| alpine meadow-steppe | −0.0050 | 0.0099 | −0.06 | 0.05 | |
| alpine steppe | −0.0018 | 0.0094 | −0.06 | 0.06 | |
| alpine desert-steppe | 0.0050 | 0.0090 | −0.03 | 0.06 | |
| temperate steppe-desert | 0.0028 | 0.0046 | −0.02 | 0.03 | |
| temperate desert | 0.0018 | 0.0038 | −0.04 | 0.03 | |
| alpine desert | 0.0042 | 0.0073 | −0.05 | 0.05 | |
| warm-temperate tussock | 0.0005 | 0.0024 | −0.01 | 0.02 | |
| warm-temperate shrub tussock | 0.0002 | 0.0022 | −0.01 | 0.02 | |
| tropical tussock | 0.0000 | 0.0014 | −0.01 | 0.02 | |
| tropical shrub tussock | −0.0003 | 0.0018 | −0.01 | 0.01 | |
| lowland meadow | 0.0015 | 0.0044 | −0.02 | 0.03 | |
| montane meadow | −0.0010 | 0.0040 | −0.04 | 0.02 | |
| alpine meadow | −0.0024 | 0.0058 | −0.05 | 0.05 | |
| swamp | −0.0014 | 0.0038 | −0.04 | 0.02 | |
| Simpson | temperate meadow-steppe | 0.0003 | 0.0022 | −0.01 | 0.02 |
| temperate steppe | 0.0010 | 0.0063 | −0.02 | 0.03 | |
| temperate desert-steppe | 0.0006 | 0.0034 | −0.02 | 0.02 | |
| alpine meadow-steppe | −0.0030 | 0.0061 | −0.04 | 0.03 | |
| alpine steppe | −0.0010 | 0.0060 | −0.03 | 0.03 | |
| alpine desert-steppe | 0.0025 | 0.0040 | −0.02 | 0.03 | |
| temperate steppe-desert | 0.0015 | 0.0026 | −0.01 | 0.02 | |
| temperate desert | 0.0009 | 0.0022 | −0.01 | 0.02 | |
| alpine desert | 0.0021 | 0.0040 | −0.02 | 0.03 | |
| warm-temperate tussock | 0.0001 | 0.0015 | −0.01 | 0.01 | |
| warm-temperate shrub tussock | 0.0000 | 0.0013 | −0.01 | 0.01 | |
| tropical tussock | 0.0000 | 0.0010 | −0.01 | 0.01 | |
| tropical shrub tussock | −0.0001 | 0.0012 | −0.01 | 0.01 | |
| lowland meadow | 0.0004 | 0.0027 | −0.02 | 0.02 | |
| montane meadow | −0.0006 | 0.0031 | −0.02 | 0.02 | |
| alpine meadow | −0.0022 | 0.0048 | −0.04 | 0.03 | |
| swamp | −0.0003 | 0.0020 | −0.01 | 0.02 | |
| Pielou | temperate meadow-steppe | −0.0007 | 0.0016 | −0.01 | 0.00 |
| temperate steppe | 0.0000 | 0.0038 | −0.02 | 0.02 | |
| temperate desert-steppe | 0.0002 | 0.0017 | −0.01 | 0.01 | |
| alpine meadow-steppe | −0.0022 | 0.0040 | −0.02 | 0.02 | |
| alpine steppe | 0.0002 | 0.0040 | −0.02 | 0.02 | |
| alpine desert-steppe | 0.0028 | 0.0036 | −0.02 | 0.02 | |
| temperate steppe-desert | 0.0012 | 0.0015 | 0.00 | 0.01 | |
| temperate desert | 0.0005 | 0.0013 | −0.01 | 0.01 | |
| alpine desert | 0.0021 | 0.0026 | −0.01 | 0.02 | |
| warm-temperate tussock | −0.0005 | 0.0010 | −0.01 | 0.00 | |
| warm-temperate shrub tussock | −0.0007 | 0.0013 | −0.01 | 0.00 | |
| tropical tussock | −0.0001 | 0.0005 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| tropical shrub tussock | −0.0003 | 0.0008 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| lowland meadow | 0.0004 | 0.0019 | −0.02 | 0.01 | |
| montane meadow | −0.0007 | 0.0021 | −0.02 | 0.01 | |
| alpine meadow | −0.0016 | 0.0037 | −0.03 | 0.02 | |
| swamp | 0.0001 | 0.0015 | −0.01 | 0.01 |
References
- Pauli, H.; Gottfried, M.; Dullinger, S.; Abdaladze, O.; Akhalkatsi, M.; Benito Alonso, J.L.; Coldea, G.; Dick, J.; Erschbamer, B.; Fernandez Calzado, R.; et al. Recent Plant Diversity Changes on Europe’s Mountain Summits. Science 2012, 336, 353–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brummitt, N.; Araujo, A.C.; Harris, T. Areas of plant diversity—What do we know? Plants People Planet 2021, 3, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Yu, C.; Fu, G. Temperature sensitivities of aboveground net primary production, species and phylogenetic diversity do not increase with increasing elevation in alpine grasslands. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2023, 43, e02464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Yu, C.; Fu, G. Asymmetric warming among elevations may homogenize plant α-diversity and aboveground net primary production of alpine grasslands. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 11, 1126651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, X.J.; Tian, Y.; Ouzhu; Fu, G. Response of forage nutrient storages to grazing in alpine grasslands. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 991287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, N.; Fu, G. Variations in species and function diversity of soil fungal community along a desertification gradient in an alpine steppe. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 131, 108197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendse, F.; van Ruijven, J.; Jongejans, E.; Keesstra, S. Loss of Plant Species Diversity Reduces Soil Erosion Resistance. Ecosystems 2015, 18, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welti, E.; Helzer, C.; Joern, A. Impacts of plant diversity on arthropod communities and plant-herbivore network architecture. Ecosphere 2017, 8, e01983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boeck, H.J.; Lemmens, C.; Gielen, B.; Bossuyt, H.; Malchair, S.; Carnol, M.; Merckx, R.; Ceulemans, R.; Nijs, I. Combined effects of climate warming and plant diversity loss on above- and below-ground grassland productivity. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2007, 60, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Shen, Z.X. Response of alpine plants to nitrogen addition on the Tibetan Plateau: A meta-analysis. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2016, 35, 974–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Fu, G. Effects of grazing on plant species and phylogenetic diversity in alpine grasslands, Northern Tibet. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 170, 106331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, P.; Penuelas, J.; Lloret, F.; Llorens, L.; Estiarte, M. Experimental drought and warming decrease diversity and slow down post-fire succession in a Mediterranean shrubland. Ecography 2009, 32, 623–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, L.; Liu, M.; Garcia-Guzman, G.; Gilbert, G.S.; Zhou, S. Dilution effect of plant diversity on infectious diseases: Latitudinal trend and biological context dependence. Oikos 2020, 129, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yu, C.; Fu, G. Warming reconstructs the elevation distributions of aboveground net primary production, plant species and phylogenetic diversity in alpine grasslands. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 133, 108355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, J.A.; Harte, J.; Zhao, X.Q. Experimental warming causes large and rapid species loss, dampened by simulated grazing, on the Tibetan Plateau. Ecol. Lett. 2004, 7, 1170–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trisos, C.H.; Merow, C.; Pigot, A.L. The projected timing of abrupt ecological disruption from climate change. Nature 2020, 580, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.P.; Duan, J.C.; Xu, G.P.; Wang, Y.F.; Zhang, Z.H.; Rui, Y.C.; Luo, C.Y.; Xu, B.; Zhu, X.X.; Chang, X.F.; et al. Effects of warming and grazing on soil N availability, species composition, and ANPP in an alpine meadow. Ecology 2012, 93, 2365–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, Q.Z.; Dong, S.K.; Liu, S.L.; Wang, X.X.; Su, X.K.; Li, Y.Y.; Tang, L.; Wu, X.Y.; Zhao, H.D. Effects of grazing and climate warming on plant diversity, productivity and living state in the alpine rangelands and cultivated grasslands of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Rangel. J. 2015, 37, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.L.; Zhang, X.Z.; Wang, T.; Liang, E.Y.; Wang, S.P.; Zhu, J.T.; Ben, N. Responses and feedback of the Tibetan Plateau’s alpine ecosystem to climate change. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 2842–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, X.; Feng, G.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; Corlett, R.T.; Hughes, A.C.; Pimm, S.; Schmid, B.; Shi, S.; et al. The global significance of biodiversity science in China: An overview. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2021, 8, nwab032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorji, T.; Hopping, K.A.; Wang, S.P.; Piao, S.L.; Tarchen, T.; Klein, J.A. Grazing and spring snow counteract the effects of warming on an alpine plant community in Tibet through effects on the dominant species. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 263, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, J.A.; Harte, J.; Zhao, X.Q. Decline in medicinal and forage species with warming is mediated by plant traits on the Tibetan Plateau. Ecosystems 2008, 11, 775–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.T.; Long, R.J.; Wang, Q.J.; Ding, L.M.; Wang, M.P. Effects of altitude on plant-species diversity and productivity in an alpine meadow, Qinghai-Tibetan plateau. Aust. J. Bot. 2007, 55, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.W.; Luo, Y.J.; Du, G.Z. Effects of clipping on diversity and above-ground biomass associated with soil fertility on an alpine meadow in the eastern region of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. N. Z. J. Agric. Res. 2007, 50, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Qin, R.M.; Zhang, S.X.; Yang, X.Y.; Xu, M.H. Effects of long-term warming on the aboveground biomass and species diversity in an alpine meadow on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau of China. J. Arid Land 2020, 12, 252–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.L.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, P.F.; Li, H.L.; Chu, C.J.; Li, X.L.; Du, G.Z. Different categories of biodiversity explain productivity variation after fertilization in a Tibetan alpine meadow community. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 3464–3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganjurjav, H.; Duan, M.J.; Wan, Y.F.; Zhang, W.N.; Gao, Q.Z.; Li, Y.; Jiangcun, W.Z.; Danjiu, L.B.; Guo, H.B. Effects of grazing by large herbivores on plant diversity and productivity of semi-arid alpine steppe on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Rangel. J. 2015, 37, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, K.C.; Choler, P.; de Bello, F.; Mirotchnick, N.; Du, G.Z.; Sun, S.C. Fertilization decreases species diversity but increases functional diversity: A three-year experiment in a Tibetan alpine meadow. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 182, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.S.; Zhang, X.; Shen, Z.; Shi, P.; Yu, C.Q. Species richness and diversity of alpine grasslands on the Northern Tibetan Plateau:effects of grazing exclusion and growing season precipitation. J. Resour. Ecol. 2012, 3, 236–242. [Google Scholar]
- Stuart Chapin, F., III; Diaz, S. Interactions between changing climate and biodiversity: Shaping humanity’s future COMMENT. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 6295–6296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Sun, W. Temperature sensitivities of vegetation indices and aboveground biomass are primarily linked with warming magnitude in high-cold grasslands. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 843, 157002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Fu, G. Quantifying plant species α-diversity using normalized difference vegetation index and climate data in alpine grasslands. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Wang, J.; Li, S. Response of forage nutritional quality to climate change and human activities in alpine grasslands. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 845, 157552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.J.; Zhou, H.K.; Yao, B.Q.; Wang, W.Y.; Dong, S.K.; Shang, Z.H.; She, Y.D.; Ma, L.; Huang, X.T.; Zhang, Z.H.; et al. Effects of nutrient addition on degraded alpine grasslands of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau: A meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 301, 106970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, D.P.; Shi, P.L.; Zhang, X.Z.; Zou, C.B. Effects of grazing exclusion on carbon sequestration and plant diversity in grasslands of China—A meta-analysis. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 94, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, M.; Yu, C.; Fu, G. The change in environmental variables linked to climate change has a stronger effect on aboveground net primary productivity than does phenological change in alpine grasslands. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 12, 798633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Li, S.W.; Sun, W.; Shen, Z.X. Relationships between vegetation carbon use efficiency and climatic factors on the Tibetan Plateau. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 42, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Yang, C.; Zhou, H.K.; Shao, X.Q. Responses of plant diversity and soil microorganism diversity to water and nitrogen additions in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 22, e01003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.H.; Willis, C.G.; Klein, J.A.; Ma, Z.; Li, J.Y.; Zhou, H.K.; Zhao, X.Q. Recovery of plant species diversity during long-term experimental warming of a species-rich alpine meadow community on the Qinghai-Tibet plateau. Biol. Conserv. 2017, 213, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, F.I.; Kelly, C.K. Responses of global plant diversity capacity to changes in carbon dioxide concentration and climate. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 1229–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halloy, S.R.P.; Mark, A.F. Climate-change effects on alpine plant biodiversity: A New Zealand perspective on quantifying the threat. Arct. Antarct. Alp. Res. 2003, 35, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolezal, J.; Dvorsky, M.; Kopecky, M.; Liancourt, P.; Hiiesalu, I.; Macek, M.; Altman, J.; Chlumska, Z.; Rehakova, K.; Capkova, K.; et al. Vegetation dynamics at the upper elevational limit of vascular plants in Himalaya. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.W.; Yu, C.Q.; Fu, G. Asymmetrical warming between elevations may result in similar plant community composition between elevations in alpine grasslands. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 9, 757943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; van Kleunen, M. Common alien plants are more competitive than rare natives but not than common natives. Ecol. Lett. 2019, 22, 1378–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, I.; Zandalinas, S.I.; Huck, C.; Fritschi, F.B.; Mittler, R. Meta-analysis of drought and heat stress combination impact on crop yield and yield components. Physiol. Plant. 2021, 171, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemoine, N.P.; Doublet, D.; Salminen, J.-P.; Burkepile, D.E.; Parker, J.D. Responses of plant phenology, growth, defense, and reproduction to interactive effects of warming and insect herbivory. Ecology 2017, 98, 1817–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, H.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, M. Precipitation controls seed bank size and its role in alpine meadow community regeneration with increasing altitude. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 5767–5777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.; Collins, S.L.; Du, G. Direct and indirect effects of temperature and precipitation on alpine seed banks in the Tibetan Plateau. Ecol. Appl. 2020, 30, e02096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Du, R.; Wang, S.; Duan, J.; Iler, A.M.; Piao, S.; Luo, C.; Jiang, L.; Lv, W.; et al. Richness of plant communities plays a larger role than climate in determining responses of species richness to climate change. J. Ecol. 2019, 107, 1944–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Shen, Z.X.; Sun, W.; Zhong, Z.M.; Zhang, X.Z.; Zhou, Y.T. A meta-analysis of the effects of experimental warming on plant physiology and growth on the Tibetan Plateau. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2015, 34, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydogan, E.L.; Budich, O.; Hardt, M.; Choi, Y.H.; Jansen-Willems, A.B.; Moser, G.; Mueller, C.; Kaempfer, P.; Glaeser, S.P. Global warming shifts the composition of the abundant bacterial phyllosphere microbiota as indicated by a cultivation-dependent and -independent study of the grassland phyllosphere of a long-term warming field experiment. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2020, 96, fiaa087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Bates, K.A.; Hoang, K.L.; Hector, T.E.; Knowles, S.C.L.; King, K.C. Experimental temperatures shape host microbiome diversity and composition. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2023, 29, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faticov, M.; Abdelfattah, A.; Roslin, T.; Vacher, C.; Hamback, P.; Blanchet, F.G.; Lindahl, B.D.; Tack, A.J.M. Climate warming dominates over plant genotype in shaping the seasonal trajectory of foliar fungal communities on oak. N. Phytol. 2021, 231, 1770–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlifa, R.; Houle, D.; Morin, H.; Kembel, S.W. Inconsistent effects of nitrogen canopy enrichment and soil warming on black spruce epiphytic phyllosphere bacterial communities, taxa, and functions. Can. J. For. Res. 2021, 51, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perazzolli, M.; Vicelli, B.; Antonielli, L.; Longa, C.M.O.; Bozza, E.; Bertini, L.; Caruso, C.; Pertot, I. Simulated global warming affects endophytic bacterial and fungal communities of Antarctic pearlwort leaves and some bacterial isolates support plant growth at low temperatures. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.-G.; Xiong, C.; Wei, Z.; Chen, Q.-L.; Ma, B.; Zhou, S.-Y.-D.; Tan, J.; Zhang, L.-M.; Cui, H.-L.; Duan, G.-L. Impacts of global change on the phyllosphere microbiome. N. Phytol. 2022, 234, 1977–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, G. Effect of long-term experimental warming on the nutritional quality of alpine meadows in the Northern Tibet. J. Resour. Ecol. 2020, 11, 516–524. [Google Scholar]
- Donoghue, M.J. A phylogenetic perspective on the distribution of plant diversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11549–11555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Telwala, Y.; Brook, B.W.; Manish, K.; Pandit, M.K. Climate-Induced Elevational Range Shifts and Increase in Plant Species Richness in a Himalayan Biodiversity Epicentre. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Burgess, K.S.; Gao, L.-M.; Li, D.-Z. Distributional responses to climate change for alpine species of Cyananthus and Primula endemic to the Himalaya-Hengduan Mountains. Plant Divers. 2019, 41, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Shen, Z.X.; Zhang, X.Z. Increased precipitation has stronger effects on plant production of an alpine meadow than does experimental warming in the Northern Tibetan Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 249, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Shen, Z. Asymmetrical warming of growing/non-growing season increases soil respiration during growing season in an alpine meadow. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 812, 152591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, F.; Yu, C.; Fu, G. Non-growing/growing season non-uniform-warming increases precipitation use efficiency but reduces its temporal stability in an alpine meadow. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1090204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.Q.; Han, F.S.; Fu, G. Effects of 7 years experimental warming on soil bacterial and fungal community structure in the Northern Tibet alpine meadow at three elevations. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 814–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Zhang, G.; Fu, G. Response of soil microbial communities to warming and clipping in alpine meadows in Northern Tibet. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Li, S.; Zhang, G.; Fu, G.; Qi, H.; Li, T. Effects of climate change and anthropogenic activities on soil pH in grassland regions on the Tibetan Plateau. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2023, 45, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusch, G.M.; Oesterheld, M. Relationship between productivity, and species and functional group diversity in grazed and non-grazed Pampas grassland. Oikos 1997, 78, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Qi, H.; Fu, G. Response of vegetation precipitation use efficiency to experimental warming in alpine grasslands of Northern Tibet. Pratacultural Sci. 2022, 39, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Z.G.; Deng, G.; Hu, G.J.; Zhang, H.B.; Pan, H.Z.; Sang, G.Q. Satellite observed spatiotemporal variability of snow cover and snow phenology over high mountain Asia from 2002 to 2021. J. Hydrol. 2022, 613, 128438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.; Tang, Z.G.; Hu, G.J.; Wang, J.W.; Sang, G.Q.; Li, J. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Snowline Altitude and Their Responses to Climate Change in the Tienshan Mountains, Central Asia, during 2001–2019. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.G.; Wang, X.R.; Deng, G.; Wang, X.; Jiang, Z.L.; Sang, G.Q. Spatiotemporal variation of snowline altitude at the end of melting season across High Mountain Asia, using MODIS snow cover product. Adv. Space Res. 2020, 66, 2629–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.G.; Wang, X.R.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Li, H.Y.; Jiang, Z.L. Spatiotemporal Variation of Snow Cover in Tianshan Mountains, Central Asia, Based on Cloud-Free MODIS Fractional Snow Cover Product, 2001–2015. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.G.; Wang, J.; Li, H.Y.; Liang, J.; Li, C.K.; Wang, X. Extraction and assessment of snowline altitude over the Tibetan plateau using MODIS fractional snow cover data (2001 to 2013). J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2014, 8, 084689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.S.; Yu, C.Q.; Fu, G. Warming alters elevation distributions of soil bacterial and fungal communities in alpine grasslands. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2022, 39, e02306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Walck, J.L.; Ma, Z.; Wang, L.; Du, G. Grazing disturbance increases transient but decreases persistent soil seed bank. Ecol. Appl. 2018, 28, 1020–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.-F.; Shi, S.-H.; Huang, X.-M.; Jiang, Y.-S.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Z.-S. A global meta-analysis of grazing effects on soil seed banks. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 33, 1892–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternberg, M.; Gutman, M.; Perevolotsky, A.; Kigel, J. Effects of grazing on soil seed bank dynamics: An approach with functional groups. J. Veg. Sci. 2003, 14, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Fu, G. Responses of plant, soil bacterial and fungal communities to grazing vary with pasture seasons and grassland types, northern Tibet. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 1821–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; He, P. Responses of forage nutrient quality to grazing in the alpine grassland of Northern Tibet. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2021, 30, 38–50. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Kan, A.; Zeng, Y.; Li, G.; Wang, M.; Ci, R. Population distribution pattern and influencing factors in Tibet based on random forest model. Acta Geogr. Sini. 2019, 74, 664–680. [Google Scholar]
- Nathan, R.; Schurr, F.M.; Spiegel, O.; Steinitz, O.; Trakhtenbrot, A.; Tsoar, A. Mechanisms of long-distance seed dispersal. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2008, 23, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cain, M.L.; Milligan, B.G.; Strand, A.E. Long-distance seed dispersal in plant populations. Am. J. Bot. 2000, 87, 1217–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, G.; Shen, Z.X. Response of alpine soils to nitrogen addition on the Tibetan Plateau: A meta-analysis. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 114, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Fu, G. Responses of phylogenetic diversity of soil fungal community to grazing in alpine grasslands of the Northern Tibet. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2022, 30, 21–28. [Google Scholar]


| Change Rate of α-Diversity | Climate Change Scenes | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Warming, Wetting, Brightening | Warming, Wetting, Dimming | Warming, Drying, Brightening | Warming, Drying, Dimming | Cooling, Wetting, Brightening | Cooling, Wetting, Dimming | Cooling, Drying, Brightening | Cooling, Drying, Dimming | ||
| Slope_SRp | <0 | 4.25 | 17.80 | 7.51 | 2.72 | 0.63 | 0.79 | 0.16 | 0.04 |
| =0 | 0.17 | 6.88 | 0.90 | 1.04 | 0.01 | 0.16 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| >0 | 5.94 | 41.18 | 4.70 | 2.29 | 0.54 | 2.15 | 0.12 | 0.03 | |
| Slope_Shannonp | <0 | 2.96 | 21.42 | 5.45 | 3.08 | 0.55 | 1.41 | 0.23 | 0.04 |
| =0 | 0.14 | 5.36 | 0.66 | 0.75 | 0.04 | 0.40 | 0.00 | 0.01 | |
| >0 | 7.25 | 39.07 | 7.00 | 2.21 | 0.60 | 1.29 | 0.05 | 0.03 | |
| Slope_Simpsonp | <0 | 2.07 | 21.77 | 4.18 | 2.84 | 0.56 | 1.70 | 0.24 | 0.04 |
| =0 | 0.09 | 2.24 | 0.55 | 0.52 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| >0 | 8.20 | 41.86 | 8.37 | 2.69 | 0.61 | 1.29 | 0.04 | 0.03 | |
| Slope_Pieloup | <0 | 1.39 | 33.71 | 2.66 | 2.74 | 0.63 | 2.43 | 0.20 | 0.05 |
| =0 | 0.13 | 1.82 | 0.59 | 0.45 | 0.01 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| >0 | 8.83 | 30.32 | 9.85 | 2.85 | 0.55 | 0.61 | 0.08 | 0.03 | |
| Slope_SRa | <0 | 4.58 | 23.62 | 7.48 | 3.45 | 0.55 | 1.27 | 0.17 | 0.01 |
| =0 | 0.29 | 8.61 | 0.62 | 1.08 | 0.08 | 0.67 | 0.00 | 0.02 | |
| >0 | 5.49 | 33.62 | 5.02 | 1.51 | 0.55 | 1.15 | 0.12 | 0.04 | |
| Slope_Shannona | <0 | 4.07 | 27.61 | 4.97 | 3.31 | 0.52 | 0.71 | 0.19 | 0.03 |
| =0 | 0.09 | 2.71 | 0.42 | 0.44 | 0.01 | 0.11 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| >0 | 6.19 | 35.54 | 7.72 | 2.29 | 0.65 | 2.28 | 0.10 | 0.04 | |
| Slope_Simpsona | <0 | 3.14 | 25.82 | 4.77 | 3.11 | 0.64 | 0.81 | 0.18 | 0.03 |
| =0 | 0.13 | 3.78 | 0.46 | 0.48 | 0.06 | 0.17 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| >0 | 7.09 | 36.26 | 7.88 | 2.46 | 0.48 | 2.12 | 0.11 | 0.04 | |
| Slope_Pieloua | <0 | 3.08 | 29.65 | 4.19 | 2.86 | 0.70 | 2.00 | 0.14 | 0.03 |
| =0 | 0.21 | 3.66 | 0.72 | 0.63 | 0.02 | 0.17 | 0.00 | 0.01 | |
| >0 | 7.07 | 32.54 | 8.21 | 2.56 | 0.46 | 0.93 | 0.14 | 0.04 | |
| Changes in the Influence Intensity of Human Activities on Plant α-Diversity | Slope_Rα-diversity | Rα-diversity | Species Richness | Shannon | Simpson | Pielou |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No change in positive influence | =0 | All > 1 | 0.80 | 0.83 | 0.08 | 0.03 |
| No change in negative influence | =0 | All < 1 | 0.21 | 0.44 | 0.96 | 1.49 |
| No change in influence, but oscillate between positive and negative influence | =0 | Not all > 1 or not all < 1 | 4.63 | 0.87 | 0.65 | 0.37 |
| The increase in positive influence | >0 | All > 1 | 0.50 | 16.37 | 8.00 | 17.10 |
| The decrease in negative influence | >0 | All < 1 | 3.86 | 1.01 | 5.72 | 3.38 |
| From negative to positive influence | >0 | Not all > 1 or not all < 1 | 38.04 | 26.59 | 30.93 | 27.40 |
| The decrease in positive influence | <0 | All > 1 | 1.04 | 17.44 | 13.24 | 11.32 |
| The increase in negative influence | <0 | All < 1 | 6.24 | 1.73 | 6.00 | 6.78 |
| From positive to negative influence | <0 | Not all > 1 or not all < 1 | 44.68 | 34.71 | 34.44 | 32.12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, S.; Fu, G. Impacts of Climate Change and Human Activities on Plant Species α-Diversity across the Tibetan Grasslands. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2947. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15112947
Huang S, Fu G. Impacts of Climate Change and Human Activities on Plant Species α-Diversity across the Tibetan Grasslands. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(11):2947. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15112947
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Shaolin, and Gang Fu. 2023. "Impacts of Climate Change and Human Activities on Plant Species α-Diversity across the Tibetan Grasslands" Remote Sensing 15, no. 11: 2947. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15112947
APA StyleHuang, S., & Fu, G. (2023). Impacts of Climate Change and Human Activities on Plant Species α-Diversity across the Tibetan Grasslands. Remote Sensing, 15(11), 2947. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15112947





