Abstract
The accurate estimation of ocean tide loading displacements is essential and necessary for geodesy, oceanic and geophysical studies. It is common knowledge that K1 and K2 tidal constituents estimated from Global Positioning System (GPS) observations are unsatisfactory because their tidal periods are nearly same to the revisit cycle or orbital period of GPS constellation. To date, this troublesome problem is not fully solved. In this paper, we revisit this important issue and develop a novel method based on the unique characteristic of tidal waves to separate GPS-system errors from astronomical K1/K2 tides. The well-known credo of smoothness indicates that tidal admittances of astronomical constituents in a narrow band can be expressed as smooth functions of tidal frequencies, while the interference of GPS-system errors seriously damages the smooth nature of observed tidal admittances. Via quadratic fitting, smooth functions of tidal frequencies for tidal admittances can be determined, thus, astronomical K1 and K2 tides can be interpolated using fitted quadratic functions. Three GPS stations are selected to demonstrate our method because of their typicality in terms of poor estimates of K1/K2 tidal parameters related to GPS-system errors. After removing GPS-systematical contributions based on our method, corrected K1/K2 tides at three GPS stations are much closer to the modeled K1/K2 tides from FES2014, which is one of the most accurate tide models. Furthermore, the proposed method can be easily applied to other areas to correct GPS-system errors because their smooth nature is valid for global tidal signals.
1. Introduction
Ocean tides are periodical sea water movements (mainly diurnal and semi-diurnal) driven by the astronomical forcing from the Moon and the Sun [1,2,3]. As a result of ocean mass redistribution caused by ocean tides, the periodical deformation of the earth’s surface is called ocean tide loading (OTL) displacement [4]. The spatial features of OTL are mainly decided by nearby ocean tides and the amplitudes of OTL can reach as high as 10 cm in some coastal regions [5,6]. Precise estimation of OTL displacement for major tidal constituents is fundamental and vital for multidisciplinary fields such as the global navigation satellite system (GNSS), as well as oceanic, geophysical and seismological studies [7,8,9].
As a powerful and widely used tool to observe OTL displacement, GPS is superior to other geodesic tools (e.g., very long baseline interferometry) in terms of high accuracy, wide coverage and low cost [5]. However, GPS-observed OTL displacements have some defects. It is well known that the revisit cycle of the GPS constellation is nearly same as K1 tidal period (23.934 h), while the orbital period of the GPS constellation is nearly the same as K2 tidal period (11.967 h) [6]. Consequently, K1 and K2 tidal amplitudes/phases estimated from GPS observations are significantly poorer than other major tidal constituents [10].
To solve this knotty problem, numerous efforts have been made. Abbaszadeh et al. (2020) [11] try to use the combination of GLONASS and GPS observations because the orbital period of GLONASS constellation is 11.25 h, which is different from K2 tidal period (11.967 h). However, it is found that the estimations for K1 and K2 tides are still unsatisfactory although there are some improvements [11]. Wei et al. (2022b) [6] go a step further by using the combination of multi-GNSS including GPS, GLONASS, Galileo and BeiDou. Every GNSS has unique orbital parameters, for example, the orbital period of Galileo satellites is ~14 h [6]. Thus, it is obvious that tidal estimations from multi-GNSS observations are less influenced by the systematic errors of GPS compared to GPS-only observations. Although multi-GNSS observations improve the estimation of OTL displacement, the method proposed by Wei et al. (2022b) [6] does not completely solve the problem because GPS-system errors still exist as long as GPS observations are used.
The purpose of this paper is to revisit this troublesome but vital issue and to propose a novel yet simple method based on the unique ability of tidal signals to fully address the problem. Our paper is structured as follows. Data and methodology are shown in Section 2. Section 3 shows the results as well as discussions, followed by the summary in Section 4.
2. Methodology and Data
Our method is established on the basis of the credo of smoothness proposed by Munk and Cartwright (1966) [12]. The credo of smoothness indicates that tidal admittances are smooth functions of tidal frequency in a narrow band [13,14]. Such smooth functions can be simply expressed as quadratic functions [12,13,14], namely, Equation (1):
.
A (w) represents tidal admittances while w is tidal frequency. Model parameters a1, a2, a3 can be determined via least squares. Tidal admittances for amplitudes (i.e., normalized amplitudes) are defined by the ratios of observed tidal amplitudes to theoretical equilibrium tidal amplitudes, while tidal admittances for phases are defined by the phase lags between observed tidal phases and theoretical equilibrium tidal phases. Note that equilibrium tidal amplitudes can be calculated based on the equilibrium tide theory via the s_equilibrium_tide function in the S_TIDE toolbox developed by the authors [15,16,17], while phase lags can be directly estimated from observations using tidal harmonic analysis. Tidal admittances represent actual tidal responses of ocean environment to the astronomical forcing, which mainly depend on the frequencies of tidal waves, water depth and coastlines. For tides in specific sea areas, tidal admittances only depend on tidal frequencies because the ocean environment is the same for all kinds of tidal waves. Semi-diurnal tides have similar tidal periods (close to 0.5 days), which means that their wave lengths are also similar. As a result, tidal responses for semi-diurnal tides are highly consistent; namely, their co-tidal charts are closely similar in terms of spatial patterns (see Figure A1 in the Appendix A). Therefore, tidal admittances for semi-diurnal tides can be approximated by the smooth functions of tidal frequencies. Diurnal tides also have similar features.
Figure A2 in Appendix A displays tidal admittances for diurnal ocean tides at Cuxhaven (Germany), located at the mouth of the Elbe river, as a typical example. Normalized amplitudes are quadratic functions of diurnal frequencies while phase lags are nearly linear functions of diurnal frequencies over these frequency ranges. As a result of the interference of non-astronomical factors (i.e., river flow), observed tidal admittances at Cuxhaven slightly deviate from the fitted curves, but their smoothness is generally robust and reliable. Since OTL originated from ocean tides, it also inherits the nature of smooth tidal admittances. Consequently, co-tidal charts of OTL for tides with similar periods also have similar spatial patterns (see in Hart-Davis et al. (2021) [9] for examples). Figure 1 displays diurnal tidal admittances for the up component based on the FES2014 OTL model [18] at Aira (31.8241°N, 130.5996°E) (location shown in Figure A3 in Appendix A), as a typical example. Both normalized amplitudes and phase lags of diurnal OTL are quadratic functions of diurnal frequencies at Aira. The existence of GPS-system errors severely destroys the smoothness of tidal admittances but also provides opportunities to remove non-astronomical contributions to K1 and K2 tidal estimations (see Section 3 for details).
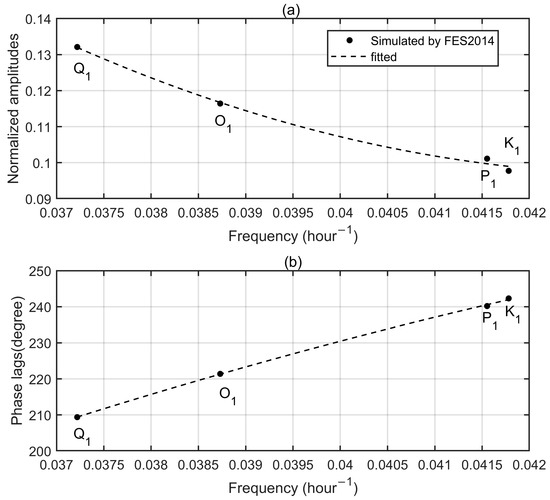
Figure 1.
Normalized tidal amplitudes (a) and phase lags (b) for Q1, O1, P1 and K1 tides for the up component at Aira based on FES2014 model data. Black dots represent simulated tidal admittances while dash lines are the fitted curves estimated by ordinary least squares.
To demonstrate our method, we use OTL displacement estimates at three GPS stations (Aira, Bill and Helj) in the CM frame provided by Yuan et al. (2013) [5]. Tidal amplitudes (denoted by H) and phase lags (denoted by G) of eight major constituents are obtained by classical harmonic analysis (Equation (2). Z(t) are GPS-observed OTL displacements while Z0 is a constant. fn, un, and vn are nodal factor, nodal angle and astronomical argument of n-th tidal constituent, which are all known:
Aira is discussed in detail due to its typicality in terms of poor estimates of K1/K2 tidal parameters related to GPS-system errors. Semi-diurnal tides are generally larger than diurnal tides at Aira. As shown in Table 1, M2 phase lag (144.0°) for the north component is close to N2 phase lag (134.3°) and their phase difference is only 9.7°. The frequency difference between S2 and K2 tides is much smaller than that between M2 and N2, therefore, the phase difference between S2 and K2 phase lags should be smaller than 9.7°. However, the GPS-observed S2 and K2 phase difference is as high as 85.4°, which clearly indicates the interference of GPS-system errors. Similarly, the phase difference between K1 and P1 tides should be much smaller than that between Q1 and O1 tides. However, unfortunately, the observed K1-P1 phase difference (20.5°) for the north component is noticeably larger than the observed Q1-O1 phase difference (4.3°).

Table 1.
Amplitudes (mm) and Greenwich phase lags (°) at the up (U), north (N), east (E) components of eight main tidal constituents at Aira GPS station. Equilibrium (Eq) tidal amplitudes (mm) are also shown.
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Results
Figure 2 displays semi-diurnal tidal admittances for the up component at Aira. Both normalized amplitudes and phase lags are quadratic functions of semi-diurnal tidal frequencies. Note that fitted quadratic curves are determined via ordinary least squares using N2, M2 and S2 tidal admittances. K2 tidal admittances are not used because they are contaminated by GPS-system errors. As shown in Figure 2, K2 tidal admittances significantly deviate from fitted quadratic curves. According to the tidal theory, S2 and K2 tides have highly close periods, thus, their admittances should also be close as long as they have astronomical origins. However, the interference of the systematic errors of GPS observations induces abnormal changes in K2 admittances. Via the interpolation, astronomical K2 admittances can be calculated (red dots in Figure 2), which are close to the observed S2 admittances. Since equilibrium K2 tidal amplitude is known, astronomical K2 amplitude and phase lag at the up component at Aira can be obtained as 2.38 mm and 149.4°, respectively.
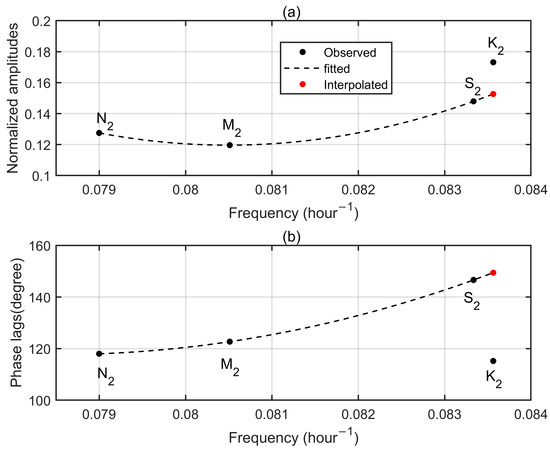
Figure 2.
Semi-diurnal tidal admittances for the up component at Aira GPS station. (a) Normalized amplitudes. (b) Phase lags. Observed tidal admittances are denoted by black dots while dash lines mean the fitted curves. Red dots represent the interpolated values according to the fitted curves.
Similar to semi-diurnal tidal admittances, diurnal tidal admittances for the up component at Aira are also quadratic functions of diurnal frequencies (Figure 3). K1 admittances unnaturally deviate from the fitted curves, especially for phase lags, due to GPS-system errors. Astronomical K1 admittances can be estimated using the interpolation (red dots in Figure 3), which are close to observed P1 admittances. Based on known equilibrium K1 tidal parameters, astronomical K1 amplitude and phase lag at the up component can be obtained as 10.17 mm and 243.43°, respectively.
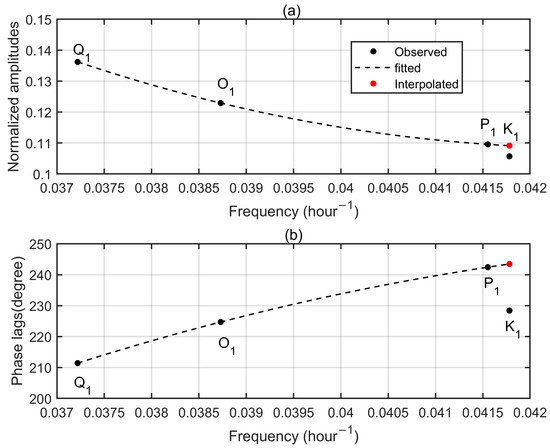
Figure 3.
Diurnal tidal admittances for the up component at Aira GPS station. (a) Normalized amplitudes. (b) Phase lags. Observed tidal admittances are denoted by black dots while dash lines mean the fitted curves. Red dots represent the interpolated values according to the fitted curves.
The observed K1 tides by GPS have two main energy sources: one is the astronomical K1 tide driven by astronomical forcing and the other is the non-astronomical K1 tide mainly induced by GPS-system errors. Hence, as displayed in Figure 4a, the observed K1 tide (black arrow) is the vectorial composition of the astronomical K1 tide (red arrow) and non-astronomical K1 tide (blue arrow). The non-astronomical K1 amplitude and phase lag are 2.64 mm and 139.0°, respectively. Although non-astronomical and astronomical K1 tides have same tidal frequency, their features (namely, amplitudes and phase lags) are distinct because they are originated from different processes.
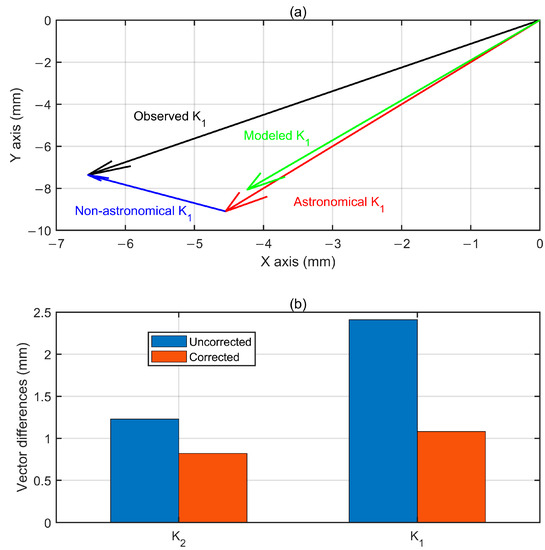
Figure 4.
(a) The vectorial composition of the astronomical K1 tide (red arrow) and non-astronomical K1 tide (blue arrow) furnishes the observed K1 tide (black arrow) at Aira. Green arrow represents the modeled K1 tidal vector (using FES2014 tidal model). (b) The vector differences (VDs) between modeled K1/K2 tidal vectors and uncorrected/corrected K1/K2 tidal vectors (corrections are performed on the basis of the credo of smoothness).
The modeled K1 amplitude and phase lag for the up component at Aira are 9.11 mm and 242.3°, respectively, based on FES2014 tide model [18]. Figure 4a clearly indicates that astronomical K1 tide obtained from our method is highly consistent with modeled K1 tide (green arrow). Note that FES2014 tide model is one of the most accurate tide models [9], thus, it is used as a reference. The vector difference (VD) between modeled K1 tidal vector and uncorrected K1 tidal vector (namely, GPS-observed K1 tide) is 2.41 mm. After correction using our method (namely, removing non-astronomical contributions), VD sharply decreases to 1.08 mm (Figure 4b), which indicates the effectiveness and reliability of our method. Similarly, corrected K2 tide is also much closer to modeled K2 tide compared to uncorrected K2 tide (Figure 4b).
Figure 5 and Figure 6 display semi-diurnal and diurnal tidal admittances for the north component at Aira. Similar to the up component, K1 and K2 tidal admittances at the north component anomalously deviate from the fitting curves, especially for phase lags. The interpolated K1 and K2 tidal admittances (red dots) are generally close to observed P1 and S2 tidal admittances, which is consistent with tidal theory. Results for the east component are depicted by Figure 7 and Figure 8 and, in addition, indicate the effectiveness of our method. Note that nearly all global tide models only provide OTL for the up component, thus, we do not compare corrected results at the north and east components with model results due to lack of model data.
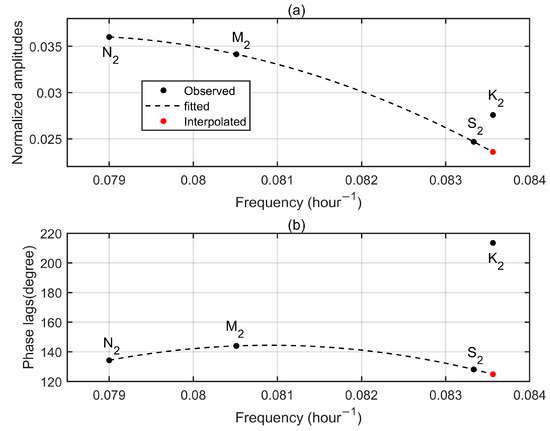
Figure 5.
Semi-diurnal tidal admittances for the north component at Aira GPS station. (a) Normalized amplitudes. (b) Phase lags. Observed tidal admittances are denoted by black dots while dash lines mean the fitted curves. Red dots represent the interpolated values according to the fitted curves.
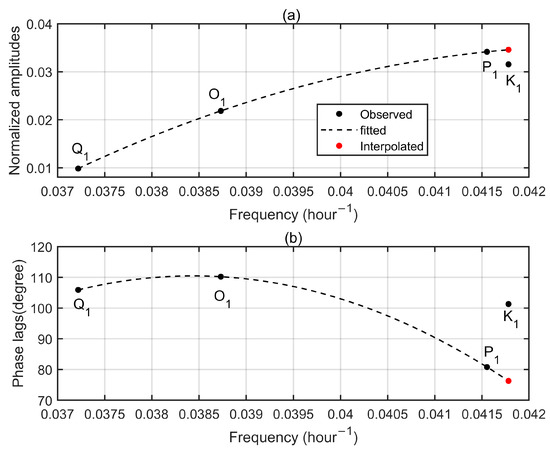
Figure 6.
Diurnal tidal admittances for the north component at Aira GPS station. (a) Normalized amplitudes. (b) Phase lags. Observed tidal admittances are denoted by black dots while dash lines mean the fitted curves. Red dots represent the interpolated values according to the fitted curves.
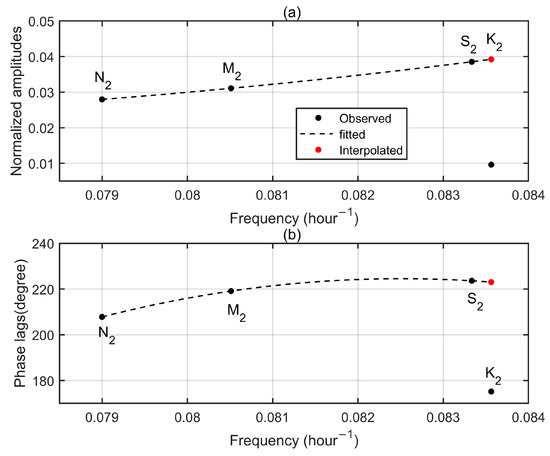
Figure 7.
Semi-diurnal tidal admittances for the east component at Aira GPS station. (a) Normalized amplitudes. (b) Phase lags. Observed tidal admittances are denoted by black dots while dash lines mean the fitted curves. Red dots represent the interpolated values according to the fitted curves.
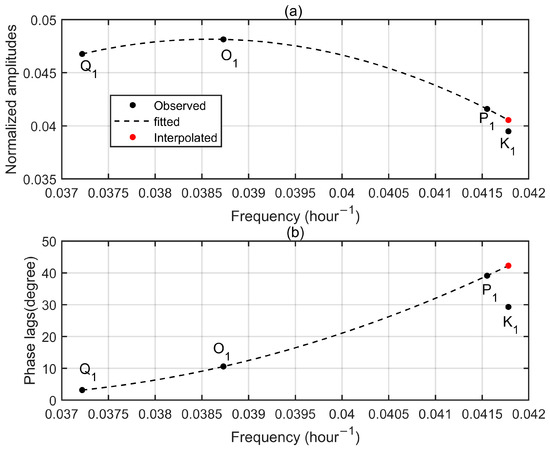
Figure 8.
Diurnal tidal admittances for the east component at Aira GPS station. (a) Normalized amplitudes. (b) Phase lags. Observed tidal admittances are denoted by black dots while dash lines mean the fitted curves. Red dots represent the interpolated values according to the fitted curves.
To further validate our method, we tested it using two other typical GPS stations called Bill (33.5782°N, 242.9354°E) and Helj (54.1745°N, 7.8931°E). As shown in Figure 9 and Figure 10, corrected K1/K2 tides at Helj and Bill are much closer to modeled K1/K2 tides compared to uncorrected K1/K2 tides. The details on smooth tidal admittances at Bill and Helj can be found in the Appendix A (Figure A4, Figure A5, Figure A6 and Figure A7) to avoid repetitions. In summary, the results of three GPS stations all show the validity of proposed method.
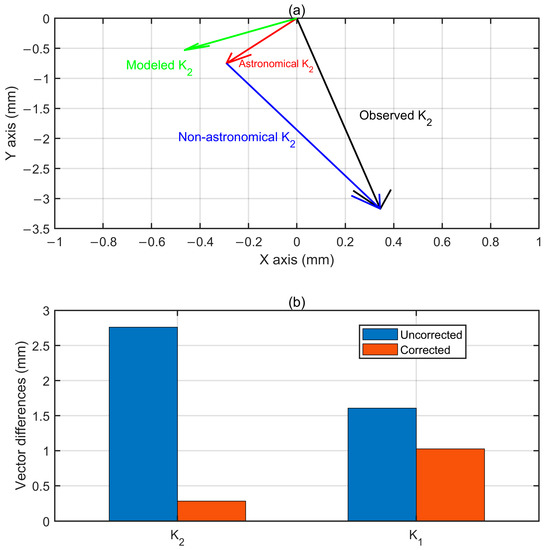
Figure 9.
(a) The vectorial composition of the astronomical K2 tide (red arrow) and non-astronomical K2 tide (blue arrow) furnishes the observed K2 tide (black arrow) at Helj. Green arrow represents the modeled K2 tidal vector (using FES2014 tidal model). (b) The vector differences (VDs) between modeled K1/K2 tidal vectors and uncorrected/corrected K1/K2 tidal vectors (corrections are performed on the basis of the credo of smoothness).
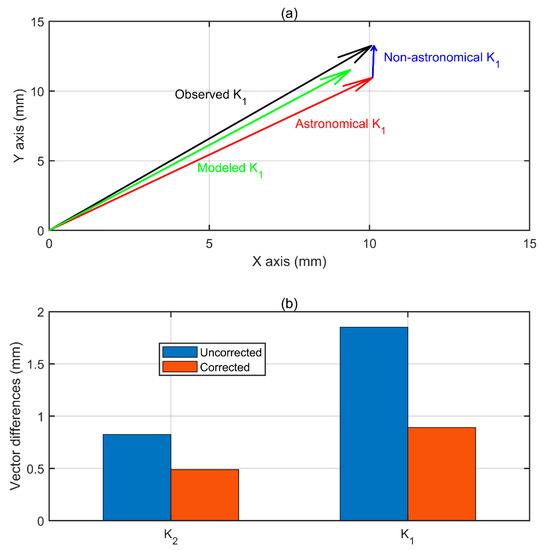
Figure 10.
(a) The vectorial composition of the astronomical K1 tide (red arrow) and non-astronomical K1 tide (blue arrow) furnishes the observed K1 tide (black arrow) at Bill. Green arrow represents the modeled K1 tidal vector (using FES2014 tidal model). (b) The vector differences (VDs) between modeled K1/K2 tidal vectors and uncorrected/corrected K1/K2 tidal vectors (corrections are performed on the basis of the credo of smoothness).
3.2. Discussions: The Advantages and Limitations of the Proposed Methodology
The proposed method has many advantages. Its principle is simple and easy to understand. The realization of this method is uncomplicated, without numerous computation resources. Although this method can be applied to the whole globe, in theory, cautions should be taken in some coastal resonant areas where significant nonlinear interactions between main tidal constituents exist. Taking K2 tide, for example, with the exception of astronomical forcing, K2 tide can also be generated by the nonlinear interaction between M2, O1 and K1 tides (i.e., M2 − O1 + K1 or K1 + K1). Furthermore, S2 seasonality can also contribute to K2 tide. In most sea areas, ocean tides are semi-diurnal, thus, astronomical contributions are dominant in the generation of K2 tide. However, for some sea areas where diurnal tidal resonance exists (such as the Gulf of Tonkin in the South China Sea [19]), local diurnal tides are abnormally larger than semi-diurnal tides, therefore, the nonlinear origin of K2 tides is important and not negligible. The proposed method not only removes the contribution of GPS-system errors to K2 tides, but it also eliminates the contributions of nonlinear interactions and S2 seasonality. Namely, the obtained K2 tide via our method is mainly astronomical.
In the construction of smooth functions of tidal admittances, we only use eight main tidal constituents but do not use minor tidal constituents such as 2Q1, J1, 2N2, NU2, LAD2 and L2. These minor diurnal and semi-diurnal tides are much smaller than major constituents in terms of equilibrium tidal amplitudes, which means that they are more easily influenced by background noises and nonlinear interactions between main tidal constituents. The frequency of 2N2 tide is the same as 2NM2 tide, which can be generated by nonlinear interactions between N2 and M2 tides (i.e., N2 + N2 − M2). The frequency of NU2 tide is the same as MLS2 tide, which can be generated by nonlinear interactions between M2, L2 and S2 tides (i.e., M2 + L2 − S2). The frequency of LAD2 tide is the same as SNM2 tide, which can be generated by nonlinear interactions between S2, N2 and M2 tides (i.e., S2 + N2 − M2). The frequency of L2 tide is the same as 2MN2 tide, which can be generated by nonlinear interactions between M2 and N2 tides (i.e., M2 + M2 − N2). In some coastal areas, the contributions of nonlinear interactions to these minor constituents may be comparable or even larger than direct astronomical contributions. Therefore, including these minor constituents may significantly distort the smoothness of tidal admittances.
In fact, major constituents can also obtain energy from nonlinear interactions. For example, M2 tidal frequency is the same as KO2 tide, which is generated from the nonlinear interaction between K1 and O1 tides (i.e., K1 + O1). M2 tide can also obtain energy from the nonlinear interaction of N2, S2 and LAD2 tides (i.e., N2 + S2 − LAD2). S2 tidal frequency is the same as KP2 tide, which is derived from the nonlinear interaction between K1 and P1 tides (i.e., K1 + P1). Furthermore, S2 tide can obtain energy from the nonlinear interaction of M2 and MU2 tides (i.e., M2 + M2 − MU2). However, compared to minor constituents, the amplitudes of major constituents contributed to by astronomical forcing are large enough to resist the interference of nonlinear contributions in most sea areas. In some resonant sea areas, like the Gulf of Tonkin, the smoothness of semi-diurnal tidal admittances may be distorted to some extent. In fact, with the exception of nonlinear interactions, radiational S2 tides driven by solar radiation also contribute to observed S2 tides. Observed S2 admittances are altered in phases by adding 5.9° and in amplitudes by multiplying by 0.97 due to radiational S2 tides [20]. Overall, radiational S2 tides only slightly distort S2 tidal admittances.
4. Conclusions
Originating from ocean tides, OTL displacements have complex and irregular spatial variations [21]. Accurate knowledge of OTL displacement is beneficial for numerous geophysical and geodetic studies [22,23]. Although GPS is widely used for observing OTL displacements due to its various advantages, it also has some disadvantages which can severely influence the accuracy of K1 and K2 tidal estimations. Tidal constants of major constituents are estimated from GPS observations via classical harmonic analysis, which is a frequency-dependent method. Therefore, tidal harmonic analysis can only obtain tidal parameters of given tidal frequencies and cannot distinguish astronomical contributions from GPS-system errors.
To fully solve this question, we propose a novel but straightforward method based on the distinct physical properties of non-astronomical and astronomical tides. For astronomical tides, their admittances in a narrow band are similar and can be expressed as smooth functions of tidal frequencies [24]. Via simple interpolation, astronomical K1 and K2 tides can be separated from GPS-system errors. Three representative GPS stations have demonstrated the validity of our method. Moreover, as a universal method, it can be easily applied to other areas to correct GPS-system errors because the credo of smoothness of tidal admittances is effective for all kinds of tidal signals. However, care should be taken in some coastal resonant sea areas where the contribution of nonlinear interactions may make up a considerable part of observed main tidal constituents. It should be noted that the proposed method always tends to eliminate all non-astronomical contributions. Furthermore, in addition to our method, artificial intelligence algorithms [25,26] may be helpful in solving this problem, which deserves further exploration.
Funding
This study is jointly supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (42206022, 42076024, 41821004), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2022M713677) and the Qingdao postdoctoral application research project (QDBSH202108).
Data Availability Statement
Water levels at Cuxhaven (ID: h825) can be downloaded from the University of Hawaii Sea Level Center (https://uhslc.soest.hawaii.edu/, accessed on 11 January 2023). OTL displacement estimates at three GPS stations can be downloaded from this website: (https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/action/downloadSupplement?doi=10.1002%2Fjgrb.50159&file=2012jb009865_table_s1.txt, accessed on 11 January 2023). S_TIDE toolbox can be downloaded from this website (https://www.researchgate.net/publication/369066450_S_TIDE_toolbox_v123_update7, accessed on 11 May 2023).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
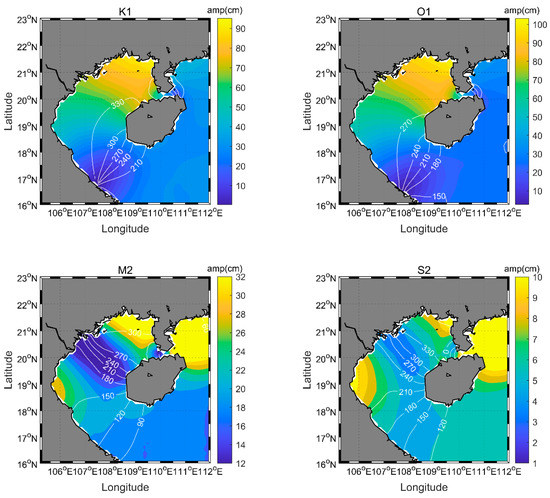
Figure A1.
Co-tidal charts for K1, O1, M2 and S2 tides in the Gulf of Tonkin. Tidal constants are obtained from EOT20 model, which is developed based on FES2014 [9]. Co-tidal charts are drawn using the s_draw_tidalchart function in the S_TIDE toolbox. Co-tidal charts for M2 and S2 tides are similar, while those for K1 and O1 tides are highly consistent.
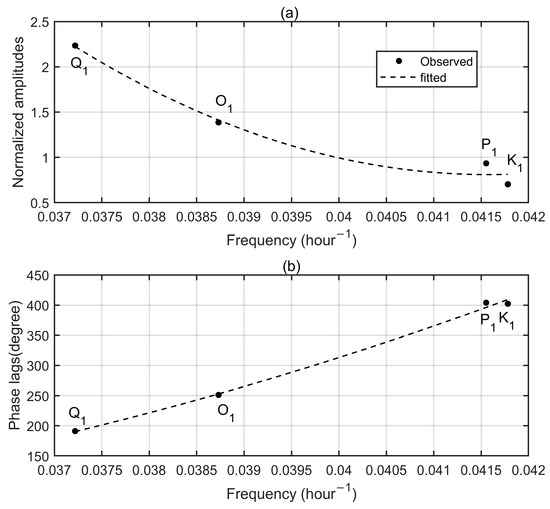
Figure A2.
(a) Normalized tidal amplitudes and (b) phase lags for Q1, O1, P1 and K1 ocean tides at Cuxhaven tide gauge, Germany. Black dots represent observed tidal admittances while dash lines are the fitted curves estimated by ordinary least squares.
Figure A3.
Locations of analyzed GPS stations. Red, pink and black dots represent Helj, Aira and Bill GPS stations, respectively.
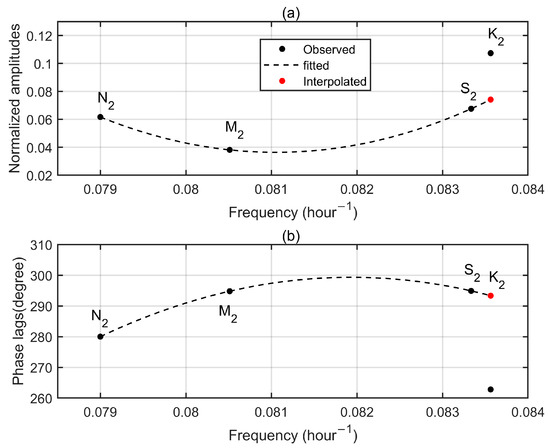
Figure A4.
Semi-diurnal tidal admittances for the up component at Bill GPS station. (a) Normalized amplitudes. (b) Phase lags. Observed tidal admittances are denoted by black dots while dash lines mean the fitted curves. Red dots represent the interpolated values according to the fitted curves.
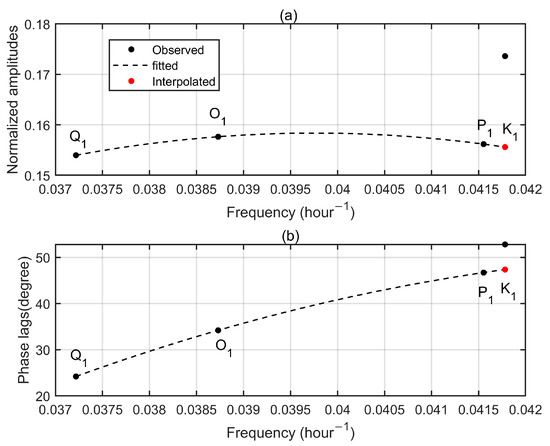
Figure A5.
Diurnal tidal admittances for the up component at Bill GPS station. (a) Normalized amplitudes. (b) Phase lags. Observed tidal admittances are denoted by black dots while dash lines mean the fitted curves. Red dots represent the interpolated values according to the fitted curves. Abnormal changes of observed K1 admittances compared to observed Q1, O1 and P1 admittances are not physical, but induced by GPS-system errors.
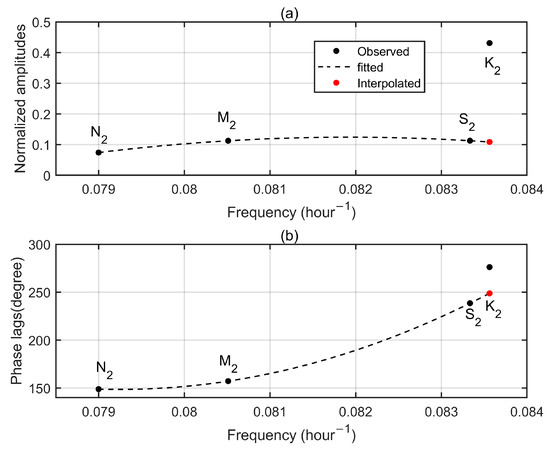
Figure A6.
Semi-diurnal tidal admittances for the up component at Helj GPS station. (a) Normalized amplitudes. (b) Phase lags. Observed tidal admittances are denoted by black dots while dash lines mean the fitted curves. Red dots represent the interpolated values according to the fitted curves.
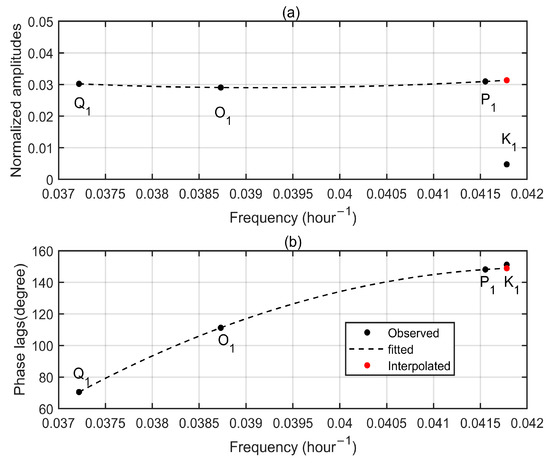
Figure A7.
Diurnal tidal admittances for the up component at Helj GPS station. (a) Normalized amplitudes. (b) Phase lags. Observed tidal admittances are denoted by black dots while dash lines mean the fitted curves. Red dots represent the interpolated values according to the fitted curves.
References
- Ray, R.D. On Tidal Inference in the Diurnal Band. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2017, 34, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, M.; Pan, H.; Chen, Y.; Pan, S. Application of the Variational Mode Decomposition (VMD) Method to River Tides. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 261, 107570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Pan, H.; Xu, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J. Development History of the Numerical Simulation of Tides in the East Asian Marginal Seas: An Overview. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Liu, X.; Yuan, J.; Jin, X.; Niu, Y.; Guo, J.; Gao, H. Seasonal Variation of GPS-Derived the Principal Ocean Tidal Constituents’ Loading Displacement Parameters Based on Moving Harmonic Analysis in Hong Kong. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Chao, B.F.; Ding, X.; Zhong, P. The tidal displacement field at Earth’ s surface determined using global GPS observations. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2013, 118, 2618–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Chen, K.; Ji, R. Improving estimates of ocean tide loading displacements with multi-GNSS: A case study of Hong Kong. GPS Solut. 2022, 26, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, W. Deformation of the Earth by surface loads. Rev. Geophys. 1972, 10, 761–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, O.; Mazzega, P. Global charts of ocean tide loading effects. J. Geophys. Res. 1990, 95, 11411–11424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart-Davis, M.; Piccioni, G.; Dettmering, D.; Schwatke, C.; Passaro, M.; Seitz, F. EOT20: A global ocean tide model from multi-mission satellite altimetry. Earth Syst. Sci. Data. 2021, 13, 3869–3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Wang, Q.; Peng, W. Accurate evaluation of vertical tidal displacement determined by GPS kinematic precise point positioning: A case study of Hong Kong. Sensors 2019, 19, 2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaszadeh, M.; Clarke, P.; Penna, N. Benefits of combining GPS and GLONASS for measuring ocean tide loading displacement. J Geod. 2020, 94, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munk, W.H.; Cartwright, D.E. Tidal spectroscopy and prediction. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London A 1966, 259, 533–581. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.; Tsimplis, M.; Woodworth, P. Nodal variations and long-term changes in the main tides on the coasts of China. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2015, 120, 1215–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Xu, T.; Wei, Z. Anomalously large seasonal modulations of shallow water tides at Lamu, Kenya. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2023, 281, 108203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Lv, X.; Wang, Y.; Matte, P.; Chen, H.; Jin, G. Exploration of Tidal-Fluvial Interaction in the Columbia River Estuary Using S_TIDE. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2018, 123, 6598–6619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Zheng, Q.; Lv, X. Temporal changes in the response of the nodal modulation of the M2 tide in the Gulf of Maine. Cont. Shelf Res. 2019, 186, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Lv, X. Is There a Quasi 60-Year Oscillation in Global Tides? Cont. Shelf Res. 2021, 222, 104433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyard, F.; Allain, D.; Cancet, M.; Carrère, L.; Picot, N. FES2014 global ocean tide atlas: Design and performance. Ocean. Sci. 2021, 17, 615–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Devlin, A.T.; Xu, T.; Lv, X.; Wei, Z. Anomalous 18.61-Year Nodal Cycles in the Gulf of Tonkin Revealed by Tide Gauges and Satellite Altimeter Records. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartwright, D.E.; Ray, R.D. On the radiational anomaly in the global ocean tide with reference to satellite altimetry. Oceanol. Acta. 1994, 17, 453–459. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, G.; Xu, X.; Wei, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Vertical displacement loading tides and self-attraction and loading tides in the Bohai, Yellow, and East China Seas. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2013, 56, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, M.; Penna, N.; Baker, T.; Clarke, P. Ocean tide loading displacements in western Europe: 2. GPS -observed anelastic dispersion in the asthenosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth. 2015, 120, 6523–6539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Ding, X.; Sun, H.; Zhong, P.; Chen, W. Determination of ocean tide loading displacements in Hong Kong using GPS technique. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2010, 53, 993–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zetler, B.D. Radiational ocean tides along the coasts of the United States. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1971, 1, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, X. Satellite data-driven and knowledge-informed machine learning model for estimating global internal solitary wave speed. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 283, 113328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, B.; Zheng, G.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Gao, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, F. Deep-learning-based information mining from ocean remote-sensing imagery. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 1584–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).