Deep Learning of High-Resolution Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Imagery for Classifying Halophyte Species: A Comparative Study for Small Patches and Mixed Vegetation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
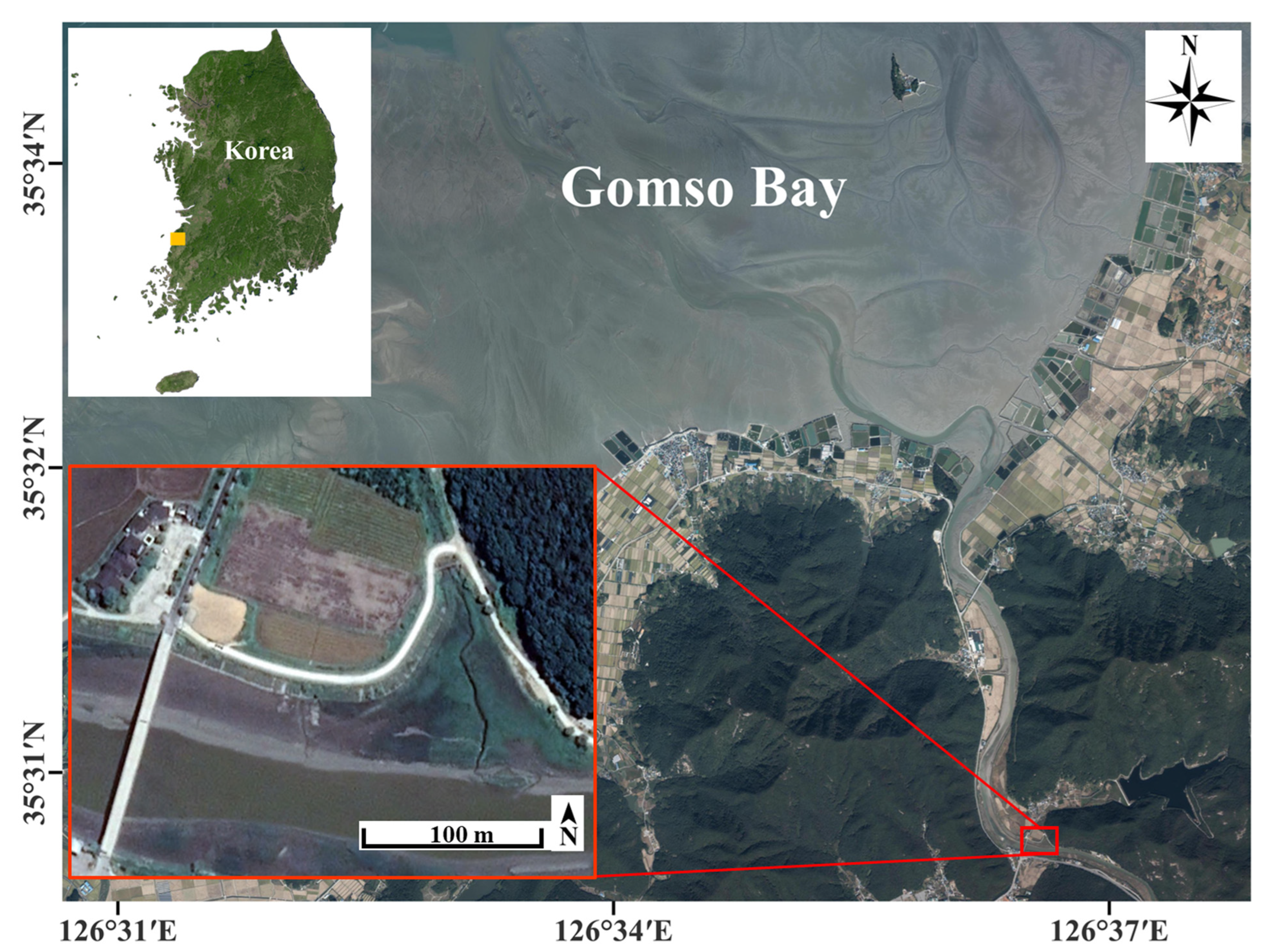
2.1. Study Area
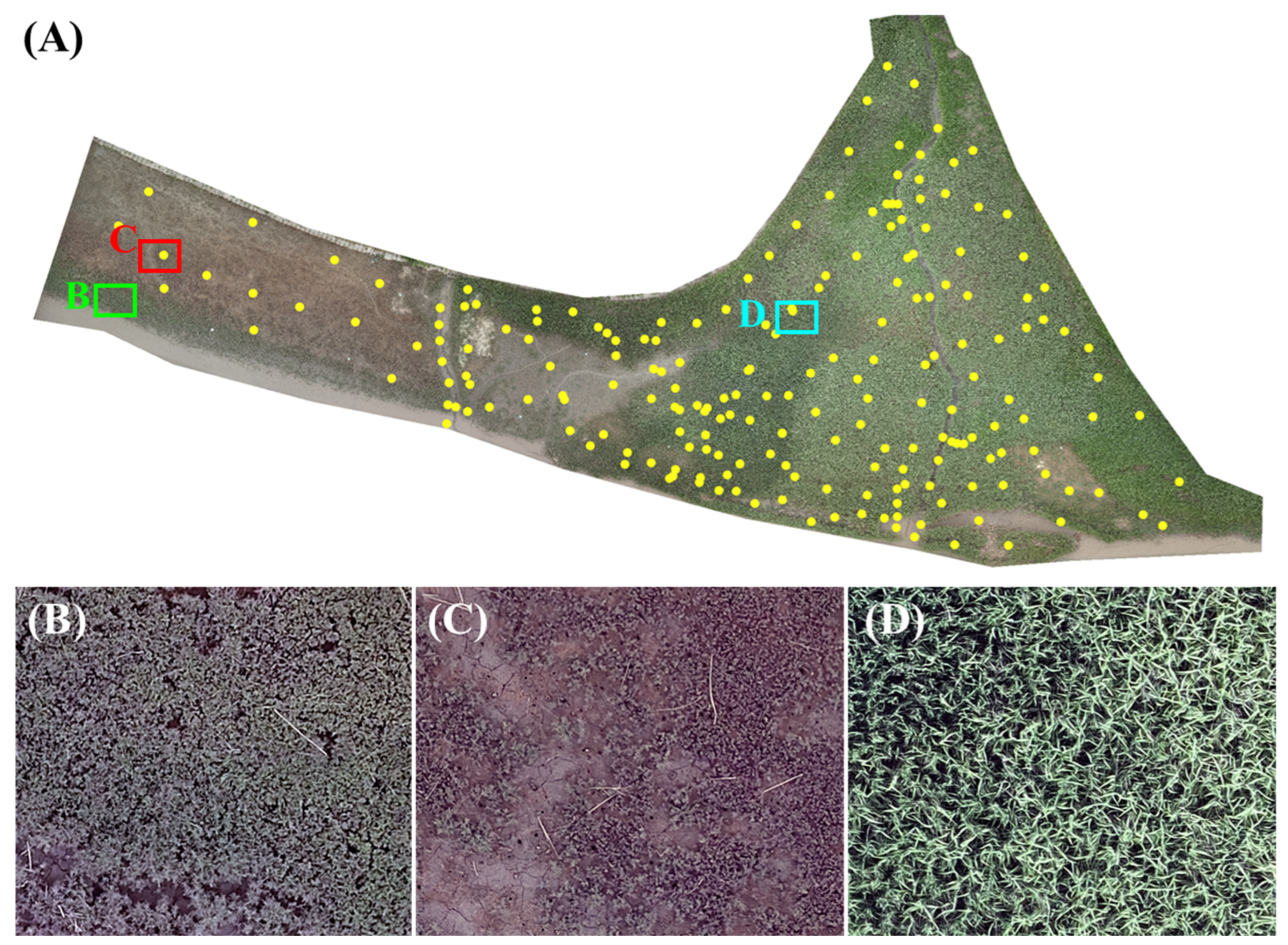
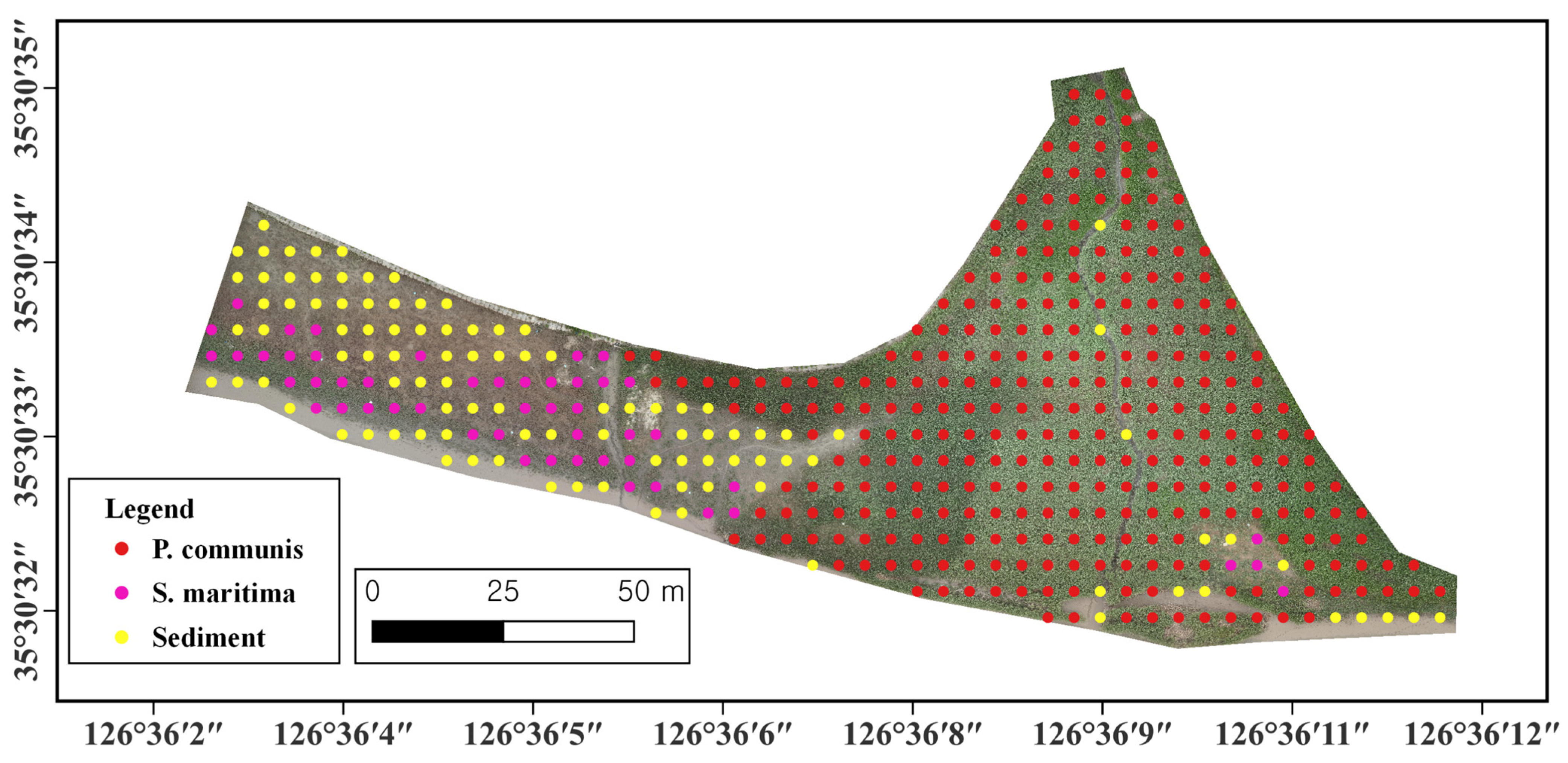
2.2. In-Situ Field Work and Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Image Acquisition
2.3. UAV Data Processing
2.4. Vegetation Classification
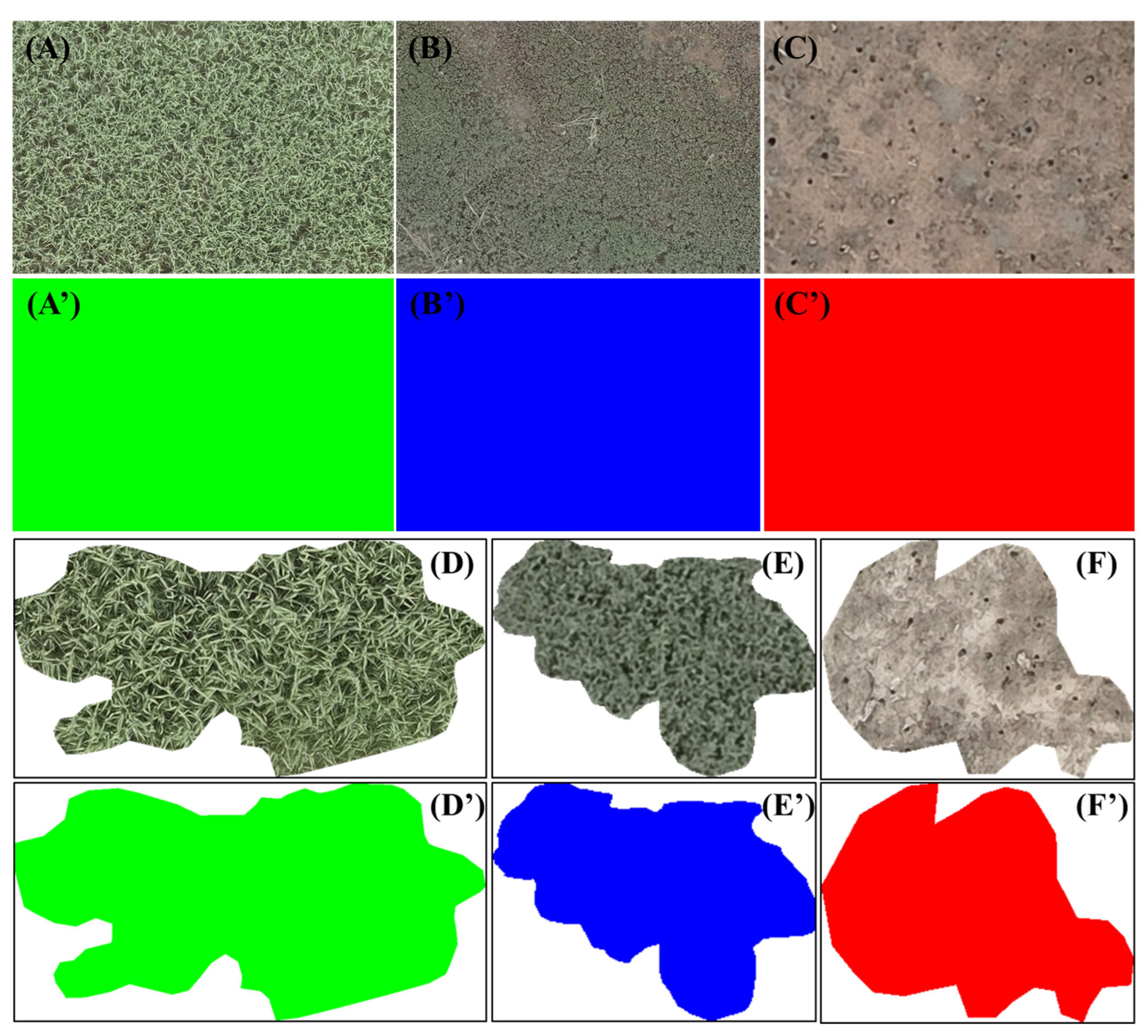
2.4.1. Pixel-Based Classification
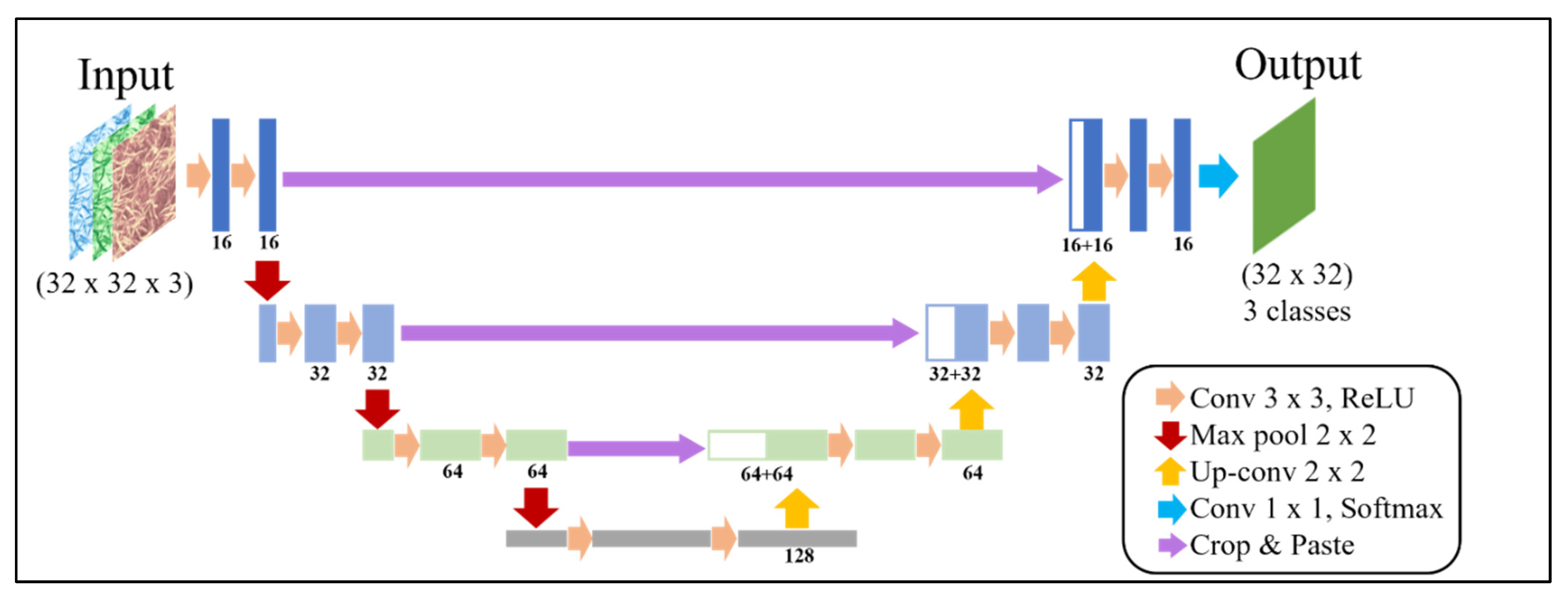
2.4.2. Deep-Learning Analysis
2.5. Classification Accuracy Assessment
3. Results
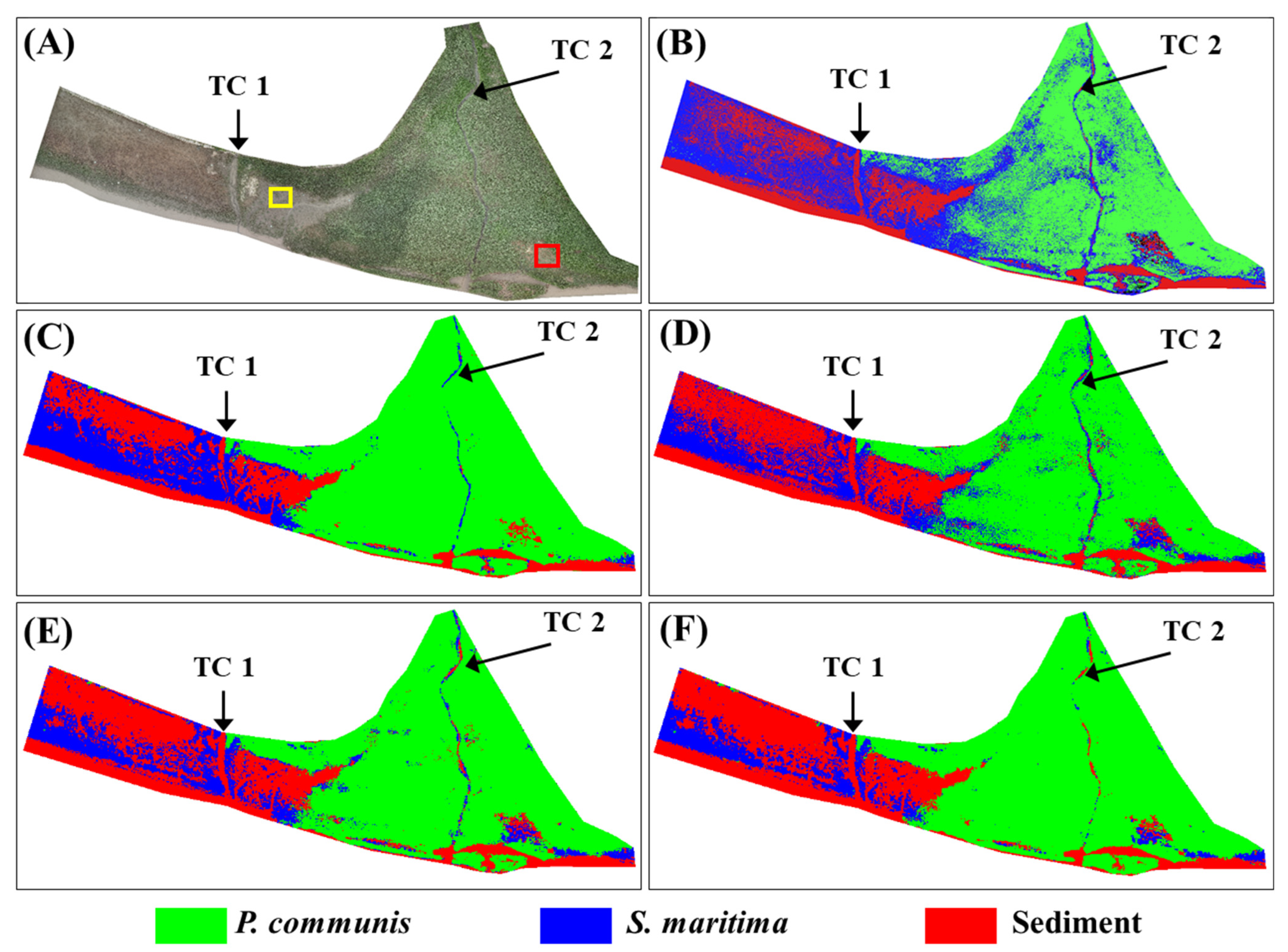
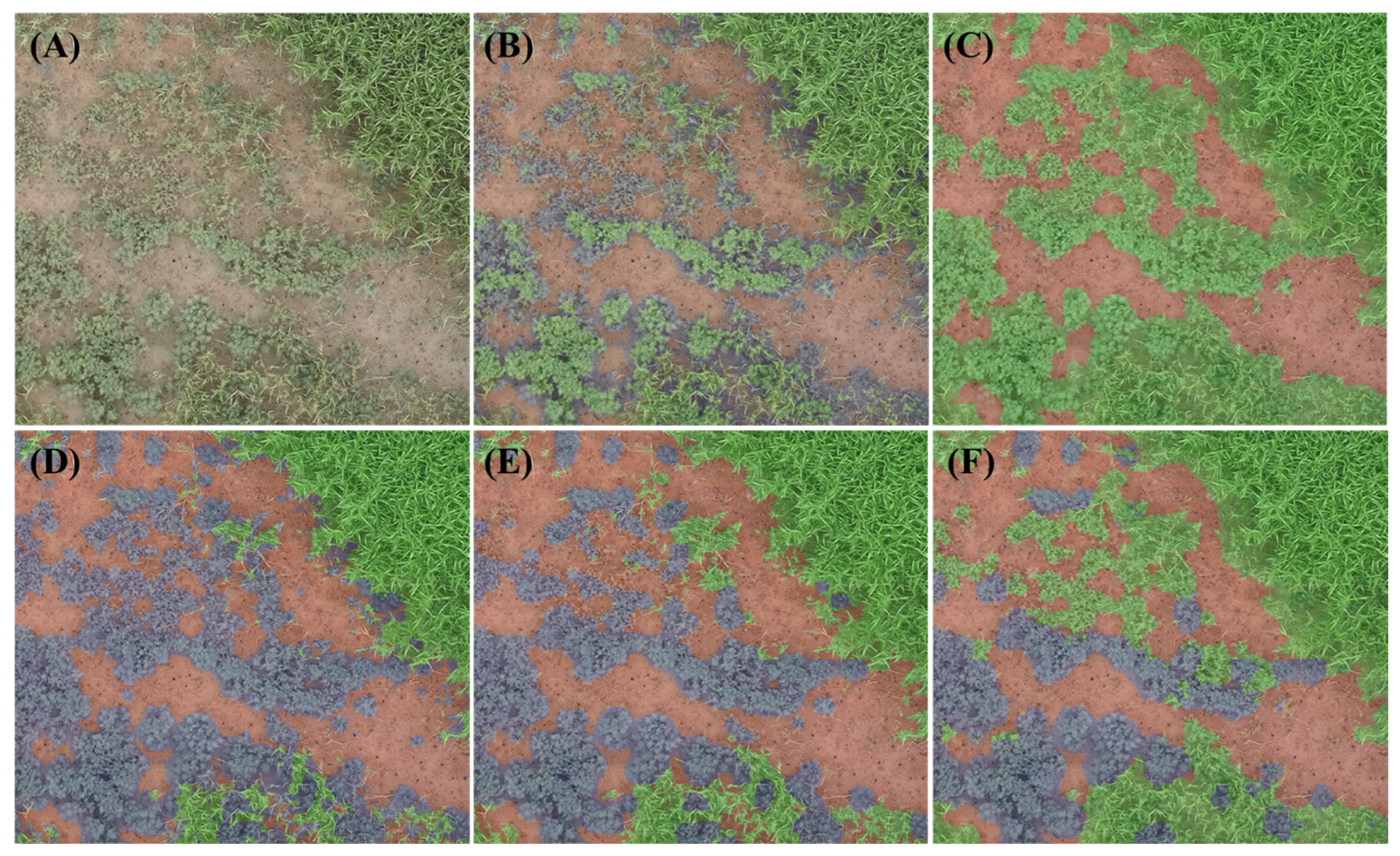
3.1. Classification of Salt Marsh Vegetation
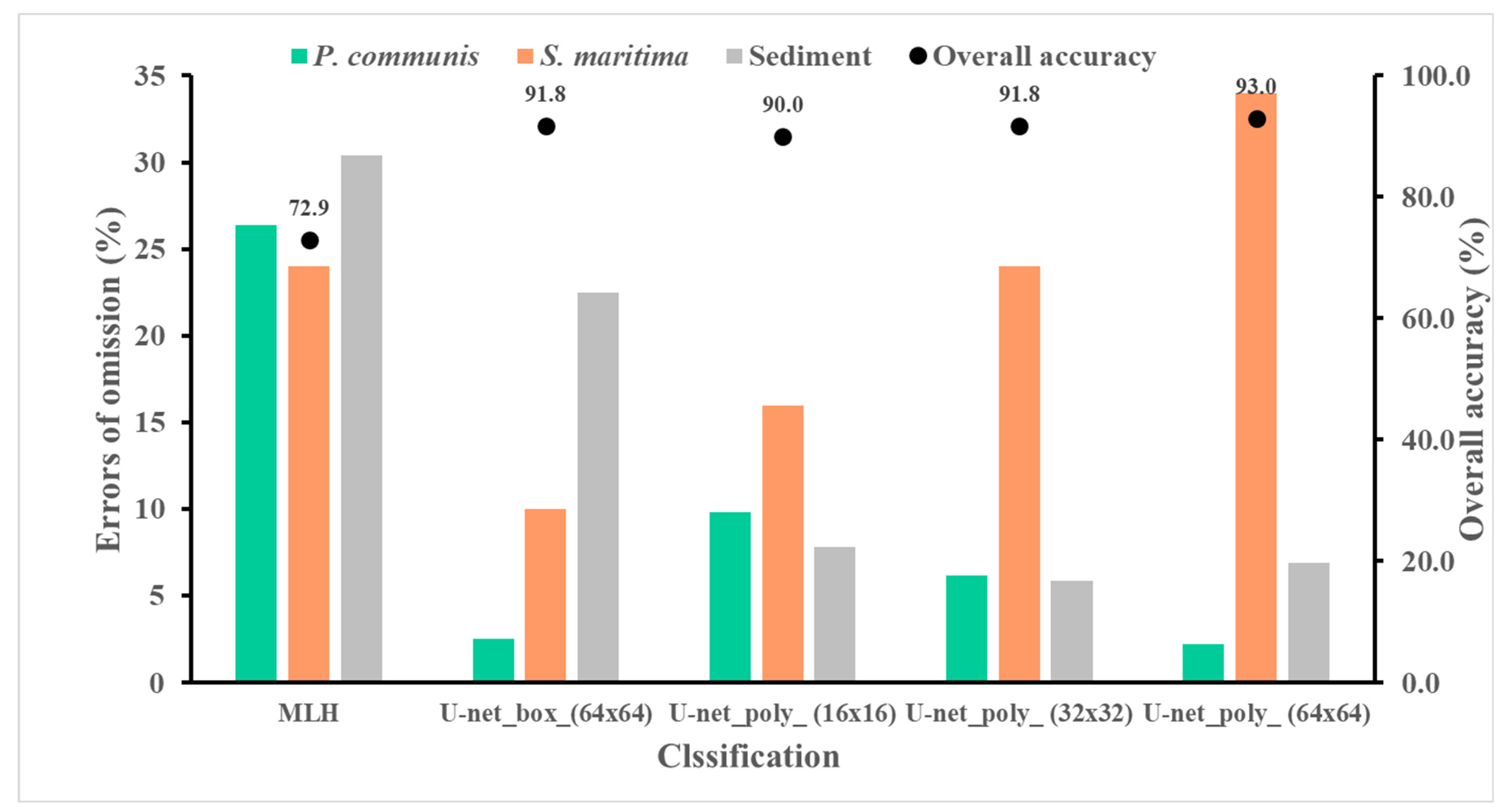
3.2. Classification Performance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barbier, E.B.; Hacker, S.D.; Kennedy, C.; Koch, E.W.; Stier, A.; Silliman, B. The value of estuarine and coastal ecosystem services. Ecol. Monogr. 2011, 81, 169–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, W. Beyond carbon: Conceptualizing payments for ecosystem services in blue forests on carbon and other marine and coastal ecosystem services. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2013, 83, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gailis, M.; Kohfeld, K.E.; Pellatt, M.G.; Garlson, D. Quantifying blue carbon for the largest salt marsh in southern British Columbia: Implications for regional coastal management. Coast. Eng. J. 2021, 3, 275–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Wiberg, P.L. The Importance of Storm Surge for Sediment Delivery to Microtidal Marshes. JGR Earth Surf. 2022, 127, e2022JF006612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedan, K.B.; Siliman, B.R.; Bertness, M.D. Centuries of human-driven change in salt marsh ecosystems. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2009, 1, 117–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrino, E.V.; Wagensommer, R.P. Crop Wild Relatives (CWRs) Threatened and Endemic to Italy: Urgent Actions for Protection and Use. Biology 2022, 11, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaselli, V.; Mantino, F.; Tarantino, C.; Albanese, G.; Adamo, M. Changing landscapes: Habitat monitoring and land transformation in a long-time used Mediterranean coastal wetland. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2023, 31, 31–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuman, C.S.; Ambrose, R.F. A Comparison of Remote Sensing and Ground-Based Methods for Monitoring Wetland Restoration Success. Restor. Ecol. 2003, 11, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zedler, J.B.; Kercher, S. Wetland Resources: Status, Trends, Ecosystem Services, and Restorability. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2005, 30, 39–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Li, J.; Sheng, C.; Xu, J.; Wu, L. A review of Wetland Remote Sensing. Sensors 2017, 17, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Fagherazzi, S.; Liu, Y. Classification mapping of salt marsh vegetation by flexible monthly NDVI time-series using Landsat imagery. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 213, 61–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneses, N.C.; Brunner, F.; Baier, S.; Geist, J.; Schneider, T. Quantification of Extent, Density, and Status of Aquatic Reed Beds Using Point Clouds Derived from UAV–RGB Imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samiappan, S.; Turnage, G.; Hathcock, L.A.; Moorhead, R. Mapping of invasive phragmites (common reed) in Gulf of Mexico coastal wetlands using multispectral imagery and small unmanned aerial systems. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 2861–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doughty, C.L.; Ambrose, R.F.; Okin, G.S.; Cavanaugh, K.C. Characterizing spatial variability in coastal wetland biomass across multiple scales using UAV and satellite imagery. Remote Sens. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 7, 411–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.; Brabyn, L.; Beard, C. Effects of class granularity and cofactors on the performance of unsupervised classification of wetlands using multi-spectral aerial photography. J. Spat. Sci. 2014, 59, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everitt, J.H.; Yang, C.; Davis, M.R.; Everitt, J.H.; Davis, M.R. Mapping wild taro with color-infrared aerial photography and image processing. J. Aquat. Plant. Manag. 2007, 45, 106–110. [Google Scholar]
- Pande-Chhetri, R.; Abd-Elrahman, A.; Liu, T.; Morton, J.; Wilhelm, V.L. Object-Based Classification of Wetland Vegetation Using Very High-Resolution Unmanned Air System Imagery. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 50, 564–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibaruddin, H.I.; Shafri, H.Z.M.; Pradhan, B.; Haron, N.A. Comparison of pixel-based and object-based image classification techniques in extracting information from UAV imagery data. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 169, 012098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dronova, I. Object-Based Image Analysis in Wetland Research: A Review. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 6380–6413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durgan, S.D.; Zhang, C.; Duecaster, A.; Fourney, F.; Su, H. Unmanned Aircraft System Photogrammetry for Mapping Diverse Vegetation Species in a Heterogeneous Coastal Wetland. Wetlands 2020, 40, 2621–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.-Y.; Hao, Y.-Y.; Wang, Y.-C.; Zhou, S.-Q.; Wu, W.-B.; Yuan, Q.; Gao, Y.; Guo, H.-Q.; Cai, X.-X.; Zhao, B. Coastal Wetland Vegetation Classification Using Pixel-Based, Object-Based and Deep Learning Methods Based on RGB-UAV. Land 2022, 11, 2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, E.; Mutanga, O.; Rugrgr, D. Multispectral and hyperspectral remote sensing for identification and mapping of wetland vegetation: A review. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2010, 18, 281–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, M.; Phinn, S. Hyperspectral data for mangrove species mapping: A comparison of pixel-based and object-based approach. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 2222–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, M.; Wang, J.; Sun, W.; Tao, R.; Du, Q. Hyperspectral and Multispectral Classification for Coastal Wetland Using Depthwise Feature Interaction Network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5512615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owers, C.J.; Rogers, K.; Woodroffe, C.D. Identifying Spatial Variability and Complexity in Wetland Vegetation Using an Object-Based Approach. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 4296–4316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correll, M.D.; Hantson, W.; Hodgman, T.P.; Cline, B.B.; Elphick, C.S.; Gregory Shriver, W.; Tymkiw, E.L.; Olsen, B.J. Fine-Scale Mapping of Coastal Plant Communities in the Northeastern USA. Wetlands 2019, 39, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, S.; Gill, L.; Ghosh, B. Drone Image Segmentation Using Machine and Deep Learning for Mapping Raised Bog Vegetation Communities. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Kim, J.W. Dynamics of zonal halophyte communities in salt marshes in the world. J. Mar. Isl. Cult. 2018, 7, 84–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.W. Studies on the Characteristics of Distribution and Environmental Factor of Halophyte Vegetation in Western and Southern Coast in Korea. Master’s Thesis, Graduate School of Kongju National University, Gongju, Republic of Korea, 2021; p. 123, (Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.I.; Hwang, Y.S.; Um, J.S. Estimating blue carbon accumulated in a halophyte community using UAV imagery: A case study of the southern coastal wetlands in South Korea. J. Coast. Res. 2021, 25, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.H. Features and Functions of Purple Pigment Compound in Halophytic Plant Suaeda japonica: Antioxidant/Anticancer Activities and Osmolyte Function in Halotolerance. Korean J. Plant Res. 2021, 31, 342–354. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Mandelli, S.; Lipari, V.; Bestagini, P.; Tubaro, S. Interpolation and Denoising of Seismic Data using Convolutional Neural Networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1901.07927. [Google Scholar]
- Isacch, J.P.; Costa, C.S.B.; Rodríguez-Gallego, L.; Conde, D.; Escapa, M.; Gagliardini, D.A.; Iribarne, O.O. Distribution of saltmarsh plant communities associated with environmental factors along a latitudinal gradient on the south-west Atlantic coast. J. Biogeogr. 2006, 33, 888–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ge, Z.; Xie, L.; Chen, W.; Yuan, L.; Wang, D.; Li, X.; Zhang, L. Ecophysiological response of native and exotic salt marsh vegetation to waterlogging and salinity: Implications for the effects of sea level rise. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curcio, A.C.; Peralta, G.; Aranda, M.; Barbero, L. Evaluating the Performance of High Spatial Resolution UAV-Photogrammetry and UAV-LiDAR for Salt Marshes: The Cádiz Bay Study Case. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Jiao, Z.; Zhang, A.; Li, F.; Fu, H.; Li, Z. Hyperspectral image-based vegetation index (HSVI): A new vegetation index for urban ecological research. Int. J. Appl. Earth Observ. Geoinform. 2021, 103, 102529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alongi, D.M. Carbon Sequestration in Mangrove Forests. Carb. Manag. 2012, 3, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmura, G.L.; Anisfeld, S.C.; Cahoon, D.R.; Lynch, J.C. Global carbon sequestration in tidal, saline wetland soils. Glob. Biogechem. Cycles 2003, 17, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macreadie, P.I.; Costa, M.D.; Atwood, T.B.; Friess, D.A.; Kelleway, J.J.; Kennedy, H.; Lovelock, C.E.; Serrano, O.; Durte, C.M. Blue Carbon as a Natural Climate Solution. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 826–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Sanders, C.J.; Santos, I.R.; Tang, J.; Schuerch, M.; Kirwan, M.L.; Kopp, R.E.; Zhu, K.; Li, X.; Yuan, J.; et al. Global blue carbon accumulation in tidal wetlands increases with climate change. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2021, 8, nwaa296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.D.; Xia, J.; Ha, N.T.; Bui, D.T.; Le, N.N.; Takeuchi, W. A Review of Remote Sensing Approaches for Monitoring Blue Carbon Ecosystems: Mangroves, Seagrasses and Salt Marshes during 2010–2018. Sensors 2019, 19, 1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauffman, J.B.; Heider, C.; Cole, T.G.; Dwire, K.A.; Donato, D.C. Ecosystem carbon stocks of Micronesian mangrove forests. Wetlands 2011, 31, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radabaugh, K.R.; Moyer, R.P.; Chappel, A.R.; Powell, C.E.; Bociu, I.; Clark, B.C.; Smoak, J.M. Coastal Blue Carbon Assessment of Mangroves, Salt Marshes, and Salt Barrens in Tampa Bay, Florida, USA. Estuaries Coasts 2018, 41, 1496–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Shang, N.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Zhao, K.; Qiu, X.; Weeks, E. Photogrammetric UAV Mapping of Terrain under Dense Coastal Vegetation: An Object-Oriented Classification Ensemble Algorithm for Classification and Terrain Correction. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Menenti, M.; Stoll, M.-P.; Belluco, E.; Marani, M. Mapping mixed vegetation communities in salt marshes using airborne spectral data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 107, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Method | Reference Data | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MLC | P. communis | S. maritima | Sediment | Total | Kappa (SE) | |
| P. communis | 203 | 1 | 1 | 205 | 0.562 (±0.032) | |
| S. maritima | 67 | 38 | 29 | 134 | ||
| Sediment | 3 | 9 | 71 | 83 | ||
| unclassified | 3 | 2 | 1 | 6 | ||
| Total | 276 | 50 | 102 | 428 | ||
| OA (%) | 72.9 | |||||
| PA (%) | 73.6 | 76.0 | 69.6 | |||
| UA (%) | 99.0 | 28.4 | 85.5 | |||
| U-Net (64 × 64) Bounding box | P. communis | S. maritima | Sediment | Total | Kappa (SE) | |
| P. communis | 269 | 2 | 4 | 275 | 0.843 (±0.024) | |
| S. maritima | 4 | 45 | 19 | 67 | ||
| Sediment | 3 | 3 | 79 | 85 | ||
| Total | 276 | 50 | 102 | |||
| OA (%) | 91.8 | |||||
| PA (%) | 97.5 | 90.0 | 77.5 | |||
| UA (%) | 97.8 | 66.2 | 92.9 | |||
| U-Net (16 × 16) Polygon | P. communis | S. maritima | Sediment | Total | Kappa (SE) | |
| P. communis | 249 | 0 | 0 | 249 | 0.815 (±0.026) | |
| S. maritima | 18 | 42 | 8 | 68 | ||
| Sediment | 9 | 8 | 94 | 111 | ||
| Total | 276 | 50 | 102 | |||
| OA (%) | 90.0 | |||||
| PA (%) | 90.2 | 84.0 | 92.2 | |||
| UA (%) | 100.0 | 61.8 | 84.7 | |||
| U-Net (32 × 32) Polygon | P. communis | S. maritima | Sediment | Total | Kappa (SE) | |
| P. communis | 259 | 0 | 1 | 260 | 0.817 (±0.026) | |
| S. maritima | 10 | 38 | 5 | 53 | ||
| Sediment | 7 | 12 | 96 | 115 | ||
| Total | 276 | 50 | 102 | |||
| OA (%) | 91.8 | |||||
| PA (%) | 93.8 | 76.0 | 94.1 | |||
| UA (%) | 99.6 | 71.7 | 83.5 | |||
| U-Net (64 × 64) Polygon | P. communis | S. maritima | Sediment | Total | Kappa (SE) | |
| P. communis | 270 | 3 | 3 | 276 | 0.863 (±0.023) | |
| S. maritima | 2 | 33 | 4 | 39 | ||
| Sediment | 4 | 14 | 95 | 113 | ||
| Total | 276 | 50 | 102 | |||
| OA (%) | 93.0 | |||||
| PA (%) | 97.8 | 66.0 | 93.1 | |||
| UA (%) | 97.8 | 84.6 | 84.1 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, K.; Lee, D.; Jang, Y.; Lee, J.; Kim, C.-H.; Jou, H.-T.; Ryu, J.-H. Deep Learning of High-Resolution Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Imagery for Classifying Halophyte Species: A Comparative Study for Small Patches and Mixed Vegetation. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15112723
Kim K, Lee D, Jang Y, Lee J, Kim C-H, Jou H-T, Ryu J-H. Deep Learning of High-Resolution Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Imagery for Classifying Halophyte Species: A Comparative Study for Small Patches and Mixed Vegetation. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(11):2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15112723
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Keunyong, Donguk Lee, Yeongjae Jang, Jingyo Lee, Chung-Ho Kim, Hyeong-Tae Jou, and Joo-Hyung Ryu. 2023. "Deep Learning of High-Resolution Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Imagery for Classifying Halophyte Species: A Comparative Study for Small Patches and Mixed Vegetation" Remote Sensing 15, no. 11: 2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15112723
APA StyleKim, K., Lee, D., Jang, Y., Lee, J., Kim, C.-H., Jou, H.-T., & Ryu, J.-H. (2023). Deep Learning of High-Resolution Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Imagery for Classifying Halophyte Species: A Comparative Study for Small Patches and Mixed Vegetation. Remote Sensing, 15(11), 2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15112723








