Detection of Solar Flares from the Analysis of Signal-to-Noise Ratio Recorded by Digisonde at Mid-Latitudes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Method of Detection
3. Analysis of Physical Characteristics of the Solar Flares and Limitations of the Detection Method
3.1. Geoeffective Hard X-ray Irradiance—Solar Altitude Angle Relationship
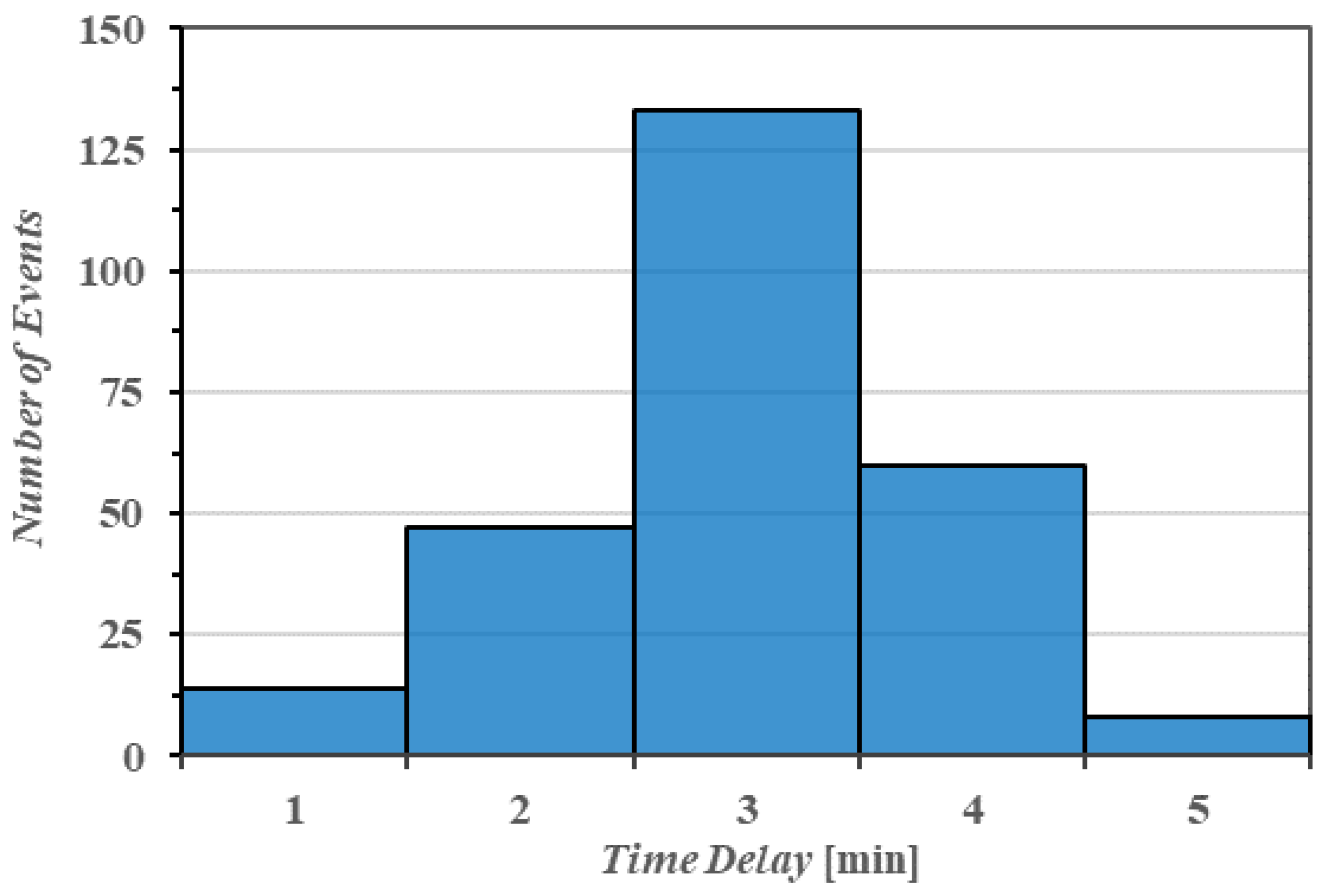
3.2. Asynchronous Measurement: Temporal Window of Detection
3.3. Geoeffective Hard X-ray Radiant Exposure
4. Solar Flare Detection Rate
5. Summary and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zolesi, B.; Cander, L. Ionospheric Prediction and Forecasting; Springer Geophysics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA; Dordrecht, The Netherlands; London, UK, 2014; p. 33. [Google Scholar]
- George, P.L.; Bradley, P.A. Relationship between HF absorption at vertical and oblique incidence. Proc. Inst. Electr. Eng. 1973, 120, 1355–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appleton, F.R.S.; Piggott, W.R. Ionospheric absorption measurements during a sunspot cycle. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1954, 5, 141–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratcliffe, J.A. Ionizations and drifts in the ionosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 1959, 64, 2102–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, S.E.; Honary, F. Storm sudden commencement and its effect on high-latitude HF communication links. Space Weather 2009, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bilitza, D.; Altadill, D.; Truhlik, V.; Shubin, V.; Galkin, I.; Reinisch, B.; Huang, X. International Reference Ionosphere 2016: From ionospheric climate to real-time weather predictions. Space Weather 2017, 15, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashimura, M.; Sinno, K.; Hirukawa, Y. Analysis of Long-Term Observations of Ionospheric Absorption Measurement (I). Observations at Kokubunji. J. Radio Res. Lab. 1969, 16, 131–138. [Google Scholar]
- Higashimura, M.; Sinno, K.; Hirukawa, Y. Analysis of Long-Term Observations of Ionospheric Absorption Measurement (II). Observations in the Northern Hemisphere. J. Radio Res. Lab. 1969, 16, 139–147. [Google Scholar]
- Blanch, E.; Marsal, S.; Segarra, A.; Torta, J.M.; Altadill, D.; Curto, J.J. Space weather effects on Earth’s environment associated to the 24–25 October 2011 geomagnetic storm. Space Weather 2013, 11, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curto, J.J.; Marsal, S.; Blanch, E.; Altadill, D. Analysis of the solar flare effects of 6 September 2017 in the ionosphere and in the Earth’s magnetic field using Spherical Elementary Current Systems. Space Weather. J. 2018, 16, 1709–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shinagawa, H.; Tao, C.; Jin, H.; Miyoshi, Y.; Fujiwara, H. Numerical prediction of sporadic E layer occurrence using GAIA. Earth Planets Space 2021, 73, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, A.P. Ionospheric Effects of Solar Flares; Astrophysics and Space Science Library; Reidel: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Barta, V.; Sátori, G.; Berényi, K.A.; Kis, Á.; Williams, E. Effects of solar flares on the ionosphere as shown by the dynamics of ionograms recorded in Europe and South Africa. Ann. Geophys. 2019, 37, 747–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsurutani, B.T.; Verkhoglyadova, O.P.; Mannucci, A.J.; Lakhina, G.S.; Li, G.; Zank, G.P. A brief review of “solar flare effects” on the ionosphere. Radio Sci. 2009, 44, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, K. Ionospheric Radio; Peter Peregrinus: London, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Handzo, R.; Forbes, J.M.; Reinisch, B. Ionospheric electron density response to solar flares as viewed by Digisondes. Space Weather 2014, 12, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, C.; Nishioka, M.; Saito, S.; Shiota, D.; Watanabe, K.; Nishizuka, N.; Tsugawa, T.; Ishii, M. Statistical analysis of short-wave fadeout for extreme space weather event estimation. Earth Planets Space 2020, 72, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, H.H.; Wilkinson, D.C. Global mapping of ionospheric HF/VHF radio wave absorption due to solar energetic protons. Space Weather 2008, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curto, J.J.; Juan, J.M.; Timote, C. Confirming geomagnetic Sfe by means of a solar flare detector based on GNSS. J. Space Weather Space Clim. 2019, 9, A42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Curto, J.J. Geomagnetic solar flare effects: A review. J. Space Weather Space Clim. 2020, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimoto, S.; Watanabe, K.; Kawai, T.; Imada, S.; Kawate, T. Validation of computed extreme ultraviolet emission spectra during solar flares. Earth Planets Space 2021, 73, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Pajares, M.; García-Rigo, A.; Juan, J.M.; Sanz, J.; Monte, E.; Aragón-Àngel, A. GNSS measurement of EUV photons flux rate during strong and mid solar flares. Space Weather 2012, 10, S12001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Natras, R.; Horozovic, D.; Mulic, M. Strong solar flare detection and its impact on ionospheric layers and on coordinates accuracy in the Western Balkans in October 2014. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Witvliet, B.A.; van Maanen, E.; Petersen, G.J.; Westenberg, A.J. Impact of a Solar X-Flare on NVIS Propagation: Daytime characteristic wave refraction and night-time scattering. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2016, 58, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olatunji, E.O. Ionospheric absorption of the extraordinary wave. Radio Sci. 1982, 17, 1335–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinisch, B.; Huang, X.; Galkin, I.; Paznukhov, V.; Kozlov, A. Recent advances in real-time analysis of ionograms and ionospheric drift measurements with digisondes. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2005, 67, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, L.C.; Su, S.Y.; Liu, C.H.; Schuh, H.; Wickert, J.; Alizadeh, M.M. Global morphology of ionospheric sporadic E layer from the FormoSat-3/COSMIC GPS radio occultation experiment. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Domeisen, D.I.V. Estimating the frequency of sudden stratospheric warming events from surface observations of the North Atlantic Oscillation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 3180–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mošna, Z.; Edemskiy, I.; Laštovička, J.; Kozubek, M.; Knížová, P.K.; Kouba, D.; Siddiqui, T. Observation of the Ionosphere in Middle Latitudes during 2009, 2018 and 2018/2019 Sudden Stratospheric Warming Events. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coy, L.; Pawson, S. The Major Stratospheric Sudden Warming of January 2013: Analyses and Forecasts in the GEOS-5 Data Assimilation System. Mon. Weather Rev. 2015, 143, 491–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machol, J.; Viereck, R. GOES X-ray Sensor (XRS) Measurements Important Notes for Users; Technical Report; NOAA: Washington, DC, USA, 2016.
- Zaalov, N.; Moskaleva, E.; Rogov, D.; Zernov, N. Influence of X-ray and polar cap absorptions on vertical and oblique sounding ionograms on different latitudes. Adv. Space Res. 2015, 56, 2527–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, P. The absorption of radiation in solar stills. Sol. Energy 1969, 12, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temmer, M.; Veronig, A.; Hanslmeier, A.; Otruba, W.; Messerotti, M. Statistical analysis of solar Hα flares. Astron. Astrophys. 2001, 375, 1049–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Curto, J.J.; Amory-Mazaudier, C.; Torta, J.M.; Menvielle, M. Solar flare effects at Ebre: Regular and reversed solar flare effects, statistical analysis (1953 to 1985), A global case study and a model of elliptical ionospheric currents. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 1994, 99, 3945–3954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayes, L.A.; O’Hara, O.S.D.; Murray, S.A.; Gallagher, P.T. Solar Flare Effects on the Earth’s Lower Ionosphere. Sol. Phys. 2021, 296, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, J.D. The formation of the sporadic-E layer in the temperate zones. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1961, 20, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, J.K. The Solar-Terrestrial Environment; Cambridge Atmospheric and Space Science Series; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Haldoupis, C. A Tutorial Review on SporadicE Layers. In Aeronomy of the Earth’s Atmosphere and Ionosphere; IAGA Special Sopron Book Series; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
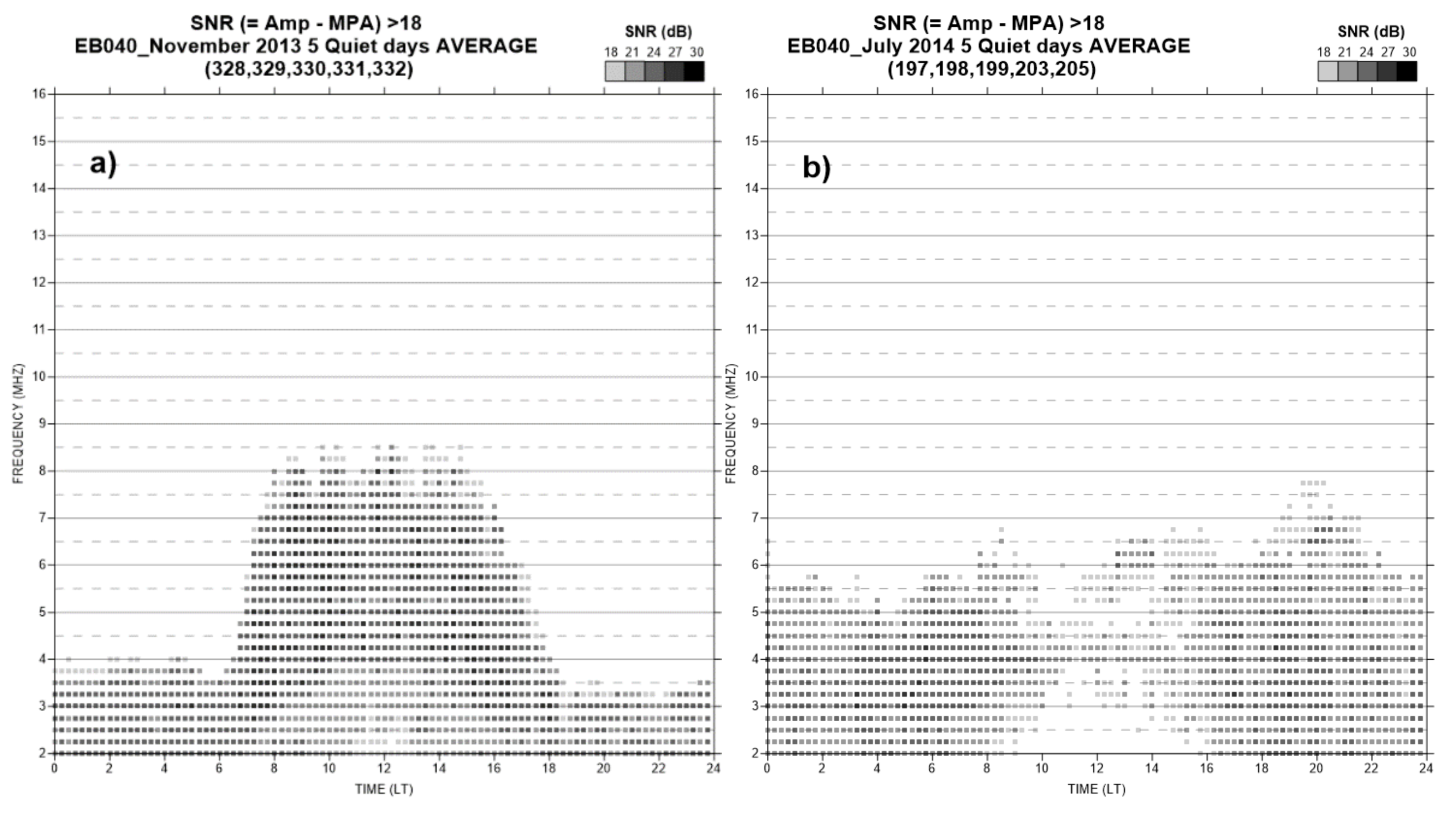
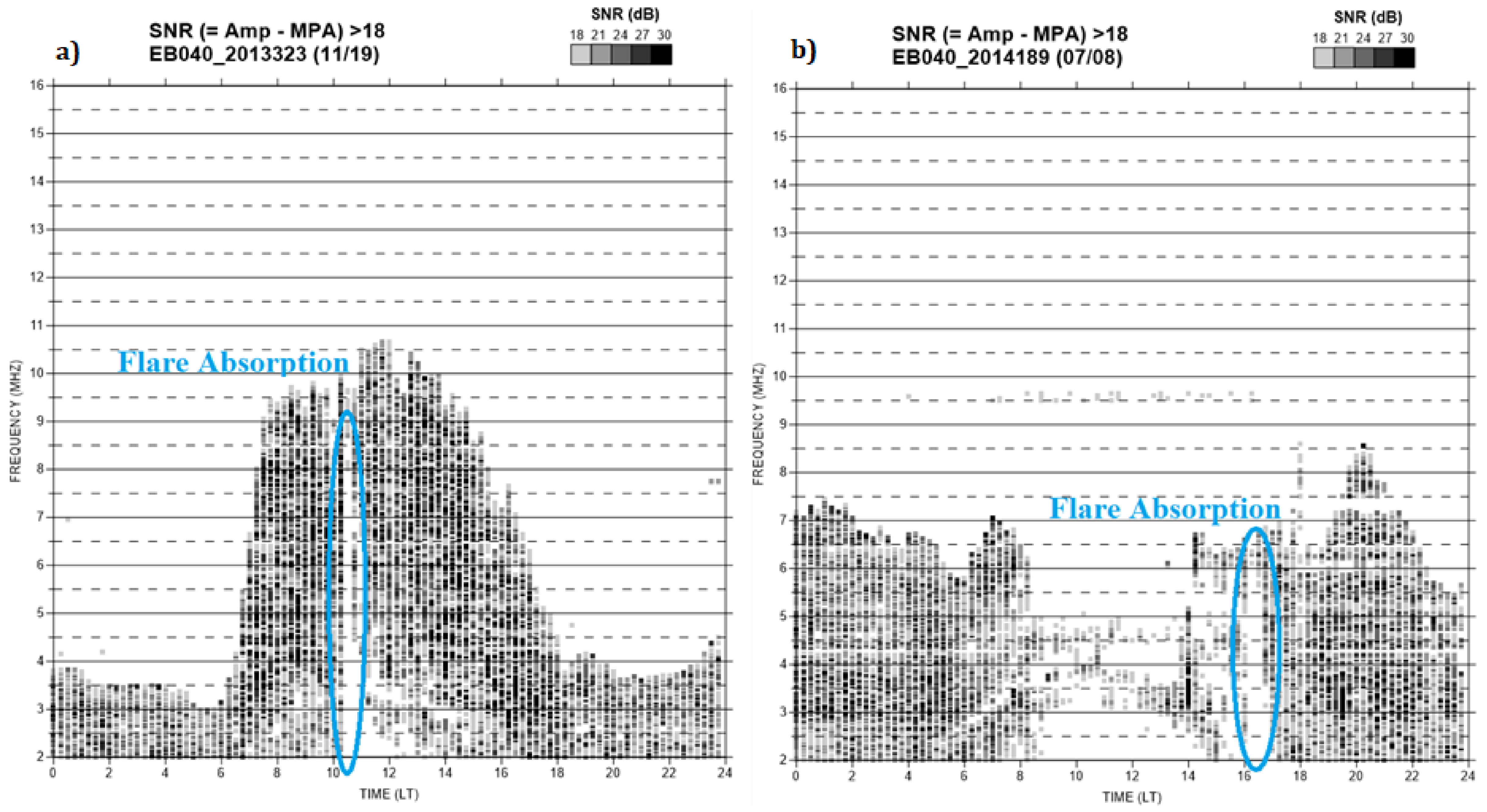
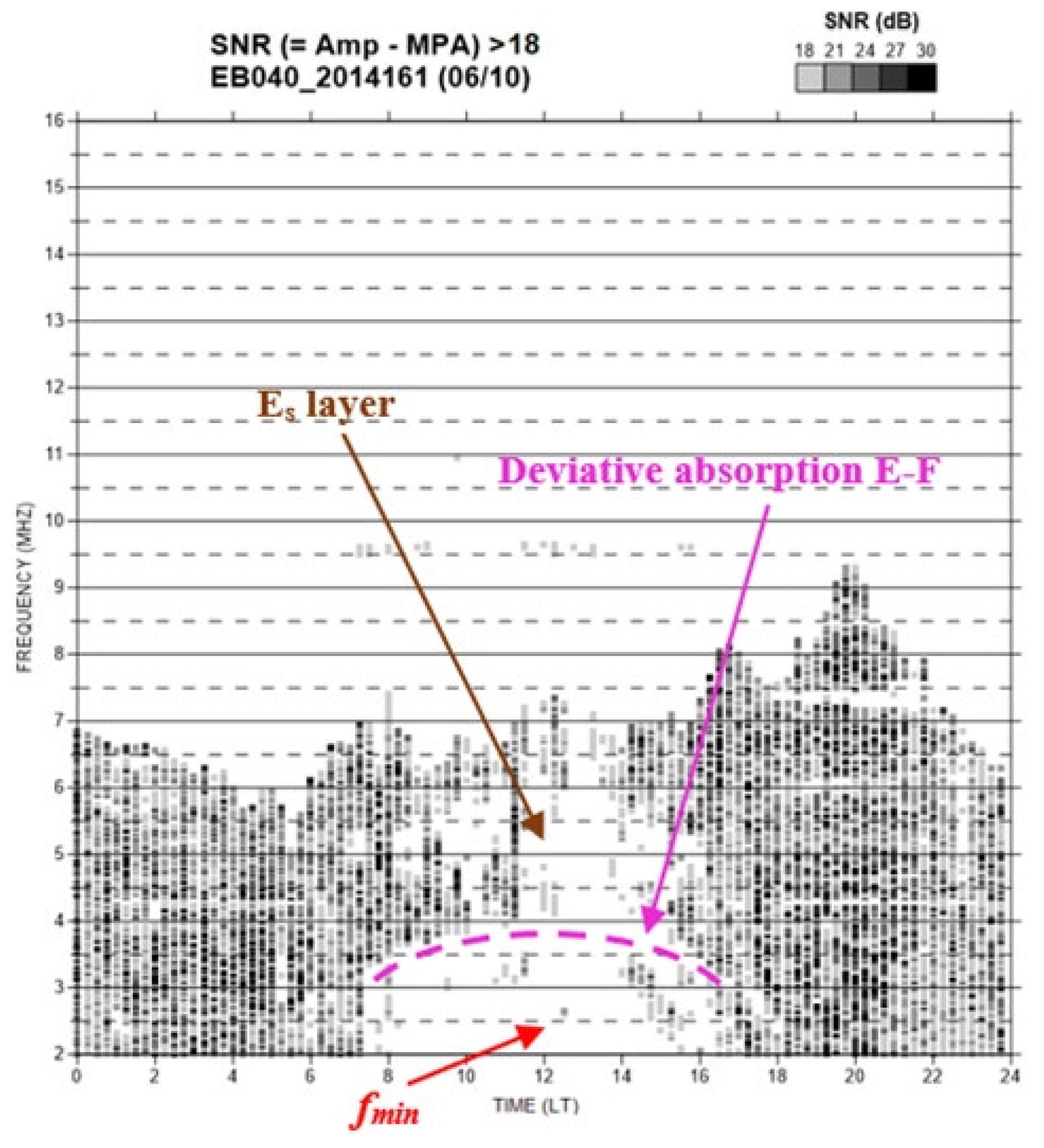
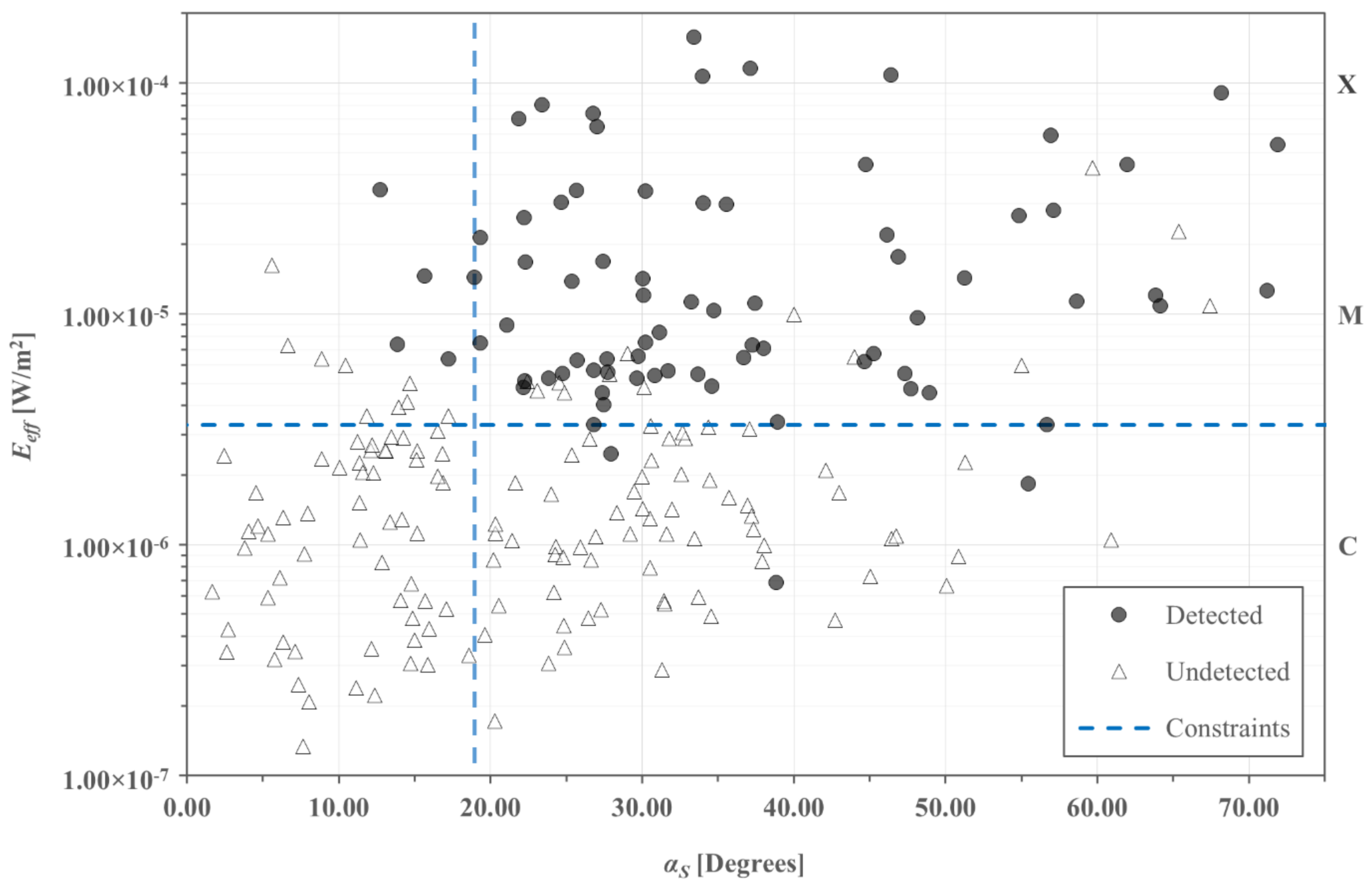

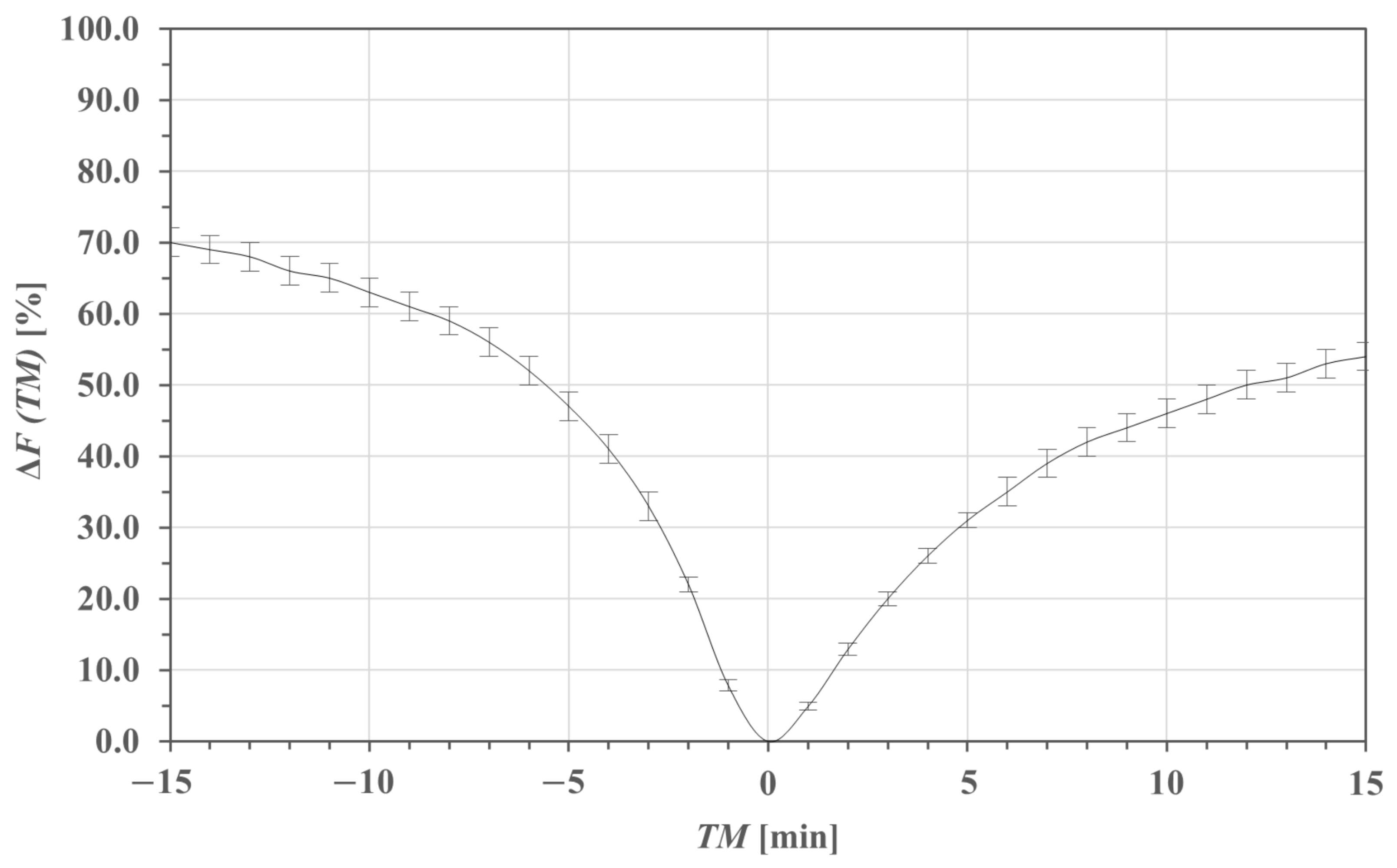
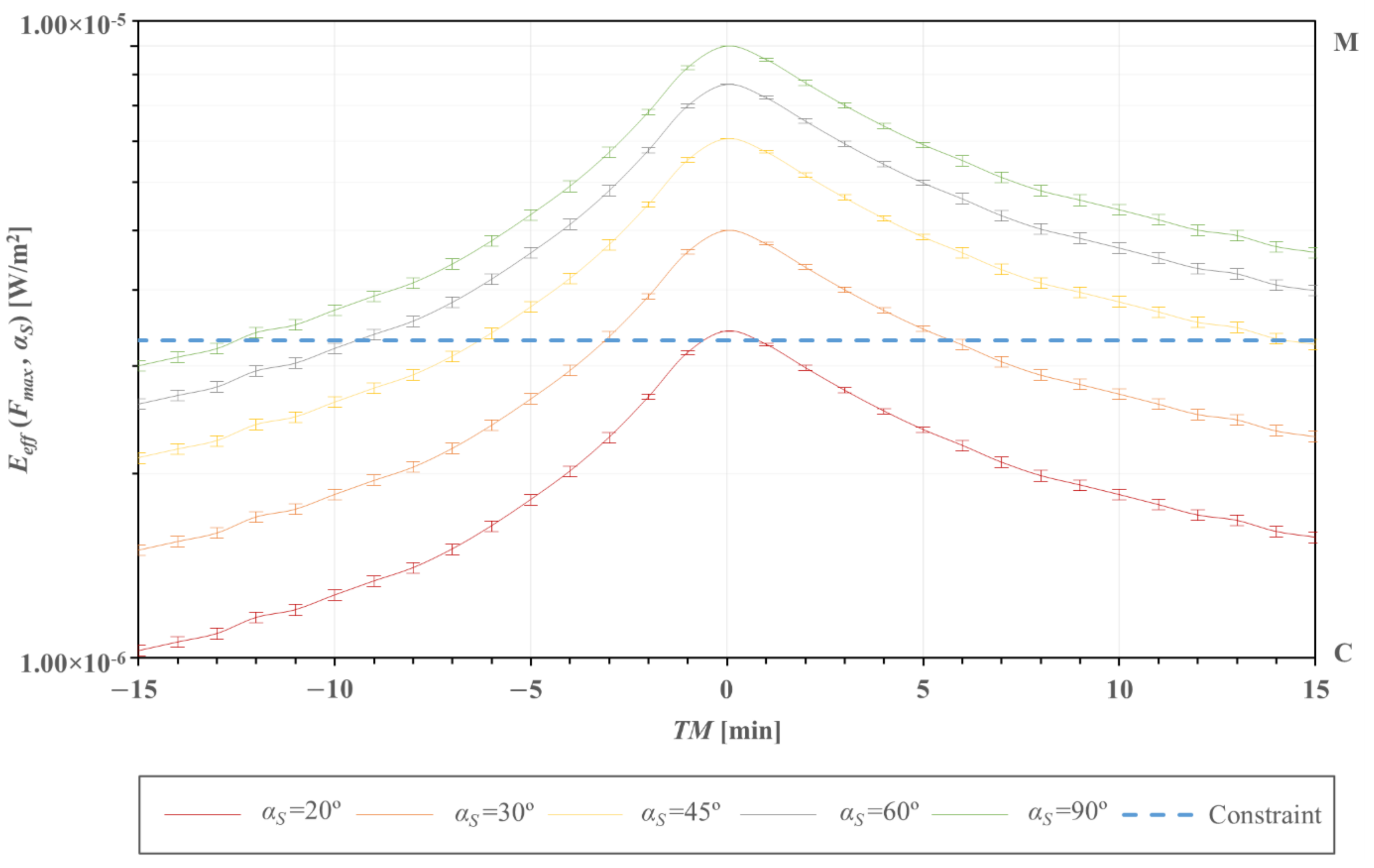
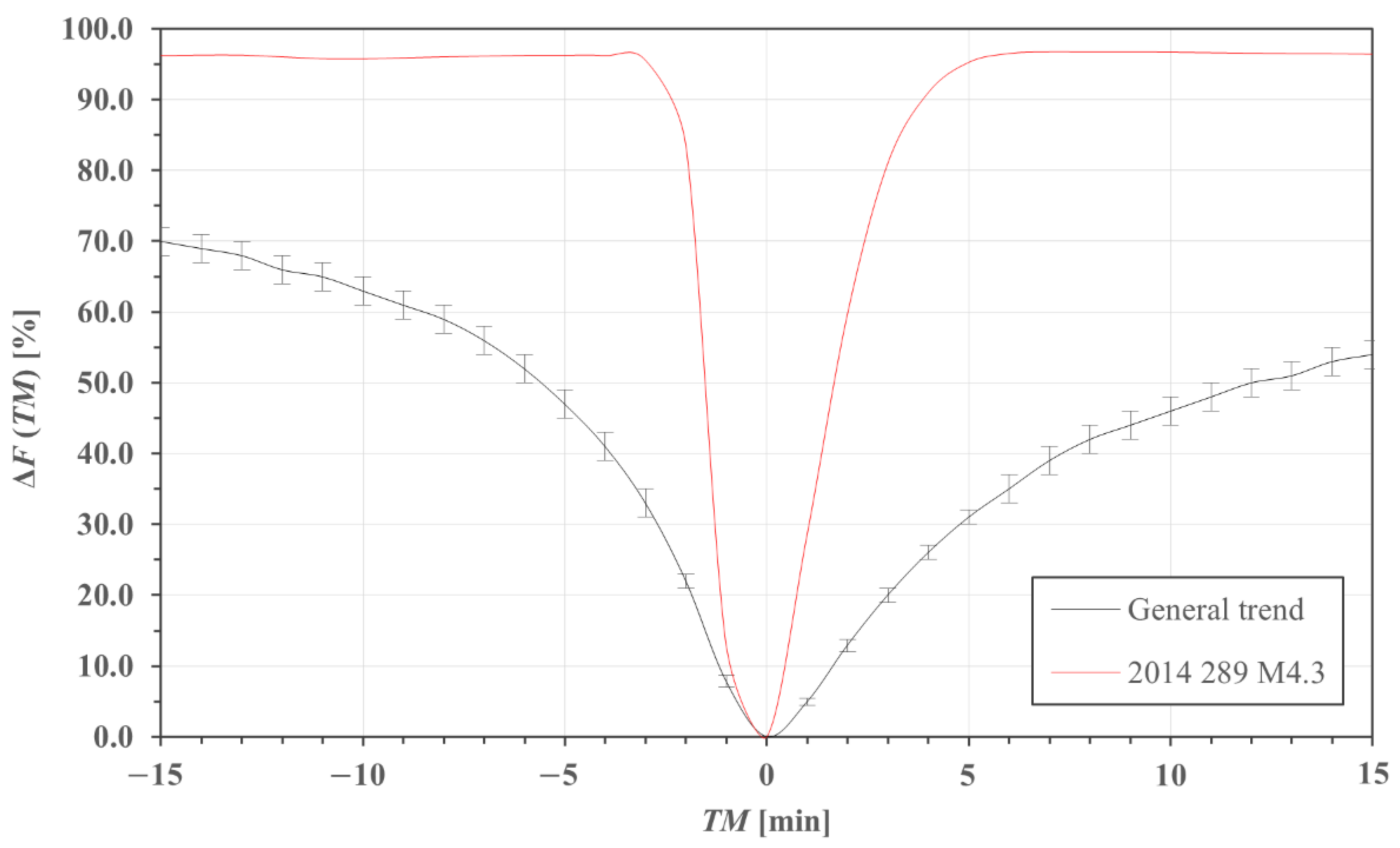
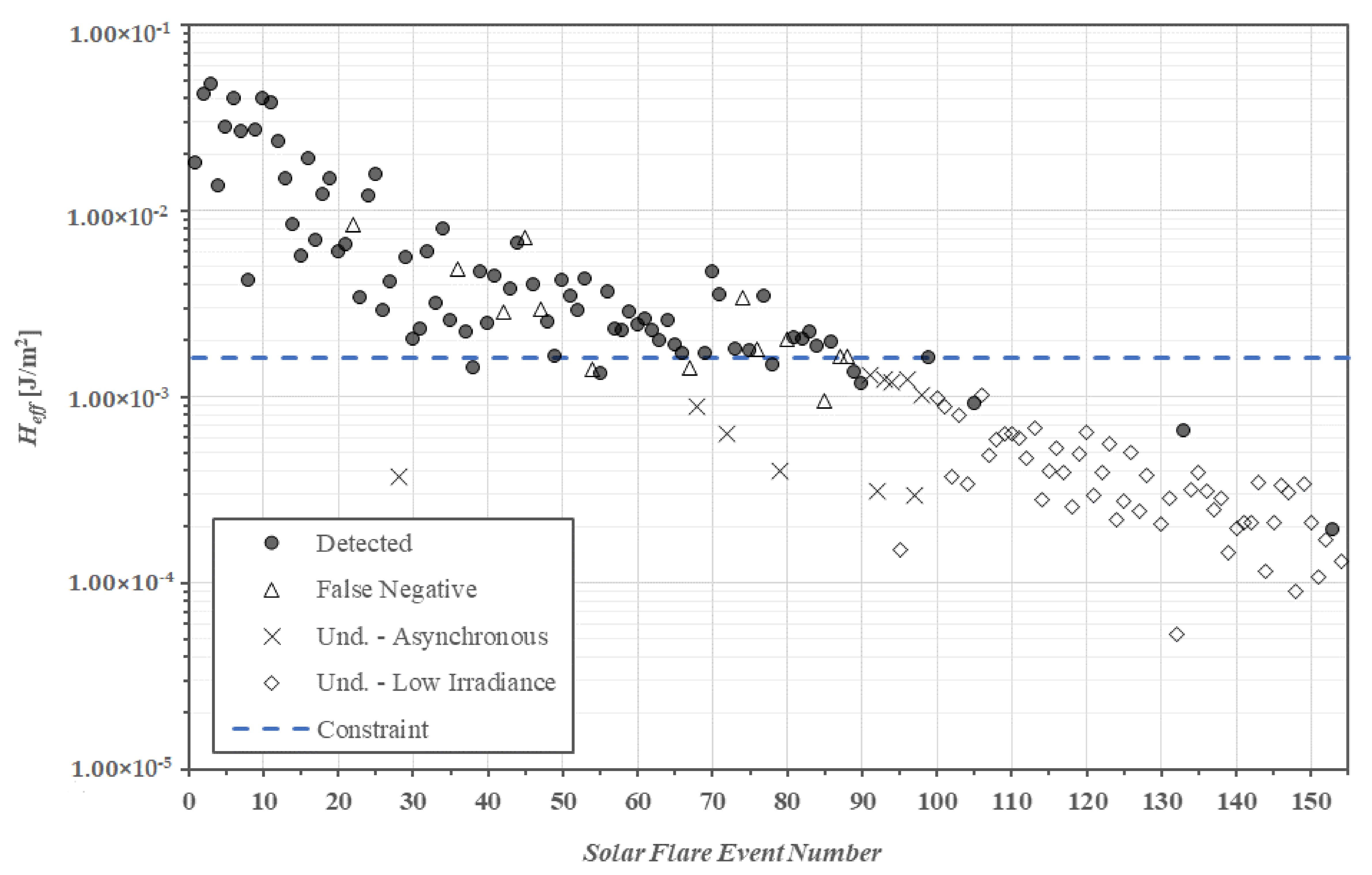
| Event [Year-DOY-Class] | Total Duration [min] | PT [LT] | IST [LT] | TM [min] | αS (Max) [°] | αS (IST) [°] | Eeff (Max) [W/m2] | Eeff (IST) [W/m2] | ΔEeff [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 296 C6.5 | 0:10 | 11:17 | 11:15 | −0:02 | 35.81 | 35.72 | 3.84 × 10−6 | 1.60 × 10−6 | 58.3 |
| 2014 028 M1.4 | 0:07 | 11:38 | 11:45 | +0:07 | 30.41 | 30.53 | 7.39 × 10−6 | 1.29 × 10−6 | 82.5 |
| 2014 033 M1.3 | 0:08 | 14:06 | 14:15 | +0:09 | 24.99 | 24.02 | 5.70 × 10−6 | 1.66 × 10−6 | 70.9 |
| 2014 034 C7.9 | 0:22 | 12:54 | 13:00 | +0:06 | 30.87 | 30.55 | 4.08 × 10−6 | 3.27 × 10−6 | 19.9 |
| 2014 045 C7.2 | 0:15 | 10:41 | 10:45 | +0:04 | 32.57 | 32.85 | 3.92 × 10−6 | 2.88 × 10−6 | 26.5 |
| 2014 110 C6.4 | 0:11 | 8:13 | 8:15 | +0:02 | 32.29 | 32.66 | 3.47 × 10−6 | 3.07 × 10−6 | 11.5 |
| 2014 163 C7.8 | 0:12 | 16:03 | 16:00 | −0:03 | 36.66 | 37.22 | 4.70 × 10−6 | 1.34 × 10−6 | 71.5 |
| 2014 182 C6.6 | 0:49 | 7:37 | 7:45 | +0:09 | 32.86 | 34.37 | 3.63 × 10−6 | 3.21 × 10−6 | 11.6 |
| 2014 289 M4.3 | 0:07 | 13:03 | 13:00 | −0:03 | 37.17 | 37.36 | 2.63 × 10−5 | 1.17 × 10−6 | 95.6 |
| 2014 294 M1.2 | 0:05 | 13:38 | 13:30 | −0:08 | 32.75 | 33.46 | 6.87 × 10−6 | 1.06 × 10−6 | 84.6 |
| 2014 303 C6.9 | 0:13 | 13:12 | 13:15 | +0:03 | 31.98 | 31.78 | 3.70 × 10−6 | 2.87 × 10−6 | 22.4 |
| Class | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1.0 | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable |
| C2.0 | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable |
| C3.0 | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable |
| C4.0 | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | [0, 0+1] | [−1, 2] |
| C5.0 | Undetectable | Undetectable | [0, 1] | [−2, 3] | [−, ] |
| C6.0 | Undetectable | Undetectable | [−, 3] | [−, ] | [−4, ] |
| C7.0 | Undetectable | [0, 1] | [−, ] | [−, ] | [−, ] |
| C8.0 | Undetectable | [−1, 2] | [−, ] | [−, ] | [−, 15] |
| C9.0 | Undetectable | [−, ] | [−5+1, ] | [−, 15] | [−, 15] |
| M1.0 | 0 | [−3+1, 5+1] | [−6+1, ] | [−, 15] | [−, 15] |
| M2.0 | [−, ] | [−, 15] | Always Detected | Always Detected | Always Detected |
| M3.0 | [−, 15] | Always Detected | Always Detected | Always Detected | Always Detected |
| M4.0 | Always Detected | Always Detected | Always Detected | Always Detected | Always Detected |
| X-Class | M-Class | C-Class | All Classes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100.0% (14/14) | 82.6% (57/69) | 46.2% (6/13) | 80.2% (77/96) |
Cause undetected events:
| Cause undetected events:
| Cause undetected events:
| Cause undetected events:
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Paula, V.; Segarra, A.; Altadill, D.; Curto, J.J.; Blanch, E. Detection of Solar Flares from the Analysis of Signal-to-Noise Ratio Recorded by Digisonde at Mid-Latitudes. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1898. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14081898
de Paula V, Segarra A, Altadill D, Curto JJ, Blanch E. Detection of Solar Flares from the Analysis of Signal-to-Noise Ratio Recorded by Digisonde at Mid-Latitudes. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(8):1898. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14081898
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Paula, Victor, Antoni Segarra, David Altadill, Juan José Curto, and Estefania Blanch. 2022. "Detection of Solar Flares from the Analysis of Signal-to-Noise Ratio Recorded by Digisonde at Mid-Latitudes" Remote Sensing 14, no. 8: 1898. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14081898
APA Stylede Paula, V., Segarra, A., Altadill, D., Curto, J. J., & Blanch, E. (2022). Detection of Solar Flares from the Analysis of Signal-to-Noise Ratio Recorded by Digisonde at Mid-Latitudes. Remote Sensing, 14(8), 1898. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14081898







