Abstract
Each of the giant planets, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune, has been observed by at least one robotic spacecraft mission. However, these missions are infrequent; Uranus and Neptune have only had a single flyby by Voyager 2. The Hubble Space Telescope, particularly the Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3) and Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) instruments, and large ground-based telescopes with adaptive optics systems have enabled high-spatial-resolution imaging at a higher cadence, and over a longer time, than can be achieved with targeted missions to these worlds. These facilities offer a powerful combination of high spatial resolution, often <0.05”, and broad wavelength coverage, from the ultraviolet through the near infrared, resulting in compelling studies of the clouds, winds, and atmospheric vertical structure. This coverage allows comparisons of atmospheric properties between the planets, as well as in different regions across each planet. Temporal variations in winds, cloud structure, and color over timescales of days to years have been measured for all four planets. With several decades of data already obtained, we can now begin to investigate seasonal influences on dynamics and aerosol properties, despite orbital periods ranging from 12 to 165 years. Future facilities will enable even greater spatial resolution and, combined with our existing long record of data, will continue to advance our understanding of atmospheric evolution on the giant planets.
1. Introduction
The giant planets have been observed for hundreds of years, first with the naked eye, and later with telescopes. However, the advent of deep space exploration ushered in a new era of discovery for the outer planets. The first planetary flybys of Jupiter (Pioneer 10, 1973), Saturn (Pioneer 11, 1979), Uranus (Voyager 2, 1986), and Neptune (Voyager 2, 1989) offered us our initial very high-spatial-resolution images of those planets and their rings and satellites. Although the Voyagers, in particular, revealed the dynamic atmospheres of these planets, we could not routinely observe them at high spatial resolution until the launch of the Hubble Space Telescope in 1990. Ground-based telescope observations have also been transformational, helping to fill in time coverage between sparse missions and Hubble data sets and making discoveries in their own right. Adaptive optics (AO) systems now rival some space-based observations, allowing truly complementary studies over many years.
A unique aspect of Hubble is its access to ultraviolet (UV) wavelengths blocked by the Earth’s atmosphere. Additionally, Hubble, and much of the ground-based AO imaging, can acquire data at near-infrared (IR) wavelengths that were not available to Voyager and which provide greatly enhanced imaging contrast, an especially important tool for understanding ice giant atmospheres. Here, we review what has been learned from a long baseline of high-spatial-resolution imaging data, where we define high resolution as 50 milliarcsec or better. We limit our discussion to atmospheric weather-layer studies in the near-UV to the near-IR range, as longer wavelengths are discussed in other papers in this volume; likewise, aurorae and upper atmosphere phenomena are also covered separately, and not included here. First, we review the history of high-resolution imaging from space-based to Earth-based observations for each of these planets. In Section 3, we summarize the overall cloud appearance (banded structure, colors, and major discrete features) for each of these planets individually. Section 4 discusses comparisons of the zonal winds, waves, and cloud structure of the gas giants, Jupiter and Saturn, and of the ice giants, Uranus and Neptune. Lastly, we examine long-term cycles on these planets, some of which are only now being realized after decades of observations.
2. History of High-Resolution Imaging
The appearance of the giant planets have been monitored on timescales ranging from decades to centuries, providing us with a substantial observational record of major changes on these dynamic worlds. For Jupiter, early monitoring included the Great Red Spot, and changing in the coloration of its bands [,]. Owing to its relatively large-scale and high-contrast cloud systems, estimates could be made of Jupiter’s wind field by the 1960s by tracking the motion of discrete cloud features []. However, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune proved to be much more challenging due to their larger heliocentric distances and smaller cloud contrasts; generally, only the largest planetary-scale cloud changes were observable from the Earth (e.g., []). On the other hand, it was possible to obtain full-disk information for deriving quantities such as temperature and trace atmospheric composition, which allowed for inferences about cloud structure (e.g., [,,]).
NASA’s early solar system exploration missions opened a new era of high-resolution imaging that changed our perspective by allowing us to see the fine details in each giant planet atmosphere—revealing many features not observable from the ground, such as Neptune’s Great Dark Spot, and finer-scale cloud features that allowed for more accurate wind tracking. The Voyager 2 mission was especially pivotal, in that it passed by all four giant planets, the only mission to ever do so, owing to a unique planetary alignment that allowed for rapid transit between the planets [,,,,,]. Unfortunately, the early frequent mission cadence of the Pioneers and Voyagers was not sustainable, leaving Uranus and Neptune largely unexplored, as shown in Table 1. This is especially problematic given the long seasonal timescales on the outer planets, as seen in Figure 1.

Table 1.
Dedicated Imaging Campaigns from Robotic Missions.
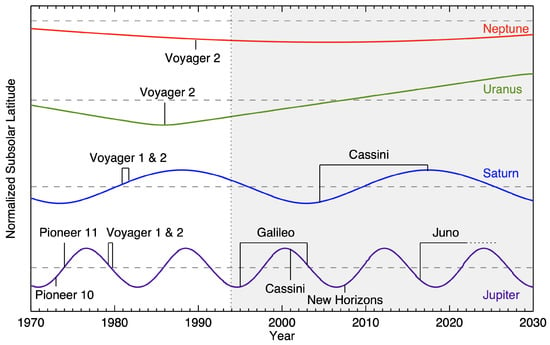
Figure 1.
Timeline of spacecraft observations relative to planetary season. Solid lines indicate the subsolar latitude (a proxy for season) for each planet and horizontal dashed lines indicate equinox crossings; peaks and trough indicate northern and southern hemisphere summer solstices, respectively. The major missions listed in Table 1 are plotted, demonstrating the lack of coverage for Uranus and Neptune. The Hubble era began in late 1993 (after the installation of corrective optics) and is indicated by the shaded area on the right.
As deep space mission technology evolved, other telescope technologies also continued to mature. First, the launch of the Hubble Space Telescope allowed detailed planetary imaging without the blurring effects of the Earth’s atmosphere. Although Hubble’s prime science area is astrophysics, early scheduling included dedicated planetary observing time. Indeed, an intensive observing campaign around the impacts of the Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 fragments into Jupiter showed the power of having a large telescope that could image a planet for long periods of time. However, there have been few multi-year, many observation, programs dedicated to the outer planets, as shown in Table 1, and those are usually centered around specific predictable events or to provide support context imaging for other operating missions, such as Galileo, Cassini, and Juno (e.g., [,]). The Outer Planet Atmospheres Legacy (OPAL) program began in 2014 to routinely monitor these planets and now observes each gas giant once per year, with examples in Figure 2 []. Note that while Table 1 presents a summary of major dedicated programs, there are other data sets from smaller Hubble programs and from other operating spacecraft missions, some of which use the outer planets as a calibration source.

Figure 2.
The giant planets’ appearance at UV and visible wavelengths from Hubble. Quasi-true color images from WFC3 data from the OPAL program show the differences amongst the planets with Jupiter and Saturn having shades of red, yellow and brown, while Uranus and Neptune are bluer. These color composites are comprised of the F631N (R), F502N (G), and 395N (B) filters for Jupiter (2021) and Saturn (2021) and F657N (R), F547M (G), and F467M (B) filters for Uranus (2015) and Neptune (2018). Images are not to scale.
Meanwhile, ground-based telescope technologies have also advanced to the point that some rival space-based observation, particularly at near-IR wavelengths. Lower-resolution data contribute to the long-term record of planetary atmosphere evolution, but to routinely achieve angular resolutions better than approximately 1” requires adaptive optics approaches [,]. AO systems have now been employed on a number of large telescopes to correct for wavefront errors introduced by atmospheric turbulence. Table 2 lists a range of AO observations of giant planet atmospheres conducted at professional observatories. Though most adaptive optics systems can produce images with resolutions at or near their theoretical diffraction limit (shown in column 1 of Table 2, at a wavelength of 1.6 micron), achieving this requires a bright guide star in close proximity to the observed body, which is often not possible. To overcome this limitation, laser guide stars are now employed at several observatories. Another solution, used at Keck observatory, is to use the target object itself (for objects with angular extent as large as Uranus) as a guide star for image correction; this method greatly simplifies the observational complexity and improves resultant image quality. Adaptive optics techniques have even been used by some amateur giant planet observers. High resolution can also be achieved using speckle or lucky imaging techniques, especially when AO is not available at particular observatories or in the necessary wavelength range.

Table 2.
Adaptive Optics Observations of Giant Planet Atmospheres.
The high spatial resolution afforded by Hubble and adaptive optics are enabling to a number of atmospheric studies. On all four giant planets, high spatial resolution allows the separation of latitude bands to determine their boundaries, both dynamically and in cloud structure. Discrete cloud features can be used to track wind fields, both regionally and, at high resolution, within the largest features. The largest features, such as anticyclonic vortices, may also drift independently of the wind field, sometimes moving in latitude as well as longitude [,,,]. Their drift rates are measurable using smaller telescopes, providing a very long time base of frequent observations for tracking location, motion, and temporal variability. However, we limit this review to the higher-resolution data, as the improved location accuracy of fine features in an image series results in higher derived velocity accuracy [].
At high spatial resolution, it is also possible to measure photometric and spectroscopic properties of homogeneous areas, rather than blending data with heterogeneous properties together; this is especially important for the auroral observations [,,,], but also for resolving the properties of individual storm systems. Similarly, the measurement of morphology and evolution of features with small angular sizes or low contrast, such as impact scars on Jupiter [] or Neptune’s and Uranus’s dark vortices [,,]. In this review, we focus on the discoveries and characterizations enabled by these high-resolution Earth-based systems.
3. Cloud Top Appearance
Each of the giant planets is unique in its coloration, convective storm activity, and zonal wind pattern. Given its size, closer proximity to Earth, and the large number of missions that have visited, Jupiter is the best observed of the four planets and is also the easiest to monitor from Earth-based facilities. Nonetheless, all four planets are now routinely observed at high spatial resolution to discern variations in their atmospheric activity; vast improvements in imaging technology and methods allow us to now track changes across all four planets. Here, we summarize the major cloud top features on each giant planet and their appearance at visible and near-IR wavelengths, with examples shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3, respectively. Note that most color images of the giant planets are contrast and color enhanced relative to naked eye viewing to bring out fine details at the expense of true color.
Aerosol scattering dominates images in the wavelength range from the near UV to the near IR, although the Rayleigh-scattering component is also important in the UV and short-wavelength visible range (e.g., []). Aerosol types differ, with diffuse layers of heavy hydrocarbons and other photochemical products predominantly in the higher-altitude stratosphere, and denser layers of molecular ices found in the deeper troposphere. Stratospheric aerosols are frequently referred to as “hazes”, and tropospheric aerosols as “clouds”, although these terms lack a rigorous definition. Distinctions between hazes and clouds have been made on the basis of the composition of the particles [], or on the basis of the optical thickness of the aerosol layers []. Thin condensed layers of hydrocarbons may also form in the stratosphere, particularly for Uranus and Neptune, and photochemical products are thought to mix into the troposphere. The term aerosol is most general, including condensed particles of any composition, found in any atmospheric layer, with either diffuse or thick densities. The stratospheric and tropospheric layers are separated by a temperature minimum, the tropopause, found at ∼100 mbar in each of the giant planets [].
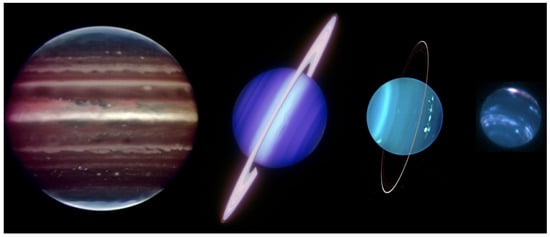
Figure 3.
The giant planets’ appearance at near-IR wavelengths with adaptive optics. This Jupiter (VLT, 2008) false-color composite at 2.02 (R), 2.14 (G), and 2.16 (B) microns highlights high polar and equatorial hazes and storms []. Saturn (Gemini, 2009) in false color at 2 (B), 2.12 (G), and 2.17 (R) microns shows equatorial structure [], credit: Gemini Observatory/AURA/Henry Roe, Lowell Observatory/Emily Schaller, Insitute for Astronomy, University of Hawai‘i. A Uranus (Keck, 2004) false-color composite at 1.26 (B), 1.62 (G), and 2.1 (R) microns, highlights both its cloud activity and its rings []. A Neptune (Keck, 2007) false-color composite from observations at 1.65 (B) and 2.1 (R) microns highlights elongated small clouds [], credit: M. van Dam, E. Schaller and W. M. Keck Observatory. Images are not to scale.
3.1. Jupiter
Jupiter’s cloud-top appearance is the most complex of the giant planets, with distinct storms, turbulent clouds, and well-defined latitude bands. These bands are often referred to as belts (darker, redder regions) and zones (brighter regions), though the boundaries were defined by historical color rather than dynamics [,]. Belt/Zone color variations are distinct even in small telescopes, but they are also not static; these bands can completely change color on timescales of months, sometimes lasting for years, and other times reverting quickly. Events where a colored band becomes whiter are colloquially referred to as “fading”, while increased coloration events are called “revivals” []. These events happen often, some on a quasi-periodic cadence, and appear to be controlled by changes in moist convection, from states of relative quiescence, to states with multiple convective plumes erupting from one or more active longitude sectors (e.g., []). Color changes are not limited to the cyclonic belts (sites of chaotic clouds structures and associated lightning), but sometimes occur within the more uniform anticyclonic zones as well. When multiple latitude bands change color consecutively over a short period of time, it is known as a “Global Upheaval” [], though the cause is not yet understood. Historically, some of the southern belts were distinctly dark and red [], but this has not been observed in the modern era, with the North Equatorial Belt often appearing darkest/reddest, as is evident in Figure 2.
Figure 4 shows an example of Jupiter’s typical appearance across visible wavelengths. Generally, Jupiter is most bland at UV wavelengths, due to Rayleigh scattering, and shows maximum brightness variation and contrast at blue wavelengths, where an unknown absorber(s) causes the typical reddish/brownish coloration [,,,,]. According to theoretical models [,], the top cloud layer is composed of ammonia ice, with deeper layers of NHSH and water ices, none of which contribute any visual color, but do have detectable near-IR spectral signatures (e.g., [,]). Trace amounts of methane gas in Jupiter’s troposphere and stratosphere cause strong absorption bands in the near IR, and images in those bands (such as the 889 nm filter image in Figure 4) are mostly dark, sensing reflection from high-altitude clouds (e.g., over vortices, the equatorial zone, and the polar domain). Conversely, “continuum” images outside of these strong absorption bands sense down to the topmost cloud deck.
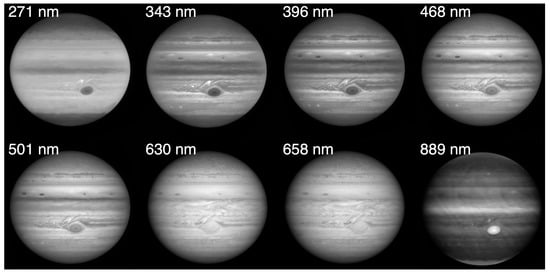
Figure 4.
Jupiter’s appearance at UV and visible wavelengths. September 2021 Hubble data show variation in Jupiter’s latitude bands with wavelength. Jupiter is dark in the 889 nm methane gas absorption band, with the highest features (the GRS and the polar haze caps) appearing brightest; artificial fringing is apparent in that image, and in all long wavelength narrow-band WFC3 filters.
Among the gas giants, Jupiter also boasts the largest number of clearly defined vortices; see Figure 5. Anticyclones, storms with counterclockwise rotation in the southern hemisphere are often oval shaped and white to beige with the exception of the Great Red Spot (GRS). Interspersed between the many anticyclones are cyclonic cells. These can be smooth-edged and oval or oblong shaped, but many have scalloped edges, and they can also vary in color, from a deep red to a bright white. For example, elongated brown cyclonic structures are known colloquially as “brown barges”, and can be seen near N latitude in Figure 5. High-resolution imaging has revealed cyclonic vortices transitioning from quiescent states with smooth edges, to turbulent convective states (e.g., []). Turbulent convective cyclones have also been associated with clusters of lightning flashes (e.g., []).
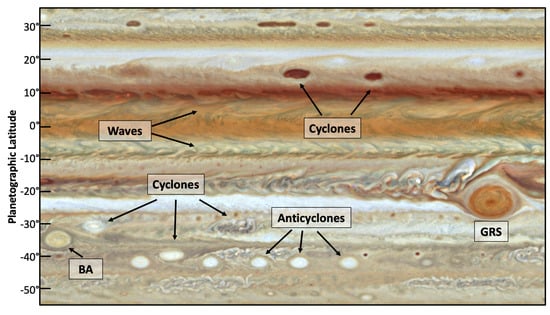
Figure 5.
Jupiter’s enduring cloud features in Hubble WFC3 data from September 2021. This map spans a subset of latitudes and ∼136 of longitude; 1 of longitude = ∼12,500 km at the equator. Jupiter’s bands contain multiple closed-circulation vortices, both cyclones and anticyclones, including the GRS and Oval BA. Waves and turbulent structures are also visible.
Jupiter’s GRS is likely the best-studied storm in the solar system owing to its size and longevity, having persisted for at least 150 years [,]. As Jupiter is observed frequently, the behavior and characteristics of the GRS are very well documented, allowing precise tracking of changes in its size, shape, colors, and motions. Over the modern era, it has decreased in longitudinal width from ∼25,000 to <15,000 km from 1979 to 2021, evolving from a length to width aspect ratio of ∼1.9 to 1.3, i.e., becoming more round over time []. Using high-resolution Hubble data, it was recently confirmed that the GRS’s internal winds have also increased by approximately 4 to 8% from 2009 to 2020, with average winds topping 130 m/s and gusts to 180 m/s [,].
This anticyclonic storm drifts westward relative to the planet’s rotation and zonal wind field, with a 90 day oscillation in its apparent speed [,]. More recently, it has been determined that its long-term average drift rate has consistently increased, perhaps in response to its smaller size; however, its oscillation period remains steady in Hubble and small telescope tracking data [,,]. In recent years, the GRS has appeared to interact with passing storms, but with no lasting changes in size, velocities, or motion, the interactions appear to only have a superficial effect [,]. The GRS also undergoes color changes, ranging from very pale pink to almost brick red, but we do not yet know if the coloration corresponds to any particular dynamical event [,,].
Another enduring feature is the Oval BA. This anticyclone is the product of the merger of three similarly-sized anticyclones in the South Temperate Belt [,]. The three “White Ovals” appeared after this belt faded in 1939 and then developed distinct segments, with ends labeled A through F. These segments coalesced into distinct anticyclonic vortices, named FA, BC, and DE. In 1998, BD and DE merged to form BE, and, in 2000, FA and BE merged [,]. This unprecedented example of large-scale vortex interactions was already unique, when in late 2005 Oval BA became quite red in color, earning the nickname “Red Spot Jr” []. It has since faded to a more typical beige color, as seen in Figure 5.
3.2. Saturn
Saturn’s colors are more muted than Jupiter’s, with a multi-layer extended haze covering the ammonia ice cloud deck []. Saturn does have distinct cloud bands, however, and these are evident with sufficient spatial resolution, as in Figure 6. Similar to Jupiter, there are fewer cloud features at UV wavelengths, while at visible wavelengths, the band colors vary over time. For example, the polar regions tend to be shades of blue in winter months, gradually turning more yellow as they emerge from the shadows, likely due to changes in the stratospheric haze [,]. Of course, the Cassini mission’s extensive observations of Saturn in reflected sunlight dominate recent findings of Saturn’s clouds [,,], but Earth-based observations played a crucial supporting role, and have allowed us to continue the time series both before and after the mission. Hubble data from 2018 to 2021 also show that individual bands can change slightly in color from year to year, without much change in altitude or atmospheric opacity [].

Figure 6.
Saturn’s appearance at UV and visible wavelengths. September 2021 Hubble data show Saturn’s cloud band variations with wavelength. At visible wavelengths, Saturn’s cloud bands are clearly seen, and the planet is very dark in the 889 nm methane absorption band.
Saturn has fewer distinct vortices than Jupiter, but a few small spots were seen during the Voyager flybys [,]. In the modern era, several spectacular storm outbreaks have resulted in remnant long-lived vortices, for example near 65 and 41N latitudes [,]. These are not high contrast and are typically only visible at high spatial resolution. Saturn does have several very long-lived atmospheric features, however, which can be seen in Figure 7. First and foremost is the north polar hexagon discovered in 1981 Voyager imaging data []. The near-stationary hexagon is a result of a wind jet pattern at 78N latitude. Laboratory studies have shown that circumpolar jets can organize themselves into polygonal shapes, or cause vortex streets, depending on the local prevailing conditions []. Recent numerical studies confirm that to reproduce both the shape and near-stationary vertices of the hexagon depends on the vertical wind shear shape of the wind profile at depth []. The hexagon has persisted until the present and can also be seen in mid-IR data sensitive to temperatures in the upper troposphere and stratosphere, high above the clouds [].
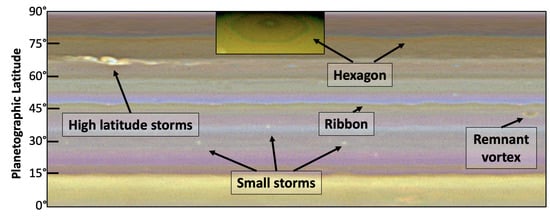
Figure 7.
Saturn’s major northern hemisphere cloud features in Hubble WFC3 data from June 2018. Individual latitude bands have slightly different colors in this contrast- and sharpness-enhanced map over ∼180 of longitude; 1 of longitude = ∼10,500 km at the equator. The small vortex near 40 is a remnant of the large 2010 storm, and small thunderstorm-like clouds are visible at mid latitudes. Inset: The polar hexagon (unmapped) was prominent in 2018, and the boundaries varied at different wavelengths, giving it a multi-colored border.
Another common feature is the Saturn “ribbon”, an eastward wind jet at 47N latitude [,]. This feature is unique in that, unlike the majority of Jupiter and Saturn’s wind jets, it meanders in latitude or appears wavy. Numerical modeling indicates that instabilities and the creation of eddies causes the jet to meander []. As with the hexagon, and a similar mid-latitude Jupiter ribbon, the wind jet speed, vertical wind shear, and the atmospheric stability determine if a jet is stable, if a string of vortices occurs, or if the wind jet meanders around eddies [,]. Saturn’s ribbon also shows temporal variability, changing in cloud color and brightness, bifurcating, and sometimes disappearing altogether [].
3.3. Uranus
Uranus is often considered the most featureless of the giant planets, owing to its uniform pale blue appearance in early Voyager 2 images []. At blue and green wavelengths, Uranus is relatively uniform in appearance, as shown in Figure 8. With the improved imaging capabilities at red and near-infrared wavelengths afforded by Hubble and adaptive optics telescopes, however, it was soon realized that Uranus has both zonal structure and discrete cloud activity, (e.g., [,]). At longer wavelengths, Uranus shows banded structure that was not evident Voyager 2 images, unless strongly enhanced, owing to that camera’s poor long wavelength sensitivity []. Although the planet becomes darker overall as the wavelength increases, the cloud contrast increases, and storms are most visible in the near IR. In the weaker methane absorption bands, at 619 and 727 nm, the banded structure is more muted.
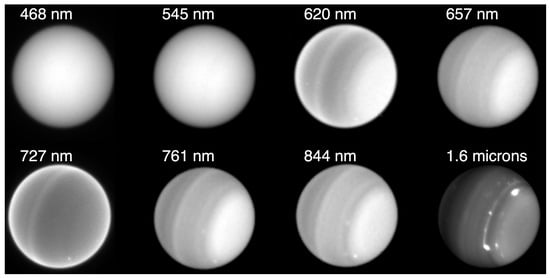
Figure 8.
Uranus’s appearance at visible and near-IR wavelengths. September 2015 Hubble and August 2014 Keck data [] show Uranus’s cloud band variations with wavelength. The north pole is to the right. Uranus is more uniform at short wavelengths than at long wavelengths, with banding and storm contrast increasing at longer wavelengths.
Uranus’s southern pole was illuminated during the 1986 Voyager 2 flyby and a Uranian year lasts 84 Earth years. However, Uranus fortuitously crossed through equinox in 2007, allowing a view of the emerging northern pole. With the changing illumination from 1986 (near southern summer solstice) to 2020 (approaching northern summer solstice), the bright southern polar “cap” faded away and the north polar region brightened dramatically; see Figure 9 [,]. Although both polar regions have been found to be depleted in upper tropospheric methane [,], the best evidence so far indicates that the temporal changes in brightness are almost entirely due to changes in scattering by polar hazes []. These changes in polar hazes may be an effect of seasonal insolation, dynamical changes, or a combination of both [].

Figure 9.
Uranus’s cloud features in Hubble ACS and WFC3 and Keck H-band images from 2004 to 2020 [,,,,,]. The Hubble ACS color composite in 2006 uses 755, 658, 550 nm in the R, G, B channels, respectively, and in 2020 the WFC3 845 nm filter is shown []. The 2012 Keck image is a high signal-to-noise, de-rotated, average image, high-pass filtered to show low-contrast cloud details []. Bright clouds are prominent in the H-band images and the south polar region has faded while the north polar region has brightened with the changing Uranian seasons.
Although bright clouds are evident in near-IR data in the H band (1.6 microns), as in Figure 8, these data can also reveal a wealth of other features. After boosting signal-to-noise-ratios by averaging multiple exposures in planetary coordinates to remove rotational smearing, then high-pass filtering, a distinct banding structure and numerous discrete features become apparent, as shown in the Keck 2012 image in Figure 9 []. Additionally, the polar region is filled with small cloud features and the equator shows a braided structure, likely tied to waves [].
Unlike on Jupiter and Saturn, the Uranian clouds are likely comprised of HS at ∼6 bars and CH ice at 1–2 bars, (e.g., [,] and references therein), though spectroscopic data indicate that both ice cloud layers are intermixed with (and perhaps dominated by) hydrocarbon hazes []. As the northern hemisphere approached equinox and received illumination, small storms were seen in the northern hemisphere, particularly near ∼30N [], including the first detection of a dark spot in 2006 [,,]. The cloud activity was sporadic and occasionally a small dark spot is seen with bright companion clouds, but these are typically only visible at longer wavelengths []. In 2004, a very IR bright feature was observed in mid southern latitudes, the first storm to be visible at 2 microns []. This feature, later nicknamed The Berg, varied in brightness and oscillated in latitude, and after reanalysis was found to be present during the Voyager flyby []. After equinox, cloud activity increased in the northern hemisphere []. Discrete features have been observed near the polar haze boundary for many years, for example in 2014 and 2020 in Figure 9, but it is not clear if it is the same persistent feature or multiple short-lived clouds, due to sparse temporal coverage.
3.4. Neptune
Neptune is known for its characteristic deep blue color. Similar to Uranus, it is somewhat bland at short wavelengths, though it does show some banding at high latitudes, apparent in Figure 10. At longer wavelengths, the planet gets darker and cloud contrast again increases, with bands demarcated by elongated small clouds. Neptune’s putative cloud structure is similar to Uranus’s with differences explained by the thickness of the different layers and their contribution to photon scattering []. They have nearly identical temperature profiles in the troposphere, though Neptune has a warmer stratosphere and stronger vertical mixing; this is evident from the high frequency and vertical extent of high-altitude methane ice clouds, which are rarely seen on Uranus [,].
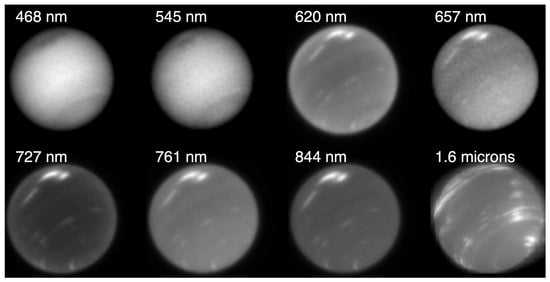
Figure 10.
Neptune’s appearance at visible and near IR wavelengths. November 2018 Hubble and August 2018 Keck data [] show Neptune’s cloud band variations with wavelength. Neptune’s 2018 northern great dark spot is visible at shorter wavelengths to the upper left, while companion clouds are brighter at longer wavelengths.
Neptune’s most notable visible wavelength atmospheric features are its dark spots. The first of these were seen by Voyager 2 in Neptune’s southern hemisphere, the Great Dark Spot (GDS) at 20S and DS2 at 55S []. Like Jupiter’s GRS, the GDS was an anticyclone of similar size, with bright orographic companion clouds []. However, it was not tightly confined by the wind field, and showed a long-term drift towards the equator with oscillations in size and shape, and possibly latitude and longitude [,]. Hubble observations in 1994 showed that the Voyager GDS had disappeared, perhaps when it drifted too close to the equator, but a new dark spot was apparent near 30N; another was seen in 1996, though it was unclear if this was the same spot [,]. In contrast with Uranus’s dark spots, Neptune’s dark spots are only visible at the shortest wavelengths while the companion clouds are visible at long wavelengths.
Figure 11 shows a new small dark spot first observed by Hubble in 2015 at 46S, the first southern hemisphere spot observed since Voyager 2. This spot decreased in size and slowly diminished until it disappeared around 2018 []. Further in 2018, a larger dark spot was discovered at 23N, forming after bright clouds were seen at that latitude in prior years []. Although predicted to disappear as it drifted equatorward, it is still present in 2022, allowing the first studies of the full life cycle of a dark spot from formation to eventual demise. With a multi-decade record of dark spots, analyses indicate that a new vortex forms every 4–6 years and many may simply have been missed due to lack of high resolution, visible wavelength, coverage [].
Another common bright cloud is the South Polar Feature (SPF), visible at both red and near-IR wavelengths and obvious in 2003, 2007, and 2015 in Figure 11. This elongated bright cloud is seen on many dates, and does not appear to be a single long-lasting feature []. Analysis of high-resolution Voyager 2 images of the SPF revealed that it was actually a region of formation of very small individual cloud elements of short lifetimes that move at high speed relative to the formation region, typically 8 of longitude/hour, forming at one end and dissipating at the other, while the 170 wide formation region was almost stationary with respect to the interior []. In some observations, the SPF is very bright and distinct, and in others it is faint or absent. The SPF can also have a complex appearance with multiple spots and structure, suggesting that it is caused by convection in the circumpolar flow []. As Neptune has an obliquity of approximately 30, and an orbital period of 165 years, we have not yet observed its north pole to search for similar circumpolar features there.
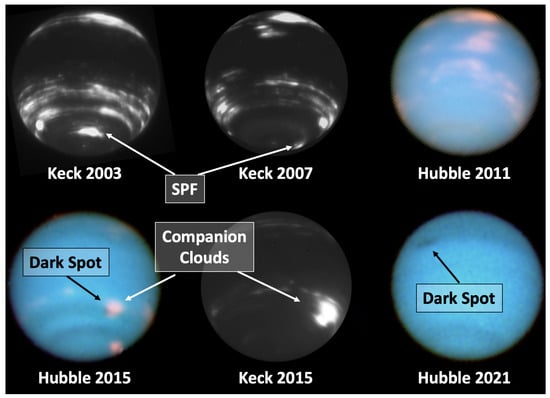
Figure 11.
Neptune’s major cloud features in Hubble WFC3 and Keck H-band images from 2003 to 2021. The Hubble color composite in 2011 uses 845, 631, 467 nm in the R, G, B channels, respectively, while in 2015 and 2021, the G channel is 547 nm, and contrast and sharpness have been enhanced. Bright clouds are prominent in the H-band images, both in bands and in dark spot companion clouds, and the SPF appears on some dates [,,]; dark spots are denoted in 2015 and 2021.
4. Dynamics and Cloud Variability
4.1. Zonal Winds
All four giant planets have high-speed zonal (latitudinally averaged) winds that are roughly axisymmetric and remarkably stable, changing little in shape or magnitude over time despite the changes in cloud coloration and opacity described in the previous section. These are typically measured using time-separated imaging of small clouds that act as wind tracers. At the spatial resolution of Hubble, Jupiter’s winds can be measured in an image pair with 5 to 10 m/s accuracy, limited by cloud distortion over a 10 hr rotation period. Advanced correlation and velocimetry techniques are now routinely used to reduce this uncertainty and to enable much finer mapping of 2D flow fields (e.g., []). For the other three giant planets, the spatial resolution is lower and there are fewer distinct small cloud tracers; large features are used with the caveat that they may not fully advect in the wind field, having internal rotation and drift rates of their own. Additionally, the altitude of the individual clouds is somewhat uncertain and may vary with the choice of filter, though in some cases this allows the measurement of vertical wind shear.
Figure 12 shows that Jupiter has the weakest cloud-top winds of the four planets, but with the largest number of alternating eastward and westward jets. These are in rough alignment with its traditionally-defined belts and zones, loosely tying the colors to regions of cyclonic and anticyclonic shear [,,,]. Speeds in some jets fluctuate by up to 10 m/s at different longitudes [], but the zonally-averaged mean speeds are stable over time at the uncertainty level. Meanwhile, Jupiter’s cloud colors are quite variable, showing that color is a less reliable indicator of belt/zone boundaries than the wind field itself. The highest speed eastward jet at 24N shows the largest temporal changes of ∼50 m/s. The majority of the changes in Jupiter’s wind field are tied to convective events, or to changes in wave activity that may mask the zonal flow [,,,,,]. Vertical shear is expected in the winds, as the thermal wind equation implies weakening/decay with altitude (e.g., [,,]). Attempts have been made to measure change with altitude from Earth-based data in visible continuum and methane absorption bands, as well as in near-IR bands sensitive to tracers in the stratosphere. These studies found mixed results, with only a few locations where vertical wind shear might be seen, primarily in the strongest jets (e.g., 24N) or in remnant debris from impacts [,,,].
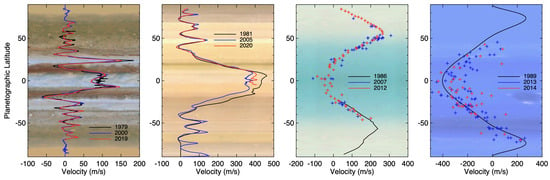
Figure 12.
The giant planets’ zonally-averaged winds measured over time. In all four panels, the black profile is from Voyager imaging measurements; for Neptune, the best-fit profile for southern latitudes is mirrored above 50N []. Jupiter’s winds show only small variations between Voyager (1979), Cassini (2000), and Hubble (2019) imaging measurements [,,], primarily in the strongest eastward jet; map from Hubble 2015 data. Saturn shows substantial change at the equator between the Voyager (1981), Cassini (2004–2006), and Hubble (2020) eras [,]; map from Cassini and Voyager 2 by B. Jonnson. Uranus shows very little variation between Voyager (1986), Keck (2007), and Keck/Gemini (2012) [,,]; map from Hubble 2021 data, mirrored for southern hemisphere coverage. Neptune’s winds show large dispersion over from the Voyager (1989) profile and within a single filter (Keck H-band measurements are shown for 2013 and 2014) [,]; map from Voyager 2 up to 50, B. Jonnson.
Saturn’s wind speeds are substantially higher than Jupiter’s and the jets are predominantly eastward with sharp peaks, dominated by a broad, high-speed, equatorial jet; see Figure 12. There may be a slight speed offset due to uncertainty in the rotation period of Saturn [], but this would not materially affect the east-west pattern or the high-speed equatorial jet. This jet shows substantial variation over time, whether due to cloud tracer altitude or a top-down adjustment by Saturn’s wave-driven stratospheric equatorial oscillation, which might be modulating the wind shears at the tropopause, (e.g., [] and references therein). Additionally, features visible at different wavelengths allow direct measurements of vertical shear on the order of 2.5 m/s per km [].
In contrast with Jupiter and Saturn, Uranus and Neptune both have only two major prograde jets, one per hemisphere, with retrograde equatorial jets. For Uranus, there are few obvious cloud tracers in the visible, unless contrast is enhanced, and the Voyager profile was limited to southern latitudes. Measurements made around equinox from Keck and Hubble images showed that the northern hemisphere has a wind jet near 45N, roughly symmetric with the one observed by Voyager near 45S, but with some dispersion at several latitudes [] seen in the points in Figure 12. Despite the wavelength differences between data sets, there is no substantial variation observed in the winds. This indicates little vertical shear is present, even though wind gradients are expected in the 100 to 800 mbar region based on the latitudinal temperature structure [,]. Measurements on images from 2012 to 2014 showed no substantial changes in the zonal wind field, though the increase in cloud features allowed the extraction of a more complete wind profile [,].
Neptune has a larger number of obvious wind tracers than Uranus, though many are large storms or cloud complexes which may not fully be advected by the winds. Recent near-IR measurements roughly match the wind profile shape measured from Voyager data; however, there is a large spread in the wind values from these features [,]. Some of this is likely due to vertical wind shear, with K’-band (2.2 microns) image measurements corresponding more closely to the Voyager measurements. H-band winds are substantially lower and correspond to deeper in altitude [,], implying a vertical wind shear of 1 to 2 m/s per km; however, this is opposite of the shear inferred from Voyager measurements []. Additionally, large velocity dispersion is still observed even within a single filter in a data set, (e.g., [,]), but this may be due to the latitudinal extent and inherent motions of the features that are tracked rather than differences in the underlying wind field.
4.2. Waves
Giant planet atmospheres display a wide variety of wave phenomena, ranging from planetary-scale Rossby waves to very fine gravity-inertia waves. These waves transport momentum and energy and may help to drive the zonal wind jets [,]. Typically, waves appear at latitudes at the peaks of the wind jets, but some are only present when large storms occur. Wave properties, including wavelength and phase speed, can be diagnostic of the atmospheric conditions, and provide insights about conditions below the visible clouds. As with wind tracers, each planet shows different amounts of wave activity.
For example, on Jupiter, the equatorial region is dominated by large Rossby waves, demarcated by bright plumes on the north side and labelled in Figure 5, and an occasional symmetric feature on the southern border called the South Equatorial Disturbance []. The usual appearance of the south equatorial zone is a smaller set of v-shaped clouds, likely a second wave superimposed on the Rossby wave []. Other small gravity-inertia waves are only visible in spacecraft imagery because of their small spatial scales (300 km and smaller), but a larger wave (∼1400-km wavelength) has been observed on the border of the North Equatorial Belt, shown in Figure 13 []. Arising near a set of cyclones and anticyclones, it was observed in 1979, but not again until 2012 [,], and has appeared sporadically at some longitudes through 2021. This wave tends to be most apparent at violet and mid-IR wavelengths, appearing only faintly in the UV [,]. It is nearly stationary and is likely an inertia-gravity wave triggered by the nearby anticyclones and cyclones [].
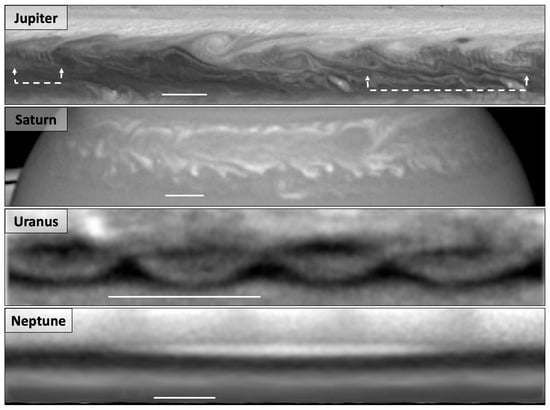
Figure 13.
Planetary waves at multiple scales; solid line indicates 10,000 km. Jupiter in 2015 at 395 nm shows fine-scale waves (dashed arrows) superimposed on a cyclone/anticyclone vortex street at 16N latitude []. Saturn in 2011 at 502 nm shows a wavy structure along the edges of the expanding storm plume at 40N latitude. Uranus in 2012 at 1.6 microns, showing braided equatorial waves []. Neptune in 2021 at 467 nm shows a wave number 1 feature centered at 55S latitude.
Even with extensive Cassini coverage, Saturn does not show obvious wave activity at visual wavelengths with the exception of during large planet encircling storm outbreaks; see Figure 13. One such equatorial storm in 1990, showed wave-like structure, but attempts to measure a phase speed were inconclusive [,]. A similar, but smaller, storm in 1994 showed velocities much lower than that of the background wind fields, again possibly attributable to waves, but the feature was compact and short-lived, and could not be further constrained []. However, a large northern hemisphere storm outbreak in 2010 was much better documented than the previous storms. This violent storm led to a long-lasting vortex near 40N, but waves were seen in the initial storm outbreak and its trailing plumes. Modeling indicated that Rossby waves were present in the storm’s initial outbreak, depositing energy high into the stratosphere, while the planet-encircling cloud propagation was due to Kelvin–Helmholtz instability or trapped gravity-Rossby waves [,].
Uranus also does not display obvious visible-wavelength waves, but in the near IR, waves can be seen near the equator, for example in Figure 9, and expanded in Figure 13. The braided appearance can be explained by two interacting waves and the pattern has persisted over multiple years []. The exact wave properties and wave type are not yet known, though given their scale and similarities to Jupiter and Saturn’s large equatorial waves, it is reasonable to assume they are Rossby waves.
The most obvious wave observed on Neptune is a transverse wavenumber 1 feature centered near 55S, visible in F467M and F547M HST images [,]. While this persistent feature may have some connection to the SPF, that has not yet been established. Smaller-spatial-scale waves have not yet been directly observed on Neptune, but there are some indications that these waves are present. First, the latitudinal oscillation of some storms is thought to be tied to wave activity. Additionally, the large dispersion in wind velocities at any given latitude may be due to the presence of waves [,]. Future high-resolution imaging, along with long-term monitoring, will reveal if Neptune also has smaller-scale waves.
4.3. Vertical Cloud Structure
As mentioned above, the altitude and composition of the cloud layers on each of the outer planets have long been estimated using thermochemical equilibrium models [,]. Figure 14 shows that Jupiter’s NH ice cloud base is as deep as 760 mbar, with deeper NHSH and HO clouds. Water cloud layers include pure water ice plus a liquid solution with dissolved NH and HS [,]. Saturn is similar, except the cloud decks reside deeper, with the NH ice cloud base as deep as 1.7 bar. For Uranus, the cloud is CH ice, with a cloud base as deep as 1 bar, assuming a 30 × solar [] enrichment of condensable species []. Neptune has the same cloud layers as Uranus, but at deeper pressure levels due to a higher volatile enrichment (80 × solar, []) and a slightly colder temperature profile.
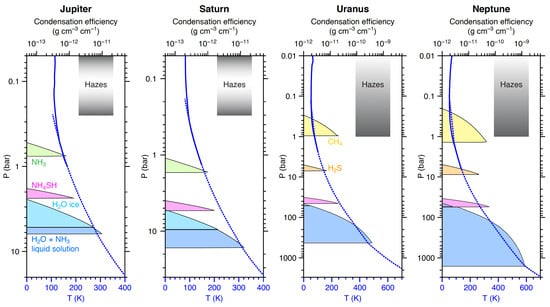
Figure 14.
Cloud layers on the giant planets. Calculations use composition described in [] (and references therein) for non-condensable species and [] (and references therein) for condensable species, with adiabatic model temperatures (dashed blue curves) matched to Voyager 2 radio occultation temperature profiles (solid blue curves, []), in the model of [,,]. Cloud condensation efficiency is plotted for each layer. Qualitative vertical ranges of photochemical hazes are shown by grey shading for comparison.
The misunderstanding that thermochemical equilibrium models are capable of directly calculating cloud densities as a function of altitude has persisted for decades (e.g., [,]). Instead, these models can calculate the cloud condensation efficiency (or cloud condensation rate) []; cloud condensation rate, , can be viewed as a cloud density potential, governed by the local pressure/temperature conditions in a saturated atmosphere. However, estimating cloud densities, , requires that this potential be multiplied by an updraft length scale, L; . The erroneous cloud densities obtained by Equations (19) and (20) of [] (instead of Equation (5) of []) come from implicitly assuming , the atmospheric-scale height (the distance over which the pressure changes by a factor of e or 2.718) [,]. Setting makes it difficult to compare cloud condensation rates at different levels, even on a qualitative basis, because varies by up to a factor of 5 across the relevant cloud layers. It is also misleading to use cloud densities from [] while stating that they are upper limits to actual cloud densities, because in some cases, it is conceivable that . Strong updrafts satisfying are consistent with detections of water ice spectral signatures in Saturn Great White Storm clouds [] and in Jovian convective plumes [], and with the Jupiter mushball scenario in which condensed water cloud particles lofted to the ammonia condensation level are invoked to explain the very deep NH depletion found by Juno [].
Equilibrium cloud models do provide an effective starting point for interpreting visible and near-IR observations, despite the issues interpreting the density values. Results from these models are sensitive to the deep volatile abundances, which are not known with high accuracy and are spatially and temporally variable. Actual cloud densities as a function of altitude would also be affected by microphysics, including supersaturation, precipitation, aerosol particle interactions, and the availability of condensation nuclei. For all four planets, in situ measurements are still needed to validate these cloud models; the Galileo probe entered a largely cloud-free clearing and could only partially resolve cloud altitudes for Jupiter [,]. Remote sensing is crucial for measuring horizontal, vertical, and temporal variation in atmospheric composition and cloud properties, providing context and constraints for both thermochemical equilibrium models and in situ measurements.
Radiative transfer modelling of high-spatial-resolution data over a broad wavelength range allows us to retrieve the vertical distribution of haze and cloud layers []. The higher the number of filters and viewing angles included, the better these properties are constrained, so combining Hubble and adaptive optics data is an exceptionally powerful tool. Spatially-resolved spectroscopy provides another lever arm, as the spectral resolution can be very high, but often at the expense of spatial resolution. Thus, while spectroscopy is a valuable tool, we largely limit this review to results from imaging studies.
Radiative transfer models assume a number of atmospheric layers to represent the cloud deck, tropospheric haze, stratospheric haze, and gas layers, as needed. To limit the number of free parameters, fewer layers are better, and most models assume three to five, but some use as many as ten. Center-to-limb brightness scans can be used to constrain a latitude band’s structure, while retrievals on discrete features, such as the Great Red Spot, require multiple viewing angles on the same feature; this is obtained with multiple images as the planet rotates, preferably over as many continuum and absorption-band wavelengths as possible.
The fitting methods vary by model, but typically an iterative fit is performed, allowing each layer’s optical depth, particle size, altitude and vertical extent to vary, sometimes while fixing the values for the other layers to reduce the number of free parameters. Additionally, some models also fit a single wavelength index of refraction or single-scattering albedo to determine which species might comprise the aerosols, and where chromophores (cloud-coloring compounds) reside. Although any particular retrieval model or data sets may have inherent biases, their true value comes in comparing different locations in the same data set, or a single location in similar, time separated, data sets.
For Jupiter, many models fit an optically thick, white, cloud layer with a top between 500 and 700 millibars and a base around one bar, though some data sets and retrieval methods seem to be more sensitive to a uniform cloud layer near 1.5 bars, possibly the NHSH cloud (e.g., [,]). Regardless of the cloud deck altitude, the models agree that the GRS has optically thick clouds/haze extending to higher altitudes than the surrounding clouds, and most find that the coloring compounds may not be the same over the GRS as over the belts or red cyclones [,,]. Fits from Galileo data (highest spatial resolution, but limited wavelengths) find the cloud deck in zones reaches a few hundred millibars higher, with much higher optical depth, than in belts. Both have similar tropospheric haze optical depth, but with lower short wavelength single-scattering albedo in the belts. Among discrete features, holes in the clouds had a thin cloud deck, while the GRS had very thick clouds and haze, and both had low single-scattering albedo [].
Fits to VLT/MUSE data (higher spectral, but lower spatial, resolution than Hubble), with a discrete layer of a colored haze, also indicate a thinner cloud deck in the belts than in the zones, but showed much more variability in the haze optical depth and vertical distribution []. Interestingly, modeling of Hubble data of the South Equatorial Belt during a fade and revival cycle showed a substantial change in cloud optical depth and haze single-scattering albedo, but not cloud height []. Similarly, modeling of the reddened Oval BA showed no obvious change in its structure, only in color []. Recent modeling of Hubble data before and after a North Temperature Belt fade event showed a change in haze opacity, and that an extended colored haze fits better than a discrete layer []. In the equatorial zone, Hubble photometry demonstrated that a large drop in cloud opacity in the period 2006–2007 was followed by a drop in haze opacity approximately 1200 days later []. Further high-resolution data sets with good temporal sampling of these global-scale transitions, particularly over an extended wavelength range, will be invaluable for understanding atmospheric structure.
Similar modelling has been performed for Saturn from Hubble imaging data. While dramatic, rapid, color changes are not observed as they are on Jupiter, Saturn does have apparent latitudinal variation in cloud structure. Hubble data of the southern hemisphere from 2002 (near southern winter solstice) are best fit with an increased optical thickness of haze towards the south pole, and with small variations in single-scattering albedo []. However, data spanning a decade show significant changes over time, with single-scattering albedo decreasing, and stratospheric haze increasing from 1995 to 2003. The tropospheric haze optical depth does not show a constant trend and varies by latitude []. As on Jupiter, modeling finds a difference in the tropospheric haze optical depth over cyclones and anticyclones, consistent with subsidence and upwelling, respectively [].
Lacking a dedicated orbital mission, we are entirely reliant on Earth-based data for radiative transfer retrievals of Uranus and Neptune cloud structure variations. Modelling of high-resolution Keck and Hubble imaging data before and around equinox found that most latitudes did not require CH clouds at the expected 1 bar level, but rather an extended haze [,]. Some models fit best with a deeper HS cloud at 6 bars, and southern latitudes showed scattering at 2 bars, increasing towards the 45S bright band [,]. Only discrete bright cloud features have been found to have a vertical extent above 1 bar, reaching to 400–500 mbar [,].
On Neptune, most models favor a cloud layer around 3 bars [,,]. However, this cloud must also be dark in the near IR, having a low single-scattering albedo at these wavelengths []. The tropospheric haze above 1 bar is optically thin, and may be extended [,,]. Interestingly, discrete bright cloud features seen in the northern hemisphere reach well into the stratosphere, with upper altitudes from 20 to 100 mbar []. In contrast, the bright southern bands and SPF are deeper, reaching only into the upper troposphere []. Spectroscopic data, which have a better sensitivity to the vertical cloud structure, along with further imaging data, are needed to fully reconcile Uranus and Neptune with the theoretical cloud structure shown in Figure 14.
5. Discussion
Cycles and long-term trends have long been documented for the outer planets using ground-based telescopes, although the causes for change were not well constrained (e.g., []). One of the great advantages of high-resolution Earth-based imaging is that atmospheric properties can be monitored over long periods of time, and with a high cadence, except near solar conjunction. The availability of frequent observations allows for characterizing quickly evolving storms and events, such as impacts. However, the combined long time base of both low- and high-resolution data is still important given the very long seasonal scales for the outer planets shown in Figure 15. The ability to use high-resolution data to determine which properties are changing over time is crucial to placing the lower-resolution data into context and to building the complete picture of seasonality on the outer planets.
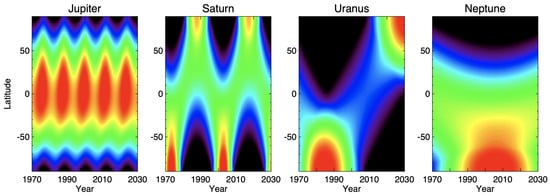
Figure 15.
Normalized solar insolation patterns from 1970 to 2030, neglecting ring shadows. The solar insolation pattern is governed by its orbital elements (period, inclination, eccentricity), as well as axial tilt, as shown in Table 3; black indicates no illumination. Jupiter, the only giant planet with little tilt, experiences only slight differences between the northern and southern hemispheres and receives ample equatorial insolation. Saturn has higher insolation at the south pole than at the north pole at their respective solstices, and ring shadows further block the winter hemisphere. Uranus was first observed near southern summer solstice and has not yet reached northern summer solstice; large portions of the planet receive no illumination for decades. Neptune has only been observed with southern illumination, due to its long orbital period.
For example, Jupiter’s belts and zones change colors with a quasi-periodic cadence, though these events do not always occur when predicted []. Attempts to tie changes in cloud color with changes in wind velocities or wave-driven equatorial oscillations have proved elusive, however, in part because of the small magnitude of the wind changes discussed above [,,]. Furthermore, the cycles of activity in the prominent bands are more likely to be associated with convective processes initiated at depths where solar influences are unimportant—such as the fade and revival of the South Equatorial Belt [], coloration episodes in the equatorial zone [], expansions of the North Equatorial Belt [], and eruptions in the north temperate belt []. The origins of these cyclic processes remain poorly understood [,], and the balance between top-down control from the stratosphere (e.g., associated with the stratospheric oscillation) and bottom-up control from the deeper weather layer is a topic of active investigation.
On Saturn, the most episodic events are the Great White storms [,]. These occur predominantly in the northern hemisphere every ∼28 years [,], or approximately once per Saturn year. While it has been suggested that solar insolation might be modulating deep convection, studies have found that the solar heat flux peaks at 200 mbars and is negligible at the cloud deck [,]. Additionally, the 2010 northern storm occurred very close to Saturn’s spring equinox, as shown in Figure 15, only shortly after these latitudes emerged from ring shadowing. However, Saturn does undergo very rapid haze coloration changes on both seasonal and more rapid timescales, particularly in the polar regions which turn blue in winter [,]. Saturn’s radiative time constant, , or the time to respond to thermal changes, was recent recalculated with revised atmospheric parameters []. At the cloud deck (1 bar), the value decreased from 28 years to 1.4 years and from 10 years to 4.7 years at the tropopause (0.1 bar) [,]. If correct, rapid color changes are conceivable, particularly in the upper tropospheric hazes, where sunlight can penetrate and the thermal response time is short; when the radiative time constant is less than the orbital period (), the seasonal response is larger [].

Table 3.
Planetary Orbital Parameters and Radiative Time Constants [].
Table 3.
Planetary Orbital Parameters and Radiative Time Constants [].
| Planet | Orbital | Orbital | Orbital | Axial | 2/ | 2/ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Period | Inclination | Eccentricity | Tilt | at 0.1 bar | at 1 bar | |
| Jupiter | 11.9 years | 1.3 | 0.049 | 3.1 | 1 | 0.2 |
| Saturn | 29.5 years | 2.5 | 0.052 | 26.7 | 1 | 0.3 |
| Uranus | 84.0 years | 0.8 | 0.047 | 97.8 | 3 | 0.7 |
| Neptune | 164.8 years | 1.8 | 0.010 | 28.3 | 2 | 0.3 |
We do not yet have a high-resolution record that spans a full Uranian year, as shown in Figure 15, but disk-averaged ground-based records show its overall brightness has a strong seasonal component [,]. High-resolution data around the 2007 equinox revealed that the polar haze brightness shifts very suddenly, as on Saturn. Approaching equinox, the previously bright southern pole darkened and the northern pole began to brighten quickly []. The revised Uranus radiative time constants are ∼9 years at 1 bar and 40 years at 0.1 bar, as shown in Table 3 [], which does not explain the rapid shift in polar haze brightness []. Additionally, a small, unexplained, global brightness increase over time remains after accounting for, and removing, the seasonal component [].
Similarly, ground-based and Hubble observations indicate that Neptune’s brightness has increased with time. This was originally thought to be a phase-lagged seasonal effect [,], but the 65 year ground-based record shows the brightness increase has persisted for longer than a seasonal cycle [,]. Other higher-frequency brightness variations are also observed to correlate with solar cycle []. These variations can be explained by solar UV or galactic cosmic rays modulated by solar activity [,]. However, as with Uranus, the steady increase in brightness over time is not yet understood []. Of course, seasons also affect photochemistry, as well as the cloud layers considered here, and [] provides a review of those properties.
Ultimately, the observed temporal changes in winds, waves, cloud and haze structure, haze composition, and even active convective outbreaks may each have a seasonal component. Disentangling effects caused by deep energy release and atmospheric circulation from those induced by solar insolation patterns will require many more observations, and modelling, particularly for Uranus and Neptune due to their long orbital periods. Continued monitoring from space and Earth-based telescopes, as well as future missions, will be crucial to our understanding of how these atmospheres evolve.
6. Summary
The Hubble Space Telescope and large ground-based adaptive optics telescopes have provided us with a wealth of high-resolution data now spanning multiple decades. In particular, the broad wavelength coverage of these facilities, from the UV to the near IR, is beyond the capability of early deep space missions, such as Voyager, enabling new analyses of the clouds, winds, and atmospheric vertical structure on the giant planets. Using these high-spatial-resolution data sets, we now know that: the overall zonal wind profiles are relatively constant, but there are variations observed in the wind jets on all four planets; convective activity and storm outbreaks occur on both periodic and stochastic timescales, with storms lasting days to years; wave activity is common, but not always observable; and Jupiter and Saturn’s vertical aerosol distributions appear to match thermochemical models reasonably well, but Uranus’s and Neptune’s do not.
Given the long timescales involved, we are just beginning to understand some seasonal aspects on the planets. Continued observations will ensure that the record is complete and that further analyses, particularly for Uranus and Neptune, are enabled. We also expect that future facilities and missions will enable ground-breaking discoveries. The successful launch of the James Webb Space Telescope in 2021 will enable high-resolution near-IR observations of the planets. Future UV-optical telescopes, both ground-based extremely large telescopes, and the next space-based telescope advocated in the Astrophysics Decadal Survey [], will be invaluable to planetary studies. A space telescope specifically focused on solar system observations could advance giant planet atmospheric science by measuring short-timescale variability over long observational campaigns []. Finally, future missions to Uranus or Neptune would allow the ultra-high-spatial-resolution studies that have been possible for Jupiter and Saturn from their dedicated missions, providing ground truth for Earth-based observations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.A.S., M.H.W., L.A.S., L.N.F. and P.M.F.; writing—original draft preparation, A.A.S. and M.H.W.; writing—review and editing, L.A.S., L.N.F. and P.M.F.; visualization, A.A.S., L.A.S. and M.H.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
A.A.S., M.H.W., L.A.S. and P.M.F. were supported by grants from the Space Telescope Science Institute associated with programs GO13937, GO16057, GO16084, GO16454). L.A.S. and P.M.F. were also supported by NASA Solar System Observing Grant 80NSSC21K0292. L.N.F. was supported by a European Research Council Consolidator Grant (under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme, grant agreement No 723890) at the University of Leicester.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This review includes observations made with the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope obtained from the Space Telescope Science Institute, which is operated by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc. (AURA), under NASA contract NAS 5–26555. These observations are associated with program(s) GO10805, GO12395, GO13937, GO14334, GO15262, GO16266, GO16454, GO16790, and GO16880. Ground-based data in Figure 2, Figure 7, Figure 8, Figure 9 and Figure 10 and Figure 12 came from the very large telescope (VLT), Gemini North, and W.M. Keck observatories. The VLT is operated by the European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere, the Gemini North Observatory is operated by AURA, and the Keck Observatory is operated as a scientific partnership among the California Institute of Technology, the University of California, and NASA. This work was enabled by the location of the Keck and Gemini telescopes within the Maunakea Science Reserve, adjacent to the summit of Maunakea. We are grateful for the privilege of conducting observations from a place that is unique in both its astronomical quality and its cultural significance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Peek, B. The Planet Jupiter; Faber and Faber: London, UK, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, J. The Giant Planet Jupiter; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, C.R. Jupiter’s Zonal Winds: Variation with Latitude. J. Atmos. Sci. 1969, 26, 986–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hide, R. Jupiter and Saturn. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. Math. Phys. Sci. 1974, 336, 63–84. [Google Scholar]
- Peebles, P. The Structure and Composition of Jupiter and Saturn. Astrophys. J. 1964, 140, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, T. The spectra of Jupiter and Saturn in the photographic infrared. Icarus 1969, 10, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, W. Thermal Models of Jupiter and Saturn. Astrophys. J. 1969, 155, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.A.; Soderblom, L.A.; Johnson, T.V.; Ingersoll, A.P.; Collins, S.A.; Shoemaker, E.M.; Hunt, G.E.; Masursky, H.; Carr, M.H.; Davies, M.E.; et al. The Jupiter System Through the Eyes of Voyager 1. Science 1979, 204, 951–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.A.; Soderblom, L.A.; Beebe, R.; Boyce, J.; Briggs, G.; Carr, M.; Collins, S.A.; Cook, A.F.; Danielson, G.E.; Davies, M.E.; et al. The Galilean Satellites and Jupiter: Voyager 2 Imaging Science Results. Science 1979, 206, 927–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.A.; Soderblom, L.; Beebe, R.; Boyce, J.; Briggs, G.; Bunker, A.; Collins, S.A.; Hansen, C.J.; Johnson, T.V.; Mitchell, J.L.; et al. Encounter with Saturn: Voyager 1 Imaging Science Results. Science 1981, 212, 163–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.A.; Soderblom, L.; Batson, R.; Bridges, P.; Inge, J.; Masursky, H.; Shoemaker, E.; Beebe, R.; Boyce, J.; Briggs, G.; et al. A New Look at the Saturn System: The Voyager 2 Images. Science 1982, 215, 504–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.; Soderblom, L.; Beebe, R.; Bliss, D.; Boyce, J.; Brahic, A.; Briggs, G.; Brown, R.; Collins, S.; Cook, A.; et al. Voyager 2 in the Uranian System: Imaging Science Results. Science 1986, 233, 43–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.A.; Soderblom, L.A.; Banfield, D.; Barnet, C.; Basilevsky, A.T.; Beebe, R.F.; Bollinger, K.; Boyce, J.M.; Brahic, A.; Briggs, G.A.; et al. Voyager 2 at Neptune: Imaging Science Results. Science 1989, 246, 1422–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Melendo, E.; Arregi, J.; Rojas, J.; Hueso, R.; Barrado-Izagirre, N.; Gómez-Forrellad, J.; Pérez-Hoyos, S.; Sanz-Requena, J.; Sánchez-Lavega, A. Dynamics of Jupiter’s equatorial region at cloud top level from Cassini and HST images. Icarus 2011, 211, 1242–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.H.; Simon, A.A.; Tollefson, J.W.; de Pater, I.; Barnett, M.N.; Hsu, A.I.; Stephens, A.W.; Orton, G.S.; Fleming, S.W.; Goullaud, C.; et al. High-resolution UV/Optical/IR Imaging of Jupiter in 2016–2019. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 2020, 247, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, A.A.; Wong, M.H.; Orton, G.S. First Results from the Hubble OPAL Program: Jupiter in 2015. Astrophys. J. 2015, 812, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckers, J.M. Adaptive Optics for Astronomy: Principles, Performance, and Applications. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1993, 31, 13–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigaut, F. Astronomical Adaptive Optics. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2015, 127, 1197–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Pater, I.; Fletcher, L.N.; Pérez-Hoyos, S.; Hammel, H.B.; Orton, G.S.; Wong, M.H.; Luszcz-Cook, S.; Sánchez-Lavega, A.; Boslough, M. A multi-wavelength study of the 2009 impact on Jupiter: Comparison of high resolution images from Gemini, Keck and HST. Icarus 2010, 210, 722–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Pater, I.; Wong, M.H.; Marcus, P.; Luszcz-Cook, S.; Ádámkovics, M.; Conrad, A.; Asay-Davis, X.; Go, C. Persistent rings in and around Jupiter’s anticyclones—Observations and theory. Icarus 2010, 210, 742–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Pater, I.; Wong, M.H.; de Kleer, K.; Hammel, H.B.; Ádámkovics, M.; Conrad, A. Keck adaptive optics images of Jupiter’s north polar cap and Northern Red Oval. Icarus 2011, 213, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hueso, R.; de Pater, I.; Simon, A.; Sánchez-Lavega, A.; Delcroix, M.; Wong, M.H.; Tollefson, J.W.; Baranec, C.; de Kleer, K.; Luszcz-Cook, S.H.; et al. Neptune long-lived atmospheric features in 2013–2015 from small (28-cm) to large (10-m) telescopes. Icarus 2017, 295, 89–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammel, H.B.; Sitko, M.L.; Lynch, D.K.; Orton, G.S.; Russell, R.W.; Geballe, T.R.; de Pater, I. Distribution of Ethane and Methane Emission on Neptune. Astron. J. 2007, 134, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sromovsky, L.A.; de Pater, I.; Fry, P.M.; Hammel, H.B.; Marcus, P. High S/N Keck and Gemini AO imaging of Uranus during 2012–2014: New cloud patterns, increasing activity, and improved wind measurements. Icarus 2015, 258, 192–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Pater, I.; Sromovsky, L.A.; Fry, P.M.; Hammel, H.B.; Baranec, C.; Sayanagi, K.M. Record-breaking storm activity on Uranus in 2014. Icarus 2015, 252, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sromovsky, L.A.; Fry, P.M. The methane abundance and structure of Uranus’ cloud bands inferred from spatially resolved 2006 Keck grism spectra. Icarus 2008, 193, 252–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sromovsky, L.A.; Fry, P.M. Spatially resolved cloud structure on Uranus: Implications of near-IR adaptive optics imaging. Icarus 2007, 192, 527–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sromovsky, L.A.; Fry, P.M.; Hammel, H.B.; de Pater, I.; Rages, K.A.; Showalter, M.R. Dynamics, evolution, and structure of Uranus’ brightest cloud feature. Icarus 2007, 192, 558–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sromovsky, L.A.; Fry, P.M. Dynamics of cloud features on Uranus. Icarus 2005, 179, 459–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammel, H.B.; de Pater, I.; Gibbard, S.G.; Lockwood, G.W.; Rages, K. New cloud activity on Uranus in 2004: First detection of a southern feature at 2.2 micron. Icarus 2005, 175, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbard, S.G.; de Pater, I.; Hammel, H.B. Near-infrared adaptive optics imaging of the satellites and individual rings of Uranus. Icarus 2005, 174, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Pater, I.; Gibbard, S.G.; Macintosh, B.A.; Roe, H.G.; Gavel, D.T.; Max, C.E. Keck Adaptive Optics Images of Uranus and Its Rings. Icarus 2002, 160, 359–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammel, H.B.; Rages, K.; Lockwood, G.W.; Karkoschka, E.; de Pater, I. New Measurements of the Winds of Uranus. Icarus 2001, 153, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tollefson, J.; de Pater, I.; Marcus, P.S.; Luszcz-Cook, S.; Sromovsky, L.A.; Fry, P.M.; Fletcher, L.N.; Wong, M.H. Vertical wind shear in Neptune’s upper atmosphere explained with a modified thermal wind equation. Icarus 2018, 311, 317–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Pater, I.; Fletcher, L.N.; Luszcz-Cook, S.; DeBoer, D.; Butler, B.; Hammel, H.B.; Sitko, M.L.; Orton, G.; Marcus, P.S. Neptune’s global circulation deduced from multi-wavelength observations. Icarus 2014, 237, 211–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, P.J.; de Pater, I.; Luszcz-Cook, S.; Wong, M.H.; Hammel, H.B. Dispersion in Neptune’s zonal wind velocities from NIR Keck AO observations in July 2009. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2014, 350, 65–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.C.; de Pater, I.; Marcus, P. Neptune’s zonal winds from near-IR Keck adaptive optics imaging in August 2001. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2012, 337, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, P.M.; Sromovsky, L.A. Keck NIRC2 photometry of Uranus, uranian satellites, and Triton in August 2004. Icarus 2007, 192, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbard, S.G.; de Pater, I.; Roe, H.G.; Martin, S.; Macintosh, B.A.; Max, C.E. The altitude of Neptune cloud features from high-spatial-resolution near-infrared spectra. Icarus 2003, 166, 359–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Max, C.E.; Macintosh, B.A.; Gibbard, S.G.; Gavel, D.T.; Roe, H.G.; de Pater, I.; Ghez, A.M.; Acton, D.S.; Lai, O.; Stomski, P.; et al. Cloud Structures on Neptune Observed with Keck Telescope Adaptive Optics. Astron. J. 2003, 125, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wizinowich, P.; Acton, D.S.; Shelton, C.; Stomski, P.; Gathright, J.; Ho, K.; Lupton, W.; Tsubota, K.; Lai, O.; Max, C.; et al. First Light Adaptive Optics Images from the Keck II Telescope: A New Era of High Angular Resolution Imagery. Pub. Astro. Soc. Pac. 2000, 112, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, T.; Kasaba, Y.; Tao, C.; Sakanoi, T.; Kagitani, M.; Fujisawa, S.; Kita, H.; Badman, S.V. Vertical emissivity profiles of Jupiter’s northern H3+ and H2 infrared auroras observed by Subaru/IRCS. J. Geophys. Res. (Space Phys.) 2014, 119, 10219–10241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kita, H.; Fujisawa, S.; Tao, C.; Kagitani, M.; Sakanoi, T.; Kasaba, Y. Horizontal and vertical structures of Jovian infrared aurora: Observation using Subaru IRCS with adaptive optics. Icarus 2018, 313, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, H.; Kita, H.; Tao, C.; Kagitani, M.; Sakanoi, T.; Kasaba, Y. Pulsation Characteristics of Jovian Infrared Northern Aurora Observed by the Subaru IRCS with Adaptive Optics. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 11547–11554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.H.; Marchis, F.; Marchetti, E.; Amico, P.; Tordo, S.; Bouy, H.; de Pater, I. A shift in Jupiter’s equatorial haze distribution imaged with the Multi-Conjugate Adaptive Optics Demonstrator at the VLT. arXiv 2008, arXiv:0810.3703. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, M.N.; Stallard, T.S.; Melin, H.; Johnson, R.E. Exploring Key Characteristics in Saturn’s Infrared Auroral Emissions Using VLT-CRIRES: H3+ Intensities, Ion Line-of-Sight Velocities, and Rotational Temperatures. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 7137–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, P.G.J.; Fletcher, L.N.; Read, P.L.; Tice, D.; de Pater, I.; Orton, G.S.; Teanby, N.A.; Davis, G.R. Spectral analysis of Uranus’ 2014 bright storm with VLT/SINFONI. Icarus 2016, 264, 72–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, P.G.J.; Wong, M.H.; Simon, A.A.; Orton, G.S.; Toledo, D. HST/WFC3 observations of Uranus’ 2014 storm clouds and comparison with VLT/SINFONI and IRTF/Spex observations. Icarus 2017, 288, 99–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braude, A.S.; Irwin, P.G.; Orton, G.S.; Fletcher, L.N. Colour and tropospheric cloud structure of Jupiter from MUSE/VLT: Retrieving a universal chromophore. Icarus 2020, 338, 113589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, P.G.J.; Dobinson, J.; James, A.; Toledo, D.; Teanby, N.A.; Fletcher, L.N.; Orton, G.S.; Pérez-Hoyos, S. Latitudinal variation of methane mole fraction above clouds in Neptune’s atmosphere from VLT/MUSE-NFM: Limb-darkening reanalysis. Icarus 2021, 357, 114277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, P.G.J.; Toledo, D.; Braude, A.S.; Bacon, R.; Weilbacher, P.M.; Teanby, N.A.; Fletcher, L.N.; Orton, G.S. Latitudinal variation in the abundance of methane (CH4) above the clouds in Neptune’s atmosphere from VLT/MUSE Narrow Field Mode Observations. Icarus 2019, 331, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, P.G.J.; Teanby, N.A.; Davis, G.R.; Fletcher, L.N.; Orton, G.S.; Calcutt, S.B.; Tice, D.S.; Hurley, J. Further seasonal changes in Uranus’s cloud structure observed by Gemini-North and UKIRT. Icarus 2012, 218, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, P.G.J.; Teanby, N.A.; Davis, G.R.; Fletcher, L.N.; Orton, G.S.; Tice, D.; Kyffin, A. Uranus’s cloud structure and seasonal variability from Gemini-North and UKIRT observations. Icarus 2011, 212, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, P.G.J.; Teanby, N.A.; Davis, G.R.; Fletcher, L.N.; Orton, G.S.; Tice, D.; Hurley, J.; Calcutt, S.B. Multispectral imaging observations of Neptune’s cloud structure with Gemini-North. Icarus 2011, 216, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, R.S.; Orton, G.S.; Stephens, A.W.; Wong, M.H.; Irwin, P.G.J.; Sinclair, J.A.; Tabataba-Vakili, F. Wave Activity in Jupiter’s North Equatorial Belt From Near-Infrared Reflectivity Observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 1232–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, M.T.; Banfield, D.; Gierasch, P.J. Aerosols and methane in the ice giant atmospheres inferred from spatially resolved, near-infrared spectra: I. Uranus, 2001–2007. Icarus 2018, 310, 54–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roddier, F.; Roddier, C.; Graves, J.E.; Northcott, M.J.; Owen, T. NOTE: Neptune’s Cloud Structure and Activity: Ground-Based Monitoring with Adaptive Optics. Icarus 1998, 136, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roddier, F.; Roddier, C.; Brahic, A.; Dumas, C.; Graves, J.E.; Northcott, M.J.; Owen, T. First ground-based adaptive optics observations of Neptune and Proteus. Planet. Space Sci. 1997, 45, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roe, H.G.; Gavel, D.; Max, C.; de Pater, I.; Gibbard, S.; Macintosh, B.; Baines, K.H. Near-Infrared Observations of Neptune’s Tropospheric Cloud Layer with the Lick Observatory Adaptive Optics System. Astron. J. 2001, 122, 1636–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenar, D.A.; Hillman, J.J.; Lelouarn, M.; Fugate, R.; Drummond, J.D. Multispectral Imagery of Jupiter and Saturn Using Adaptive Optics and Acousto-Optic Tuning. Pub. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1997, 109, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sromovsky, L.A. Latitudinal and Longitudinal Oscillations of Cloud Features on Neptune. Science 1991, 254, 684–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigo-Rodriguez, J.; Sánchez-Lavega, A.; Gómez, J.; Lecacheux, J.; Colas, F.; Miyazaki, I. The 90-day oscillations of Jupiter’s Great Red Spot revisited. Planet. Space Sci. 2000, 48, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, A.A.; Tabataba-Vakili, F.; Cosentino, R.; Beebe, R.F.; Wong, M.H.; Orton, G.S. Historical and Contemporary Trends in the Size, Drift, and Color of Jupiter’s Great Red Spot. Astron. J. 2018, 155, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Juberías, R.; Simon, A.A.; Cosentino, R.G. Analysis of the long-term drift rates and oscillations of Jupiter’s largest vortices. Icarus 2022, 372, 114732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.H.; Marcus, P.S.; Simon, A.A.; de Pater, I.; Tollefson, J.W.; Asay-Davis, X. Evolution of the Horizontal Winds in Jupiter’s Great Red Spot From One Jovian Year of HST/WFC3 Maps. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL093982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammel, H.B.; Wong, M.H.; Clarke, J.T.; de Pater, I.; Fletcher, L.N.; Hueso, R.; Noll, K.; Orton, G.S.; Pérez-Hoyos, S.; Sánchez-Lavega, A.; et al. Jupiter after the 2009 Impact: Hubble Space Telescope Imaging of the Impact-Generated Debris and its Temporal Evolution. Astrophys. J. 2010, 715, L150–L154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hsu, A.I.; Wong, M.H.; Simon, A.A. Lifetimes and Occurrence Rates of Dark Vortices on Neptune from 25 Years of Hubble Space Telescope Images. Astron. J. 2019, 157, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammel, H.B.; Lockwood, G.W.; Mills, J.R.; Barnet, C.D. Hubble Space Telescope Imaging of Neptune’s Cloud Structure in 1994. Science 1995, 268, 1740–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sromovsky, L.; Hammel, H.; de Pater, I.; Fry, P.; Rages, K.; Showalter, M.; Merline, W.; Tamblyn, P.; Neyman, C.; Margot, J.L.; et al. Episodic bright and dark spots on Uranus. Icarus 2012, 220, 6–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sromovsky, L.; Fry, P.; Dowling, T.; Baines, K.; Limaye, S. Neptune’s Atmospheric Circulation and Cloud Morphology: Changes Revealed by 1998 HST Imaging. Icarus 2001, 150, 244–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atreya, S.K.; Romani, P.N. Photochemistry and clouds of Jupiter, Saturn and Uranus. In Recent Advances in Planetary Meteorology; Hunt, G.E., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1985; pp. 17–68. [Google Scholar]
- West, R.A.; Strobel, D.F.; Tomasko, M.G. Clouds, aerosols, and photochemistry in the Jovian atmosphere. Icarus 1986, 65, 161–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindal, G.F. The Atmosphere of Neptune: An Analysis of Radio Occultation Data Acquired with Voyager 2. Astron. J. 1992, 103, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaller, E.L.; Roe, H.G.; Schneider, T.; Brown, M.E. Storms in the tropics of Titan. Nature 2009, 460, 873–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, L.N.; Orton, G.; Rogers, J.; Giles, R.; Payne, A.; Irwin, P.; Vedovato, M. Moist convection and the 2010–2011 revival of Jupiter’s South Equatorial Belt. Icarus 2017, 286, 94–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, A.A.; Sanchez-Lavega, A.; Legarreta, J.; Sanz-Requena, J.F.; Perez-Hoyos, S.; Garcia-Melendo, E.; Carlson, R.W. Spectral comparison and stability of red regions on Jupiter. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2015, 120, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeffler, M.J.; Hudson, R.L.; Chanover, N.J.; Simon, A.A. The spectrum of Jupiter’s Great Red Spot: The case for ammonium hydrosulfide (NH4SH). Icarus 2016, 271, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, R.; Baines, K.; Anderson, M.; Filacchione, G.; Simon, A. Chromophores from photolyzed ammonia reacting with acetylene: Application to Jupiter’s Great Red Spot. Icarus 2016, 274, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sromovsky, L.; Baines, K.; Fry, P.; Carlson, R. A possibly universal red chromophore for modeling color variations on Jupiter. Icarus 2017, 291, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidenschilling, S.; Lewis, J. Atmospheric and cloud structures of the Jovian planets. Icarus 1973, 20, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atreya, S.K. Atmospheres and Ionospheres of the Outer Planets and Their Satellites; Springer: London, UK, 1986; p. 90. [Google Scholar]
- Baines, K.H.; Carlson, R.W.; Kamp, L.W. Fresh Ammonia Ice Clouds in Jupiter. I. Spectroscopic Identification, Spatial Distribution, and Dynamical Implications. Icarus 2002, 159, 74–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon-Miller, A.A.; Conrath, B.; Gierasch, P.J.; Beebe, R.F. A Detection of Water Ice on Jupiter with Voyager IRIS. Icarus 2000, 145, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon-Miller, A.A.; Gierasch, P.J.; Beebe, R.F.; Conrath, B.; Flasar, F.; Achterberg, R.K. New Observational Results Concerning Jupiter’s Great Red Spot. Icarus 2002, 158, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beebe, R. Jupiter The Giant Planet; Smithsonian: Washington, DC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Lavega, A.; Anguiano-Arteaga, A.; Iñurrigarro, P.; Garcia-Melendo, E.; Legarreta, J.; Hueso, R.; Sanz-Requena, J.F.; Pérez-Hoyos, S.; Mendikoa, I.; Soria, M.; et al. Jupiter’s Great Red Spot: Strong Interactions With Incoming Anticyclones in 2019. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2021, 126, e2020JE006686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Lavega, A.; Orton, G.; Morales, R.; Lecacheux, J.; Colas, F.; Fisher, B.; Fukumura-Sawada, P.; Golisch, W.; Griep, D.; Kaminski, C.; et al. The Merger of Two Giant Anticyclones in the Atmosphere of Jupiter. Icarus 2001, 149, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, A.; Marcus, P.S. The dynamics of jovian white ovals from formation to merger. Icarus 2003, 162, 74–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon-Miller, A.A.; Chanover, N.J.; Orton, G.S.; Sussman, M.; Tsavaris, I.G.; Karkoschka, E. Jupiter’s White Oval turns red. Icarus 2006, 185, 558–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DelGenio, A.D.; Achterberg, R.K.; Baines, K.H.; Flasar, F.M.; Read, P.L.; Sánchez-Lavega, A.; Showman, A.P. Saturn Atmospheric Structure and Dynamics. In Saturn from Cassini-Huygens; Dougherty, M.K., Esposito, L.W., Krimigis, S.M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 113–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, L.N.; Greathouse, T.K.; Guerlet, S.; Moses, J.I.; West, R.A. Saturn’s Seasonally Changing Atmosphere: Thermal Structure, Composition and Aerosols. In Saturn in the 21st Century; Baines, K.H., Flasar, F.M., Krupp, N., Stallard, T., Eds.; Cambridge Planetary Science, Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2018; pp. 251–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sromovsky, L.; Baines, K.; Fry, P. Evolution of Saturn’s north polar color and cloud structure between 2012 and 2017 inferred from Cassini VIMS and ISS observations. Icarus 2021, 362, 114409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnarson, J.L.; Sayanagi, K.M.; Blalock, J.J.; Fletcher, L.N.; Ingersoll, A.P.; Dyudina, U.A.; Ewald, S.P.; Draham, R.L. Saturn’s New Ribbons: Cassini Observations of Planetary Waves in Saturn’s 42N Atmospheric Jet. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 7399–7408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, A.; Hueso, R.; Sanchez-Lavega, A.; Wong, M.H. Midsummer Atmospheric Changes in Saturn’s Northern Hemisphere from the Hubble OPAL Program. Planet. Sci. J. 2021, 2, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Lavega, A.; del Río-Gaztelurrutia, T.; Delcroix, M.; Legarreta, J.J.; Gómez-Forrellad, J.M.; Hueso, R.; García-Melendo, E.; Pérez-Hoyos, S.; Barrado-Navascués, D.; Lillo, J.; et al. Ground-based observations of the long-term evolution and death of Saturn’s 2010 Great White Spot. Icarus 2012, 220, 561–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Río-Gaztelurrutia, T.; Sánchez-Lavega, A.; Antuñano, A.; Legarreta, J.; García-Melendo, E.; Sayanagi, K.M.; Hueso, R.; Wong, M.H.; Pérez-Hoyos, S.; Rojas, J.F.; et al. A planetary-scale disturbance in a long living three vortex coupled system in Saturn’s atmosphere. Icarus 2018, 302, 499–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfrey, D. A Hexagonal feature around Saturn’s north pole. Icarus 1988, 76, 335–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa Aguiar, A.; Read, P.; Wordsworth, R.; Salter, T.; Yamazaki, Y. A laboratory model of Saturn’s North Polar Hexagon. Icarus 2010, 206, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Juberias, R.; Sayanagi, K.; Simon, A.; Fletcher, L.; Cosentino, R. Meandering Shallow Atmospheric Jet as a Model of Saturn’ North-Polar Hexagon. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2015, 806, L18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, L.N.; Orton, G.S.; Sinclair, J.A.; Guerlet, S.; Read, P.L.; Antuñano, A.; Achterberg, R.K.; Flasar, F.M.; Irwin, P.G.J.; Bjoraker, G.L.; et al. A hexagon in Saturn’s northern stratosphere surrounding the emerging summertime polar vortex. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sromovsky, L.A.; Revercomb, H.E.; Krauss, R.J.; Suomi, V.E. Voyager 2 Observations of Saturn’s Northern Mid-Latitude Cloud Features: Morphology, Motions, and Evolution. J. Geophys. Res. 1983, 88, 8650–8666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayanagi, K.M.; Morales-Juberías, R.; Ingersoll, A.P. Saturn’s Northern Hemisphere Ribbon: Simulations and Comparison with the Meandering Gulf Stream. J. Atmos. Sci. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cosentino, R.G.; Simon, A.; Morales-Juberias, R.; Sayanagi, K.M. Observations and Numerical Modeling of the Jovian Ribbon. Astrophys. J. 2015, 810, L10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkoschka, E. Clouds of High Contrast on Uranus. Science 1998, 280, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkoschka, E. Uranus’ southern circulation revealed by Voyager 2: Unique characteristics. Icarus 2015, 250, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sromovsky, L.A.; Karkoschka, E.; Fry, P.M.; de Pater, I.; Hammel, H.B. The methane distribution and polar brightening on Uranus based on HST/STIS, Keck/NIRC2, and IRTF/SpeX observations through 2015. Icarus 2019, 317, 266–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, L.N. The Atmosphere of Uranus. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.06377. [Google Scholar]
- Sromovsky, L.A.; Karkoschka, E.; Fry, P.M.; Hammel, H.B.; de Pater, I.; Rages, K. Methane depletion in both polar regions of Uranus inferred from HST/STIS and Keck/NIRC2 observations. Icarus 2014, 238, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkoschka, E.; Tomasko, M. The haze and methane distributions on Uranus from HST-STIS spectroscopy. Icarus 2009, 202, 287–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, D.; Irwin, P.G.; Rannou, P.; Teanby, N.A.; Simon, A.A.; Wong, M.H.; Orton, G.S. Constraints on Uranus’s haze structure, formation and transport. Icarus 2019, 333, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammel, H.; Sromovsky, L.; Fry, P.; Rages, K.; Showalter, M.; de Pater, I.; van Dam, M.; LeBeau, R.; Deng, X. The Dark Spot in the atmosphere of Uranus in 2006: Discovery, description, and dynamical simulations. Icarus 2009, 201, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Pater, I.; Sromovsky, L.; Hammel, H.B.; Fry, P.; Le Beau, R.; Rages, K.; Showalter, M.; Matthews, K. Post-equinox observations of Uranus: Berg’s evolution, vertical structure, and track towards the equator. Icarus 2011, 215, 332–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hueso, R.; Sanchez-Lavega, A. Atmospheric Dynamics and Vertical Structure of Uranus and Neptune’s Weather Layers. Space Sci. Rev. 2019, 215, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hueso, R.; Guillot, T.; Sánchez-Lavega, A. Convective storms and atmospheric vertical structure in Uranus and Neptune. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2020, 378, 20190476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, P.G.J.; Teanby, N.A.; Fletcher, L.N.; Toledo, D.; Orton, G.S.; Wong, M.H.; Roman, M.T.; Perez-Hoyos, S.; James, A.; Dobinson, J. Hazy blue worlds: A holistic aerosol model for Uranus and Neptune, including Dark Spots. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.04516. [Google Scholar]
- Sromovsky, L.; Fry, P.; Hammel, H.; Ahue, W.; de Pater, I.; Rages, K.; Showalter, M.; van Dam, M. Uranus at equinox: Cloud morphology and dynamics. Icarus 2009, 203, 265–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Moses, J.I.; Cavalié, T.; Fletcher, L.N.; Roman, M.T. Atmospheric chemistry on Uranus and Neptune. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2020, 378, 20190477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molter, E.; de Pater, I.; Luszcz-Cook, S.; Hueso, R.; Tollefson, J.; Alvarez, C.; Sánchez-Lavega, A.; Wong, M.H.; Hsu, A.I.; Sromovsky, L.A.; et al. Analysis of Neptune’s 2017 bright equatorial storm. Icarus 2019, 321, 324–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sromovsky, L.; Fry, P.; Dowling, T.; Baines, K.; Limaye, S. Coordinated 1996 HST and IRTF Imaging of Neptune and Triton: III. Neptune’s Atmospheric Circulation and Cloud Structure. Icarus 2001, 149, 459–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammel, H.; Lockwood, G. Atmospheric Structure of Neptune in 1994, 1995, and 1996: HST Imaging at Multiple Wavelengths. Icarus 1997, 129, 466–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.H.; Tollefson, J.; Hsu, A.I.; de Pater, I.; Simon, A.A.; Hueso, R.; Sánchez-Lavega, A.; Sromovsky, L.; Fry, P.; Luszcz-Cook, S.; et al. A New Dark Vortex on Neptune. Astron. J. 2018, 155, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, A.A.; Wong, M.H.; Hsu, A.I. Formation of a New Great Dark Spot on Neptune in 2018. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 3108–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sromovsky, L.A.; Limaye, S.S.; Fry, P.M. Dynamics of Neptune’s Major Cloud Features. Icarus 1993, 105, 110–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luszcz-Cook, S.; de Pater, I.; Ádámkovics, M.; Hammel, H. Seeing double at Neptune’s south pole. Icarus 2010, 208, 938–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, A.A. The Structure and Temporal Stability of Jupiter’s Zonal Winds: A Study of the North Tropical Region. Icarus 1999, 141, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tollefson, J.; Wong, M.H.; de Pater, I.; Simon, A.A.; Orton, G.S.; Rogers, J.H.; Atreya, S.K.; Cosentino, R.G.; Januszewski, W.; Morales-Juberías, R.; et al. Changes in Jupiter’s Zonal Wind Profile preceding and during the Juno mission. Icarus 2017, 296, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Lavega, A.; Sromovsky, L.A.; Showman, A.P.; Del Genio, A.D.; Young, R.M.B.; Hueso, R.; Garcia-Melendo, E.; Kaspi, Y.; Orton, G.S.; Barrado-Izagirre, N.; et al. Zonal Jets: Phenomenology, Genesis, and Physics; Galperin, B., Read, P.L., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 72–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.E.; Morales-Juberías, R.; Simon, A.; Gaulme, P.; Wong, M.H.; Cosentino, R.G. Longitudinal variability in Jupiter’s zonal winds derived from multi-wavelength HST observations. Planet. Space Sci. 2018, 155, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banfield, D.; Gierasch, P.J.; Squyres, S.W.; Nicholson, P.D.; Conrath, B.J.; Matthews, K. 2 micron Spectrophotometry of Jovian Stratospheric Aerosols—Scattering Opacities, Vertical Distributions, and Wind Speeds. Icarus 1996, 121, 389–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Melendo, E.; Sánchez-Lavega, A. A Study of the Stability of Jovian Zonal Winds from HST Images: 1995–2000. Icarus 2001, 152, 316–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porco, C.C.; West, R.A.; McEwen, A.; Del Genio, A.D.; Ingersoll, A.P.; Thomas, P.; Squyres, S.; Dones, L.; Murray, C.D.; Johnson, T.V.; et al. Cassini Imaging of Jupiter’s Atmosphere, Satellites, and Rings. Science 2003, 299, 1541–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Read, P.; Dowling, T.; Schubert, G. Saturn’s rotation period from its atmospheric planetary-wave configuration. Nature 2009, 460, 608–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Lavega, A.; García-Melendo, E.; Pérez-Hoyos, S.; Hueso, R.; Wong, M.H.; Simon, A.; Sanz-Requena, J.F.; Antuñano, A.; Barrado-Izagirre, N.; Garate-Lopez, I.; et al. An enduring rapidly moving storm as a guide to Saturn’s Equatorial jet’s complex structure. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrath, B.J.; Gierasch, P.J.; Ustinov, E.A. Thermal Structure and Para Hydrogen Fraction on the Outer Planets from Voyager IRIS Measurements. Icarus 1998, 135, 501–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, L.N.; de Pater, I.; Orton, G.S.; Hofstadter, M.D.; Irwin, P.G.J.; Roman, M.T.; Toledo, D. Ice Giant Circulation Patterns: Implications for Atmospheric Probes. Space Sci. Rev. 2020, 216, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limaye, S.S.; Sromovsky, L.A. Winds of Neptune: Voyager observations of cloud motions. J. Geophys. Res. 1991, 96, 18941–18960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Schneider, T. Mechanisms of Jet Formation on the Giant Planets. J. Atmos. Sci. 2010, 67, 3652–3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Schneider, T. Convective Generation of Equatorial Superrotation in Planetary Atmospheres. J. Atmos. Sci. 2011, 68, 2742–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon-Miller, A.A.; Rogers, J.H.; Gierasch, P.J.; Choi, D.; Allison, M.D.; Adamoli, G.; Mettig, H.J. Longitudinal variation and waves in Jupiter’s south equatorial wind jet. Icarus 2012, 218, 817–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, A.; Hueso, R.; Iñurrigarro, P.; Sánchez-Lavega, A.; Morales-Juberías, R.; Cosentino, R.; Fletcher, L.; Wong, M.; Hsu, A.; de Pater, I.; et al. A New, Long-lived, Jupiter Mesoscale Wave Observed at Visible Wavelengths. Astron. J. 2018, 156, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, L.N.; Melin, H.; Adriani, A.; Simon, A.A.; Sanchez-Lavega, A.; Donnelly, P.T.; Antuñano, A.; Orton, G.S.; Hueso, R.; Kraaikamp, E.; et al. Jupiter’s Mesoscale Waves Observed at 5 microns by Ground-based Observations and Juno JIRAM. Astron. J. 2018, 156, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beebe, R.; Barnet, C.; Sada, P.; Murrell, A. The onset and growth of the 1990 equatorial disturbance on Saturn. Icarus 1992, 95, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnet, C.; Westphal, J.; Beebe, R.; Huber, L. Hubble space telescope observations of the 1990 equatorial disturbance on Saturn: Zonal winds and central meridian albedos. Icarus 1992, 100, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Lavega, A.; Lecacheux, J.; Gomez, J.M.; Colas, F.; Laques, P.; Noll, K.; Gilmore, D.; Miyazaki, I.; Parker, D. Large-Scale Storms in Saturn’s Atmosphere During 1994. Science 1996, 271, 631–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Melendo, E.; Sánchez-Lavega, A. Shallow water simulations of Saturn’s giant storms at different latitudes. Icarus 2017, 286, 241–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Lavega, A.; Fischer, G.; Fletcher, L.N.; García-Melendo, E.; Hesman, B.; Pérez-Hoyos, S.; Sayanagi, K.M.; Sromovsky, L.A. The Great Saturn Storm of 2010–2011. In Saturn in the 21st Century; Baines, K., Flasar, F., Krupp, N., Stallard, T., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2018; pp. 377–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asplund, M.; Grevesse, N.; Sauval, A.J.; Scott, P. The Chemical Composition of the Sun. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 47, 481–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousis, O.; Atkinson, D.H.; Ambrosi, R.; Atreya, S.; Banfield, D.; Barabash, S.; Blanc, M.; Cavalié, T.; Coustenis, A.; Deleuil, M.; et al. In Situ exploration of the giant planets. Exp. Astron. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atreya, S.K.; Hofstadter, M.H.; In, J.H.; Mousis, O.; Reh, K.; Wong, M.H. Deep Atmosphere Composition, Structure, Origin, and Exploration, with Particular Focus on Critical in situ Science at the Icy Giants. Space Sci. Rev. 2020, 216, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.H.; Atreya, S.K.; Kuhn, W.R.; Romani, P.N.; Mihalka, K.M. Fresh clouds: A parameterized updraft method for calculating cloud densities in one-dimensional models. Icarus 2015, 245, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sromovsky, L.A.; Baines, K.H.; Fry, P.M. Saturn’s Great Storm of 2010–2011: Evidence for ammonia and water ices from analysis of VIMS spectra. Icarus 2013, 226, 402–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillot, T.; Stevenson, D.J.; Atreya, S.K.; Bolton, S.J.; Becker, H.N. Storms and the Depletion of Ammonia in Jupiter: I. Microphysics of “Mushballs”. J. Geophys. Res. (Planets) 2020, 125, e06403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragent, B.; Colburn, D.S.; Rages, K.A.; Knight, T.C.D.; Avrin, P.; Orton, G.S.; Yanamandra-Fisher, P.A.; Grams, G.W. The clouds of Jupiter: Results of the Galileo Jupiter mission probe nephelometer experiment. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 22891–22910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.E.; Travis, L.D. Light scattering in planetary atmospheres. Space Sci. Rev. 1974, 16, 527–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon-Miller, A.A.; Banfield, D.; Gierasch, P.J. Color and the Vertical Structure in Jupiter’s Belts, Zones, and Weather Systems. Icarus 2001, 154, 459–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Hoyos, S.; Sanz-Requena, J.; Barrado-Izagirre, N.; Rojas, J.; Sánchez-Lavega, A. The 2009–2010 fade of Jupiter’s South Equatorial Belt: Vertical cloud structure models and zonal winds from visible imaging. Icarus 2012, 217, 256–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.H.; de Pater, I.; Asay-Davis, X.; Marcus, P.S.; Go, C.Y. Vertical structure of Jupiter’s Oval BA before and after it reddened: What changed? Icarus 2011, 215, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Hoyos, S.; Sánchez-Lavega, A.; Sanz-Requena, J.; Barrado-Izagirre, N.; Carrión-González, O.; Anguiano-Arteaga, A.; Irwin, P.; Braude, A. Color and aerosol changes in Jupiter after a North Temperate Belt disturbance. Icarus 2020, 352, 114031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lii, P.S.; Wong, M.H.; de Pater, I. Temporal variation of the tropospheric cloud and haze in the jovian equatorial zone. Icarus 2010, 209, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Hoyos, S.; Sánchez-Lavega, A.; French, R.; Rojas, J. Saturn’s cloud structure and temporal evolution from ten years of Hubble Space Telescope images (1994–2003). Icarus 2005, 176, 155–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Requena, J.; Pérez-Hoyos, S.; Sánchez-Lavega, A.; del Rio-Gaztelurrutia, T.; Irwin, P.G. Hazes and clouds in a singular triple vortex in Saturn’s atmosphere from HST/WFC3 multispectral imaging. Icarus 2019, 333, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luszcz-Cook, S.; de Kleer, K.; de Pater, I.; Adamkovics, M.; Hammel, H. Retrieving Neptune’s aerosol properties from Keck OSIRIS observations. I. Dark regions. Icarus 2016, 276, 52–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, P.; Lellouch, E.; de Bergh, C.; Courtin, R.; Bézard, B.; Fletcher, L.; Orton, G.; Teanby, N.; Calcutt, S.; Tice, D.; et al. Line-by-line analysis of Neptune’s near-IR spectrum observed with Gemini/NIFS and VLT/CRIRES. Icarus 2014, 227, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockwood, G.; Thompson, D. Photometric Variability of Neptune, 1972–2000. Icarus 2002, 156, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon-Miller, A.A.; Gierasch, P.J. On the long-term variability of Jupiter’s winds and brightness as observed from Hubble. Icarus 2010, 210, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antuñano, A.; Fletcher, L.N.; Orton, G.S.; Melin, H.; Rogers, J.H.; Harrington, J.; Donnelly, P.T.; Rowe-Gurney, N.; Blake, J.S.D. Infrared Characterization of Jupiter’s Equatorial Disturbance Cycle. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 10987–10995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, L.N.; Orton, G.S.; Sinclair, J.A.; Donnelly, P.; Melin, H.; Rogers, J.H.; Greathouse, T.K.; Kasaba, Y.; Fujiyoshi, T.; Sato, T.M.; et al. Jupiter’s North Equatorial Belt expansion and thermal wave activity ahead of Juno’s arrival. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 7140–7148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Lavega, A.; Orton, G.S.; Hueso, R.; García-Melendo, E.; Pérez-Hoyos, S.; Simon-Miller, A.; Rojas, J.F.; Gómez, J.M.; Yanamandra-Fisher, P.; Fletcher, L.; et al. Depth of a strong jovian jet from a planetary-scale disturbance driven by storms. Nature 2008, 451, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antuñano, A.; Fletcher, L.N.; Orton, G.S.; Melin, H.; Milan, S.; Rogers, J.; Greathouse, T.; Harrington, J.; Donnelly, P.T.; Giles, R. Jupiter’s Atmospheric Variability from Long-term Ground-based Observations at 5 micron. Astron. J. 2019, 158, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Lavega, A.; Colas, F.; Lecacheux, J.; Laques, P.; Miyazaki, I.; Parker, D. The Great White Spot and disturbances in Saturn’s equatorial atmosphere during 1990. Nature 1991, 353, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Hoyos, S.; Sánchez-Lavega, A. Solar flux in Saturn’s atmosphere: Penetration and heating rates in the aerosol and cloud layers. Icarus 2006, 180, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Le, T.; Zhang, X.; Yung, Y.L. A high-performance atmospheric radiation package: With applications to the radiative energy budgets of giant planets. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2018, 217, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrath, B.J.; Gierasch, P.J.; Leroy, S.S. Temperature and circulation in the stratosphere of the outer planets. Iarus 1990, 83, 255–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockwood, G.; Jerzykiewicz, M. Photometric variability of Uranus and Neptune, 1950–2004. Icarus 2006, 180, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammel, H.; Lockwood, G. Long-term atmospheric variability on Uranus and Neptune. Icarus 2007, 186, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sromovsky, L.; Fry, P.; Limaye, S.; Baines, K. The nature of Neptune’s increasing brightness: Evidence for a seasonal response. Icarus 2003, 163, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aplin, K.L.; Harrison, R.G. Determining solar effects in Neptune’s atmosphere. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, J.I.; Fletcher, L.N.; Greathouse, T.K.; Orton, G.S.; Hue, V. Seasonal stratospheric photochemistry on Uranus and Neptune. Icarus 2018, 307, 124–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. Pathways to Discovery in Astronomy and Astrophysics for the 2020s; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, C.; Wong, M.H.; Sayanagi, K.M.; Curry, S.; Jessup, K.L.; Becker, T.; Hendrix, A.; Chanover, N.; Milam, S.; Holler, B.J.; et al. The science enabled by a dedicated solar system space telescope. Bull. Am. Astron. Soc. 2021, 53, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).