Fine-Spatial Boreal–Alpine Single-Tree Albedo Measured by UAV: Experiences and Challenges
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
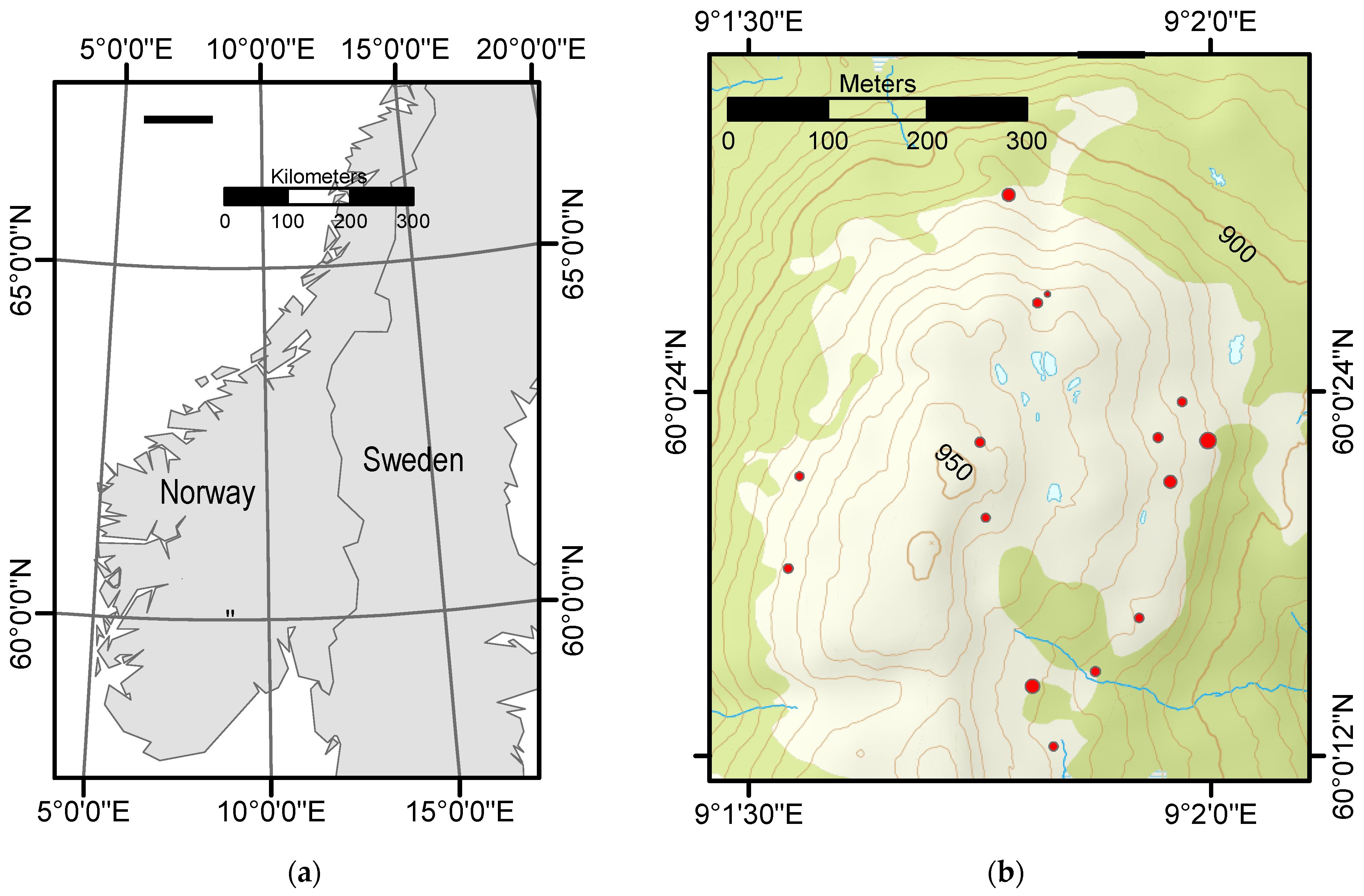
2.1. Study Site Description and Ground Measurements
2.2. UAV Platform for Measuring Albedo
2.3. Radiation Data
2.4. Airborne Laser Scanner Data
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
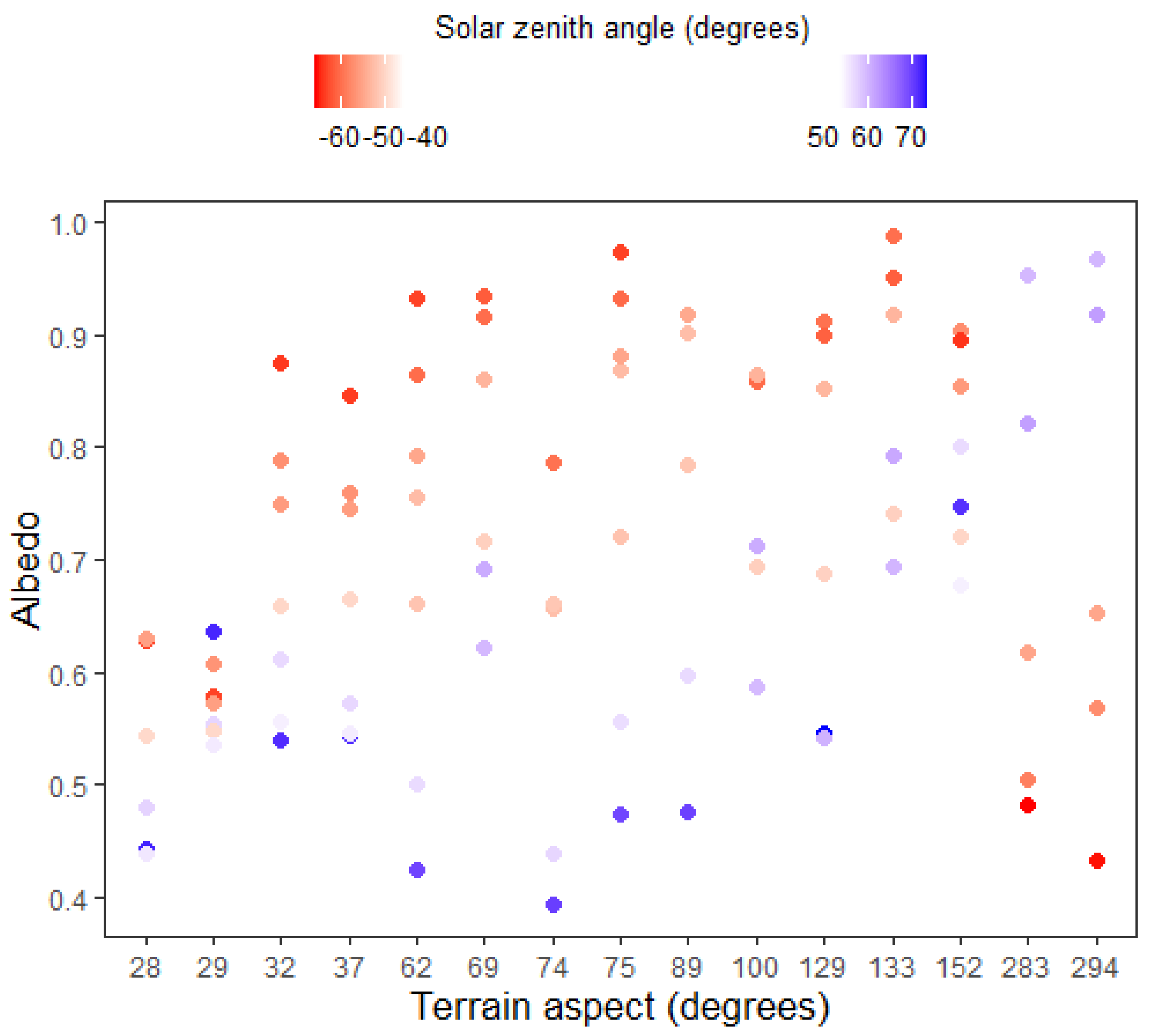
3.1. Solar Angle and Snow-Masking Effects on Albedo
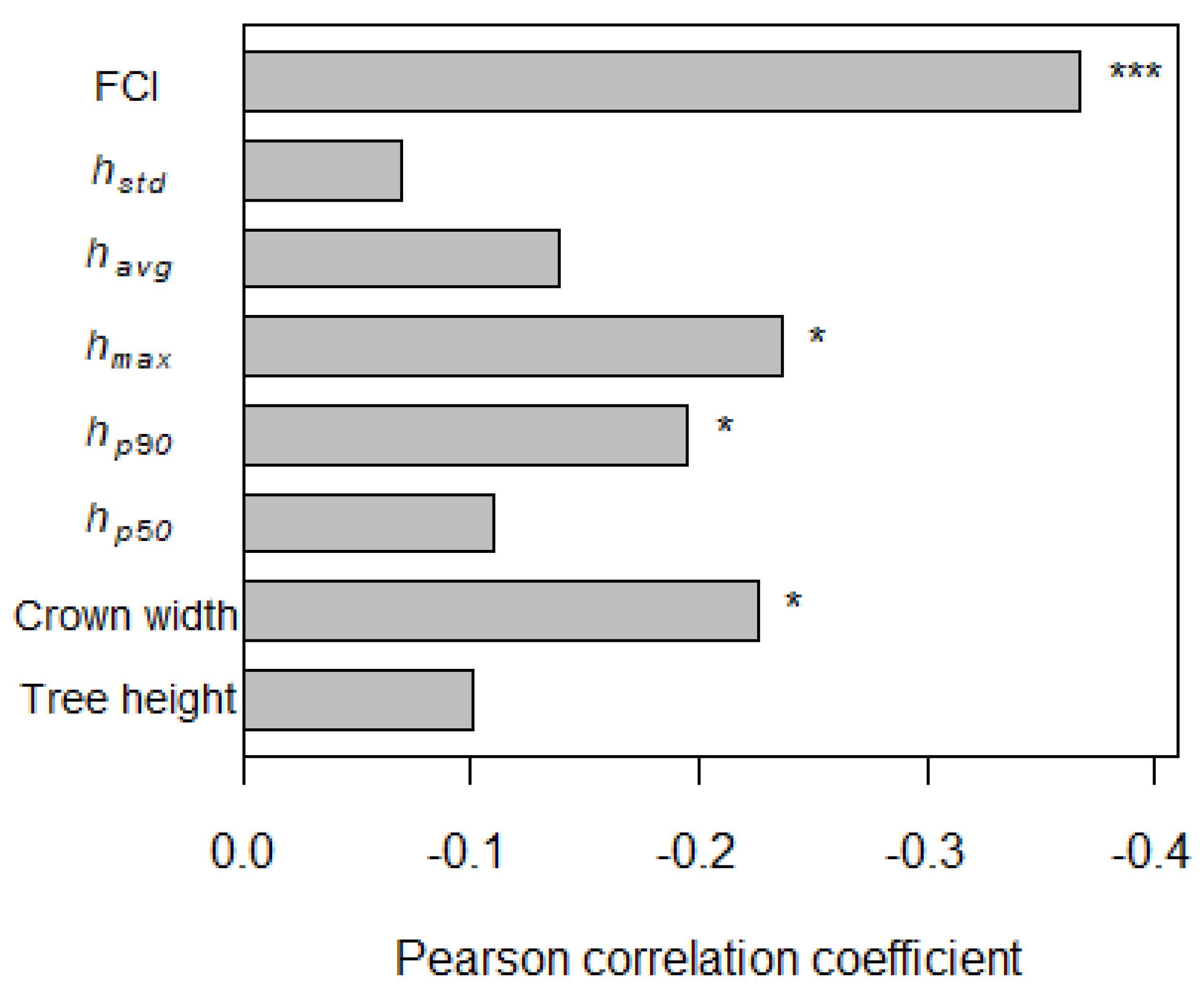
3.2. Tree Structural Effects on Albedo
4. Discussion
4.1. Statistical Assessment of LMMs
4.2. Assessment of Tree Structural Variables in Relation to Albedo
4.3. Challenges of Single-Tree Albedo Measurements by UAV
4.3.1. Effects of Diurnal Solar Course and Sloping Terrain
4.3.2. Effects of Measurement Errors for Large Solar Zenith Angles
4.3.3. Effects of Imprecise Spatial Resolution and Heading of the Hoovering Position
4.4. Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Frost, G.V.; Epstein, H.E. Tall shrub and tree expansion in Siberian tundra ecotones since the 1960s. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 1264–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallinger, M.; Manthey, M.; Wilmking, M. Establishing a missing link: Warm summers and winter snow cover promote shrub expansion into alpine tundra in Scandinavia. New Phytol. 2010, 186, 890–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rundqvist, S.; Hedenås, H.; Sandström, A.; Emanuelsson, U.; Eriksson, H.; Jonasson, C.; Callaghan, T.V. Tree and shrub expansion over the past 34 years at the tree-line near Abisko, Sweden. Ambio 2011, 40, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, S.D.; Nilsson, C. Arctic alpine vegetation change over 20 years. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2009, 15, 1676–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danby, R.K.; Hik, D.S. Variability, contingency and rapid change in recent subarctic alpine tree line dynamics. J. Ecol. 2007, 95, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullman, L. Tree line population monitoring of Pinus sylvestris in the Swedish Scandes, 1973–2005: Implications for tree line theory and climate change ecology. J. Ecol. 2006, 95, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullman, L. Recent tree-limit history of Piceaabies in the southern Swedish Scandes. Can. J. For. Res. 1986, 64, 1682–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasser, E.; Walde, J.; Tappeiner, U.; Teutsch, A.; Noggler, W. Land-use changes and natural reforestation in the Eastern Central Alps. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2007, 118, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speed, J.D.M.; Austrheim, G.; Hester, A.J.; Mysterud, A. Experimental evidence for herbivore limitation of the treeline. Ecology 2010, 91, 3414–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryn, A.; Hemsing, L. Impacts of land use on the vegetation in three rural landscapes of Norway. Int. J. Biodivers. Sci. Ecosyst. Serv. Manag. 2012, 8, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrig-Fasel, J.; Guisan, A.; Zimmermann, N.E. Tree line shifts in the Swiss Alps: Climate change or land abandonment? J. Veg. Sci. 2007, 18, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, M.; Takata, K.; Kawamiya, M.; Watanabe, S. Vegetation masking effect on future warming and snow albedo feedback in a boreal forest region of northern Eurasia according to MIROC-ESM. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 9245–9261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brovkin, V.; Raddatz, T.; Reick, C.H.; Claussen, M.; Gayler, V. Global biogeophysical interactions between forest and climate. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L07405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Wit, H.A.; Bryn, A.; Hofgaard, A.; Karstensen, J.; Kvalevåg, M.M.; Peters, G. Climate warming feedback from mountain birch forest expansion: Reduced albedo dominates carbon uptake. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 2344–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wramneby, A.; Smith, B.; Samuelsson, P. Hot spots of vegetation-climate feedbacks under future greenhouse forcing in Europe. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Betts, A.K.; Ball, J.H. Albedo over the boreal forest. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 28901–28909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loranty, M.M.; Berner, L.; Goetz, S.; Jin, Y.; Randerson, J.T. Vegetation controls on northern high latitude snow-albedo feedback: Observations and CMIP5 model simulations. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 20, 594–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartlett, P.A.; Verseghy, D.L. Modified treatment of intercepted snow improves the simulated forest albedo in the Canadian Land Surface Scheme. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 3208–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenfell, T.C.; Warren, S.G.; Mullen, P.C. Reflection of solar radiation by the Antarctic snow surface at ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared wavelengths. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1994, 99, 18669–18684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beringer, J.; Chapin, F.S.; Thompson, C.C.; McGuire, A.D. Surface energy exchanges along a tundra-forest transition and feedbacks to climate. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2005, 131, 143–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, T.R. Boundary Layer Climates, 2nd ed.; Routlege: London, UK, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, C.; Jonas, T. Influence of canopy shading and snow coverage on effective albedo in a snow-dominated evergreen needleleaf forest. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 214, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuusinen, N.; Stenberg, P.; Korhonen, L.; Rautiainen, M.; Tomppo, E. Structural factors driving boreal forest albedo in Finland. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 175, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forzieri, G.; Alkama, R.; Miralles, D.G.; Cescatti, A. Satellites reveal contrasting responses of regional climate to the widespread greening of Earth. Science 2017, 356, 1180–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lukeš, P.; Rautiainen, M.; Manninen, T.; Stenberg, P.; Mõttus, M. Geographical gradients in boreal forest albedo and structure in Finland. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 152, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lukeš, P.; Stenberg, P.; Rautiainen, M. Relationship between forest density and albedo in the boreal zone. Ecol. Model. 2013, 261-262, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovi, A.; Lindberg, E.; Lang, M.; Arumäe, T.; Peuhkurinen, J.; Sirparanta, S.; Pyankov, S.; Rautiainen, M. Seasonal dynamics of albedo across European boreal forests: Analysis of MODIS albedo and structural metrics from airborne LiDAR. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 224, 365–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuusinen, N.; Tomppo, E.; Shuai, Y.; Berninger, F. Effects of forest age on albedo in boreal forests estimated from MODIS and Landsat albedo retrievals. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 145, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bright, R.M.; Antón-Fernández, C.; Astrup, R.; Strømman, A.H. Empirical models of albedo transitions in managed boreal forests: Analysis of performance and transportability. Can. J. For. Res. 2015, 45, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuusinen, N.; Lukeš, P.; Stenberg, P.; Levula, J.; Nikinmaa, E.; Berninger, F. Measured and modelled albedos in Finnish boreal forest stands of different species, structure and understory. Ecol. Model. 2014, 284, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virtanen, T.; Ek, M. The fragmented nature of tundra landscape. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 27, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramtvedt, E.N.; Bollandsås, O.M.; Næsset, E.; Gobakken, T. Relationships between single-tree mountain birch summertime albedo and vegetation properties. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2021, 307, 108470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, C.R.; Burakowski, E.; Richardson, A.D. Novel Measurements of Fine-Scale Albedo: Using a Commercial Quadcopter to Measure Radiation Fluxes. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryan, J.C.; Hubbard, A.; Box, J.E.; Brough, S.; Cameron, K.; Cook, J.M.; Cooper, M.; Doyle, S.H.; Edwards, A.; Holt, T.O.; et al. Derivation of High Spatial Resolution Albedo from UAV Digital Imagery: Application over the Greenland Ice Sheet. Front. Earth Sci. 2017, 5, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Næsset, E. Vertical Height Errors in Digital Terrain Models Derived from Airborne Laser Scanner Data in a Boreal-Alpine Ecotone in Norway. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 4702–4725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ham, J.M. Useful equations and tables in micrometeorology. Micrometeorol. Agric. Syst. 2005, 47, 533–560. [Google Scholar]
- Knapp, R.H., Jr.; Williamson, R.L. Crown shadow area equations. For. Sci. 1984, 30, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelsson, P. DEM generation from laser scanner data using adaptive TIN models. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2000, 33, 110–117. [Google Scholar]
- Soininen, A. TerraScan User’s Guide. Available online: https://www.terrasolid.com/download/tscan.pdf (accessed on 21 March 2017).
- Harter, H.L. In Order Statistics and Their Use in Testing and Estimation; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Næsset, E. Predicting forest stand characteristics with airborne scanning laser using a practical two-stage procedure and field data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 80, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, L.; Korpela, I.; Heiskanen, J.; Maltamo, M. Airborne discrete-return LIDAR data in the estimation of vertical canopy cover, angular canopy closure and leaf area index. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1065–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solberg, S.; Næsset, E.; Hanssen, K.H.; Christiansen, E. Mapping defoliation during a severe insect attack on Scots pine using airborne laser scanning. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 102, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Patterson, H.D.; Thompson, R. Recovery of inter-block information when block sizes are unequal. Biometrika 1971, 58, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gałecki, A.; Burzykowski, T. Linear Mixed-Effects Model; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 245–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, S.; Schielzeth, H. A general and simple method for obtainingR2from generalized linear mixed-effects models. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2012, 4, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, Y.; Sakamoto, T.; Terajima, T.; Kitamura, K.; Shirai, T. The effect of canopy-snow on the energy balance above a co-niferous forest. Hydrol. Process. 1999, 13, 2371–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stähli, M.; Jonas, T.; Gustafsson, D. The role of snow interception in winter-time radiation processes of a coniferous sub-alpine forest. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 23, 2498–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knief, U.; Forstmeier, W. Violating the normality assumption may be the lesser of two evils. Behav. Res. Methods 2021, 53, 2576–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Næsset, E. Effects of different sensors, flying altitudes, and pulse repetition frequencies on forest canopy metrics and biophysical stand properties derived from small-footprint airborne laser data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzinger, N.; Andretta, M.; Van Gorsel, E.; Vogt, R.; Ohmura, A.; Rotach, M.W. Surface radiation budget in an Alpine valley. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2003, 129, 877–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georg, W.; Albin, H.; Georg, N.; Katharina, S.; Enrico, T.; Peng, Z. On the energy balance closure and net radiation in complex terrain. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2016, 226-227, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iqbal, M. An Introduction to Solar Radiation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiser, U.; Olefs, M.; Schöner, W.; Weyss, G.; Hynek, B. Correction of broadband snow albedo measurements affected by unknown slope and sensor tilts. Cryosphere 2016, 10, 775–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, K.W.; Rosenberg, N.J.; Doraiswamy, P.C. Shading inverted pyranometers and measurements of radiation reflected from an Alfalfa Crop. Water Resour. Res. 1970, 6, 1782–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirmhirn, I.; Eaton, F.D. Some Characteristics of the Albedo of Snow. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1975, 14, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muneer, T. Solar Radiation and Daylight Models, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sailor, D.J.; Resh, K.; Segura, D. Field measurement of albedo for limited extent test surfaces. Sol. Energy 2006, 80, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eitel, J.U.; Maguire, A.; Boelman, N.; Vierling, L.A.; Griffin, K.L.; Jensen, J.; Magney, T.S.; Mahoney, P.J.; Meddens, A.J.; Silva, C.; et al. Proximal remote sensing of tree physiology at northern treeline: Do late-season changes in the photochemical reflectance index (PRI) respond to climate or photoperiod? Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 221, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Tree Structural Variable | Mean | Range | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tree height (m) | 4.31 | 2.42–6.70 | 1.07 |
| Crown width (m) | 2.12 | 1.08–3.38 | 0.63 |
| FCI | 0.56 | 0.17–0.76 | 0.18 |
| Snow Depth | Tree Height | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 2.0 (m) | 5.0 (m) | 8.0 (m) | |
| 0.5 (m) | 22.9 | 124.7 | 314.2 |
| 1.0 (m) | 13.9 | 102.0 | 277.6 |
| 1.5 (m) | 6.2 | 81.7 | 243.3 |
| Explanatory Variable | Pearson Correlation Coefficient | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Solar zenith angle | –0.45 | 4.10 × 10−6 |
| Solar azimuth angle | –0.48 | 1.17 × 10−6 |
| Terrain slope angle | –0.36 | 0.0004 |
| Terrain aspect angle | 0.17 | 0.0924 |
| Ashadow | –0.45 | 5.19 × 10−6 |
| Tree Structural Variable | MAE | % Variance Explained by Difference between Trees 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tree height | 0.23 | 0.0916 | 23.2 |
| Crown width | 0.27 | 0.0929 | 19.4 |
| 0.23 | 0.0932 | 23.2 | |
| 0.28 | 0.0911 | 21.3 | |
| 0.27 | 0.0940 | 18.7 | |
| 0.24 | 0.0926 | 22.7 | |
| 0.19 | 0.0956 | 22.5 | |
| FCI | 0.28 | 0.1042 | 6.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramtvedt, E.N.; Gobakken, T.; Næsset, E. Fine-Spatial Boreal–Alpine Single-Tree Albedo Measured by UAV: Experiences and Challenges. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14061482
Ramtvedt EN, Gobakken T, Næsset E. Fine-Spatial Boreal–Alpine Single-Tree Albedo Measured by UAV: Experiences and Challenges. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(6):1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14061482
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamtvedt, Eirik Næsset, Terje Gobakken, and Erik Næsset. 2022. "Fine-Spatial Boreal–Alpine Single-Tree Albedo Measured by UAV: Experiences and Challenges" Remote Sensing 14, no. 6: 1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14061482
APA StyleRamtvedt, E. N., Gobakken, T., & Næsset, E. (2022). Fine-Spatial Boreal–Alpine Single-Tree Albedo Measured by UAV: Experiences and Challenges. Remote Sensing, 14(6), 1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14061482






