Columnar Water Vapor Retrieval by Using Data from the Polarized Scanning Atmospheric Corrector (PSAC) Onboard HJ-2 A/B Satellites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data
2.1. PSAC Data
2.2. Ground-Based CWV Data
3. Method
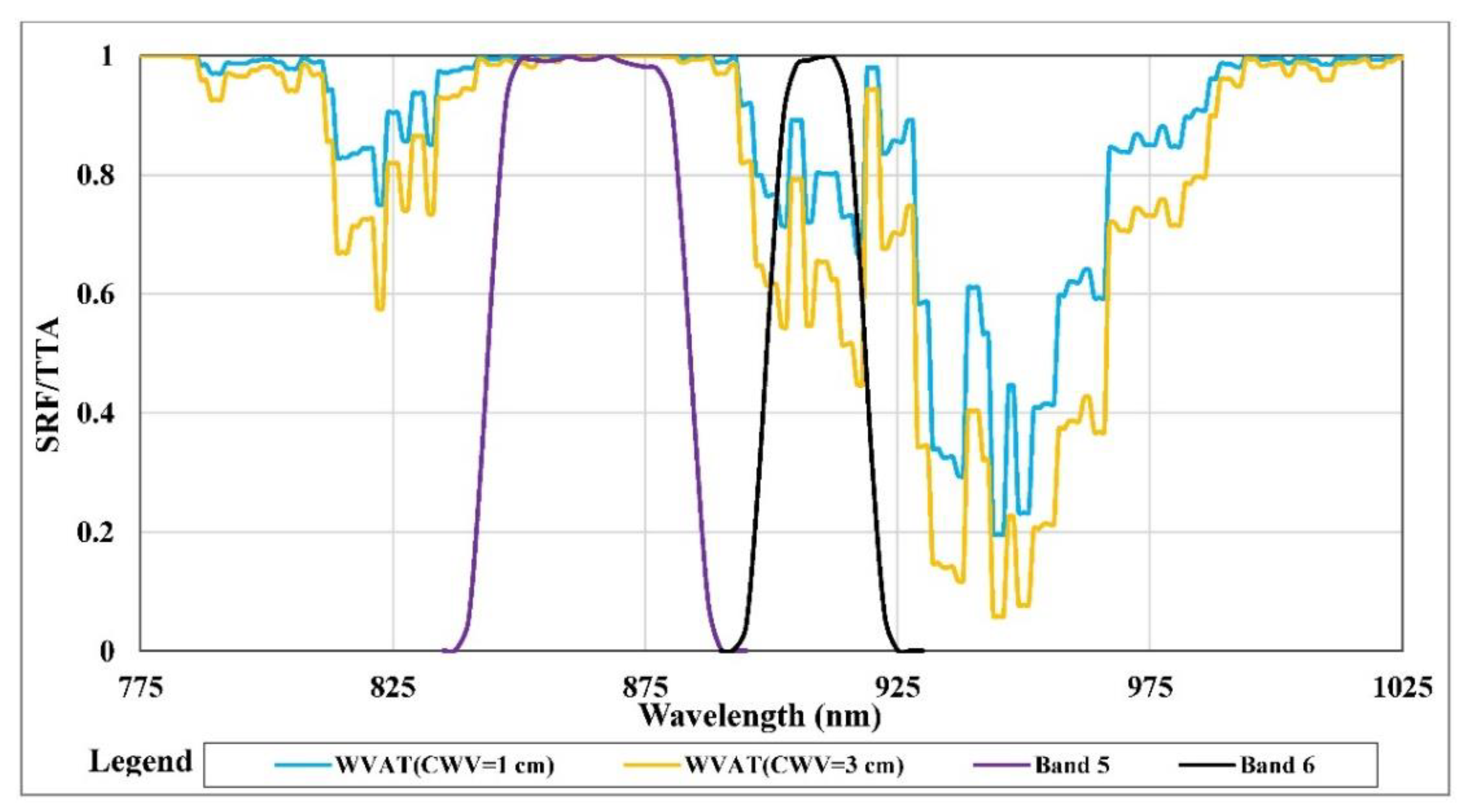
3.1. Water Vapor Retrieval
3.2. Cloud Mask
4. Results
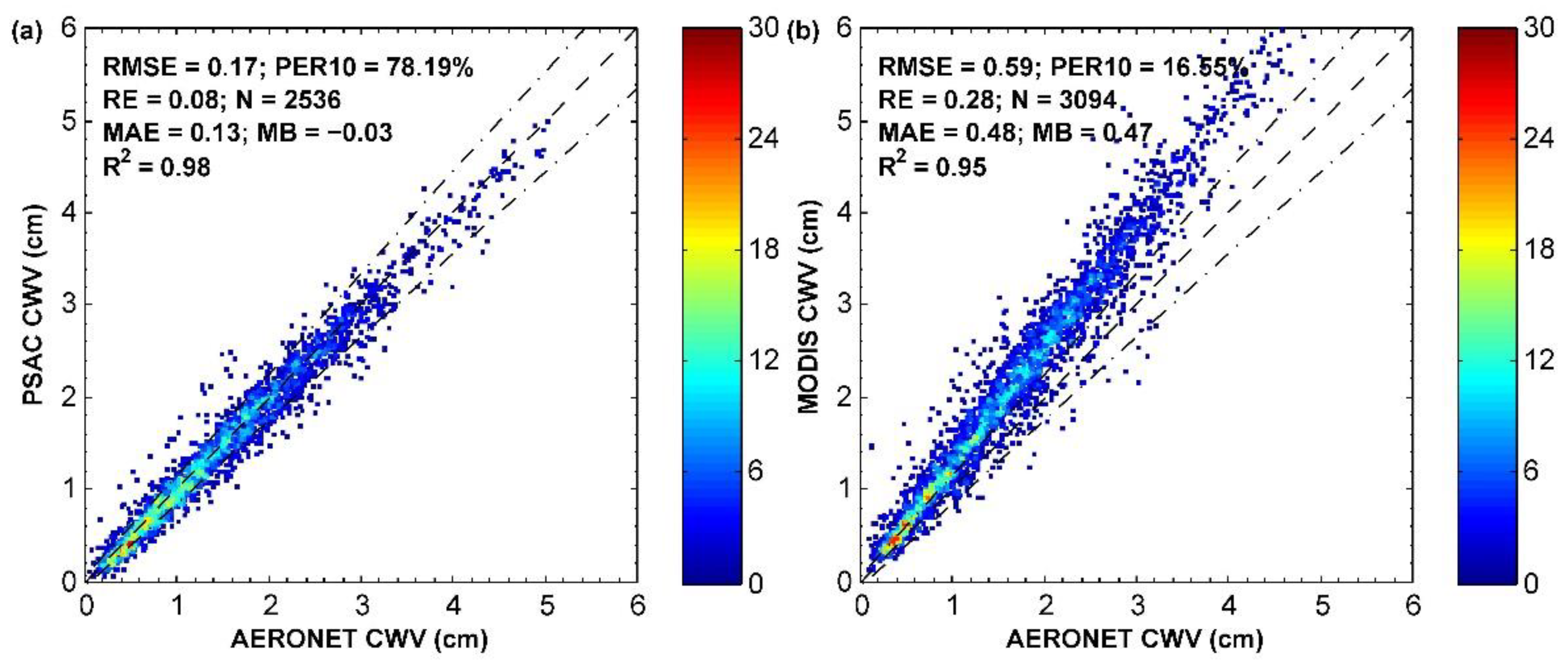
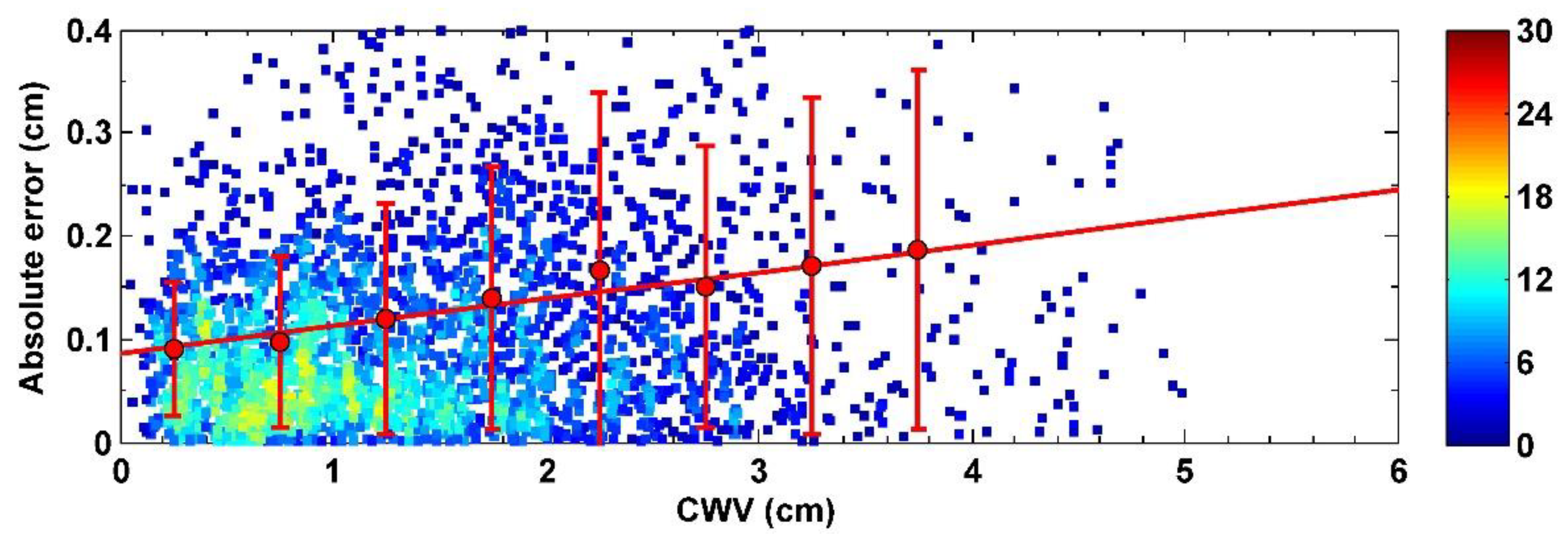
4.1. Overall Validation Results
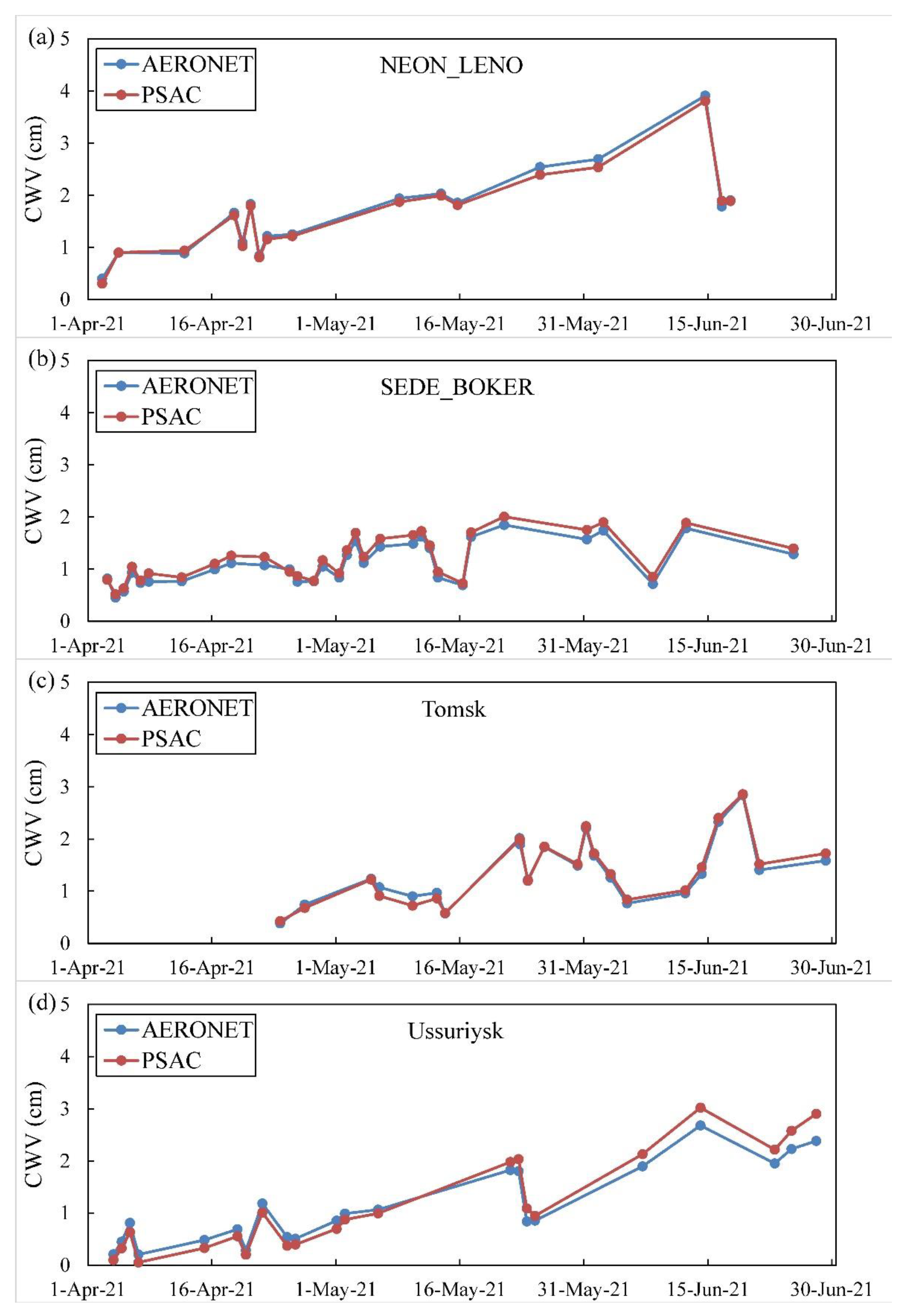
4.2. Analysis of Day-to-Day Variation in CWV
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lyngwa, R.V.; Nayak, M.A. Atmospheric river linked to extreme rainfall events over Kerala in August 2018. Atmos. Res. 2021, 253, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, H.V.; Wade, A.J.; Lavers, D.A.; Watts, G. Atmospheric river orientation determines flood occurrence. Hydrol. Processes 2020, 34, 4547–4555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Held, I.M.; Soden, B.J. Water Vapor Feedback and Global Warming. Annu. Rev. Energy Environ. 2000, 25, 441–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessler, A.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, P. Water-vapor climate feedback inferred from climate fluctuations, 2003–2008. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; He, X.W.; Xu, H.; Guang, J.; Guo, J.P.; Mei, L.L. China Collection 2.0: The aerosol optical depth dataset from the synergetic retrieval of aerosol properties algorithm. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 95, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Hou, W.; Qiu, Z.; Ge, B.; Xie, Y.; Hong, J.; Ma, Y.; Peng, Z.; Fang, W.; Zhang, D.; et al. Preliminary On-Orbit Performance Test of the First Polarimetric Synchronization Monitoring Atmospheric Corrector (SMAC) On-Board High-Spatial Resolution Satellite Gao Fen Duo Mo (GFDM). IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, R.; Schläpfer, D.; Müller, A. An automatic atmospheric correction algorithm for visible/NIR imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 2077–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Xie, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, H.; Hu, Z.; Song, C.; Lin, J.; Huang, H.; Lei, X.; Ge, B.; et al. Preliminary Study on the Multispectral Measurement Simulations of Polarized Scanning Atmospheric Corrector Image; SPIE: Beijing, China, 2020; Volume 11566. [Google Scholar]
- Vermote, E.F.; El Saleous, N.Z.; Justice, C.O. Atmospheric correction of MODIS data in the visible to middle infrared: First results. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.-C.; Montes, M.J.; Davis, C.O.; Goetz, A.F.H. Atmospheric correction algorithms for hyperspectral remote sensing data of land and ocean. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, S17–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.C.; Kaufman, Y.J. Water vapor retrievals using moderate resolution Imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) near-infrared channels. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N. AVHRR split window temperature differences and total precipitable water over land surfaces. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1994, 15, 567–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.L.; Liu, Y.X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.G.; He, X.F.; Xu, W.X.; Ge, M.R.; Schuh, H. Validating HY-2A CMR precipitable water vapor using ground-based and shipborne GNSS observations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 4963–4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Souri, A.H.; Gonzalez Abad, G.; Liu, X.; Chance, K. Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) Total Column Water Vapor version 4 validation and applications. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 5183–5199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heise, S.; Wickert, J.; Beyerle, G.; Schmidt, T.; Reigber, C. Global monitoring of tropospheric water vapor with GPS radio occultation aboard CHAMP. Adv. Space Res. 2006, 37, 2222–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Lu, D.R.; Xue, Z.G. A Non-Linear Inverse Method for Retrieval of Water Vapour from Radio Occultation Measurements. Chinese J. Geophys. 2005, 48, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koulali, A.; Ouazar, D.; Bock, O.; Fadil, A. Study of seasonal-scale atmospheric water cycle with ground-based GPS receivers, radiosondes and NWP models over Morocco. Atmos. Res. 2012, 104, 273–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campmany, E.; Bech, J.; Rodríguez-Marcos, J.; Sola, Y.; Lorente, J. A comparison of total precipitable water measurements from radiosonde and sunphotometers. Atmos. Res. 2010, 97, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.L.; Valks, P.; Slijkhuis, S.; Köhler, C.; Loyola, D. Total column water vapor retrieval for Global Ozone Monitoring Experience-2 (GOME-2) visible blue observations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 4169–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, B.; Qin, Z.H.; Du, W.H.; Fan, J.L.; Zhao, C.L.; Hang, Q.Y.; Zhao, S.H.; Li, S.F. An Algorithm to Retrieve Total Precipitable Water Vapor in the Atmosphere from FengYun 3D Medium Resolution Spectral Imager 2 (FY-3D MERSI-2) Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradizadeh, M.; Momeni, M.; Saradjian, M.R. Estimation and validation of atmospheric water vapor content using a MODIS NIR band ratio technique based on AIRS water vapor products. Arab. J. Geosci. 2014, 7, 1891–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Pang, J. A comparison between atmospheric water vapour content retrieval methods using MSG2-SEVIRI thermal-IR data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 5075–5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.L.; Ji, D.B.; Shi, J.C.; Wang, Y.Q.; Lei, T.J.; Zhang, P.; Letu, H. The Retrieval of Total Precipitable Water over Global Land Based on FY-3D/MWRI Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Tanre, D.; Buis, J.P.; Setzer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Nakajima, T.; et al. AERONET—A federated instrument network and data archive for aerosol characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ramírez, D.; Whiteman, D.N.; Smirnov, A.; Lyamani, H.; Holben, B.N.; Pinker, R.; Andrade, M.; Alados-Arboledas, L. Evaluation of AERONET precipitable water vapor versus microwave radiometry, GPS, and radiosondes at ARM sites. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 9596–9613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrov, M.D.; Schmid, B.; Turner, D.D.; Cairns, B.; Oinas, V.; Lacis, A.A.; Gutman, S.I.; Westwater, E.R.; Smirnov, A.; Eilers, J. Columnar water vapor retrievals from multifilter rotating shadowband radiometer data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, V.S.; Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y.J.; Giles, D.M.; Smirnov, A.; Slutsker, I.; Korkin, S. Global validation of columnar water vapor derived from EOS MODIS-MAIAC algorithm against the ground-based AERONET observations. Atmos. Res. 2019, 225, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, D.M.; Sinyuk, A.; Sorokin, M.G.; Schafer, J.S.; Smirnov, A.; Slutsker, I.; Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Lewis, J.R.; Campbell, J.R.; et al. Advancements in the Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) Version 3 database—Automated near-real-time quality control algorithm with improved cloud screening for Sun photometer aerosol optical depth (AOD) measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 169–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, R.S.; Kaufman, Y.J. The Relative Importance of Aerosol Scattering and Absorption in Remote-Sensing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1985, 23, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.E.; Travis, L.D. Light scattering in planetary atmospheres. Space Sci. Rev. 1974, 16, 527–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouffies, S.; Breon, F.M.; Tanre, D.; Dubuisson, P. Atmospheric water vapor estimate by a differential absorption technique with the polarisation and directionality of the Earth reflectances (POLDER) instrument. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 3831–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennartz, R.; Fischer, J. Retrieval of columnar water vapour over land from backscattered solar radiation using the Medium Resolution Imaging Spectrometer. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 78, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.K.; Wang, Y.; Tao, J.H.; Wang, Z.F.; Fan, M.; de Leeuw, G.; Chen, L.F. Preliminary Investigation of a New AHI Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) Retrieval Algorithm and Evaluation with Multiple Source AOD Measurements in China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, B.Y.; Li, Z.Q.; Liu, L.; Yang, L.K.; Chen, X.F.; Hou, W.Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.H.; Li, L.; Qie, L.L. A Dark Target Method for Himawari-8/AHI Aerosol Retrieval: Application and Validation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermote, E.F.; Tanre, D.; Deuze, J.L.; Herman, M.; Morcrette, J.J. Second Simulation of the Satellite Signal in the Solar Spectrum, 6S: An overview. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, J.V.; Tanré, D.; Remer, L.; Kaufman, Y.; Mattoo, S.; Levy, R. MODIS Cloud screening for remote sensing of aerosols over oceans using spatial variability. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, MOD4-1–MOD4-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.L.; Xin, J.Y.; Yang, L.K.; Cong, Z.Y.; Liu, R.X.; Ma, Y.N.; Wang, Y.S.; Lu, X.F.; Zhao, L. The first validation of the precipitable water vapor of multisensor satellites over the typical regions in China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 206, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, K.; Che, H.; Chen, Q.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, T.; Liao, T.; Wang, H.; et al. Evaluation of radiosonde, MODIS-NIR-Clear, and AERONET precipitable water vapor using IGS ground-based GPS measurements over China. Atmos. Res. 2017, 197, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Li, Z.; Hou, W.; Guang, J.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Yang, D. Validation of FY-3D MERSI-2 Precipitable Water Vapor (PWV) Datasets Using Ground-Based PWV Data from AERONET. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bright, J.M.; Gueymard, C.A.; Killinger, S.; Lingfors, D.; Sun, X.X.; Wang, P.; Engerer, N.A. Climatic and Global Validation of Daily MODIS Precipitable Water Data at AERONET Sites for Clear-Sky Irradiance Modelling; International Solar Energy Society: Freiburg, Germany, 2018; pp. 1490–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berk, A.; Conforti, P.; Kennett, R.; Perkins, T.; Hawes, F.; Bosch, J. MODTRAN6: A major upgrade of the MODTRAN radiative transfer code. In Proceedings of the 6th Workshop on Hyperspectral Image and Signal Processing: Evolution in Remote Sensing (WHISPERS), Lausanne, Switzerland, 24–27 June 2014; Volume 9088, p. 90880H. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Hu, X.Q.; Xu, N.; Chen, L. Water Vapor Retrievals from Near-infrared Channels of the Advanced Medium Resolution Spectral Imager Instrument onboard the Fengyun-3D Satellite. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 38, 1351–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| No. | Center Wavelength | Spectral Range | Spectral Width | Spatial Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Band 1 | 0.410 μm | 0.400–0.420 μm | 20 nm | 6 km |
| Band 2 | 0.443 μm | 0.433–0.453 μm | 20 nm | 6 km |
| Band 3 | 0.555 μm | 0.545–0.565 μm | 20 nm | 6 km |
| Band 4 | 0.670 μm | 0.660–0.680 μm | 20 nm | 6 km |
| Band 5 | 0.865 μm | 0.845–0.885 μm | 40 nm | 6 km |
| Band 6 | 0.910 μm | 0.900–0.920 μm | 20 nm | 6 km |
| Band 7 | 1.380 μm | 1.360–1.400 μm | 40 nm | 6 km |
| Band 8 | 1.610 μm | 1.580–1.640 μm | 60 nm | 6 km |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, Y.; Hou, W.; Li, Z.; Zhu, S.; Liu, Z.; Hong, J.; Ma, Y.; Fan, C.; Guang, J.; Yang, B.; et al. Columnar Water Vapor Retrieval by Using Data from the Polarized Scanning Atmospheric Corrector (PSAC) Onboard HJ-2 A/B Satellites. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1376. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14061376
Xie Y, Hou W, Li Z, Zhu S, Liu Z, Hong J, Ma Y, Fan C, Guang J, Yang B, et al. Columnar Water Vapor Retrieval by Using Data from the Polarized Scanning Atmospheric Corrector (PSAC) Onboard HJ-2 A/B Satellites. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(6):1376. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14061376
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Yanqing, Weizhen Hou, Zhengqiang Li, Sifeng Zhu, Zhenhai Liu, Jin Hong, Yan Ma, Cheng Fan, Jie Guang, Benyong Yang, and et al. 2022. "Columnar Water Vapor Retrieval by Using Data from the Polarized Scanning Atmospheric Corrector (PSAC) Onboard HJ-2 A/B Satellites" Remote Sensing 14, no. 6: 1376. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14061376
APA StyleXie, Y., Hou, W., Li, Z., Zhu, S., Liu, Z., Hong, J., Ma, Y., Fan, C., Guang, J., Yang, B., Lei, X., Huang, H., Sun, X., Liu, X., Zhang, Y., Song, M., Zou, P., & Qiao, Y. (2022). Columnar Water Vapor Retrieval by Using Data from the Polarized Scanning Atmospheric Corrector (PSAC) Onboard HJ-2 A/B Satellites. Remote Sensing, 14(6), 1376. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14061376








