Ha Long—Cam Pha Cities Evolution Analysis Utilizing Remote Sensing Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
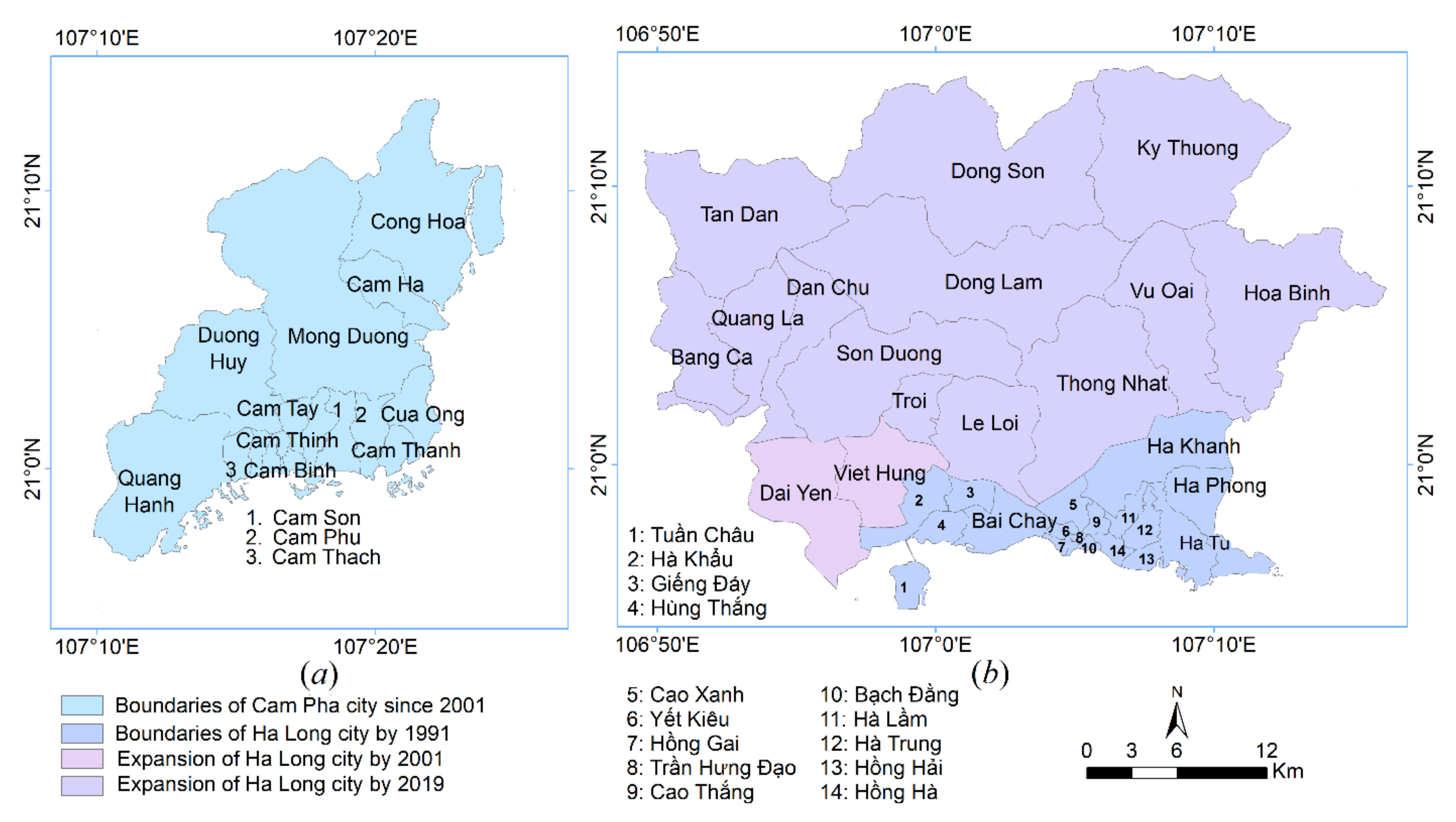
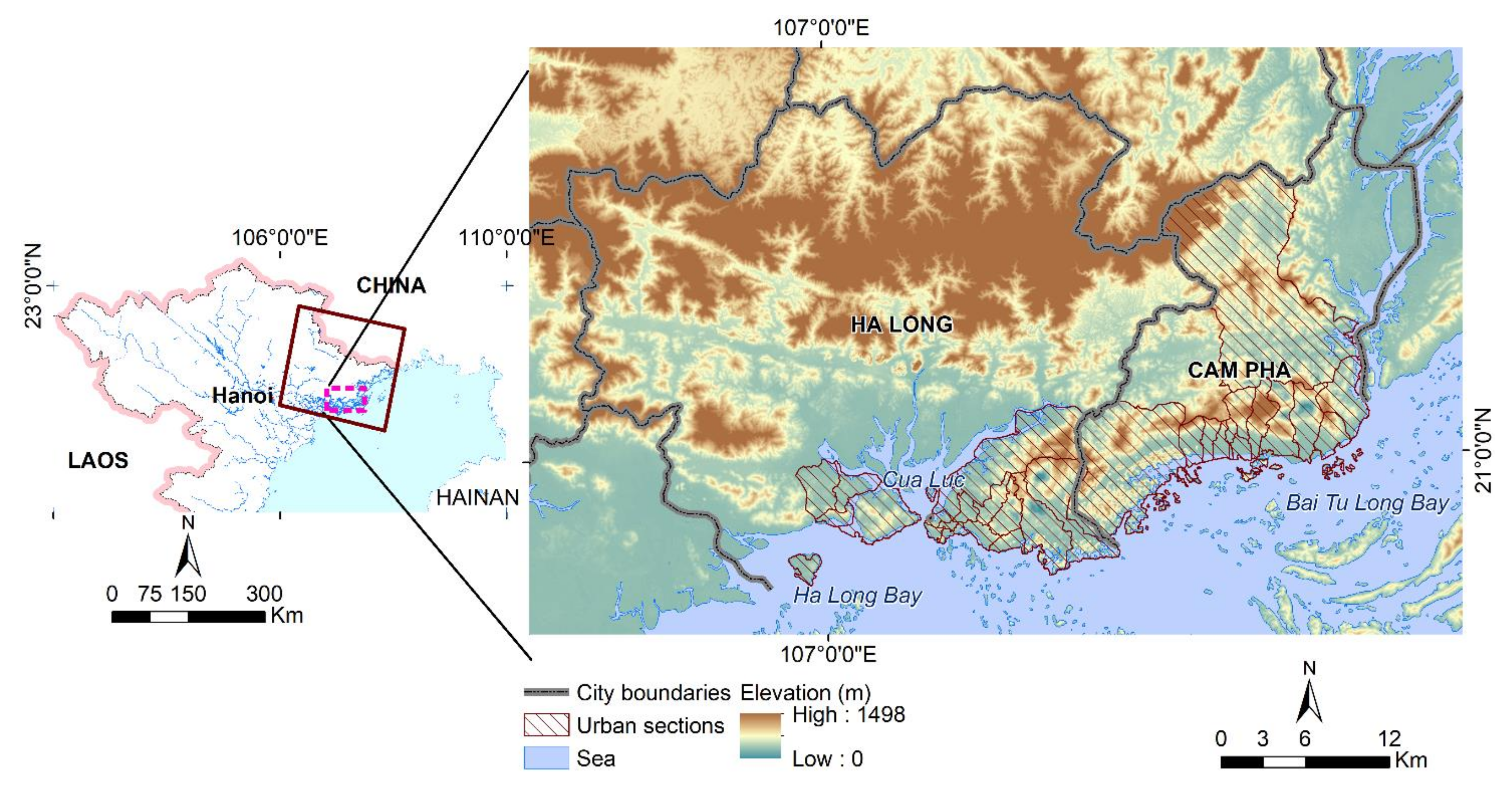
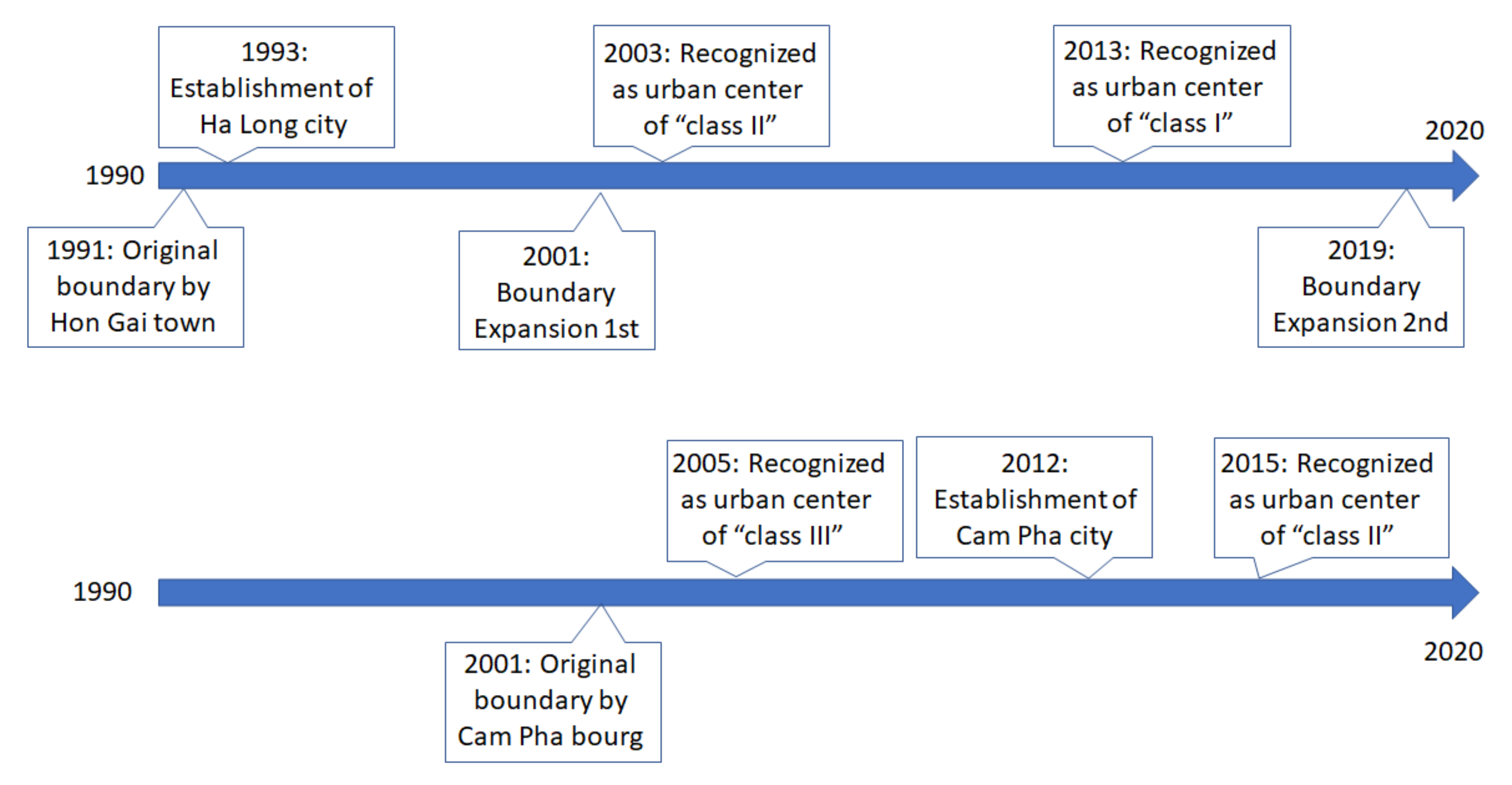
2. Study Area
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data
3.1.1. Landsat Images
3.1.2. High Spatial Resolution Imagery from Google Earth
3.1.3. Digital Elevation Model
3.1.4. Field Campaign
3.2. Method
3.2.1. Pre-Processing
- Co-registration with respect to each image ensures that the images become spatially aligned thus that all features in one image overlap as well as possible with its footprint in other images. Accurate image co-registration is a prerequisite to the accurate extraction of features, and it may subsequently provide correct land cover mapping results.
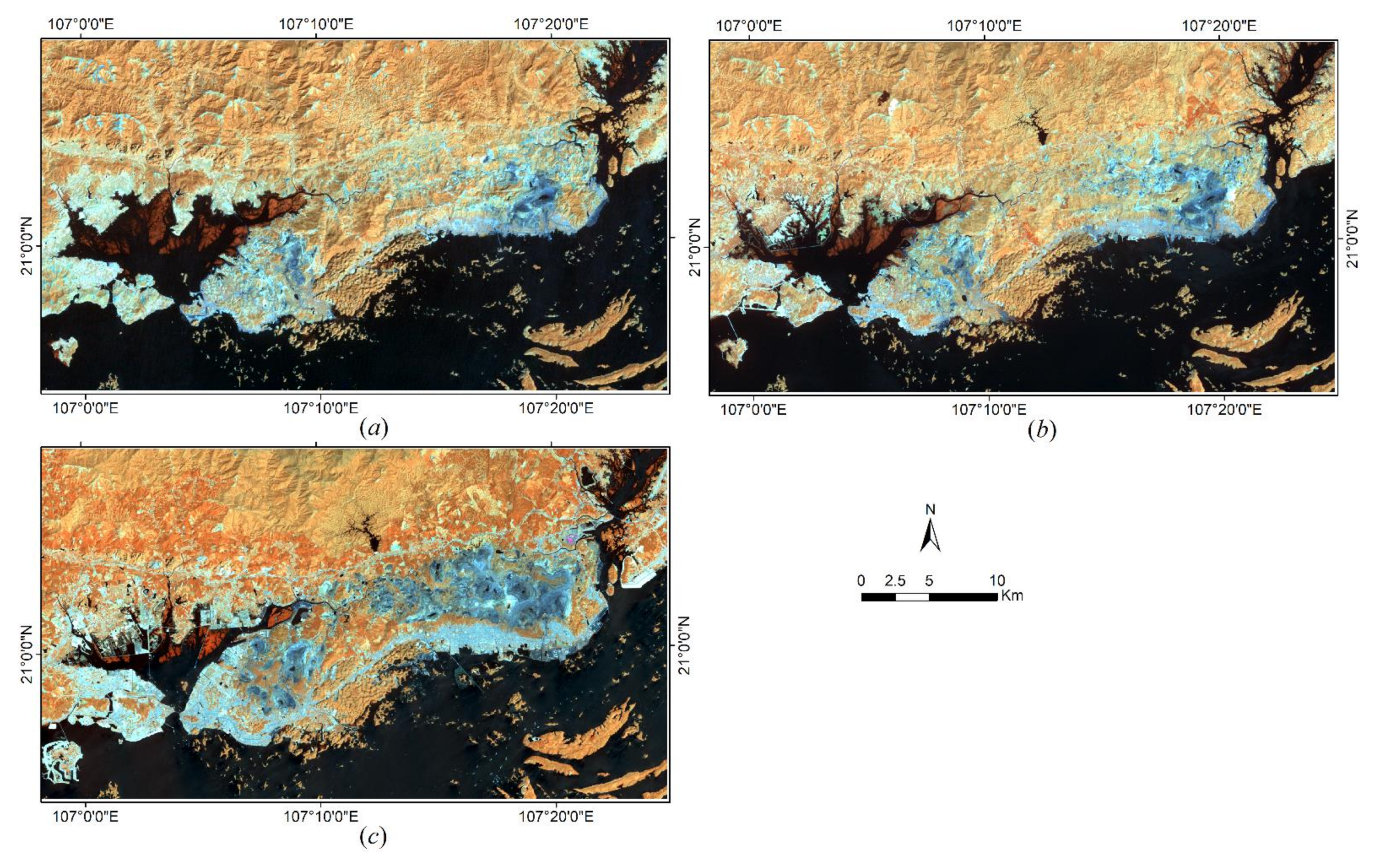
- Cropping image aims to discard the unwanted portion outer areas from Landsat’s scene for preserving the important part—the study area (Figure 1).
- Stacking layers address to combine several channels of Landsat image with the identical frame of reference, thus that multi-channels can be processed later in the image processing software.
3.2.2. Image Classification
4. Results
4.1. Validation
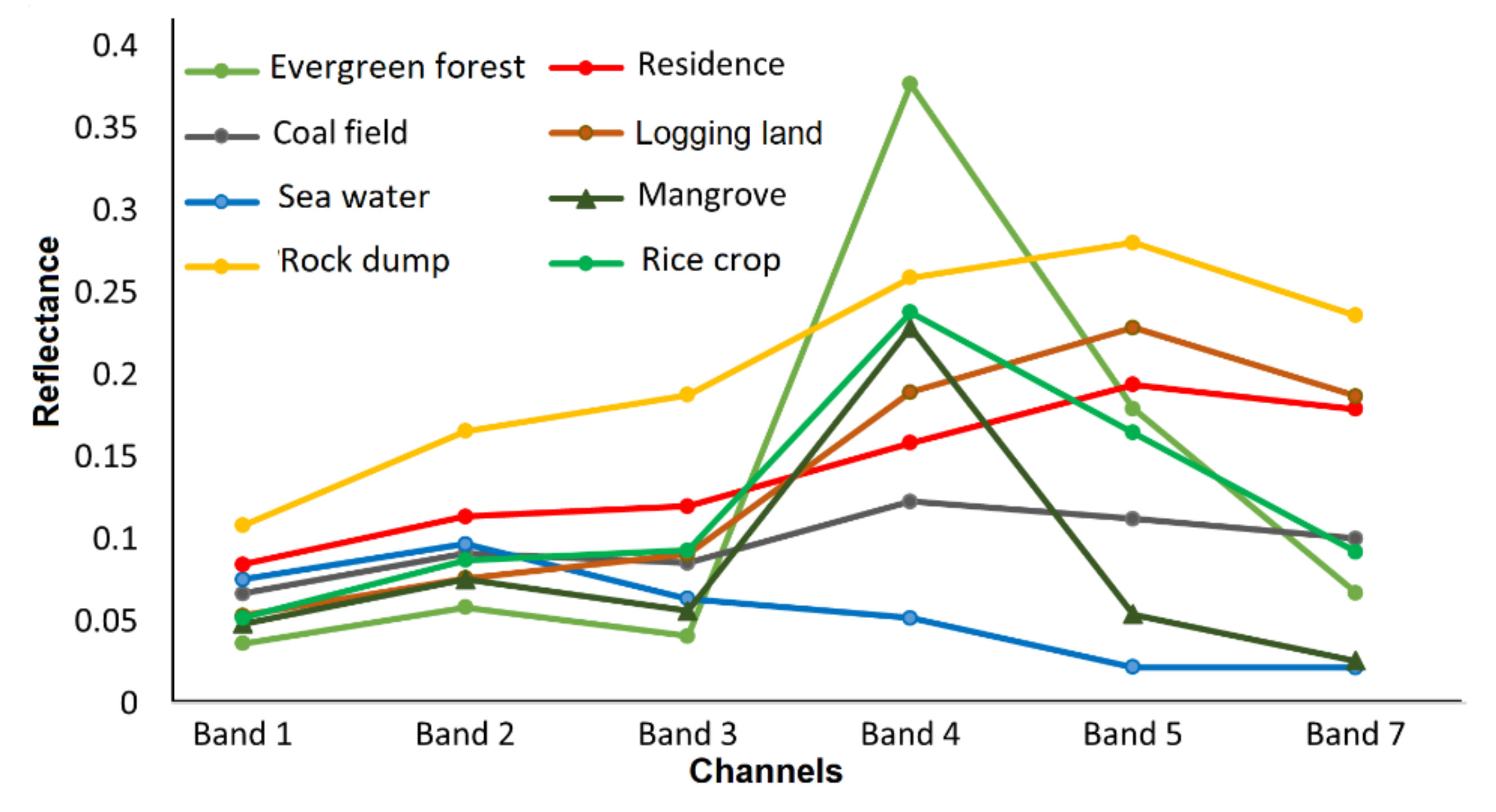
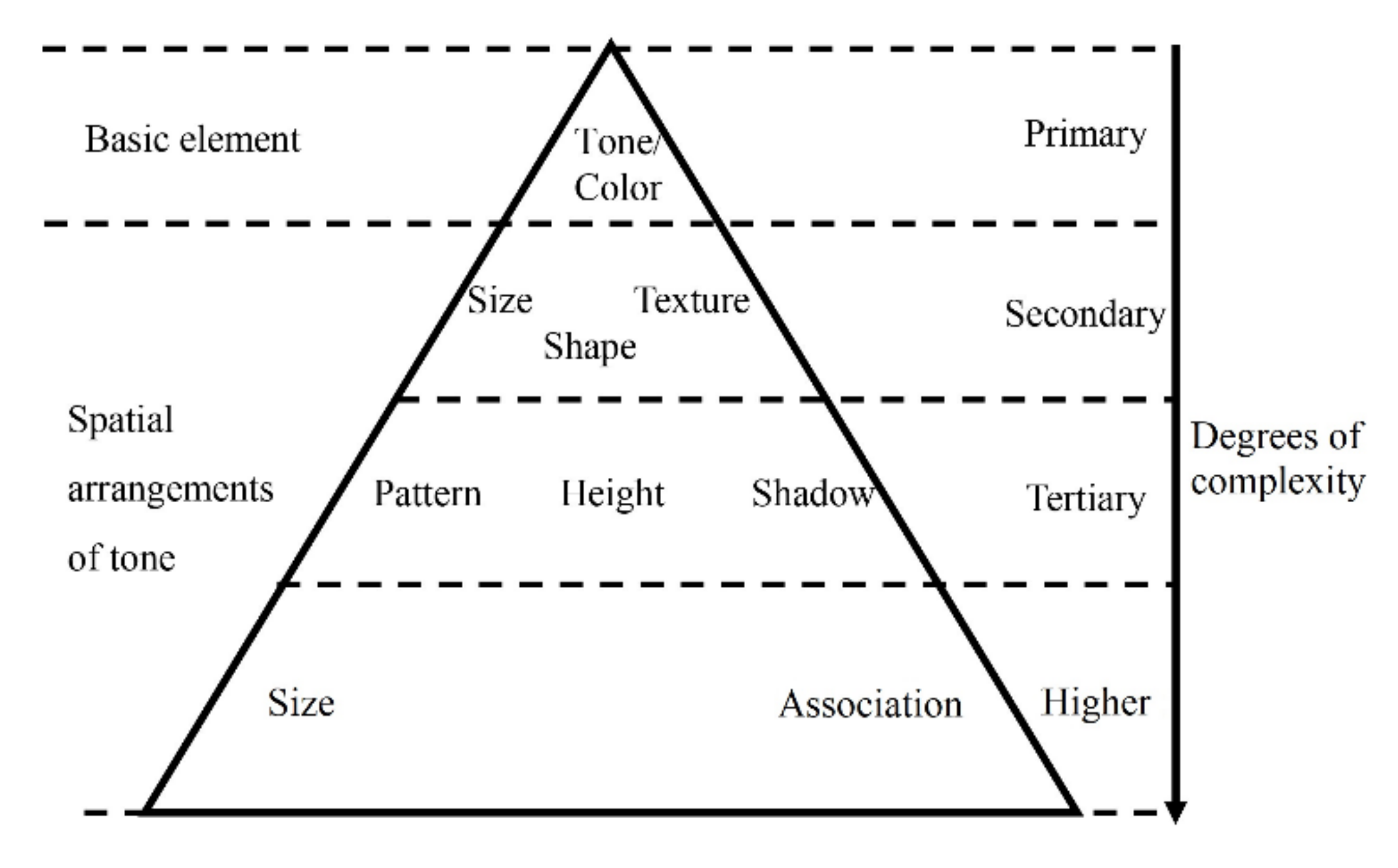
4.1.1. Keys for Visual Interpretation
4.1.2. Accuracy Assessment
4.1.3. Comparison with High Spatial Resolution Image
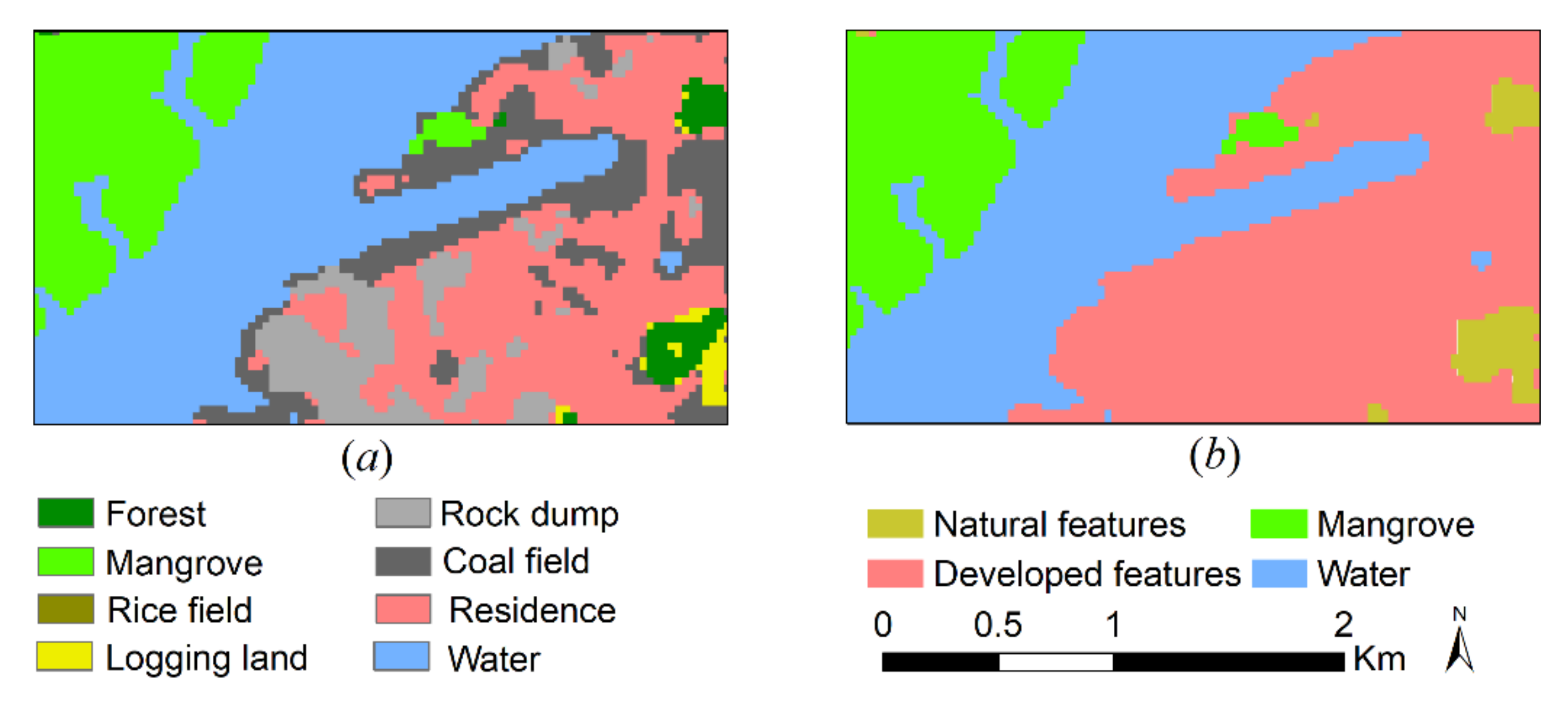
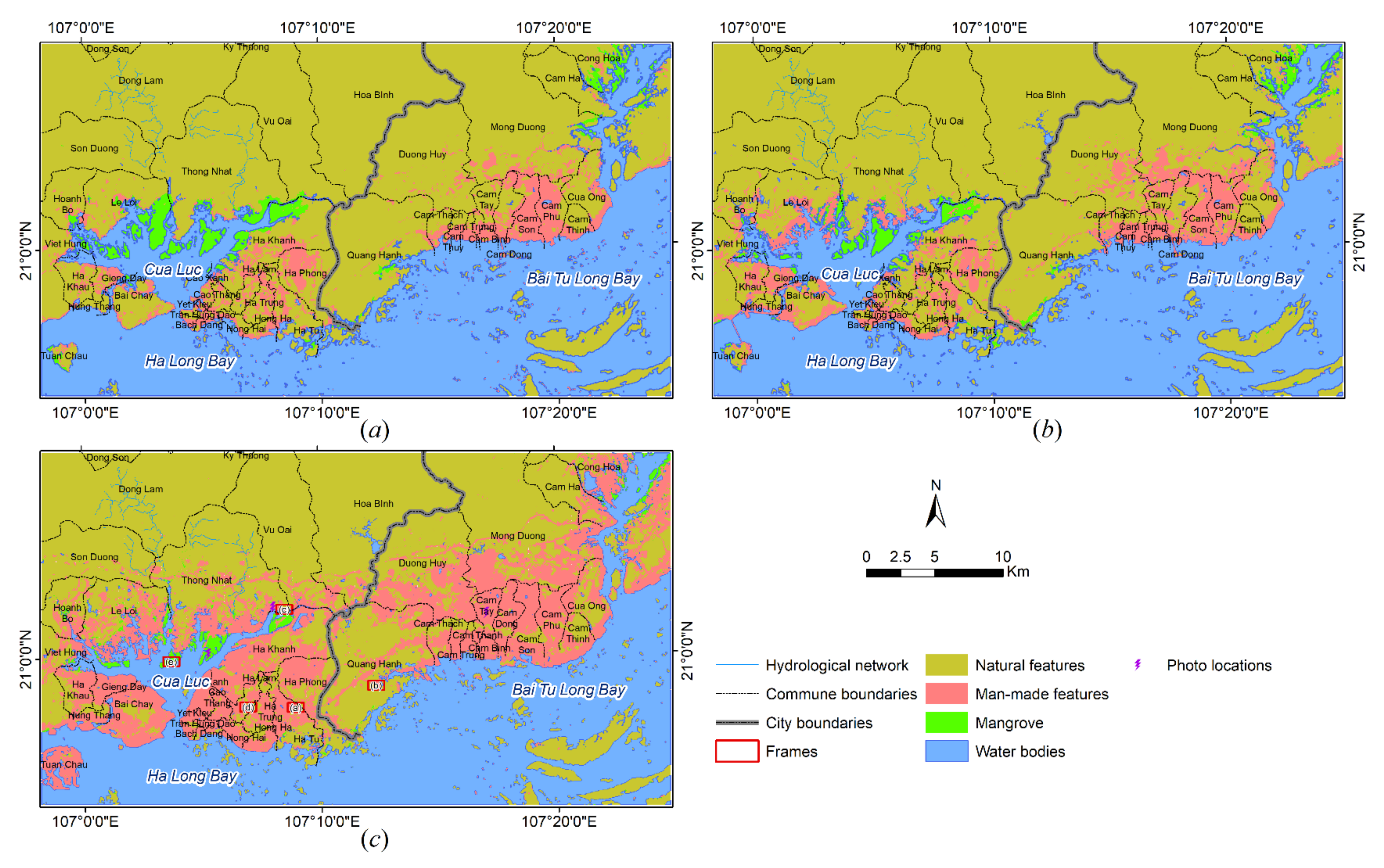
4.2. Land Cover Maps
4.2.1. Filtering Noise
4.2.2. Combining Classes
5. Discussion
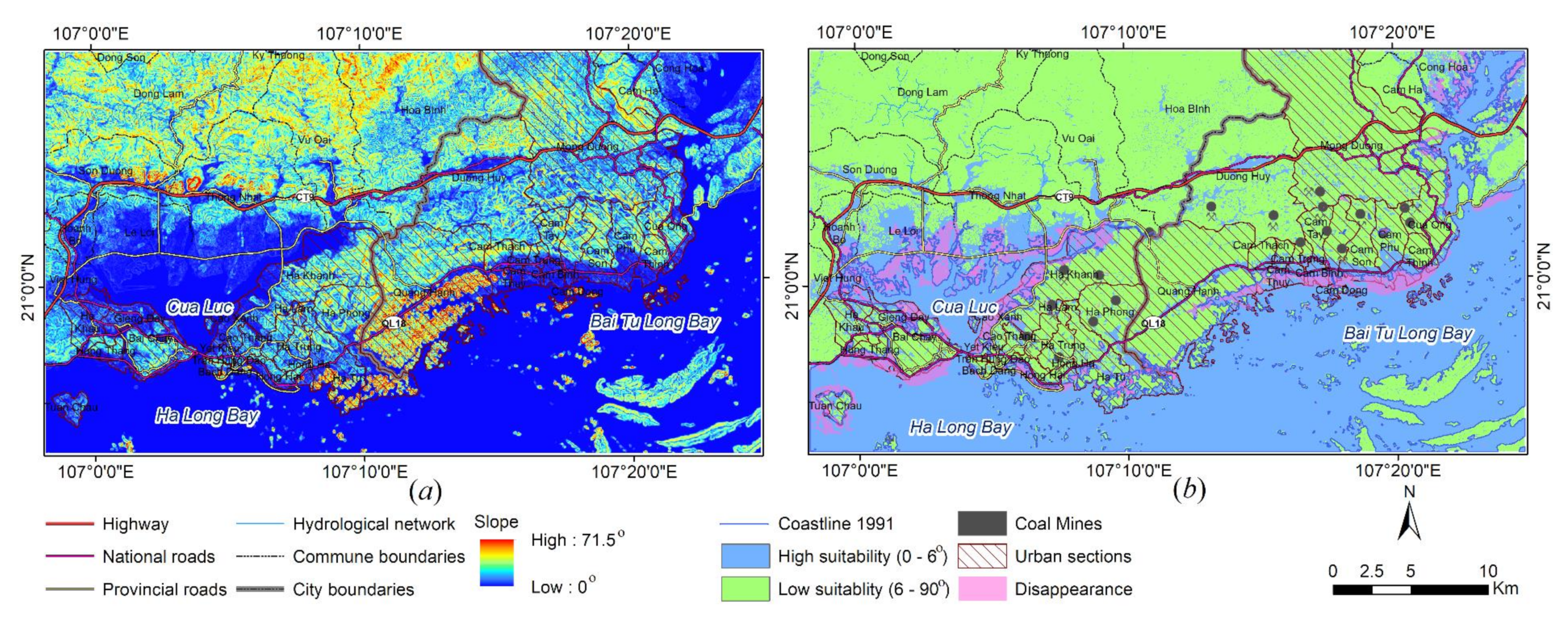
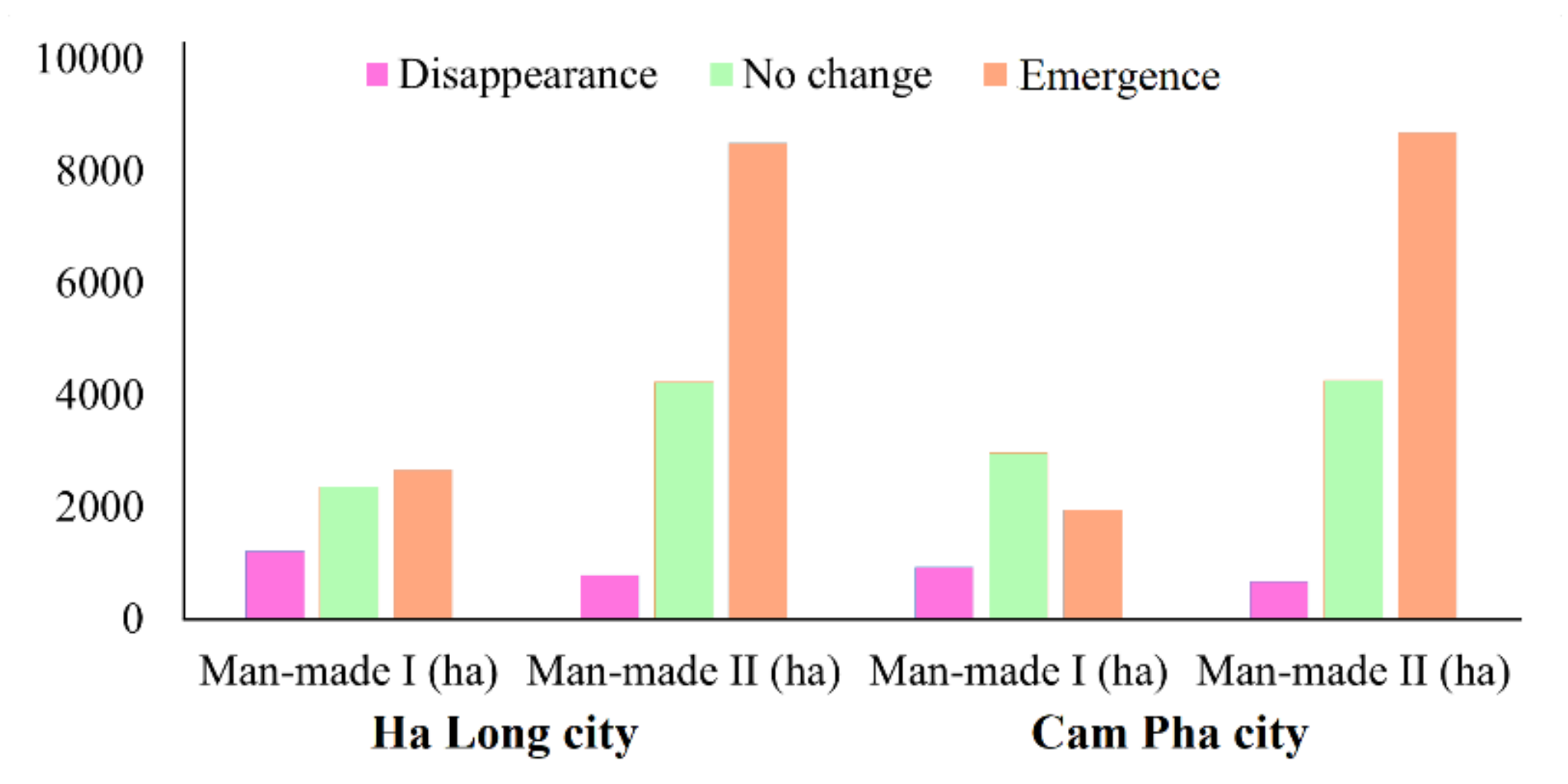
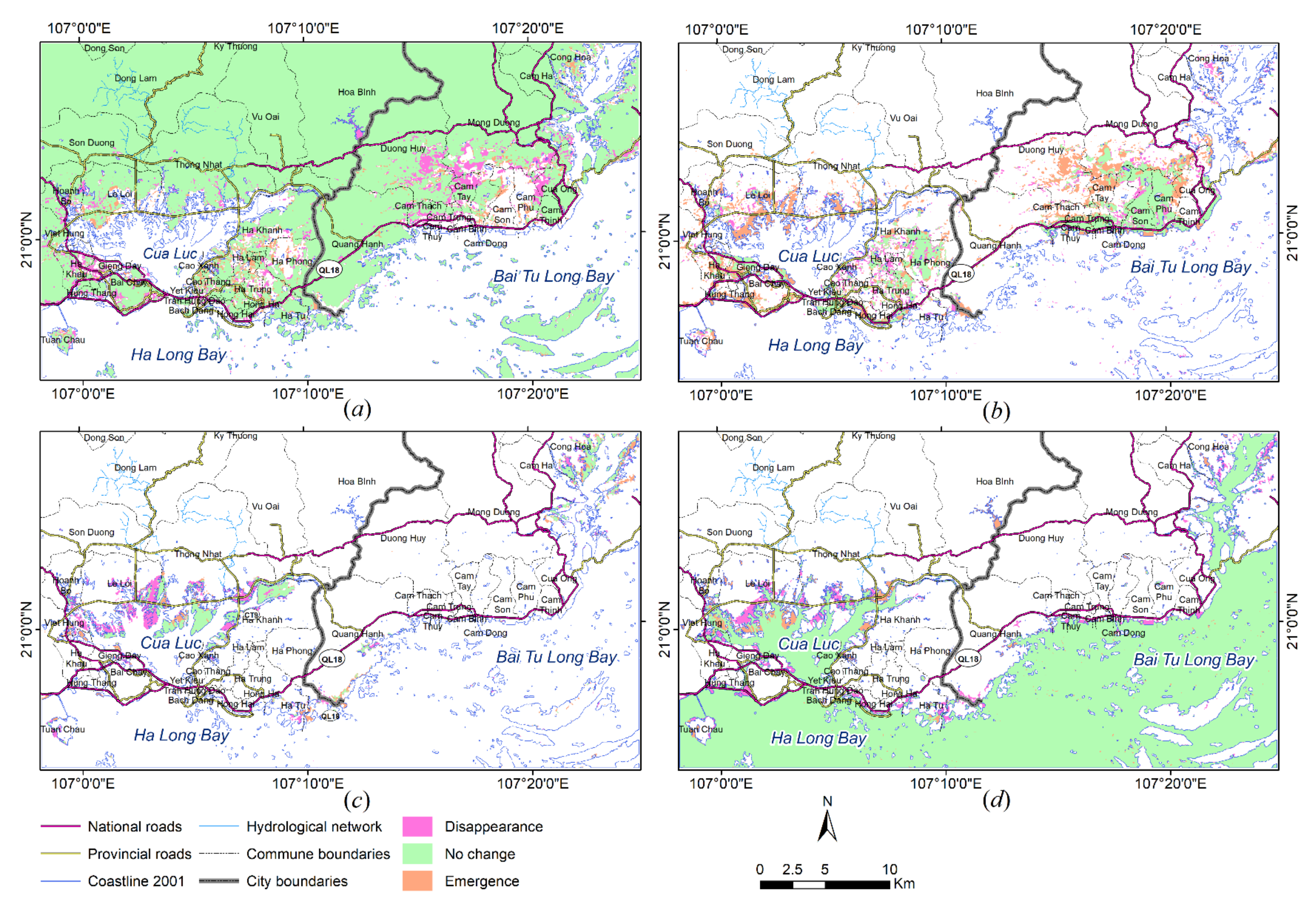
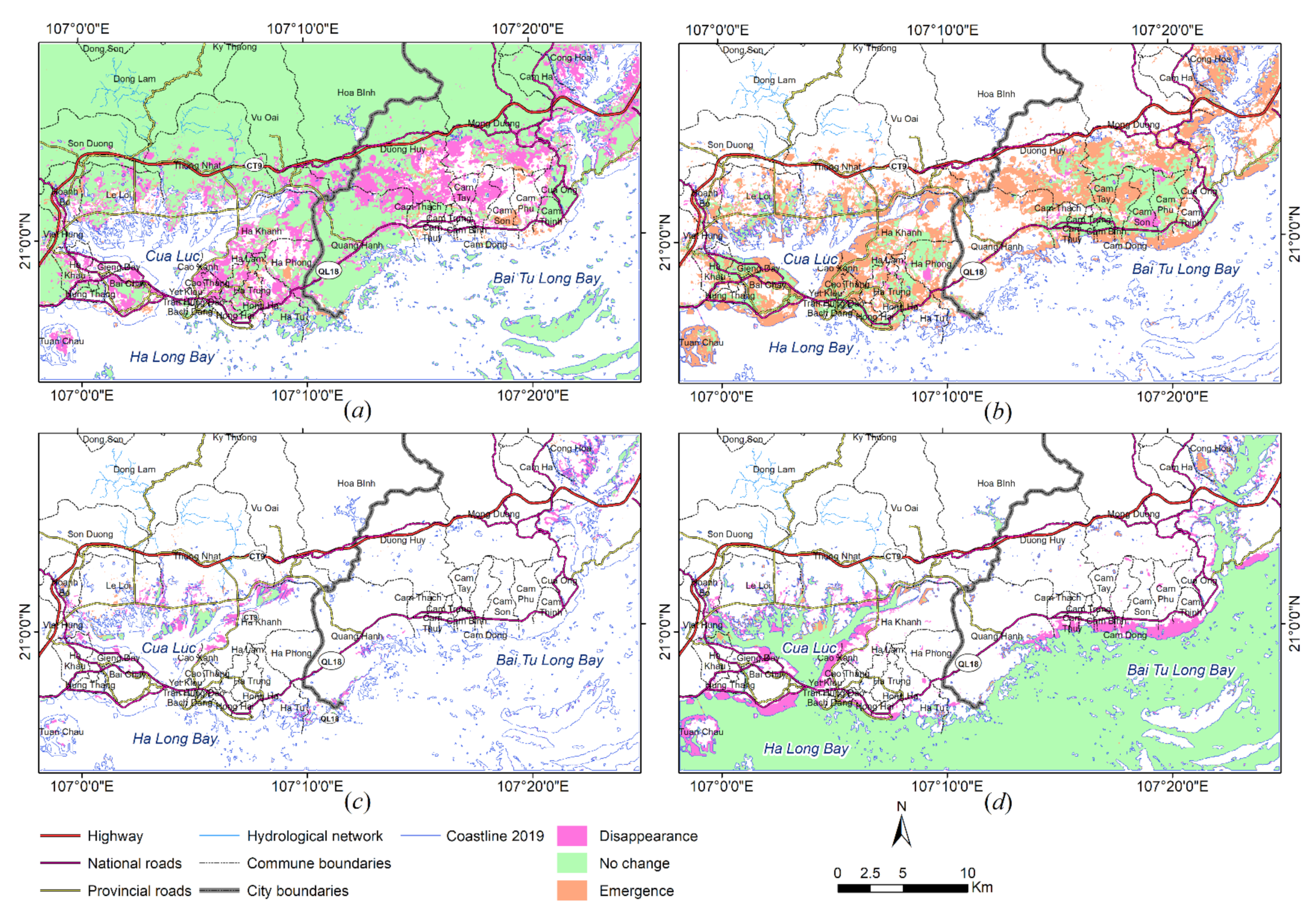
5.1. Change Detection
5.2. Analysis of Urban Evolution
5.3. Analysis of the Urban Development
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BOA | Bottom Of Atmosphere reflectance |
| GDP | Gross Domestic Product |
| NAFOSTED | Vietnam National Foundation for Science and Technology Development |
| NASA | National Aeronautics and Space Administration |
| ROI | region of interest |
| SITS | Satellite Image Time Series |
| SRTM | Shuttle Radar Topography Mission |
| SVMs | Support Vector Machines |
| UNESCO | United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization |
| USGS | United States Geological Survey |
References
- UNDP. Urban Population. Available online: https://population.un.org/wup/ (accessed on 19 August 2021).
- Duc, T. Vietnam Has 826 Urban Centres with Contribution of 70% GDP. Vietnam Government Electronic Paper, 26 December 2020. Available online: https://baochinhphu.vn/ca-nuoc-co-862-do-thi-dong-gop-70-gdp-102284985.htm (accessed on 21 January 2022).
- Hoang, C.L. Challenges in the Urbanization of Vietnam. Economy and Forecast Review, 18 June 2013. Available online: https://kinhtevadubao.vn/nhung-bat-cap-trong-qua-trinh-do-thi-hoa-o-viet-nam-9757.html (accessed on 21 January 2022).
- Tran, D.T. The Geological History of Ha Long Bay; The World Publishing House: Hanoi, Vietnam, 1998; p. 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GSO. Completed Results of the 2019 Vietnam Population and Housing Cencus; Statistical Publishing House: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hens, L.; Nierynck, E.; Tran, V.Y.; Nguyen, H.Q.; Le, T.T.H.; Le, A.D. Land Cover Changes in the Extended Ha Long City Area, North-Eastern Vietnam During the Period 1988–1998. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2000, 2, 235–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafin, M.G.; Tran, T.S.; Tran, M.H. Comprehensive impact assessment development of the Coal field Campha in Vietnam to the coastal territory. In Proceedings of the Construction and Architecture: Theory and Practice of Innovative Development, Kislovodsk, Russia, 1–5 October 2019; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, T.T.T.; Do, C.T.; Le, V.N.; Pham, T.K.; Nguyen, V.B.; Dinh, H.N. Assessment of Sea Water Quality in some Limestone Island and Archipelagos Areas, Vietnam. VNU J. Sci. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 36, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dang, V.K.; Nguyen, T.D.; Dao, N.H.; Duong, T.L.; Dinh, X.V.; Weber, C. Land subsidence induced by underground coal mining at Quang Ninh, Vietnam: Persistent scatterer interferometric synthetic aperture radar observation using Sentinel-1 data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 42, 3563–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatta, B. Causes and Consequences of Urban Growth and Sprawl. In Analysis of Urban Growth and Sprawl from Remote Sensing Data; Bhatta, B., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 17–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN-HABITAT. International Guidelines on Urban and Territorial Planning; United Nations Human Settlements Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2015; p. 40. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, F.; Sawaya, K.E.; Loeffelholz, B.C.; Bauer, M.E. Land cover classification and change analysis of the Twin Cities (Minnesota) Metropolitan Area by multitemporal Landsat remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 98, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, K.C.; Fragkias, M.; Güneralp, B.; Reilly, M.K. A Meta-Analysis of Global Urban Land Expansion. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Zhang, M. The impact of urbanisation on energy consumption: A 30-year review in China. Urban Clim. 2018, 24, 940–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, B.; Gough, W.; Mohsin, T. The impact of urbanization and the urban heat island effect on day to day temperature variation. Urban Clim. 2015, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrane, S.J. Impacts of urbanisation on hydrological and water quality dynamics, and urban water management: A review. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2016, 61, 2295–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; He, C.; Wu, J. The Relationship between Habitat Loss and Fragmentation during Urbanization: An Empirical Evaluation from 16 World Cities. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Xu, Y.; Pu, Z. Urbanization and Its Effects on Industrial Pollutant Emissions: An Empirical Study of a Chinese Case with the Spatial Panel Model. Sustainability 2016, 8, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuissl, H.; Siedentop, S. Urbanisation and Land Use Change. In Sustainable Land Management in a European Context: A Co-Design Approach; Weith, T., Barkmann, T., Gaasch, N., Rogga, S., Strauß, C., Zscheischler, J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 75–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starzomski, B. Indicators of Ecosystem Change. In Encyclopedia of Quality of Life and Well-Being Research; Michalos, A.C., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 3205–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phiri, D.; Simwanda, M.; Salekin, S.; Nyirenda, V.R.; Murayama, Y.; Ranagalage, M. Sentinel-2 Data for Land Cover/Use Mapping: A Review. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingram, K.; Knapp, E.; Robinson, J. Change Detection Technique Development for Improved Urbanized Area Delineation; Computer Sciences Corporation: Tysons Corner, VA, USA, 1981; p. 136. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez, C.; White, J.C.; Wulder, M.A. Optical remotely sensed time series data for land cover classification: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 116, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantakumar, L.N.; Neelamsetti, P. Multi-temporal land use classification using hybrid approach. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2015, 18, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Ongsomwang, S. Multitemporal Land Use and Land Cover Classification from Time-Series Landsat Datasets Using Harmonic Analysis with a Minimum Spectral Distance Algorithm. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goward, S.; Arvidson, T.; Williams, D.; Faundeen, J.; Irons, J.; Franks, S. Historical record of Landsat global coverage: Mission operations, NSLRSDA, and international cooperator stations. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2006, 72, 1155–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloiber, S.M.; Brezonik, P.L.; Bauer, M.E. Application of Landsat imagery to regional-scale assessments of lake clarity. Water Res. 2002, 36, 4330–4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulder, M.A.; Loveland, T.R.; Roy, D.P.; Crawford, C.J.; Masek, J.G.; Woodcock, C.E.; Allen, R.G.; Anderson, M.C.; Belward, A.S.; Cohen, W.B.; et al. Current status of Landsat program, science, and applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 225, 127–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markham, B.L.; Arvidson, T.; Barsi, J.A.; Choate, M.; Kaita, E.; Levy, R.; Lubke, M.; Masek, J.G. Landsat Program. In Comprehensive Remote Sensing; Liang, S., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2018; pp. 27–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulder, M.A.; Masek, J.G.; Cohen, W.B.; Loveland, T.R.; Woodcock, C.E. Opening the archive: How free data has enabled the science and monitoring promise of Landsat. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 122, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemati, M.A.; Hasanlou, M.; Mahdianpari, M.; Mohammadimanesh, F. A Systematic Review of Landsat Data for Change Detection Applications: 50 Years of Monitoring the Earth. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruzzone, L.; Bovolo, F. A Novel Framework for the Design of Change-Detection Systems for Very-High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images. Proc. IEEE 2013, 101, 609–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A. Review Article Digital change detection techniques using remotely-sensed data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1989, 10, 989–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radke, R.J.; Andra, S.; Al-Kofahi, O.; Roysam, B. Image change detection algorithms: A systematic survey. IEEE Trans. Image Processing 2005, 14, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-doski, J.; Mansor, S.B.; Shafri, H.Z.M. Change Detection Process and Techniques. Civ. Environ. Res. 2013, 3, 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Hay, G.J.; Carvalho, L.M.T.; Wulder, M.A. Object-based change detection. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 4434–4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Chen, D.; Cheng, A.; Wei, H.; Stanley, D. Change detection from remotely sensed images: From pixel-based to object-based approaches. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 80, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Mausel, P.; Brondízio, E.; Moran, E. Change detection techniques. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 2365–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panuju, D.R.; Paull, D.J.; Griffin, A.L. Change Detection Techniques Based on Multispectral Images for Investigating Land Cover Dynamics. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewkesbury, A.P.; Comber, A.J.; Tate, N.J.; Lamb, A.; Fisher, P.F. A critical synthesis of remotely sensed optical image change detection techniques. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 160, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z. Change detection using landsat time series: A review of frequencies, preprocessing, algorithms, and applications. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 130, 370–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, H.S.; Goldin, S.E.; Rezgui, A.; El-Islam, B.N.; Ait-Aoudia, S. What is a remote sensing change detection technique? Towards a conceptual framework. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 1788–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, H.S.; Ait-Aoudia, S.; Rezgui, A.; Goldin, S.E. Change detection in urban areas from remote sensing data: A multidimensional classification scheme. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 6635–6679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, C.M.; Oliveira, S.; Oliveira, S.C.; Rocha, J. Land Use/Land Cover Change Detection and Urban Sprawl Analysis. In Spatial Modeling in GIS and R for Earth and Environmental Sciences; Pourghasemi, H.R., Gokceoglu, C., Eds.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 621–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppin, P.; Jonckheere, I.; Nackaerts, K.; Muys, B.; Lambin, E. Digital change detection methods in ecosystem monitoring: A review. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 1565–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Réjichi, S.; Chaabane, F. Satellite image time series classification and analysis using an adapted graph labeling. In Proceedings of the 2015 8th International Workshop on the Analysis of Multitemporal Remote Sensing Images (Multi-Temp), Annecy, France, 22–24 July 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Simoes, R.; Camara, G.; Queiroz, G.; Souza, F.; Andrade, P.R.; Santos, L.; Carvalho, A.; Ferreira, K. Satellite Image Time Series Analysis for Big Earth Observation Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatsavai, R.; Graesser, J. Probabilistic Change Detection Framework for Analyzing Settlement Dynamics Using Very High-resolution Satellite Imagery. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2012, 9, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thonfeld, F.; Hecheltjen, A.; Menz, G. Bi-temporal Change Detection, Change Trajectories and Time Series Analysis for Forest Monitoring. Photogramm. Fernerkund. Geoinf. 2015, 2015, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Batistella, M.; Moran, E. Multitemporal Spectral Mixture Analysis for Amazonian Land-Cover Change Detection. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 30, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khelifi, L.; Mignotte, M. Deep Learning for Change Detection in Remote Sensing Images: Comprehensive Review and Meta-Analysis. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 126385–126400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brömme, K.; Stolpe, H.; Jolk, C.; Greassidis, S.; Borgmann, A.; Zindler, B.; Mien, T. Development of Methods for Post-Mining Land Use Planning for Coal Mines in Urban Areas in Quang Ninh, Vietnam. In Proceedings of the Beijing International Symposium Land Reclamation and Ecological Restoration, LRER, Beijing, China, 16–19 October 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalilov, S.-M.; Chen, Y.; Quang, N.H.; Nguyen, M.N.; Leighton, B.; Paget, M.; Lazarow, N. Estimation of Urban Land-Use Efficiency for Sustainable Development by Integrating over 30-Year Landsat Imagery with Population Data: A Case Study of Ha Long, Vietnam. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, T.V.; Chou, T.-Y.; Fang, Y.-M.; Chen, M.; Yeh, M.; Nguyen, X.L. Evaluation Vulnerability of Climate Change Impacts to Quang Ninh Province, Vietnam. Int. J. Adv. Remote Sens. GIS 2018, 7, 2758–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, S. Hydrodynamic Study of Ha Long Bay; University of Western Australia: Perth, Australia, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Cerrano, C.; Azzini, F.; Bavestrello, G.; Calcinai, B. Marine lakes of Karst islands in Ha Long Bay (Vietnam). Chem. Ecol. 2006, 22, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuong, T. Quang Ninh tourism: Efforts to Revive after a Long Hibernation due to Covid 19. Trade Mark and Public Opinion, 29 October 2021. Available online: https://thuonghieucongluan.com.vn/du-lich-quang-ninh-no-luc-hoi-sinh-sau-ky-ngu-dong-dai-vi-covid-19-a159763.html (accessed on 21 January 2022).
- Pham, T. Quang Ninh—Coal Mining Sector: Closely Sticking The Information Gate of Quang Ninh Province, 1 January 2021. Available online: https://www.quangninh.gov.vn/chuyen-de/dichcorona/Trang/ChiTietTinTuc.aspx?nid=95826 (accessed on 21 January 2022).
- EROS. Digital Elevation—Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) Void Filled; USGS: Denver, CO, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cira, D.; Dastur, A.; Jewell, H.; Kilroy, A.; Lozano, N.; Phan, T.P.H.; Wang, H.G. Vietnam Urbanization Review: Technical Assistance Report; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; p. 263. [Google Scholar]
- NIURP. City development strategies for medium size cities in Vietnam: Can Tho and Ha Long. In Technical Report; National Institute of Urban and Rural Planning: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2012; p. 205. [Google Scholar]
- Ta, D.H. Using Landsat Dataset for Assessing Urban Development of Ha Long City (Quang Ninh Province) during the Period 1990–2020; Hanoi National University of Education: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Malarvizhi, K.; Kumar, S.; Porchelvan, P. Use of High Resolution Google Earth Satellite Imagery in Landuse Map Preparation for Urban Related Applications. Procedia Technol. 2016, 24, 1835–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesiv, M.; See, L.; Bayas, J.C.L.; Sturn, T.; Schepaschenko, D.; Karner, M.; Moorthy, I.; McCallum, I.; Fritz, S. Characterizing the Spatial and Temporal Availability of Very High Resolution Satellite Imagery in Google Earth and Microsoft Bing Maps as a Source of Reference Data. Land 2018, 7, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr, T.; Rosen, P.; Caro, E.; Crippen, R.; Duren, R.; Hensley, S.; Kobrick, M.; Paller, M.; Rodriguez, E.; Roth, L.; et al. The Shuttle Radar Topography Mission. Rev. Geophys. 2007, 45, RG2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Shrivastava, P.; Dhurvey, P. Change Detection Techniques in Remote Sensing: A Review. Int. J. Wirel. Mob. Commun. Ind. Syst. 2017, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dueker, K.J.; Horton, F.E. Urban-change detection systems: Remote-sensing inputs. Photogrammetria 1972, 28, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Weng, Q. A survey of image classification methods and techniques for improving classification performance. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 823–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, J.; Phinn, S.; Woodcock, C.; Rogan, J. Rationale and conceptual framework for classification approaches to assess forest resources and properties. In Methods and Applications for Remote Sensing of Forests: Concepts and Case Studies; Wulder, M., Franklin, S., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Boston, MA, USA, 2003; pp. 279–300. [Google Scholar]
- Sayler, K. Landsat 4-7-8 Collection 2 (C2) Level 2 Science Product (L2SP) Guide; US Geological Survey: Rapid City, SD, USA, 2020; p. 43. [Google Scholar]
- Civco, D.L. Artificial neural networks for land-cover classification and mapping. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 1993, 7, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R. Land Use and Land Cover Mapping Using Fuzzy Logic. In Ecosystem Assessment and Fuzzy Systems Management; Cao, B.-Y., Ma, S.-Q., Cao, H.-H., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; Huang, G.; Troy, A.; Cadenasso, M.L. Object-based land cover classification of shaded areas in high spatial resolution imagery of urban areas: A comparison study. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1769–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbek, F.S.; Özkan, C.; Taberner, M. Comparison of maximum likelihood classification method with supervised artificial neural network algorithms for land use activities. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 1733–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Marchine Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vapnik, V. The Nature of Statistical Learning Theory; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1995; p. 314. [Google Scholar]
- Hermes, L.; Frieauff, D.; Puzicha, J.; Buhmann, J. Support vector machines for land usage classification in Landsat TM imagery. In Proceedings of the IEEE 1999 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. IGARSS’99 (Cat. No.99CH36293), Hamburg, Germany, 28 June–2 July 1999; pp. 348–350. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.; Davis, L.S.; Townshend, J.R.G. An assessment of support vector machines for land cover classification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 725–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taati, A.; Sarmadian, F.; Mousavi, A.; Pour, C.T.H.; Shahir, A.H.E. Land Use Classification using Support Vector Machine and Maximum Likelihood Algorithms by Landsat 5 TM Images. Walailak J. Sci. Technol. 2014, 12, 681–687. [Google Scholar]
- Colas, F.; Brazdil, P. Comparison of SVM and Some Older Classification Algorithms in Text Classification Tasks; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2006; pp. 169–178. [Google Scholar]
- Medina, J.A.V.; Atehortúa, B.E.A. Comparison of maximum likelihood, support vector machines, and random forest techniques in satellite images classification. Tecnura 2019, 23, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mountrakis, G.; Im, J.; Ogole, C. Support vector machines in remote sensing: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Lunetta, R.S. Comparison of support vector machine, neural network, and CART algorithms for the land-cover classification using limited training data points. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2012, 70, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paneque-Gálvez, J.; Mas, J.; Moré, G.; Rosselló, J.C.; Orta-Martinez, M.; Luz, A.; Gueze, M.; Macía, M.; Reyes-García, V. Enhanced land use/cover classification of heterogeneous tropical landscapes using support vector machines and textural homogeneity. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2013, 23, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemmour, H.; Chibani, Y. Multiple support vector machines for land cover change detection: An application for mapping urban extensions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2006, 61, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongzhu, X.; Zhengdong, Z.; Feng, C. Comparison of artificial neural network and support vector machine methods for urban land use/cover classifications from remote sensing images A Case Study of Guangzhou, South China. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Computer Application and System Modeling (ICCASM 2010), Taiyuan, China, 22–24 October 2010; pp. 52–56. [Google Scholar]
- Andrimont, R.; Verhegghen, A.; Meroni, M.; Lemoine, G.; Strobl, P.; Eiselt, B.; Yordanov, M.; Martinez-Sanchez, L.; Velde, M. LUCAS Copernicus 2018: Earth Observation relevant in-situ data on land cover throughout the European Union. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2020, 13, 1119–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labib, S.M.; Harris, A. The potentials of Sentinel-2 and LandSat-8 data in green infrastructure extraction, using object based image analysis (OBIA) method. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 51, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorais, A.; Cardille, J. Strategies for Incorporating High-Resolution Google Earth Databases to Guide and Validate Classifications: Understanding Deforestation in Borneo. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 1157–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, K.N.; Chatterjee, C. Remote Sensing and GIS Application. Available online: http://ecoursesonline.iasri.res.in/course/view.php?id=53 (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Congalton, R.G.; Green, K. Assessing the Accuracy of Remotely Sensed Data: Principles and Practices; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. A Coefficient of Agreement for Nominal Scales; New York Univesity: New York, NY, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, Z.; Zhang, X.; Benediktsson, J.A. Developing a general post-classification framework for land-cover mapping improvement using high-spatial-resolution remote sensing imagery. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 8, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.-C. A filter-based post-processing technique for improving homogeneity of pixel-wise classification data. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 49, 531–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Z.; van der Aa, N.; Gemeren, C.v.; Veltkamp, R. A combined post-filtering method to improve accuracy of variational optical flow estimation. Pattern Recognit. 2014, 47, 1926–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NSCEL. Construction Planning of Quang Ninh Province to 2030, Vision to 2050 and beyond 2050; Quang Ninh People Committee: Ha Long, Vietnam, 2014; p. 374. [Google Scholar]
- VIUP. General Planning of Ha Long City to 2040, Vision to 2050; Vietnam Institute for Urban and Rural Planning: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2021; p. 159. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, T. Cam Pha City: Green Economic Development. Quang Ninh Online, 23 October 2020. Available online: https://baoquangninh.com.vn/tp-cam-pha-phat-trien-kinh-te-xanh-2506178.html (accessed on 17 January 2022).
- VNA. Halong Property Market Sees Rising Demand for Mid-End Apartments. Vietnam Investment Review, 3 October 2018. Available online: https://vir.com.vn/halong-property-market-sees-rising-demand-for-mid-end-apartments-62841.html (accessed on 21 January 2022).
- Lofrano, G.; Carotenuto, M.; Maffettone, R.; Todaro, P.; Sammataro, S.; Kalavrouziotis, I.K. Water Collection and Distribution Systems in the Palermo Plain during the Middle Ages. Water 2013, 5, 1662–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.S.; He, Y.M.; Xu, M.J. Analysis on the principle of terrain slope impact on land suitability for urban construction in mountainous areas. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Sustainable Development (ICSD 2015), New York, NY, USA, 23–24 September 2015; pp. 278–286. [Google Scholar]
- Rivkin, L.R.; Santangelo, J.S.; Alberti, M.; Aronson, M.F.J.; Keyzer, C.W.D.; Diamond, S.E.; Fortin, M.J.; Frazee, L.J.; Gorton, A.J.; Hendry, A.P.; et al. A roadmap for urban evolutionary ecology. Evol. Appl. 2019, 12, 384–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.D. Decision approving the adjustment of the general construction planning of Ha Long city, Quang Ninh province to 2020. In 251/2003/QĐ-CP; 20 November 2003 Edition; Government Office: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2003; Volume 1, pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, V.H. Decision approving the adjustment of the general construction planning of Cam Pha bourg, Quang Ninh province to 2020. In 1100/QĐ-UBND; 26 April 2000 Edition; Provincial People’s Committees: Ha Long, Vietnam, 2000; Volume 1, pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, H. Quang Ninh Province: Close the Opencast Coal Mine of Nui Beo Company. Resources and Environment, 19 February 2021. Available online: https://baotainguyenmoitruong.vn/quang-ninh-dong-cua-mo-than-lo-thien-cua-cong-ty-cp-than-nui-beo-334022.html (accessed on 21 January 2022).
- Nguyen, C.L. Geological and Mineral Resources Map of Vietnam; Geological and Mineral Resources Administration: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2005. [Google Scholar]


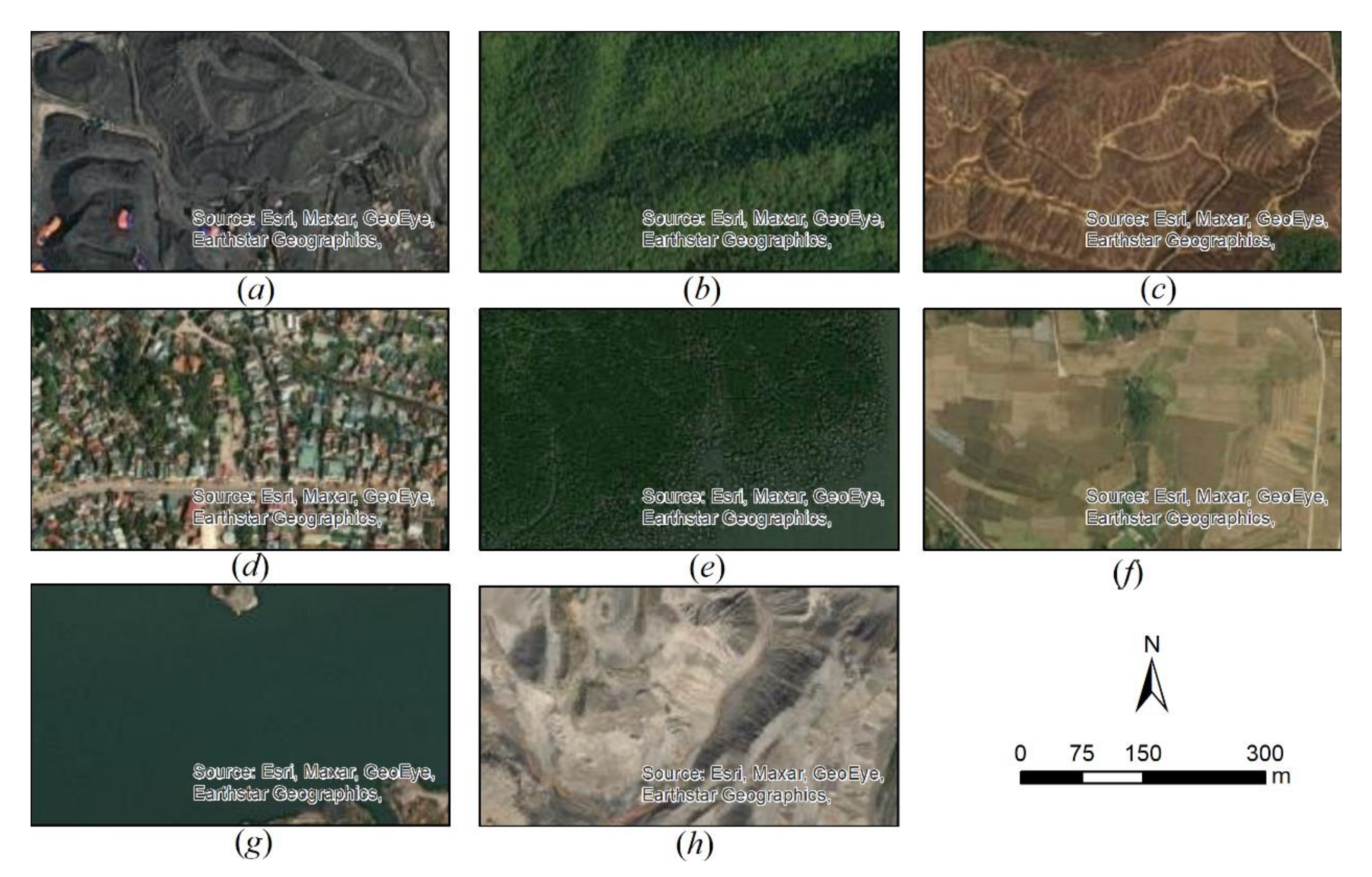


| Satellite | Landsat 5 | Landsat 7 | Landsat 8 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sensor | TM | ETM+ | OLI |
| Processing level | 2A | 2A | 2A |
| Date | 28 October 1991 | 29 September 2001 | 23 September 2019 |
| Cloud cover | 0% | 1% | 0% |
| WRS-2 (Path, Row) | 126; 45 | 126; 45 | 126; 45 |
| Grayscale level | 16 bits | 16 bits | 16 bits |
| Level 1 | Level 2 |
|---|---|
| Woodland | Evergreen forest, mangrove, etc. |
| Artificial land | Rock dump, coalfield, residence, etc. |
| Cropland | Rice field, vegetables, etc. |
| Bare land | Logging land, outcrop, sand, etc. |
| Water bodies | Sea, reservoir, lake, river, coal pit, etc. |
| Land Covers | 1991 | 2001 | 2019 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Producer’s | User’s | Producer’s | User’s | Producer’s | User’s | |
| Forest | n/a | n/a | 100.0 | 96.0 | 99.6 | 72.3 |
| Mangrove | n/a | n/a | 99.6 | 99.6 | 100.0 | 99.1 |
| Rock dump | n/a | n/a | 98.4 | 96.2 | 89.3 | 99.2 |
| Coal field | n/a | n/a | 99.5 | 99.4 | 99.58 | 83.8 |
| Residence | n/a | n/a | 92.1 | 99.3 | 100.0 | 76.3 |
| Water | n/a | n/a | 100.0 | 99.8 | 99.43 | 100.0 |
| Logging land | n/a | n/a | 79.3 | 83.2 | 79.9 | 100.0 |
| Rice field | n/a | n/a | 86.4 | 95.9 | 98.3 | 99.7 |
| Land Cover Categories | 1991 | 2001 | 2019 | I (1991–2001) | II (2001–2019) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area (ha) | Area (ha) | Area (ha) | Area (ha) | (%) | Area (ha) | (%) | |
| Natural features | 65,714.31 | 64,230.91 | 53,067.94 | −1483.4 | −1.25 | −11,162.97 | −9.39 |
| Man-made features | 7473.96 | 9952.06 | 25,693.65 | +2478.1 | +2.08 | +15,741.59 | +13.24 |
| Mangrove | 3404.43 | 2661.83 | 1075.7 | −742.6 | −0.62 | −1586.13 | −1.33 |
| Water | 42293.7 | 42,041.55 | 39,048.93 | −252.15 | −0.21 | −2992.62 | −2.52 |
| Land Covers | I (1991–2001) | II (2001–2019) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (−) ha | (0) ha | (+) ha | (−) ha | (0) ha | (+) ha | |
| Natural features | 3726.26 | 61,988.05 | 2242.85 | 12,908.89 | 51,322.02 | 1747.93 |
| Man-made features | 2138.31 | 5335.65 | 4616.41 | 1445.21 | 8506.86 | 17,186.79 |
| Mangrove | 1598.56 | 1805.82 | 855.91 | 1886.92 | 774.81 | 300.96 |
| Water | 2061.89 | 40,231.81 | 1809.74 | 4658.68 | 37,382.86 | 1666.07 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, G.C.; Dang, K.V.; Vu, T.A.; Nguyen, A.K.; Weber, C. Ha Long—Cam Pha Cities Evolution Analysis Utilizing Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14051241
Nguyen GC, Dang KV, Vu TA, Nguyen AK, Weber C. Ha Long—Cam Pha Cities Evolution Analysis Utilizing Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(5):1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14051241
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Giang Cong, Khac Vu Dang, Tuan Anh Vu, Anh Khac Nguyen, and Christiane Weber. 2022. "Ha Long—Cam Pha Cities Evolution Analysis Utilizing Remote Sensing Data" Remote Sensing 14, no. 5: 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14051241
APA StyleNguyen, G. C., Dang, K. V., Vu, T. A., Nguyen, A. K., & Weber, C. (2022). Ha Long—Cam Pha Cities Evolution Analysis Utilizing Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sensing, 14(5), 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14051241






