Estimation of Aerosol Extinction Coefficient Using Camera Images and Application in Mass Extinction Efficiency Retrieval
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
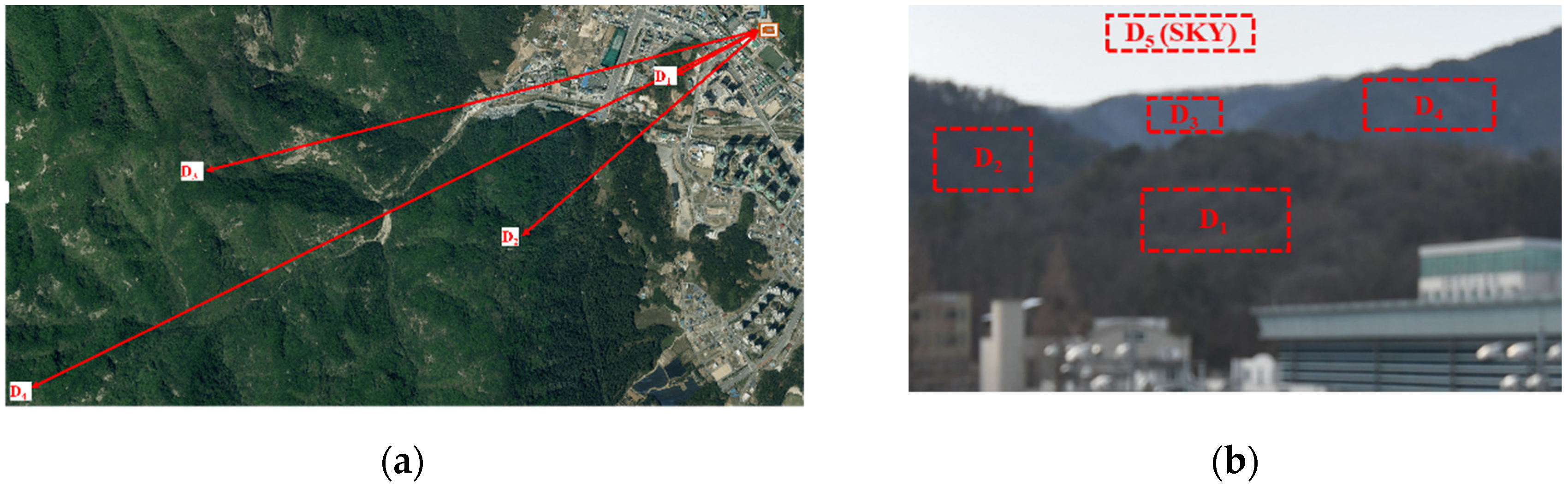
2.1. Calculation of the Extinction Coefficient from the Camera Images
2.2. Calculation of the Extinction Coefficient and Efficiency Using Visibility Data
2.3. Measurement Period and Site
3. Results and Discussion
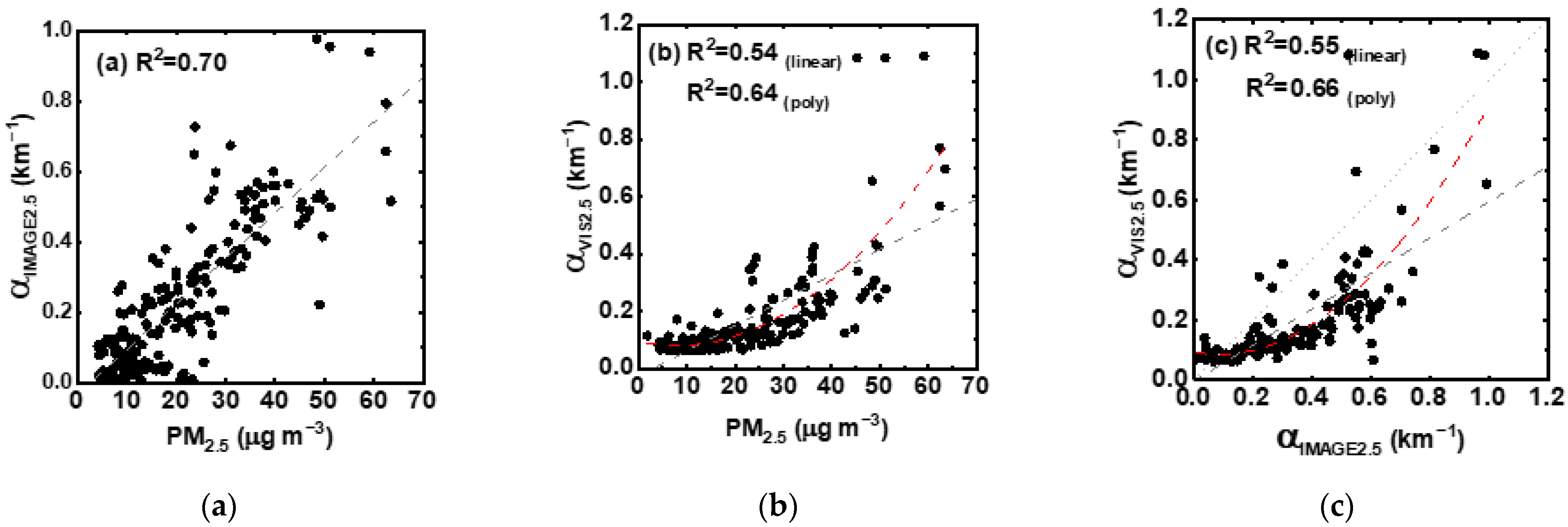
3.1. Extinction Coefficient
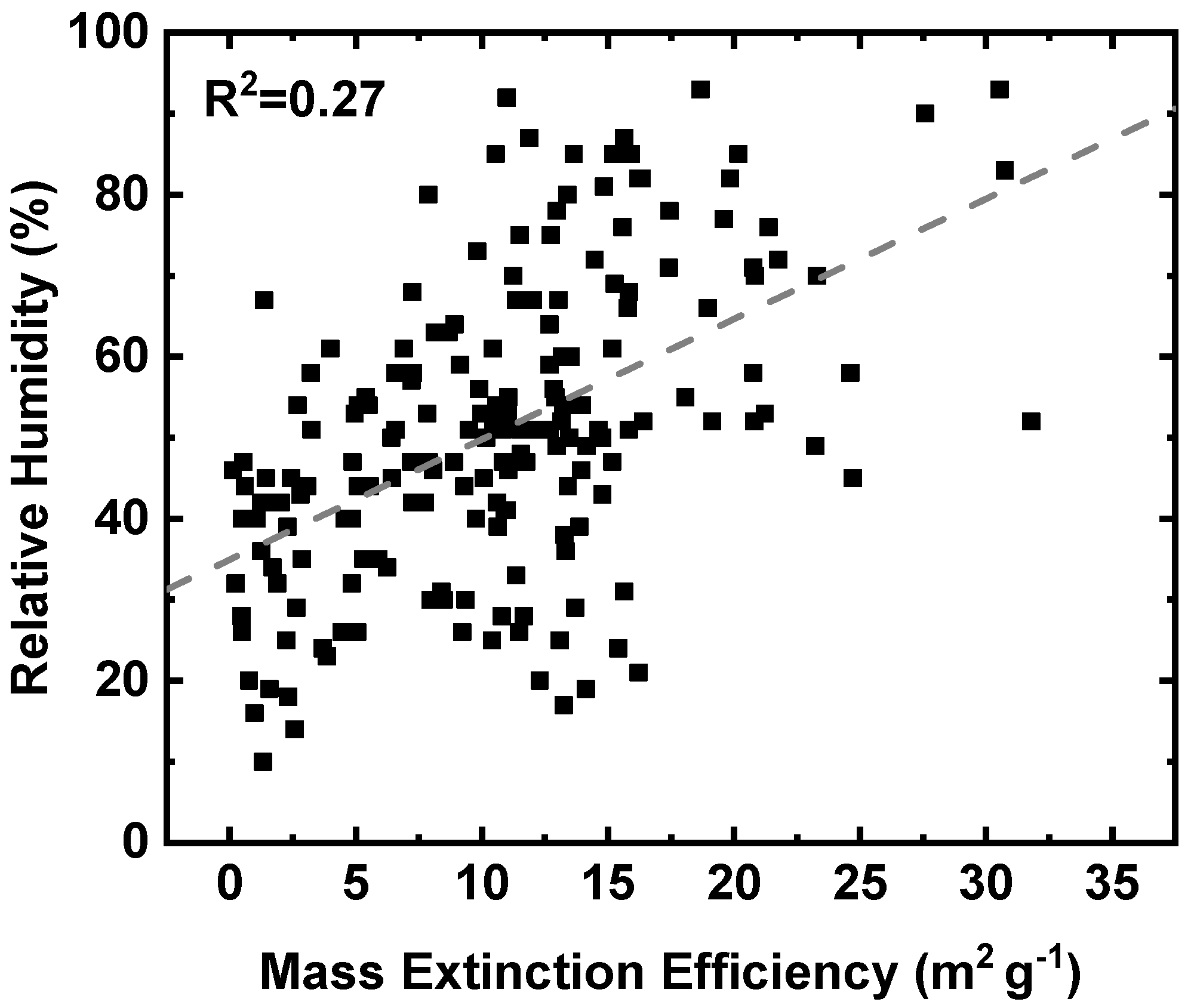
3.2. Mass Extinction Efficiency
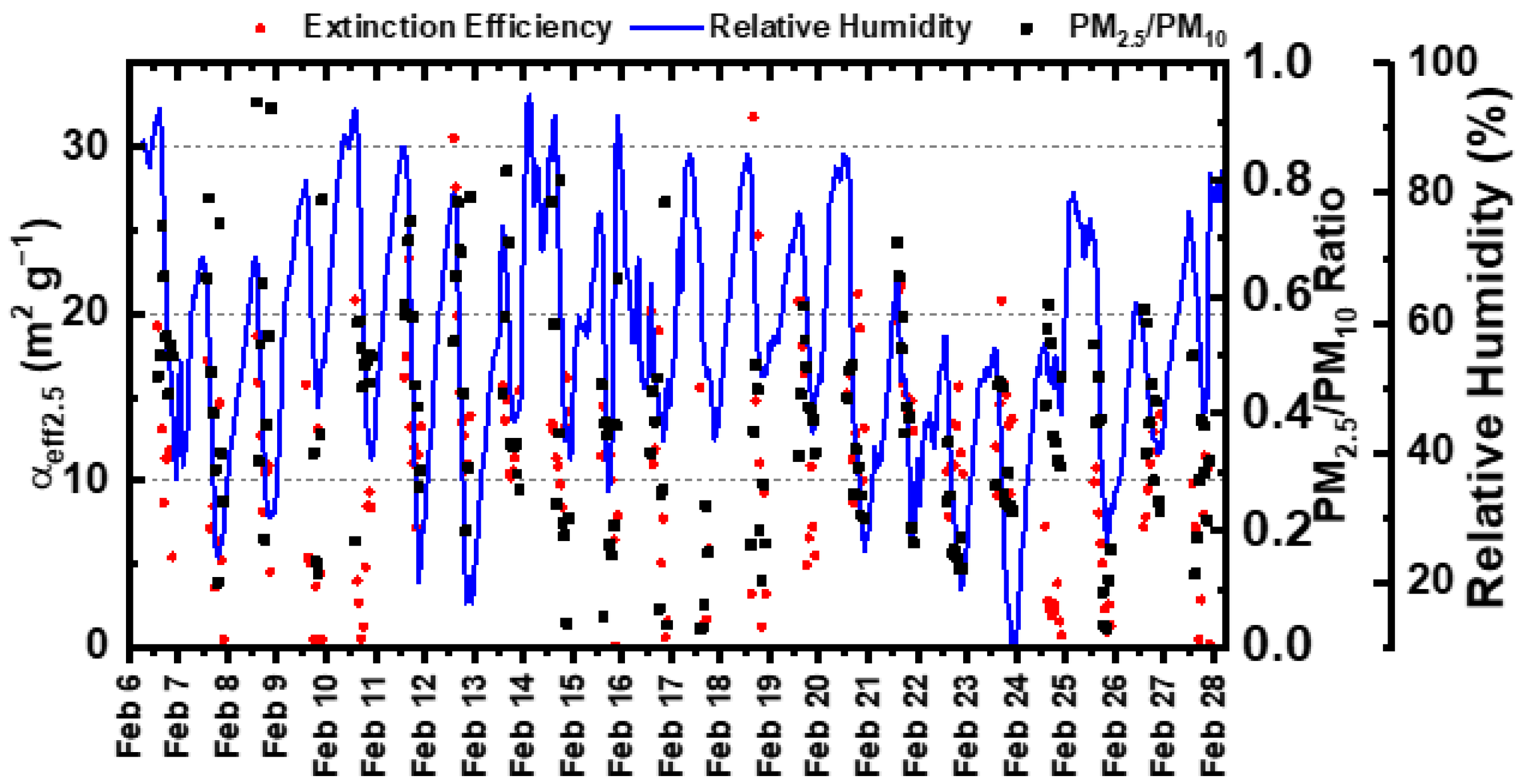
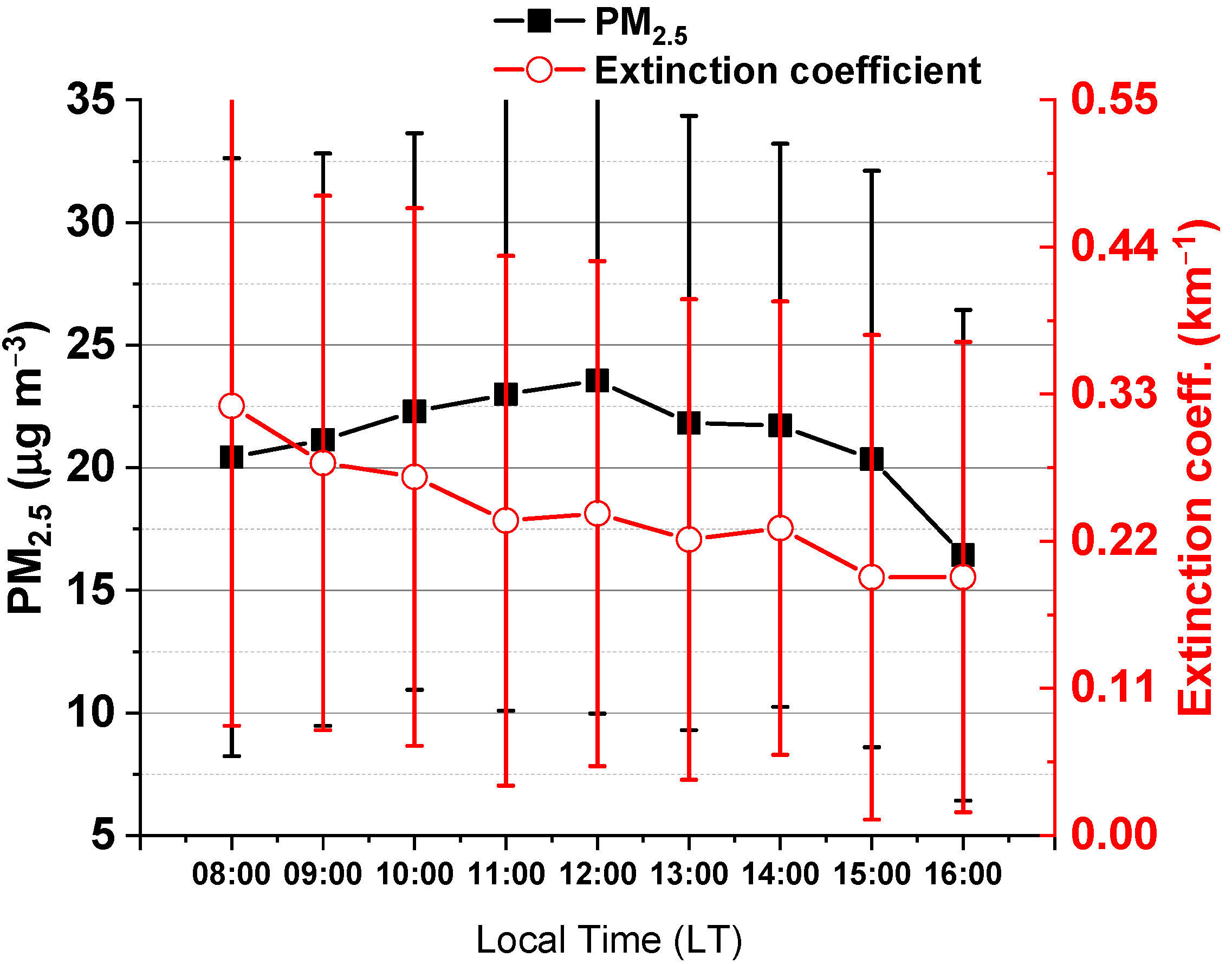
3.3. Diurnal Variation Patterns
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brook, R.D.; Rajagopalan, S.; Pope, C.A., 3rd; Brook, J.R.; Bhatnagar, A.; Diez-Roux, A.V.; Holguin, F.; Hong, Y.; Luepker, R.V.; Mittleman, M.A.; et al. Particulate matter air pollution and cardiovascular disease: An update to the scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2010, 121, 2331–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.-H.; Kabir, E.; Kabir, S. A review on the human health impact of airborne particulate matter. Environ. Int. 2015, 74, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. The World Health Report 2006: Working Together for Health; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. WHO 2021 Air Quality Guidelines; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Amarillo, A.; Carreras, H.; Krisna, T.; Mignola, M.; Tavera Busso, I.; Wendisch, M. Exploratory analysis of carbonaceous PM2.5 species in urban environments: Relationship with meteorological variables and satellite data. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 245, 117987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Li, H.; Jin, S.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, R.; Liu, B.; Gong, W. Estimation of the vertical distribution of particle matter (PM2.5) concentration and its transport flux from lidar measurements based on machine learning algorithms. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2021, 21, 17003–17016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meskhidze, N.; Sutherland, B.; Ling, X.; Dawson, K.; Johnson, M.S.; Henderson, B.; Hostetler, C.A.; Ferrare, R.A. Improving Estimates of PM2.5 Concentration and Chemical Composition by Application of High Spectral Resolution Lidar (HSRL) and Creating Aerosol Types from Chemistry (CATCH) Algorithm. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 250, 118250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stebel, K.; Stachlewska, I.S.; Nemuc, A.; Horálek, J.; Schneider, P.; Ajtai, N.; Diamandi, A.; Benešová, N.; Boldeanu, M.; Botezan, C.; et al. SAMIRA-SAtellite Based Monitoring Initiative for Regional Air Quality. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollingsworth, A.; Engelen, R.; Textor, C.; Benedetti, A.; Boucher, O.; Chevallier, F.; Dethof, A.; Elbern, H.; Eskes, H.; Flemming, J. Toward a monitoring and forecasting system for atmospheric composition: The GEMS project. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2008, 89, 1147–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, M.; Choi, M. Monitoring aerosol properties in east asia from geostationary orbit: GOCI, MI and GEMS. In Air Pollution in Eastern Asia: An Integrated Perspective; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 323–333. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.; Kim, J.; Torres, O.; Ahn, C.; Kim, W.; Jeong, U.; Go, S.; Liu, X.; Moon, K.J.; Kim, D.-R. Optimal estimation-based algorithm to retrieve aerosol optical properties for GEMS measurements over Asia. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Jeong, U.; Ahn, M.-H.; Kim, J.H.; Park, R.J.; Lee, H.; Song, C.H.; Choi, Y.-S.; Lee, K.-H.; Yoo, J.-M. New era of air quality monitoring from space: Geostationary Environment Monitoring Spectrometer (GEMS). Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 101, E1–E22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gultepe, I.; Müller, M.D.; Boybeyi, Z. A new visibility parameterization for warm-fog applications in numerical weather prediction models. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2006, 45, 1469–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, S.S.; Flecker, B.; Leitgeb, E.; Gebhart, M. Characterization of fog attenuation in terrestrial free space optical links. Opt. Eng. 2007, 46, 066001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Shi, G.; Uchiyama, A.; Yamazaki, A.; Chen, H.; Goloub, P.; Zhang, X. Intercomparison between aerosol optical properties by a PREDE skyradiometer and CIMEL sunphotometer over Beijing, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 3199–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olmo, F.J.; Cazorla, A.; Alados-Arboledas, L.; López-Álvarez, M.A.; Hernández-Andrés, J.; Romero, J. Retrieval of the optical depth using an all-sky CCD camera. Appl. Opt. 2008, 47, H182–H189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, J.; Lü, D. Preliminary retrieval of aerosol optical depth from all-sky images. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2010, 27, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Shafin, S.H.; Li, Y.; Hao, H. A prototype system for atmospheric visibility estimation based on image analysis and learning. J. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2014, 11, 4577–4585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Chen, Y.; Gao, Y. Real-time visibility distance evaluation based on monocular and dark channel prior. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2015, 10, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Peng, H.; Tang, J.; Zou, B.; Tang, C. Visibility detection approach to road scene foggy images. KSII Trans. Internet Inf. Syst. 2016, 10, 4419–4441. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, M.; Iwabuchi, H.; Murata, I. Estimation of spectral distribution of sky radiance using a commercial digital camera. Appl. Opt. 2016, 55, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; He, L.; Cai, X.; Ruan, S. A new video-camera-based visiometer system. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2019, 20, e925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.H.; Kim, Y.J. Satellite remote sensing of Asian aerosols: A case study of clean, polluted, and Asian dust storm days. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2010, 3, 1771–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.; Noh, Y. An Aerosol Extinction Coefficient Retrieval Method and Characteristics Analysis of Landscape Images. Sensors 2021, 21, 7282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narasimhan, S.G.; Nayar, S.K. Vision and the atmosphere. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2002, 48, 233–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, N.; Newsam, S. Using visibility cameras to estimate atmospheric light extinction. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Workshop on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Washington, DC, USA, 5–7 January 2011; pp. 577–584. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Kim, D. Aerosol-extinction Retrieval Method at Three Effective RGB Wavelengths Using a Commercial Digital Camera. Korean J. Opt. Photonics 2020, 31, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohren, C.F.; Huffman, D.R. Absorption and Scattering of Light by Small Particles; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Koschmieder, H. Theorie der horizontalen sichtweite, Beitrage zur Physik der Freien Atmosphare. Meteorol. Z. 1924, 12, 3353. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Z.; Ma, X.; He, Y.; Jiang, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Sheng, L.; Hu, J.; Yan, N. Mass extinction efficiency and extinction hygroscopicity of ambient PM2.5 in urban China. Env. Res 2017, 156, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, S.M.; Cass, G.R. Characteristics of summer midday low-visibility events in the Los Angeles area. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1989, 23, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucholtz, A. Rayleigh-scattering calculations for the terrestrial atmosphere. Appl. Opt. 1995, 34, 2765–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitchford, M.; Malm, W.; Schichtel, B.; Kumar, N.; Lowenthal, D.; Hand, J. Revised algorithm for estimating light extinction from IMPROVE particle speciation data. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2007, 57, 1326–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.H.; Zhang, J.P.; Xue, H.W. The challenge of improving visibility in Beijing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 7821–7827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, Z.; Wang, S.; Jiang, J.; Fu, Q.; Chen, C.; Xu, B.; Yu, J.; Fu, X.; Hao, J. Long-term trend of haze pollution and impact of particulate matter in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 182, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Zhou, G.; Geng, F.; Gao, W.; Yu, W. Spatial distribution of aerosol hygroscopicity and its effect on PM2.5 retrieval in East China. Atmos. Res. 2016, 170, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hand, J.; Malm, W. Review of aerosol mass scattering efficiencies from ground-based measurements since 1990. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, D16203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, J.G. Visibility: Science and regulation. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2002, 52, 628–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lv, L.; Liu, W.; Zhang, T.; Chen, Z.; Dong, Y.; Fan, G.; Xiang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Yang, N.; Chu, B. Observations of particle extinction, PM2. 5 mass concentration profile and flux in north China based on mobile lidar technique. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 164, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Huang, Z.; Qi, S.; Huang, J.; Zhang, S.; Dong, Q.; Wang, X. Ten-year global particulate mass concentration derived from space-borne CALIPSO lidar observations. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 721, 137699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, C.; Dong, Y.; Hu, Q.; Liu, T.; Zhu, Y.; Xing, C. Profiling of Dust and Urban Haze Mass Concentrations during the 2019 National Day Parade in Beijing by Polarization Raman Lidar. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Bergin, M.; Yu, X.; Liu, G.; Zhao, J.; Carrico, C.; Baumann, K. Measurement of aerosol chemical, physical and radiative properties in the Yangtze delta region of China. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Lee, H.; Kim, Y.J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, J.; Fan, S. Aerosol chemistry and the effect of aerosol water content on visibility impairment and radiative forcing in Guangzhou during the 2006 Pearl River Delta campaign. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 3231–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Niu, T.; Zhang, X.C.; Gong, S.L.; Zhang, Y.M.; Sun, J.Y. Atmospheric aerosol compositions in China: Spatial/temporal variability, chemical signature, regional haze distribution and comparisons with global aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 779–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Ren, C.; Huang, X.; Nie, W.; Wang, J.; Sun, P.; Chi, X.; Ding, A. Increased Aerosol Extinction Efficiency Hinders Visibility Improvement in Eastern China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL090167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, S.; Naghmeh, D.; Noh, Y. A Study on the Characteristic Variations of Fine Particle in Busan and Ulsan through Particle Extinction Efficiency Analysis. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 37, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Deng, Z.; Sun, X.; Ran, L.; Xia, X.; Fu, D.; Song, Z.; Wang, P.; Wu, Y.; Tian, P.; et al. Estimation of PM2.5 Mass Concentration from Visibility. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2020, 37, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Liu, Y. Analysis of long-term variations of fog and haze in China in recent 50 years and their relations with atmospheric humidity. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Yu, Y.; Kuang, Y.; Tao, J.; Zhao, G. Recent progress of aerosol light-scattering enhancement factor studies in China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2019, 36, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyslop, N.P. Impaired visibility: The air pollution people see. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zhao, C.; Göbel, T.; Hallbauer, E.; Nowak, A.; Ran, L.; Xu, W.; Deng, Z.; Ma, N.; Mildenberger, K. Hygroscopic properties of aerosol particles at high relative humidity and their diurnal variations in the North China Plain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 3479–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, M.; Chan, C.K.; Li, Y.J.; Su, H.; Ma, Q.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Z.; Ge, M.; Hu, M.; et al. A review of experimental techniques for aerosol hygroscopicity studies. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 12631–12686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N. Thermodynamics of Aerosols. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change; John Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 412–414. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, S.T. Phase transitions of aqueous atmospheric particles. Chem. Rev. 2000, 100, 3403–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Location | Year | MEE | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 24 cities of China | 2013–2014 | 4.4 ± 0.84 | Cheng et al. (2017) [30] |
| YRD | 2011–2012 | 4.1 | Cheng et al. (2013) [35] |
| Eastern China | 2014 | 5 | He et al. (2016) [36] |
| Beijing | 2006 | 4.3 | Jung et al. (2009) [43] |
| Lin’an | 1999 | 5 | Xu et al. (2002) [42] |
| Beijing | 2003–2008 | 4.7 | Zhang et al. (2010) [34] |
| Nanjing | 2013 2018 | 7.1 9.3 | Liu et al. (2020) [45] |
| Busan, Korea | 2015–2019 | 12.1 ± 8.3 | Joo et al. (2021) [46] |
| Daejeon, Korea | 2021 | 10.8 ± 6.9 (6.9 ± 5.0) 1 | This research |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shin, J.; Kim, D.; Noh, Y. Estimation of Aerosol Extinction Coefficient Using Camera Images and Application in Mass Extinction Efficiency Retrieval. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1224. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14051224
Shin J, Kim D, Noh Y. Estimation of Aerosol Extinction Coefficient Using Camera Images and Application in Mass Extinction Efficiency Retrieval. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(5):1224. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14051224
Chicago/Turabian StyleShin, Juseon, Dukhyeon Kim, and Youngmin Noh. 2022. "Estimation of Aerosol Extinction Coefficient Using Camera Images and Application in Mass Extinction Efficiency Retrieval" Remote Sensing 14, no. 5: 1224. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14051224
APA StyleShin, J., Kim, D., & Noh, Y. (2022). Estimation of Aerosol Extinction Coefficient Using Camera Images and Application in Mass Extinction Efficiency Retrieval. Remote Sensing, 14(5), 1224. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14051224






