Decoupling Relationship between Urbanization and Carbon Sequestration in the Pearl River Delta from 2000 to 2020
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
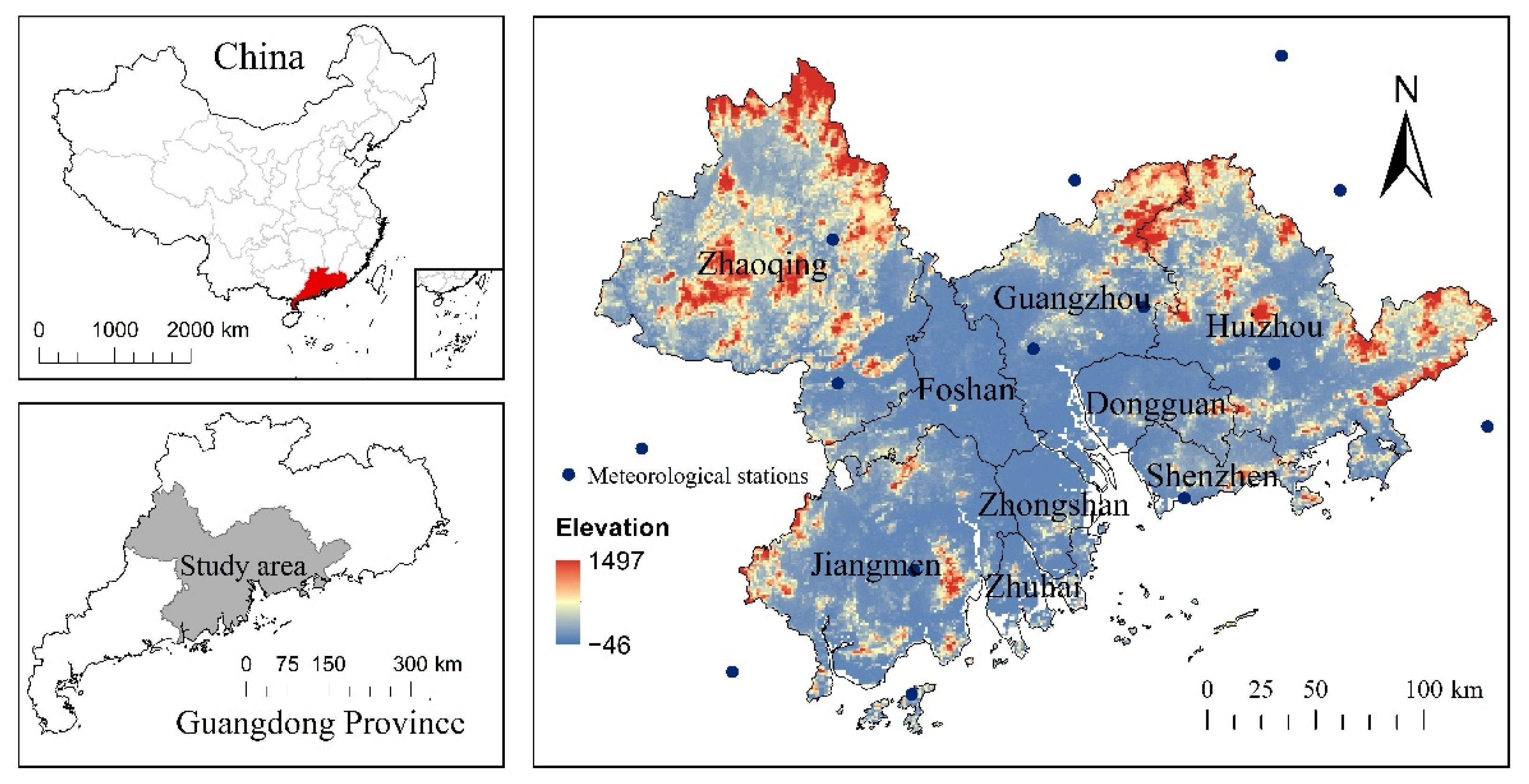
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Available Data
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Theil–Sen Median Trend Analysis and Mann–Kendall Trend Test
2.3.2. Contributions of Climatic Factors and Human Activities to NPP
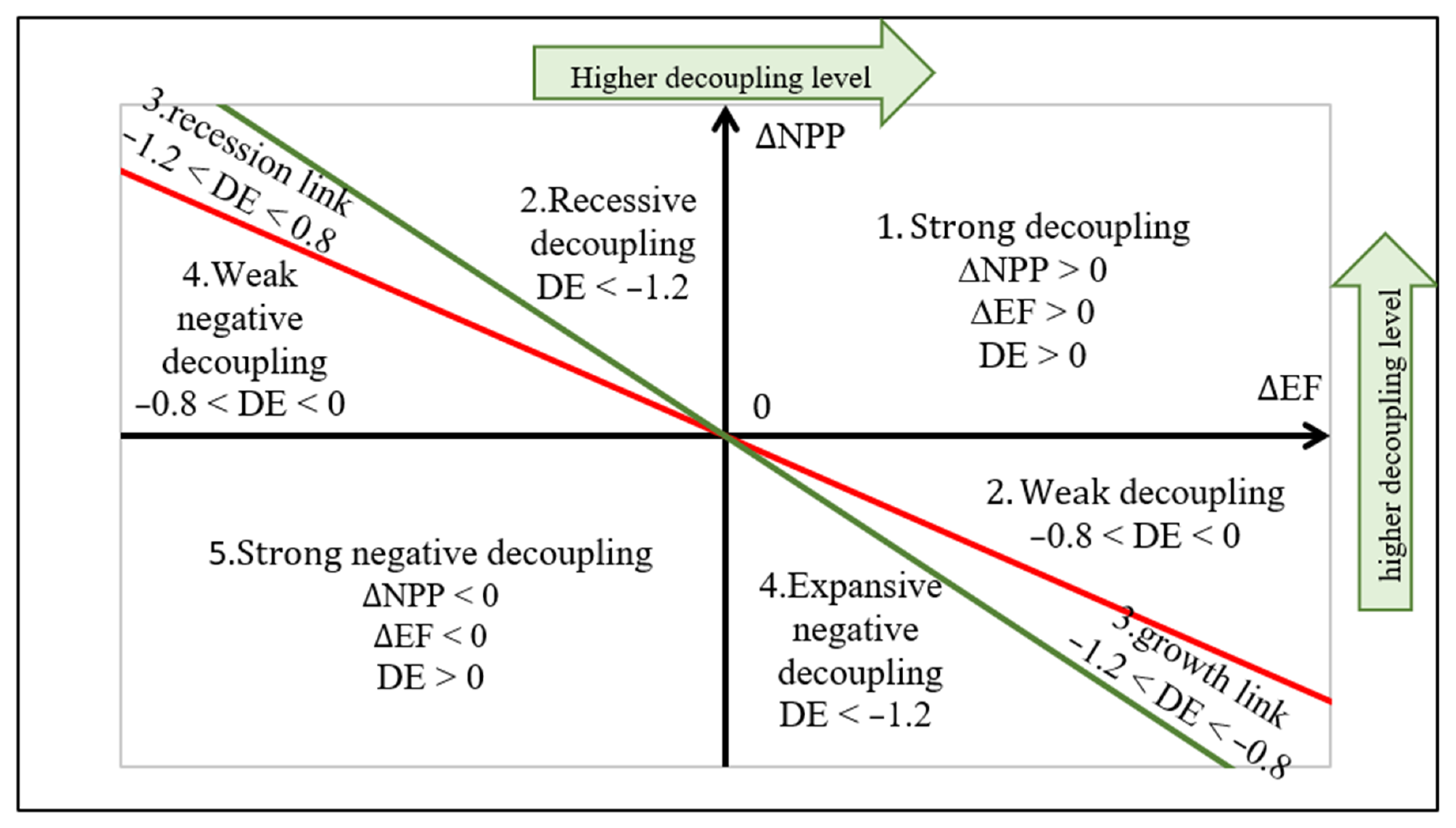
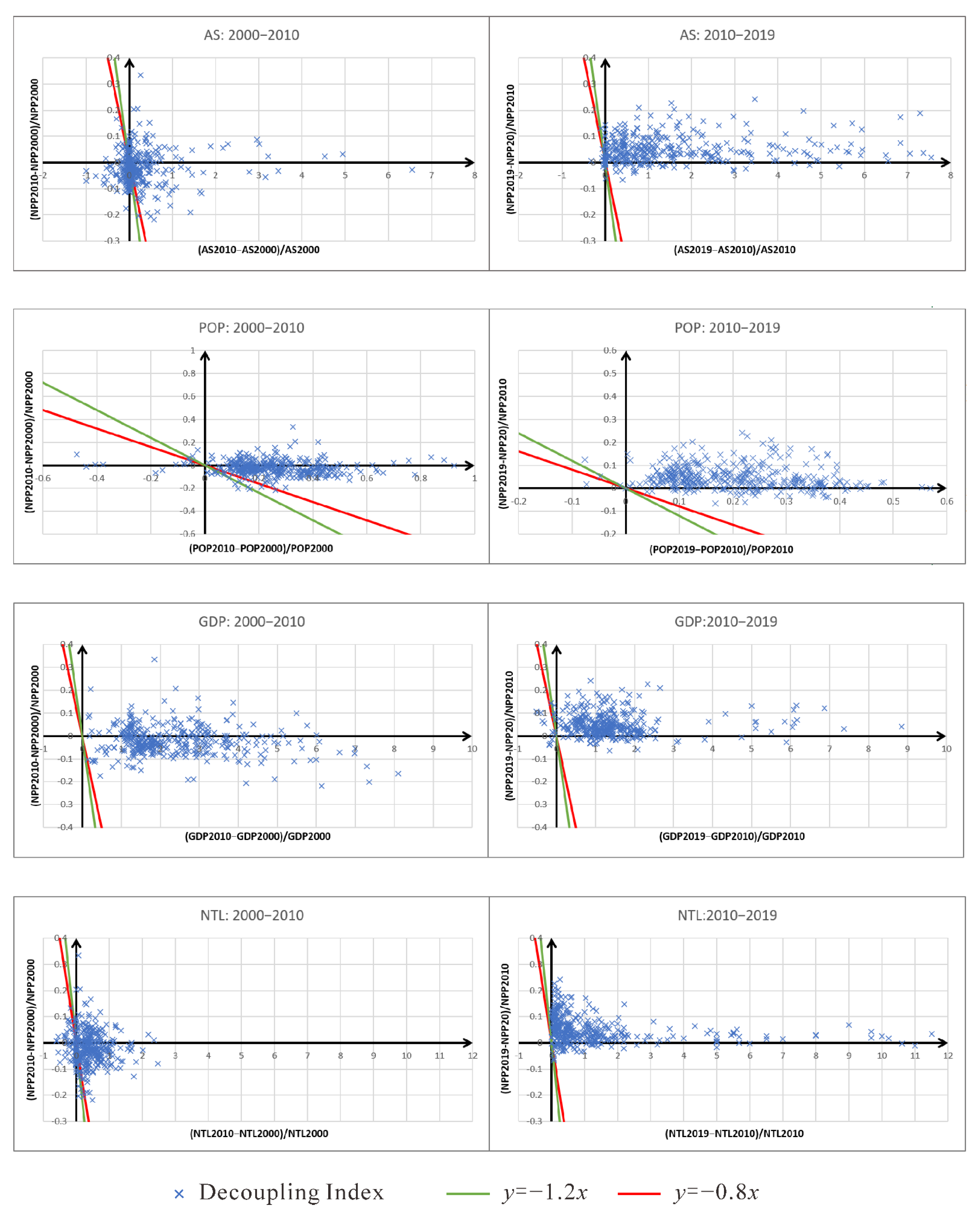
2.3.3. Tapio Decoupling
3. Results
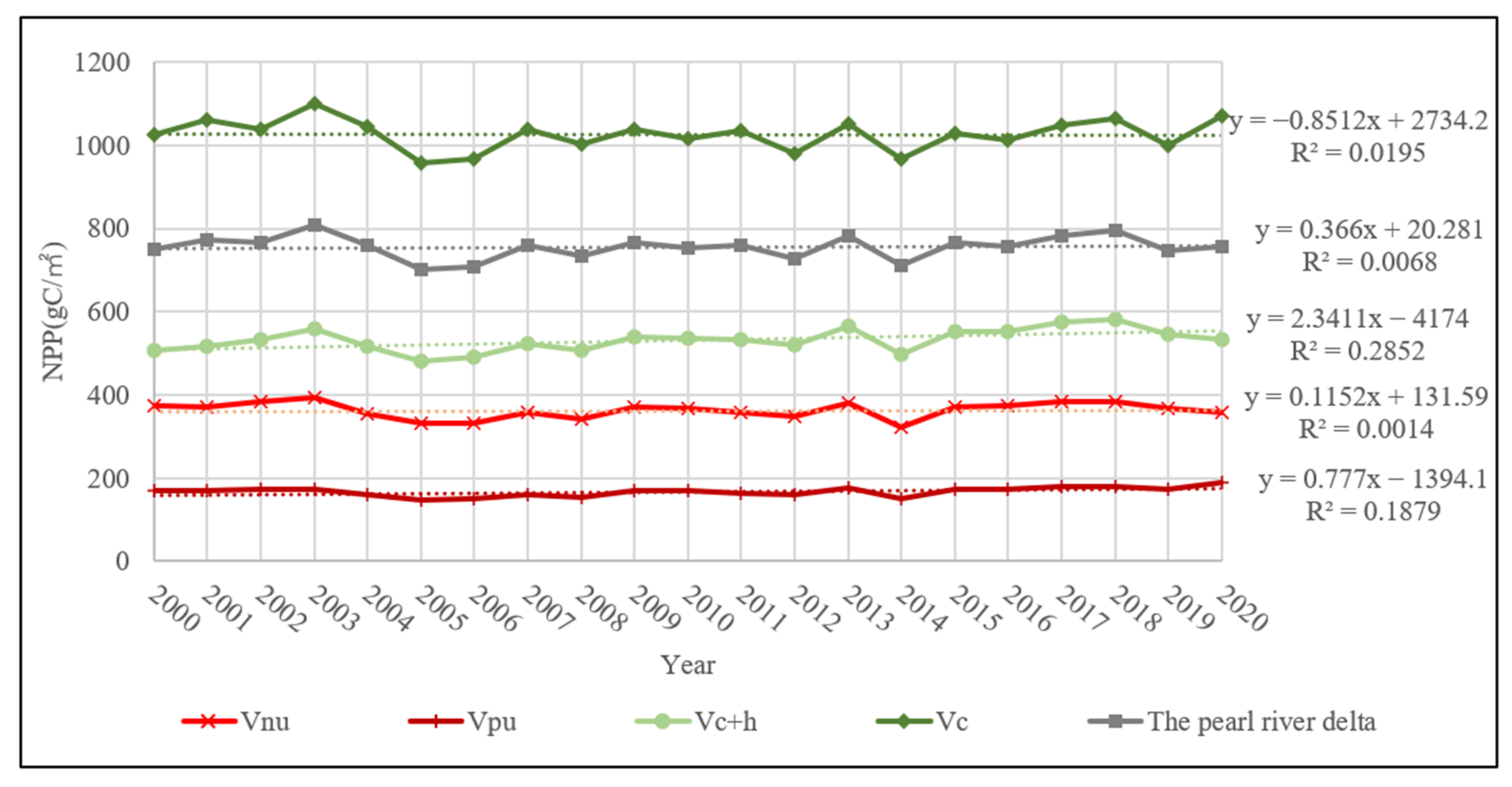
3.1. Influence of Urbanization on Change in NPP
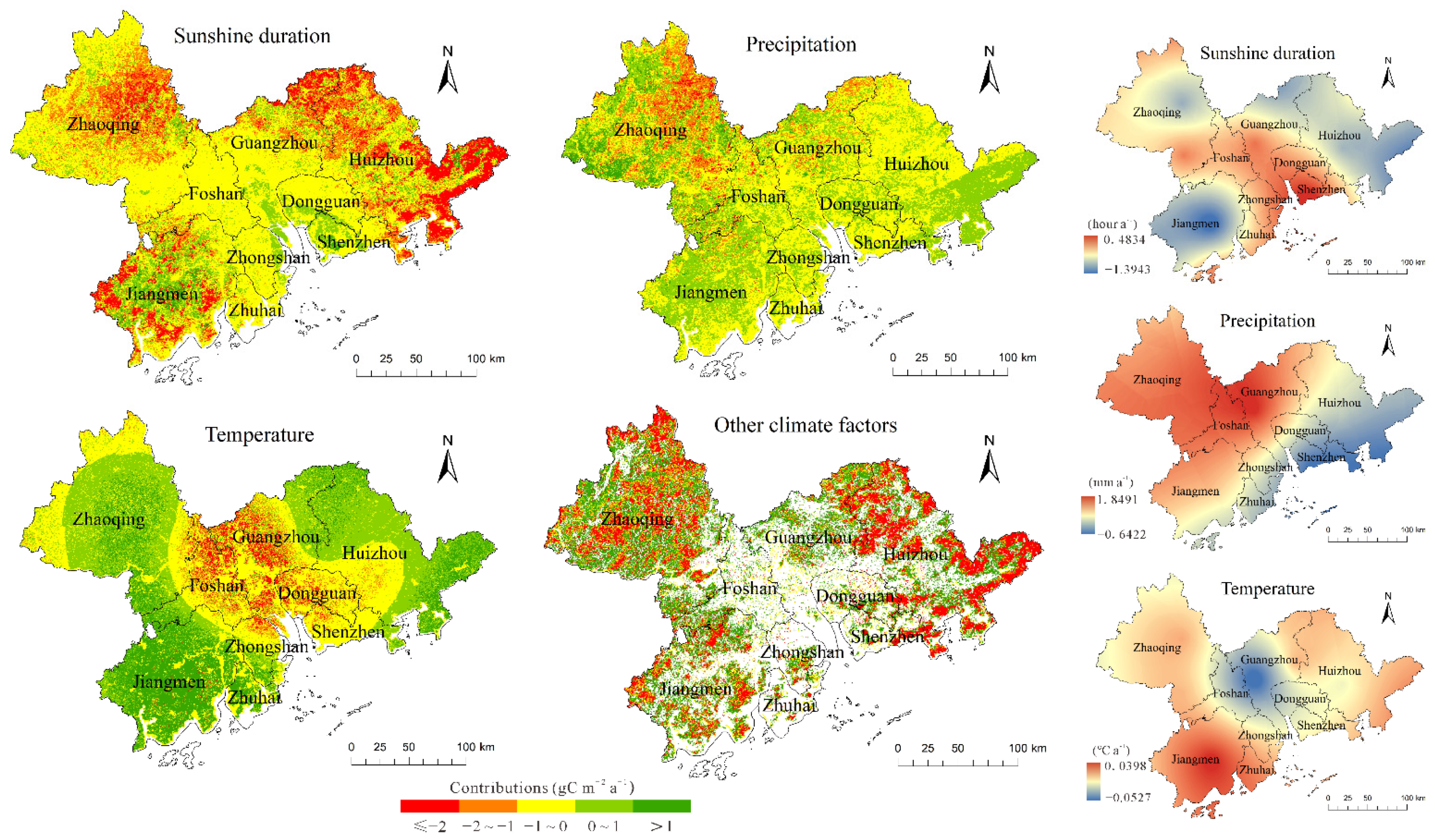
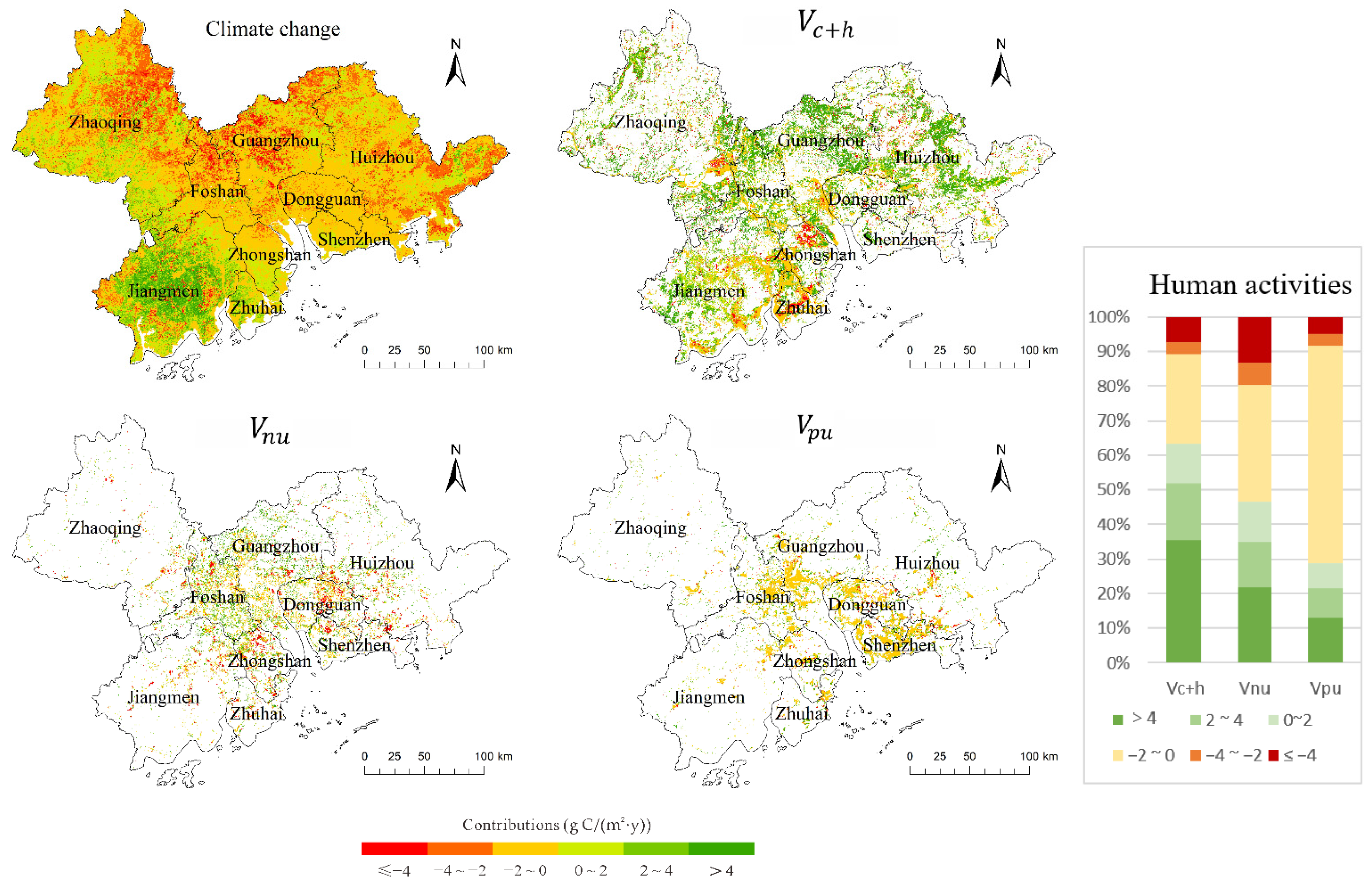
3.2. Contributions of Human Activities and Climate Change to NPP
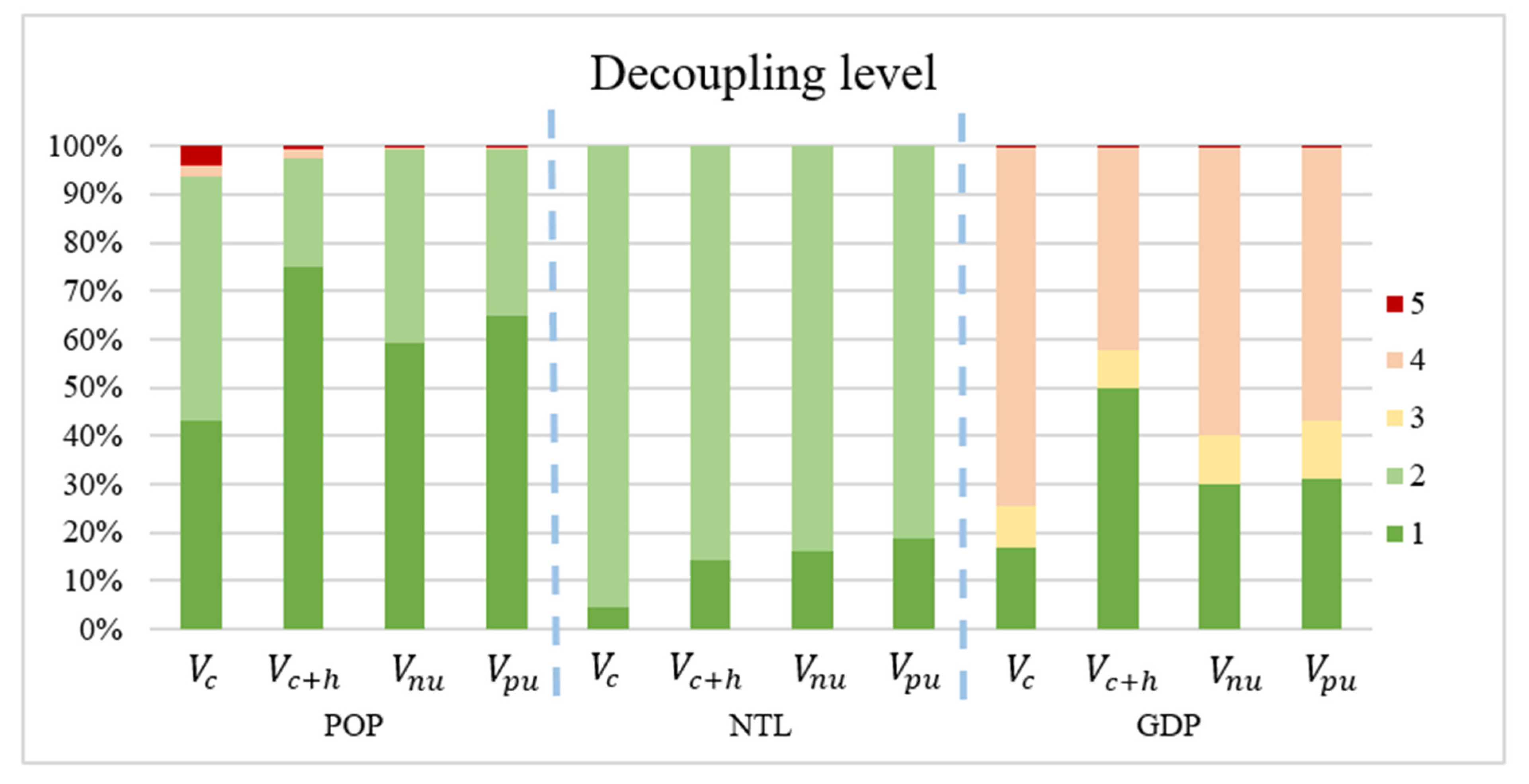
3.3. Decoupling Index of Socioeconomic Factors and Carbon Sequestration Service Capacity
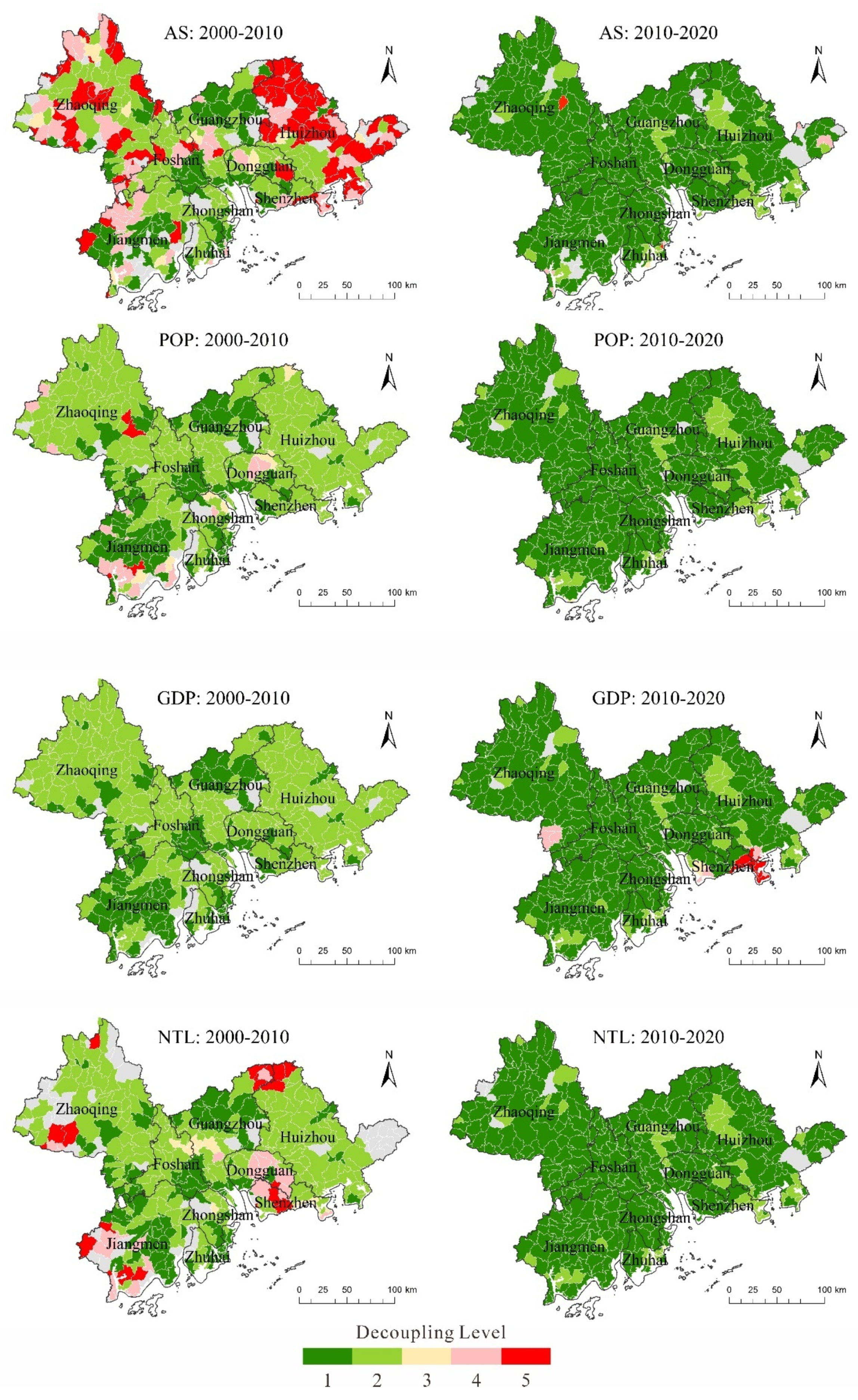
3.4. Change in the Decoupling Index in the Process of Urban Development
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Raich, J.W.; Schlesinger, W.H. The global carbon dioxide flux in soil respiration and its relationship to vegetation and climate. Tellus Ser. B 1992, 44B, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciais, P.; Reichstein, M.; Viovy, N.; Granier, A.; Ogée, J.; Allard, V.; Aubinet, M.; Buchmann, N.; Bernhofer, C.; Carrara, A.; et al. Europe-wide reduction in primary productivity caused by the heat and drought in 2003. Nature 2005, 437, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemani, R.R.; Keeling, C.D.; Hashimoto, H.; Jolly, W.M.; Piper, S.C.; Tucker, C.J.; Myneni, R.B.; Running, S.W. Climate-driven increases in global terrestrial net primary production from 1982 to 1999. Science 2003, 300, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Lai, C. Severe drought events inducing large decrease of net primary productivity in mainland China during 1982–2015. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 135541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, M.; Zeng, L.; Hu, W.; Wang, P.; Yan, Z.; He, W.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Xiao, W. The impacts of climate changes and human activities on net primary productivity vary across an ecotone zone in Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Guo, J.; Peng, Q.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, R. The effects of climate factors and human activities on net primary productivity in Xinjiang. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2020, 64, 765–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Y.; Wu, Z.F.; Yu, S.X. Quantitative assessment of the impacts of human activities on net primary productivity. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 28, 1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Dai, E.; Zheng, D.; Wang, Y.; Ma, L.; Tong, M. What drives the vegetation dynamics in the Hengduan Mountain region, southwest China: Climate change or human activity? Ecol. Indic. 2020, 112, 106013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, T.; Wang, J.; Fang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Huang, L.; Chen, Y. Assessing ecological risks caused by human activities in rapid urbanization coastal areas: Towards an integrated approach to determining key areas of terrestrial-oceanic ecosystems preservation and restoration. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 135153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, W.; Deng, L.; Wang, F.; Han, J. Quantifying the contributions of human activities and climate change to vegetation net primary productivity dynamics in China from 2001 to 2016. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 145648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Pei, F.; Wen, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Wu, C.; Cai, Y.; Wu, J.; Chen, J.; Feng, K.; et al. Global urban expansion offsets climate-driven increases in terrestrial net primary productivity. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.; Liu, X.; Bai, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yang, J.; Lin, K.; Pei, F.; Yan, Y. Determining the impacts of climate change and urban expansion on terrestrial net primary production in China. J. Environ. Manage. 2019, 240, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhoff, M.L.; Bounoua, L.; Ricketts, T.; Loucks, C.; Harriss, R.; Lawrence, W.T. Global patterns in human consumption of net primary production. Nature 2004, 429, 870–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Liu, Z.; He, C.; Gou, S.; Bai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shen, M. The occupation of cropland by global urban expansion from 1992 to 2016 and its implications. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 084037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krausmann, F.; Erb, K.H.; Gingrich, S.; Haberl, H.; Bondeau, A.; Gaube, V.; Lauk, C.; Plutzar, C.; Searchinger, T.D. Global human appropriation of net primary production doubled in the 20th century. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 10324–10329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welegedara, N.P.Y.; Grant, R.F.; Quideau, S.A.; Landhäusser, S.M.; Merlin, M.; Lloret, E. Modelling plant water relations and net primary productivity as affected by reclamation cover depth in reclaimed forestlands of northern Alberta. Plant Soil 2020, 446, 627–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Q.; Chen, X.; Ding, J.; Karamage, F. Isolating and quantifying the effects of climate and CO2 changes (1980–2014) on the net primary productivity in arid and semiarid China. Forests 2017, 8, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Bao, A.; Jiapaer, G.; Guo, H.; Zheng, G.; Jiang, L.; Chang, C.; Tuerhanjiang, L. Disentangling the relative impacts of climate change and human activities on arid and semiarid grasslands in Central Asia during 1982–2015. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 1311–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Cao, L.; Jia, J.; Gong, H.; Qi, X.; Xu, X. Effects of land use changes on the nonlinear trends of net primary productivity in arid and semiarid areas, China. L. Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 2183–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, R.; Peng, D.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, J.; Bai, J.; Li, Q. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Net Primary Productivity in China’s Urban Lands during 1982–2015. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhong, X.; Deng, S.; Xu, H. Assessment of the impact of LUCC on NPP and its influencing factors in the Yangtze River basin, China. Catena 2021, 206, 105542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, A.; Li, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hao, H.; Li, Y.; Sun, F.; Zhou, H.; Zhu, C.; Hao, X. The effects of ecological rehabilitation projects on the resilience of an extremely drought-prone desert riparian forest ecosystem in the Tarim River Basin, Xinjiang, China. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Li, H.B.; Liu, Y.J. Spatio-temporal differentiation and influencing factors of vegetation net primary productivity using GIS and CASA: A case study in Yuanyang county, Yunnan. Chin. J. Ecol. 2018, 37, 948–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, L.; Cheng, Y.; Ju, W.; Chen, H.Y.H.; Ruan, H. Afforestation promotes the enhancement of forest LAI and NPP in China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2020, 462, 117990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Piao, S.; Li, X.; Chen, A.; Qin, D. Global patterns of vegetation carbon use efficiency and their climate drivers deduced from MODIS satellite data and process-based models. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 256–257, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhang, X.; Tao, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, J.; Shi, P.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, C. The impact of climate change and anthropogenic activities on alpine grassland over the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 189–190, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.L.; Gong, R.; Wu, F.M.; Fan, W.W. Temporal and spatial variation characteristics of China shrubland net primary production and its response to climate change from 2001 to 2013. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2017, 41, 925–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rong, T.; Long, L.H. Quantitative Assessment of NPP Changes in the Yellow River Source Area from 2001 to 2017. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Zhuhai, China, 15–17 January 2021; Volume 687. [Google Scholar]
- He, C.; Tian, J.; Gao, B.; Zhao, Y. Differentiating climate- and human-induced drivers of grassland degradation in the Liao River Basin, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.; Jia, J.; Liu, H.; Lin, Z. Relative importance of climate change and human activities for vegetation changes on China’s silk road economic belt over multiple timescales. Catena 2019, 180, 224–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Wang, K.; Yue, Y.; Brandt, M.; Liu, B.; Zhang, C.; Liao, C.; Fensholt, R. Quantifying the effectiveness of ecological restoration projects on long-term vegetation dynamics in the karst regions of Southwest China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 54, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Shen, H.; Li, X.; Gan, W.; Zhang, L. A long-term and comprehensive assessment of the urbanization-induced impacts on vegetation net primary productivity. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 669, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhou, S.; Chen, D.; Wei, Z.; Dai, L.; Li, X. Determining the contributions of urbanisation and climate change to NPP variations over the last decade in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Jiang, H.; Chen, Y.; Cai, Z. Spatial-temporal patterns of net primary production in Anji (China) between 1984 and 2014. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 110, 105954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Feng, Z.; Zhao, H.; Wu, K. Identification of ecosystem service bundles and driving factors in Beijing and its surrounding areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 134687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Adhikari, K.; Zhuang, Q.; Gu, H.; Jin, X. Impacts of urbanization on soil organic carbon stocks in the northeast coastal agricultural areas of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 721, 137814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijhuis, S.; Xiong, L.; Cannatella, D. Towards a Landscape-based Regional Design Approach for Adaptive Transformation in Urbanizing Deltas. Res. Urban Ser. 2021, 6, 55–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Wang, L.; Fu, M.; Huang, N. An integrated system for rapid assessment of ecological quality based on remote sensing data. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 32779–32795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, C.; Ban, Y.; Li, S. Open access to Earth land-cover map. Nature 2014, 514, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, X. A harmonized global nighttime light dataset 1992–2018. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Gang, C.; An, R.; Li, J. Vegetation dynamics and its driving forces from climate change and human activities in the Three-River Source Region, China from 1982 to 2012. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 563–564, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. A time-series approach to detect urbanized areas using biophysical indicators and landsat satellite imagery. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 9210–9222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Tao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhou, G. Spatiotemporal distribution of net primary productivity and its driving factors in the Nanliu River basin in the Beibu Gulf. Shengtai Xuebao/Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 8156–8171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, M.; He, S.; Gan, M.; Yang, L.; Wang, K. Impacts of urbanization and landscape pattern on habitat quality using OLS and GWR models in Hangzhou, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huilei, L.; Jian, P.; Yanxu, L.; Yi’na, H. Urbanization impact on landscape patterns in Beijing City, China: A spatial heterogeneity perspective. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 82, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonit, S.; Perrings, C. Bundling ecosystem services in the Panama Canal watershed. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9326–9331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapio, P. Towards a theory of decoupling: Degrees of decoupling in the EU and the case of road traffic in Finland between 1970 and 2001. Transp. Policy 2005, 12, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, C.; Chen, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, Y. A three-step strategy for decoupling economic growth from carbon emission: Empirical evidences from 133 countries. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 646, 524–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, M.; Qiu, S.; Wu, J. Urbanization impact on the supply-demand budget of ecosystem services: Decoupling analysis. Ecosyst. Serv. 2020, 44, 101139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, M.; Luo, J. The tapio decoupling principle and key strategies for changing factors of chinese urban carbon footprint based on cloud computing. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Cai, W.; Cai, W.; Dong, L. Whether carbon intensity in the commercial building sector decouples from economic development in the service industry? Empirical evidence from the top five urban agglomerations in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 222, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S. Has “The Outline of the Plan for the Reform and Development of the Pearl River Delta” Promoted to the Coordination of Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. Mod. Econ. 2019, 10, 1348–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Luo, Y.; Wu, J. Decoupling Relationship between Urbanization and Carbon Sequestration in the Pearl River Delta from 2000 to 2020. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 526. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030526
Li X, Luo Y, Wu J. Decoupling Relationship between Urbanization and Carbon Sequestration in the Pearl River Delta from 2000 to 2020. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(3):526. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030526
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xuechen, Yuhang Luo, and Jiansheng Wu. 2022. "Decoupling Relationship between Urbanization and Carbon Sequestration in the Pearl River Delta from 2000 to 2020" Remote Sensing 14, no. 3: 526. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030526
APA StyleLi, X., Luo, Y., & Wu, J. (2022). Decoupling Relationship between Urbanization and Carbon Sequestration in the Pearl River Delta from 2000 to 2020. Remote Sensing, 14(3), 526. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030526




