Abstract
Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) ship recognition can obtain location and class information from SAR scene images, which is important in military and civilian fields, and has turned into a very important research focus recently. Limited by data conditions, the current research mainly includes two aspects: ship detection in SAR scene images and ship classification in SAR slice images. These two parts are not yet integrated, but it is necessary to integrate detection and classification in practical applications, although it will cause an imbalance of training samples for different classes. To solve these problems, this paper proposes a ship recognition method on the basis of a deep network to detect and classify ship targets in SAR scene images under imbalance data. First, RetinaNet is used as the backbone network of the method in this paper for the integration of ship detection and classification in SAR scene images. Then, taking into account the issue that there are high similarities among various SAR ship classes, the squeeze-and-excitation (SE) module is introduced for amplifying the difference features as well as reducing the similarity features. Finally, considering the problem of class imbalance in ship target recognition in SAR scene images, a loss function, the central focal loss (CEFL), based on depth feature aggregation is constructed to reduce the differences within classes. Based on the dataset from OpenSARShip and Sentinel-1, the results of the experiment suggest that the the proposed method is feasible and the accuracy of the proposed method is improved by 3.9 percentage points compared with the traditional RetinaNet.
1. Introduction
For the past few years, due to the prompt growth of radar imaging technology, great progress has been made in the synthetic aperture radar (SAR) field. Possessing a special imaging mechanism, SAR is not influenced by weather, light and other environmental factors, thus being able to monitor the target at any time [1,2]. In addition, ship target interpretation plays a vital role for a contemporary intelligent maritime monitoring machine [3]. In SAR images, ship target interpretation has turned into a hot research field and has long become a focus in academia and even industry.
Traditionally, the SAR automatic target recognition (ATR) [4] system consists of the following parts, which are, respectively, preconditioning, detection and classification. Some classical ATR methods have been described in the literature [5,6,7,8,9]. Typical detection methods incorporate the constant false alarm rate (CFAR) algorithm [10]. However, it is not very effective for the CFAR method to suppress clutter and control nearshore false alarms. Recently, some improved methods for CFAR have gradually emerged [11], and the recognition part has consisted of feature extraction as well as classification. There are also a number of algorithms for feature extraction, which are described in [12,13]. For classification methods, there are several common classification examples in [14]. The conventional SAR ATR algorithms are heavily dependent on manual features while the generalization ability is relatively poor. The classification accuracy of the system is affected by the problems at any stage. In addition, when there is rapid improvement in the field of SAR picture processing, great limitations have appeared for traditional methods in the detection and classification stage.
However, the generation of deep networks has changed the steps of traditional ATR methods, and it is very easy to achieve automatic classification of objects. Although the ATR technology in optical images is very mature and widely used in all walks of life, the characteristics of SAR ship targets are scarcer compared to optical images under the same conditions. Nowadays, ship detection for SAR scene images does not require sea–land division and the detection accuracy is relatively high [15,16,17,18,19]. On the basis of deep networks, the precision of ship classification for SAR slice images has gradually improved [20,21]. However, it is not ideal for the current application of chip-based classification methods in practical scenarios. In line with the size of ships in SAR images, a deep network approach has been adopted for detecting and roughly classifying ships [22]. In recent years, an intelligent SAR ship target classification framework has also appeared [23], but ship detection for SAR scene images and ship classification for SAR slice images have not been integrated.
At present, both the detection effect in SAR scene images and the classification effect in SAR slice images have reached a very high level. Taking SAR scene images as an example, the detection accuracy of SSDD, a public data set in the SAR image field, has reached more than 90% [24], while when taking SAR slice images as an example, the classification accuracy of MSTAR, a public data set in the SAR image field, has reached more than 95% [25]. In practice, it is necessary to integrate ship detection for SAR scene images and ship classification for SAR slice images, but this causes an imbalance of different classes of training samples [26]. This is because when SAR scene images are directly used for detection and classification, the number of different ship classes often varies greatly, resulting in this problem. There are also typical examples of class imbalance in everyday life, such as cancer detection [27] and credit card fraud detection [28]. This class imbalance problem leads to a performance degradation of existing models [29], the main reason being that during the training procedure, the model focuses more on the classes possessing more fitting samples and less on the classes with a smaller number of samples. Nowadays, there are two main ways to cope with this issue. An easy way to do this is through data [30,31]. By sampling, the method depending on data can make the overall training data close to being balanced, which signifies the number of samples of various classes is basically the same; the other way is achieved from the perspective of algorithm optimization. By optimizing the loss function [32,33,34], the phenomenon of “under-learning” the classes which include less training samples is corrected [35]. In addition, there are often few distinctive features for different ships, but a large number of similar features [36].
The method of data reuse is simple and intuitive. A good oversampling [37] or undersampling [38] model is able to productively increase its expressive capacity, but there are also some shortcomings for oversampling and undersampling methods. Oversampling techniques can easily lead to overfitting of the model to repeated samples. In order to minimize overfitting caused by oversampling techniques, techniques such as synthetic minority oversampling technique (SMOTE) [39] are used to generate samples of infrequent classes. In addition, the undersampling technology reduces the training data of each class, thus causing a declining expression of the training model and leading to issues such as underfitting. In the literature [40,41,42], migration learning with optical datasets and simulated SAR datasets to deal with data imbalance has been demonstrated. However, the data-level method does not consider the essence of solving the problem of imbalanced classes.
In contrast, the methods based on an algorithm utilize cost-sensitive learning methods to improve the classification module [32,33,43]. The weight redistribution method is regarded as a cost-sensitive method, and the basic idea of the cost-sensitive method for class imbalance is to distribute different weights to different classes. The methods based on an algorithm are mainly the following ones: Focal Loss was proposed for figuring out the issue of the ratio of positive and negative examples not being balanced in a one-stage target detection, and the effect were still significant in the problem of class imbalance [44]. Reference [45] proposed a marginal loss function based on label distribution awareness that could focus more on minority classes. An innovative loss function was also proposed to figure out the question of imbalanced classes in SAR images, and it achieved good results as well [46].
The above studies show that deep learning is growing rapidly within the scope of ship detection for SAR scene images and ship classification for SAR slice images, but the integration of the two, namely ship recognition in SAR scene images, has not been realized. In addition, in the process of realizing ship recognition, that is, being able to detect and classify ships in SAR scene images, there is serious class imbalance problem and high class feature similarity. Therefore, in this paper, a ship target recognition method including detection and classification for SAR scene images is proposed firstly. Secondly, for the problem of the high similarity of ship class features, the squeeze-and-excitation (SE) structure is introduced for amplifying the difference features as well as reducing similar features. Thirdly, for the sake of solving the issue of imbalanced classes induced by ship recognition in SAR scene images, that is, being able to detect and classify ships, an innovative loss function is put forward on the basis of the original loss function.
This paper integrates ship detection in SAR scene images with the ship classification in SAR slice images, thus realizing ship recognition for SAR scene images. In the meantime, the improvement is applied to the issue of imbalanced classes and the high class feature similarity problem in the recognition process. In the second section, the proposed methods are introduced as well as how they can be improved, and in the third section, experiments are conducted to validate the proposed methods.
2. Method
In this section, an image-based method for recognizing ships in SAR scenes is proposed, and its network structure and loss function are improved. Firstly, considering that SAR scene image detection of ships and SAR slice image classification of ships are relatively simple, a recognition method which can detect and classify ship targets in SAR scene images is presented. Then, the SE module is added to improve our network’s structure. Finally, the proposed method is enhanced by introducing an innovative loss function.
2.1. The Recognition Network in SAR Scene Images
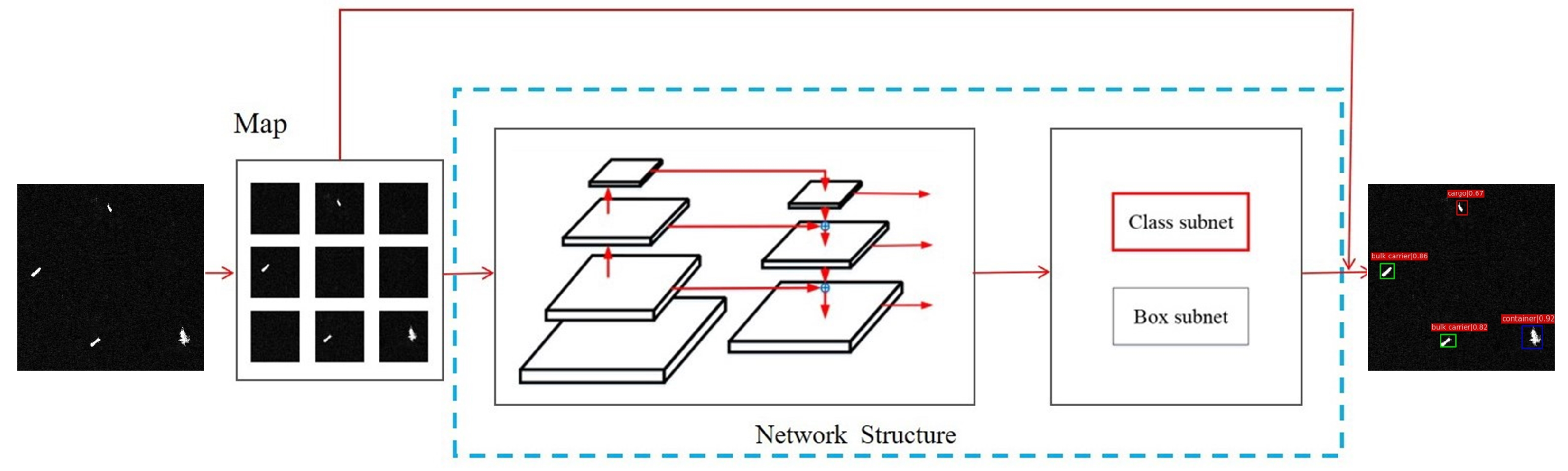
As mentioned above, at present, ship detection in SAR scene images and ship classification in SAR slice images have not been integrated. Therefore, we propose a method which is able to recognize ships in SAR scene images. Figure 1 illustrates our presented method’s diagram. This method is capable of completing the recognition of ships including ship detection as well as ship classification in SAR scene images and is mainly composed of three parts. The first part is the image preprocessing part, which gets the same-size image by fast sliding cutting. The second part is the deep network module, which mainly extracts target features for detection and classification. The third part is the resulting image composition, which combines the predicted small images into the original image. Each part of the recognition network is described in detail below.
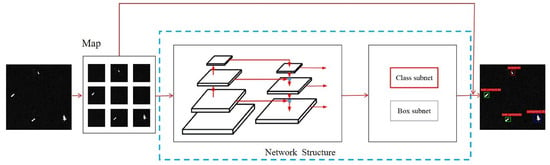
Figure 1.
The diagram of our presented method.
2.1.1. Image Preprocessing
Through image preprocessing, the irrelevant information in the image can be eliminated and the useful real information can be recovered. At the same time, the detectability of related information is enhanced and the data are simplified to the greatest extent [47]. For this paper, the preprocessing method for images was mainly to perform a geometric transformation, then image enhancement and finally, image segmentation. In this way, the SAR image of a large scene can be segmented into multiple images of the same size, which are then transmitted to the network backbone for the next step of the recognition.
2.1.2. Network Base
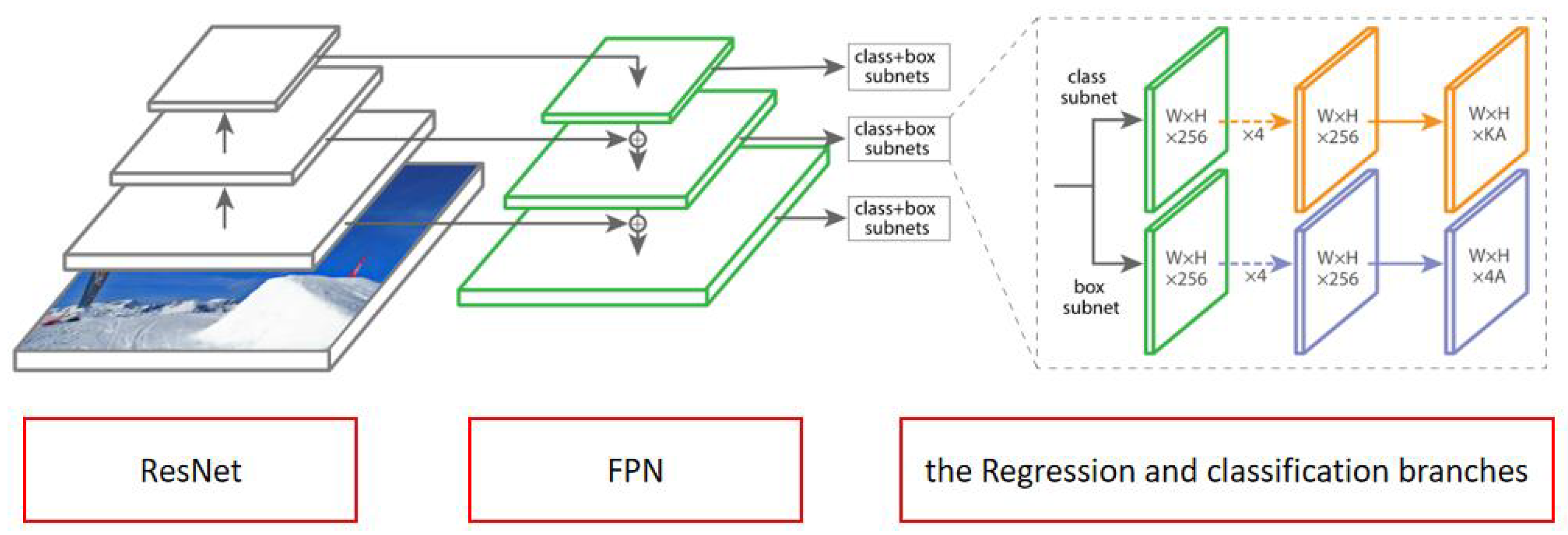
As the entire framework for the network, RetinaNet [44] was chosen; it mainly consists of three parts, namely, the backbone network ResNet [48], the neck feature pyramid network (FPN) [49], the regression and classification branches. Figure 2 illustrates the network structure of RetinaNet, and each part of its network is going to be discussed.
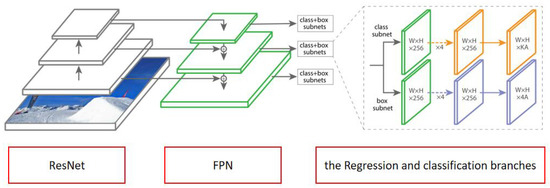
Figure 2.
A diagram of RetinaNet’s network structure.
The first part is the backbone network, which uses a deep residual network, ResNet, corresponding to the leftmost part of Figure 2. When solving a complex problem, a large number neural networks is usually used for modeling to obtain better performance. However, as a result of the increase in the number of layers of the networks, it not only consumes a lot of training resources, but also leads to the instability of the reverse transmission gradient in the network, thus making the network’s weight reduce. To solve this problem, ResNet uses skip connections to make deeper network structures easy.
The second part is the neck, in which the feature pyramid network (FPN) is adopted, shown in the neutral position in Figure 2; it improves the richness of convolutional networks by adopting top-down directional and lateral connection methods. At the same time, single-resolution images can be constructed by FPN, resulting in a large number of multiscale feature pyramids, and each pyramid can be used to detect different object sizes.
The third part is the regression and classification branches, shown on the far right of Figure 2. Each layer of the FPN is followed by a classification and bounding-box regression subnetwork in order to generate the target class and a rotating bounding box. Both the classification and bounding-box regression branches follow roughly the same design, but no parameters are shared between them.
2.1.3. The Generation of Result Images
A result image is the final result obtained by combining the subimages according to the segmentation relationship.
2.2. The Improved Classification Subnetwork
For different classes of ships, the differences between them are not very obvious, which causes great difficulties for ship classification. However, the current classification network can only classify major classes. Some examples are road and building classification [50] in SAR images as well as ship classification, but the network cannot match ship classification accuracy. As a result of ships’ small size, it is difficult to extract features. Another reason is that the features of different ship classes are very similar, and it is difficult to distinguish them.
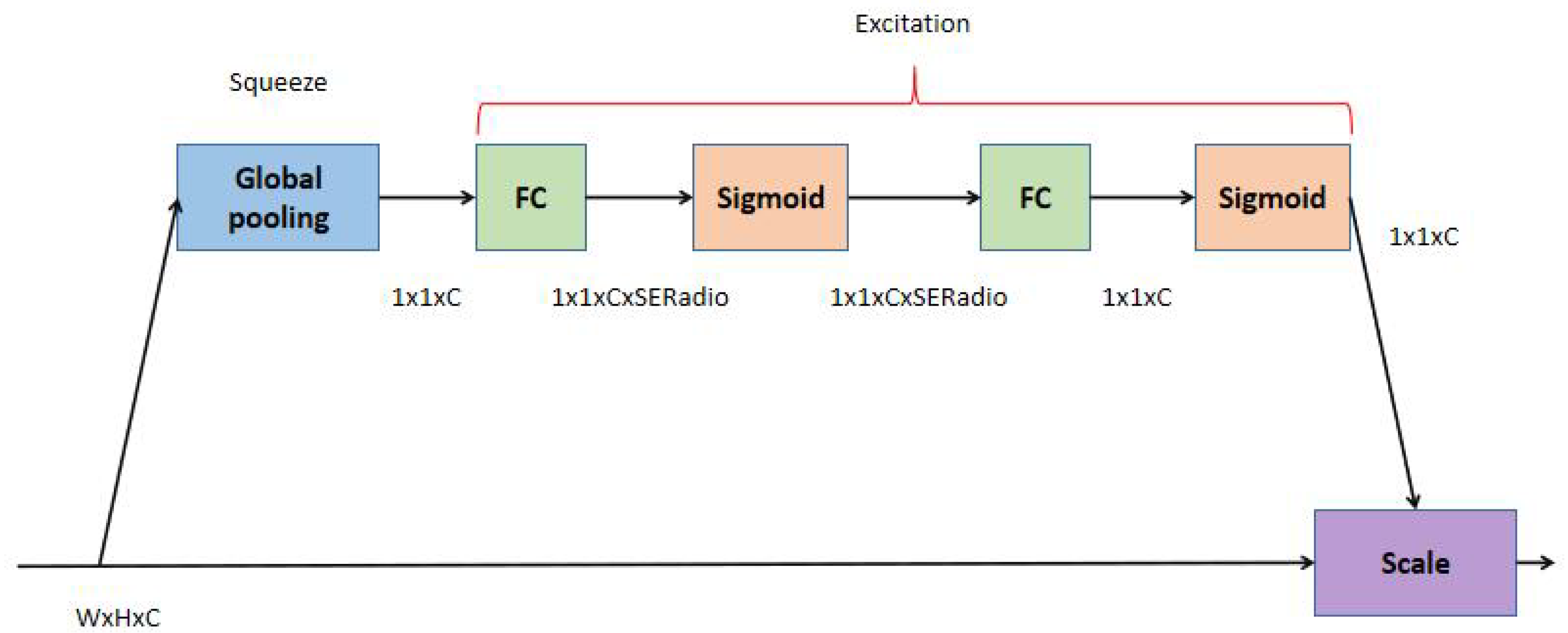
Therefore, we introduce the squeeze-and-excitation (SE) [51] method to increase the distinguishing features and reduce similar features to solve the existed issue of a high degree of similarity between the features of the classes.
As shown in Figure 3, the SE module consists primarily of a pooling layer, two fully connected layers as well as two sigmoid activation functions. For the feature map with input size WxHxC, a global average pooling is used to compress the feature map into a 1 × 1 × C vector. The excitation operation is then carried out, mainly through two fully connected layers, while a sigmoid activation function follows each of them. Finally, the scale operation is carried out, which means the channel weights are multiplied.
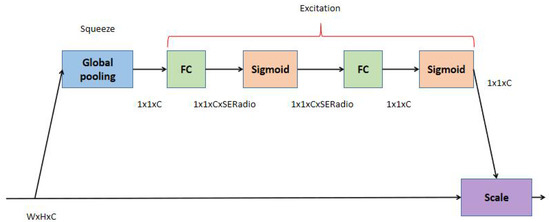
Figure 3.
SE module.
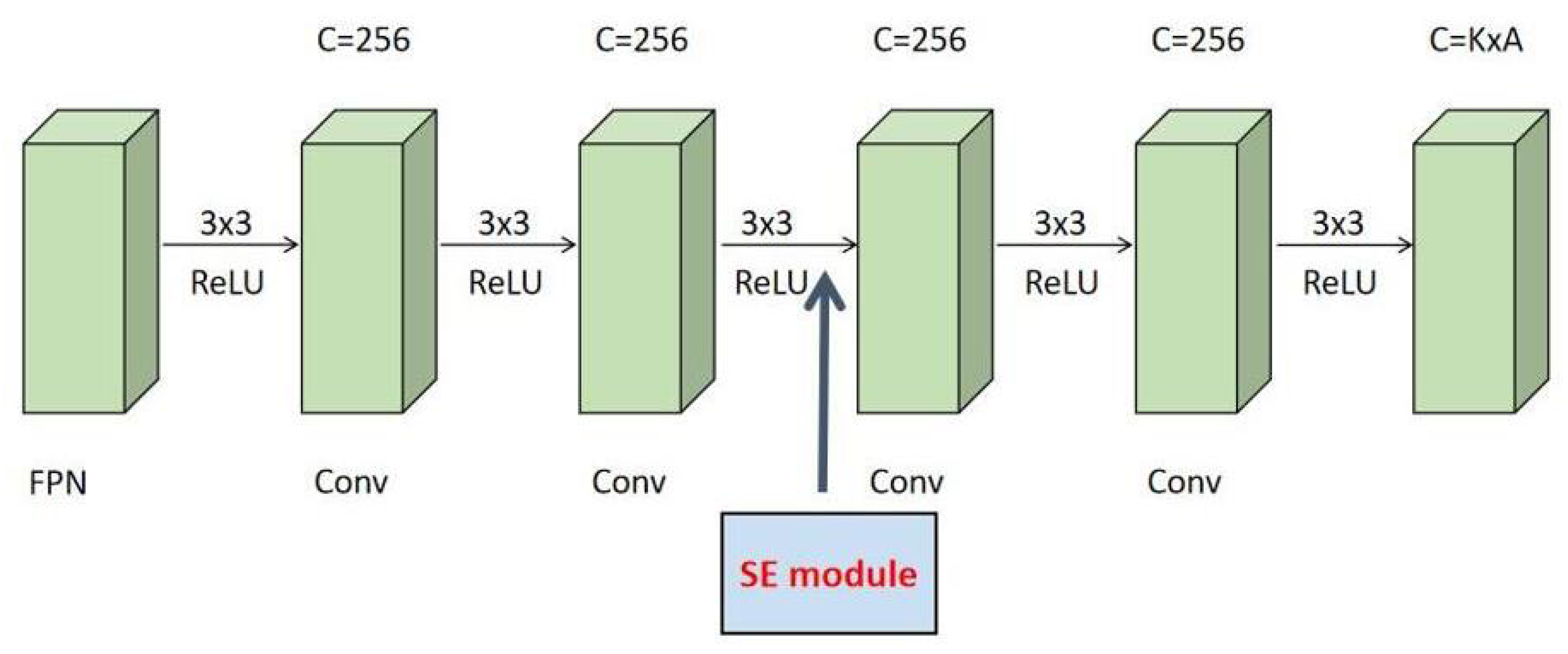
In the network of this paper, by adding an SE module at the beginning of the third convolutional layer that is shown in Figure 4, a feature channel’s importance can be automatically obtained according to the current task so as to promote useful features. Of course, the feasibility is based on the good portability of the SE module.
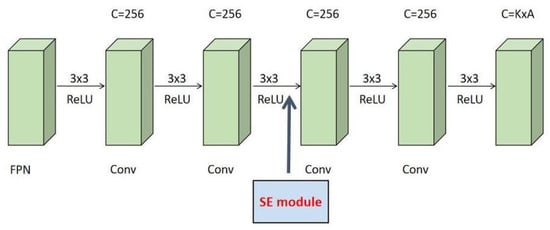
Figure 4.
Location diagram of the SE module.
2.3. The Improvement of the Loss Function under Imbalance Data
Performing ship recognition in SAR scene images leads to the generation of a class imbalance problem, which is mainly manifested in the form of underlearning for classes with few samples. The general solution is to start from a cost-sensitive point of view. In other words, it is to increase the cost of misclassification of the class with few examples in the loss function. This allows the network model to be adjusted by optimizing the loss function, in order for the network’s attention to be directed toward classes with fewer samples. At present, with the focal Loss, weights are modified so that infrequent classes have a large weight and frequent classes have a small weight.
The appearance of the focal loss helps to attenuate the influence caused by the class imbalance in the one-stage target detection. From a functional point of view, it is an improvement on the basis of the cross-entropy loss function. Furthermore, the form for the binary cross-entropy loss function is:
where for a positive sample , the larger the output probability p, the smaller the loss; for a negative sample , the smaller the output probability , the smaller the loss.
The focal loss is an improvement based on the above cross-entropy, increasing a new parameter, the factor, mainly to decrease the loss of easy-to-classify samples, so as to concentrate more on hard-to-classify samples. For the imbalanced proportion of positive and negative examples, a balance factor is added to figure it out. In particular, the weight of negative samples with high frequency is reduced, while the weight of positive samples with low frequency is increased. The focal Loss can be calculated by the following formula:
Some concerned researchers conducted extensive experiments to arrive at the best values of the parameters, namely, and . Therefore, we can get the final formula for the focal loss as:
Through the focal loss, the false alarms in the background can be effectively suppressed, but the classification accuracy of ships in SAR images is still very low.
The loss function used for classification when introducing RetinaNet in Section 2.1 is the focal loss, which is an improvement on the cross-entropy loss function and can reduce the loss of easy-to-classify samples and focus more on difficult and misclassified samples. However, the feature spaces based on both cross-entropy and softmax loss function have the situation that the deep features are scattered, and the deep features are not sufficiently discriminative because they show significant intraclass differences [52]. Therefore, the network is limited to directly using these features for classification, so it is necessary to further enhance the compactness of intraclass features while keeping different classes separable.
Inspired by the literature [53], in order to enhance the intraclass compactness, we improved the original loss function and propose the central focal loss (CEFL), which obtains the class center by finding the 2-norm from the feature point to the feature center. The expression of this loss function is as follows:
where represents the average feature of all sample features of the class corresponding to sample i or the class center of class , corresponds to the features prior to the fully connected layer, while m represents the batch size. As a weight factor, the parameter is used for adjusting the ratio between both parts of the loss function.
For the parameter , the adjustment does not adopt an ordinary linear relationship, but uses an exponential function with relatively large changes, so as to better shorten the training time and find the optimal value of the parameter . The exponential form of is as follows:
Thus, the central focal loss has the following form:
In the formula, directly affects the entire loss function above. We still choose the optimal value of the parameter of the focal loss as the first half of central focal loss. There are two reasons for that: On the one hand, this loss function increases the focus on the intraclass features based on the original loss function to improve the classification effect, which corresponds to the second half of equation. We did not adjust the parameters of the first half to verify the effect of the second half. On the other hand, based on the idea of the control variable method, adjusting the newly added parameters under the condition of choosing the optimal values of the existing parameters tends to obtain the best model results in the most efficient way. The formula shows that when the loss is smaller, the classification is easier.
3. Experiments
For the purpose of testing the feasibility of our proposed method, experiments and analysis were conducted and are presented in this section in three parts: (1) the configuration of the experiment, including the hardware environment of the experiment and the data set required by the experiment; (2) SAR image tests of a simple and a complex background, including a nearshore SAR image with a complex background and a large far-shore scene SAR image, which demonstrate the recognition effect by the presented algorithm; (3) an ablation experiment is conducted on the improved classification branch and the proposed new loss function, and the test mAP of several typical SAR target detection algorithms are compared, which fully reflect the availability of our proposed method.
3.1. Experimental Configuration
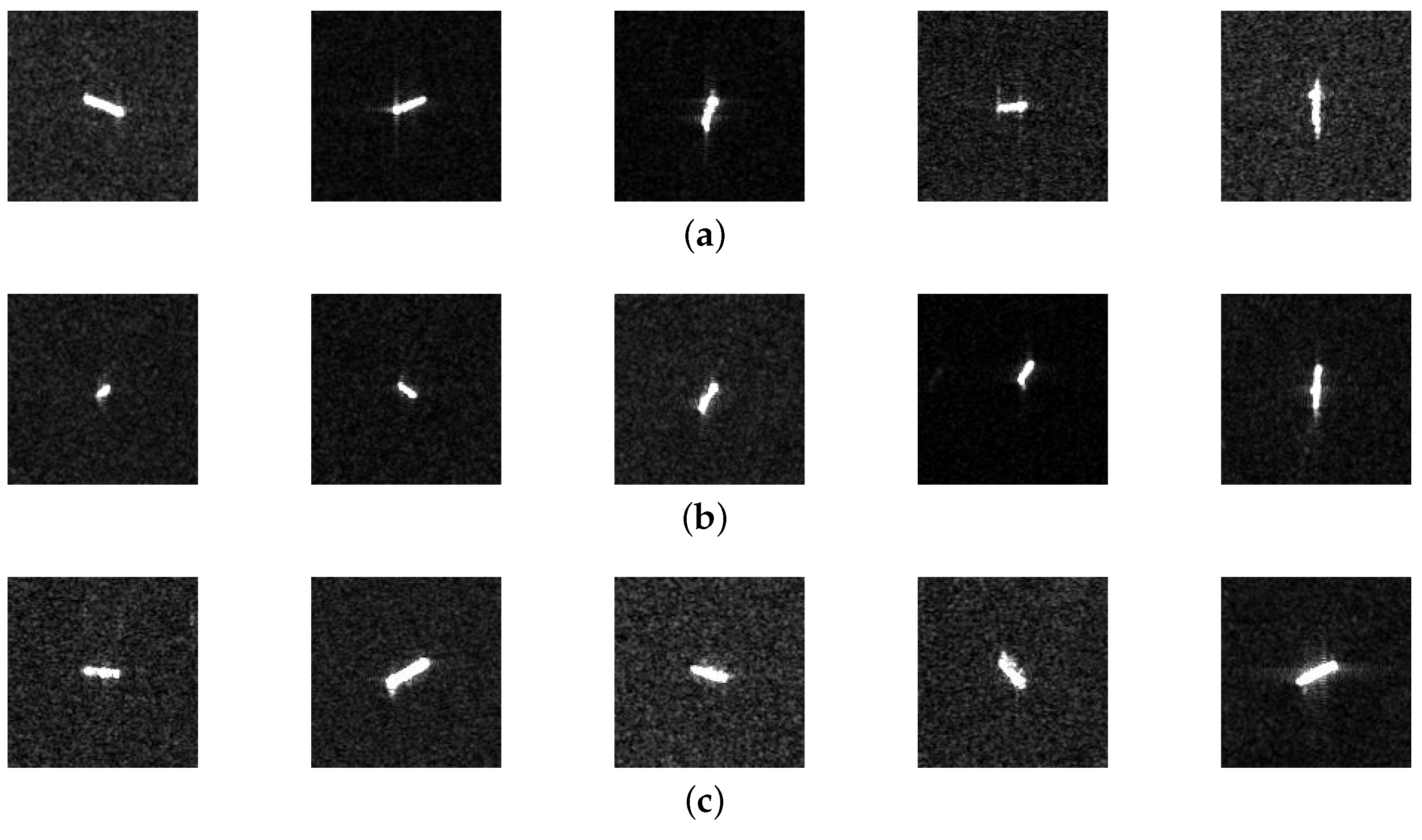
The data sources of the experiment were mainly OpenSARShip [21] and Sentinel-1 [22], which were mainly designed for the recognition of sea targets. At the same time, five representative ports with dense maritime traffic were selected, and then parts of the data were screened through manual screening and an AIS cross-validation. A total of 990 images including three classes of ships were selected. In Figure 5, the ships of three classes of ships are revealed.
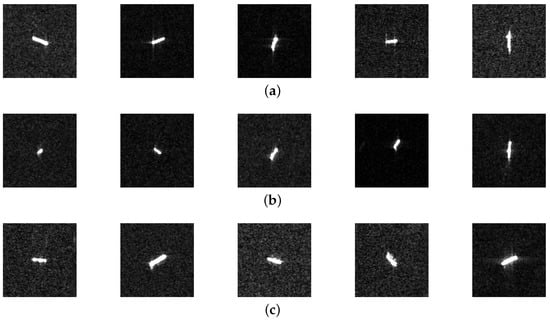
Figure 5.
The three types of SAR image chips available for ships: (a) bulk carrier ships; (b) cargo ships; (c) container ships.
During the test, all experiments were carried out in the pytorch 1.6.0 environment. An NVIDIA GTX1080 GPU as well as an Intel Core i7-8700k CPU were used for network training on the computer. In order to better carry out the experiment, we divided the 990 data pictures into training data and test data with a ratio of 9:1, and we set the learning rate value as 0.0001 and the maximum number of iterations to 96. In the training set, the proportion of the quantity of ships in the three classes was approximately 1:1:2. In addition, as our network’s initialization model, resnet50 was utilized.
3.2. Assessment Criteria
We selected a variety of evaluation indicators to evaluate the expression of our presented algorithm, which incorporate the recall rate, average precision (AP) as well as the mean average precision (mAP). The evaluation index can be calculated through four parts that consist of true positive (TP), false positive (FP), true negative (TN) and false negative (FN). For each class of ships, TP and FN represent the number of ships which are properly recognized as that class and the number of ships which are not recognized as that class, respectively. TN and FP represent the number of ships that are not in that class correctly identified as the ships that are not in that class and the number of ships that are not in this class incorrectly identified as ships in that class, respectively.
For each class of ships, the recall rate refers to the proportion of the number of properly recognized ships in that class to the total number of ships in that class. It is calculated as
For each class of ships, AP is employed for recognizing the average accuracy of such ships. It is calculated as
where P corresponds to the value of a certain point of the precision rate, while R is representative of the value of a certain point of the recall rate. In addition, the mAP is the mean of the AP of each class.
3.3. The Proposed Recognition Method Validation Experiment
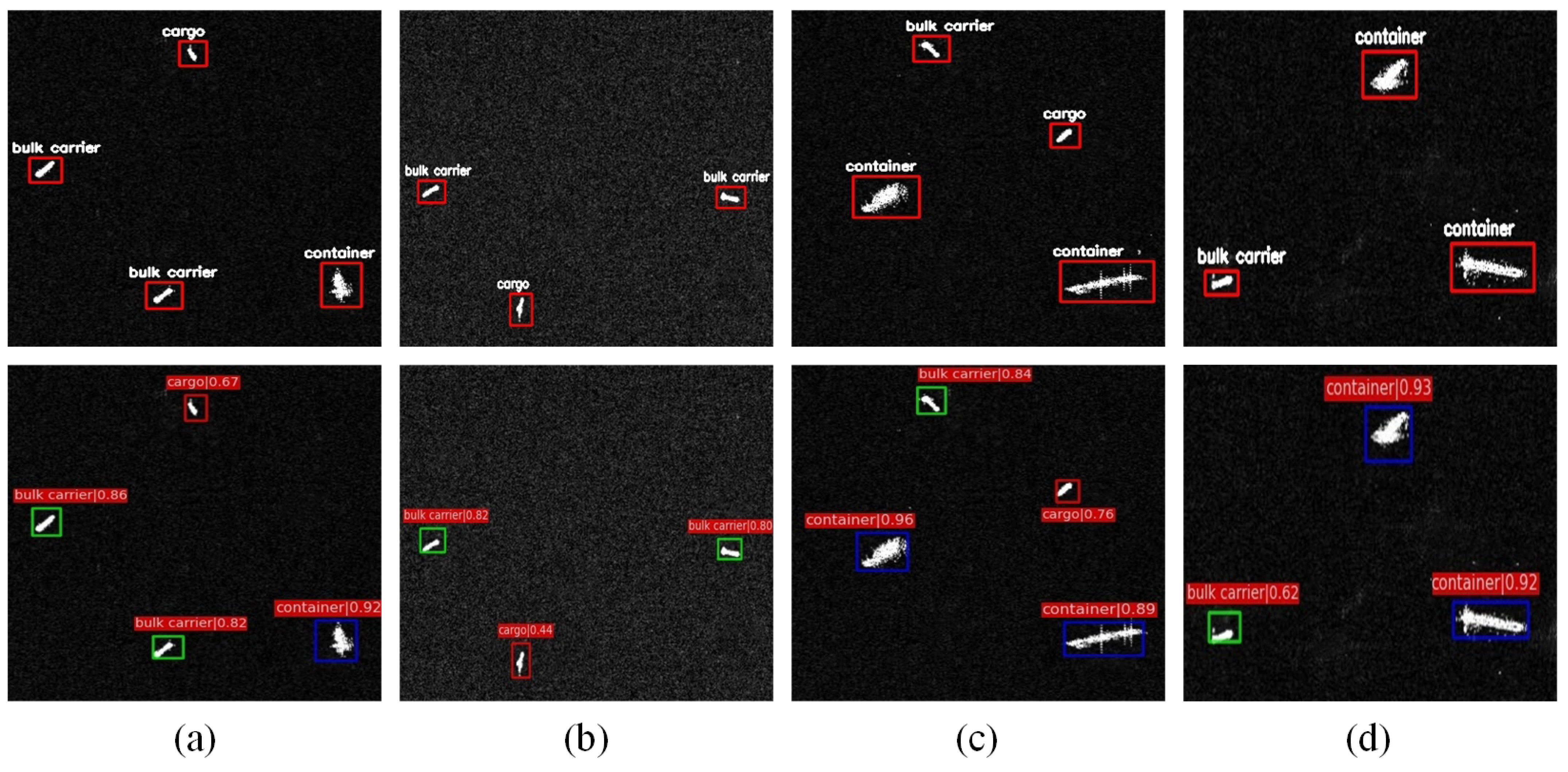
For the objective of examining our proposed recognition mean for SAR scene images, the ship targets in a simple background and a complex background in SAR images were tested, respectively. In Figure 6, the test results of the ship targets with a simple background are demonstrated, while in Figure 7 and Figure 8, the test results of ships in a complex background are shown.
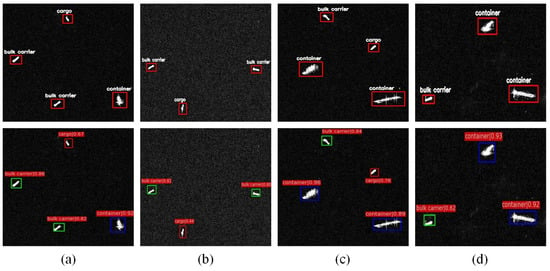
Figure 6.
Simple background ship target experiments. All images at the top are images with truth boxes, and the images at the bottom are images of the detection results of our method.
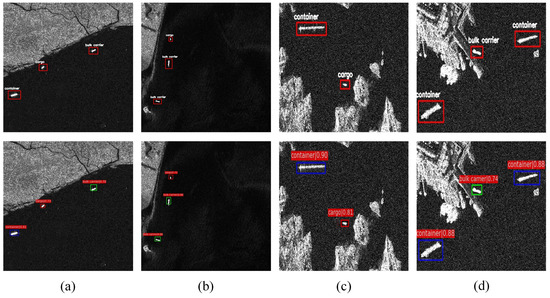
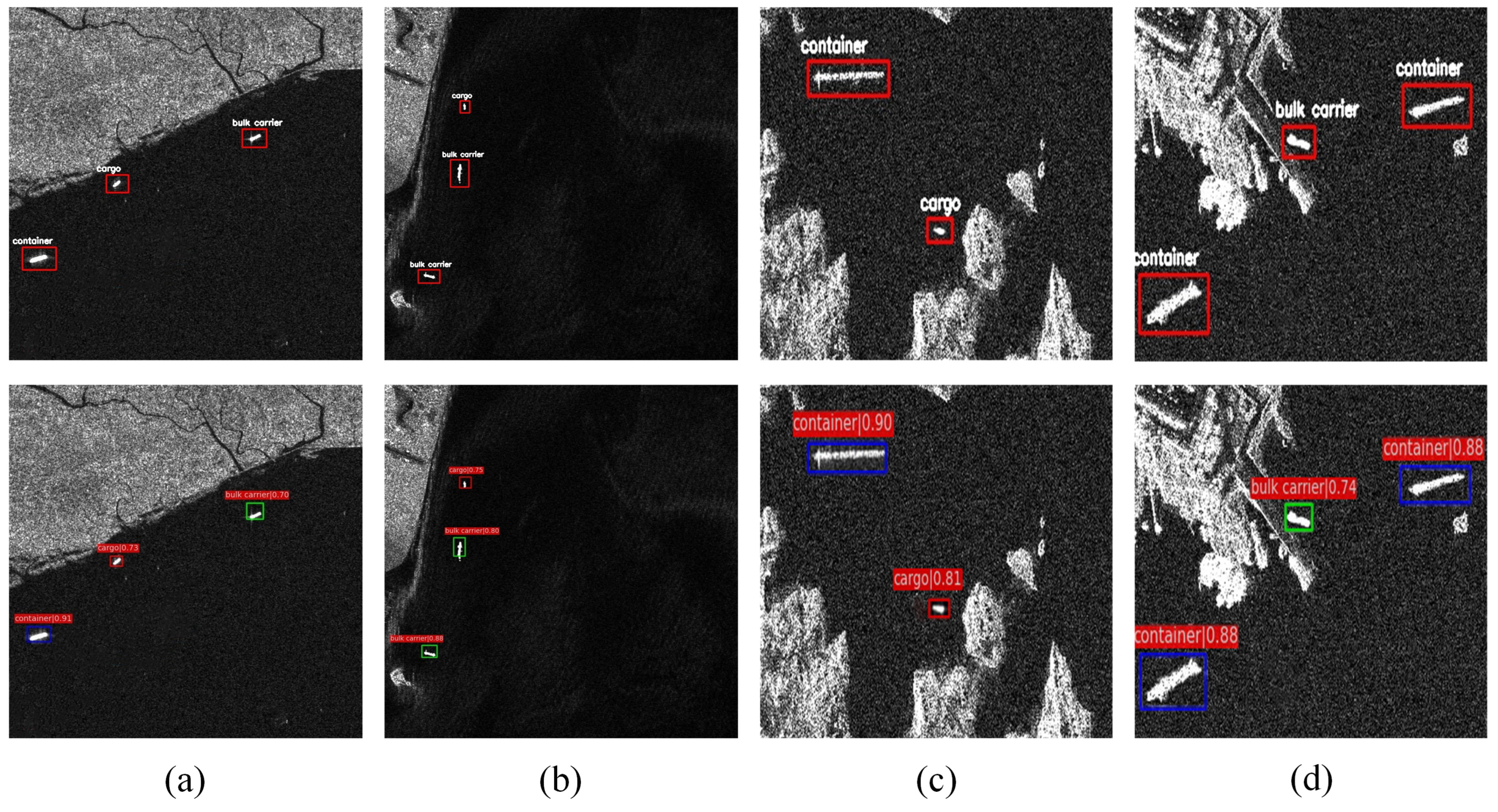
Figure 7.
Nearshore background ship target experiments. All images at the top are images with truth boxes, and the images at the bottom are images of the detection results of our method.
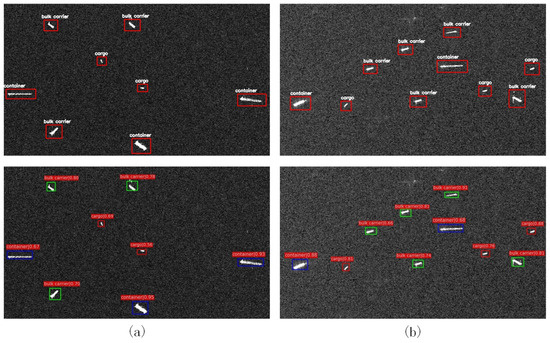
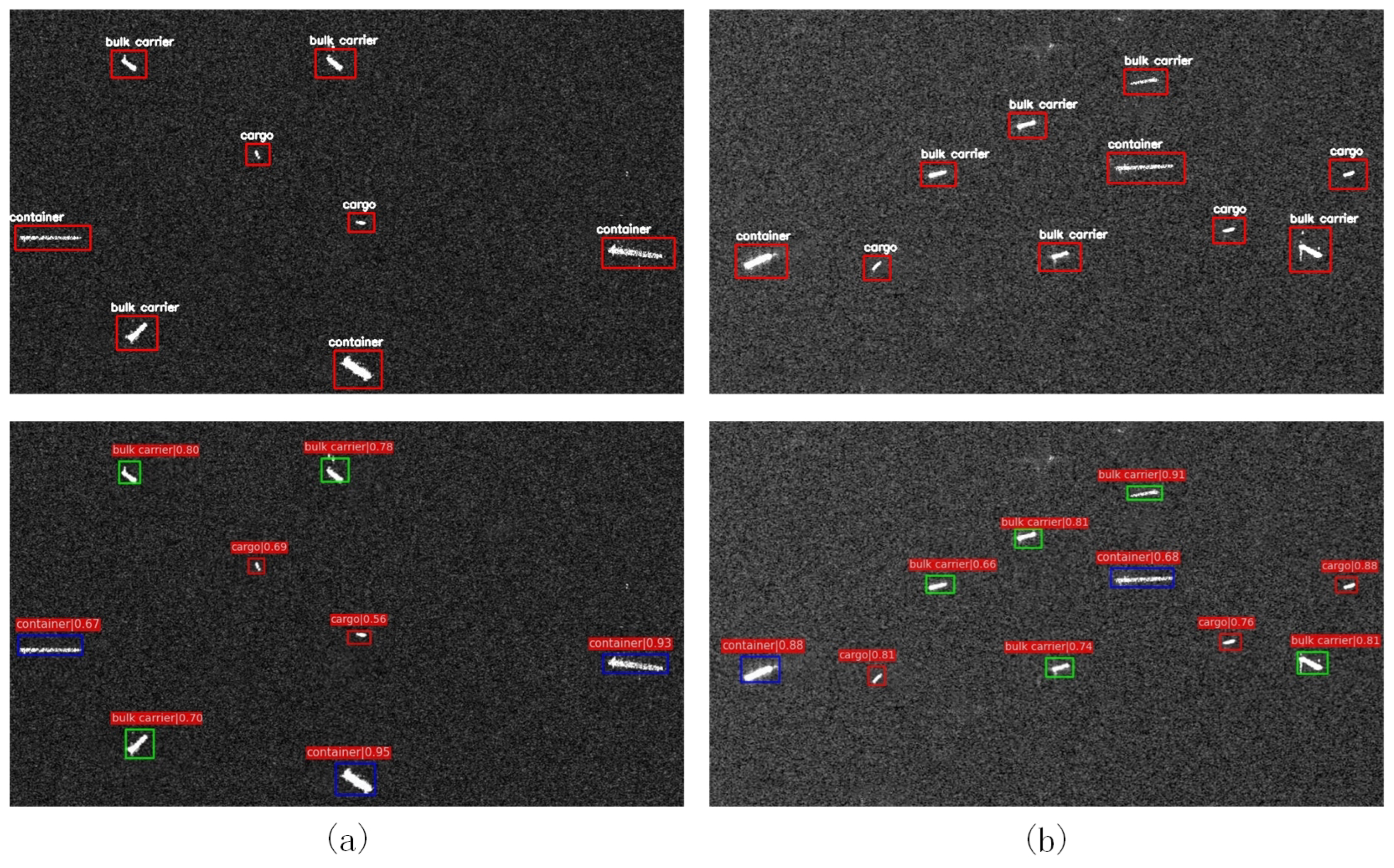
Figure 8.
Ocean experiments in large SAR scene. The images at the top are with the target truth boxes, and the images at the bottom are the detection results of the proposed method.
As shown in Figure 6, through the contrast of the truth box and the detection box for four simple background images, it was found that the ship recognition method had a pretty good effect on multiclass simple background images.
The next experiments were carried out according to the adjacent shore background and ocean scene images, through which the feasibility of the proposed recognition method was further demonstrated.
It can be seen from Figure 7, in nearshore complex background images, whether they were weakly or strongly reflective images, our proposed recognition method could detect as well as classify ships well, and the false alarm from nearshore images could be well inhibited.
Moreover, as can be seen from Figure 8, when faced with large-scene images on the far shore containing various ship targets, the targets could still be recognized well by our method.
3.4. Comparison Experiments
For the purpose of examining the effect of the classification branch for the mesh structure improvement of Section 2.2 and the new classification loss function proposed in Section 2.3, several comparison experiments were conducted.
In Table 1 and Table 2, there are six parameters enumerated as follows: Class 1 (the class of the boat is bulk carrier), Class 2 (the class of the boat is cargo), Class 3 (the class of the boat is container ship), recall, AP, mAP.

Table 1.
Ablation experiment with RetinaNet.

Table 2.
Contrast results of disparate algorithms.
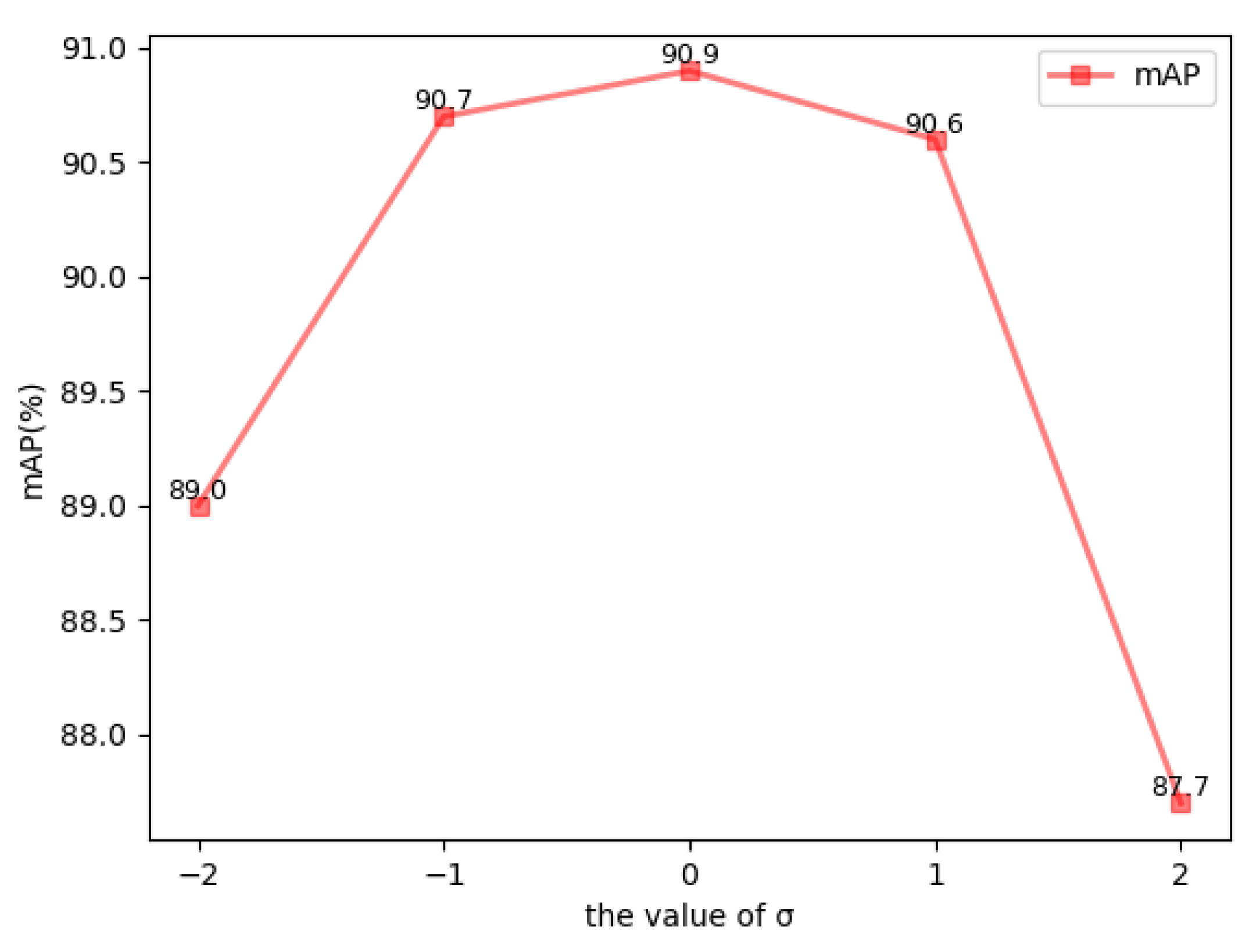
3.4.1. The Choice of the Parameter in the Central Focal Loss
It can be seen from Equation (6) that the parameter is used to adjust the ratio of the two parts of the central focal loss.
The mAP value on the test set when takes different values is shown in Figure 9. As can be seen from the picture, when is zero, the value is one, and the maximum mAP value on the test set is 90.9%.
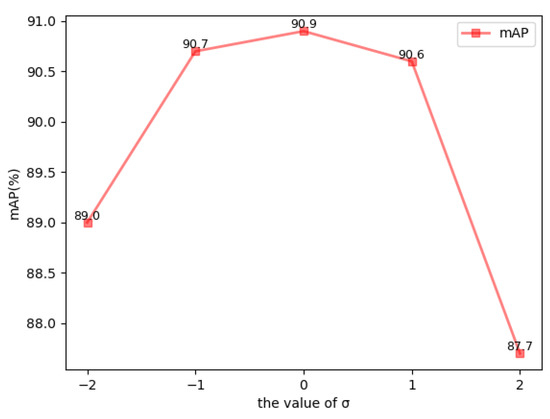
Figure 9.
Test set mAP changes with parameter .
3.4.2. Ablation Experiment with RetinaNet
As shown in Table 1, using identical data, ablation experiments were performed on the RetinaNet module.
From Table 1, we can draw the conclusion that after appending the SE module and central focal loss, the recall rate, AP and mAP on the dataset all have a noticeable improvement. Replacing focal loss with central focal loss alone resulted in a 3.1-point improvement in the mAP of the model, while adding only the SE module to the original model resulted in a 0.9-point improvement in the mAP. Replacing the focal loss with central focal loss and adding the SE module resulted in a 3.9-point increase in mAP.
3.4.3. Contrast Results of Disparate Algorithms
In Table 2, the results of experiments conducted using different methods are presented, which include SSD [54], Faster RCNN [55], RetinaNet and our proposed method.
From Table 2, we find that the proposed method improved greatly compared to the original method. In addition, compared with SSD and Faster RCNN, the recognition effect for our method was much better. Our method had a significantly improved recall and AP in all classes compared to the original RetinaNet, and the final mAP improved by 3.9 percentage points.
4. Discussion
In Section 3, the configuration of the experiment was described in detail, and the recognition performance in SAR scene images with simple and complex backgrounds were tested. Then, an ablation experiment was carried out and various methods were compared. The experimental part is analyzed in detail below.
4.1. Analysis of the Proposed Recognition Method Validation Experiment
In Section 3.3, the recognition method was examined by testing ship targets in SAR scene images with simple and complex backgrounds.
From Figure 6a–d, we come to the conclusion that the proposed recognition method can recognize a ship target with a simple background very well.
In Figure 7a–d, the results of the recognition method looked very close to the real values under nearshore scene conditions, and it could not only recognize the target but it also suppresses the false alarms from the shore.
From Figure 8a,b, we draw the conclusion that the proposed method has a good performance, as it not only detected all the targets, but also correctly classified all the targets in the complex SAR image of the far-shore ocean scene.
4.2. Analysis on the Comparison Experiments
In Section 3.4.1, the parameter value of our proposed central focal loss was tested. From Figure 9, we know the fact that when the size of is greater than one, the mAP on the test set drops more seriously. This means that when the proportion of the second half of the central focal loss is large, the proportion of the intraclass features of the target becomes too large, which has the opposite impact on the model effect. According to the experimental results, we are aware of the verdict that when the best result is gained for the test set, the parameter takes the value zero.
In Section 3.4.2, the original RetinaNet, the RetinaNet with only the SE module, the RetinaNet with only the new classification loss function and the RetinaNet with both the SE module and the new classification loss function were tested. The laboratory data from Table 1 showed that the mAP on our test data was enhanced by adding the SE module and the new loss function. Especially when the two worked together, the mAP on the entire test set reached 91.7%, which was 3.9 percentage points higher than that of the original RetinaNet. This fully showed that the improvement was effective.
In Section 3.4.3, typical one-stage detection and two-stage detection algorithms were selected for comparative experiments under the same data set. We can see that from Table 2 that the average recognition accuracy for the original RetinaNet, Faster RCNN and SSD was not much different. The improved RetinaNet was more than four points higher than the recognition mAP of the two algorithms, which proved that the added module and the proposed new loss function were effective.
5. Conclusions
A method for recognizing ships in SAR scene images was described in this paper, which could automatically detect and classify ship targets in an end-to-end module. Considering that the class similarity was too high, an SE module was introduced to amplify the difference features as well as reduce the similarity features. According to the class imbalance problem caused by integrating ship detection as well as ship classification in SAR scene images, an innovative loss function, the central focal loss (CEFL), was proposed so as to improve the performance of our model. The final experimental results showed a 3.9% improvement in mean average accuracy (mAP) on the selected dataset. However, the complexity of the sea state affected the ship recognition method in this paper, and the recognition accuracy decreased with the increase in complexity. In the meantime, most of the current SAR ship datasets only provide a “ship” label, but no specific class of ship. Therefore, we made the experimental data as simple as possible so that there were fewer images in complex sea conditions and so that there were certain missing ships and false positives in parts of the images. In future research, we will gradually increase the complexity of the sea state in which the data are located to test the robustness of the model. With the publication of more SAR datasets, we will further validate the effectiveness of our method.
Author Contributions
Algorithm design and implementation, R.Z.; paper writing, R.Z.; algorithm design, Z.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 62271116.
Data Availability Statement
The images used in this paper come from OpenSARShip and Sentinel-1.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely appreciate the anonymous reviewers for improving this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Curlander, J.C.; Mcdonough, R.N. Synthetic Aperture Radar: Systems and Signal Processing; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Pu, W.; Huang, Y.; Yang, J.; Yang, H. Bistatic Forward-Looking SAR Focusing Using ω–k Based on Spectrum Modeling and Optimization. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 4500–4512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusch, S.; Lehner, S.; Fritz, T.; Soccorsi, M.; Soloviev, A.; van Schie, B. Ship Surveillance With TerraSAR-X. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 1092–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhanu, B.; Jones, T. Image understanding research for automatic target recognition. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 1993, 8, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Principe, J. Support vector machines for SAR automatic target recognition. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2001, 37, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, L.; Owirka, G.; Weaver, A. Automatic target recognition using enhanced resolution SAR data. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1999, 35, 157–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, V.; Shaw, A.; Williams, R. Improved automatic target recognition using singular value decomposition. In Proceedings of the 1998 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, ICASSP ’98 (Cat. No. 98CH36181), Seattle, WA, USA, 15 May 1998; Volume 5, pp. 2717–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tison, C.; Pourthie, N.; Souyris, J.C. Target recognition in SAR images with Support Vector Machines (SVM). In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Barcelona, Spain, 23–28 July 2007; pp. 456–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, L. Analysis of multiplicative speckle models for template-based SAR ATR. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2001, 37, 1424–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robey, F.C.; Fuhrmann, D.R.; Kelly, E.J.; Nitzberg, R. A Cfar Adaptive Matched-Filter Detector. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1992, 28, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.L.; Xiong, W.; Lv, Y.F.; Liu, H.Y. A New Method Based on Two-Stage Detection Mechanism for Detecting Ships in High-Resolution SAR Images. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Electronic Information Technology and Computer Engineering (Eitce 2017), Zhuhai, China, 23–24 September 2017; Volume 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Sarkar, U.; Taraphder, S.; Datta, S.; Swain, D.; Saikhom, R.; Panda, S.; Laishram, M. Principal Component Analysis. Int. J. Livest. Res. 2017, 7, 60–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, L.; Antoine, J.P. Wavelet Transforms and Their Applications. Phys. Today 2003, 56, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jijo, B.; Mohsin Abdulazeez, A. Classification Based on Decision Tree Algorithm for Machine Learning. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. Trends 2021, 2, 20–28. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Z.; Li, Q.; Cao, Z.; Liu, N. Dense Attention Pyramid Networks for Multi-Scale Ship Detection in SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 8983–8997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, N.; Cao, Z.; Yang, J. Ship Detection in Large-Scale SAR Images Via Spatial Shuffle-Group Enhance Attention. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Cui, Z.; Zang, Z.; Meng, X.; Cao, Z.; Yang, J. UltraHi-PrNet: An Ultra-High Precision Deep Learning Network for Dense Multi-Scale Target Detection in SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xiao, S.; Yang, J.; Cheng, C. A Tiny Model for Fast and Precise Ship Detection via Feature Channel Pruning. Sensors 2022, 22, 9331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suo, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, S.; Hu, Y. BoxPaste: An Effective Data Augmentation Method for SAR Ship Detection. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, J.; Heng, W.; Ren, K.; Song, J. Transfer Learning with Convolutional Neural Networks for SAR Ship Recognition. Mater. Sci. Eng. Conf. Ser. 2018, 322, 072001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Guan, J.; Yin, L.; Chen, J.; Zhang, G.; Feng, P. Joint Convolutional Neural Network for Small-Scale Ship Classification in SAR Images. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2019—2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 2619–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Jiang, P.; Yuan, Q.; Liu, M. Detection and Recognition of SAR Small Ship Objects Using Deep Neural Network. Xibei Gongye Daxue Xuebao/J. Northwestern Polytech. Univ. 2019, 37, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Wang, H.; Song, Q.; Ao, W.; Shi, Y.; Qian, Y. Intelligent Ship Recongnition from Synthetic Aperture Radar Images. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2018—2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018; pp. 4387–4390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Lei, Y.; Leng, X.; Xiong, B.; Ji, K. An Improved Oriented Ship Detection Method in High-Resolution SAR Image Based on YOLOv5. In Proceedings of the 2022 Photonics & Electromagnetics Research Symposium (PIERS), Hangzhou, China, 25–29 April 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 647–653. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, J.; Huang, Y.; Huo, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Yeo, T.S. SAR Automatic Target Recognition Based on Multiview Deep Learning Framework. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 2196–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japkowicz, N.; Stephen, S. The Class Imbalance Problem: A Systematic Study. Intell. Data Anal. 2002, 6, 429–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.B.; Krishnan, S.; Niculescu, R.S. Data mining for improved cardiac care. SIGKDD Explor. 2006, 8, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Li, J.; Cao, L.; Ou, Y.; Chen, J. Effective detection of sophisticated online banking fraud on extremely imbalanced data. World Wide Web 2013, 16, 449–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.W.; Lee, C.H. Classification of Imbalanced Data Using Deep Learning with Adding Noise. J. Sens. 2021, 2021, 1735386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodda, S.; Erothi, U.S.R. Class imbalance problem in the Network Intrusion Detection Systems. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Electrical, Electronics, and Optimization Techniques (ICEEOT), Chennai, India, 3–5 March 2016; pp. 2685–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataramanan, S.; Kijak, E.; Amsaleg, L.; Avrithis, Y. AlignMixup: Improving Representations By Interpolating Aligned Features. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 19152–19161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Dayoub, F.; Sünderhauf, N. VarifocalNet: An IoU-aware Dense Object Detector. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 8510–8519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, W.H.; Hu, X.L.; Li, J.; Tang, J.H.; Yang, J. Generalized Focal Loss V2: Learning Reliable Localization Quality Estimation for Dense Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/Cvf Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2021, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 11627–11636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, M.; Sala, E.; Schönlieb, C.B.; Rundo, L. Unified Focal loss: Generalising Dice and cross entropy-based losses to handle class imbalanced medical image segmentation. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2022, 95, 102026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Z. A Normal Distribution-Based Over-Sampling Approach to Imbalanced Data Classification. In Advanced Data Mining and Applications; Tang, J., King, I., Chen, L., Wang, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 83–96. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Cheng, C.; Guo, W.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, W. Exploring Similarity in Polarization: Contrastive Learning with Siamese Networks for Ship Classification in Sentinel-1 SAR Images. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2022—2022 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Virtual, 17–22 July 2022; pp. 835–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Garcia, E.A. Learning from Imbalanced Data. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2009, 21, 1263–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Park, M.; Kim, J. Plankton classification on imbalanced large scale database via convolutional neural networks with transfer learning. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Phoenix, AZ, USA, 25–28 September 2016; pp. 3713–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, N.V.; Bowyer, K.W.; Hall, L.O.; Kegelmeyer, W.P. SMOTE: Synthetic Minority Over-Sampling Technique. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2011, 16, 321–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, W.; Tao, R.; Wang, S. Transfer Learning for Optical and SAR Data Correspondence Identification With Limited Training Labels. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 1545–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmgren-Hansen, D.; Kusk, A.; Dall, J.; Nielsen, A.A.; Engholm, R.; Skriver, H. Improving SAR Automatic Target Recognition Models With Transfer Learning From Simulated Data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 1484–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Sun, Y.; Hu, L. SAR Target Recognition Using Only Simulated Data for Training by Hierarchically Combining CNN and Image Similarity. IEEE Geosci. Remote. Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 4503505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, F.; Li, K.C.; Shen, J.; Zhou, Q.; Xuhui, Y. Using Cost-Sensitive Learning and Feature Selection Algorithms to Improve the Performance of Imbalanced Classification. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 69979–69996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 42, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Wei, C.; Gaidon, A.; Aréchiga, N.; Ma, T. Learning Imbalanced Datasets with Label-Distribution-Aware Margin Loss. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.07413. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Qu, C.; Peng, S. Ship classification for unbalanced SAR dataset based on convolutional neural network. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2018, 12, 035010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Dzurisin, D. Recent Advances in InSAR Image Processing and Analysis. In InSAR Imaging of Aleutian Volcanoes: Monitoring a Volcanic Arc from Space; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature Pyramid Networks for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zheng, Q. Recognition of roads and bridges in SAR images. In Proceedings of the Proceedings International Radar Conference, Alexandria, VA, USA, 8–11 May 1995; pp. 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Albanie, S.; Sun, G.; Wu, E. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 42, 2011–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Jia, M.; Lin, T.Y.; Song, Y.; Belongie, S. Class-Balanced Loss Based on Effective Number of Samples. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 9260–9269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Zhang, K.; Li, Z.; Qiao, Y. A Discriminative Feature Learning Approach for Deep Face Recognition. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2016; Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 499–515. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.Y.; Berg, A.C. SSD: Single Shot MultiBox Detector. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2016; Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).