Multiple Band Prioritization Criteria-Based Band Selection for Hyperspectral Imagery
Abstract
1. Introduction
- This work regards BS as an MCDM problem and proposes a novel unsupervised BS method for hyperspectral imagery, namely MCBS. The integration of multiple BPs enables a comprehensive band evaluation, and makes MCBS more robust against different data sets.
- To balance the contributions of various BP criteria, MCBS also provides two weight estimation approaches, which can adaptively attach weight to each criterion from information diversity and correlation perspectives.
- This work also provides an extended version of MCBS, which incorporates the SP strategy to further reduce the correlation of the selected bands. Extensive experiments demonstrate its superiority over the state-of-the-art methods.
2. MCBS Framework
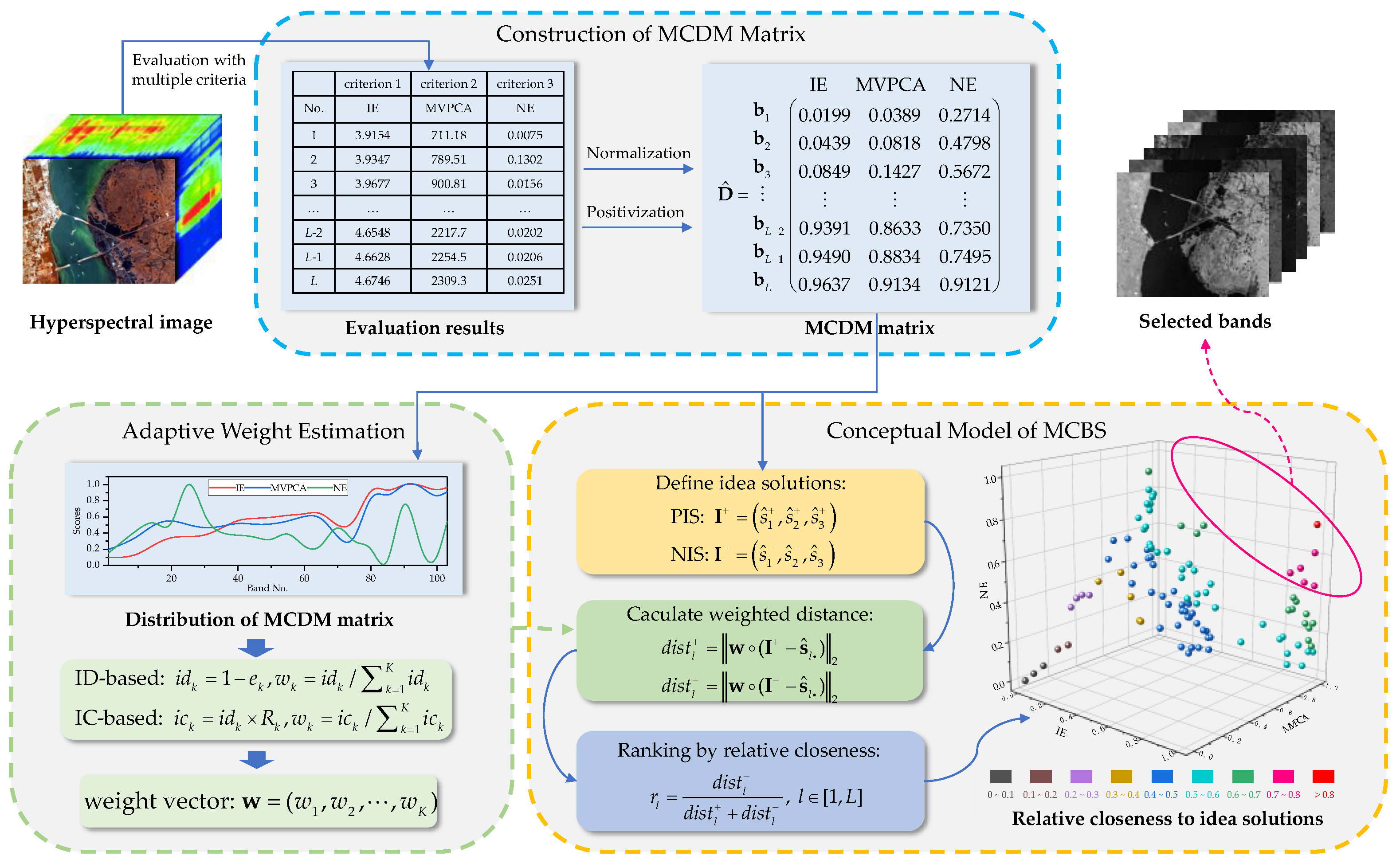
2.1. Construction of MCDM Matrix
2.2. Conceptual Mode of MCBS
2.3. Adaptive Weight Estimation by MCBS
2.3.1. ID-Based Weight Estimation
2.3.2. IC-Based Weight Estimation
2.4. Extended Version of MCBS
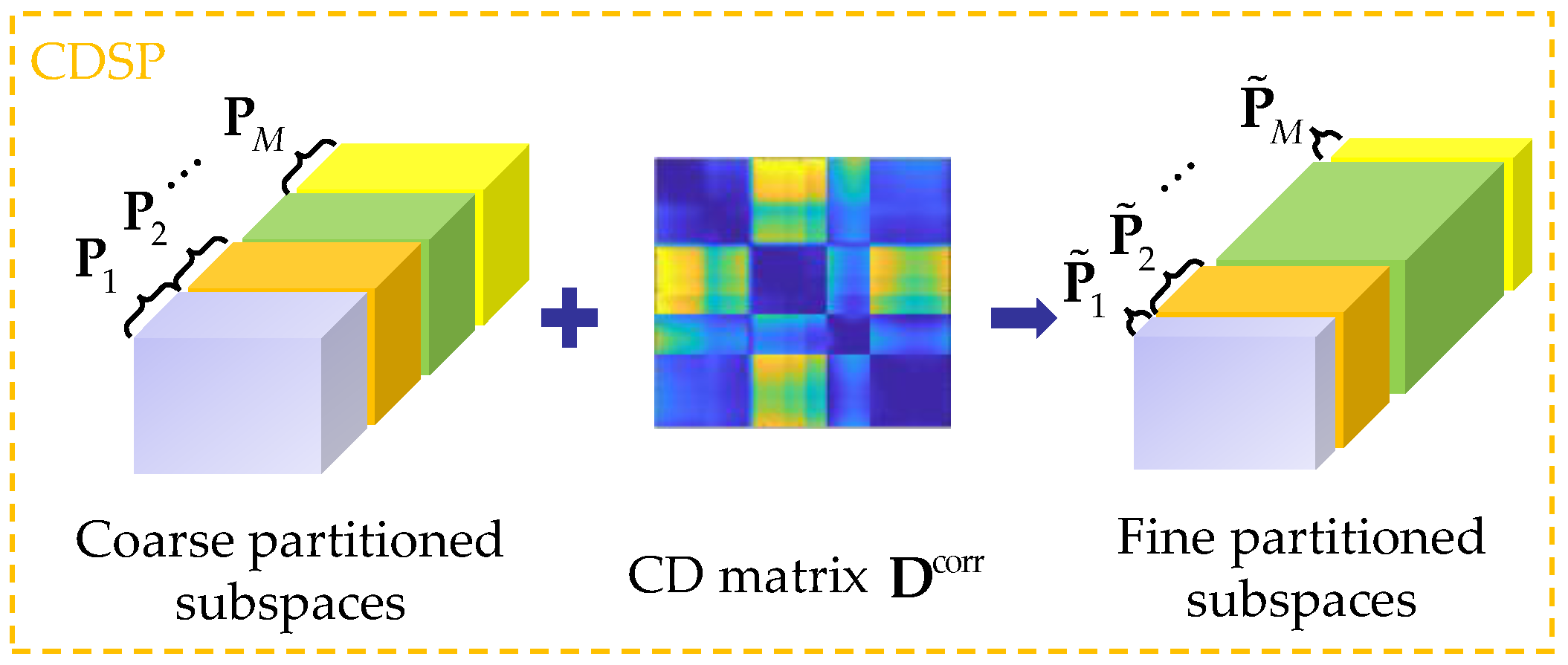
2.4.1. CDSP
2.4.2. SP-MCBS
| Algorithm 1 SP-MCBS |
| Input: HSI data , the number of selected bands M |
| Output: The selected band subset |
|
3. Experiments and Results
3.1. Experimental Setup
3.1.1. Data Sets
3.1.2. Classifier and Parameter Settings
3.1.3. Number of Selected Bands
3.2. Effectiveness of MCBS Framework
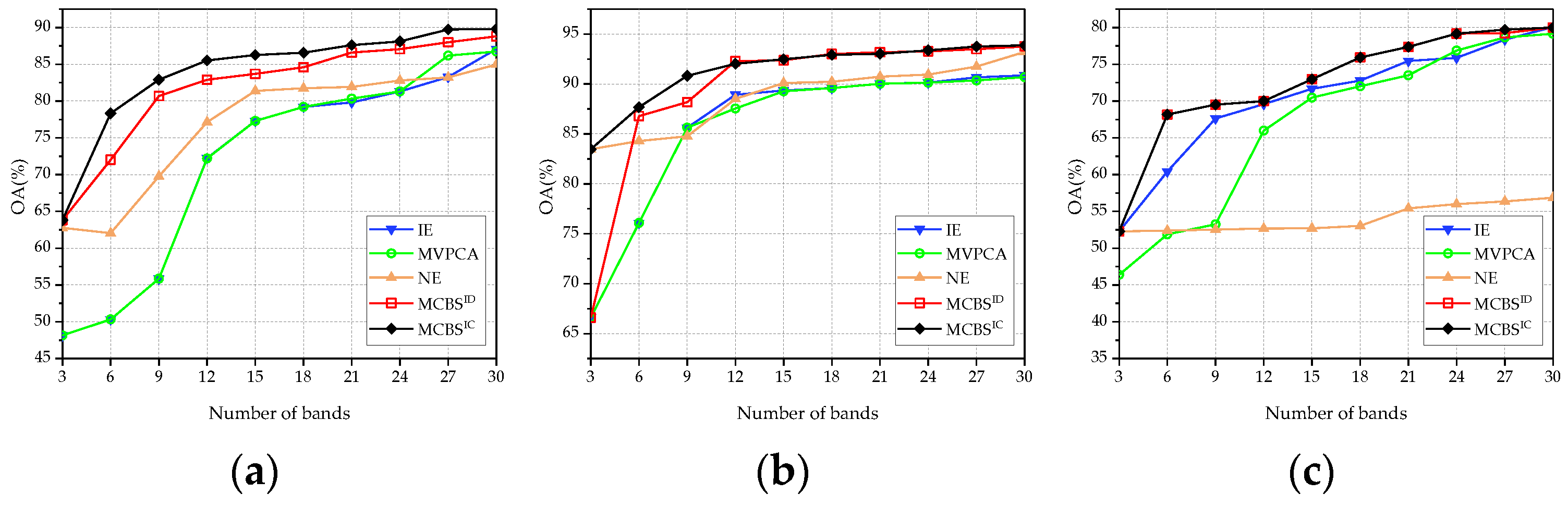
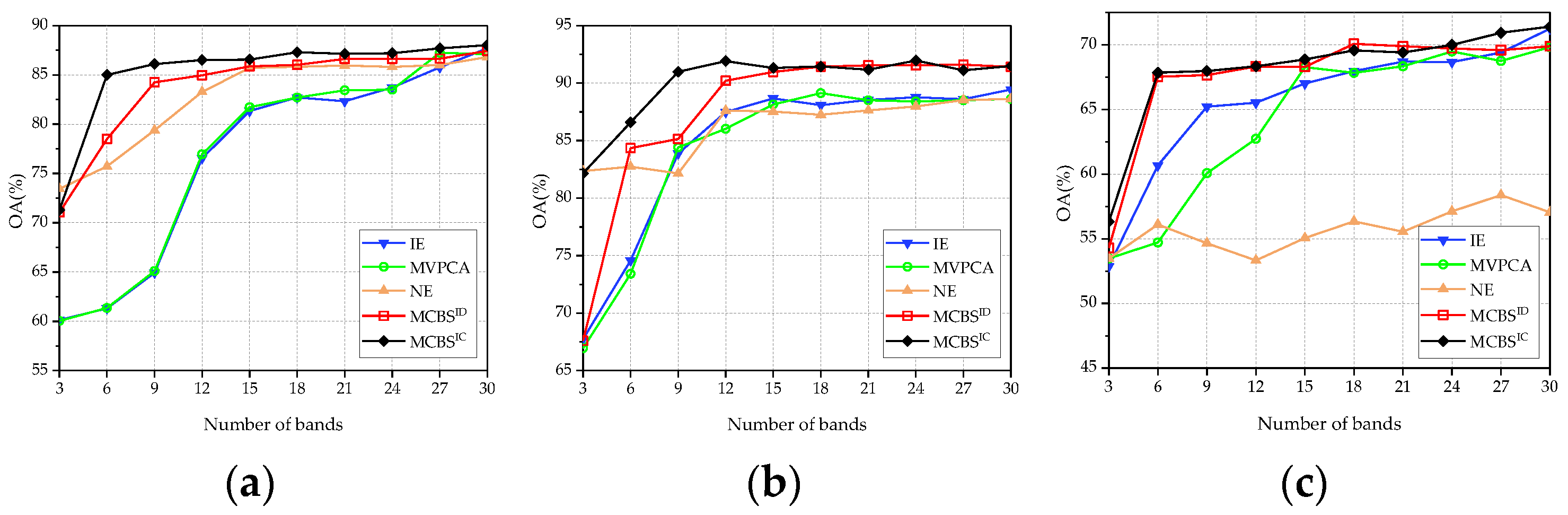
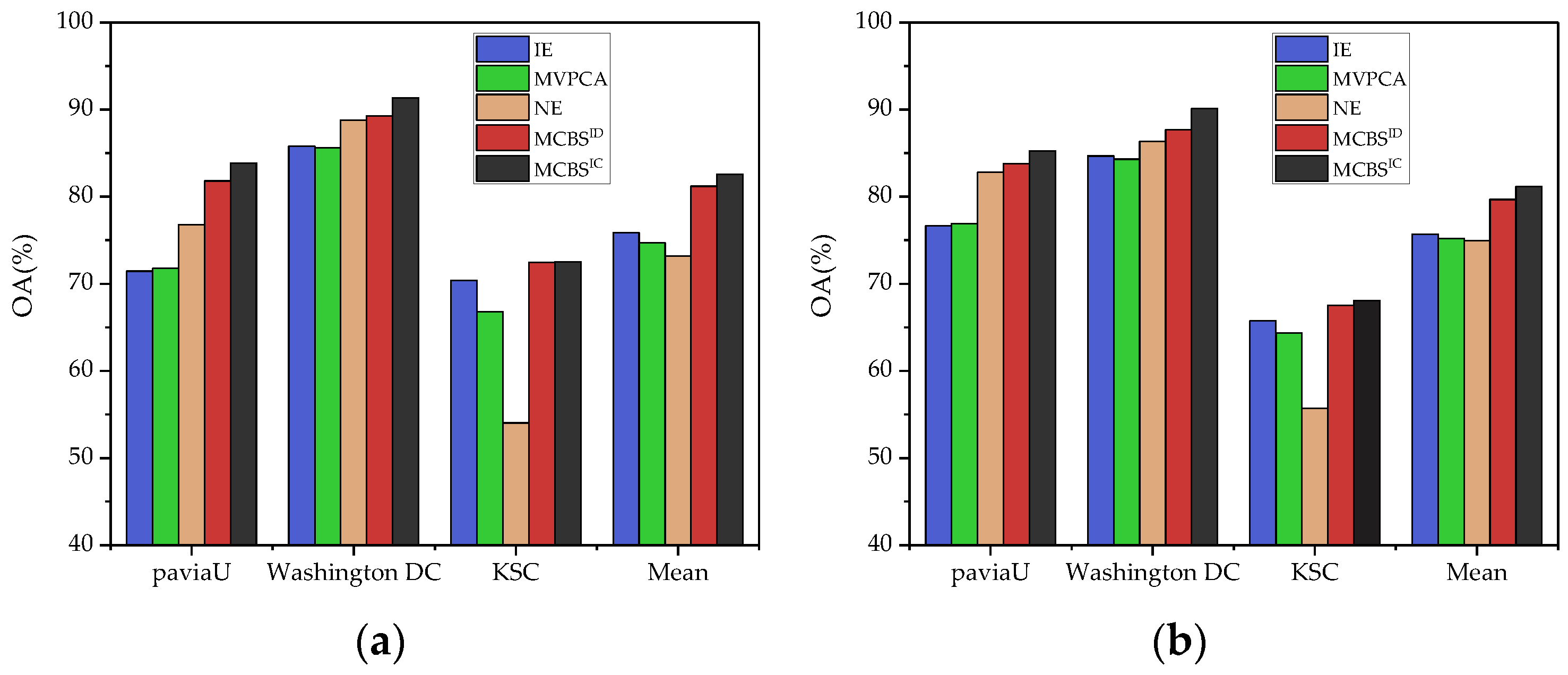
3.2.1. Classification Performance
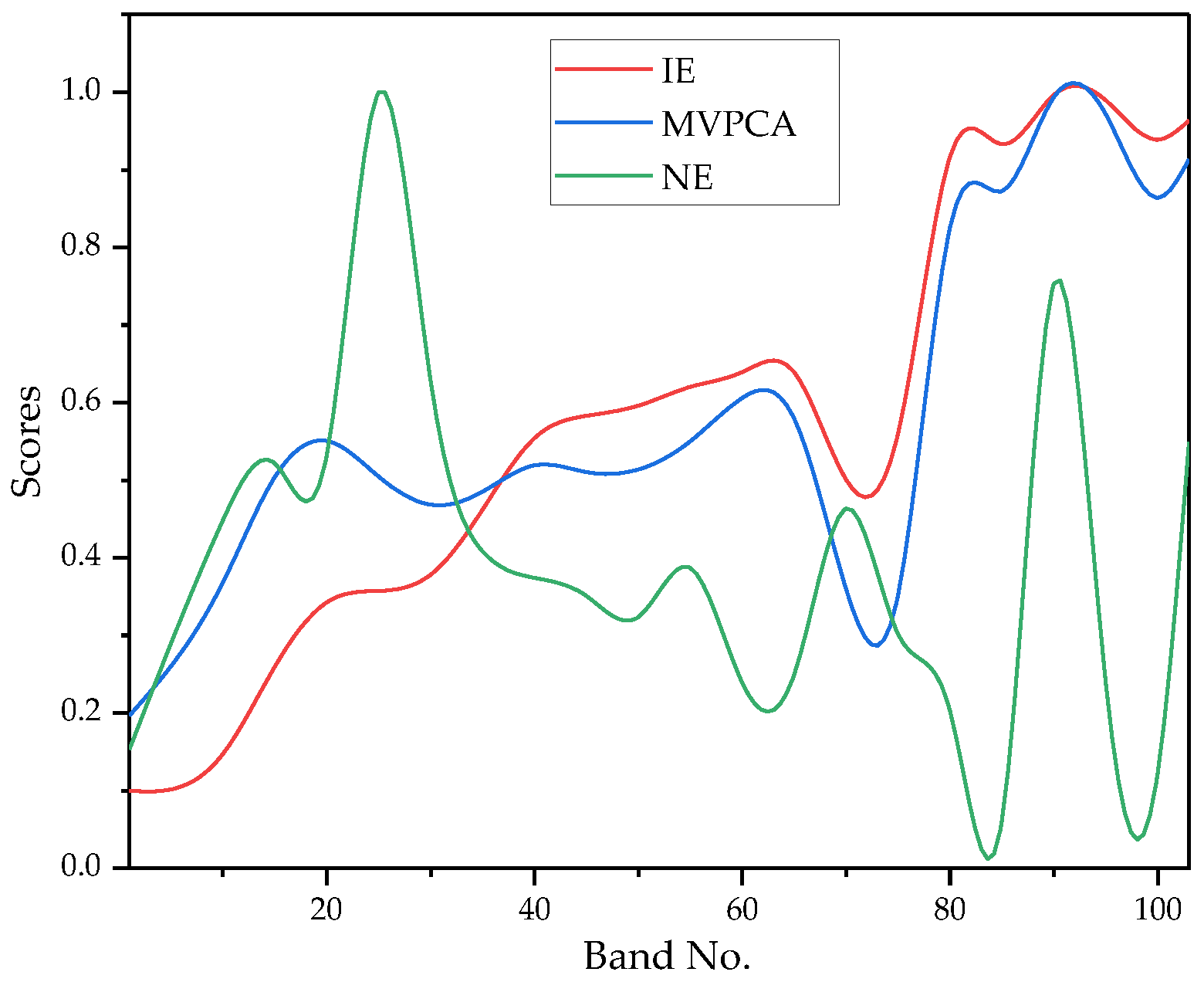
3.2.2. Analysis of Weight Estimation
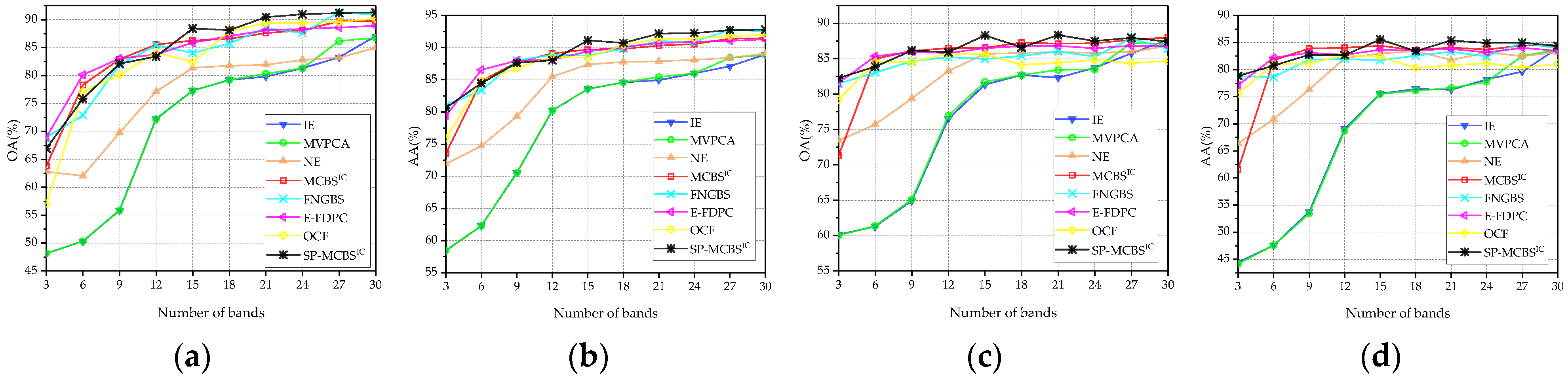
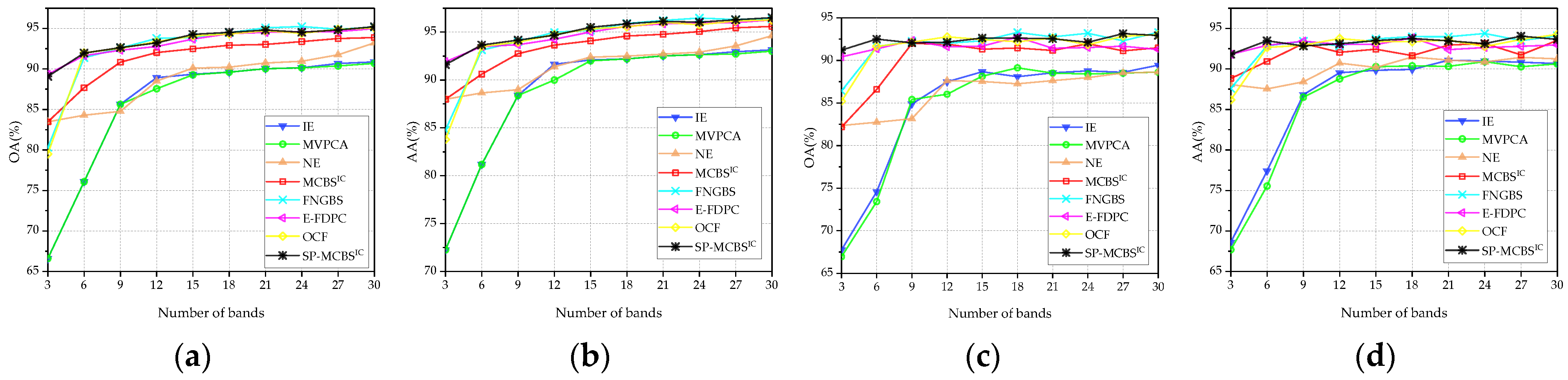
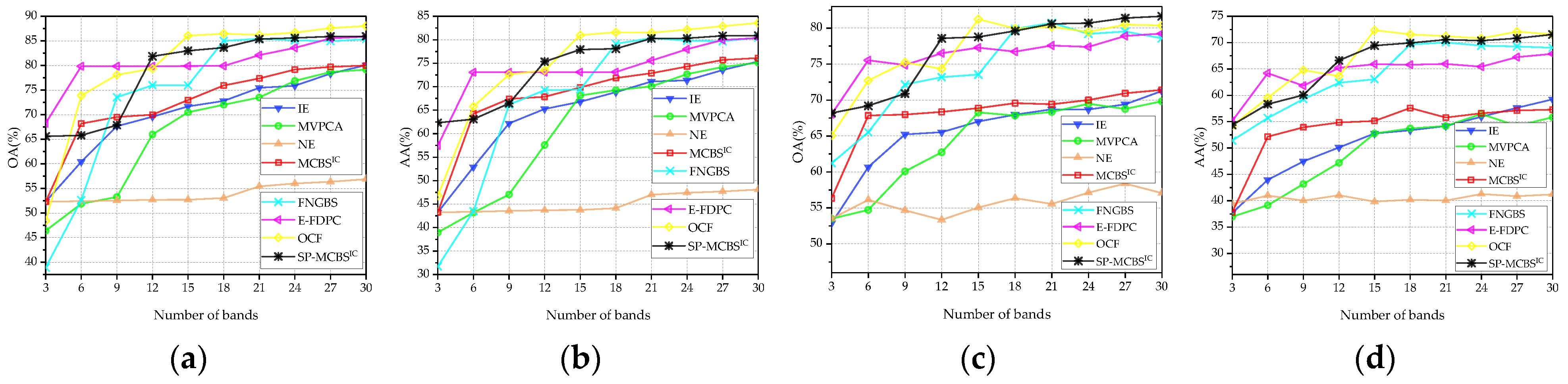
3.3. Comparison with State-of-the-Art Methods
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
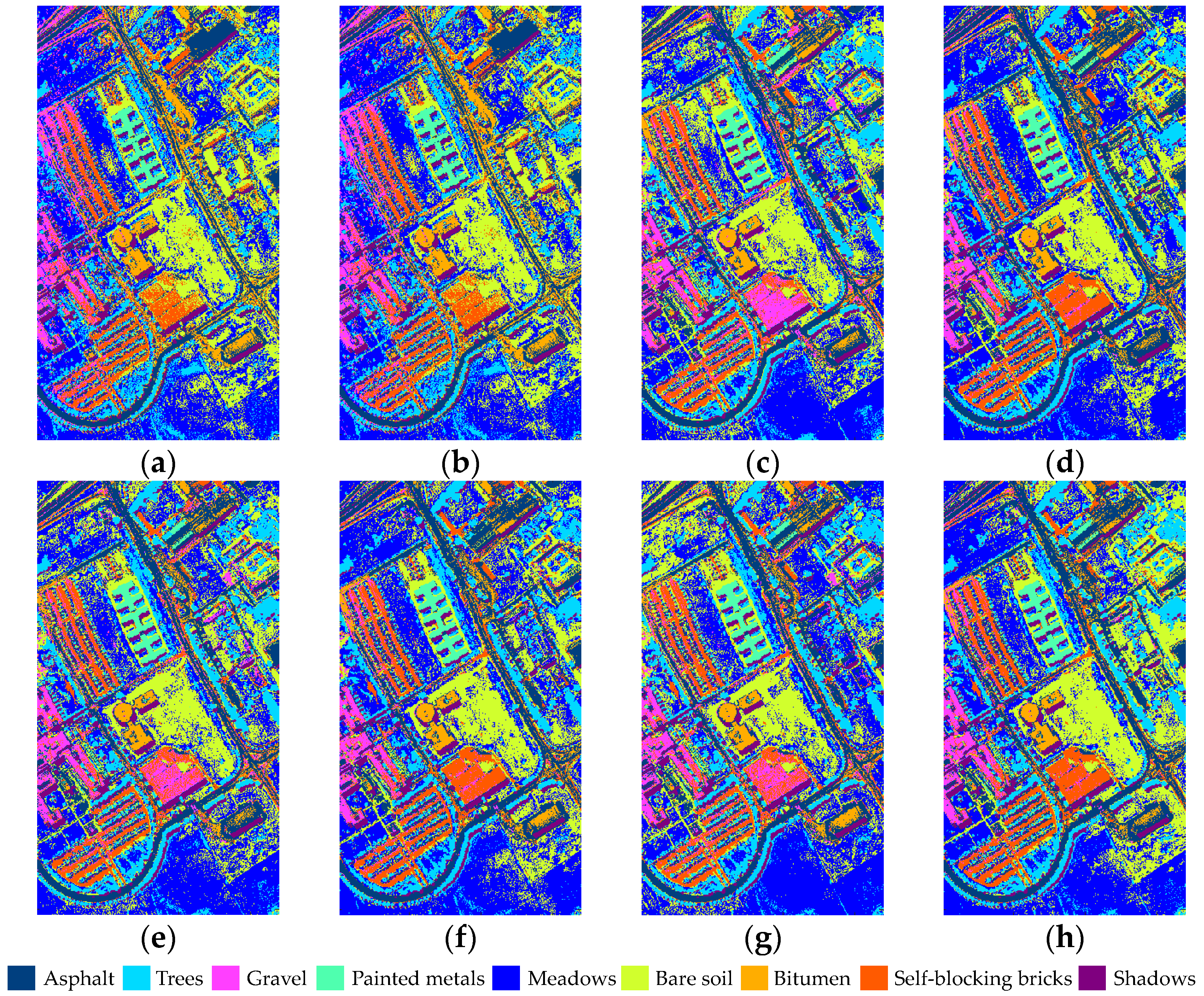
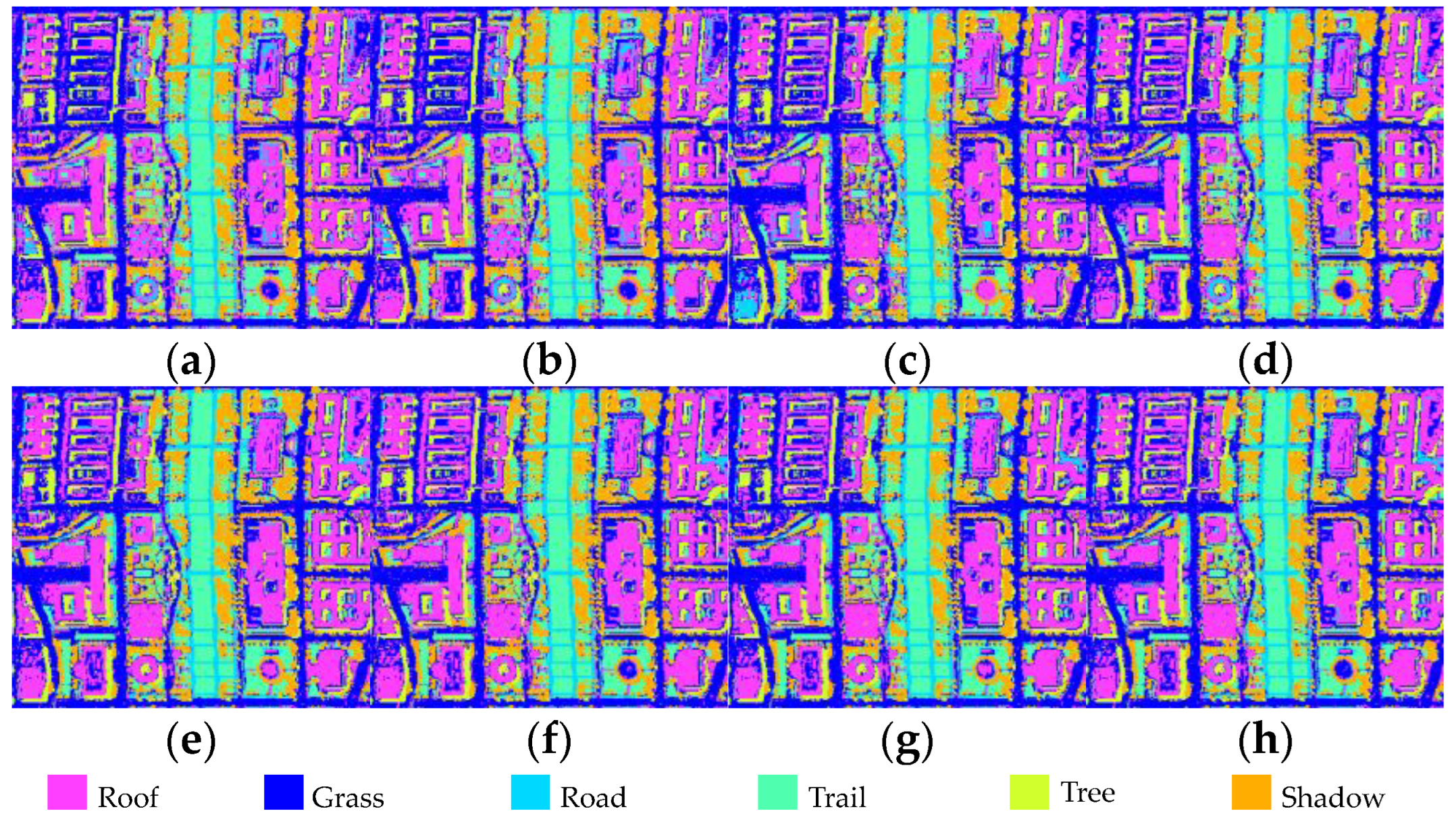
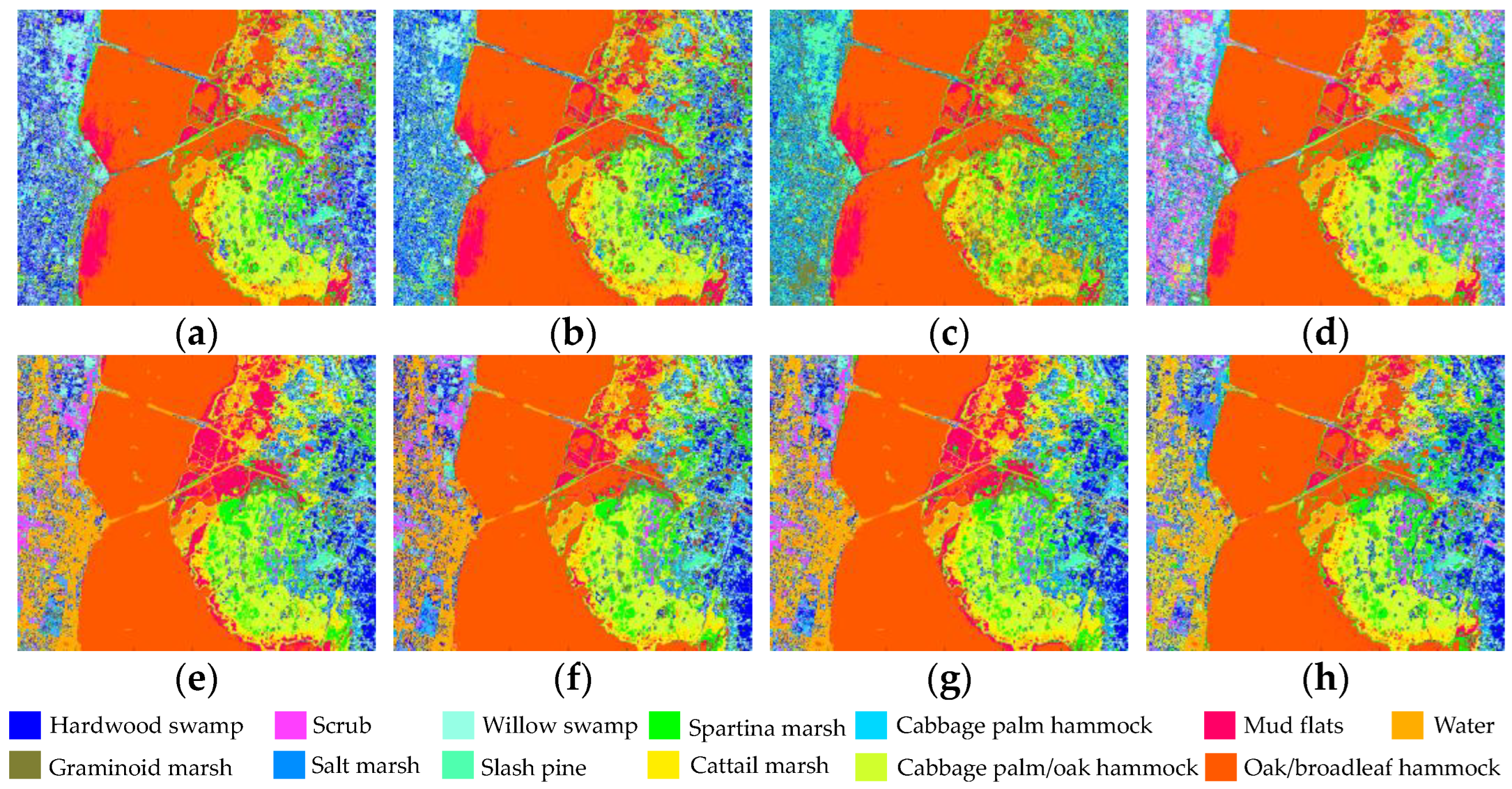
| Datasets | Methods | Band Subset 1 |
|---|---|---|
| Pavia University | IE | 91, 90, 88, 92, 89, 87, 95, 93, 94, 96, 82, 83, 86, 97, 103 |
| MVPCA | 91, 88, 90, 89, 87, 92, 93, 95, 94, 96, 82, 86, 83, 97, 103 | |
| NE | 25, 24, 33, 21, 28, 19, 31, 58, 16, 39, 90, 29, 54, 17, 69 | |
| MCBSIC | 90, 87, 103, 58, 101, 83, 25, 89, 54, 21, 24, 39, 33, 19, 28 | |
| FNGBS | 3, 11, 18, 19, 32, 33, 45, 46, 53, 61, 67, 79, 84, 88, 94 | |
| E-FDPC | 61, 92, 33, 19, 52, 99, 82, 37, 42, 90, 50, 56, 54, 48, 86 | |
| OCF 2 | 61, 88, 33, 19, 53, 48, 29, 99, 36, 15, 65, 8, 80, 72, 3 | |
| SP-MCBSIC | 8, 14, 21, 25, 33, 39, 48, 54, 58, 69, 77, 83, 90, 96, 103 | |
| Washington DC Mall | IE | 81, 82, 80, 79, 83, 78, 84, 94, 77, 95, 70, 112, 113, 93, 71 |
| MVPCA | 81, 82, 80, 79, 83, 78, 94, 84, 77, 95, 112, 93, 70, 113, 111 | |
| NE | 173, 185, 11, 182, 191, 172, 10, 180, 175, 34, 166, 187, 149, 177, 170 | |
| MCBSIC | 173, 185, 11, 182, 34, 191, 172, 81, 10, 82, 149, 80, 175, 180, 79 | |
| FNGBS | 6, 18, 22, 46, 52, 65, 80, 92, 105, 118, 127, 142, 149, 162, 178 | |
| E-FDPC | 179, 48, 63, 152, 119, 25, 80, 96, 128, 112, 123, 95, 99, 141, 68 | |
| OCF | 179, 150, 63, 49, 27, 80, 162, 92, 19, 35, 8, 188, 41, 52, 4 | |
| SP-MCBSIC | 11, 18, 34, 51, 53, 68, 81, 95, 111, 117, 136, 149, 166, 173, 185 | |
| KSC | IE | 51, 50, 52, 49, 53, 48, 54, 47, 56, 55, 46, 57 |
| MVPCA | 133, 174, 51, 50, 1, 52, 49, 176, 53, 54, 55, 56 | |
| NE | 50, 51, 52, 89, 65, 83, 60, 71, 69, 62, 61, 87 | |
| MCBSIC | 50, 51, 52, 72, 67, 68, 53, 49, 54, 56, 55, 74 | |
| FNGBS | 5, 16, 24, 45, 49, 69, 78, 97, 117, 128, 152, 155 | |
| E-FDPC | 65, 53, 22, 9, 66, 81, 82, 87, 84, 86, 89, 96 | |
| OCF | 65, 51, 23, 10, 17, 45, 78, 42, 6, 38, 33, 35 | |
| SP-MCBSIC | 1, 28, 45, 50, 72, 75, 100, 107, 133, 134, 160, 174 |
References
- Shang, X.; Song, M.; Wang, Y.; Yu, C.; Yu, H.; Li, F.; Chang, C.I. Target-constrained interference-minimized band selection for hyperspectral target detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 6044–6064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakob, S.; Zimmermann, R.; Gloaguen, R. The need for accurate geometric and radiometric corrections of drone-borne hyperspectral data for mineral exploration: Mephystoa toolbox for pre-processing drone-borne hyperspectral data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, A.B.; Park, T.Y.S.; Park, Y.; Hong, J.K.; Zoheir, B.; Pradhan, B.; Ayoobi, I.; Hashim, M. Application of multi-sensor satellite data for exploration of Zn-Pb sulfide mineralization in the Franklinian Basin, North Greenland. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnenkamp, D.; Behmann, J.; Mahlein, A.K. In-field detection of yellow rust in wheat on the ground canopy and UAV scale. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Q.; Xie, Y.Q.; Hou, W.Z.; Liu, Z.H.; Bai, Z.G.; Hong, J.; Ma, Y.; Huang, H.L.; Lei, X.F.; Sun, X.B.; et al. In-orbit test of the polarized scanning atmospheric corrector (PSAC) onboard Chinese environmental protection and disaster monitoring satellite constellation HJ-2 A/B. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 4108217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Sun, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Hu, M.H.; Chen, J.G.; Wen, Y.; Li, Q.L. Identification of melanoma from hyperspectral pathology image using 3D convolutional networks. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2021, 40, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.M.; Wang, H.C.; Chai, J.W.; Chen, C.C.C.; Xue, B.; Wang, L.; Yu, C.Y.; Wang, Y.L.; Song, M.P.; Chang, C.I. A hyperspectral imaging approach to white matter hyperintensities detection in brain magnetic resonance images. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.D.; Song, M.P.; Wang, Y.L.; Yu, H.Y. Residual-driven band selection for hyperspectral anomaly detection. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 6004805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, F.H.; Li, X.L. Hyperspectral band selection via optimal neighborhood reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 8465–8476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, S.S.; Chang, C.I.; Ginsberg, I.W. Unsupervised target detection in hyperspectral images using projection pursuit. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 1380–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q. Modified fisher’s linear discriminant analysis for hyperspectral imagery. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2007, 4, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauvel, M.; Chanussot, J.; Benediktsson, J.A. Kernel principal component analysis for the classification of hyperspectral remote sensing data over urban areas. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2009, 2009, 783194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Prasad, S.; Fowler, J.E.; Bruce, L.M. Locality-preserving dimensionality reduction and classification for hyperspectral image analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 1185–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Prasad, S.; Fowler, J.E. Noise-adjusted subspace discriminant analysis for hyperspectral imagery classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 1374–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Roweis, S.T.; Saul, L.K. Nonlinear dimensionality reduction by locally linear embedding. Science 2000, 290, 2323–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.F.; Niyogi, P. Locality preserving projections. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 16; Bradford: Chester, NJ, USA, 2004; pp. 153–160. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Cai, D.; Han, J. Learning a maximum margin subspace for image retrieval. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2008, 20, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.P.; Shang, X.D.; Sun, X.D.; Yu, H.Y.; Song, M.P.; Chang, C.I. Underwater hyperspectral target detection with band selection. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Y.; Peng, B.D.; Fang, L.; Li, Q. Hyperspectral band selection via optimal combination strategy. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Jiao, L.C.; Liu, F.; Sun, T.; Zhang, X.R. Mutual-information-based semi-supervised hyperspectral band selection with high discrimination, high information, and low redundancy. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 2956–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.I.; Du, Q.; Sun, T.L.; Althouse, M.L.G. A joint band prioritization and band-decorrelation approach to band selection for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 2631–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, H.C.; Xue, B.; Chang, C.I. Constrained band subset selection for hyperspectral imagery. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 2032–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.F.; Liu, D.Z.; Li, X.H.; Liu, Z.G. A saliency-based band selection approach for hyperspectral imagery inspired by scale selection. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 572–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.C.; Zuo, Z.Y.; Han, Q.L. A divisive hierarchical clustering approach to hyperspectral band selection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Uso, A.; Pla, F.; Sotoca, J.M.; Garcia-Sevilla, P. Clustering-based hyperspectral band selection using information measures. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 4158–4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Tang, G.H.; Zhu, J.S.; Li, Q.Q. A novel ranking-based clustering approach for hyperspectral band selection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, F.H.; Li, X.L. Optimal clustering framework for hyperspectral band selection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 5910–5922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, Q.; Li, X.L. Hyperspectral band selection via adaptive subspace partition strategy. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 4940–4950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.D.; Zhang, H.Q.; Xu, F.Q.; Zhu, Y.; Fu, X.P. Constrained-target band selection with subspace partition for hyperspectral target detection. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 9147–9161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, Q.; Li, X.L. A fast neighborhood grouping method for hyperspectral band selection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 5028–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.M.; Liu, X.B.; Cai, Z.H. Bs-nets: An end-to-end framework for band selection of hyperspectral image. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 1969–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Z.Y.; Gao, K.; Zhang, X.D.; Wang, H.; Han, L. Band selection of hyperspectral images using attention-based autoencoders. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 18, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Q.; Sun, X.D.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, F.Q.; Fu, X.P. A global-local spectral weight network based on attention for hyperspectral band selection. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Liu, X.B.; Cai, Y.M.; Cai, Z.H. Band selection of hyperspectral images using multiobjective optimization-based sparse self-representation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.W.; Jiang, M.; Li, W.Y.; Liu, Y.N. A symmetric sparse representation-based band selection method for hyperspectral imagery classification. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Wang, H.M.; Ma, Z.Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, Q.; Li, X.L. Unsupervised hyperspectral band selection based on hypergraph spectral clustering. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 5509905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Pratiher, S.; Kyal, C.; Ghamisi, P. Sparsity regularized deep subspace clustering for multicriterion-based hyperspectral band selection. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 4264–4278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Q.; Lu, P.; Zhang, H.Y.; Chen, X.H. Method of multi-criteria group decision-making based on cloud aggregation operators with linguistic information. Inf. Sci. 2014, 274, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, P.J.; Xu, Z.S.; Gou, X.J. Pythagorean fuzzy TODIM approach to multi-criteria decision making. Appl. Soft. Comput. 2016, 42, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Eckert, C.M.; Earl, C. A review of fuzzy AHP methods for decision-making with subjective judgements. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 161, 113738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, M.; Ilyas, F.; Garg, H. Multi-criteria group decision-making based on ELECTRE I method in Pythagorean fuzzy information. Soft Comput. 2020, 24, 3425–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.Y. Effects of the entropy weight on TOPSIS. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 168, 114186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hong, H.Y.; Chen, W.; Li, S.J.; Pamucar, D.; Gigovic, L.; Drobnjak, S.; Bui, D.T.; Duan, H.X. A hybrid GIS multi-criteria decision-making method for flood susceptibility mapping at Shangyou, China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, R. MCDM-based parametric selection of cloud deployment models for an academic organization. IEEE Trans. Cloud Comput. 2022, 10, 863–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Wang, Y.; Putrus, G.; Kotter, R.; Marzband, M.; Herteleer, B.; Warmerdam, J. Multi-objective techno-economic-environmental optimisation of electric vehicle for energy services. Appl. Energy 2020, 257, 113541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adem, A.; Cakit, E.; Dagdeviren, M. Selection of suitable distance education platforms based on human-computer interaction criteria under fuzzy environment. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 7919–7931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
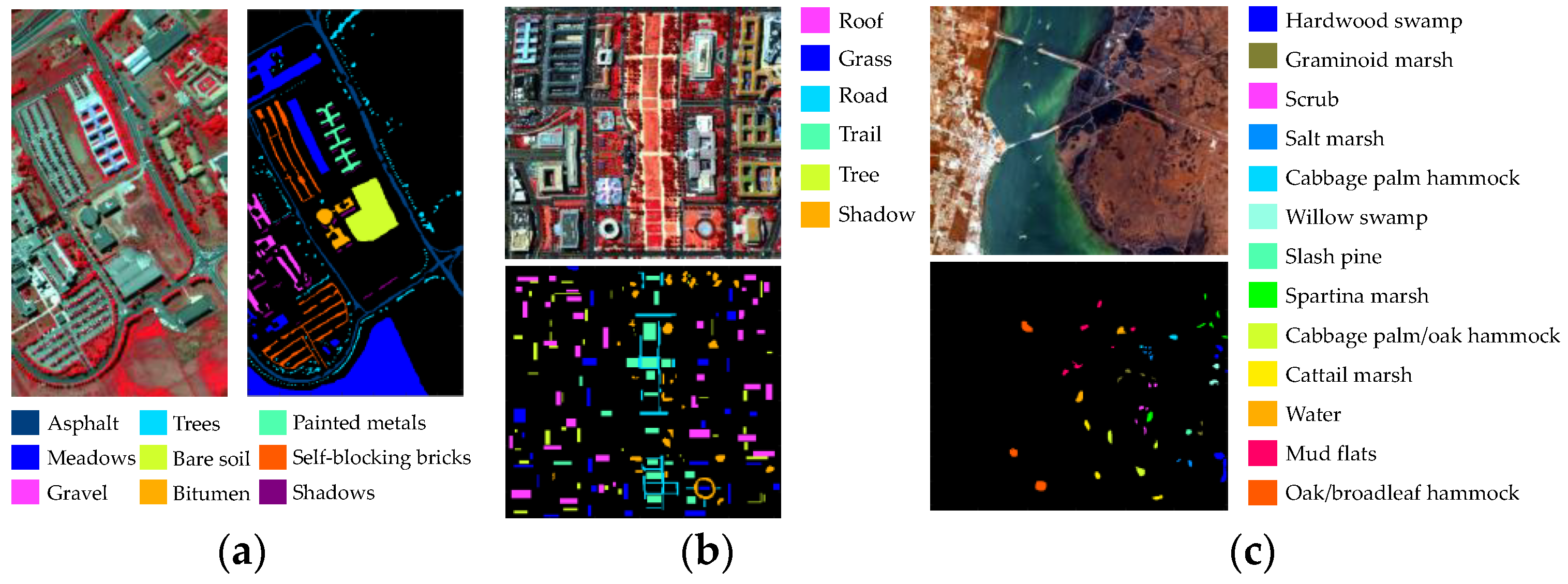
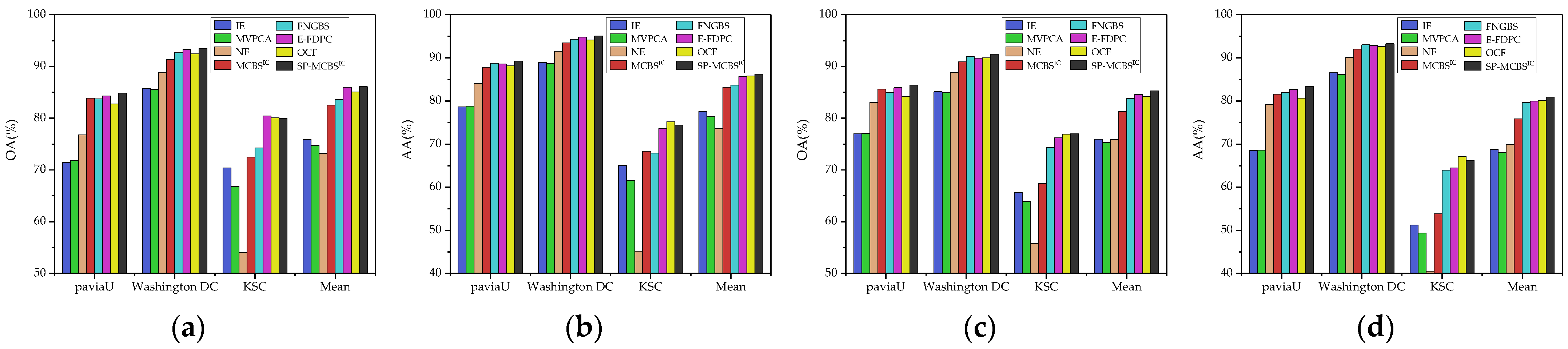
| Data Sets | Pixels | Wavelength Range | Classes | Bands |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pavia University | 610 × 340 | 0.4–2.5 μm | 9 | 103 |
| Washington DC Mall | 280 × 307 | 0.4–2.4 μm | 6 | 191 |
| KSC | 512 × 614 | 0.4–2.5 μm | 13 | 176 |
| Weights in MCBSID | Weights in MCBSIC | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IE | MVPCA | NE | IE | MVPCA | NE | |
| Pavia University | 0.3170 | 0.3129 | 0.3701 | 0.2227 | 0.2641 | 0.5132 |
| Washington DC Mall | 0.3054 | 0.3543 | 0.3403 | 0.2311 | 0.3177 | 0.4512 |
| KSC | 0.3620 | 0.4309 | 0.2071 | 0.2420 | 0.5420 | 0.2169 |
| Datasets | Classifier (Measure) | IE | MVPCA | NE | MCBSIC | FNGBS | E-FDPC | OCF 1 | SP-MCBSIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pavia University | SVM (OA) | 71.45 ± 0.14 | 71.76 ± 0.15 | 76.77 ± 0.09 | 83.87 ± 0.08 | 83.74 ± 0.07 | 84.28 ± 0.06 | 82.74 ± 0.10 | 84.88 ± 0.08 |
| SVM (AA) | 78.67 ± 0.11 | 78.84 ± 0.11 | 84.01 ± 0.06 | 87.84 ± 0.05 | 88.71 ± 0.04 | 88.55 ± 0.04 | 88.16 ± 0.05 | 89.26 ± 0.04 | |
| KNN (OA) | 76.96 ± 0.10 | 77.05 ± 0.10 | 83.06 ± 0.05 | 85.60 ± 0.05 | 85.04 ± 0.02 | 85.89 ± 0.02 | 84.21 ± 0.02 | 86.44 ± 0.02 | |
| KNN (AA) | 68.48 ± 0.14 | 68.6 ± 0.15 | 79.27 ± 0.06 | 81.59 ± 0.07 | 82.02 ± 0.02 | 82.69 ± 0.02 | 80.66 ± 0.02 | 83.37 ± 0.02 | |
| Washington DC Mall | SVM (OA) | 85.79 ± 0.08 | 85.59 ± 0.08 | 88.80 ± 0.03 | 91.34 ± 0.03 | 92.67 ± 0.05 | 93.27 ± 0.02 | 92.48 ± 0.05 | 93.50 ± 0.02 |
| SVM (AA) | 88.90 ± 0.07 | 88.69 ± 0.07 | 91.57 ± 0.02 | 93.45 ± 0.02 | 94.33 ± 0.04 | 94.80 ± 0.01 | 94.11 ± 0.04 | 95.04 ± 0.02 | |
| KNN (OA) | 85.12 ± 0.08 | 84.93 ± 0.08 | 88.85 ± 0.02 | 90.89 ± 0.02 | 91.94 ± 0.02 | 91.60 ± 0.01 | 91.67 ± 0.02 | 92.39 ± 0.01 | |
| KNN (AA) | 86.57 ± 0.08 | 86.12 ± 0.08 | 90.09 ± 0.02 | 92.03 ± 0.01 | 93.03 ± 0.02 | 92.88 ± 0.01 | 92.64 ± 0.02 | 93.27 ± 0.01 | |
| KSC | SVM (OA) | 70.41 ± 0.09 | 66.82 ± 0.12 | 54.03 ± 0.02 | 72.51 ± 0.08 | 74.28 ± 0.16 | 80.46 ± 0.05 | 80.08 ± 0.12 | 79.93 ± 0.09 |
| SVM (AA) | 65.06 ± 0.10 | 61.62 ± 0.14 | 45.18 ± 0.02 | 68.34 ± 0.10 | 67.94 ± 0.17 | 73.68 ± 0.06 | 75.14 ± 0.12 | 74.41 ± 0.07 | |
| KNN (OA) | 65.65 ± 0.06 | 63.96 ± 0.07 | 55.74 ± 0.01 | 67.35 ± 0.05 | 74.35 ± 0.07 | 76.21 ± 0.03 | 76.90 ± 0.05 | 76.96 ± 0.05 | |
| KNN (AA) | 51.23 ± 0.07 | 49.36 ± 0.07 | 40.47 ± 0.01 | 53.82 ± 0.06 | 63.93 ± 0.07 | 64.46 ± 0.04 | 67.18 ± 0.06 | 66.20 ± 0.06 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, X.; Shen, X.; Pang, H.; Fu, X. Multiple Band Prioritization Criteria-Based Band Selection for Hyperspectral Imagery. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5679. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225679
Sun X, Shen X, Pang H, Fu X. Multiple Band Prioritization Criteria-Based Band Selection for Hyperspectral Imagery. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(22):5679. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225679
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Xudong, Xin Shen, Huijuan Pang, and Xianping Fu. 2022. "Multiple Band Prioritization Criteria-Based Band Selection for Hyperspectral Imagery" Remote Sensing 14, no. 22: 5679. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225679
APA StyleSun, X., Shen, X., Pang, H., & Fu, X. (2022). Multiple Band Prioritization Criteria-Based Band Selection for Hyperspectral Imagery. Remote Sensing, 14(22), 5679. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225679






