Abstract
In close-range or unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) photogrammetry, Schneider concentric circular coded targets (SCTs), which are public, are widely used for image matching and as ground control points. GSI point-distributed coded targets (GCTs), which are only mainly applied in a video-simultaneous triangulation and resection system (V-STARS), are non-public and rarely applied in UAV photogrammetry. In this paper, we present our innovative detailed solution to identify GCTs. First, we analyze the structure of a GCT. Then, a special 2D P2-invariant of five coplanar points derived from cross ratios is adopted in template point registration and identification. Finally, the affine transformation is used for decoding. Experiments indoors—including different viewing angles ranging from 0° to 80° based on 6 mm-diameter GCTs, smaller 3 mm-diameter GCTs, and different sizes mixed—and outdoors with challenging scenes were carried out. Compared with V-STARS, the results show that the proposed method can preserve the robustness and achieves a high accuracy rate in identification when the viewing angle is not larger than 65° through indoor experiments, and the proposed method can achieve approximate or slightly weaker effectiveness than V-STARS on the whole. Finally, we attempted to extend and apply the designed GCTs in UAV photogrammetry for a preliminary experiment. This paper demonstrates that GCTs can be designed, printed, and identified easily through our method. It is expected that the proposed method may be helpful when applied to image matching, camera calibration, camera orientation, or 3D measurements or serving as control points in UAV photogrammetry for scenarios with complex structures in the future.
1. Introduction
According to the feature type in experimental scenes, the photogrammetric measurement mode mainly contains two types: artificial target based, and natural feature based [1]. For the identification and extraction of natural features, traditional methods such as scale-invariant feature transform (SIFT) [2] and modern methods such as deep learning [3,4] are widely adopted. Artificial targets are easier to identify than natural features and are suitable for scenes lacking texture features, such as geometric feature detection in industry [5,6]. In addition, in image processing, artificial targets and background information can be easily distinguished, and then the process can be accelerated by filtering out useless background information, which leads to the improvement of accuracy and reliability of measurement [7].
Artificial targets include two types: common targets and coded targets [8]. In terrestrial laser scanning or unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) applications, common targets can be used for the registration of a multi-station scanning point cloud or as control points [9]. For example, Mohammadi et al. [10,11] adopted technology combining terrestrial laser scanning and UAV photogrammetry for the application of bridge monitoring. Coded targets are distinguishable targets, so they can be automatically identified and quickly matched due to the unique identities, which can be used not only in close-range photogrammetry but also in machine vision, robot navigation, augmented reality, three-dimensional (3D) scanning surface reconstruction, and many other fields [12,13,14]. In close-range or UAV photogrammetry and 3D reconstruction, coded targets are always used as tie points between images with overlapping regions, which is crucial for bundle adjustment [15]. Coded targets can also be used as well-organized control points to carry out automatic resection to obtain the camera’s external orientation elements [16]; for coded reflective targets, they can be used to automatically calibrate the sensor’s pose of light detection and ranging (LiDAR) [17]. In addition, based on the accurate relative orientation of cameras, they are helpful in finding the corresponding features by the calculation of epipolar relationships [18]. Finally, for 3D dimensional measurement, coded targets may be a reference scale when lacking a dedicated scale bar [19].
In close-range photogrammetry and computer vision, many kinds of coded targets have been used, which can be found in [7,15,20]. These types of coded targets include cyber code, circular point-distributed code, circular ring-shaped code, QR code, Chinese character code, etc. The current studies about coded targets aim at how to identify them, how to expand the capacity, how to strengthen the stability, and how to improve the identification accuracy or the positioning precision [7,18,19,20,21]. Different coded targets differ in processing algorithms. The methods based on conventional image processing are popular; however, when faced with new backgrounds and illumination conditions, low robustness can be its limitation. Recently, a method based on deep learning has been adopted to try to solve the issue [22].
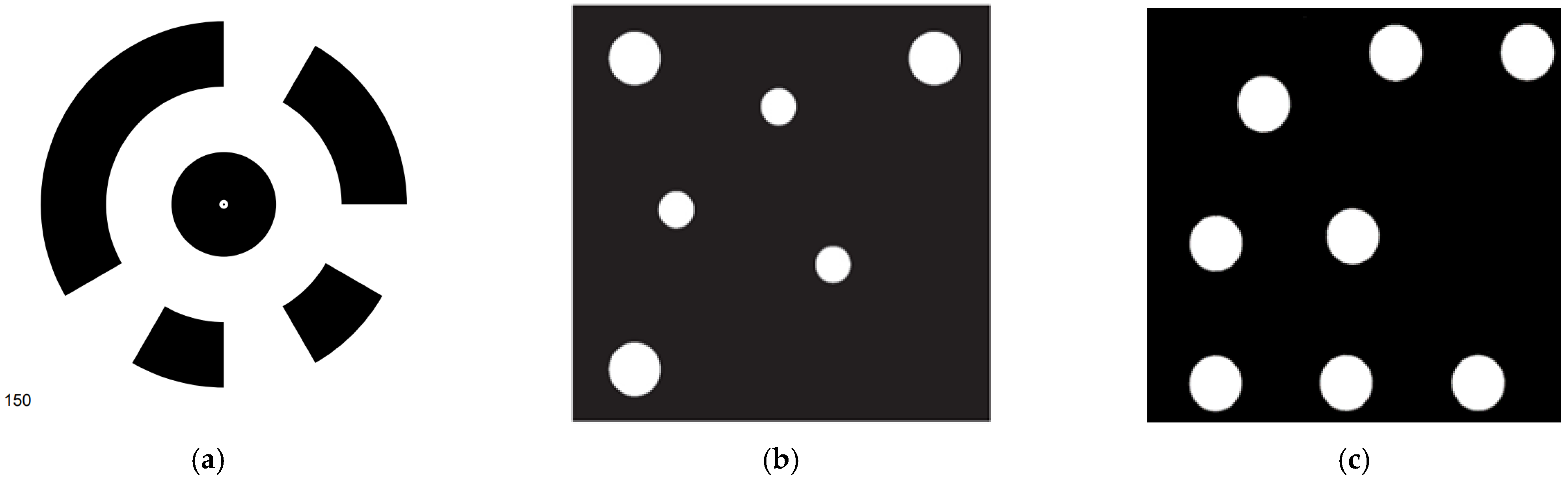
Three representative coded targets are shown in Figure 1: Schneider centripetal circle coded targets (SCTs) [23] (Figure 1a) used in fully automatic 3D modeling software Agisoft Metashape, Hattori point-dispersing coded targets (HCTs) [24] (Figure 1b), and Geodetic Systems Inc (GSI) coded targets (GCTs) used in Video-Simultaneous Triangulation and Resection System (V-STARS) [25,26] (Figure 1c). It should be pointed out that GCTs are also applied in another close-range photogrammetric software called AUSTRALIS [27,28]. They have been applied to many fields, such as industrial metrology, machine vision, robot navigation, dynamic tracking, archaeology, and architecture due to its advantages of high speed, high accuracy, and high degree of automation [29,30].
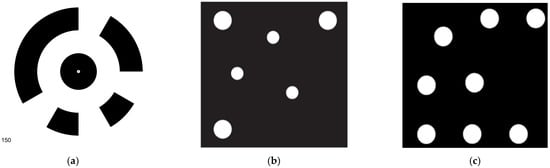
Figure 1.
Three classical types of coded targets in photogrammetry: (a) SCT; (b) HCT; (c) GCT.
SCT adopts ring designs [23]. The central circle is for positioning, and the ring band surrounding it is for decoding. It employs binary encoding, i.e., using values of 0 and 1. The ring is divided into several encoding bits, where the black bit represents 1 and the white bit represents 0. Every shape corresponds to a unique identity of coding serial number, and the coding serial number is 150 as shown in Figure 1a. HCT adopts point-distributing designs [24]. Three bigger circular points remain fixed, which define the coding coordinate system, and three smaller points are changeable, which are for decoding. GCT is somewhat similar to HCT but more complex than HCT [25]. It contains eight equal-sized points, in which five remain fixed and the other three are changeable. The coding capacity of SCTs is determined by all possible combinations of binary encoding bits. The coding capacity of HCTs and GCTs are determined by all possible combinations of three decoding points’ distributions. The coding capacity of SCTs, HCTs, and GCTs is 256, 420, and 505, respectively [7]. This means 505 GCTs can be placed in one measurement scenario at once, so the GCTs can be applied in a more complex or larger working environment compared with SCTs and HCTs. In another aspect, SCTs and HCTs are not stable and are prone to false identification due to noise, while GCTs are more stable and are not easily disturbed by noise [31]. Considering the limitations of SCTs and HCTs, it is of importance to adopt GCTs for high-standard demands.
The identification method of SCTs and HCTs has now been made public, so we can learn the identification theory from public papers [23,24]. However, as Tushev et al. [20] mentioned, the identification method of GCTs has not been disclosed, which is embedded in closed-source system V-STARS and the details are not publicly available due to commercial interest. As introduced in V-STARS acceptance test results by GSI [32], the estimated accuracy of the single camera system is as high as 8.5 ppm, so it is necessary to pay more attention to V-STARS. Since the identification of GSI coded targets is of great significance and complicated, we herein present our detailed analysis about the design of GCTs and propose a very effective and robust identification method. Based on the proposed method, the GCTs can be easily designed, printed, and identified independently.
2. Methods
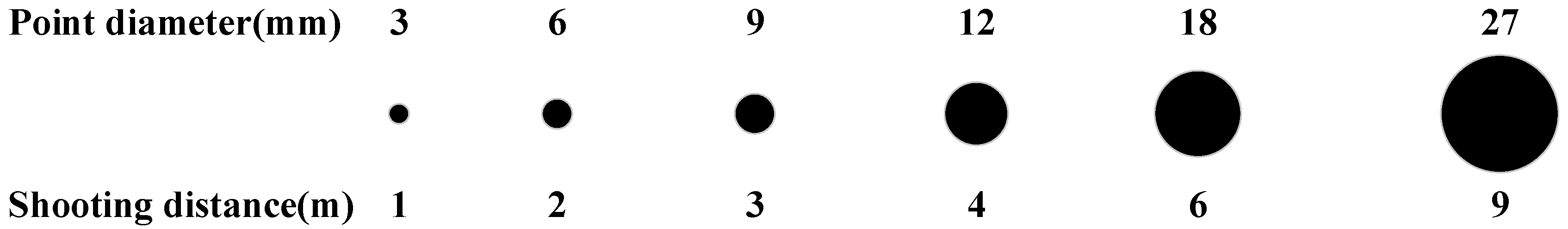
Different sizes of measured objects rely on different shooting distances, which also correspond to different sizes of coded targets. The relationship between point diameter and shooting distance is illustrated in Figure 2. In image processing, the corresponding relationship can also be adopted to achieve pseudo-target removal through geometric constraints. The GCTs contain different kinds of sizes. As Sukhovilov et al. [19] introduced, in V-STARS, 3 mm, 6 mm, and 12 mm are mostly used.

Figure 2.
The relationship between point diameter and shooting distance.
2.1. Construction of GCTs
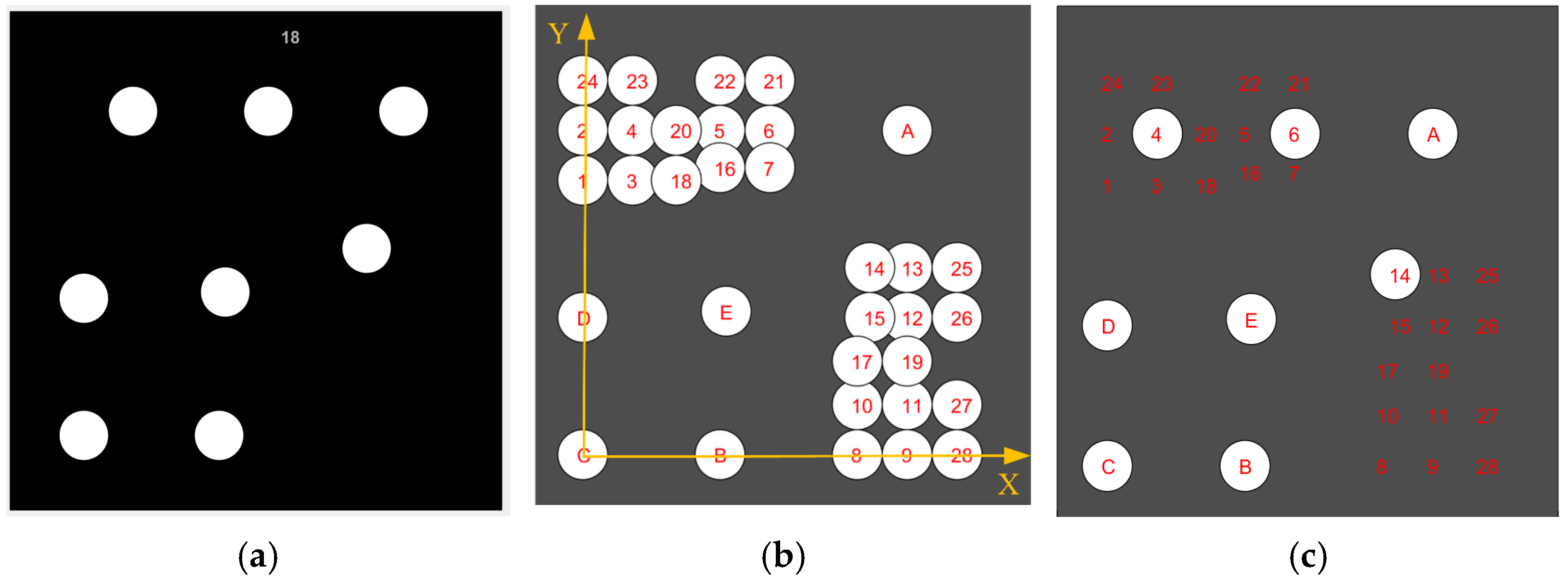
Figure 3a shows a GCT, which consists of eight points. Now, we analyze the structure of a GCT. Five points remain fixed while the other three points are changeable. Thus, we define the five points as template points and the other three points as encoding/decoding points. Figure 3b is a distribution reproduced according to the coding structures and rules of GCTs. Each GCT in the coding library contains five template points (A, B, C, D, and E), whose roles are as follows: E is the positioning center of a GCT; B, C, and D together form an independent planar coordinate system as shown in Figure 3b; A, E, and C are collinear. The other three decoding points are randomly combined from the two groups of points in the upper left and lower right. What should be ensured is that the two decoding points adopted in the same group are separated by at least one point, and all three decoding points cannot be in the same group.
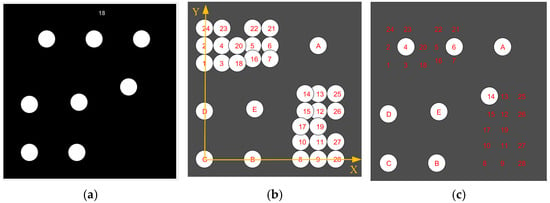
Figure 3.
The structure of a GCT: (a) a GCT named CODE18; (b) deployment of all possible GCTs with identical template points; (c) the decoding points’ number and distribution of CODE18.
The designed coordinates of the five template points and twenty-eight coding/decoding points are pre-stored as known values, as shown in Table 1. Different combinations of decoding point numbers can obtain different coding values, and each coding value corresponds to the coding serial number uniquely, as shown in Table 2. The coordinate values, coding values, and coding serial numbers of these known decoding points together constitute the coding library. The designed GCTs take the sum of the second power of the three decoding points’ number as the coding value. For example, the numbers of the three decoding points in Figure 3c are 4, 6, and 14, respectively, so the decimal coding value is 24 + 26 + 214 = 16,464. In the coding library, the coding value 16,464 corresponds to CODE18, so the coding serial number of the GCT is CODE18. A total of 505 coding serials are stored in the coding library, namely CODE1-CODE505, which means the coding capacity of GCTs is 505.

Table 1.
Designed coordinate values of GCTs.

Table 2.
The decoding library of GCTs.
2.2. Identification of Template Points
A, B, C, D, and E are the template points of a coded target and are the most important identities of the coded target. In order to identify the template points in the case of image distortion, a geometric invariant of the five points’ relationship under projective transformation should be found. We know that under the projective deformation, the cross ratio contains geometric invariants [33]. It is well known as the one-dimensional (1D) cross ratio based on collinear four points [34,35]. Lei [36] performed recognition of planar objects in 3D space using a cross ratio invariant. For A, B, C, D, and E, we seek a cross ratio invariant of five coplanar points. In ref [37], a two-dimensional (2D) cross ratio invariant is adopted to achieved correspondence of coplanar features for two patterns, both of which contain five points. Inspired by [37], we adopt the 2D cross ratio invariant to achieve correspondence of template points. First, the 1D cross ratio is introduced, and then the 2D cross ratio based on five coplanar points is introduced.
2.2.1. P2-Invariant of Four Collinear Points
The 1D cross ratio of collinear four points ( = 1…4) can be defined as follows:
where denotes the oriented distance constructed by and . The above cross ratio remains constant under any projective transformation. However, the permutation order of the points affects the value of the cross ratio. Four collinear points contain 4! = 24 different sequences.
As a result, a 1D Projective and Permutation Invariant (P2-Invariant) [37,38,39] has been proposed to solve the problem of efficient registration of four collinear disorderly points.
Define function , = 1,2.
Polynomial functions and are unbounded, but their ratios are bounded.
The value of is between 2 and 2.8 [37] and can be used as the P2-invariant for the registration of four disordered collinear points.
2.2.2. P2-Invariant of Five Coplanar Points
The 2D cross ratio is based on the 1D cross ratio. Similarly, the 2D P2-invariant can be evolved from the 1D P2-invariant.
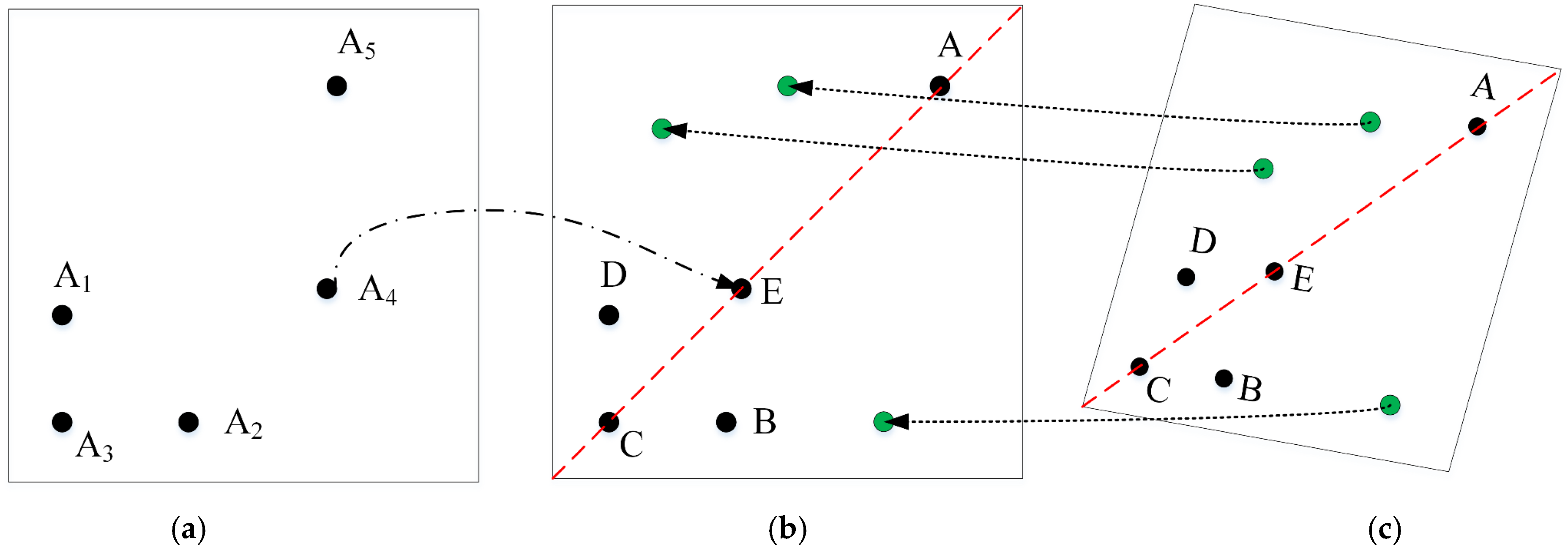
As shown in Figure 4a, the five coplanar points in total contain 5! = 120 different sequences. Next, we identify a P2-invariant to realize efficient registration for five disorderly coplanar points. Using each point as a vertex reference, five coplanar points can give five different 2D cross ratios: , , , , and . The last three cross ratios can be expressed as the function of the first two independent cross ratios, namely and , as shown in Equation (4) [37].
where is the oriented area of the triangle formed by the points , , and . is the shared point by all four triangles for . Similarly, , , , and are the shared points by all four triangles for , , , and , respectively. With one point as the common point of the triangle, the remaining four points can produce 24 different orderings. It can be seen from Equation (4) that the P2-invariant based on each shared point can be obtained from . The 2D P2-invariants corresponding to five different points can be expressed as a function of and , and , = 1…5.
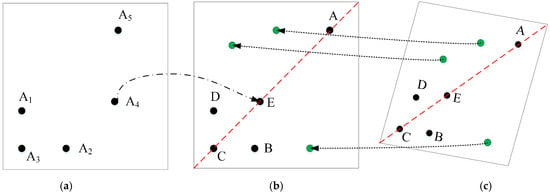
Figure 4.
Five coplanar points. (a) Common coplanar points; (b) template points with three collinear points; (c) template points under projective deformation.
Sorting Equation (5) in ascending order, , a new vector can be obtained:
is regarded as the 2D P2-invariant of five coplanar points. Then, it can be used as the registration feature of two point sets under projective transformation.
The five template points of GCTs are coplanar, and Equation (6) can be considered for registration and identification for template points. That is, , , , , and in Figure 4a correspond to D, B, C, E, and A in Figure 4b, respectively. It should be noted that Equation (6) requires that any three of the five coplanar points are not collinear; otherwise, the oriented area of is probably equal to zero. Among the five template points, C, E, and A are indeed collinear. Therefore, Equation (6) cannot be applied directly. For these five special coplanar points, we will adopt a special way to deal with them.
2.2.3. Identification of Template Points under Collinear Condition
In the template points, C, E, and A are collinear, which can be regarded as , , and being collinear. Therefore, none of the collinear points are suitable as shared points, whereas template points D and B can be shared points. C, E, and A are collinear and E is between C and A. Under projective transformation, except that the collinear relationships do not change, E is still in the middle of the three collinear points. Therefore, E can be clearly used as an anchor point, and there is ambiguity between C and A. D and B are on either side of the line , and there is ambiguity between them. Therefore, when C, E, and A are collinear, D and B serve as the shared points to solve and , respectively. Now, the vector is the P2-invariant of five coplanar points when three points are collinear. Put simply, we further propose using the maximum element in the vector as our P2-invariant.
Supposing that the P2-invariant of template points in the designed image is and the P2-invariant in the projective transformed image is , they should be approximately equal; that is,
where denotes the threshold. The point that meets this condition can be identified as a template point; that is, it can be preliminarily identified as a coded target.
According to the designed coordinates of five template points in Table 1, the calculated truth value of P2-invariant is 2.402.
2.3. Decoding
When the five template points are identified, the remaining three points are regarded as decoding points, as shown in Figure 4b,c. The solution of decoding points depends on the transformation parameters between the designed coordinate system and the image coordinate system determined by template points. The scenes used for GCTs mainly belong to close-range photogrammetry, so projective deformation can be simplified to affine deformation [40]. In ref [24], the three small circular points were applied by affine transformation to decode the HCTs. So, inspired by that, we adopt the affine transformation to decode the GCTs.
(x,y) and (u,v) represent the coordinates under the designed coordinate system and under the image coordinate system, respectively. By substituting the designed coordinates and the actual image coordinates of five template points into Equation (9), six affine transformation parameters (,,,,,) can be solved by using the least square method. By substituting the image coordinates of the three decoding points into Equation (9), the coordinates under the designed coordinate system can be obtained. By comparing with the designed coordinate values, three points with minimum error are selected for decoding. As shown in Figure 4b,c, the coordinates of the decoding points after affine transformation are most similar to those of the decoding points no. 4, 6, and 14, so the corresponding coding value is 16,464 and the decoded serial number is CODE18.
The following describes the detailed decoding process of CODE18. The image coordinates of its eight points and the corresponding designed coordinates of the five template points are shown in Table 3. By substituting image coordinates of the five template points into Equations (9), the calculated P2-invariant is 2.475. I, II, and III are the number-undetermined decoding points.

Table 3.
Image coordinates and designed coordinates of template points.
Substituting and of A, B, C, D, E into Equation (9), the six parameters of affine transformation can be solved as shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
Six parameters of affine transformation.
Through affine transformation parameters, the transformed coordinates in the designed coordinate system of decoding points (I, II, and III) in Table 5 can be obtained from image coordinates. Compared with designed coordinates in the decoding library in Table 2, the most proximate corresponding coordinates are selected, and the positioning bias and point numbers are shown in Table 5.

Table 5.
Decoding of a GCT (unit: mm).
According to the coding library in Section 2.1, the encoding or decoding value of this GCT is 16,464, and the corresponding decoding serial number is CODE18, as shown in Figure 5.
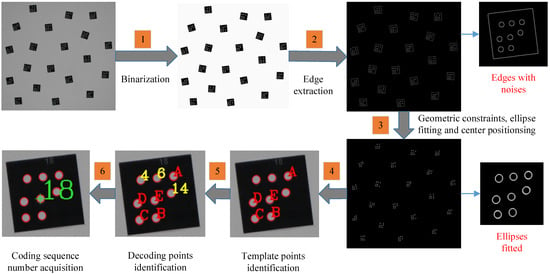
Figure 5.
Procedure of identification.
2.4. Identification Process of GCTs
The identification process of GCTs involves some details to obtain ideal results. So firstly, we present several important technical instructions and then present the procedure of identification.
- (1)
- Geometric Constraints
To recognize the target point, the ellipse edge should be extracted in advance. The edge noises which can disturb the ellipse detection should be removed, as shown in Figure 5. As introduced in Section 2.1, specific geometric constraints can filter out most useless false point information when the point diameter and shooting distance are certain. Here, perimeter C, area S, and roundness K are used to detect ellipse edges [7]. In OpenCV [41], function cvFindContours can obtain the detected edges separately, and functions cvArcLength and cvContourArea can obtain the perimeter and area of every edge. The roundness K represents how close an ellipse is to a circle and is defined as Equation (10). The range of K is 0~1. The larger the viewing angle, the greater the ellipticity and the smaller the K.
As shown in Figure 5, the rectangular frame belongs to edge noises for ellipses, and it can be filtered out by constraints of geometric parameters shown in Table 6.

Table 6.
The parameter ranges of geometric constraints.
- (2)
- Center Positioning of Points
To obtain the center position of points, ellipses are fitted in this paper. CvFitEllipse [41] is used to fit ellipses for the contour of each potential point. Once the elliptic equation is determined, the center coordinate of each point is obtained.
- (3)
- Point-set Search
Point-set search is used to find points belonging to the same GCT from all possible ellipses. We adopt neighborhood search to obtain the point-set. D represents the search scope, as shown in Equation (3), where represents the length of the major axis of an ellipse, represents the count of ellipses, and is a scaling factor.
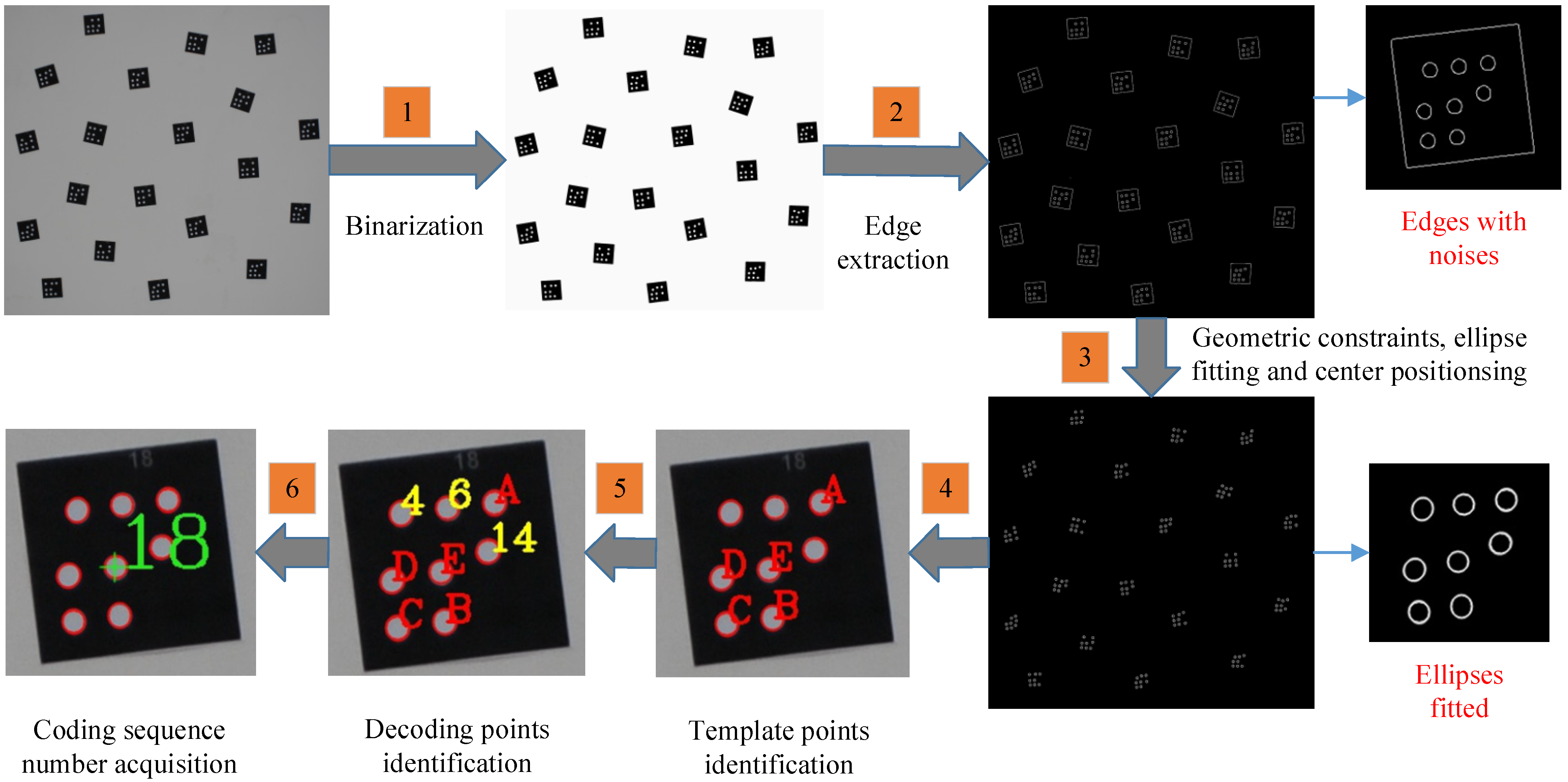
The following is a detailed description of the entire identification process. As shown in Figure 5, six steps in total are needed to perform the identification of GCTs.
Step 1. Binarization. Firstly, the image is converted into a grayscale image, and then the grayscale image is binarized to peel the coded targets from the background. The binary threshold can be adjusted according to the illumination intensity and circumstance. A value of 100 is applicable for most conditions.
Step 2. Edge extraction. Based on a binarized image, the edge is extracted to obtain edge features, including elliptical markers and uninteresting objects. In this paper, we adopt Canny to track edges and obtain contours.
Step 3. Geometric constraints, ellipse fitting, and center positioning. By setting filtering conditions such as roundness, circumference, and area, the edge features of non-interested targets are removed to obtain pure elliptical edge features belonging to coded targets. The elliptical markers are obtained by fitting the elliptical edges with least square ellipse fitting, and then the center coordinates of each elliptical marker are obtained.
Step 4. Template point identification. The key is to search the point set and determine which five points can be template points with the best possibility. This first step is to find the set of points that make up each complete coded target. We traverse each elliptical marker, based on each elliptical marker as the center, and search within a certain radius to find the nearest seven points to constitute an eight-point set. Then, we find out the template points according to the following constraints:
- Find three collinear points among the eight points, and then check the remaining five points. Make sure that three points are on one side of the line formed by these three collinear points and that the other two points are on the other side.
- Choose a point separately from either side of the line, which together with the three collinear points form five coplanar points to construct P2-invariant. Except for the three collinear points, two of the remaining five points are selected to join with the three collinear points to construct template points. The two points are constrained by the geometric restricted condition , where is the distance from the positioning point E to D or B. The applicable value of is 2.5.
Step 5. Decoding point identification. The key is to calculate the affine transformation parameters. Firstly, we solve the corresponding affine transformation parameters according to five template points, and then execute coordinate transformation for the remaining three decoding points according to the transformation parameters. Thus, we can obtain the calculated coordinates of the remaining three decoding points in the designed coordinate system. By comparing with the designed coordinates in the decoding library, we select the three adequate decoding points which satisfy the following distance constraint condition: , where is set as 1.0.
Step 6. Coding serial number acquisition. Based on the numbers of three identified decoding points, we calculate the decoding value, find the corresponding decoding value in the coding library, and then realize the decoding of the coded target.
3. Results
As introduced in Section 2, the point diameter sizes 3 mm, 6 mm, and 12 mm are three representative coded targets used in V-STARS. The size 6 mm is the most widely used in common scenarios [19], so we adopted this size type of GCTs for the main experiments. The size 3 mm was also adopted for the aided experiment, which is fit for small measured objects. The size 12 mm is fit for a large measured object and long distance. We designed and printed GCTs with ordinary A4 paper ourselves. Indoor and outdoor experiments were carried out with a digital single lens reflex camera (Nikon D300S, whose resolution is 4288 * 2848) using a lens equipped with a Nikon AF NIKKOR (20 mm F/2.8D). We also performed a UAV test. All the experiments are compared with V-STARS 4.7 Edition. It is worth mentioning that the identification results of V-STARS are grayscale, not colored.
3.1. Experiment for Indoor Scenes
Usually, the brightness indoors is uniform and balanced. Most applications of GCTs are carried out indoors. Therefore, indoor experiments are the core of this paper.
- (1)
- Experiments with Increasing Step of Viewing Angles
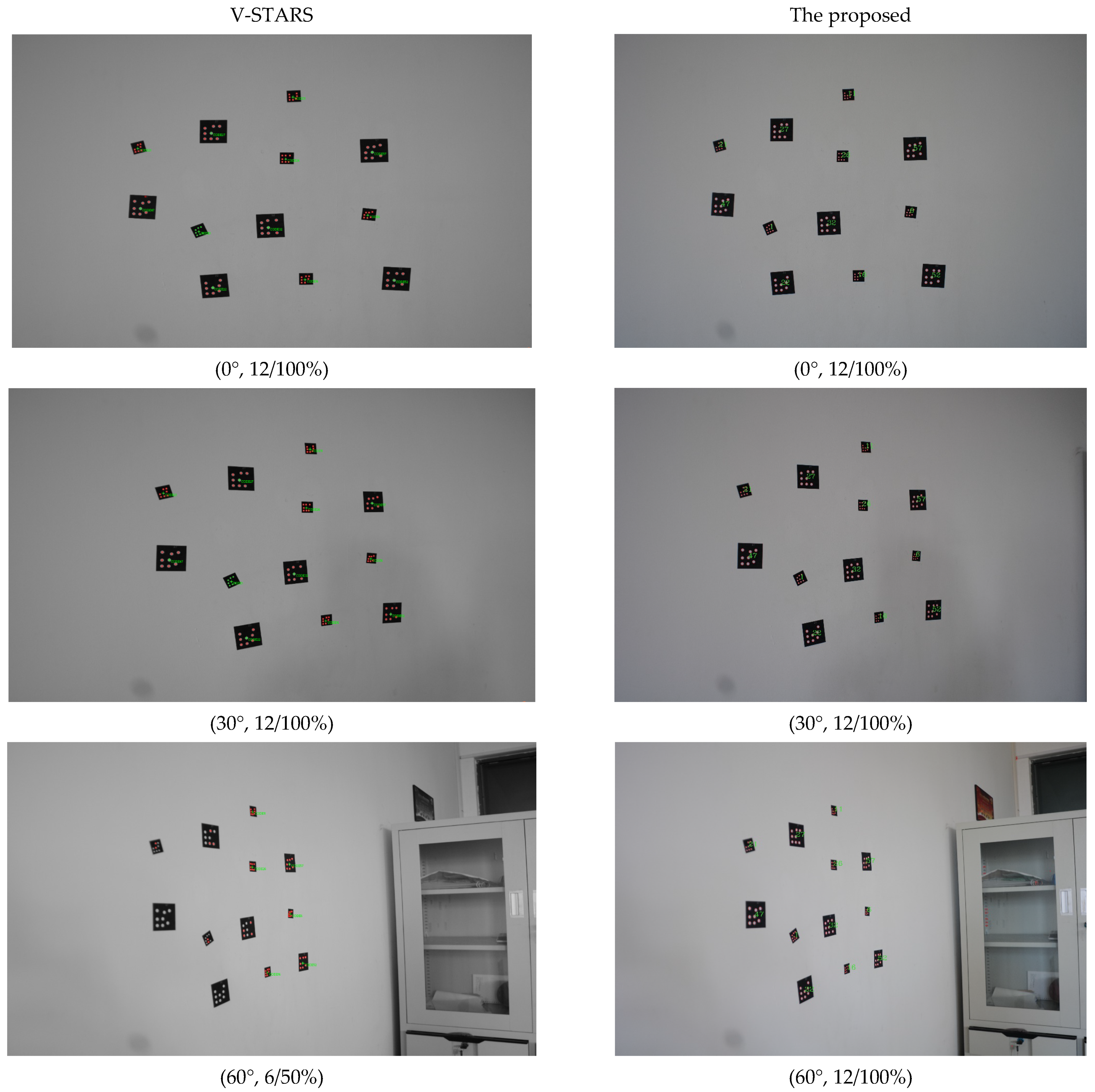
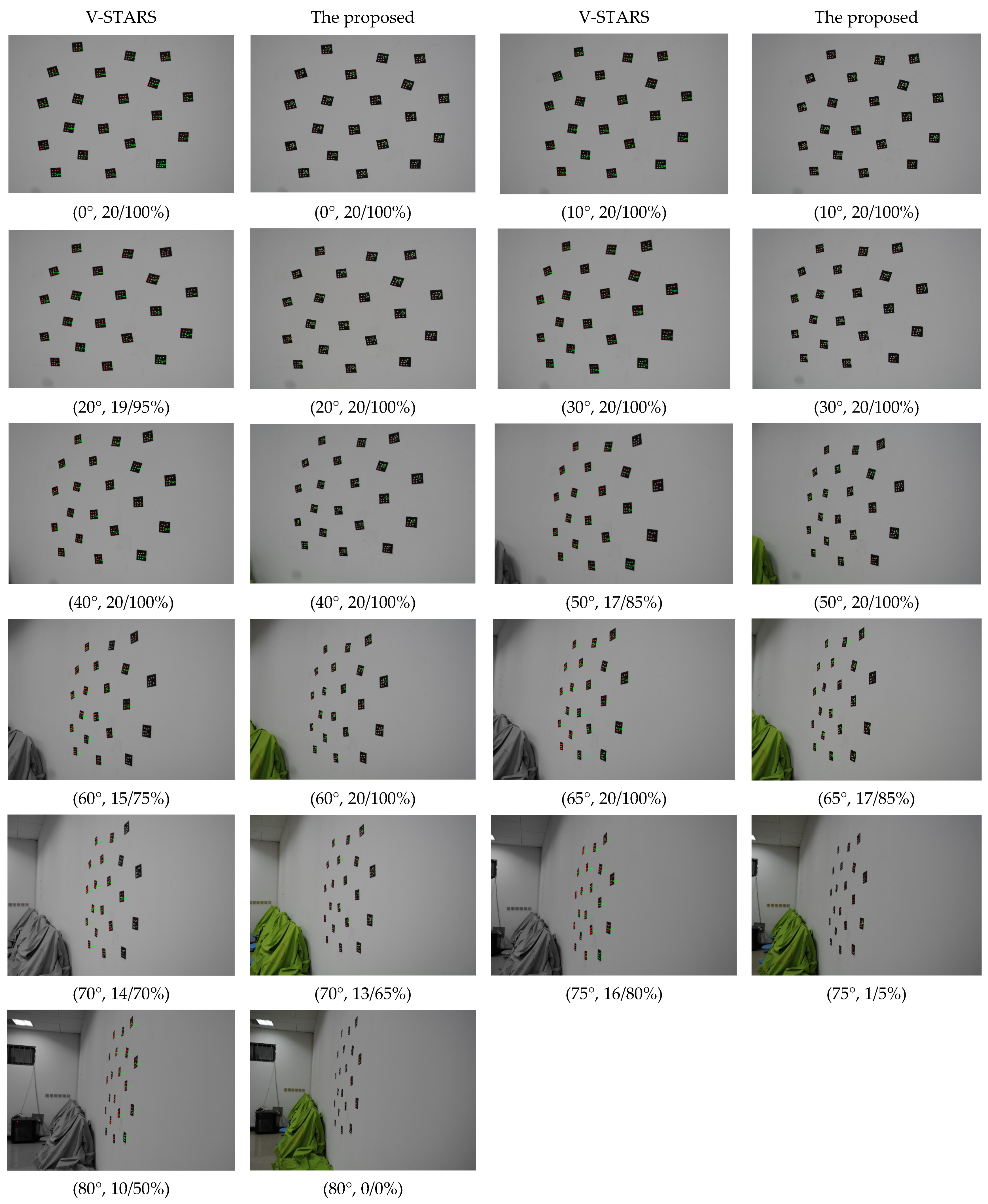
The image deformation is affected by perspective projection transformation. When the viewing angle is larger, the perspective deformation is more serious, which may affect the identification of GCTs. Therefore, experiments at viewing angles of 0°, 10°, 20°, 30°, 40°, 50°, 60°, 65°, 70°, 75°, and 80° were performed to verify the stability and the effectiveness of the identification method. Twenty 6 mm GCTs were pasted on the white planar wall. The shooting distance was close to 2 m. The binarization gray threshold was set to 90. The parameters below every image represent the viewing angle, correct identifications, and accurate identification rate, respectively.
As shown in Figure 6, the proposed method can achieve a very good identification result when the viewing angle is smaller than 60°. The correct identification ratio is 100%. When the viewing angle reached 70°, the correct identification ratio dropped to 65%, and only one GCT was identified when the viewing angle was 75°. It failed when the viewing angle was 80°. Compared with V-STARS, the proposed method showed better performance when the viewing angle was smaller than 60°, but showed worse performance when the viewing angle was larger than 60°. When the viewing angles were larger than 70°, many GCTs could not be identified, although the ellipses were extracted. So, it can be deduced that the ellipses extracted were not accurate and the center positioning was no longer unknown. When the viewing angles were larger than 75°, many ellipses could not be extracted; however, they could be extracted by V-STARS. We can infer that the algorithm of ellipse extraction is different between V-STARS and the proposed method in this paper.
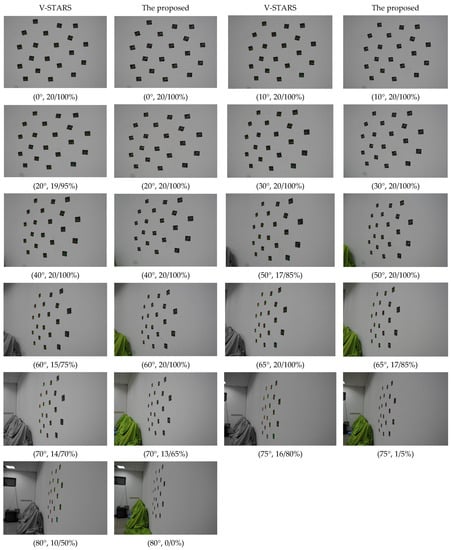
Figure 6.
Identification results of different viewing angles with increasing steps for 6 mm GCTs.
- (2)
- Experiments with Small GCTs
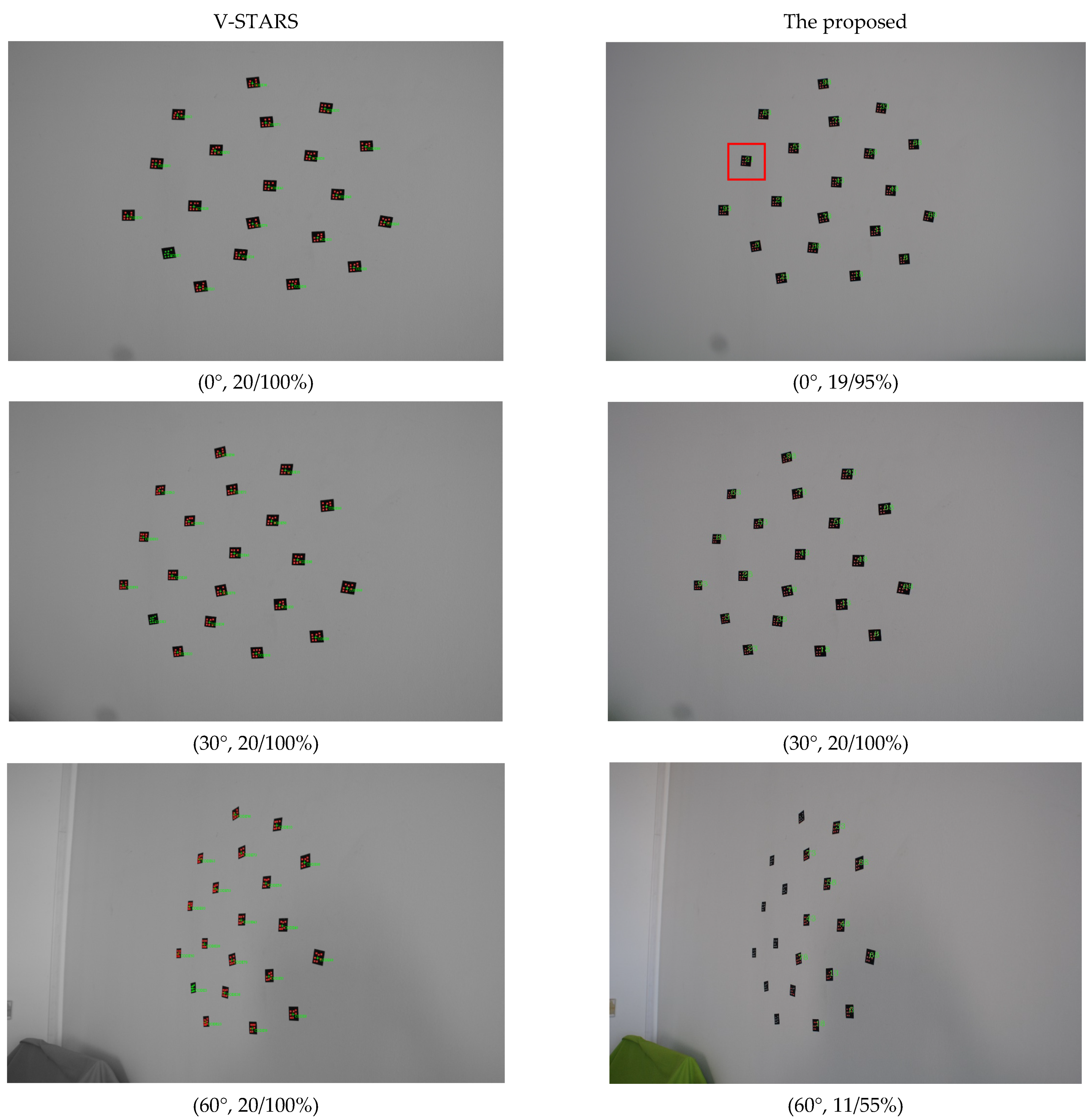
Experiments at viewing angles of 0°, 30°, and 60° were performed to verify the stability and effectiveness of the identification method with twenty small 3 mm GCTs. The shooting distance was close to 1 m. The comparison results are shown in Figure 7.
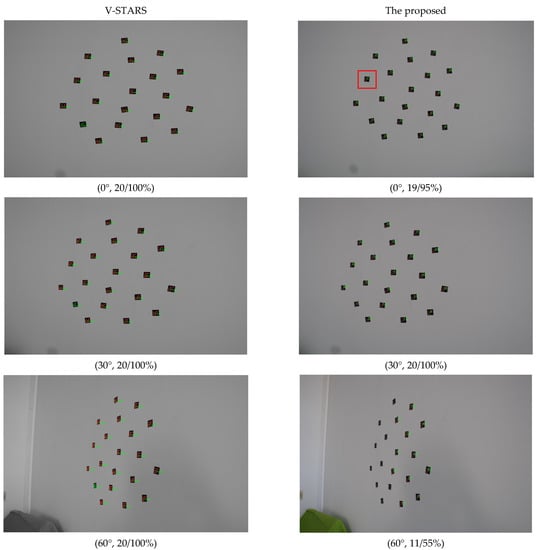

Figure 7.
Identification results of small 3 mm GCTs.
For small GCTs, V-STARS can achieve rather good results, with all GCTs correctly identified. The proposed method behaves a little worse. It had a false identification when the viewing angle was 0° (CODE83 was misidentified as CODE21). The reason is that the structures of CODE21 and CODE85 are very similar or mirror symmetric, so the decoding points number 6 and 14 were regarded as template points D and B by mistake. So, it is important to improve the identification precision for GCTs that have slight differences between each other.
- (3)
- Experiments with mixed GCTs
Six 6 mm GCTs and six 3 mm GCTs were mixed and pasted on the wall. The shooting distance was 1.5 m. The comparison results are shown in Figure 8.
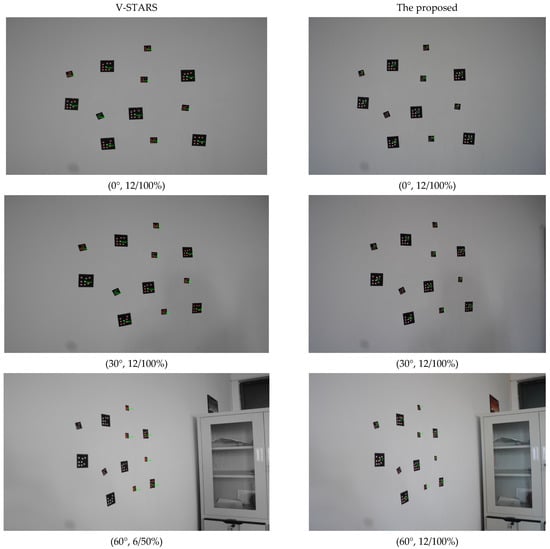

Figure 8.
Identification results of mixed GCTs with 3 mm and 6 mm.
When the GCTs are mixed, the proposed method can obtain a better result than V-STARS, as seen from the comparison results for 60°. For the proposed method, the half of the GCTs close to the camera have a better identification result compared to V-SATRS, which again indicates that the algorithm of ellipse extraction applied in this paper differs from V-STARS.
3.2. Experiment for Outdoor Scenes
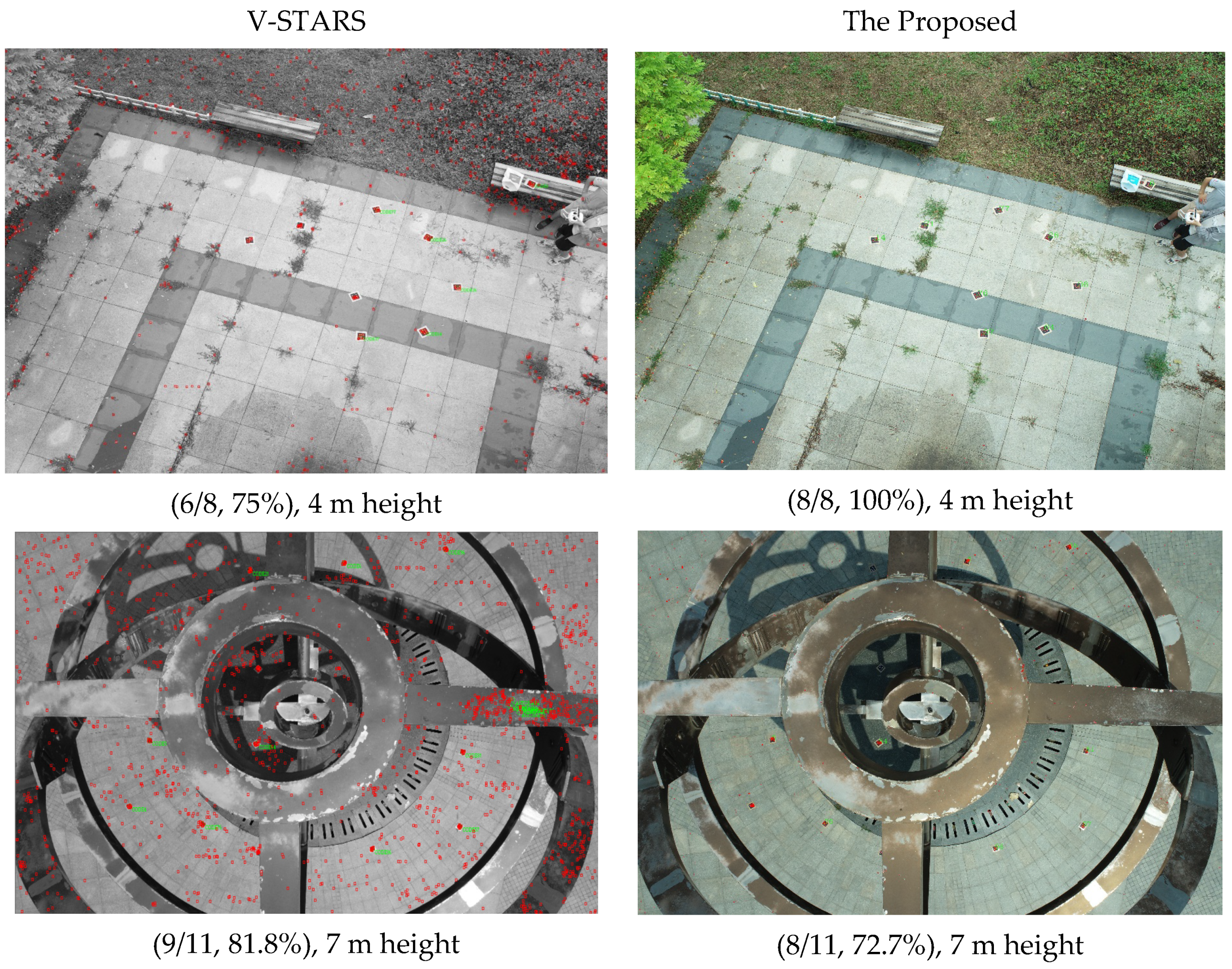
Outdoor scenes are usually more challenging than indoor scenes. To illustrate the effectiveness for outdoor scenes with complex structures and brightness, we chose a building to test outdoors. The shooting distance was 2 m. Figure 9 shows that scenes illuminated to varying degrees can be processed smoothly. Although there is a lot of false elliptical noise in the outdoor images, almost all the GCTs are correctly identified as the noise can be filtered or abandoned automatically by constraints, which fully demonstrates the effectiveness of this innovative method. We can determine that the proposed method and V-STARS can both achieve a good identification result at close range outdoors.
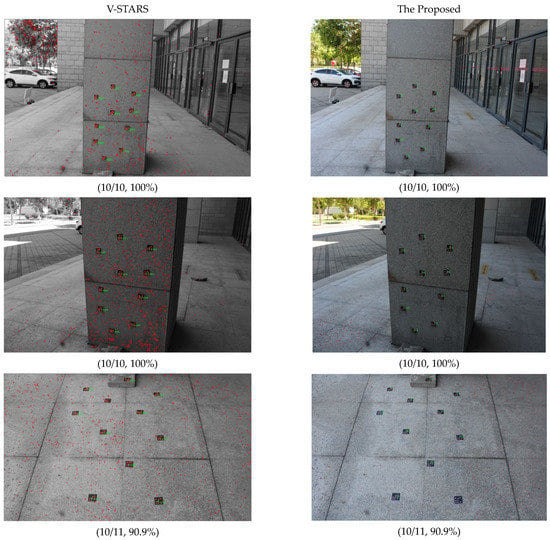

Figure 9.
Experiment for outdoor scenes. The second column represents the count of GCTs contained in the image.
From the indoor and outdoor tests, all the coded targets can be basically accurately identified, which indicates that the template points are accurately identified. It also shows the effectiveness of adopting the proposed P2-invariant of five coplanar points to identify the GCTs. It can be found that V-STARS can extract more noise. This noise presented as many red elliptic dots, which can potentially interfere with the identification of GCTs, but the identification results are still good. V-STARS can almost identify every GCT once the eight elliptic points of this GCT are extracted. However, the proposed method cannot always identify every GCT, even though the eight elliptic points of this GCT are extracted, which illustrates that the ellipse extraction in this paper is not as accurate as the ellipse extraction applied in V-STARS.
3.3. Experiment for UAV
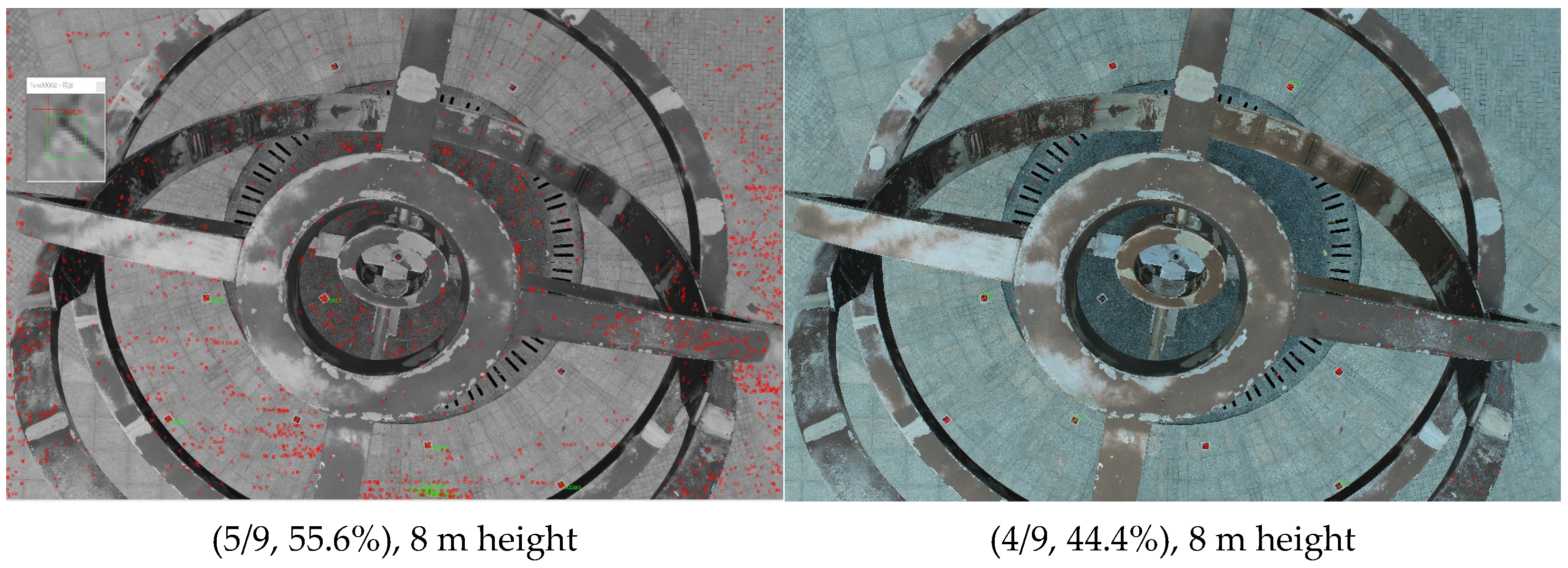
To verify the possibility of use in UAV photogrammetry, additional experiments were carried out with a DJI Phantom 4 RTK. The camera was FC6310R (the resolution is 5472 * 3648), and the GCTs were 12 mm in diameter. The height represents the distance from the UAV to the ground vertically. The sunlight is non-uniform and there are shadows inside the second image. The three images have been captured with different lighting conditions at different times.
From Figure 10, as a whole, the identification performance of the proposed method is equal or a little inferior to V-STARS. When the fly height is moderate, the proposed method behaves rather well, but when the distance is higher, the proposed method behaves barely satisfactorily. The higher targets are vaguer; larger GCTs are needed if a better result is desired. In addition, the GCTs in the shade in the second image cannot be identified with the GCTs in the sunlight at the same time, which is also a challenge for UAV application in the field.
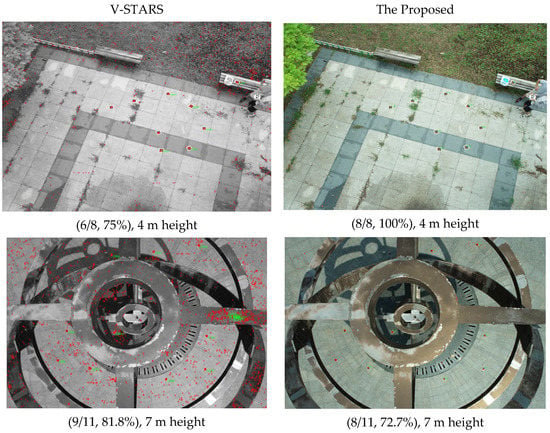

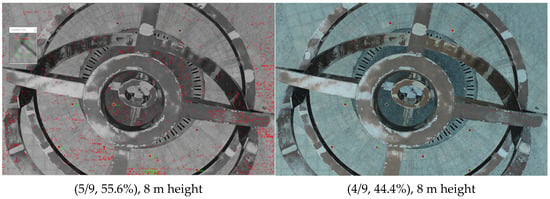
Figure 10.
Experiment for UAV.
4. Discussion
From the experiment results above, we can see that the identification is relatively robust and effective; however, some GCTs cannot be identified or correctly identified. So, in this section, we will discuss the reasons why our method shows robustness and effectiveness, and why some GCTs are not correctly identified.
Herein, a robustness and accuracy analysis is presented. Two parameters, the P2-invariant of template points and the identification bias of decoding points, are adopted to analyze the influence of different viewing angles on the robustness and accuracy of GCTs. The precision of P2-invariant can affect the identification robustness of the five template points, and the identification bias of decoding points can affect the identification accuracy of the GCTs. Finally, the precision of center positioning of GCTs is shown to evaluate the precision of ellipsis extraction for the proposed method. Analysis data are chosen from the experiments in Figure 6 with increasing steps of viewing angle.
4.1. The P2-Invariant of Template Points
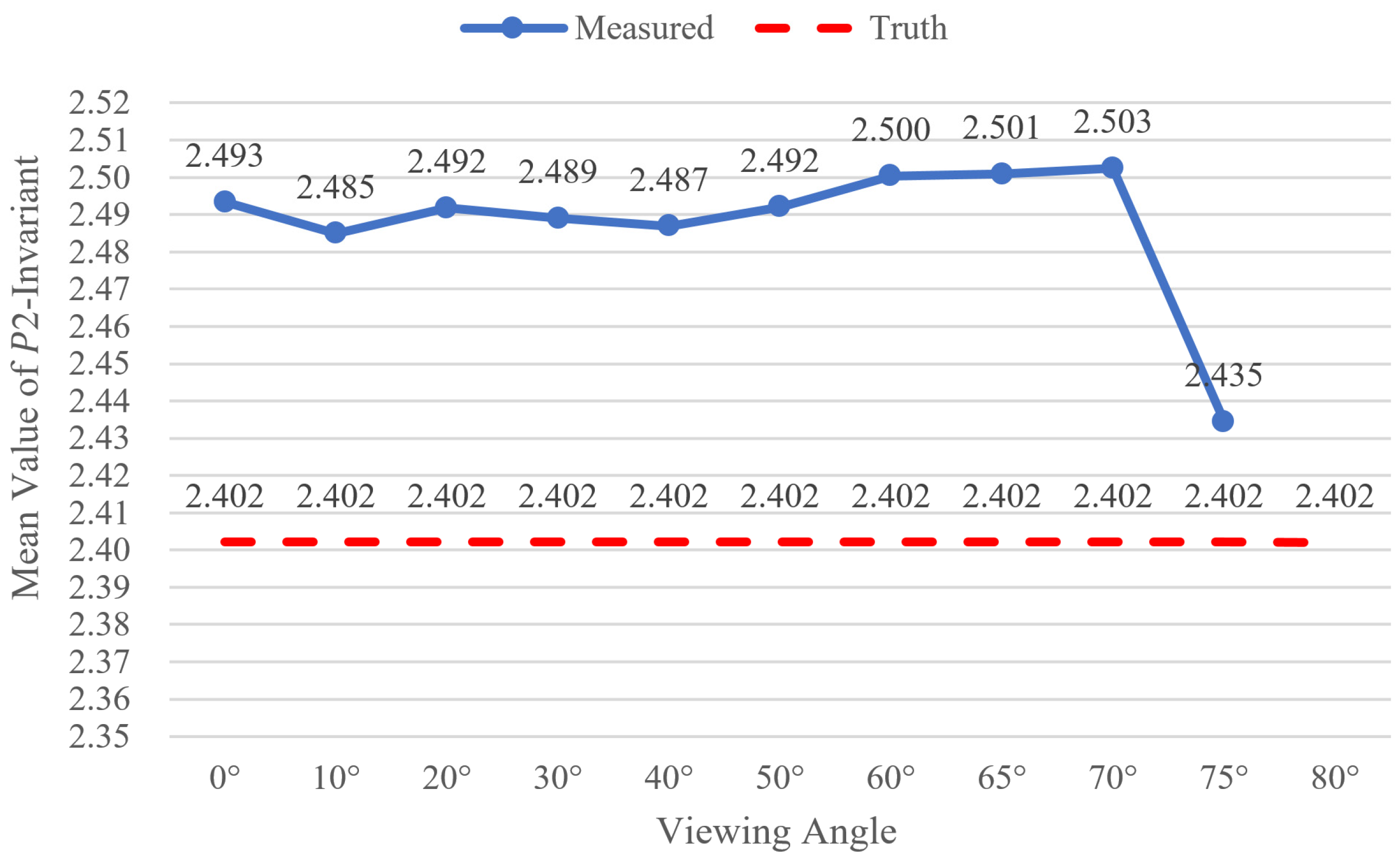
The theoretical or designed value of P2-invariant is 2.402. The mean values of P2-invariant of all GCTs under each viewing angle are given in Figure 11. The data reflect that the mean values of P2-invariant of the eleven viewing angle experiments are similar and close to the theoretical value.
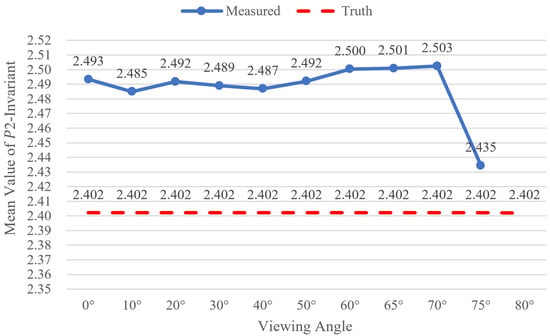
Figure 11.
The variation in mean value of P2-invariant with increasing steps of viewing angle.
For each experiment, the range, mean, and root mean square error (RMSE) of P2-invariant values of all GCTs are shown in Table 7. The minimum value is 2.401 and the maximum value is 2.587, so the amplitude of variation is as small as 0.186, which can be an appropriate threshold for the difference between the calculated and the designed P2-invariant. The minimum exists under a viewing angle of 75°, the maximum exists under a viewing angle of 65°, and the maximum RMSE 0.048 also exists under a viewing angle of 75°, which indicates the precision of P2-invariant decrease at a viewing angle larger than 65°. However, as the mean values have no apparent discrepancy, the ∆ P2_RMS also remains small and stable at every viewing angle. The ∆ P2_RMS remains at around 0.025, which is stable and matches the descriptions in another study [37] in which the P2-invariant was used to achieve the correspondence of coplanar features. Meanwhile, ref [38], which used P2-invariant of collinear four points to achieve the recognition and detection of a Pi-Tag maker, also showed good performance. Compared with refs [37,38], it was proven that the coplanar P2-invariant derived from collinear P2-invariant was also valid for recognizing a coded target. However, in refs [37,38], they did not give sufficient statistics results under different viewing angles. From the detailed analysis in this paper, it is indicated that P2-invariant is a robust key to perform the role for identifying GCTs, and it also ensures that the GCTs can be very effective and robust.

Table 7.
The range and precision of P2-invariant.
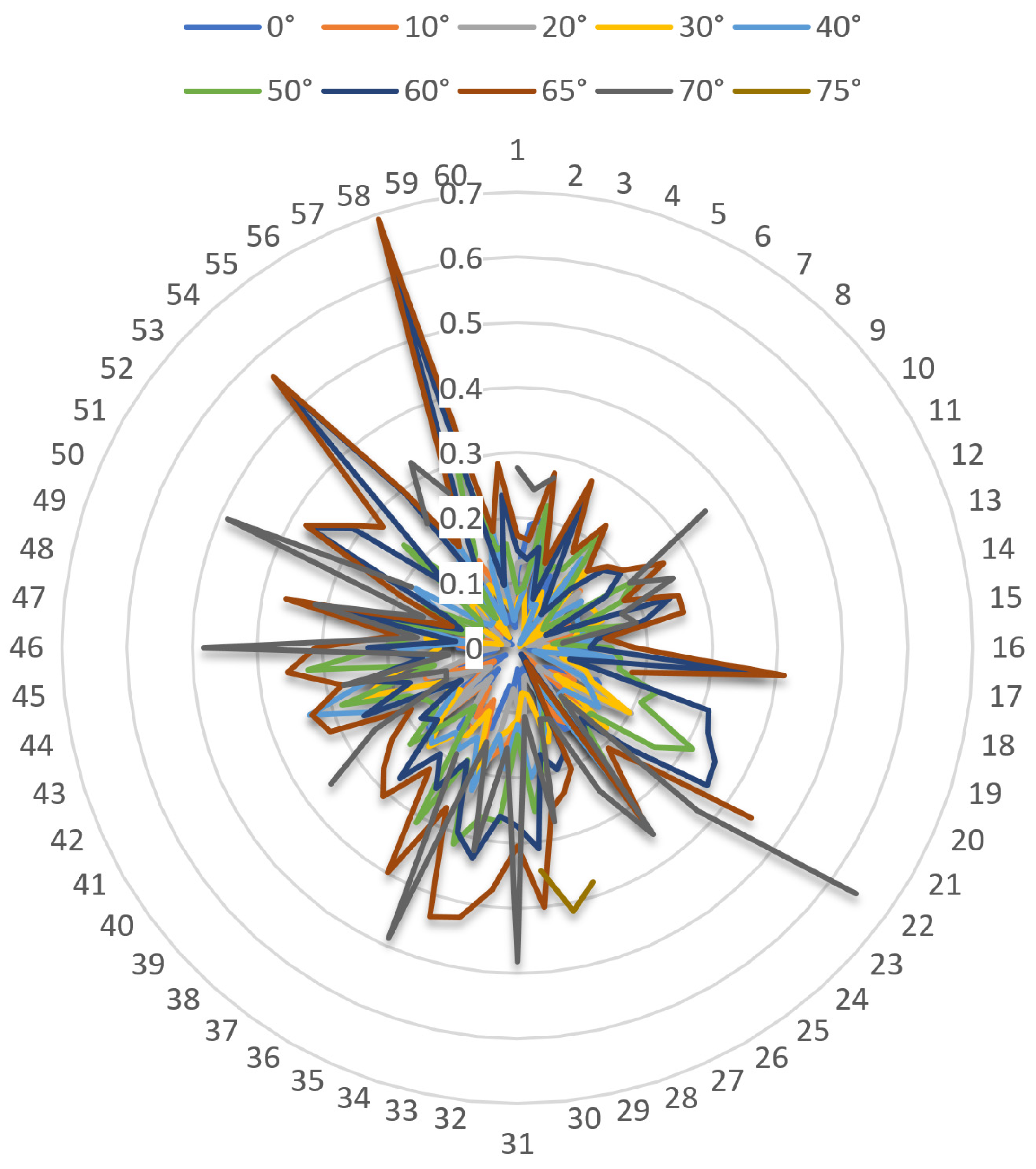
4.2. The Identification Positioning Bias of Decoding Points
Every GCT includes three decoding points. So, the twenty GCTs include sixty decoding points. The identification positioning bias of sixty decoding points under different viewing angles is shown in Figure 12. The positioning bias ranges from 0 to 0.7 (unit: mm). It is obvious that the identification positioning bias of decoding points increases as the viewing angle increases, which reflects that the image deformation increases when the viewing angle increases. Even so, the maximum positioning bias is not larger than 0.7, which ensures that the identification is of high precision. According to this analysis, for standard 6 mm-diameter GCTs, when the threshold of positioning bias of decoding points is set at 1.0, good identification results can be obtained. Compared with the decoding descriptions in ref [30], which just presented a simple description of a mathematical algorithm without presenting any data, we present detailed bias values and threshold values to provide more reference information. Ref [42] imitated the HCT to design a novel cross-circular coded target, and the bias of decoding points between the designed coordinates and solved coordinates were listed. However, regarding limitations, the experiments were mainly simulations and lacked detailed analysis under various viewing angles.
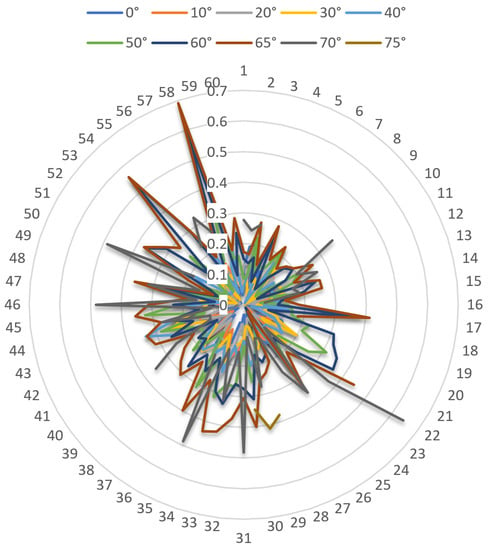
Figure 12.
The positioning bias of decoding points with increasing steps of viewing angle.
4.3. The Precision of Center Positioning of GCTs
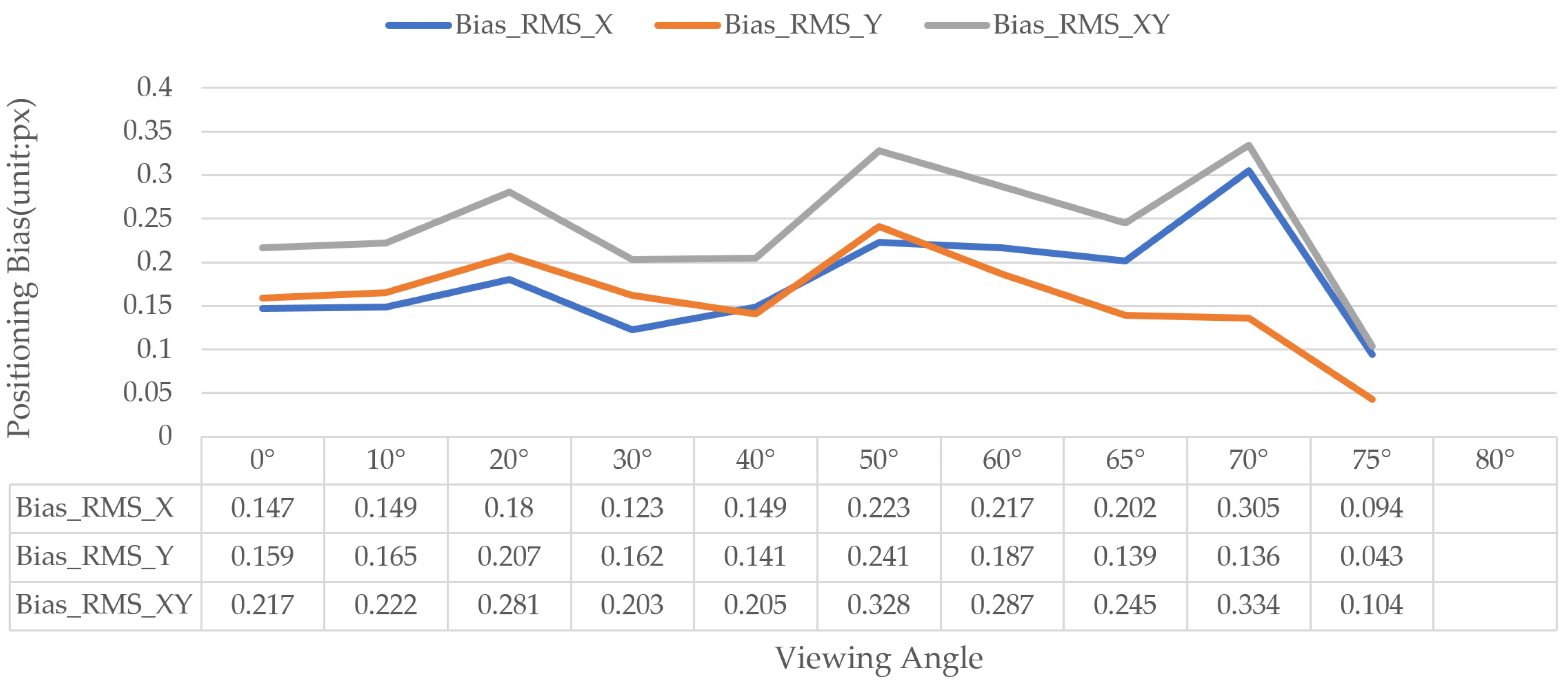
The key for identification of GCTs is to obtain the correct coding serial number and accurate center coordinates to perform high-precision measurement or tracking. So, it is very important to evaluate the center positioning precision. V-STARS claims to have a typical high measurement precision of 5 μm + 5 μm/m [32,43], so its center positioning coordinates are regarded as the truth. All the center coordinates of identified GCTs by V-STARS corresponding to the proposed method have been calculated. Bias_RMS_X, Bias_RMS_Y, and Bias_RMS_XY represent the RMSE of bias between the proposed and V-STARS at image coordinates in the X direction, Y direction, and plane direction, respectively. The detailed values under the viewing angle at 0° can be seen in Table 8. The details for comparisons under the other viewing angles are similar, so we give the statistical results directly in Figure 13. Although ref [31], which paid attention to ring-shaped coded targets, also gave out the positioning coordinates, it did not include a concrete comparison with the true value or with the standard software.

Table 8.
The center positioning coordinates and positioning bias compared with V-STARS under the viewing angle at 0°.
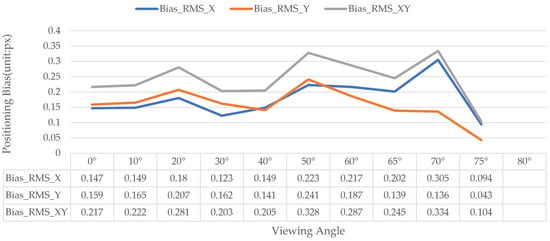
Figure 13.
The center positioning precision under different viewing angles.
From Figure 13, we can see that the bias of center positioning is relatively stable under different viewing angles. However, the center positioning precision is 0.2 px–0.3 px, which is a big error in terms of high-precision measurement [44]. It is necessary to improve the center positioning precision to 0.1 px or even 0.05 px [32,45]. In addition, when the center positioning precision was low, a GCT could not be identified, although eight ellipses were extracted. Just as was mentioned in [46], when the precision of circle extraction is low, the precision of center positioning will be bad, and it will affect the precision of subsequent measurements.
From the above experiments and data analysis, it is confirmed that the proposed method is very credible. Through ref [7], the circular geometric constraint can be used to screen out valid circular points. Through refs [41,44], ellipse extraction and fitting can be used to obtain the positions of all points. Through ref [37], the coplanar P2-invariant can be used to detect template points. Through ref [30], the affine transformation can be used to decode a GCT.
Compared with applications that do not rely on GSI coded targets, the proposed method can be very useful when performing automatic image matching, camera orientation, object tracking, aided 3D reconstruction, etc. Compared with V-STARS, the proposed method can achieve approximate identification results and can deal with mixed GCTs better. However, this paper has some limitations. The first is the low precision of ellipse extraction and center positioning, which is the main factor triggering uncertainty and error. The second is that the binarization threshold is not self-adaptive. The third is that the key parameters for distance constraints such as and were set empirically and were not self-adaptive, which is not flexible and will cause restrictions in complicated scenes. Only if the precision of center positioning is improved, it can be applied to high-precision applications [19]. Only if the binarization threshold can be self-adaptive, it can be better applied in more complicated or volatile large scenarios with non-uniform background illumination [47].
As ref [20] pointed out, the commercial photogrammetric systems V-STARS remains closed source. The details related to the key principles of its internal architecture, including the identification principle of coded targets, are not publicly available and are of commercial interest. Therefore, there is a limited number of available papers related to the identification of GCTs. It is hard to make comparisons with other related published papers, so we have compared with V-STARS directly. This paper may represent the first time that a detailed identification method for GCTs in the whole chain has been published. However, because the method adopted in V-STARS is excellent, our aim is not to surpass V-STARS, but to approximate it. So, we wish to describe these experiences of identifying GCTs and hope that other researchers can put forward a better method to identify GCTs based on the insights offered by the present paper.
In future research, we will adopt a high-precision edge extraction and center positioning method, as mentioned by ref [48]. We will also consider a faster ellipse extraction method from ref [49] that can be used to replace the current method to adapt to fast processing or dynamic scenarios. Then, we will learn from ref [50] to try to improve the adaptive capability aiming at the non-uniform sunlight in UAV experiments outdoors; we will also strive to find a self-adaptive or parameter-free identification method. Furthermore, another close-range photogrammetric software named AUSTRALIS [27,28], which was not used as a comparison with the proposed method, should be considered in future work.
5. Conclusions
This paper shares an innovative method and detailed procedures for identifying closed-source coded targets that have been commercially applied in visual measurement software V-STARS. Indoor experiments with common-sized coded targets under different viewing angles ranging from 0° to 80°, small-sized coded targets, and mixed-size coded targets and outdoor experiments with non-uniform brightness were carried out to verify the effectiveness and robustness of the proposed method. The results and analysis show that the proposed P2-invariant of five coplanar points with three collinear points, which served as the identification feature of template points for a GSI coded target, is very stable and not affected by the viewing angle. The UAV experiment proved the effectiveness further and indicated preliminarily that the proposed method could potentially be applied to UAV photogrammetry. In the future, we expect GCTs and this method to be applied in Agisoft Metashape for UAV photogrammetry and 3D reconstruction, as well as in dynamic geographical scenes for object tracking and positioning.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.W. and Z.Z.; formal analysis, Q.W. and Y.G.; investigation, Y.G.; methodology, Q.W.; project administration, X.C.; resources, S.W. and H.Z.; software, Y.L. and Y.G.; supervision, X.C.; validation, S.W.; visualization, H.Z.; writing—original draft, Q.W. and Y.L.; writing—review and editing, Q.W. and Y.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 42001412, 52274169, 42071445, 41971306) and the Key Research and Development Plan of Guilin (No. 20210214-2).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The experiment data and developed software that support the findings of this study are openly available at the following URL/DOI: https://figshare.com/articles/software/GSI_CodedTarget_Identification/20696923 (accessed on 28 August 2022).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Tushev, S.; Sukhovilov, B.; Sartasov, E. Architecture of industrial close-range photogrammetric system with multi-functional coded targets. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Ural Conference on Measurements (UralCon), Chelyabinsk, Russia, 16–19 October 2017; pp. 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, W.; Burge, M.J. Scale-invariant feature transform (SIFT). In Digital Image Processing; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 709–763. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Qin, L.; Liu, J.; Liu, X. UTRNet: An Unsupervised Time-Distance-Guided Convolutional Recurrent Network for Change Detection in Irregularly Collected Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 4410516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Cheng, J.; Gao, Y.; Guo, S.; Yang, X.; Xu, X.; Cen, Y. Deep belief network for feature extraction of urban artificial targets. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 2387823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.M.; Yu, S.Y.; Ren, S.; Cheng, S.; Liu, J.Z. Close-range industrial photogrammetry and application: Review and outlook. In Proceedings of the AOPC 2020: Optics Ultra Precision Manufacturing and Testing, Beijing, China, 30 November–2 December 2020; Volume 11568, pp. 152–162. [Google Scholar]
- Barbero-García, I.; Cabrelles, M.; Lerma, J.L.; Marqués-Mateu, Á. Smartphone-based close-range photogrammetric assessment of spherical objects. Photogramm. Rec. 2018, 33, 283–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Song, X.; Wang, G.; Zhang, H. A Novel Capacity Expansion and Recognition Acceleration Method for Dot-dispersing Coded Targets in Photogrammetry. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2022, 33, 125016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, L. Design of Chinese character coded targets for feature point recognition under motion-blur effect. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 124467–124475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Rashidi, M.; Mousavi, V.; Yu, Y.; Samali, B. Application of TLS Method in Digitization of Bridge Infrastructures: A Path to BrIM Development. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Rashidi, M.; Mousavi, V.; Karami, A.; Yu, Y.; Samali, B. Quality Evaluation of Digital Twins Generated Based on UAV Photogrammetry and TLS: Bridge Case Study. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Rashidi, M.; Mousavi, V.; Karami, A.; Yu, Y.; Samali, B. Case study on accuracy comparison of digital twins developed for a heritage bridge via UAV photogrammetry and terrestrial laser scanning. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Structural Health Monitoring of Intelligent Infrastructure, SHMII, Porto, Portugal, 30 June–2 July 2021; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Fang, S.; Kong, B.; Li, Y. Design of a color coded target for vision measurements. Optik 2014, 125, 3727–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.; Zakariyaeinejad, Z.; Sadeghi-Niaraki, A.; Ahmadabadian, A.H. A new method for automatic and accurate coded target recognition in oblique images to improve augmented reality precision. Trans. GIS 2022, 26, 1509–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Zhang, X.; Fayek, S.; Yin, Z. A table method for coded target decoding with application to 3-D reconstruction of soil specimens during triaxial testing. Acta Geotech. 2021, 16, 3779–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurník, J.; Zatočilová, A.; Paloušek, D. Circular coded target system for industrial applications. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2021, 32, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, V.; Khosravi, M.; Ahmadi, M.; Noori, N.; Haghshenas, S.; Hosseininaveh, A.; Varshosaz, M. The performance evaluation of multi-image 3D reconstruction software with different sensors. Measurement 2018, 120, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novosad, M. Lidar Pose Calibration Using Coded Reflectance Targets. Bachelor’s Thesis, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Czech Technical University in Prague, Prague, Czech Republic, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Shortis, M.R.; Seager, J.W. A practical target recognition system for close range photogrammetry. Photogramm. Rec. 2014, 29, 337–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhovilov, B.M.; Sartasov, E.M.; Grigorova, E.A. Improving the accuracy of determining the position of the code marks in the problems of constructing three-dimensional models of objects. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Industrial Engineering, Chelyabinsk, Russia, 19–20 May 2016; pp. 19–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tushev, S.; Sukhovilov, B.; Sartasov, E. Robust coded target recognition in adverse light conditions. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Industrial Engineering, Applications and Manufacturing (ICIEAM), Moscow, Russia, 15–18 May 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.; Deng, H.; Quan, Q. Active Infrared Coded Target Design and Pose Estimation for Multiple Objects. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Macau, China, 4–8 November 2019; pp. 6885–6890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kniaz, V.V.; Grodzitskiy, L.; Knyaz, V.A. Deep learning for coded target detection. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2021, 4421, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.T.; Sinnreich, K. Optical 3-D measurement systems for quality control in industry. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 1993, 29, 56–59. Available online: www.isprs.org/proceedings/xxix/congress/part5/56_xxix-part5.pdf (accessed on 26 June 2022).
- Hattori, S.; Akimoto, K.; Fraser, C.; Imoto, H. Automated procedures with coded targets in industrial vision metrology. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2002, 68, 441–446. Available online: www.asprs.org/wp-content/uploads/pers/2002journal/may/2002_may_441-446.pdf (accessed on 25 June 2022).
- Fraser, C.S. Innovations in automation for vision metrology systems. Photogramm. Rec. 1997, 15, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.D.; Dold, J. V-STARS—A system for digital industrial photogrammetry. In Optical 3-D Measurement Techniques III; Gruen, A., Kahmen, H., Eds.; Wichmann Verlag: Heidelberg, Germany, 1995; pp. 12–21. [Google Scholar]
- Fraser, C.S.; Edmundson, K.L. Design and implementation of a computational processing system for off-line digital close-range photogrammetry. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2000, 55, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kharaz, A.A.; Chong, A. Reliability of a close-range photogrammetry technique to measure ankle kinematics during active range of motion in place. Foot 2021, 46, 101763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filion, A.; Joubair, A.; Tahan, A.S.; Bonev, I.A. Robot calibration using a portable photogrammetry system. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2018, 49, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, S.; Akimoto, K.; Ohnishi, Y.; Miura, S. Semi-automated tunnel measurement by vision metrology using coded-targets. In Modern Tunneling Science and Technology, 1st ed.; Adachi, T., Tateyama, K., Kimura, M., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK, 2017; pp. 285–288. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, J.; Meng, L. Design of a New Coded Target with Large Coding Capacity for Close—Range Photogrammetry and Research on Recognition Algorithm. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 220285–220292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J. V-STARS/S Acceptance Test Results. In: Seattle: Boeing Large Scale Optical Metrology Seminar. 1998. Available online: http://gancell.com/papers/S%20Acceptance%20Test%20Results%20-%20metric%20version.pdf (accessed on 25 August 2022).
- Hartley, R.; Zisserman, A. Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, S.; Bi, D.; Li, Z.; Yan, N.; Zhang, X. A static and fast calibration method for line scan camera based on cross-ratio invariance. J. Mod. Opt. 2022, 69, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, D.; Bender, A.; Sukkarieh, S. Improved cross-ratio invariant-based intrinsic calibration of a hyperspectral line-scan camera. Sensors 2018, 18, 1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, G. Recognition of planar objects in 3-D space from single perspective views using cross-ratio. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1990, 6, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meer, P.; Ramakrishna, S.; Lenz, R. Correspondence of coplanar features through p2-invariant representations. In Proceedings of the Joint European-US Workshop on Applications of Invariance in Computer Vision, Ponta Delgada, Portugal, 9–14 October 1993; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993; pp. 473–492. [Google Scholar]
- Bergamasco, F.; Albarelli, A.; Torsello, A. Pi-tag: A fast image-space marker design based on projective invariants. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2013, 24, 1295–1310. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00138-012-0469-6 (accessed on 25 September 2022). [CrossRef]
- Cha, J.; Kim, G. Camera motion parameter estimation technique using 2D homography and LM method based on projective and permutation invariant features. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Science and Its Applications, Glasgow, UK, 8–11 May 2006; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 432–440. [Google Scholar]
- Min, C.; Gu, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, F. Non-rigid infrared and visible image registration by enhanced affine transformation. Pattern Recognit. 2020, 106, 107377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaehler, A. Learning OpenCV Computer Vision in C++ with the OpenCV Library Early Release; O’Relly: Springfield, MO, USA, 2013; p. 575. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Pang, Y.; Ahmat, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, A. A novel cross-circular coded target for photogrammetry. Optik 2021, 244, 167517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Why V-STARS? Available online: https://www.geodetic.com/v-stars/ (accessed on 27 August 2022).
- Kanatani, K.; Sugaya, Y.; Kanazawa, Y. Ellipse fitting for computer vision: Implementation and applications. Synth. Lect. Comput. Vis. 2016, 6, 1–141. [Google Scholar]
- Setan, H.; Ibrahim, M.S. High Precision Digital Close Range Photogrammetric System for Industrial Application Using V-STARS: Some Preliminary Result. In Proceedings of the International Geoinformation Symposium, Bogotá, Colombia, 24–26 September 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Su, X.; Guo, X.; Suo, T.; Yu, Q. A Novel Concentric Circular Coded Target, and Its Positioning and Identifying Method for Vision Measurement under Challenging Conditions. Sensors 2021, 21, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalak, H.; Okarma, K. Adaptive image binarization based on multi-layered stack of regions. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Analysis of Images and Patterns, Salerno, Italy, 2–5 September 2019; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 281–293. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, S.; Ma, J.; Su, Z.; Li, C. Robust circular marker localization under non-uniform illuminations based on homomorphic filtering. Measurement 2021, 170, 108700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Fan, X.; Luo, Z.; Song, L.; Qiu, T. A fast ellipse detector using projective invariant pruning. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 3665–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalak, H.; Okarma, K. Fast adaptive image binarization using the region based approach. In Proceedings of the Computer Science On-line Conference, Vsetin, Czech Republic, 25–28 April 2018; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 79–90. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).