Regional Typhoon Track Prediction Using Ensemble k-Nearest Neighbor Machine Learning in the GIS Environment
Abstract
1. Introduction
- To introduce a new approach of ensemble techniques in machine learning for typhoon prediction;
- As a benchmark problem to providing a fast simulation, high accuracy, and long duration results of typhoon track prediction methods compared to several existing approaches;
- To provide a detailed algorithm for readers to use in their future studies;
- To provide an early warning to reduce the higher risk of typhoon impact.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data
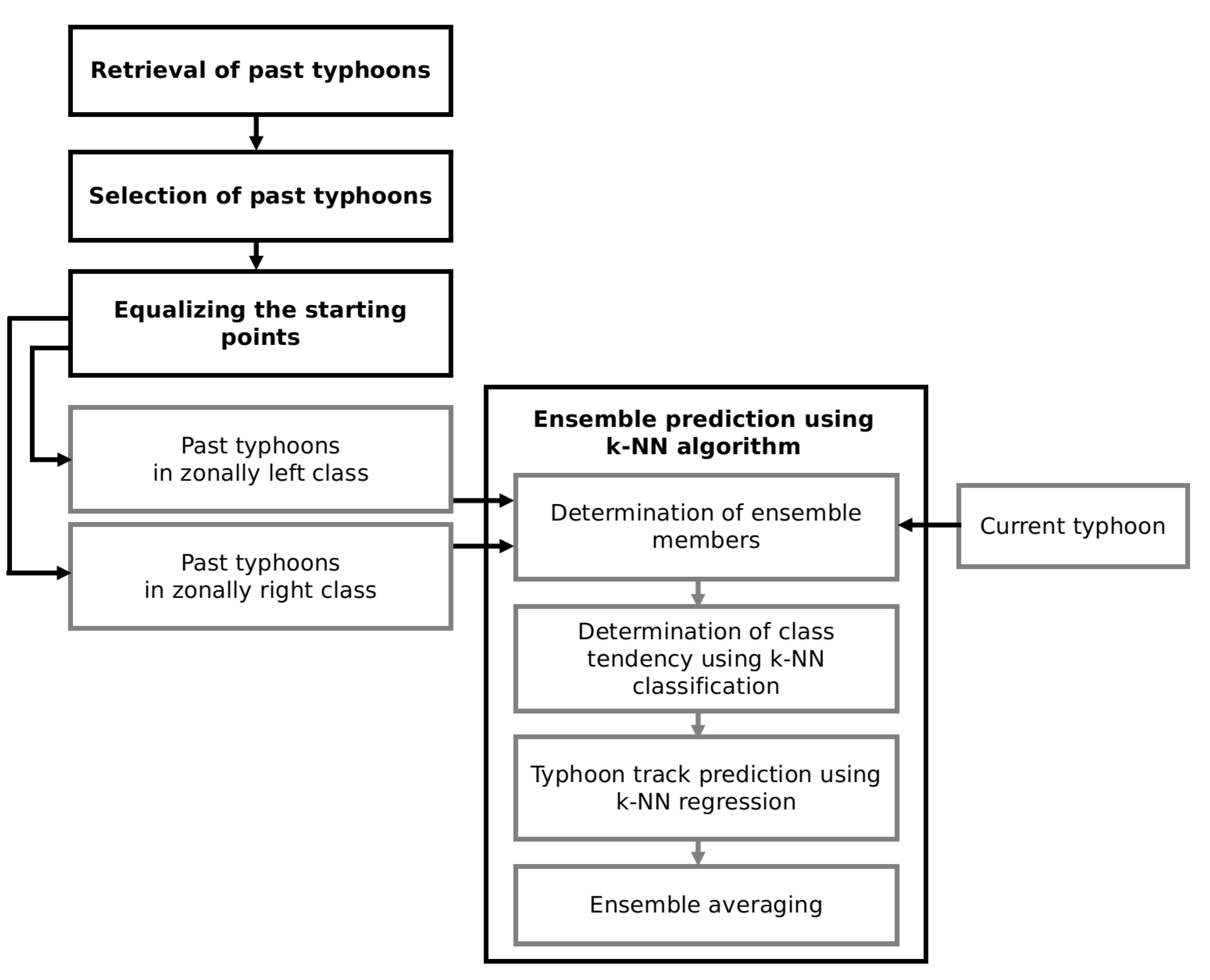
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Retrieval of All Typhoon Tracks
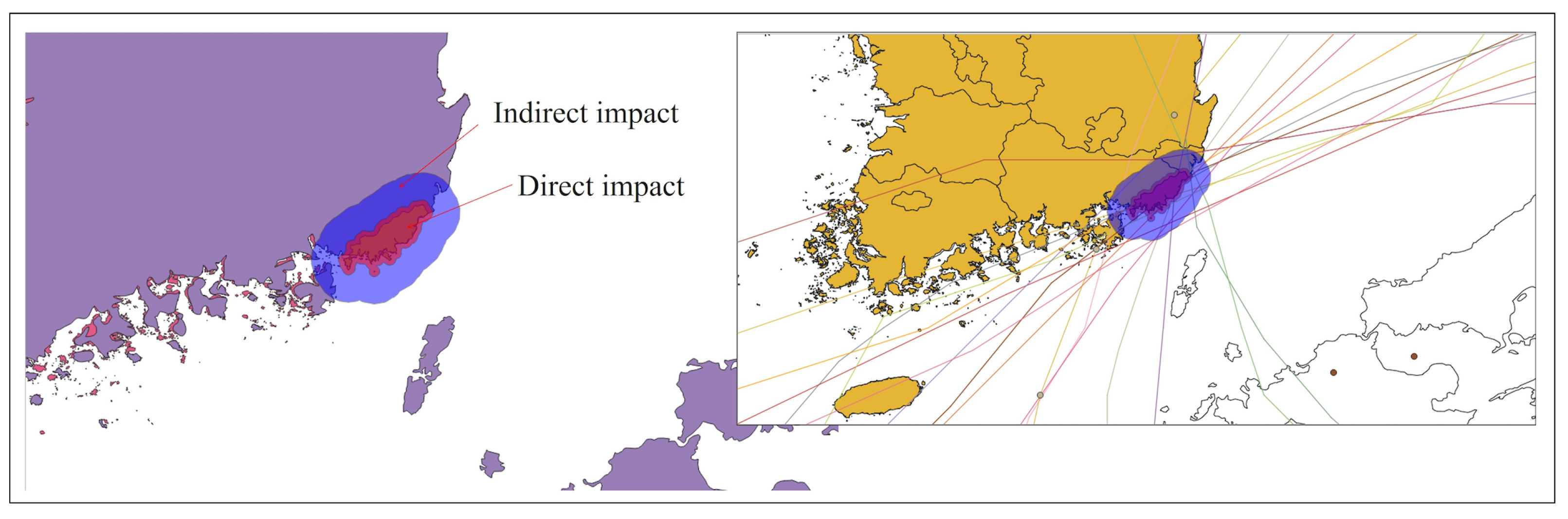
2.2.2. Selection of Typhoon Tracks Impacting the Study Region
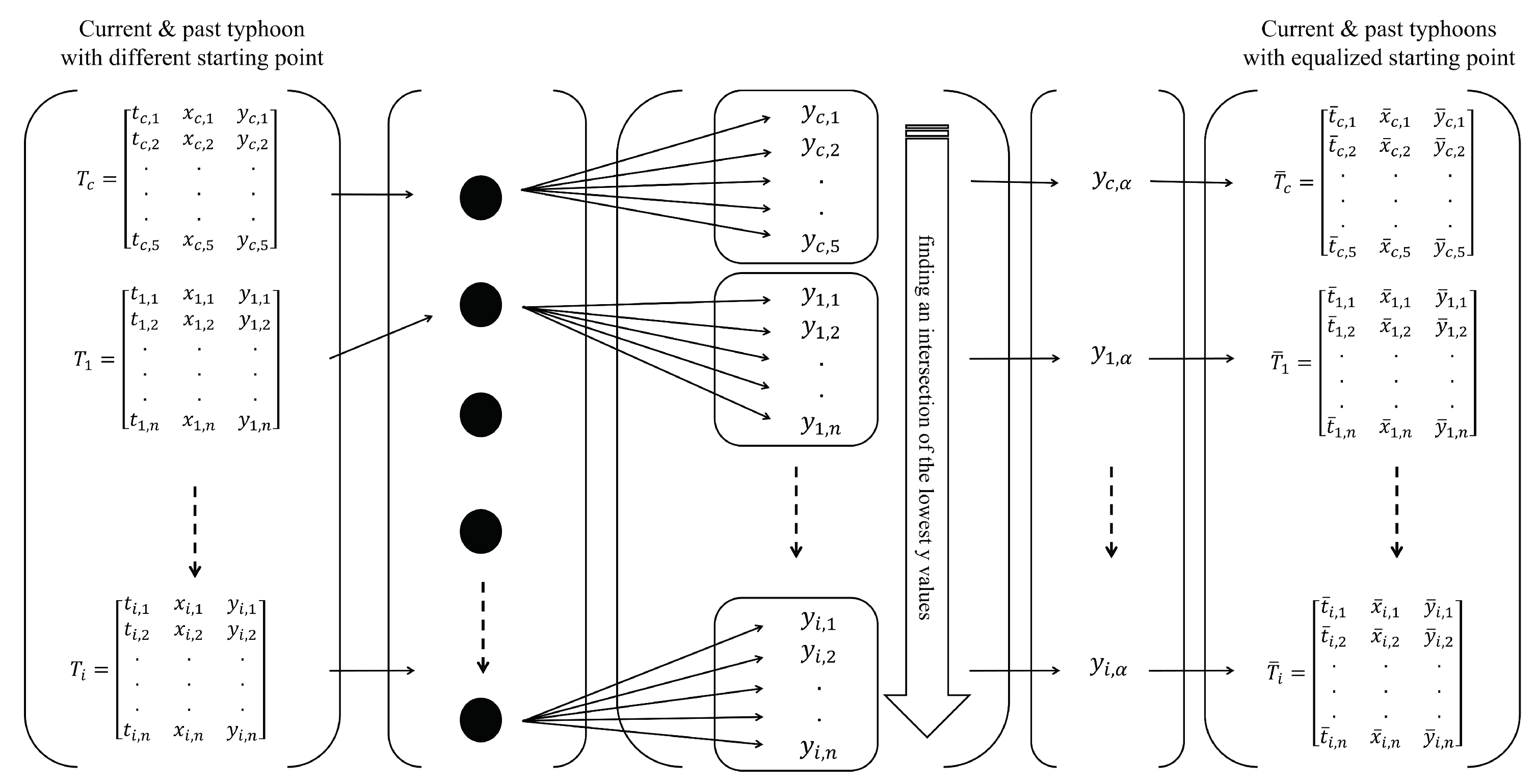
2.2.3. Equalizing the Starting Points of Historical and Sample Typhoons
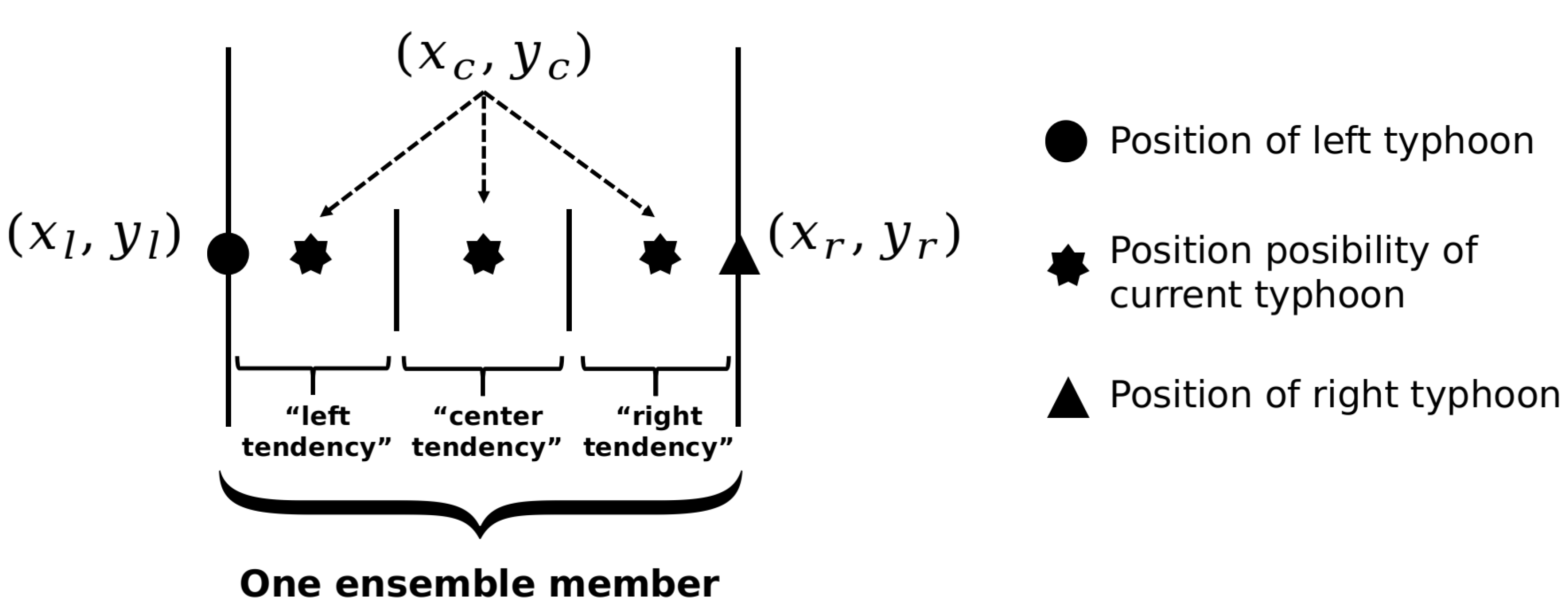
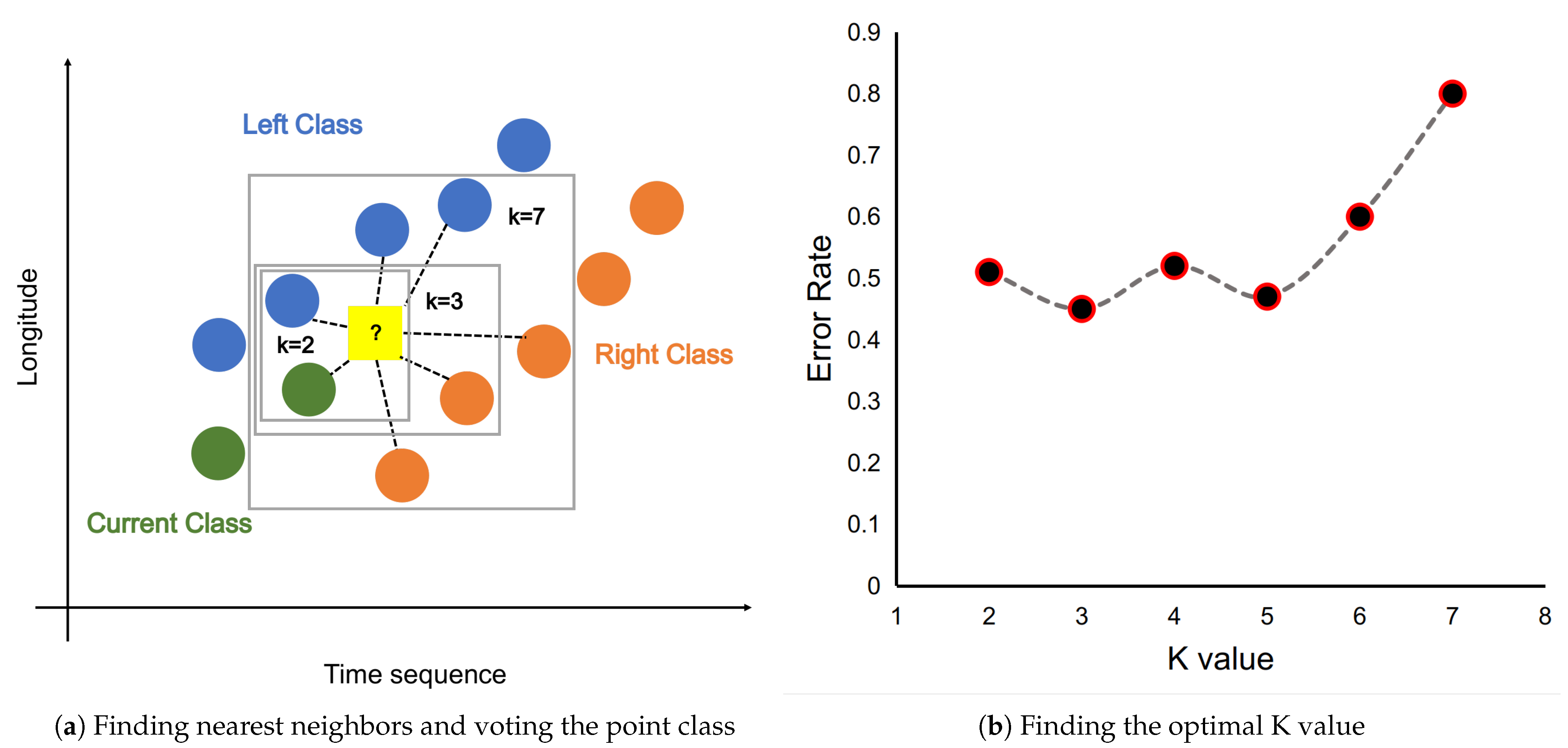
2.2.4. Ensemble Prediction Using k-NN Algorithm
- The class value of the sample typhoon is “left”, when:
- The class value of the sample typhoon is “right”, when:
- The class value of the current typhoon is “center”, when:
2.2.5. Evaluation Method
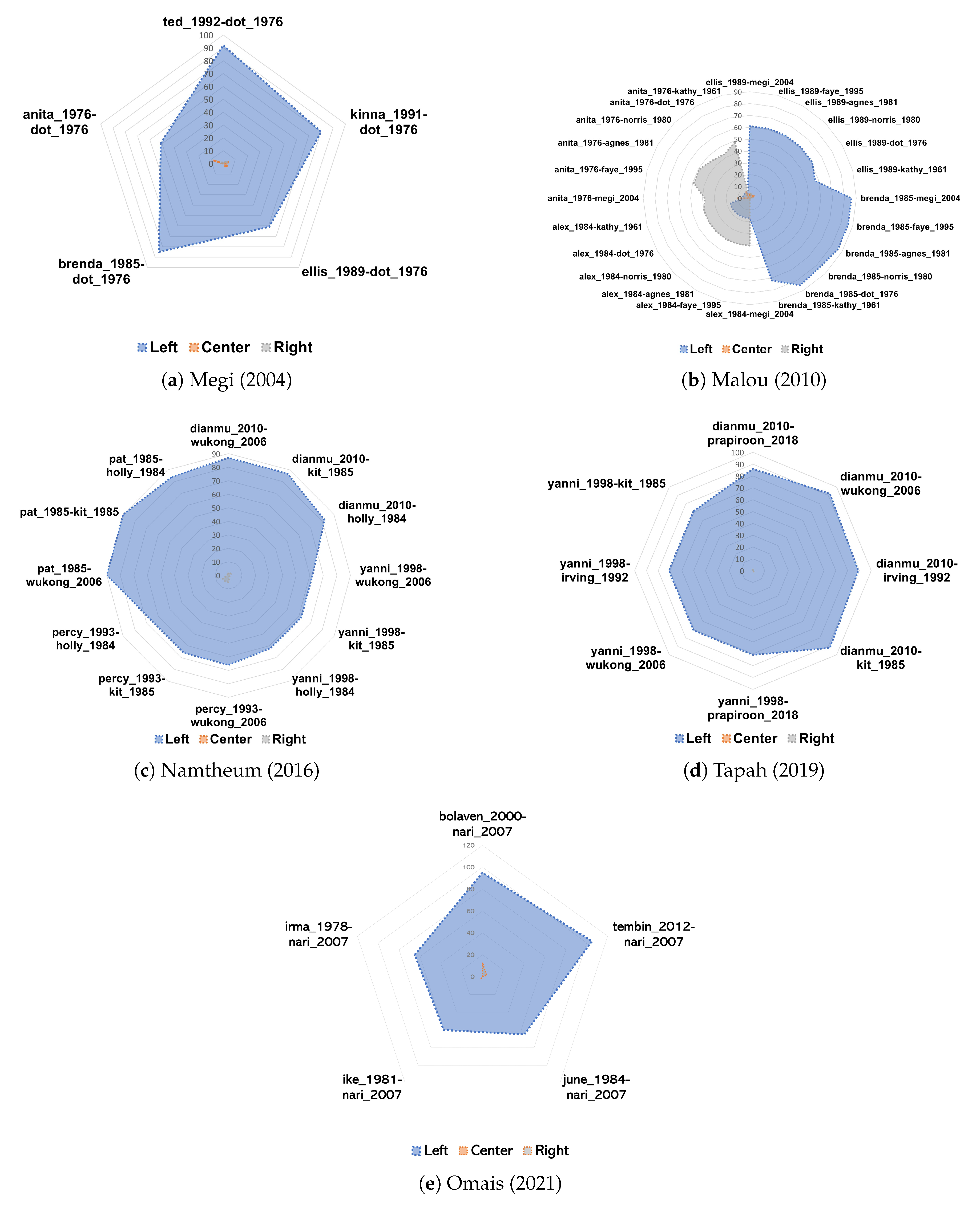
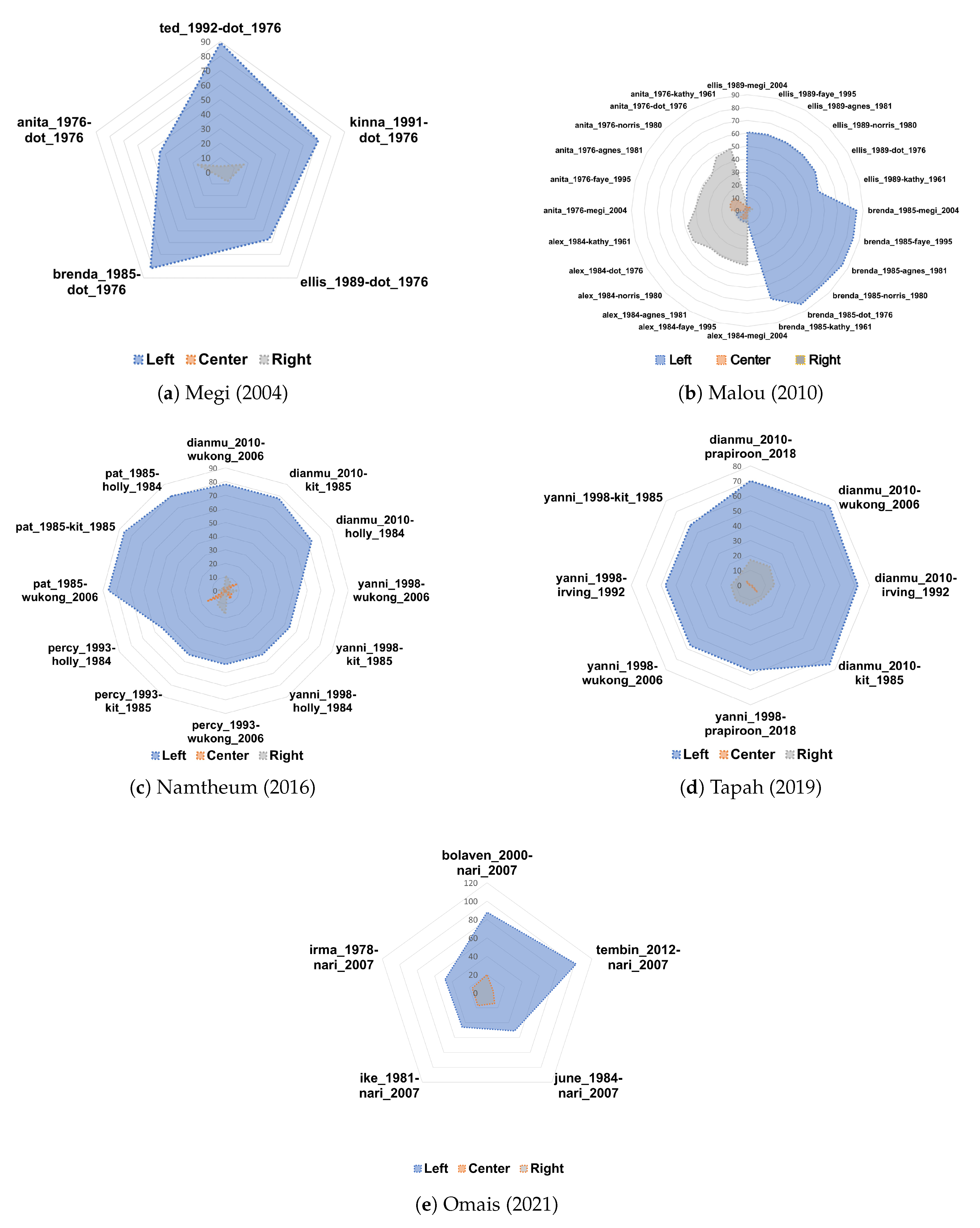
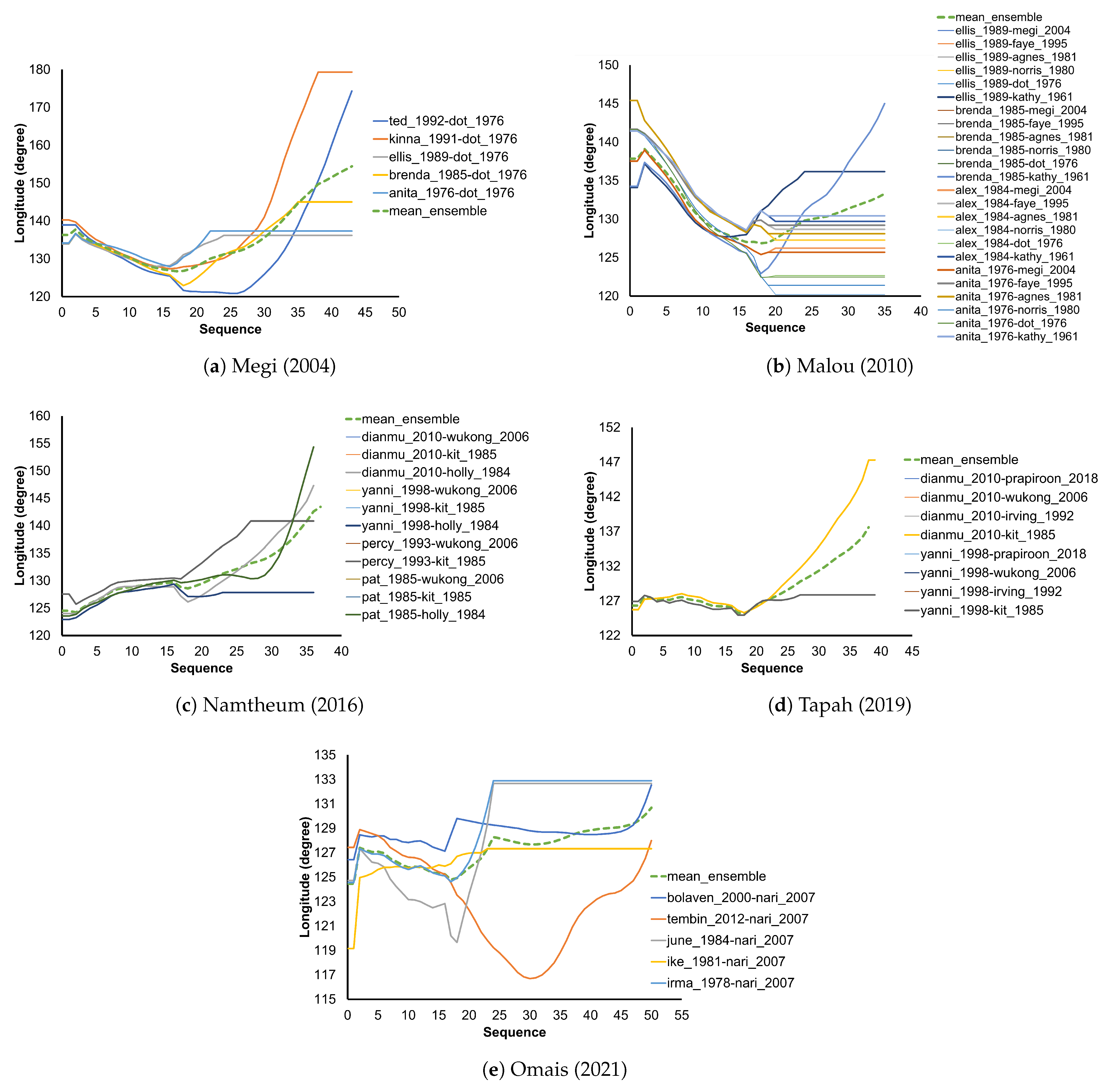
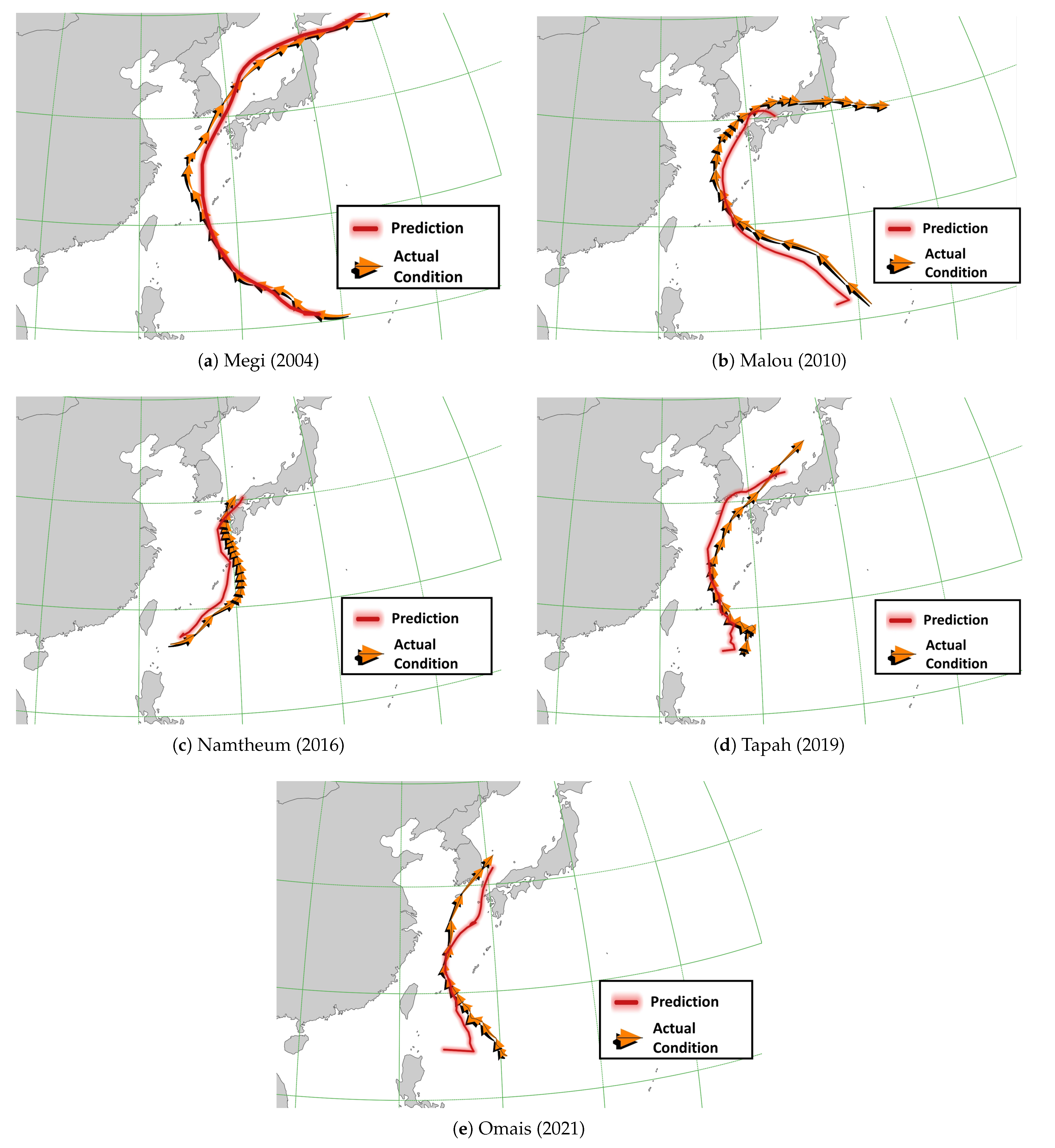
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| TS 1 | Megi 2004 | Malou 2010 | Namtheun 2016 | Tapah 2019 | Omais 2019 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Error (degree 2) | Error (km) | Error (degree) | Error (km) | Error (degree) | Error (km) | Error (degree) | Error (km) | Error (degree) | Error (km) | |
| 0 | 1.02 | 112.72 | 3.58 | 397.19 | 1.28 | 142.60 | 2.40 | 266.12 | 5.53 | 614.23 |
| 1 | 1.02 | 112.72 | 3.58 | 397.19 | 1.28 | 142.60 | 2.40 | 266.12 | 5.53 | 614.23 |
| 2 | 0.49 | 54.34 | 1.25 | 138.87 | 1.60 | 177.93 | 1.22 | 135.51 | 2.61 | 298.57 |
| 3 | 1.19 | 131.73 | 2.14 | 237.61 | 0.72 | 79.67 | 1.39 | 154.26 | 2.79 | 309.71 |
| 4 | 0.97 | 108.05 | 2.01 | 223.24 | 1.03 | 114.51 | 1.69 | 187.18 | 2.65 | 294.46 |
| 5 | 1.23 | 137.00 | 1.78 | 197.25 | 1.26 | 140.37 | 1.64 | 182.44 | 2.61 | 289.72 |
| 6 | 0.88 | 97.64 | 1.77 | 196.72 | 1.88 | 208.52 | 1.87 | 207.50 | 2.04 | 226.75 |
| 7 | 0.81 | 89.79 | 2.99 | 331.74 | 1.06 | 117.87 | 1.29 | 142.88 | 1.89 | 209.94 |
| 8 | 0.23 | 25.69 | 2.67 | 295.82 | 1.72 | 190.87 | 0.19 | 20.68 | 1.02 | 113.24 |
| 9 | 0.27 | 29.46 | 3.81 | 422.58 | 1.78 | 197.98 | 0.95 | 105.60 | 1.21 | 134.07 |
| 10 | 0.74 | 82.23 | 2.90 | 322.34 | 1.73 | 191.48 | 1.12 | 123.96 | 1.41 | 156.68 |
| 11 | 0.16 | 18.07 | 1.80 | 199.51 | 1.64 | 182.26 | 1.31 | 145.68 | 1.16 | 128.23 |
| 12 | 0.13 | 14.82 | 1.35 | 149.97 | 1.58 | 175.24 | 0.65 | 72.69 | 0.57 | 63.14 |
| 13 | 0.18 | 20.03 | 0.91 | 101.06 | 1.47 | 162.39 | 0.93 | 103.62 | 0.50 | 55.16 |
| 14 | 0.31 | 34.60 | 0.28 | 31.40 | 1.36 | 150.78 | 0.52 | 57.38 | 0.56 | 62.31 |
| 15 | 0.33 | 36.33 | 0.13 | 14.71 | 1.13 | 125.45 | 0.26 | 28.78 | 0.33 | 36.55 |
| 16 | 0.30 | 33.50 | 0.22 | 23.90 | 0.88 | 98.09 | 0.05 | 5.23 | 0.24 | 26.50 |
| 17 | 0.51 | 56.21 | 0.06 | 6.50 | 1.38 | 152.71 | 0.31 | 34.56 | 0.10 | 11.58 |
| 18 | 1.40 | 155.06 | 0.68 | 75.12 | 1.01 | 112.11 | 1.40 | 155.72 | 0.27 | 30.38 |
| 19 | 1.07 | 118.51 | 0.77 | 85.17 | 0.61 | 67.32 | 1.30 | 144.41 | 0.45 | 49.78 |
| 20 | 1.14 | 127.07 | 1.04 | 115.83 | 0.23 | 25.92 | 1.13 | 125.28 | 0.37 | 40.67 |
| 21 | 1.35 | 149.68 | 1.57 | 173.81 | 0.26 | 29.05 | 1.66 | 184.08 | 0.65 | 72.45 |
| 22 | 1.48 | 164.11 | 1.74 | 193.48 | 0.81 | 90.30 | 2.28 | 253.34 | 0.95 | 105.99 |
| 23 | 0.93 | 103.06 | 1.63 | 180.54 | 1.11 | 123.70 | 2.77 | 307.46 | 1.81 | 201.01 |
| 24 | 0.25 | 27.39 | 1.52 | 168.37 | 0.80 | 88.46 | 3.21 | 356.59 | 2.71 | 301.11 |
| 25 | 0.77 | 86.02 | 1.22 | 135.48 | 1.14 | 126.83 | 2.70 | 299.79 | 2.61 | 289.36 |
| 26 | 0.55 | 60.56 | 1.33 | 147.63 | 1.77 | 196.33 | 2.15 | 238.66 | 2.49 | 276.59 |
| 27 | 1.09 | 121.00 | 0.73 | 81.58 | 2.46 | 272.61 | 1.50 | 166.51 | 2.38 | 263.87 |
| 28 | 2.06 | 228.50 | 1.27 | 140.97 | 1.03 | 114.07 | 2.26 | 251.36 | ||
| 29 | 2.81 | 311.61 | 0.46 | 51.05 | 0.61 | 67.75 | 2.19 | 243.01 | ||
| 30 | 1.56 | 172.99 | 0.88 | 97.88 | 1.44 | 159.80 | ||||
| 31 | 1.55 | 172.52 | 1.21 | 134.71 | 0.79 | 87.19 | ||||
| 32 | 2.22 | 246.55 | 1.55 | 171.62 | 0.06 | 6.67 | ||||
| 33 | 3.21 | 356.74 | 1.88 | 208.28 | 0.68 | 75.58 | ||||
| 34 | 1.26 | 140.06 | 1.26 | 139.83 | ||||||
| 35 | 0.77 | 85.64 | ||||||||
| 36 | 1.68 | 186.08 | ||||||||
| 37 | 0.18 | 20.03 | ||||||||
| 38 | 4.10 | 455.19 | ||||||||
| 39 | 5.33 | 592.08 | ||||||||
| 40 | 4.34 | 481.51 | ||||||||
| 41 | 7.43 | 852.23 | ||||||||
| 42 | 6.50 | 721.59 | ||||||||
| 43 | 5.57 | 618.18 | ||||||||
| No. | Typhoon Name | Birth (UTC) | Death (UTC) | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Kathy | 1961-08-15 12:00 | 1961-08-17 18:00 | 2 Days 6 Hours |
| 2 | Anita | 1976-07-23 06:00 | 1976-07-25 00:00 | 1 Days 18 Hours |
| 3 | Dot | 1976-08-19 00:00 | 1976-08-21 12:00 | 2 Days 12 Hours |
| 4 | Irma | 1978-09-11 18:00 | 1978-09-15 18:00 | 4 Days 0 Hours |
| 5 | Norris | 1980-08-25 06:00 | 1980-08-28 18:00 | 3 Days 12 Hours |
| 6 | Ike | 1981-06-09 00:00 | 1981-06-14 18:00 | 5 Days 18 Hours |
| 7 | Agnes | 1981-08-27 00:00 | 1981-09-03 18:00 | 7 Days 18 Hours |
| 8 | Holly | 1984-08-16 00:00 | 1984-08-22 12:00 | 6 Days 12 Hours |
| 9 | June | 1984-08-28 00:00 | 1984-08-31 12:00 | 3 Days 12 Hours |
| 10 | Alex | 1984-07-01 18:00 | 1984-07-04 12:00 | 2 Days 18 Hours |
| 11 | Pat | 1985-08-26 06:00 | 1985-09-01 12:00 | 6 Days 6 Hours |
| 12 | Kit | 1985-08-03 06:00 | 1985-08-11 00:00 | 7 Days 18 Hours |
| 13 | Brenda | 1985-09-30 12:00 | 1985-10-05 12:00 | 5 Days 0 Hours |
| 14 | Ellis | 1989-06-22 18:00 | 1989-06-24 03:00 | 1 Days 9 Hours |
| 15 | Kinna | 1991-09-11 06:00 | 1991-09-14 12:00 | 3 Days 6 Hours |
| 16 | Irving | 1992-08-02 00:00 | 1992-08-04 12:00 | 2 Days 12 Hours |
| 17 | Ted | 1992-09-19 06:00 | 1992-09-24 15:00 | 5 Days 9 Hours |
| 18 | Percy | 1993-07-28 06:00 | 1993-07-30 12:00 | 2 Days 6 Hours |
| 19 | Faye | 1995-07-17 12:00 | 1995-07-24 12:00 | 7 Days 0 Hours |
| 20 | Yanni | 1998-09-28 00:00 | 1998-09-30 09:00 | 2 Days 9 Hours |
| 21 | Bolaven | 2000-07-25 18:00 | 2000-07-31 00:00 | 5 Days 6 Hours |
| 22 | Megi | 2004-08-16 06:00 | 2004-08-20 09:00 | 4 Days 3 Hours |
| 23 | Wukong | 2006-08-13 00:00 | 2006-08-19 12:00 | 6 Days 12 Hours |
| 24 | Nari | 2007-09-13 00:00 | 2007-09-17 00:00 | 4 Days 0 Hours |
| 25 | Dianmu | 2010-08-08 12:00 | 2010-08-12 18:00 | 4 Days 6 Hours |
| 26 | Malou | 2010-09-04 00:00 | 2010-09-08 03:00 | 4 Days 3 Hours |
| 27 | Tembin | 2012-08-19 06:00 | 2012-08-30 12:00 | 11 Days 6 Hours |
| 28 | Namtheun | 2016-09-01 00:00 | 2016-09-04 18:00 | 3 Days 18 Hours |
| 29 | Prapiroon | 2018-06-29 00:00 | 2018-07-04 06:00 | 5 Days 6 Hours |
| 30 | Tapah | 2019-09-19 00:00 | 2019-09-23 00:00 | 4 Days 0 Hours |
| 31 | Omais | 2021-08-20 12:00 | 2021-08-24 00:00 | 3 Days 12 Hours |
References
- Chen, R.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X. Machine learning in tropical cyclone forecast modeling: A review. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.B.; Chen, H.; Hsiao, S.C.; Chang, C.H.; Lin, L.Y. Wind forcing effect on hindcasting of typhoon-driven extreme waves. Ocean Eng. 2019, 188, 106260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, M.C.; Su, J.L.; Chien, S.W. Transportation infrastructure disaster impact and lessons learned after typhoon MORAKOT. In Proceedings of the 9th Asia Pacific Transportation Development Conference, Chongqing, China, 29 June–1 July 2012; pp. 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishijima, K.; Maruyama, K.; Graf, M. A preliminary impact assessment of typhoon wind risk of residential buildings in Japan under future climate change. Hydrol. Res. Lett. 2012, 6, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.; Joo, W.; Jeong, C.H.; Kim, W.; Park, S.W.; Song, Y. The Downscaling Study for Typhoon-Induced Coastal Inundation. Water 2020, 12, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, J.; Ahn, K.; T, Y.J.; Suh, K.D.; Kim, M. Projection of extreme typhoon waves: Case study at Busan, Korea. J. Coast. Res. 2013, 65, 684–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, S.H.; Seo, J.W. Storm surge prediction using an artificial neural network model and cluster analysis. Nat. Hazards 2009, 51, 97–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Son, K.; Yoo, Y.; Lee, D.; Kim, D.Y. Identifying risk indicators of building damage due to typhoons: Focusing on cases of South Korea. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, C.; Kovordányi, R. Tropical cyclone track forecasting techniques—A review. Atmos. Res. 2012, 104, 40–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsberry, R.L. Recent advancements in dynamical tropical cyclone track predictions. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 1995, 56, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffries, R.A.; Miller, R.J. Tropical Cyclone Forecasters Reference Guide; Technical Report No. NRL/PU/7515-93-0011; Naval Research Laboratory: Monterey, CA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Diagne, M.; David, M.; Lauret, P.; Boland, J.; Schmutz, N. Review of solar irradiance forecasting methods and a proposition for small-scale insular grids. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 27, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MA, L.M. Research Progress on China typhoon numerical prediction models and associated major techniques. Prog. Geophys. 2014, 29, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar]
- Chien, T.Y.; Chen, S.Y.; Huang, C.Y.; Shih, C.P.; Schwartz, C.S.; Liu, Z.; Bresch, J.; Lin, J.Y. Impacts of Radio Occultation Data on Typhoon Forecasts as Explored by the Global MPAS-GSI System. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolgikh, G.I.; Chupin, V.A.; Gusev, E.S. Research of the Area of Generation of High-Frequency Infrasound Oscillations in the Sea of Japan, Caused by Typhoons. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolgikh, G.I.; Chupin, V.A.; Gusev, E.S.; Timoshina, G.A. Cyclonic Process of the “Voice of the Sea” Microseism Generation and Its Remote Monitoring. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.J.; Huh, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Ho, C.H.; Park, S.K. Typhoon Track Prediction by a Support Vector Machine Using Data Reduction Methods. In International Conference on Computational and Information Science; Computational Intelligence and Security; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, X.; Liang, Z.; Lu, X. Fast prediction of typhoon tracks based on a similarity method and GIS. Disaster Adv. 2013, 6, 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Han, L.; Lin, Y.J.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, W. A tropical cyclone similarity search algorithm based on deep learning method. Atmos. Res. 2018, 214, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, F.; Qui, W.; Ding, C.; Jiang, X.; Wu, L.; Xu, Y.; Duan, Y. An Objective Track Similarity Index and Its Preliminary Application to Predicting Precipitation of Landfalling Tropical Cyclones. Weather Forecast. 2018, 33, 1725–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute of Informatics. Digital Typhoon: Typhoon Images and Information. Available online: http://agora.ex.nii.ac.jp/digital-typhoon/index.html.en (accessed on 15 July 2022).
- Lee, T.R.; Wood, W.T.; Phrampus, B.J. A Machine Learning (kNN) Approach to Predicting Global Seafloor Total Organic Carbon. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2019, 33, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeniran, A.A.; Adebayo, A.R.; Salami, H.O.; Yahaya, M.O.; Abdulraheem, A. A competitive ensemble model for permeability prediction in heterogeneous oil and gas reservoirs. Appl. Comput. Geosci. 2019, 1, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khelifi, F.; Jiang, J. K-NN Regression to Improve Statistical Feature Extraction for Texture Retrieval. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2011, 20, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaffar, M.S.B.A.; Khan, U.S.; Iqbal, J.; Rashid, N.; Hamza, A.; Qureshi, W.S.; Tiwana, M.I.; Izhar, U. Improving classification performance of four class FNIRS-BCI using Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCC). Infrared Phys. Technol. 2021, 112, 103589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, H.; Yu, R.; Jiang, W.; Yang, W. Efficient implementation of k-nearest neighbor classifier using vote count circuit. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2014, 61, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodrich, J.P.; Wall, A.M.; Campbell, D.I.; Fletcher, D.; Wecking, A.R.; Schipper, L.A. Improved gap filling approach and uncertainty estimation for eddy covariance N2O fluxes. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2021, 297, 108280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, K.L.; Swamy, M.N.S. Clustering I: Basic Clustering Models and Algorithms. In Neural Networks and Statistical Learning; Springer: London, UK, 2014; pp. 215–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graser, A. Learning Qgis; Packt Publishing Ltd.: Birmingham, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Du, Z.; Liu, R. Unified Spatial Intersection Algorithms Based on Conformal Geometric Algebra. Math. Probl. Eng. 2016, 2016, 7412373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Moon, I.J.; Kim, M. Statistical prediction of typhoon-induced accumulated rainfall over the Korean Peninsula based on storm and rainfall data. Meteorol. Appl. 2020, 27, e1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skamarock, W.C.; Klemp, J.B.; Dudhia, J.; Gill, D.O.; Liu, Z.; Berner, J.; Wang, W.; Powers, J.G.; Duda, M.G.; Barker, D.M.; et al. A Description of the Advanced Research WRF Model Version 4; National Center for Atmospheric Research: Boulder, CO, USA, 2019; p. 145. [Google Scholar]
- Cha, D.H.; Jin, C.S.; Lee, D.K.; Kuo, Y.H. Impact of intermittent spectral nudging on regional climate simulation using Weather Research and Forecasting model. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, D10103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüttgers, M.; Lee, S.; Jeon, S.; You, D. Prediction of a typhoon track using a generative adversarial network and satellite images. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, F.; Xu, D.; Li, H.; Min, J.; Liu, R. Assimilation of GPM Microwave Imager Radiance data with the WRF hybrid 3DEnVar system for the prediction of Typhoon Chan-hom (2015). Atmos. Res. 2021, 251, 105422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyakwah, W.; Lin, Y.L. Generation and enhancement mechanisms for extreme orographic rainfall associated with Typhoon Morakot (2009) over the Central Mountain Range of Taiwan. Atmos. Res. 2021, 247, 105160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Predictor | Classification Target | Regression Target | Typhoon |
|---|---|---|---|
| | | | | ||
| “left”/“center”/“right”? | | | current | |
| “left” | | | left class | |
| “right” | | | right class | |
| “left”/“center”/“right”? | | | current | |
| “left” | | | left class | |
| “right” | | | right class | |
| ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ |
| “left”/“center”/“right”? | | | current | |
| “left” | | | left class | |
| “right” | | | right class |
| No | Sample Typhoon | Correlation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zonal Component | Meridional Component | ||
| 1 | Megi 2004 | 0.97 | 0.98 |
| 2 | Malou 2010 | 0.78 | 0.97 |
| 3 | Namtheum 2016 | 0.81 | 0.96 |
| 4 | Tapah 2019 | 0.79 | 0.94 |
| 5 | Omais 2021 | 0.47 | 0.96 |
| - | Average | 0.76 | 0.96 |
| No | Sample Typhoon | The Proposed Method | WRF | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min. Error (km) | Max. Error (km) | Proc. Runtime (min.) | Min. Error (km) | Max. Error (km) | Proc. Runtime (min.) | ||
| 1 | Megi 2004 | 14.8 | 852.2 | 5.4 | 16.6 | 505.8 | 195 |
| 2 | Malou 2010 | 6.5 | 422.6 | 21.3 | 17.4 | 299.2 | 204 |
| 3 | Namtheum 2016 | 25.9 | 272.6 | 11.6 | 85.5 | 402.2 | 154 |
| 4 | Tapah 2019 | 5.2 | 356.6 | 8.3 | 32.5 | 290.9 | 222 |
| 5 | Omais 2021 | 11.6 | 614.2 | 5.1 | 12.6 | 310.3 | 143 |
| - | Average | 12.8 | 503.6 | 10.3 | 32.9 | 361.7 | 183.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tamamadin, M.; Lee, C.; Kee, S.-H.; Yee, J.-J. Regional Typhoon Track Prediction Using Ensemble k-Nearest Neighbor Machine Learning in the GIS Environment. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5292. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14215292
Tamamadin M, Lee C, Kee S-H, Yee J-J. Regional Typhoon Track Prediction Using Ensemble k-Nearest Neighbor Machine Learning in the GIS Environment. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(21):5292. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14215292
Chicago/Turabian StyleTamamadin, Mamad, Changkye Lee, Seong-Hoon Kee, and Jurng-Jae Yee. 2022. "Regional Typhoon Track Prediction Using Ensemble k-Nearest Neighbor Machine Learning in the GIS Environment" Remote Sensing 14, no. 21: 5292. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14215292
APA StyleTamamadin, M., Lee, C., Kee, S.-H., & Yee, J.-J. (2022). Regional Typhoon Track Prediction Using Ensemble k-Nearest Neighbor Machine Learning in the GIS Environment. Remote Sensing, 14(21), 5292. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14215292







